Baby food iron rich
Best Iron-Rich Foods for Babies, Toddlers, & Kids (+50 Recipes!)
Ensuring that our kids eat a well balanced diet, including iron-rich foods, can be hard when they’re eating unpredictably. I hope this info on iron-rich foods for kids (and the recipe ideas at the bottom) helps to set your mind at ease!
Iron-Rich Foods
Ensuring that your kids are getting enough iron can seem hard when they’re in a phase of picky eating—or just not eating a ton. But since iron deficiency and iron deficiency anemia are still common issues with kids and it can impact their development and behavior, it’s important to try to include iron-rich foods in their daily meals.
For some context, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics, “Among children ages 1 to 3 years, iron deficiency occurs in 6.6 percent to 15.2 percent of toddlers, depending on ethnicity and socioeconomic status.” Which is much higher than I would have expected. They say that preterm infants, exclusively breastfed infants, and infants at risk of developmental disabilities are at higher risk for deficiencies.
I never want any parents to worry excessively about their child’s nutritional intake and thankfully, adding iron to a diet is actually quite easy.
(My favorite iron-rich recipes include Spinach Muffins, Extra-Veggie Baby Pasta, Oatmeal Bars, Meatballs, Chicken Puree, Butter Chicken, Chicken Tacos and Spinach Eggs. For more, scroll down.)
How much iron does my child need?
Toddlers ages 1 to 3 years need 7 mg/day of iron. Kids aged 4-8 need 10 mg/day. For context:
- ¾ cup of Cheerios: 6 mg
- 1 serving fortified infant oatmeal: 5 mg
- 4 ounce hamburger: 5 mg
- 2 ounces Banza chickpea pasta: 4 mg
- ½ cup dried peaches: 3.2 mg
- 2 ounces Barilla red lentil pasta: 3 mg
- ½ cup of lentils: 3 mg
- 1 cup prune juice: 3 mg
- Spinach Quesadilla: 2.1 mg
- ½ cup dried apricots: 1.7 mg
- ½ cup oatmeal: 1.7 mg
- Simple Green Smoothie: 1.7 mg
- Spinach Banana Muffin: 1.4 mg
- 1 egg: 1.4 mg iron
- ½ cup raisins: 1.
 5 mg
5 mg - 1 slice whole wheat bread: 0.7 mg
- ½ cup fortified baby puffs: 0.7 mg
- 1 ounce hummus: 0.7 mg
- 2 tbsp peanut butter: 0.6 mg
- ½ cup edamame beans: 0.5 mg
- 1 cup watermelon: 0.4 mg
TIP: It’s possible that your kiddo is already getting enough just by eating normal toddler-size servings.
Does my child need an iron supplement?
This question will vary a lot by child so it’s best to check in with your doctor. Kids are routinely screened for iron deficiency when they’re babies and toddlers, so definitely discuss this with your pediatrician if you don’t remember what those results were, if your child is older, or if you’re just curious about supplementing.
It can be hard to find a multivitamin with iron, so check your label, or consider a separate iron supplement in consultation with your doctor.
What are the best sources of iron for kids?
The AAP recommends that iron comes from iron-rich foods first and foremost. The type of iron in meat, fish, and poultry is easier for our bodies to absorb, but adding a range of iron-rich foods is your best bet. Here are some examples of foods with a good dose of iron.
The type of iron in meat, fish, and poultry is easier for our bodies to absorb, but adding a range of iron-rich foods is your best bet. Here are some examples of foods with a good dose of iron.
- Red meats like beef and lamb
- Dark meat poultry
- Fish including shrimp and oysters
- Iron-rich vegetables including dark leafy greens (think Popeye!), baked potatoes, and pumpkin
- Beans and legumes like kidney beans, lentils, and tofu
- Fortified cereals like Cheerios and some hot cereals including baby oatmeal
- Whole grains and whole grain products (including some of the newer bean pastas like Banza)
TIP: A toddler-size serving of meat is 2 tablespoons to ¼ cup. A toddler-size serving of produce is 2 tbsp to ¼ cup. A serving of beans and legumes is 1-2 tablespoons for younger kids and ¼ cup for older kids. (Find more specifics in my Daily Toddler Nutrition Guide.)
Top 10 Best Iron-Rich Foods for Babies
Here are my go-to foods with a lot of iron that you can feed to a baby who’s eating purees or baby led weaning style foods.
- Beef, ground
- Bean puree
- Beans, very soft and lightly mashed
- Bean pasta, cooked very soft (like Banza)
- Chicken, finely shredded or ground or Chicken Puree
- Eggs, scrambled or Egg Yolk Puree
- Green bean puree
- Infant cereal like baby oatmeal, fortified
- Oatmeal
- O cereal
- Smoothies with spinach or kale (serve on a spoon or in a reusable pouch)
- Sweet potatoes, mashed
- Pea puree
- Peanut butter puree
- Strawberry puree
TIP: Iron stores in babies start to run out starting around 6 months, so you’ll want to incorporate these foods into your baby’s diet from an early age.
Top 15 Best Iron-Rich Foods for Toddlers and Big Kids
These foods are easy to prepare and packed with iron for kids.
- Apricots, dried
- Beans
- Bean pasta (like Banza with marinara sauce)
- Beef burgers
- Broccoli
- Eggs
- Green beans
- Oatmeal
- Peanut butter
- Raisins
- Smoothies with spinach or kale
- Spinach Pesto
- Strawberries
- Watermelon
- Wheat bread
TIP: Aim to serve 2-3 of these foods (from either the baby or toddler list) most days and you should easily provide enough opportunities for your child to eat enough iron.
Add Vitamin C for Increased Iron Absorption
If you pair iron-rich foods with produce with plenty of Vitamin C—think citrus, strawberries, kiwi, tomatoes, dark greens, and bell peppers—the iron will be more readily absorbed by the body. Some ideas to consider:
- Pasta with Meatballs (Vitamin C from tomatoes, iron from beef)
- Bean Burritos with salsa (iron in beans, Vitamin C from salsa)
- Bean Quesadillas with chopped tomatoes on the side (iron in beans and whole grain tortilla, Vitamin C from tomatoes)
- Simple Green Smoothie (iron from greens, Vitamin C from fruit)
- Spinach Banana Muffins with Banana with kiwi (iron in spinach, Vitamin C from kiwi)
Limit Milk to No More than 24 Ounces Each Day to Avoid Limiting Iron Absorption
Experts at the Mayo Clinic also advise against letting the kids have more than 24 ounces of milk in a day (or three 8 ounce servings) which could negatively impact iron absorption. That much milk could also make them less hungry for other foods, which could also limit how much iron they’re able to eat through foods.
50 Best Iron-Rich Recipes for Babies, Toddlers, and Kids
Here are some of my favorite recipes for kids of all ages that are rich in iron. (The list is organized alphabetically for easy reference, not in order of preference!)
- Bean Puree
- Bean Pasta with Marinara Sauce
- Beef Burritos with Veggies
- Black Bean Quesadillas
- Black Bean Soup with Citrus
- Broccoli Pesto
- Broccoli Cheddar Soup
- BBQ Shredded Chicken
- Cheesy Meat Buns
- Chicken Meatballs with Sweet Potato
- Chocolate Smoothie with Hidden Veggies
- Green Smoothie
- Kale Bites
- Lentils and Rice with Dried Fruit
- Lentils with Tomatoes and Italian Spices
- Lentil Soup with Veggies
- Lentil Falafel
- Meatballs with Hidden Veggies
- Mini Egg Muffins
- Mexican Egg Muffins with Spinach
- Moroccan Lamb Meatballs
- No-Bake Energy Bites
- Nut-Free Hummus
- Oatmeal with Apple and Raisins
- Oatmeal Bars
- Oatmeal with Pumpkin
- Pesto Chicken and Brown Rice
- Potato Nachos
- Pumpkin Oatmeal Bars
- Pumpkin Oatmeal Muffins
- Slow Cooker Chicken and Bean Tacos
- Slow Cooker Black Bean Soup
- Slow Cooker Chicken Tacos
- Spinach Banana Muffins with Banana
- Spinach Pancakes
- Spinach Eggs
- Spinach Pesto
- Spinach Quesadillas
- Strawberry Puree
- Strawberry Smoothie
- Strawberry Muffins
- Sweet Potato Quesadillas
- Sweet Potato Baby Food
- Tofu Nuggets
- Tofu, Baked
- Tofu with Sesame
- Whole Wheat Bread
- Veggie Chili
- Veggie Chili Mac
- Zucchini Burgers
Printable Iron-Rich Foods List
For easy reference, you can print this list of iron-rich foods for kids keep in your kitchen, or save the image on your phone. Simply sign up for my newsletter and gain access to my entire FREE Resource Library of printables.
Simply sign up for my newsletter and gain access to my entire FREE Resource Library of printables.
Related Recipes
I’d love to hear if iron has been an issue for you with your kids. Chime in below in the comments!
9 Best Iron-Rich Foods for Babies
When little ones start eating solid food, iron is essential to help their brains grow. Here the best iron-rich foods for babies that are happy and healthy!
1 / 10
Syda Productions/Shutterstock
Infants are typically born with enough stored-up iron to see them through the first few months of life—plus they get iron from breast milk or formula. As they begin to rely more on solid foods, though, it’s easy to become deficient. But growing babies need iron!
It’s what helps their bodies make hemoglobin, which sends oxygen to cells throughout important organs and muscles. It’s also what helps their brains develop normally.
Are you concerned your baby’s iron levels are low? Curious about how to boost iron through diet? Here’s a closer look at our recommended iron-rich foods for babies.
2 / 10
colnihko/Shutterstock
Dark Greens
Leafy greens such as kale and spinach are great sources of iron for your wee one. You can saute them in oil and puree them with other cooked vegetables or meats to enhance taste. You can also throw them into fruit smoothies. Bonus: The vitamin C in fruits such as oranges or strawberries enhances iron absorption.
Here’s how to cook kale—and make it delicious—for the whole family.
3 / 10
SMarina/Shutterstock
Lentils
There’s a good reason lentils are beloved by vegetarians and meat-eaters alike. They’re not only versatile and delicious, but they’re also one of the best plant-based sources of iron available. Use cooked lentils in a wide range of purees to give baby an iron boost.
Use cooked lentils in a wide range of purees to give baby an iron boost.
4 / 10
LightField Studios/Shutterstock
Eggs
The yolk of an egg is naturally high in iron. It’s also fairly simple to cook and serve to your child. Offer it alongside some orange juice to give your child a boost of vitamin C as well as small taste of adult-style breakfasts to come.
Want another reason to give your baby eggs? Check out this research that suggests eggs are baby brain food!
5 / 10
casanisa/Shutterstock
Beef
When most people think about foods rich in iron, they think of meat. Just 3.5 ounces contain 15% of an adult’s recommended daily intake. To make beef a baby-friendly food, try cooking some until soft and pureeing with a little water to make it blend smoothly. Serve with one of these homemade baby food recipes.
6 / 10
New Africa/Shutterstock
Quinoa
Certain grains are good sources of iron, including quinoa, a gluten-free seed that can be cooked like rice. Adding cooked quinoa to purees is a great way to get a little more iron in your baby’s routine. Just one cup contains 2.8 milligrams of iron! The rest of the family will love these healthy quinoa recipes.
7 / 10
denio109/Shutterstock
White Beans
Like other legumes, white beans are an excellent source of iron and, thanks to their mild taste, an easy sell to most babies. Cook them until soft, and puree solo or with other foods to create iron-rich baby food for your little one.
8 / 10
nadi555/Shutterstock
Liver
Hear us out: Of any type of meat, beef liver offers the highest amount of iron per serving, making it a perfect choice for boosting iron intake efficiently. Because the idea of liver may not be as naturally appealing as other foods, try combining it with other ingredients or flavors for a more palatable taste.
Because the idea of liver may not be as naturally appealing as other foods, try combining it with other ingredients or flavors for a more palatable taste.
9 / 10
MarkoBr/Shutterstock
Broccoli
The cruciferous vegetable broccoli is more than a good source of folate, fiber and vitamins C and K. It’s also another whole food that naturally contains iron. Whether you steam, saute or roast this vegetable, pureeing it makes it a great iron-rich food to try for your baby.
10 / 10
Amallia Eka/Shutterstock
Sweet Potatoes
What’s great about sweet potatoes is that they not only contain iron, but also vitamin C, which makes all that iron easier for baby’s body to absorb. Even better, pureed sweet potatoes are usually appealing to babies thanks to their natural sweetness.
Originally Published: May 20, 2019
Shanna Mallon
Shanna Mallon is an experienced copywriter and food blogger with a master's degree in Writing. She likes tested recipes, organized refrigerators and the pleasure of a good bite.
She likes tested recipes, organized refrigerators and the pleasure of a good bite.
Iron products for children
Proteins, fats and carbohydrates are the main nutrients that are the building blocks and source of energy for all living things. But no less significant biological role belongs to minerals. Despite their insignificant presence in the human body, they take part in numerous reactions and metabolic processes, therefore they are absolutely necessary for normal life in any of the periods of life. Minerals are part of enzymes, hormones and other biologically active molecules that, like conductors, direct and regulate metabolic processes. 81 chemical elements have been found in the human body, and the stability of their regular intake is a prerequisite for health. Minerals are not synthesized on their own, they come from outside and are absorbed with food and water. Their sufficient amount is especially important during periods of active growth and development, which determines the importance of a rational and balanced diet for pregnant women and children, because a deficiency of even one of the elements can adversely affect health.
Content: Hide
- Lack of iron
- manifestations of iron deficiency anemia
- Causes of deficiency
- Prevention of deficiency
- enriched products
 The main part of iron is found in the blood in the structure of hemoglobin. This protein binds with oxygen to transport it to every cell of the body, providing tissue respiration, and hence the operation of all organs and systems. Then, having given up oxygen, hemoglobin combines with carbon dioxide and transports it for subsequent release by the lungs from the human body. It is hemoglobin that colors blood red. In addition to blood cells, iron is found in the bone marrow, liver, muscles, and spleen. This mineral is part of enzymes that accelerate DNA synthesis during cell division.
The main part of iron is found in the blood in the structure of hemoglobin. This protein binds with oxygen to transport it to every cell of the body, providing tissue respiration, and hence the operation of all organs and systems. Then, having given up oxygen, hemoglobin combines with carbon dioxide and transports it for subsequent release by the lungs from the human body. It is hemoglobin that colors blood red. In addition to blood cells, iron is found in the bone marrow, liver, muscles, and spleen. This mineral is part of enzymes that accelerate DNA synthesis during cell division. IMPORTANT! The effective operation of these structures is especially necessary during periods of growth and maturation of organs. Iron is also a structural component of about 50% of the enzymes involved in energy metabolism, as well as in the reactions of neutralizing foreign substances in the liver. Without it, the normal functioning of brain cells is impossible.
Iron deficiency
Unfortunately, insufficient intake of minerals is a common phenomenon in the modern world among both adults and children. Iron deficiency disrupts the work of all body cells, especially if their functioning requires intensive metabolism and oxygen supply. The changes concern the main organs and systems, manifested by a decrease in the activity of all processes and the ability to withstand the negative impact of external factors. A late and already pronounced manifestation of iron deficiency is the development of anemia, in the common people - anemia. In this condition, the amount of hemoglobin decreases, and the formation of altered erythrocytes (red blood cells) also occurs - they become pale and reduced in size. In humans, the total iron content in the blood serum decreases.
Iron deficiency disrupts the work of all body cells, especially if their functioning requires intensive metabolism and oxygen supply. The changes concern the main organs and systems, manifested by a decrease in the activity of all processes and the ability to withstand the negative impact of external factors. A late and already pronounced manifestation of iron deficiency is the development of anemia, in the common people - anemia. In this condition, the amount of hemoglobin decreases, and the formation of altered erythrocytes (red blood cells) also occurs - they become pale and reduced in size. In humans, the total iron content in the blood serum decreases.
Manifestations of iron deficiency anemia
The symptoms of this disease are varied and not always specific. In infancy, the manifestations may be erased, and the main signs of iron deficiency will be insufficient growth or a delay in the formation of motor skills, deviations in neuropsychic development. In older children, iron deficiency can be manifested by problems in assimilation of information and learning, low concentration of attention and behavioral anomalies.
IMPORTANT! With a significant lack of iron, changes in the skin and mucous membranes are often observed: pallor and dryness, the appearance of cracks on the arms, legs and around the mouth, layering and increased fragility of nails, dull hair. Babies often develop painful sores in the oral cavity and changes in the tongue - manifestations of stomatitis.
Other typical symptoms of this micronutrient deficiency are muscle weakness, irritability and sleep disturbances. The child quickly gets tired, does not cope well with the usual load for his age. People with iron deficiency anemia often have altered taste and appetite, and may also develop a desire to eat inedible items such as chalk and lime.
Causes of deficiency
In young children and pregnant women, the main factor in iron deficiency in the body is its low intake from food. Indeed, due to intensive growth and development, first intrauterine, and then independent, the need for this trace element is very high.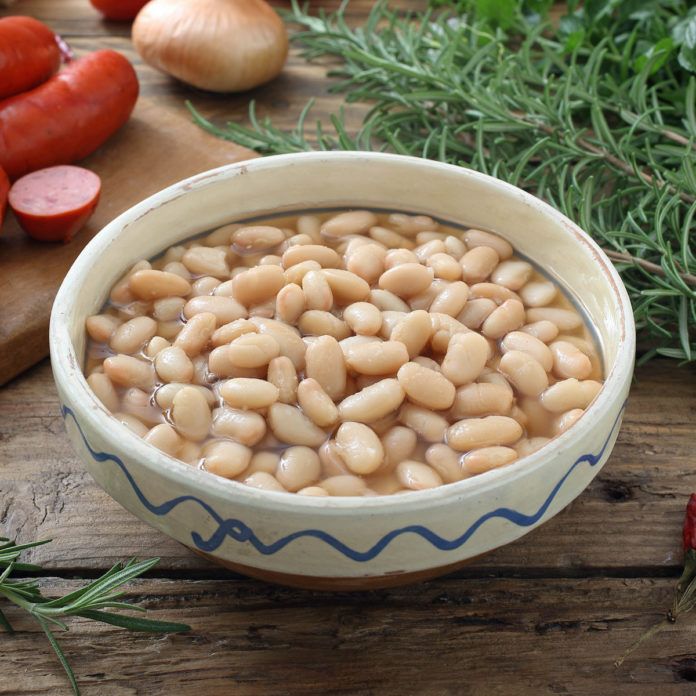 That is, in these groups, iron deficiency is always associated with its negative balance - insufficient intake compared to the need for daily expenditure. This leads first to depletion from the depot, and then to the depletion of the mineral reserves in the body. Why is this happening? In the modern life of an urban person, refined foods are often used in nutrition, and food is depleted in vitamins and minerals.
That is, in these groups, iron deficiency is always associated with its negative balance - insufficient intake compared to the need for daily expenditure. This leads first to depletion from the depot, and then to the depletion of the mineral reserves in the body. Why is this happening? In the modern life of an urban person, refined foods are often used in nutrition, and food is depleted in vitamins and minerals.
IMPORTANT! Iron deficiency during pregnancy and then during breastfeeding is transmitted to the infant from the mother and can have an adverse and even sometimes irreversible effect on his health. Therefore, it is extremely important that the nutrition of a pregnant and lactating woman is complete, containing all the necessary nutrients in sufficient quantities and enriched with useful substances.
It is impossible to neglect the recommendations for taking vitamin-mineral complexes during pregnancy and lactation, since very often it is not possible to make a woman's diet sufficient and balanced. On the contrary, babies in their first year of life get everything they need from food, without the use of special preparations for the prevention of deficient conditions. In the first half of the year, the main role in the nutrition of the child belongs to breast milk, the main source of essential substances, vitamins and minerals, including iron. However, by the sixth month of life, exclusively natural feeding can only satisfy the child's needs for iron by 6-7%. At the same time, the nutrition of the mother at this age does not significantly affect the supply of this trace element to the baby. The main task is not to delay and start the introduction of complementary foods on time to meet the high demand for this element in the second half of life.
On the contrary, babies in their first year of life get everything they need from food, without the use of special preparations for the prevention of deficient conditions. In the first half of the year, the main role in the nutrition of the child belongs to breast milk, the main source of essential substances, vitamins and minerals, including iron. However, by the sixth month of life, exclusively natural feeding can only satisfy the child's needs for iron by 6-7%. At the same time, the nutrition of the mother at this age does not significantly affect the supply of this trace element to the baby. The main task is not to delay and start the introduction of complementary foods on time to meet the high demand for this element in the second half of life.
Deficiency prevention
What foods are rich in this micronutrient, and what complementary foods for children can be sources of iron? The leader in the amount of iron in the composition is food of animal origin, its highest content is in meat, fish and eggs. Different types of meat products differ in the presence of minerals and vitamins.
Different types of meat products differ in the presence of minerals and vitamins.
IMPORTANT! Thus, the highest content of iron is found in red meat - veal and beef, and there is also a lot of it in the liver of animals. In addition, they contain iron in an easily digestible heme form, which increases the absorption of this element in the intestine.
Modern industrial technologies for the production of baby food allow the production of products with a very high degree of grinding - a homogeneous consistency. Therefore, meat complementary foods can be safely included in the diet of babies from 6 months old, and this is one of the fundamental innovations in the nutrition of children in the first year of life. Previously, meat complementary foods were introduced only to children older than 7 months.
Other sources
Are there iron-rich foods among plant foods? Yes, this trace element is present in legumes, nuts and seeds, grains, and some types of greens (parsley, thyme, lettuce). But compared to meat products, the content of iron in them, as well as the degree of its absorption in the intestines, is lower. Among the foods of plant origin, buckwheat should be singled out, which is used in whole grain form and is several times superior to other crops in terms of iron content.
But compared to meat products, the content of iron in them, as well as the degree of its absorption in the intestines, is lower. Among the foods of plant origin, buckwheat should be singled out, which is used in whole grain form and is several times superior to other crops in terms of iron content.
IMPORTANT! Therefore, at the age of 4–5 months, when deciding on the start of the introduction and choice of complementary foods, preference should be given to porridge, especially in babies at risk of developing iron deficiency anemia and poorly gaining weight. In addition, in cases of late start of the introduction of complementary foods, this is also a good choice as a start.
And buckwheat at this age should be singled out as a priority among cereals due to the high content of vegetable protein and rich mineral and vitamin composition. Another important feature that must be taken into account when compiling a menu for babies is the fact that when meat puree is combined with grains, the degree of absorption of non-heme iron from a vegetable source increases and its biological value increases. Therefore, in children older than 6 months, cereal complementary foods are included in the diet not only in the form of milk porridge, but also as a component of meat and vegetable dishes, in which meat is balanced with dairy-free porridge.
Therefore, in children older than 6 months, cereal complementary foods are included in the diet not only in the form of milk porridge, but also as a component of meat and vegetable dishes, in which meat is balanced with dairy-free porridge.
Fortified foods
Despite the high nutritional value and varied vitamin and mineral composition of natural products recommended in baby food, the content of micronutrients in the finished meal does not always satisfy the high need for these substances at an early age.
IMPORTANT! The way out of this situation is to use in the nutrition of babies products that are additionally enriched with biologically active substances that are vital during periods of active growth and development. An example of such specialized products is the line of instant cereals Bebi Premium. Their composition is developed in accordance with the age characteristics of babies of the first year of life, enriched with the most necessary vitamins and minerals for normal physical and mental development in the recommended amount and ratio.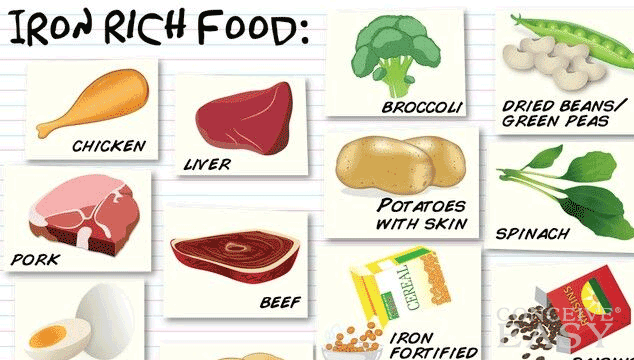
All cereals and children's instant biscuits of this manufacturer are enriched with iron, which covers from 10 to 30% of the recommended daily requirement for this trace element and is an effective prevention of the development of iron deficiency conditions. The preparation of complementary foods of the Bebi Premium line does not require aggressive cooking, which allows you to save biologically active substances in the most useful and easily digestible form.
11 IRON-RICH FOODS FOR BABY! MedUnion will tell you!📝
Everyone knows that young children are picky eaters, but there are plenty of iron-rich foods that even the pickiest little ones will appreciate.
Small children refuse food for various reasons - maybe it is too red or too green, too mushy, etc. Parents of course worry about the lack of nutrients that growing bodies of babies need.
Iron deficiency is a fairly common problem in children, and it is estimated that about 8 percent of babies are iron deficient.
In this article, you'll learn how much iron babies need, 11 iron-rich foods, and recipes and ways to include these foods in your baby's diet.
WHAT AMOUNT OF IRON DO BABY NEED?
According to the National Institutes of Health, children should receive the following amount of iron in milligrams (mg) daily:
- Infants 7-12 months old - 11mg0010
- Children 4-8 years 10 mg
However, the recommended amount of iron varies depending on the foods infants eat.
There are two types of iron: heme and non-heme. Heme iron is found only in animal products such as meat and seafood. Non-heme iron is found in plant foods and fermented foods.
Both forms of iron can help a person meet their daily iron requirement. However, heme iron is more easily broken down by the body. For this reason, people who get iron from non-animal sources, including vegans, vegetarians, and picky toddlers, should consume 1.8 times the amount of iron recommended for their age group.
11 FOODS WITH THE MOST IRON
Oatmeal is a rich source of iron for babies
Many children are incredibly cranky and will refuse food many times before they start eating, so do not be discouraged and continue to offer healthy food.
For a balanced diet, change your iron sources more often and encourage your little ones to try different foods.
Almost all babies love foods that are a great source of iron, such as:
- 1. Iron-fortified breakfast cereals
Many breakfast cereals are fortified with iron. They usually contain 100 percent of the daily value of iron for adults. The iron content can be found on the packaging.
Remember that many breakfast cereals are high in sugar and salt. This type of breakfast can be given occasionally as a treat or in small portions with a balanced diet.
- 2. Oatmeal
Oatmeal is a nutritious snack that many children love. According to one source, 0.75 cups of oatmeal contains about 4.5 - 6.6 mg of iron.
According to one source, 0.75 cups of oatmeal contains about 4.5 - 6.6 mg of iron.
Oatmeal is also rich in fiber, which is good for children with digestive problems, including constipation.
To make porridge more appetizing, sprinkle it with cinnamon, a little brown sugar and a handful of raisins.
- 3. Meat
All meat products are rich in iron. Although many toddlers often refuse meat, there are a few ways to convince them to give it a try:
- Use fun cutters to cut meat products. The iron content can be increased by placing a piece of cold cuts on white bread, which will add another 1 mg of iron.
- Try chicken nuggets. Many toddlers who refuse meat enjoy eating chicken nuggets. However, be careful as they are high in salt and saturated fat.
- Try mixing ground beef or duck with a little milk before cooking for a creamier texture that many babies love.
- 4. Peanut Butter Sandwiches
The amount of iron in peanut butter varies by brand, but typically contains about 0. 56 mg of iron per teaspoon. To get extra iron, you can make a sandwich with white bread, which will provide another 1 mg of iron.
56 mg of iron per teaspoon. To get extra iron, you can make a sandwich with white bread, which will provide another 1 mg of iron.
Peanut butter is also high in protein, which is a great option for kids who don't eat meat.
Peanut butter and honey or banana sandwiches can be made as an alternative to cookies and other low-nutrient snacks.
- 5. Dark Chocolate
Dark chocolate is a rich source of antioxidants and helps your baby get the right amount of iron. Second after meat, dark chocolate is one of the richest foods in terms of iron content, containing 7 mg of iron per 90 grams of product.
Some children do not like the bitter taste of dark chocolate. You can try melting it and mixing it with peanut butter and then spreading it on bread.
- 6. Eggs
A hard-boiled egg contains 1 mg of iron. Many children love to peel eggs from the shell. Snacking can be made even more fun by coloring the eggs first.
If your little one doesn't like hard-boiled eggs, try making scrambled eggs instead, or use animal molds.
Some children like fried egg sandwiches. Lightly fry the egg, then place it on a piece of bread and add some ketchup.
- 7. Legumes
Legumes are an excellent source of iron. White beans are considered to be one of the richest sources of iron and contain 8 mg per serving.
To get kids to eat legumes, use the following recipes:
- Cook beans and potatoes, mash them and add some cinnamon
- Legumes can be made into odd-shaped patties or put on bread
- 8. Nuts
Nuts, including cashews and pistachios, are an excellent source of iron, protein and other essential nutrients.
However, nuts can pose a risk of choking in children, so do not give whole nuts to children who are just learning to chew.
You can make nut crumbs or spread nut butter on crackers or whole grain bread.
- 9. Fish
Consider including fish in your baby's diet as it is highly nutritious and a great source of protein, and some species, such as mackerel and salmon, are high in omega-3 saturated fatty acids that are good for brain work.
Canned tuna contains 1 mg of iron per serving. You can make tuna crackers or put it on bread.
Canned tuna is also suitable for children who like to dip one food into another. You can mix tuna with avocado for a creamier texture that's easy to dip into crackers or chips.
- 10. Vegetables
Children refusing to eat vegetables is a common problem. Try making a vegetable smoothie for a nutritious, iron-rich snack that even the pickiest of kids will love.
You can try the following recipes:
- Boil and puree spinach. Spinach contains 0.81 mg of iron per cup. Next, mix it with watermelon, frozen blueberries, raspberries and a slice of avocado for a hearty and nutritious smoothie.

- Mix a teaspoon of honey with mashed broccoli, add chard, honey melon and figs for a delicious treat.
- 11. Fruits
Some fruits are excellent sources of iron. The following amount of iron is found in 1 cup of these fruits:
- Raisins, 4 mg
- Dried apricots, 3.46 mg
- Red-skinned cherries, 0.71 mg
- Diced watermelon, 0.36 mg
- Prunes, 0.36 mg
Fruit smoothie tastes even better when mixed with a little yogurt and honey.
Your baby's favorite fruit can be made into popsicles. Freeze fruit puree for 2-3 hours and enjoy healthy iron-rich ice cream.
WHAT ARE THE SIGNS OF IRON DEFICIENCY IN CHILDREN?
Low energy levels in babies can be a sign of iron deficiency
If you're worried that your baby may be iron deficient, don't wait until symptoms appear. See your doctor to have your baby's blood tested for iron. Continue giving your child iron-rich foods and ask your doctor to prescribe an iron supplement.