10 week old baby feeding how much formula
Formula Feeding FAQs: How Much and How Often (for Parents)
Whether you plan to formula feed your baby from the start, want to supplement your breast milk with formula, or are switching from breast milk to formula, you probably have questions.
Here are answers to some common questions about formula feeding.
How Often Should I Feed My Baby Formula?
Newborns and young babies should be fed whenever they seem hungry. This is called on-demand feeding.
After the first few days of life, most healthy formula-fed newborns feed about every 2–3 hours. As they get bigger and their tummies can hold more milk, they usually eat about every 3–4 hours. As babies get older, they’ll settle into a more predictable feeding routine and go longer stretches at night without needing a bottle.
Talk to your doctor if you have concerns about feeding your baby, especially if your baby is very small, is not gaining weight, or was born early (prematurely).
How Can I Tell When My Baby Is Hungry?
Signs that babies are hungry include:
- moving their heads from side to side
- opening their mouths
- sticking out their tongues
- placing their hands, fingers, and fists to their mouths
- puckering their lips as if to suck
- nuzzling again their mothers' breasts
- showing the rooting reflex (when a baby moves its mouth in the direction of something that's stroking or touching its cheek)
Babies should be fed before they get upset and cry. Crying is a late sign of hunger. But every time your baby cries is not because of hunger. Sometimes babies just need to be cuddled or changed. Or they could be sick, tired, too hot or too cold, in pain, or have colic.
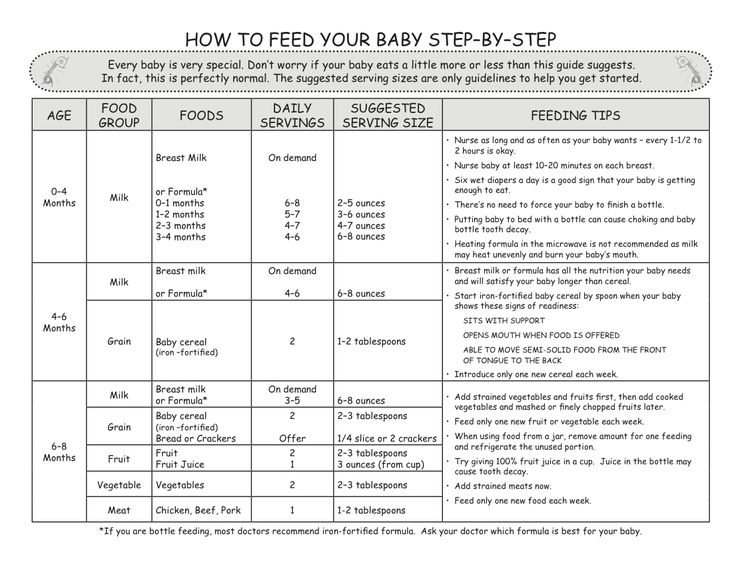
How Much Formula Should I Feed My Baby?
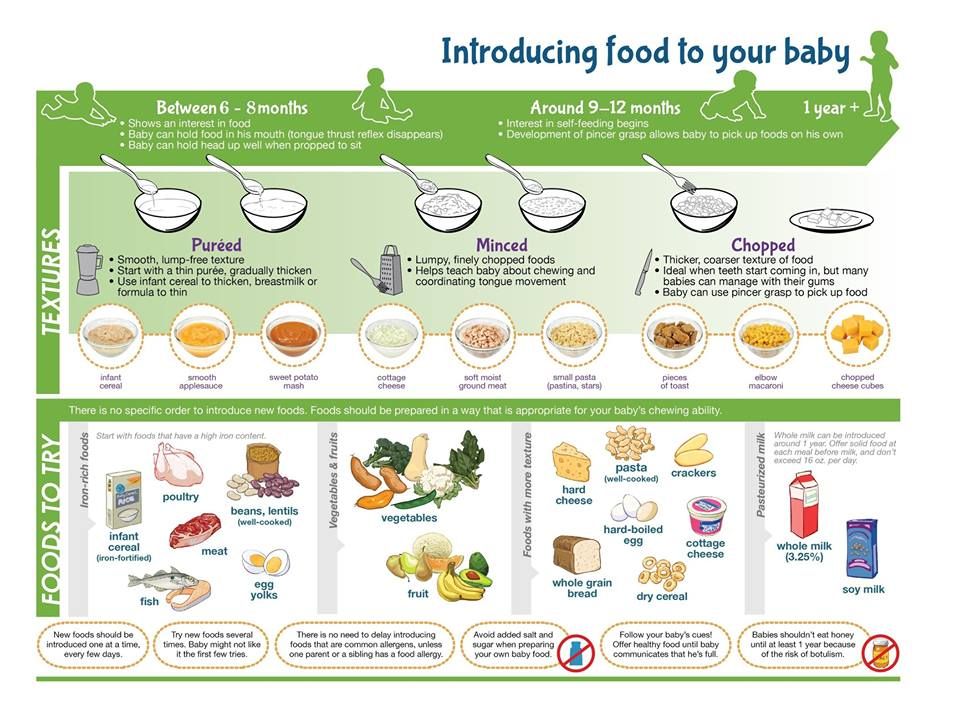
In the first few weeks, give 2- to 3-ounce (60- to 90-milliliter) bottles to your newborn. Give more or less depending on your baby’s hunger cues.
Here's a general look at how much your baby may be eating at different ages:
- On average, a newborn drinks about 1.5–3 ounces (45–90 milliliters) every 2–3 hours. This amount increases as your baby grows and can take more at each feeding.
- At about 2 months, your baby may drink about 4–5 ounces (120–150 milliliters) every 3–4 hours.
- At 4 months, your baby may drink about 4–6 ounces (120-180 milliliters) at each feeding, depending on how often they eat.
- By 6 months, your baby may drink 6–8 ounces (180–230 milliliters) about 4–5 times a day.

Watch for signs that your baby is hungry or full. Respond to these cues and let your baby stop when full. A baby who is full may suck with less enthusiasm, stop, or turn away from the bottle.
Why Does My Baby Seem Hungrier Than Usual?
As babies grow, they begin to eat more at each feeding and can go longer between feedings. Still, there may be times when your little one seems hungrier than usual.
Your baby may be going through a period of rapid growth (called a growth spurt). These can happen at any time, but in the early months are common at around:
- 7–14 days old
- between 3–6 weeks
- 4 months
- 6 months
During these times and whenever your baby seems especially hungry, follow their hunger cues and continue to feed on demand, increasing the amount of formula you give as needed.
Is My Baby Eating Enough?
At times, you may wonder whether your baby is getting enough nutrients for healthy growth and development. Babies who get enough to eat seem satisfied after eating and are regularly peeing and pooping.
Babies who get enough to eat seem satisfied after eating and are regularly peeing and pooping.
At your baby’s checkups, the doctor will review your baby’s growth chart, track your little one’s development, and answer any questions. Talk to your doctor if you have any concerns about your baby’s feeding and nutrition.
Reviewed by: Mary L. Gavin, MD
Date reviewed: November 2021
Formula Feeding FAQs: Getting Started (for Parents)
Whether you plan to formula feed your baby from the start, want to supplement your breast milk with formula, or are switching from breast milk to formula, you probably have questions.
Here are answers to some common questions about formula feeding.
What Supplies Do I Need?
Start with the basics:
- formula
- water (tap water is fine, but use bottled if you are concerned about water safety)
- bottles
- nipples
Keep burp cloths and a bottle/nipple brush handy.
You don’t need a bottle sterilizer, but do sterilize bottles and nipples by boiling them for 5 minutes before the first use.
What Kind of Bottle Should I Use?
Bottles come in different shapes and sizes. They can be made of glass, plastic, silicone, or stainless steel. Here are some differences:
Plastic bottles are now "BPA-free"— meaning they don't contain the chemical bisphenol A (BPA). This chemical may be harmful and is found in some plastics, but is banned from baby bottles. Years ago, some plastic baby bottles had BPA in them, but none do now.
Glass bottles. Glass bottles can cause injury if broken, but silicone sleeves make them easier to grip and help prevent breaks.
Silicone bottles and stainless steel bottles are newer options. They are unbreakable but tend to be more expensive than plastic or glass.
Some babies do better with certain bottle shapes, vented bottles, or bottles with liners on the inside.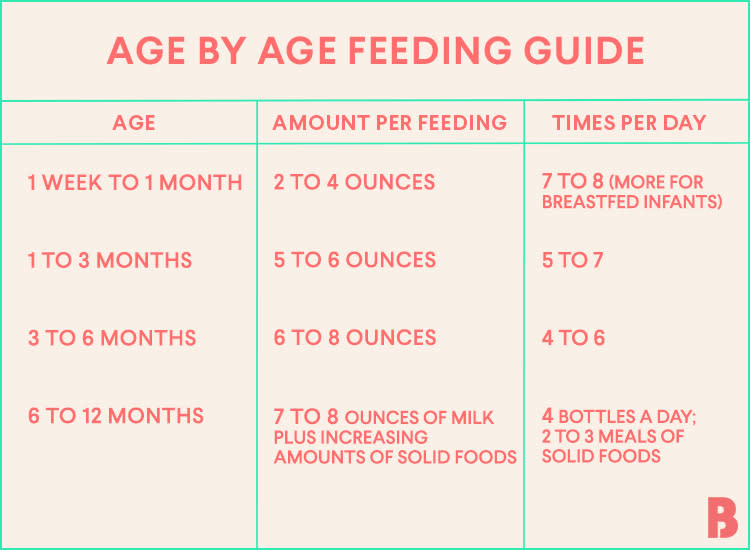 You may need to try a few kinds before you find what works best for you and your baby.
You may need to try a few kinds before you find what works best for you and your baby.
To get you through the first week or so, be sure to have enough formula, water, bottles, and nipples.
Over time, you may want to buy more or different kinds of bottles. You also may find it's worth getting other supplies, like a bottle drying rack or special dishwasher basket.
What Kind of Nipple Should I Use?
Nipples can be made of silicone (clear) or latex (brown) with many different shapes. The varieties include standard or traditional nipples, orthodontic nipples, wide-based nipples, and flat-top nipples. Use whatever type your baby seems to prefer.
Nipples also often come in different numbers, "stages," or "flow rates" to reflect the size of the nipple's hole, which affects the flow (i.e., slow, medium, or fast) of formula or breast milk. The holes get bigger as babies get older and are ready to handle faster flows of milk. Flows that are too fast can make younger babies gag by giving them more milk than they can handle. Slower flows may frustrate some babies and make them suck harder and gulp too much air.
Slower flows may frustrate some babies and make them suck harder and gulp too much air.
Start your newborn on the slowest flow nipple. As your baby gets older, you can increase the flow if you want to. Some babies may be content throughout infancy to use the same kind and size of nipple. If your baby seems fussy or frustrated with the nipple, try a different kind (like one with a larger hole) to see if it makes a difference.
How Often Should Nipples Be Replaced?
That depends on how the nipples you use hold up to cleaning and everyday use. Check them regularly for signs of wear and replace them about every 2 months or sooner if you notice tears or damage.
What Type of Formula Should I Use?
Many different formulas are available these days. Ask your doctor which kind is best for your baby.
Do not try to make your own formula at home. Online recipes may look healthy and promise to be nutritionally complete, but they can have too little — or too much — of important nutrients and cause serious health problems for your baby.
There are many different brands of formula, and all that are made in the United States (name brands, store brands, and generic) must meet strict nutrition and safety standards.
Formula types include:
- cow's milk-based formulas. Most formulas are made from cow's milk. These formulas have added iron, which babies need. Use only iron-fortified formula, unless your doctor advises you not to.
- soy-based formulas. These are for babies born with congenital lactase deficiency or galactosemia. This type of formula is also used by parents who do not want their babies to eat animal protein. Give only iron-fortified soy formula, unless your doctor says otherwise. (Many babies who are allergic to cow's milk also are allergic to the protein in soy formulas, so soy-based formulas generally don't help with milk-protein allergies.)
- hypoallergenic formulas for babies who can't tolerate cow’s milk or soy formulas, like those with allergies to milk or soy proteins.
 The proteins in hypoallergenic formulas are broken down so they are easier to digest.
The proteins in hypoallergenic formulas are broken down so they are easier to digest. - specialized formulas. These are designed for premature babies.
How Do I Prepare Formula?
Formula comes in three basic forms:
- powders that require mixing with water and cost the least
- concentrates, which are liquids that require diluting with water
- ready-to-use (or ready-to-feed) liquids that can be poured right into bottles. These are the most expensive but are convenient if you're traveling or can't get to a clean water supply.
Carefully follow directions on the label when preparing formula. Do not add more water than directed.
Whatever formula you choose, check the expiration date on all cans and bottles of formula, and don't use formula from leaky, dented, or otherwise damaged containers. Do not water-down formula — this is dangerous, as it reduces the amount of nutrients in each bottle.
Formula Can Be Pricey. How Can I Save Money?
Shop around for the best deals on the formula you've chosen:
- Take advantage of the free samples and coupons sent to you in the first few months after your baby is born.
- Clip coupons and sign up for online coupon clubs and apps that let you print and save coupons.
- Sign up for formula companies' clubs and special programs (through the mail or online) that may offer discounts, coupons, and/or free formula and other products.
- Compare prices on formula at online retailers. Some online stores have special "mom" clubs that let you save regularly on some products every month.
- Check for specials at your grocery store, baby store retailer, or local wholesale/bulk items store.
What if I Need Help Paying for Formula?
If you can't afford formula, talk to your doctor or call 211 to help you find local resources. You and your family may be eligible for assistance through:
- Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC)
- Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP)
- Temporary Assistance for Needy Families
How much formula should a child eat?
Tiunova Elena
Published: 01/16/2023
Reading time: 6 min
12443
The breastfed child largely regulates the amount of food and the frequency of feeding. In the first month of life, he receives breasts on demand, and then a more or less stable diet is developed naturally. If for some reason the baby is deprived of breast milk and receives milk formula, then a free feeding schedule is impossible. The child eats according to the schedule, and the mother has to adhere to the recommended regimen.
In the first month of life, he receives breasts on demand, and then a more or less stable diet is developed naturally. If for some reason the baby is deprived of breast milk and receives milk formula, then a free feeding schedule is impossible. The child eats according to the schedule, and the mother has to adhere to the recommended regimen.
How to tell if a child is full
Signs that a child is full are universal: good mood, good sleep, regular bowel movements.
If we consider not the momentary condition of the child, but a longer period, then it is necessary to observe weight gain and skin condition. A baby who has enough nutrition will increase weight within the age norm - this will be assessed by the doctor during the control weighing. The baby's skin will be pink and firm.
Accordingly, a hungry child will worry, scream, cry, or may become lethargic and lethargic. He will rarely urinate and poop. A dry diaper for several hours is an alarming sign.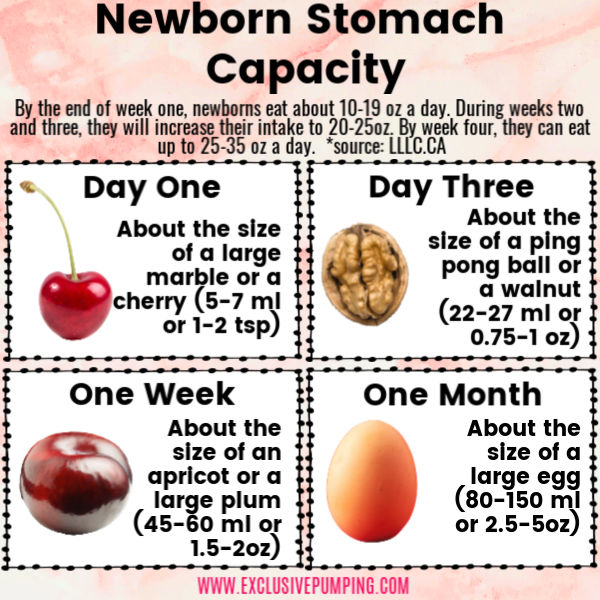 Over time, the baby will begin to lag behind in weight, his skin may become pale, dry.
Over time, the baby will begin to lag behind in weight, his skin may become pale, dry.
But do not rush to give a supplement if the child has drunk the mixture and continues to grab the pacifier. Most likely, he ate, but did not satisfy the sucking reflex. Offer him a pacifier and watch for other signs: whether he will continue to worry, how his sleep will be. If you continue to doubt whether your baby is getting enough nutrition, check with your pediatrician.
How much formula should a child eat per month
A formula-fed newborn should receive formula every 2.5-3 hours, that is, 8-10 times a day, including night feedings. The stomach of an infant in the first month of life is still too small to accommodate a large amount of food, so it is not recommended to take long night breaks between feedings at this age.
As for the volume of the mixture, it will depend not only on the age, but also on the weight of the baby.
In the first decade, that is, the first 10 days of life, the daily volume of the mixture is usually calculated as follows:
- if the baby's weight is less than 3 kg 200 g, then the number of days he lived is multiplied by 70;
- if the weight is more than 3 kg 200 g, then the age in days is multiplied by 80.
For example, a 6 day old baby weighs 3 kg 400 g. Multiply 6 x 80 = 480 ml. We divide this volume by the number of feedings. Let's say you feed your baby 8 times, which means that in one feeding he should receive 60 ml of the mixture.
For a child older than 10 days, the formula calculation algorithm changes.
To calculate how much a child should eat mixtures per 1 month per day, you need to divide his body weight by 5. ⅕ of the child's body weight is the daily amount of food.
For example, the same baby gained 4 kg by the 25th day of life. Divide 4 kg by 5, we get 800. Therefore, if the child continues to receive formula 8 times a day, then his single portion will be 100 g.
How much formula should a child eat at 2 months
For a child of the second month of life, the same formula for formula calculation continues to apply: ⅕ of the weight is the daily volume. Divide by the number of feedings, we get a single serving.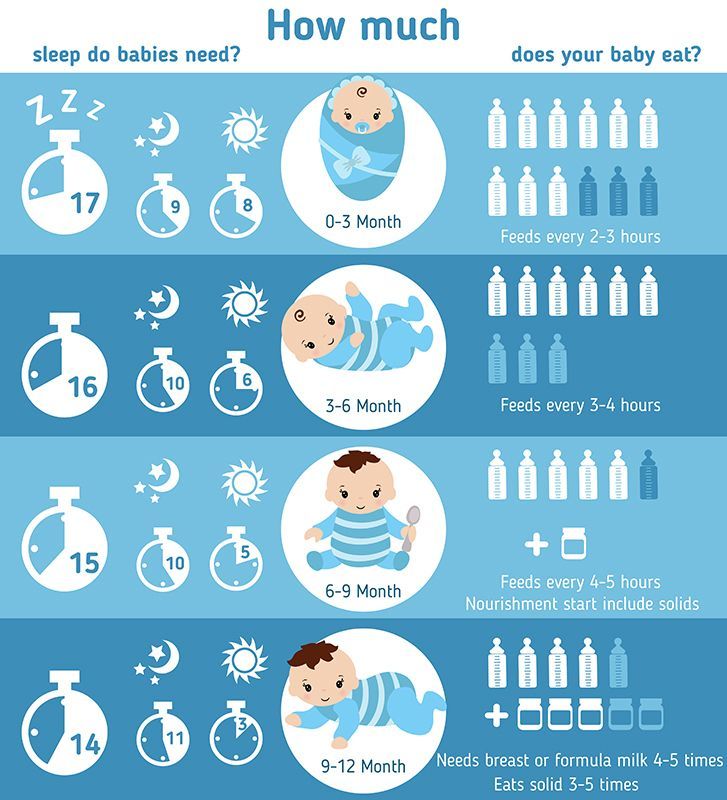
In the third month, the number of feedings is reduced to 7-8. If the child ate 10 times, gradually transfer to 8 times, if 8, then to 7.
But when calculating how much the child should eat the mixture at 2 months and older, we use a different formula. The daily volume of the mixture should now be ⅙ of the child's weight. On average, this is 750 ml or more.
How much formula should a baby eat at 3 months
To determine how much formula a baby should eat at 3 months, divide its weight by 6 again. For example, a baby weighs 5 kg 400 g. 900 g.
The number of feedings at 3 months remains the same - 7-8 times. Let our conditional child eat 7 times a day. We divide 900 by 7, we get approximately 130 g of the mixture per feeding.
Formula Injection Chart
Use the following chart* to help you choose the right amount of formula for your child's age and weight. It contains average data, but since all children are different, the doctor should clarify the nutritional norm for a particular child.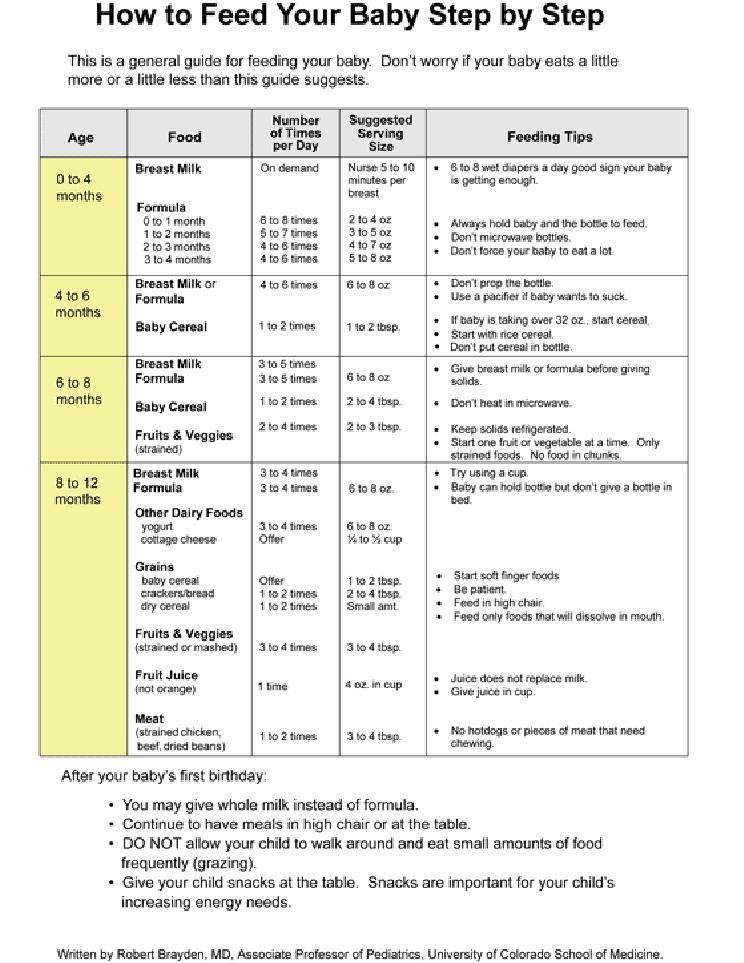
| Child's age | Ratio of food and body weight per day | Daily formula in ml | Number of feedings |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 days to 2 months | 1/5 | 700-850 | 8-10 |
| 2-4 months | 1/6 | 750-900 | 7-8 |
| 4-6 months | 1/7 | 850-1000 | 6 |
| Second half of life (6-12 months) | 1/8-1/9 | 950-1100 | 5-6 |
*calculation of the required amount of formula in this table is suitable for healthy full-term babies who are gaining weight and height in accordance with age.
What to do if the baby is not full of formula
First of all, you need to understand by what signs you have determined that the baby is not full. If he keeps asking for a bottle when he's finished formula, it doesn't necessarily mean he's hungry. Perhaps the child wants to continue the process itself, because the sucking reflex in children on artificial feeding is less satisfied than in children on breastfeeding.
If the baby starts to worry and cry much before the next feeding time, consider if the breaks between meals are too long. With pronounced "hungry" anxiety of the child, feed early, but the volume of the mixture should correspond to a single volume.
This is important!
Do not make the mixture “thicker” for satiety, add more dry product than indicated in the instructions! This can lead to constipation and other health problems for the baby.
If your baby is not gaining weight well, often worries, sleeps poorly, consult your pediatrician.
At each preventive visit, the pediatrician weighs and then, taking into account also the age of the child and his state of health, the specialist must calculate the required volume of the mixture (or, if necessary, recommend another mixture).
We draw conclusions:
- The child eats up the mixture if he actively plays, sleeps soundly and goes to the toilet regularly.
- In a month, a child should eat a mixture per day in the amount of ⅕ of his weight, or 700-750 ml.
- At 2 months, the amount of formula is ⅙ of the baby's weight, or 750-800 ml per day.
- At 3 months, the ratio of body weight and the amount of the mixture remains - ⅙, which is approximately 800-850 ml.
- If you suspect your child is malnourished, seek medical advice.
Author of article
Tiunova Elena
Pediatrician of the highest category, nutritionist, candidate of medical sciences, associate professor of the department of faculty pediatrics and propaedeutics of childhood diseases, Ural State Medical University
About the author
Share on Vkontakte Share on Odnoklassniki
Article content
- How to tell if a child is full
- How much formula should a child eat per month
- How much formula should a baby eat at 2 months
- How much formula should a baby eat at 3 months
- Mixture Rate Chart
- What to do if the child does not fill up with formula
Products from article
Nutrilak Premium Baby Powder COMFORT
Powdered infant formula Nutrilak Premium 1
0 to 6 months
Nutrilak Premium 2 infant formula
6 to 12 months
May be interested
- Allergy to formula in a child
- How to switch to mixture
- Bedtime formula and night formula feeds
- How do you know if formula isn't right for your baby?
How much formula should be given to a child depending on age,
- Polina Alexandrovna, when might a baby need powdered milk formula?
- There are several situations when a mother is physically unable to breastfeed her baby and switches to artificial or mixed feeding (covers the baby's nutritional needs partly from breast milk, partly from formula):
- Contraindications to breastfeeding by mother and / or child.

- Lack of milk is true hypogalactia.
- Psychological reasons why a mother is not ready to breastfeed.
- The child needs a special medical formula.
- What determines the amount of formula that a child eats, and how to calculate how much formula a child needs?
- Often mothers think that the amount of formula depends only on age, but the weight of the child is also an important factor . Each age has its own formulas for calculating the mixture for one meal.
Important! The weight of children of the same age, especially the first months of life, can be radically different. Accordingly, the volume of the milk mixture for them will be different.
On mixed feeding, the total amount of milk nutrition per day that the child should consume depends on the amount of breast milk. The main part of the mother gives breast milk, and the amount that is not enough for the daily norm, replenishes, feeding the mixture.
- Let's talk about how much formula a child needs and what a baby can do at different periods of development. Let's start from the first days of the baby: how much formula should a newborn baby receive?
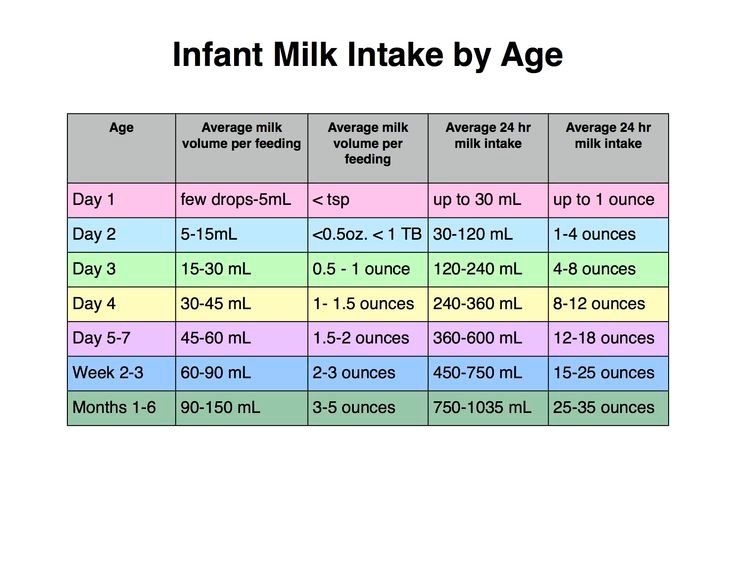
- The stomach of a newborn holds about 10 ml per feeding. With each subsequent day, the volume of the stomach and nutrition increases by 10 ml, that is, on the second day of life it is 20 ml, on the third - 30 ml, by the seventh day - 70 ml. Formula-fed baby receives power at intervals of three hours.
The volume of the mixture on artificial feeding up to 1 month:
- the amount of food per day is 500-700 ml,
- the number of feedings in one day is 8-10.
Read also
- how to calculate the nutrition of a newborn
HOW MUCH FORMULA SHOULD BE GIVED IN 1 MONTH
- By one month, the child has a feeding regimen. By this age, the baby begins to open his eyes more often and fix his eyes on his mother, especially at the time of feeding (the distance at which the baby can focus his eyes is 20 cm, this is the distance from the mother’s chest to her eyes). Some babies gradually learn to hold their heads: it doesn’t work out completely, but they are already trying.
By this age, the baby begins to open his eyes more often and fix his eyes on his mother, especially at the time of feeding (the distance at which the baby can focus his eyes is 20 cm, this is the distance from the mother’s chest to her eyes). Some babies gradually learn to hold their heads: it doesn’t work out completely, but they are already trying.
The volume of the mixture on artificial feeding from 1 to 2 months:
- the amount of food per day - 600-900 ml,
- the number of feedings in one day is 7-8.
HOW MUCH FORMULA DOES A 3 MONTH BABY NEED
- The baby continues to grow and gain weight. He raises his head more confidently. She can smile at her mother and start laughing closer to four months.
Volume formula formula fed 3 to 4 months:
- the amount of food per day - 750-950 ml,
- the number of feedings in one day is 6-7.

HOW MUCH FORMULA DOES A 4 MONTH BABY NEED
- The baby recognizes his mother very well. At this age, a “complex of revival” appears - when mom or dad, a close relative, comes into the room, the baby comes to life (begins to walk, move arms and legs). In physical development, this is the period of the first attempts to roll over, and some babies begin to roll over from their tummy to their back.
Volume formula formula fed 4 to 5 months:
- the amount of food per day - 850-1000 ml,
- the number of feedings in one day is 5-6.
HOW MUCH FORMULA DOES A 5 MONTH BABY NEED
- The baby recognizes his mother very well. At this age, a “complex of revival” appears - when mom or dad, a close relative, comes into the room, the baby comes to life (begins to walk, move arms and legs). In physical development, this is the period of the first attempts to roll over, and some babies begin to roll over from their tummy to their back.
Volume formula formula fed 5 to 6 months:
- the amount of food per day - 850-1000 ml,
- the number of feedings in one day is 5-6.
RECOMMENDED AMOUNT OF BREAST-MILK SUBSTITUTE FOR BREAST-FEEDING
HOW MUCH FORMULA DOES A 6 MONTHS BABY NEED
- Some babies can crawl or are just learning to do so. Others follow a different scenario and learn to sit - they begin to sit down and hold in this position. Usually a child does one thing: either learns to sit and then begins to crawl, or begins to crawl and from this position begins to sit.
HOW MUCH FORMULA DOES A 6-12 MONTHS BABY NEED
- The baby becomes more mobile and can move wherever he wants. Begins to be interested in subjects that were previously inaccessible to him. Gradually preparing for walking - learned to crawl, began to get on his knees and then fully on his legs, move, holding the handles on the supports, then walk by one handle.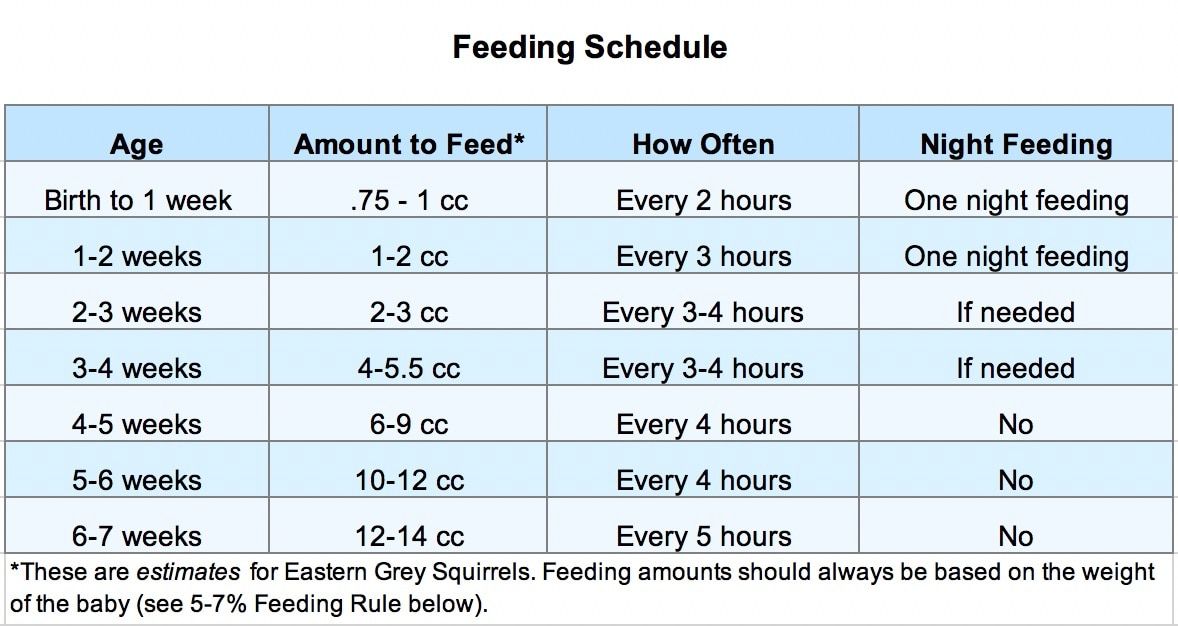 At about 12 months, the baby takes its first steps.
At about 12 months, the baby takes its first steps.
HOW MUCH FORMULA DOES A 12 MONTH BABY NEED
— The kid is mature enough and independent. There is an active development of walking, speech. The child becomes a smaller copy of an adult with his own desires and needs.
After 6 months, children receive complementary foods, and this happens differently for different babies, so it is not possible to specify the total amount of food for all. At this age, everything is calculated individually, and the amount of supplementary feeding with a mixture depends on the amount of complementary foods , which the child receives.
- How to work out the optimal frequency of feeding?
- It is advisable to focus on the indicators of the table. For example, on the packaging of each formula of the MAMAKO ® Premium mixture, there is a feeding table that is averagely suitable for babies of different ages. If the child eats little and often, then this can become a problem at the stage of complementary feeding (the child gets used to eating every hour, but he will not be given complementary foods on demand). By the time complementary foods are introduced, it is desirable that the child has established 5 meals a day (maximum 6 meals a day), not counting night feedings.
If the child eats little and often, then this can become a problem at the stage of complementary feeding (the child gets used to eating every hour, but he will not be given complementary foods on demand). By the time complementary foods are introduced, it is desirable that the child has established 5 meals a day (maximum 6 meals a day), not counting night feedings.
How to determine how much formula a baby needs
- Polina Alexandrovna, is it worth focusing on the behavior of the child and considering that his body "knows how best", or should we try to do everything clearly according to the standards?
“Parents need to follow the rules. If you know the norm of the amount of food, you can assess how much the child, following his desires, consumes this norm - whether he has enough, whether he eats less or asks for food in excess. If you focus only on the wishes of the child, you will not be able to assess how normal the situation is.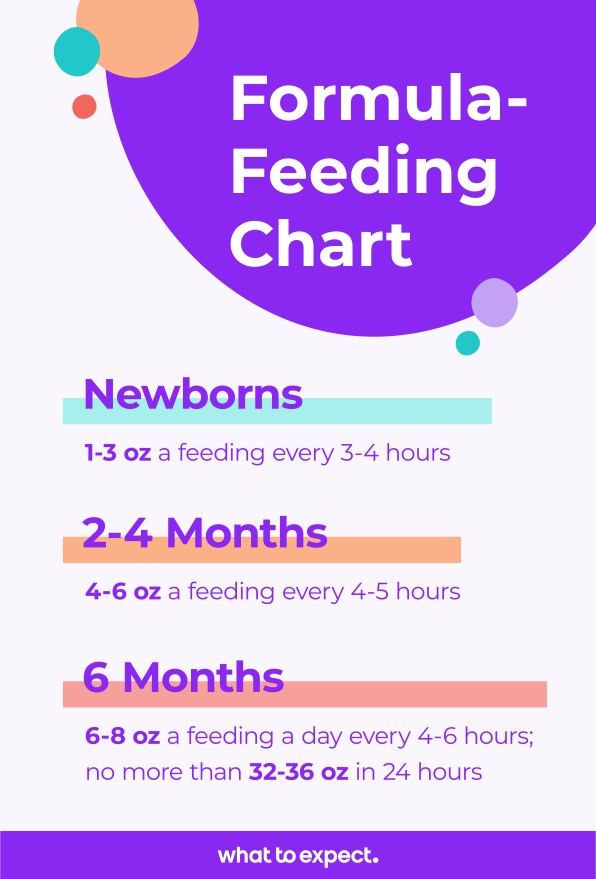
Usually, if the baby does not eat up the amount of food, he does not gain weight and is slightly behind in development. Nothing good comes out of this, just like if a child goes over the norm. We must try to stay within the norm. However, sometimes it is permissible to deviate from the rules for a short time (the baby is sick and has a poor appetite).
- How to understand that the child has enough formula and does not need to try to supplement?
- According to the signs that are noticeable to the mother or that can be assessed:
- behavior - the child is calm, active, in a good mood - he is unlikely to be malnourished;
- appearance — the child gains weight well or, conversely, began to look thinner;
- weighing — if the child gains weight and height within the normal range, we can say that the food is sufficient
See also
- what to do if the baby is not gaining weight well
— How does underfeeding manifest itself?
- Underfeeding is primarily manifested by the behavior of the child - he becomes whiny, irritable, can be constantly excited.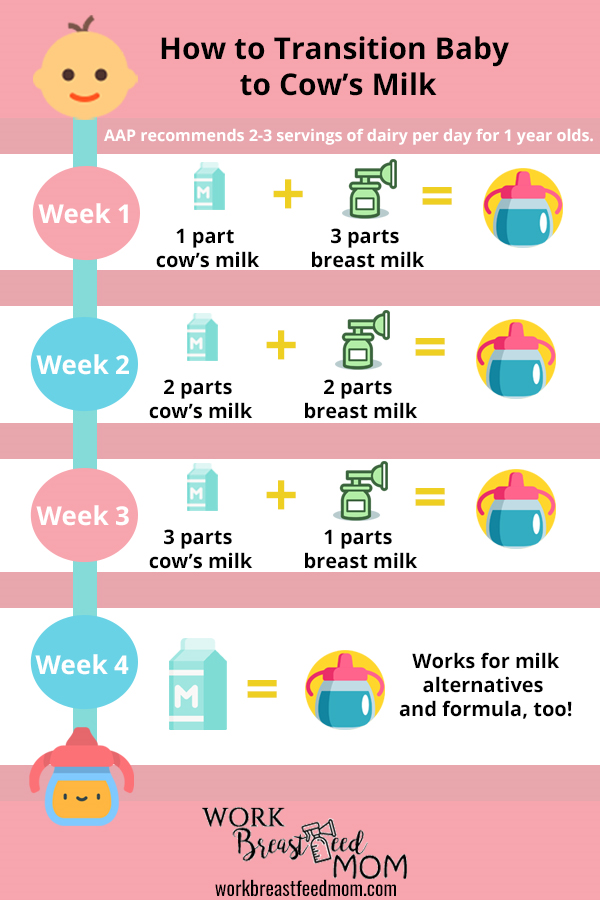 Outwardly, it is noticeable that the child is not gaining weight well or has lost weight.
Outwardly, it is noticeable that the child is not gaining weight well or has lost weight.
Important! The child is constantly lethargic and sleepy, there are long breaks between feedings - this may indicate extreme underfeeding and is a reason to see a doctor.
— How does overfeeding manifest itself?
- If overfeeding is one-time, then most often the child spits up an excessive amount of formula milk or breast milk. If a child is regularly fed more than normal, then the main indicator of overfeeding will be excessive weight gain - growth will continue to increase evenly, but the weight will not correspond to growth.
— Polina Aleksandrovna, is it possible to distinguish a child's anxiety from hunger from other problems?
- It is necessary to objectively assess at what time the child is worried.
- If a child is anxious 2.5 hours after feeding, it can be assumed that he cannot stand the three-hour interval between feedings and is hungry before the due date.

- If the child is worried 15-20 minutes after feeding, then most likely the reason is not hunger. Wet diaper, wants to sleep, high body temperature, environmental conditions become uncomfortable, tired of lying on one side and wants to roll over - you always need to assess the situation objectively.
Advice to mom: at the first concern of the child, you should not assume that he is hungry and try to feed him. The reasons for concern can be varied.
MAMAKO ® 1 Premium with 2'-FL Human Milk Oligosaccharides is an important step in the evolution of baby nutrition.
- How to supplement if the child does not eat his norm for feeding?
- First you need to determine whether the norm is adequate for the age and weight of the child. Mothers think that a child needs one amount of food, but according to his weight, it may be less. If the child is undernourished and there is insufficient weight gain and growth, then it makes sense to supplement him during sleep, add night feedings.
Mothers think that a child needs one amount of food, but according to his weight, it may be less. If the child is undernourished and there is insufficient weight gain and growth, then it makes sense to supplement him during sleep, add night feedings.
Feeding around dreams is feeding during sleep, when the baby is not awake and cannot stop eating.
— What to do if the child has eaten his norm and continues to ask for food?
- A child who has eaten his norm and is worried, most likely, is not so acutely hungry that he should be supplemented. Try to distract the baby, switch his attention and see how he behaves further. At the same time, you need to be sure of the relevance of the nutritional norm calculated for the child, and always check it for compliance with the age and weight of the baby.
At each age, each child has his own rate of consumption of milk formula. How many milliliters of the mixture a child should eat, the doctor calculates, taking into account the age and weight of your baby.