3 week old baby food intake
Formula Feeding FAQs: How Much and How Often (for Parents)
Whether you plan to formula feed your baby from the start, want to supplement your breast milk with formula, or are switching from breast milk to formula, you probably have questions.
Here are answers to some common questions about formula feeding.
How Often Should I Feed My Baby?
Newborns and young babies should be fed whenever they seem hungry. This is called on-demand feeding.
After the first few days of life, most healthy formula-fed newborns feed about every 2–3 hours. As they get bigger and their tummies can hold more milk, they usually eat about every 3–4 hours. As babies get older, they’ll settle into a more predictable feeding routine and go longer stretches at night without needing a bottle.
Talk to your doctor if you have concerns about feeding your baby, especially if your baby is very small, is not gaining weight, or was born early (prematurely).
How Can I Tell When My Baby Is Hungry?
Signs that babies are hungry include:
- moving their heads from side to side
- opening their mouths
- sticking out their tongues
- placing their hands, fingers, and fists to their mouths
- puckering their lips as if to suck
- nuzzling again their mothers' breasts
- showing the rooting reflex (when a baby moves its mouth in the direction of something that's stroking or touching its cheek)
Babies should be fed before they get upset and cry. Crying is a late sign of hunger. But every time your baby cries is not because of hunger. Sometimes babies just need to be cuddled or changed. Or they could be sick, tired, too hot or too cold, in pain, or have colic.
How Much Should My Baby Drink?
In the first few weeks, give 2- to 3-ounce (60- to 90-milliliter) bottles to your newborn. Give more or less depending on your baby’s hunger cues.
Here's a general look at how much your baby may be eating at different ages:
- On average, a newborn drinks about 1.5–3 ounces (45–90 milliliters) every 2–3 hours. This amount increases as your baby grows and can take more at each feeding.
- At about 2 months, your baby may drink about 4–5 ounces (120–150 milliliters) every 3–4 hours.
- At 4 months, your baby may drink about 4–6 ounces (120-180 milliliters) at each feeding, depending on how often they eat.
- By 6 months, your baby may drink 6–8 ounces (180–230 milliliters) about 4–5 times a day.

Watch for signs that your baby is hungry or full. Respond to these cues and let your baby stop when full. A baby who is full may suck with less enthusiasm, stop, or turn away from the bottle.
Why Does My Baby Seem Hungrier Than Usual?
As babies grow, they begin to eat more at each feeding and can go longer between feedings. Still, there may be times when your little one seems hungrier than usual.
Your baby may be going through a period of rapid growth (called a growth spurt). These can happen at any time, but in the early months are common at around:
- 7–14 days old
- between 3–6 weeks
- 4 months
- 6 months
During these times and whenever your baby seems especially hungry, follow their hunger cues and continue to feed on demand, increasing the amount of formula you give as needed.
Is My Baby Eating Enough?
At times, you may wonder whether your baby is getting enough nutrients for healthy growth and development. Babies who get enough to eat seem satisfied after eating and are regularly peeing and pooping.
Babies who get enough to eat seem satisfied after eating and are regularly peeing and pooping.
At your baby’s checkups, the doctor will review your baby’s growth chart, track your little one’s development, and answer any questions. Talk to your doctor if you have any concerns about your baby’s feeding and nutrition.
Reviewed by: Mary L. Gavin, MD
Date reviewed: November 2021
Feeding Your Newborn (for Parents)
How you feed your newborn is the first nutrition decision you make for your child. These guidelines on breastfeeding and bottle feeding can help you know what's right for you and your baby.
Breast or Bottle?
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommends that babies be breastfed exclusively for about the first 6 months. After they start on solid foods, babies should breastfeed through the first year of life and even beyond, if desired.
But breastfeeding isn't possible or preferable for all new moms. Deciding to breastfeed or bottle feed a baby is usually based on the mother's comfort level with breastfeeding and her lifestyle. In some cases, breastfeeding may not be recommended for a mom and her baby. If you have any questions about whether to breastfeed or formula feed, talk to your pediatrician.
In some cases, breastfeeding may not be recommended for a mom and her baby. If you have any questions about whether to breastfeed or formula feed, talk to your pediatrician.
Remember, your baby's nutritional and emotional needs will be met whether you choose to breastfeed or formula feed.
Benefits of Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding your newborn has many benefits. Perhaps most important, breast milk is the perfect food for a baby's digestive system. It has the nutrients that a newborn needs, and it’s easily digested. Commercial formulas try to imitate breast milk, and come close, but can't match it exactly.
Breast milk has
antibodiesthat help protect babies from many infections, including diarrhea and ear and lung infections. Breastfed babies are less likely to develop medical problems such as diabetes, high cholesterol, asthma, and allergies. Breastfeeding also might make a child less likely to become overweight.
Breastfeeding is great for moms too. It burns calories, so can help nursing moms lose the weight gained during pregnancy. Breastfeeding also may offer protection from breast cancer and ovarian cancer.
It burns calories, so can help nursing moms lose the weight gained during pregnancy. Breastfeeding also may offer protection from breast cancer and ovarian cancer.
Some moms find breastfeeding easier and quicker than formula feeding — it needs no preparation, and you don't run out of breast milk in the middle of the night. Also, breastfeeding costs little. Nursing mothers do need to eat more and may want to buy nursing bras and pads, a breast pump, or other equipment. But these expenses are generally less than the cost of formula.
Breastfeeding meets a variety of emotional needs for both moms and babies. The skin-to-skin contact can enhance the emotional connection, and providing complete nourishment can help new moms feel confident in their ability to care for their newborn.
Limitations of Breastfeeding
With all the good things known about breastfeeding, why doesn't every mother choose to breastfeed?
Breastfeeding requires a big commitment from a mother. Some new moms feel tied down by the demands of a nursing newborn. Because breast milk is easily digested, breastfed babies tend to eat more often than babies who are fed formula. This means moms can be in demand as often as every 2 or 3 hours in the first few weeks. This can be tiring, but it's not long before babies feed less often and sleep longer at night.
Some new moms feel tied down by the demands of a nursing newborn. Because breast milk is easily digested, breastfed babies tend to eat more often than babies who are fed formula. This means moms can be in demand as often as every 2 or 3 hours in the first few weeks. This can be tiring, but it's not long before babies feed less often and sleep longer at night.
Some new mothers need to get back to work outside the home or separate from their babies from time to time for other reasons. Some opt for formula feeding so other caregivers can give the baby a bottle. Mothers who want to continue breastfeeding can use a breast pump to collect breast milk to be given in a bottle, so their babies still get its benefits even when mom isn't there to breastfeed.
Fathers and other family members may want to share in feeding the baby. When mom is breastfeeding, dad or siblings may want to stay close by. Helping mom get comfortable, or providing a burp cloth when needed, will let them be part of the experience.
When breastfeeding is going well, other family members can help by giving the baby pumped breast milk in a bottle when mom needs a break.
Some moms may feel embarrassed or worried about breastfeeding. These feelings usually end after a successful breastfeeding process is set. It can help to get advice from those who've gone through the experience. Most hospitals and birthing centers offer in-depth instruction on breastfeeding to new moms. Your pediatrician, nurse practitioner, or nurse can answer questions or put you in touch with a lactation consultant or a breastfeeding support group.
In some cases, a mother's health may affect her ability to breastfeed. Moms getting chemotherapy for cancer and those who have HIV should not breastfeed, for example.
If you have a medical condition or take any medicines regularly, talk with your doctor about whether it's OK to breastfeed. If you have to stop nursing temporarily, continue to pump breast milk to maintain milk production. If you or your baby are sick, continue to breastfeed if you can. Talk to the doctor if you have any concerns.
If you or your baby are sick, continue to breastfeed if you can. Talk to the doctor if you have any concerns.
In some situations, it may not possible to breastfeed, such as when a baby is very sick or born early. Mothers should talk with their baby's doctor about expressing and storing milk. Often, a baby who can't breastfeed can get breast milk through a feeding tube or bottle.
Some moms who have inverted nipples may have trouble breastfeeding, but a lactation consultant usually can help them overcome this. Likewise, women who have had plastic surgery on their breasts should be able to successfully breastfeed. Talk with your doctor if you have any concerns.
Hold off on pacifiers or bottles until your baby has gotten used to and is good at breastfeeding. Lactation professionals recommend waiting until a baby is about 3–4 weeks old before offering artificial nipples of any kind (including pacifiers).
Benefits of Formula Feeding
Commercially prepared infant formula is a nutritious alternative to breast milk.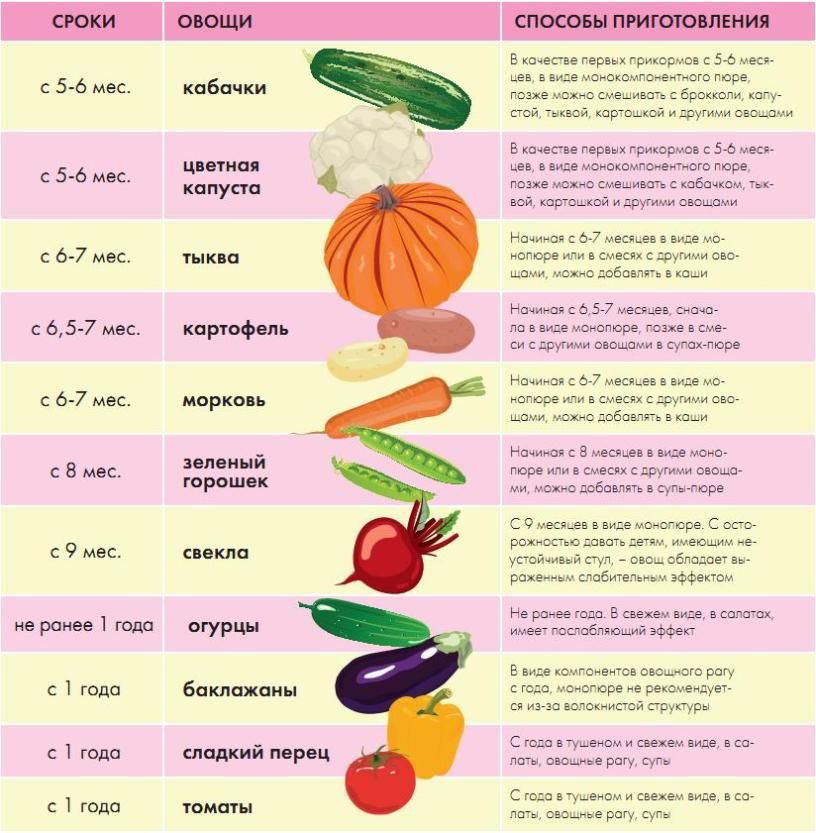 Bottle feeding can offer more freedom and flexibility for moms, and make it easier to know how much the baby is getting.
Bottle feeding can offer more freedom and flexibility for moms, and make it easier to know how much the baby is getting.
Because babies digest formula more slowly than breast milk, a baby who is getting formula may need fewer feedings than one who breastfeeds. Formula feeding also can make it easier to feed the baby in public, and lets the father and other family members help feed the baby, which can enhance bonding.
Limitations of Formula Feeding
Just as breastfeeding has its unique demands, so does bottle feeding. Bottle feeding takes organization and preparation, especially if you want to take your baby out. Store-bought formula can be pretty expensive, but do not try to make your own formula at home.
It's important to make sure that you have enough formula on hand, and bottles that are clean and ready to be used.
Here are a few guidelines for formula feeding:
- Carefully follow directions on the label when preparing formula. Do not add more water than directed.
- Bottles left out of the refrigerator longer than 1 hour and any formula left in the bottle that a baby doesn't finish should be discarded.
- Prepared bottles of formula can be stored in the refrigerator up to 24 hours and carefully warmed just before feeding. You don't have to warm formula, but most babies prefer it.
- A bottle of formula can be warmed by holding it in running warm water or setting it in a pan of warm water. A bottle of formula (or breast milk) should never be warmed in a microwave. The bottle can heat unevenly and leave "hot spots" that can burn a baby's mouth.
How Often Do Newborns Eat?
Your newborn will nurse about 8 to 12 times per day during the first weeks of life. In the beginning, mothers may want to try nursing 10–15 minutes on each breast, then adjust the time as needed.
Breastfeeding should be on demand (when your baby is hungry), which is generally every 1–3 hours. As newborns get older, they'll nurse less often and have longer stretches between feedings. Newborn babies who are getting formula will likely take about 2–3 ounces every 2–4 hours. Newborns should not go more than about 4–5 hours without feeding.
Newborn babies who are getting formula will likely take about 2–3 ounces every 2–4 hours. Newborns should not go more than about 4–5 hours without feeding.
Signs that babies are hungry include:
- moving their heads from side to side
- opening their mouths
- sticking out their tongues
- placing their hands and fists to their mouths
- puckering their lips as if to suck
- nuzzling against their mothers' breasts
- crying
A feeding schedule is not necessary — you and your baby will get into a routine. Babies know (and will let their parents know) when they're hungry and when they've had enough. Watch for signs that your baby is full (slowing down, spitting out the bottle or unlatching from breast, closing the mouth, turning away from the breast or bottle) and stop the feeding when these signs appear.
As babies grow, they begin to eat more at each feeding and can go longer between feedings. There may be other times when your infant seems hungrier than usual. Continue to nurse or feed on demand. Nursing mothers need not worry — breastfeeding stimulates milk production, and your supply of breast milk will adjust to your baby's demand for it.
Continue to nurse or feed on demand. Nursing mothers need not worry — breastfeeding stimulates milk production, and your supply of breast milk will adjust to your baby's demand for it.
Is My Newborn Getting Enough to Eat?
New parents often worry about whether their babies are getting enough to eat.
Babies are getting enough to eat if they:
- seem satisfied
- have about 6–8 wet diapers a day
- have regular bowel movements (poops)
- sleep well
- are alert when awake
- are gaining weight
A baby who is fussing, crying, seems hungry, does not appear satisfied after feeding, and has fewer wet diapers may not be getting enough to eat. If you're concerned that your baby isn't getting enough to eat, call your doctor.
Most infants "spit up" a small amount after eating or during burping, but a baby should not vomit after feeding. Vomiting after every feeding might be a sign of an allergy, digestive problem, or other problem that needs medical care. If you have concerns that your baby is spitting up too much, call your doctor.
If you have concerns that your baby is spitting up too much, call your doctor.
Should Newborns Get Nutritional Supplements?
Breast milk has the right combination of vitamins and easily absorbed iron for newborns. A healthy infant being nursed by a healthy mother doesn't need extra vitamins or nutritional supplements, with the exception of vitamin D. Breastfed babies should begin vitamin D supplements within the first few days of life, continuing until they get enough vitamin D-fortified formula or milk (after 1 year of age).
Breastfeeding mothers who follow vegetarian diets that do not include animal products need vitamin B12 supplements.
Iron-fortified formula has the right blend of vitamins and minerals for a baby, so supplements usually aren't needed. Infants drinking less than 1 liter, or about a quart, of formula a day may need a vitamin D supplement.
Water, juice, and other foods usually aren't necessary during a baby's first 6 months. Breast milk and formula provide everything babies need nutritionally until they start eating solid foods. Talk to your doctor if you have any questions about feeding your newborn.
Talk to your doctor if you have any questions about feeding your newborn.
Reviewed by: Mary L. Gavin, MD
Date reviewed: February 2021
how much milk a child needs for 1 feeding, the rate of formula and breast milk
The birth of a baby is a very joyful event. However, along with the joy of parents, many more questions arise. After all, it is so important that the baby grows up healthy and actively develops. One of the first such questions is usually: "How much does a newborn eat per feeding?" It would seem that feeding is such a natural process that it should not cause difficulties. However, most mothers are concerned that the baby does not have enough milk or, on the contrary, he overeats. How to strike a balance? Let's talk about it in this article. nine0003
Content: Hide
- Features of breastfeeding
- On colostrum
- Consumption norms
- How to calculate the volume of feeding
- What is important to take into account artificial feeding
Prevention.
 As a rule, the most difficult in the matter of feeding is the first week after childbirth. At this time, mother and child are only learning to understand each other. But there is no doubt that breast milk is the best food for a baby. This product is perfect by nature and has everything you need at every stage. nine0003
As a rule, the most difficult in the matter of feeding is the first week after childbirth. At this time, mother and child are only learning to understand each other. But there is no doubt that breast milk is the best food for a baby. This product is perfect by nature and has everything you need at every stage. nine0003 Breastfeeding is good for both the baby and the mother:
- it helps the baby to get the substances necessary for growth, development and immunity and just satisfy hunger;
- promotes active contraction of the woman's uterus (under the influence of sucking movements) and a faster recovery process after childbirth.
About colostrum
Newborns eat little, their sucking reflex is just developing and is beginning to be put into practice. In addition, a woman's milk is not produced immediately. In the mammary glands at the end of pregnancy and in the first hours after childbirth, colostrum is formed. This is not exactly milk, it even outwardly differs from mature milk, and in its chemical composition it is similar to blood. This is a very valuable product. It is high in fat and contains immunoglobulins and antitoxins, which strengthen the immune system and protect the baby's body from infections. After a few days, colostrum is replaced by transitional milk. It is lighter, but also quite oily. nine0003
This is a very valuable product. It is high in fat and contains immunoglobulins and antitoxins, which strengthen the immune system and protect the baby's body from infections. After a few days, colostrum is replaced by transitional milk. It is lighter, but also quite oily. nine0003
Read also: Complementary foods for artificial feeding
Consumption rates
This is important!
A mother should not worry that her baby was hungry, even if she applied it 10 times to the breast, but it seems that he did not eat almost a drop. The size of the stomach of a newborn is very small, so only about 10 ml is eaten per feeding. Thus, for the whole day the baby can drink up to 100 ml.
On average, milk arrives 3-4 days after birth and its quantity gradually increases. The stomach of the baby also grows. This means that the amount of milk consumed also increases. So, for the first day, a newborn can drink 10 ml per feeding, for the second day - 20 ml, and for the third - 30 ml. But remember that each organism is individual and there are no strict limits here. However, if by the 4-5th day of life the child's body weight does not increase, but only decreases (by more than 8%), then this requires the attention of a specialist. nine0003
But remember that each organism is individual and there are no strict limits here. However, if by the 4-5th day of life the child's body weight does not increase, but only decreases (by more than 8%), then this requires the attention of a specialist. nine0003
There is a folk way to determine the rate of consumption of breast milk. You need to multiply the number of days that have passed since the day of birth by 10. But this method is inaccurate and has no scientific confirmation.
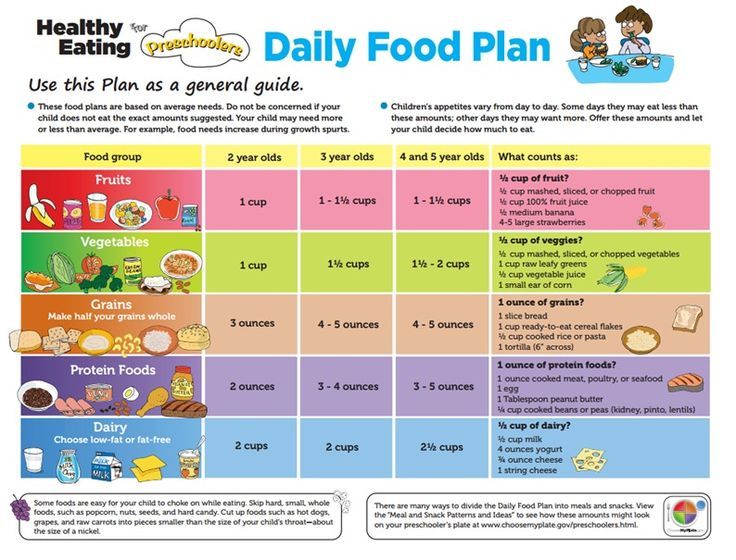
So how much should a newborn eat per feeding? The table shows the daily and one-time volume of milk by months for children under 1 year old.
| Child's age | Molo volume for one feeding (ml) | Milk rate per day (ml) |
| 3-4 days | 20-60 | 9000 200-300 | 666
| 1 week | 50–80 | 400 |
| 2 weeks | 60–90 | 20 % of body weight |
| 9000 1 month 1 month 1 month 1 months0002 100–110 | 600 | |
| month | 120–1503 | 800 |
9000 3 months | 9000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 150000061 | 1/6 body weight | |
| 4 months | 180–210 | |
| 9000 month | 210–24000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 | 1/7 body weight |
| 7–12 months | 210–240 | 1/8–1/9 body weight |
do not forget that children with children located breastfeeding, complementary foods are introduced at about 6 months. This means that the amount of milk consumed is reduced, giving way to more adult food. nine0003
This means that the amount of milk consumed is reduced, giving way to more adult food. nine0003
How to calculate the amount eaten
In terms of measuring the amount eaten, formula feeding seems to be just perfect. Here is a bottle with a scale, here is water, here is a measuring spoon. However, in terms of its benefits, formula milk will never be compared with breast milk. And besides, making measurements is not as difficult as it seems at first glance. Babies just need to be weighed before and after feeding on a baby scale. To ensure the accuracy of the result, you need to weigh several times a day. If nothing threatens the health of the baby, he does not look thin and pale, develops according to age, and the mother has enough milk, then monthly weighing in the clinic is usually enough. nine0003
Feeding schedule
For breastfed babies, there is a rule - to put the baby to the breast on demand. Previously, it was believed that it was necessary to maintain an interval of 3 hours, but now pediatricians agree that the breaks between feedings can be 1. 5–2 hours. This does not mean at all that the baby will overeat.
5–2 hours. This does not mean at all that the baby will overeat.
Video: Does a baby get enough food in the first months of life?
Author: pediatrician, Ph.D. Komarovsky E.O. nine0003
The duration of one feeding is usually 15-30 minutes. Although there are deviations from the norm. For example, a woman has a lot of milk, and the child is full in 5-10 minutes. Or, on the contrary, there is not enough milk, and the baby can suck out the remains for a long time. Some babies just enjoy suckling and use their mother's breast as a pacifier.
What is important to consider
At first, mother and baby are just getting used to the ongoing changes, so the feeding regimen may not be ideal. However, you should adhere to the following rules. nine0003
- In the first couple of weeks, a woman needs a lot of dedication, because the interests of the child in the matter of satisfying hunger come to the fore.
 You can’t refuse food to a baby, even if it costs a sleepless night.
You can’t refuse food to a baby, even if it costs a sleepless night. - If there is any doubt that the baby is undernourished or overeating, it is best to start monitoring the frequency of feedings. So, you need to mark the time at which the baby was really hungry, mark the intervals between feedings. This information may also be useful at the appointment with the pediatrician. nine0010
- It is impossible to establish a clear feeding regime, as with artificial feeding, especially in the first weeks after birth. Maintaining intervals of more than 2–3 hours during the day and 3–4 hours at night is highly discouraged.
- Do not try to force feed your baby. He is still too young to realize the need for food, and is guided solely by his feeling of hunger. If the baby persistently refuses the breast, you need to try to offer him to eat a little later. If the interval is too large, it is better to contact a specialist for advice. nine0010
- It is important that your baby latch on correctly.
 His mouth should capture not only the nipple, but also the areola. Thus, the milk will properly enter the mouth, and the woman will reduce the risk of cracked nipples.
His mouth should capture not only the nipple, but also the areola. Thus, the milk will properly enter the mouth, and the woman will reduce the risk of cracked nipples. - Soothers and bottles are not recommended for breastfed babies. Such products can reduce the intensity of sucking movements.
- It is best to give your baby only one breast at a time. In the mammary gland, fore milk is formed, with which the baby quenches his thirst, and hind milk, with which he "eats up", since it is more nutritious in composition. nine0010
- Hold the baby upright for about 10 minutes after each feed. This helps to free the tummy from air and excess milk.
As a rule, with a normal feeding regimen and a sufficient amount of milk from the mother, by the month the weight of the child increases by 500–600 g. Now consider the situation when the mother does not have the opportunity to breastfeed the baby. In this case, it is necessary to choose a quality milk formula that will cover the nutritional needs. The pediatrician should help in this matter. The doctor will always take into account the peculiarities of the child's health and will be able to advise a regular or medicinal product. Do not forget that when breastfeeding, the baby makes more effort. He drinks milk gradually and feels full. When feeding with a formula, a strict dosage is needed, since usually saturation does not come immediately, and the baby may require a supplement that he does not really need (the feeling of hunger should disappear after a few minutes). nine0003
The pediatrician should help in this matter. The doctor will always take into account the peculiarities of the child's health and will be able to advise a regular or medicinal product. Do not forget that when breastfeeding, the baby makes more effort. He drinks milk gradually and feels full. When feeding with a formula, a strict dosage is needed, since usually saturation does not come immediately, and the baby may require a supplement that he does not really need (the feeling of hunger should disappear after a few minutes). nine0003
Consumption rates
Almost all known mixtures require 8 or 7 meals a day with an interval of 3 hours. Night feedings are also included. When the baby grows up a little, it will be possible to skip them and sleep 5-6 hours until morning. With regard to formula milk, the principle of feeding on demand is not suitable. Therefore, it is necessary to observe both the dosage indicated by the manufacturer and the regimen.
It will not be difficult to calculate how much the baby eats for feeding.
| Age | Daily milk rate from body weight |
| 10 days - 1.5 months | 9000 1/5 | 9000 9000 1.5–4 months | 1/6 |
| 4–6 months | 1/7 |
| 6–8 months | 1/8 |
| 9000 8 months - 1 year 9000 | 1/9 |
For example, a baby is 2 months old and weighs 4800 grams. According to the table, we divide 4800 by 6 and get the daily rate - 800 ml of milk formula per day. To calculate the volume of one feeding, divide 800 by 6 (number of feedings per day). Thus, the child eats about 130 ml of formula at a time.
Not everyone can find the right mixture right away, but do not despair. Even with allergies, digestive problems, cow's milk protein intolerance, you can find a suitable product, but only under the strict supervision of a doctor.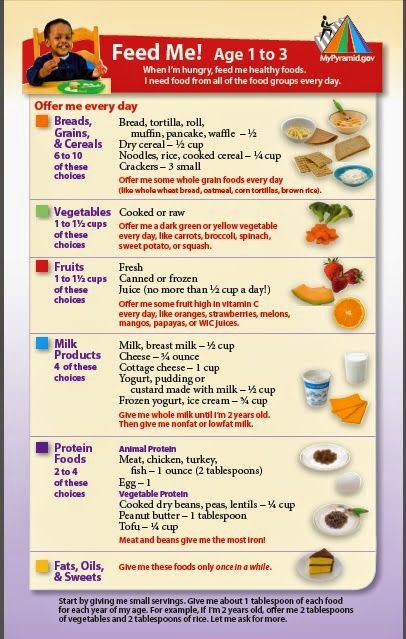 nine0064
nine0064
#Nutrition for children up to a year
How much a newborn should eat: feeding table
0-6 months
Article
5/5 2 reviews
As soon as the long-awaited event has happened and the baby is born, the mother is faced with many questions. One of the most frequently asked: how to feed and how much should a newborn eat? Indeed, this is a very important point, since a properly selected and debugged diet allows the child to grow and develop harmoniously, promotes good health and strengthens the immune system. How to calculate the norm for a baby from the first days of life to a year? nine0003
8 min. for reading Feb. 17, 2022
Contents
Listen to the experts
Calculation norms
- First weeks of life
- One to four months
- Five to six months
- Seven to twelve months
How much breast milk a newborn should eat: table
Not enough breast milk or not at all: what to do
Norms and stages of the introduction of complementary foods
- First stage - vegetables
- Second stage - cereals
- Third stage - fruits
- Fourth stage - meat
- Fifth stage - new flavors
An example of a daily diet for a 6-8 month old baby
Frequently Asked Questions
Listen to the experts baby's age.
 All these data are usually voiced to parents during a doctor's appointment and entered into the card for further assessment of the child's condition. Comparison of the actual weight and the prescribed norms allows you to find out whether the child is eating well enough and, if necessary, to correct mistakes made during feeding. If something is not clear to you at the appointment with the pediatrician, do not be afraid to ask again and clarify. After all, only a specialist can give competent recommendations specifically for your baby, based on the results of an examination or analysis. The advice of friends, grandmothers and mothers from various forums may be good, but they do not take into account the individual characteristics and needs of your child's body. So, they may not work or even hurt. nine0003
All these data are usually voiced to parents during a doctor's appointment and entered into the card for further assessment of the child's condition. Comparison of the actual weight and the prescribed norms allows you to find out whether the child is eating well enough and, if necessary, to correct mistakes made during feeding. If something is not clear to you at the appointment with the pediatrician, do not be afraid to ask again and clarify. After all, only a specialist can give competent recommendations specifically for your baby, based on the results of an examination or analysis. The advice of friends, grandmothers and mothers from various forums may be good, but they do not take into account the individual characteristics and needs of your child's body. So, they may not work or even hurt. nine0003 Be part of Nestle Baby&Me®
Each stage of a baby's development is unique and is associated with new questions from parents. Get advice from experts.
Registration
Calculation norms
1.
 The first month of life
The first month of life As soon as the baby is born, it is immediately brought to the mother's breast to feed. This helps to strengthen the immunity of the baby and stimulates lactation in the mother. During this period, there is still no milk in the breast, but there is a very nutritious transparent sweetish liquid - colostrum. It is released in the first two or three days after birth and supplies the child with all the necessary substances. To eat, the baby needs a few drops: on the first day of life, the small stomach holds only 7 milliliters. On the second day of life, the baby begins to eat more often. It needs to be fed on demand or every two to three hours, while the baby eats within 10-20 milliliters at one time. Thus, per day the norm will be approximately 90 milliliters. Starting from the third day after birth, the mother actively produces breast milk, the volume of which increases as the child grows. In the first week of life, the baby should eat from 50 to 80 milliliters of milk at a time, and 400 milliliters per day. At two weeks of age, the daily ration should be 20% of the weight of the newborn, and closer to a month - about 600 milliliters. It is important to note that these figures are approximate. Each baby needs its own, certain amount of milk or mixture, depending on individual characteristics: height, weight, mother's milk quality, calorie content of the mixture and the rate of development of the baby. nine0003
See also: Breastfeeding: the first steps after childbirth
2. From one to four months
Every day the baby grows, gains weight and increases its daily portions of milk. Having reached the month, the baby is already eating 90-100 milliliters six to seven times a day. After one month, the norms become as follows:
- At two months, the child should eat from 120 to 150 milliliters at a time. The daily norm, therefore, is 700-800 milliliters. nine0010
- A three-month-old baby should eat between 150 and 180 milliliters. In this case, it is recommended to observe the frequency of feeding no more than six to seven times a day.
- From the fourth month, babies need 180-210 milliliters of milk or infant formula. The average amount per day is not less than 1/6 of the baby's weight.
3.Five-six months
A six-month-old child normally eats 210-240 milliliters at a time, and the total amount of food per day should be 1/7 of body weight, or 800-1000 milliliters. Also, if there are no contraindications, complementary foods are introduced from six months. nine0003
4. From seven to twelve months
During this period, a single portion of breast milk for a baby ranges from 210 to 240 milliliters. At the same time, the average amount per day is not less than 1/8 of the child's body weight. Vegetable, fruit and meat purees, dairy-free and milk porridges are introduced into the diet (if the baby is not allergic to cow's milk proteins).
Below is a table detailing the daily dietary intake of a newborn for each age up to a year.
How much breast milk should a newborn eat: table
| Child's age | The amount of milk eaten per feeding, ml | The amount of milk eaten per day, ml |
| 3-4 days | 20–60 | 200-300 |
| 1 week | 50-80 | 400 |
| 2 weeks | 60–90 | 1/5 child weight |
| 1 month | 100–110 | 600 |
| 2 months | 120-150 | 800 |
| 3 months | 150-180 | 1/6 weight baby |
| 4 months | 180-210 | 1/6 weight baby |
| 5-6 months | 210-240 | 1/7 child weight (800-1000) |
| 7-12 months | 210-240 | 1/8 weight baby |
Important!
Remember that every child is unique, has individual characteristics and needs. Therefore, slight deviations from the standard indicators are quite possible.
Therefore, slight deviations from the standard indicators are quite possible.
Not enough breast milk or not at all: what to do
When a baby cries after waking up, he is hungry. Modern doctors do not advise mothers to maintain any strict feeding schedule. If the mother gives the baby a breast when he asks, and the baby eats for her own pleasure and at the same time sleeps soundly and well, smiles and is not naughty, then she is full and completely satisfied. nine0003
But if the baby cries and sleeps badly, then perhaps he does not have enough milk. In this case, check if the baby is eating his age norm, and try to keep track of this indicator in the future. Found that you don't have enough breast milk? Do not worry, it is better to immediately consult a doctor. The specialist will help you find a way to support milk production and improve lactation.
If you cannot solve the problem and normalize lactation, consult a pediatrician and find the right supplemental formula for your child.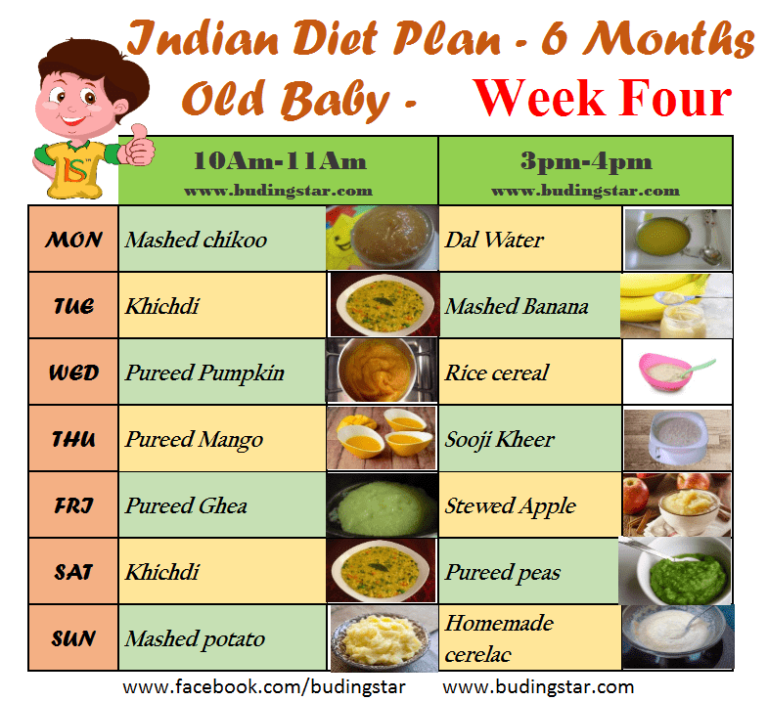 With strict observance of all the doctor's recommendations, instructions for preparation and dosages indicated on the package, the mixture makes it possible to compensate for the lack of breast milk and provide the baby with the necessary amount of nutrients. nine0003
With strict observance of all the doctor's recommendations, instructions for preparation and dosages indicated on the package, the mixture makes it possible to compensate for the lack of breast milk and provide the baby with the necessary amount of nutrients. nine0003
Important!
Even if you don't have enough breast milk to fully meet your baby's needs, try to remain on partial breastfeeding for as long as possible. After all, the ideal food for a child is mother's milk.
Complementary feeding rules and stages
As a rule, complementary foods are introduced from the age of six months. Before you start exploring new products, you should consult with your pediatrician. In general, different types of food are introduced in stages, starting with very small portions. nine0003
1.First step - vegetables
According to the World Health Organization, the best starter is a one-component vegetable puree, such as zucchini, broccoli, cauliflower or potatoes.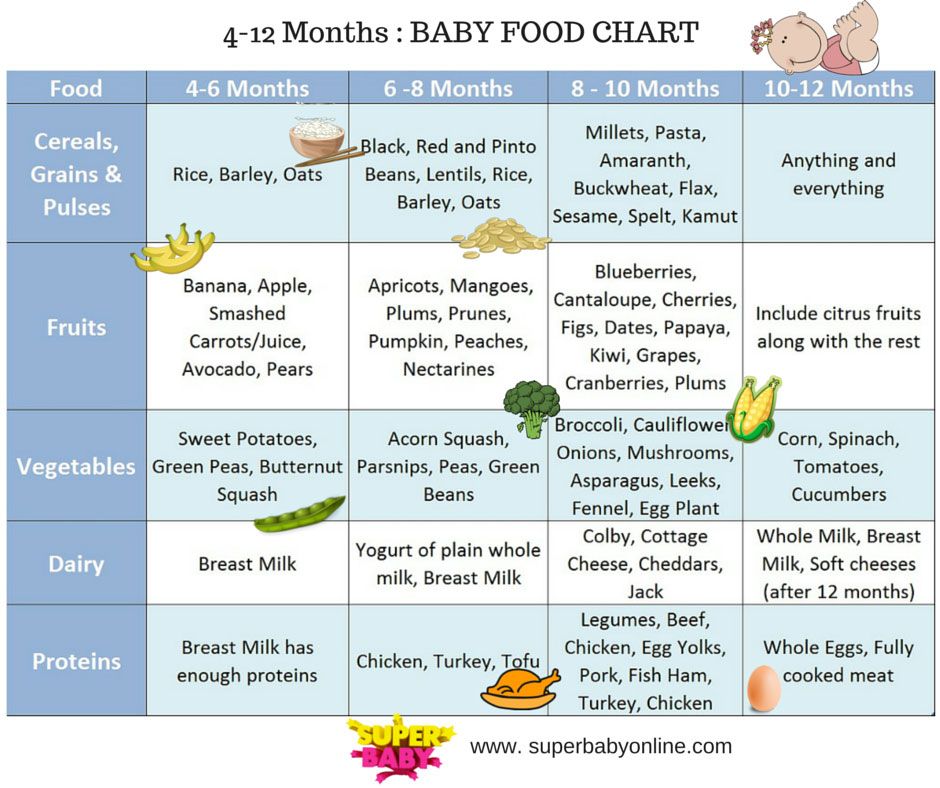 If everything goes well, you can try pumpkin, carrot, pea and tomato puree a little later.
If everything goes well, you can try pumpkin, carrot, pea and tomato puree a little later.
It takes seven to ten days to fully introduce the product into the baby's diet. We start with half or a whole teaspoon once a day until breastfeeding. If there are no allergic or other adverse reactions, you can continue the introduction of this product, gradually increasing the dose to a full serving - 100-150 grams. nine0003
2. The second stage - cereals
After the introduction of vegetable puree, we recommend diversifying the baby's menu with cereals. For acquaintance, it is better to choose liquid one-component gluten-free cereals, for example, rice or buckwheat. Then you can add oatmeal or semolina.
The initial portion of porridge is half or one teaspoon. Gradually increase the portion to a full - 150 grams.
3.Third stage — fruits
We also start fruit complementary foods with one-component low-allergenic purees, such as apple, pear, plum, banana.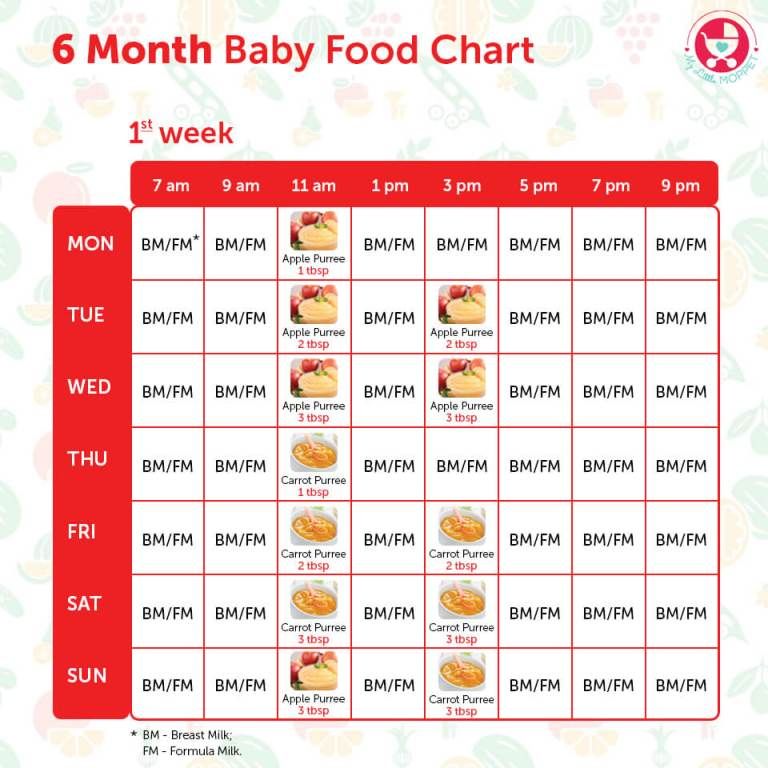 These products are not only tasty, but also contain vitamins and minerals necessary for the child. nine0003
These products are not only tasty, but also contain vitamins and minerals necessary for the child. nine0003
Fruit purees are also introduced with caution, starting with half or a whole teaspoon. Gradually, the portion increases to 100-150 grams.
Find out more: Gerber Baby Food: Puree Range
4.Stage Four - Meat
Meat is an essential product for development, rich in iron and protein, which is well absorbed in the body. It is introduced in the form of a homogeneous one-component puree from dietary turkey, rabbit, chicken, veal or lamb. nine0003
At the beginning we give a try - half or one teaspoon, over time we bring the portion to 60 grams.
5. The fifth stage - new tastes
After the successful introduction of the above products, the baby forms a full-fledged varied menu. So you can introduce the young gourmet to new flavors that could previously provoke an allergy: multi-component purees, fruit and cereal cocktails, children's snacks, pieces of fresh fruits and vegetables.
See also: Introduction of complementary foods to children with food allergies
Example of a daily diet for a baby at 6-8 months
A child from six to eight months should be given complementary foods three times a day. Further, at the age of nine to eleven months, the amount is increased to four times a day. To make it easier and clearer, check out two options for a full-fledged daily diet, which outlines what and how much a newborn should eat.
See also: Nutrition for a 7-month-old baby: making a menu for a baby
Popular questions
1. How to warm up breast milk?
Use the bottle warmer to warm breast milk that has been stored in the refrigerator. If this is not at hand, put a tightly closed bottle in a container of warm water and hold it there until the milk warms to body temperature - 37 ° C.
2. How often should a newborn eat? nine0409
A newborn needs to be fed every 2-3 hours, ie 10-12 times a day.
3. How much milk does a newborn eat?
During the first days of life, the baby has a very small stomach and a poorly developed sucking reflex. Therefore, for one feeding, the newborn eats 7-9 milliliters of colostrum. Breast milk from the mother appears only on the third or fourth day.
4. How to calculate how much a child should eat? nine0409
To understand how much a newborn should eat, you need to know his age and weight. Data for calculation: from 10 days to 1.5 months, the baby needs such an amount of food, the weight of which is approximately 1/5 of the child's body weight; from 1.5 to 4 months - 1/6, from 4 to 6 months - 1/7; from 6 to 8 months - 1/8; from 8 to 12 months - 1/9 of the body weight.
Articles on the topic:
Breastfeeding: benefits for the baby, health for the mother 12 rules of healthy nutrition for children Baby does not eat well, how to feed? nine0409
Latest reviews
Average customer rating
2 customer ratings
Snapshot of community ratings
- five 2
- four 0
- 3 0
- 2 0
- 1 0
Recommended Articles
0-6 months
Article nine0003
Quantity and quality of protein in breast milk
The amount of protein in breast milk is perfectly adapted to your baby's age and needs at every stage of their development.
0-6 months
Article
The diet of a child at 7 months: we make a menu for the baby
What should be the menu of a child at 7 months? What foods and in what quantity can be introduced into the diet at this age? When and at what intervals to give the baby to eat? We will help develop an approximate menu for a 7-month-old baby and answer the most exciting questions regarding the nutrition of a baby up to a year old. nine0003
0-6 months
Article
Buying and storing baby food
Organizing a safe and wholesome diet is an important task that is entirely the responsibility of adults. This means that every parent must know the rules for choosing, storing and feeding the smallest.
0-6 months
Article
Proper nutrition is the basis of future health nine0394
During the first 1000 days of a baby's life, optimal nutrition largely determines the growth and development of the child in the present and future. A balanced diet, which contains the most important macro and micronutrients, is an important investment in a child's future health.
A balanced diet, which contains the most important macro and micronutrients, is an important investment in a child's future health.
0-6 months
Article
Feeding a nursing mother
Most of the nutrients your baby gets through breast milk come from your body's stores. Therefore, do not forget that the menu of a nursing mother plays an important role! nine0003
0-6 months
Article
Diet during lactation
During lactation, the mother's body uses nutrients primarily for milk production and then for itself.
0-6 months
Article
Major food allergens
An allergic reaction in a child, just like in an adult, occurs when the body mistakenly perceives a substance as harmful, in other words, it is a defensive reaction to an invasion that actually did not occur. nine0003
nine0003
0-6 months
Article
How to help your baby sleep
0 reviews
Babies love to sleep, eat and then repeat. Correctly? Yes, except that sleep sometimes takes effort. Unfortunately, there is no magic sleep formula that works for everyone. But we have put together a few ways to help your baby fall asleep. Try our tips and you may soon find that your baby's sleep has improved. nine0003
0-6 months
Article
nut allergy
About 1% of the population is known to be allergic to nuts.
0-6 months
Article
How to increase the amount of breast milk?
0 reviews
Breast milk is the healthiest and healthiest food for a baby.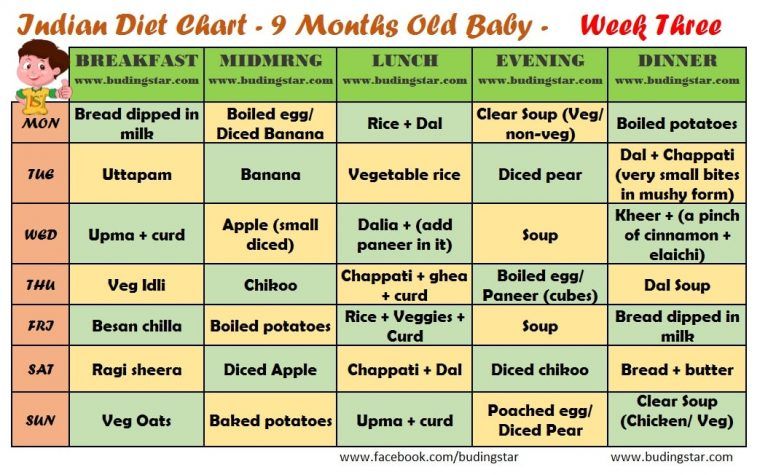 It contains all the substances necessary for a small organism. nine0054
It contains all the substances necessary for a small organism. nine0054
0-6 months
Article
Barley in a child: what to do and how to treat?
0 reviews
Barley is an inflamed abscess at the edge of the eyelid that can occur even in the smallest children. At the same time, it is important for parents to quickly and correctly provide assistance to the baby in order to reduce discomfort and avoid complications. What are the causes of barley, what to do when it appears and how to avoid relapses in the future? nine0003
0-6 months
Article
How to help a child with colic
0 reviews
Babies cry. Some babies cry more than others.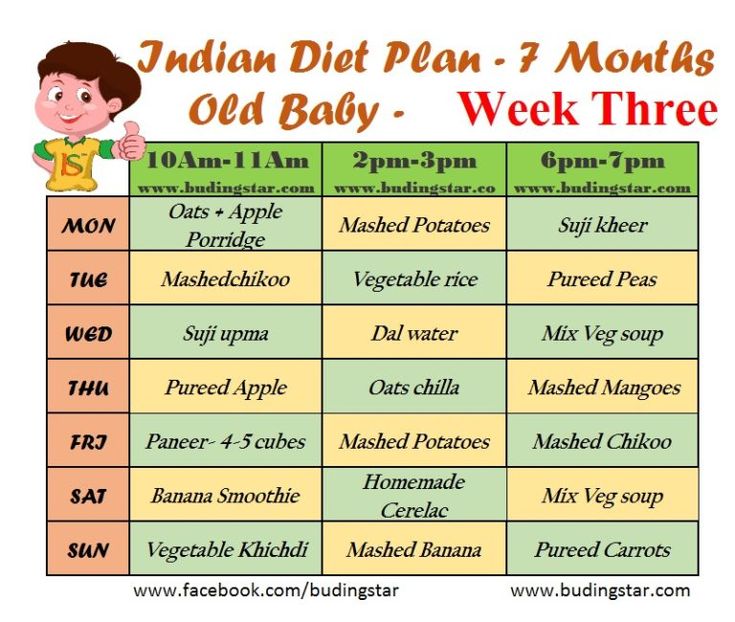 If your otherwise healthy baby under five months of age has repeated bouts of uncontrollable crying, it could be newborn colic. And this is equally unpleasant for both parents and crumbs. We have prepared a list of recommendations on how to help your baby with colic. nine0003
If your otherwise healthy baby under five months of age has repeated bouts of uncontrollable crying, it could be newborn colic. And this is equally unpleasant for both parents and crumbs. We have prepared a list of recommendations on how to help your baby with colic. nine0003
0-6 months
Article
Constipation in a newborn: what to do?
0 reviews
The appearance of a baby in the house is accompanied by both joy and feelings of young parents . Each change in the behavior and condition of baby alarms the mother, especially if it causes discomfort and tears in the baby. One such phenomenon is is constipation in a newborn .
0-6 months
Article
Herpes in children: advice to parents
Herpesvirus infections (HVI) are a group of diseases characterized by rapid epidemic transmission and a variety of clinical symptoms. This is one of the most common viral diseases. The percentage of infection and morbidity with them is growing every year. More than half of all people on the planet are infected with one or another herpes virus. nine0003
This is one of the most common viral diseases. The percentage of infection and morbidity with them is growing every year. More than half of all people on the planet are infected with one or another herpes virus. nine0003
0-6 months
Article
Why is the baby crying
0 reviews
What causes a baby to cry? If you're struggling to figure out what your baby is trying to tell you with their cry, check out this list. Here you can find probable causes of newborn crying and tips on how to soothe your baby.
0-6 months
nine0002 ArticleWhat fruits can a nursing mother: nutrition while breastfeeding
Fruit is one of the most important sources of vitamins for humans. Both mother and child need them. What fruits with HB can a nursing mother? And is it true that strawberries and citrus fruits should be excluded from the daily diet? We will try to answer these in our article.
0-6 months
Article
Vomiting in a child: what to do to help the baby
0 reviews
What can cause a child to vomit and how to provide first aid before the doctor arrives.
0-6 months
Article
Smart kid - mom's dream
Every mother dreams that her child will grow up smart and intelligent. The full development of the child from birth is influenced by many factors, one of which is a balanced diet. nine0003
0-6 months
Article
How to make a home safe for a child
0 reviews
How to secure your apartment or house for a child? Use our checklist to prepare everything in advance and minimize the risk of accidents.