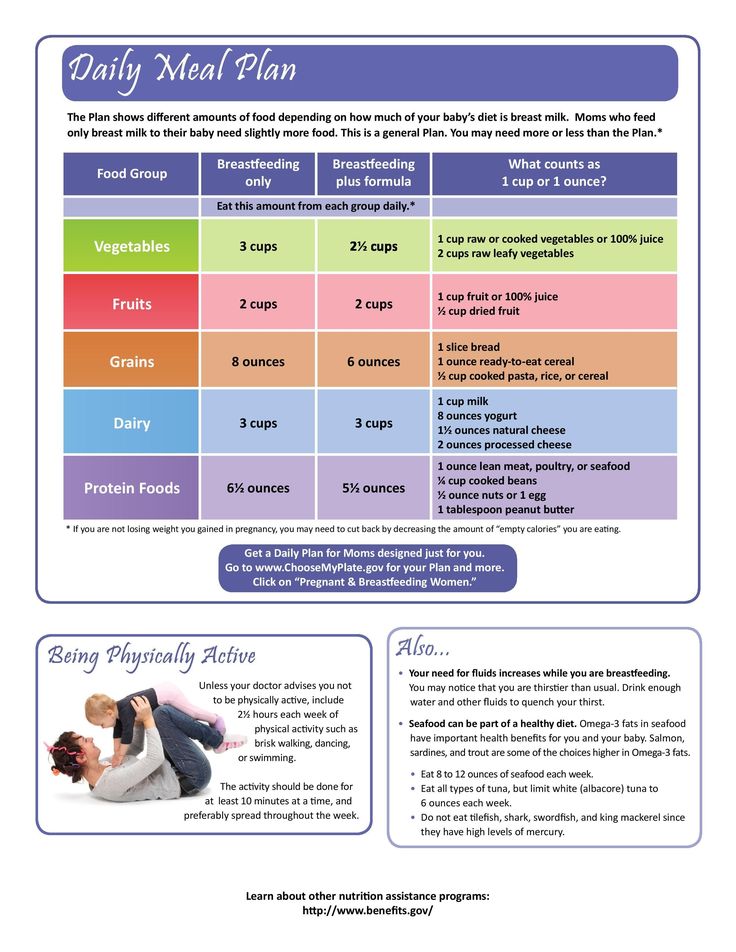
Baby food sample menu
Sample Menu for a Baby 8 to 12 Months Old
Log in | Register
Ages & Stages
Ages & Stages
Listen
Español
Text Size
Now that your baby is eating solid foods, planning meals can be more challenging. At this age, your baby needs between 750 and 900 calories each day, of which about 400 to 500 should come from
breast milk or formula (if you are not breastfeeding)—roughly 24 ounces (720 mL) a day. Breast milk and formula contain vitamins, minerals, and other important components for brain growth.
At about eight months, you may want to introduce foods that are slightly coarser than strained pureed foods. They require more chewing than baby foods. You can expand your baby's diet to include soft foods such as yogurt, oatmeal, mashed banana, mashed potatoes, or even thicker or lumpy pureed vegetables. Eggs (including scrambled) are an excellent source of protein, as are cottage cheese, Greek yogurt, and avocado.
Sample menu ideas for an 8- to 12-month-old baby:
1 cup = 8 ounces = 240 ml
¾ cup = 6 ounces = 180 ml
½ cup = 4 ounces = 120 ml
¼ cup = 2 ounces = 60 ml
Breakfast
2 to 4 ounces cereal, or 1 mashed or scrambled egg
2 to 4 ounces mashed or diced fruit
Breastmilk or 4 to 6 ounces formula
Snack
Lunch
2 to 4 ounces yogurt or cottage cheese, or pureed or diced beans or meat
2 to 4 ounces cooked pureed or diced yellow or orange vegetables
Breastmilk or 4 to 6 ounces formula
Snack
Dinner
2 to 4 ounces diced diced poultry, meat, or tofu
2 to 4 ounces cooked green vegetables
2 to 4 ounces cooked soft-whole grain pasta or potato
2 to 4 ounces diced or mashed fruit
Breastmilk or 4 to 6 ounces formula
Before bedtime
Breastmilk or 6 to 8 ounces formula, or water. (If breastmilk or formula, follow with water or
brush teeth afterward).
(If breastmilk or formula, follow with water or
brush teeth afterward).
More information
- Sample Menu for a One-Year-Old
- Starting Solid Foods
- Breastfeeding Mealtime Milestones
- Ask the Pediatrician: Is it OK to make my own baby food?
- Last Updated
- 8/12/2022
- Source
- Caring for Your Baby and Young Child: Birth to Age 5 7th Edition (Copyright © 2019 American Academy of Pediatrics)
The information contained on this Web site should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician. There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
Sample Menu for a 1-Year-Old Child
Ages & Stages
Listen
Español
Text Size
Babies and young toddlers should get about half of their calories from fat.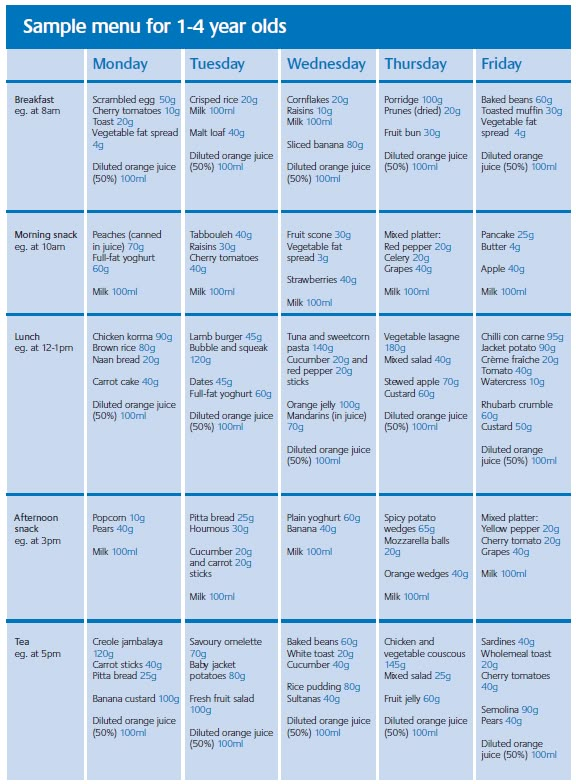 Healthy fats are very important for normal growth and development at this stage of their development.
Healthy fats are very important for normal growth and development at this stage of their development.
All fats are not created equal, though. Healthy fats like those found in avocado, olive oil, fish, nut butters, and dairy are good for your child (and you). Unhealthy fats such as those found in fried foods, fast foods and many packaged foods are not healthy at any age. If you keep your child's daily caloric intake at about 1,000 calories, you needn't worry about overfeeding and risk of weight gain
Here is a sample menu for a one-year-old child who weighs about 21 pounds (9.5 kg):
1 cup = 8 ounces = 240 ml
1 ounce = 2 tablespoons = 30 ml
½ ounce = 1 tablespoon = 15 ml = 3 teaspoons
1 teaspoon = ¹⁄³ tablespoon = 5 ml
BREAKFAST
½ cup iron-fortified breakfast cereal or 1 cooked egg
½ cup whole or 2% milk
½ banana, sliced
2 to 3 large sliced strawberries
SNACK
1 slice toast or whole-wheat muffin with 1–2 tablespoons cream cheese or peanut butter, or ½ cup yogurt with cut-up fruit
Water or ½ cup whole or 2% milk
LUNCH
½ sandwich: sliced turkey or chicken, tuna, egg salad or peanut butter
½ cup cooked green vegetables
½ cup whole or 2% milk
SNACK
1 to 2 ounces cubed or string cheese, or
2 to 3 tablespoons fruit or berries
Water or ½ cup whole or 2% milk
DINNER
2 to 3 ounces cooked meat, ground or diced
½ cup cooked yellow or orange vegetables
½ cup whole-grain pasta or potato
½ cup whole or 2% milk
Remember
Talk with your child's pediatrician if you have any questions or concerns about your baby's diet.
More information
- Discontinuing the Bottle
- Unsafe Foods for Toddlers
- Selecting Snacks for Toddlers
- Water & Juice
- Last Updated
- 8/12/2022
- Source
- Caring for Your Baby and Young Child: Birth to Age 5 7th Edition (Copyright © 2019 American Academy of Pediatrics)
The information contained on this Web site should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician. There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
Menu for a 1 year old child: a detailed guide for parents
A man is already a year old, he has acquired teeth, watches with interest what adults eat and constantly tries to catch something from their plate.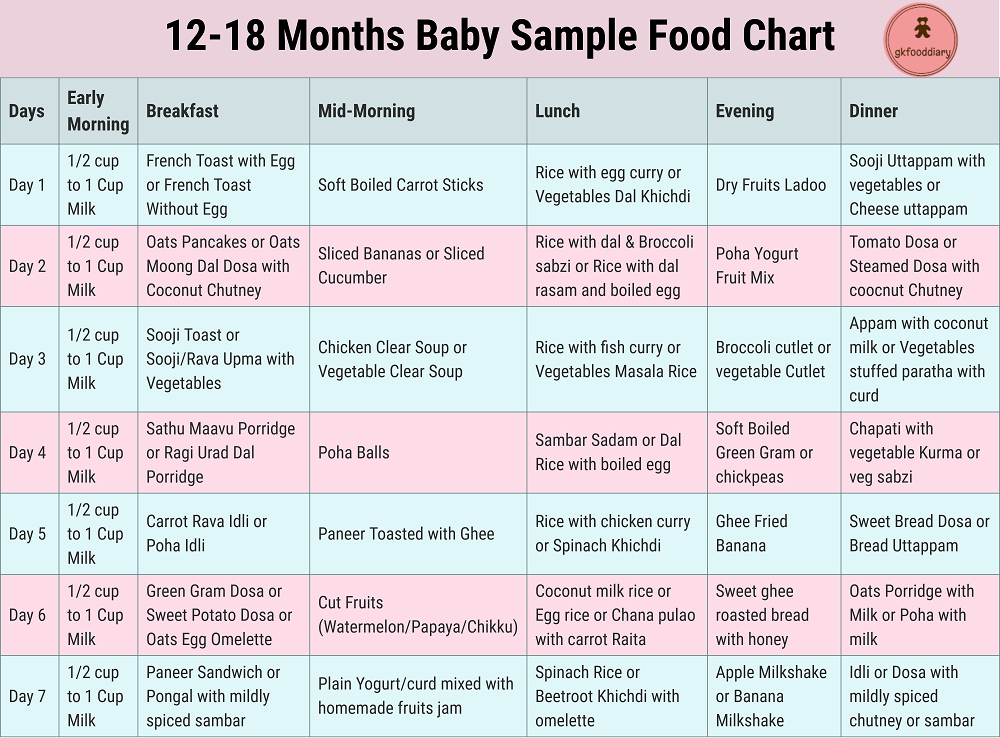 And here comes the one who instructively says to the parents: “It’s time to transfer to the common table!” And it won't be right. We find out what the child’s menu should be per year so that he grows up healthy, active and happy.
And here comes the one who instructively says to the parents: “It’s time to transfer to the common table!” And it won't be right. We find out what the child’s menu should be per year so that he grows up healthy, active and happy.
What to feed a child in a year
A child's menu of 1 year should include daily dairy and meat products, vegetables and fruits, bread and cereals, vegetable and butter. Twice a week - fish and eggs. Let's figure out what exactly and in what quantity to give the baby - let's look at the pyramid of the children's diet in detail.
Milk
The very first and most important milk for a child is mother's milk. It not only nourishes, but also supports the immune system, and the feeding process itself is useful for the baby emotionally. After a year, the child ceases to be a baby by definition, but this does not mean that breastfeeding should be hastily “curtailed”. Pediatric experts, including the World Health Organization, recommend continued breastfeeding until the child is two years old. But the number of attachments to the chest can be reduced - now one or two times a day is enough.
But the number of attachments to the chest can be reduced - now one or two times a day is enough.
After a year, the baby can be introduced to cow's and goat's milk. Up to a year, animal milk is prohibited, primarily because children's kidneys are not yet ready to properly remove the excess phosphorus contained in the product.
Together with phosphorus, they get rid of calcium and vitamin D, and this is fraught with the development of a severe form of rickets in a child.
Like any new product, it is necessary to introduce milk into the children's diet gradually, especially since it is often allergic. First, give half a spoonful during breakfast and observe the reaction throughout the day. If there is no allergy, you can double the portion every day. The milk standard for a one-year-old child is 200 ml per day, plus 100 ml for cooking.
When choosing milk for a child, remember that it should not be:
- fat: no more than 2.
 5–3.5%, otherwise the load on the digestive organs and biliary tract is great;
5–3.5%, otherwise the load on the digestive organs and biliary tract is great; - fat-free: no nutritional value, no fat-soluble vitamins;
- unprocessed: "live" milk from the farm must be boiled. Yes, there will be fewer vitamins, but the nutrients will remain, and the milk will become microbially safe.
Fermented milk products
Fermented milk products appear in a child's diet even before the age of one. They are rich in protein and calcium, improve intestinal motility, increase immunity and should be on the child's menu every day. But they should be given no more than the recommended rate, so as not to overload the baby's kidneys.
40 g of cottage cheese and 150 ml of fermented milk drink: kefir, biolact, yogurt, etc. are enough per day for a one-year-old child.
The menu of a one-year-old child can be varied with 10-15% fat sour cream. The daily norm is 5-9 g. It can be added to soup, salad or served with the same cheesecakes.
In the year of the child for the first time you can treat cheese: just give a piece to gnaw or add it to pasta, casserole, scrambled eggs. Cheese is rich in calcium - 600–900 mg per 100 g of product.
But cheese should be given to the baby in limited quantities - no more than 5 g per day, because it contains a lot of sodium. Choose hard or semi-hard varieties with a fat content of 30-35%. Remember that blue cheese, smoked, processed, spicy, brine and with various additives, such as nuts and peppers, are not suitable for baby food.
Meat
Every day in the diet of a one-year-old child should be meat, the norm is 100 g. You can give beef, veal, lean pork, rabbit meat, turkey and chicken. Offal diversifies the menu: language and heart. The liver is also useful, but it is advised to give it no more than 1 time in 7-10 days, since it contains a large amount of toxic substances.
Duck and goose meat is not suitable for baby food because it is very fatty. The same with lamb. Not a place in the children's menu and sausages. Sausages, sausages, sausages are harmful for adults, and even more so for children.
The same with lamb. Not a place in the children's menu and sausages. Sausages, sausages, sausages are harmful for adults, and even more so for children.
Fish
Twice a week it would be good to replace part of the meat portion with a portion of fish. 30–50 g will be enough. Fish is easily digestible, contains iodine, fluorine, copper, zinc, vitamins A and D, B vitamins, polyunsaturated fatty acids and iron.
For the first acquaintance with fish dishes, nutritionists advise choosing not river, but marine inhabitants - they have a priority in terms of environmental cleanliness and the content of useful elements. In addition, they are less bony. You can start with low-fat varieties, such as pollock, cod, flounder. And later add haddock, navaga and horse mackerel to the diet.
The advantage of river fish is that it is not as allergic as sea fish. The most suitable for the children's menu are: hake, carp, river trout and river perch.
A strict taboo in baby food for smoked and salted fish, as well as caviar - so much salt is definitely not good for a child.
It is too early to indulge your baby with seafood: all kinds of crabs, shrimps, squids, mussels, lobsters and lobsters are too dangerous from an allergenic point of view.
Eggs
It is desirable that eggs be on the baby's menu 2-3 times a week. Starting from a year, a child can be given not only the yolk, but also the protein. It is better to choose chicken or quail eggs, which, by the way, are less allergenic. Eggs of waterfowl - ducks, geese, etc. - are banned, as they are most often infected with salmonella.
Because of the potential for infection, any eggs must be cooked before being placed on the baby's table. The “soft-boiled” and “pouched” options are not for the baby. The child can be fed with a hard-boiled egg, scrambled eggs with milk, or dishes with the addition of an egg.
Vegetables and fruits
About four times a day the child should eat vegetables and fruits. The kid has already met many of them. During the year, culinary acquaintances continue, you can try beets, turnips, tomatoes, cherries, cherries, strawberries, chokeberries, raspberries, blackberries, cranberries, lingonberries, apricots, peaches, kiwi and citrus fruits.
When your child is one and a half years old, you can add seaweed salad to his diet. Naturally, it should not contain vinegar! Laminaria is rich in iodine, macro- and microelements, and is easily digestible.
Do not forget about dried fruits, compared to fresh fruits, they are several times more fiber and minerals: magnesium, iron, potassium.
Slowly start introducing greens into your baby's menu: cut them finely and add them to salads, soups, main dishes. Dill, parsley, cilantro, celery are especially useful - they have a lot of vitamin C.
Legumes
Legumes contain a lot of vegetable protein, fiber, B vitamins, vitamins C, E, PP, carotene, calcium, potassium, phosphorus, zinc, magnesium, iron, etc. But they should not be more often in the menu of a one-year-old child 2-3 times a week, because they are known for their ability to cause increased gas formation in the intestines. Before giving a child legumes, they must be thoroughly boiled and, if possible, cleaned of coarse fibrous skin. Green peas (fresh or frozen) and green beans are best suited for a children's menu.
Green peas (fresh or frozen) and green beans are best suited for a children's menu.
Cereals
Cereals are the basis of the food pyramid, they should be present in the child's diet every day. In the morning - in the form of porridge, with or without milk. For lunch, as a side dish. Buckwheat and oatmeal have the first place in nutritional value. From these cereals, they usually cook, even before a year, the first porridge for the baby. Among the "firsts" are also corn grits and rice.
When the child has already tasted cereals from the main cereals, you can experiment with millet and cereals obtained from wheat - wheat and semolina. Note that semolina porridge is not held in high esteem by nutritionists, because it is the poorest in vitamins and minerals. It is not often advised to give it to a child, only for the sake of a variety of taste sensations.
Healthy barley and barley porridges are heavy for a delicate children's stomach. Barley porridge can be given to the baby only after one and a half years. Barley - after three.
Barley - after three.
Pasta and bread
Pasta is a lifeline for a mother who is drowning in business, but has to feed her child urgently. Kids usually like pasta too. And only nutritionists are dissatisfied, they remind that pasta:
- can be entered into the menu of a child at 1 year old no more than 1-2 times a week;
- is better not to give to overweight children;
- should be excluded when the child is constipated.
Babies can be given bread per year, but not more than 60 g per day. It is better to start with wheat or rye-wheat. It is desirable to dry it slightly in advance so that it becomes easier to digest. Rye bread is made from sour dough, which causes fermentation in the intestines, so it is advised to treat a child to it only after a year and a half.
Butter
Butter not only improves the taste of dishes, but also enriches the diet with vitamins D, E, K, A. A one-year-old child can eat 10–20 g of the product per day, as part of dishes or spread on bread.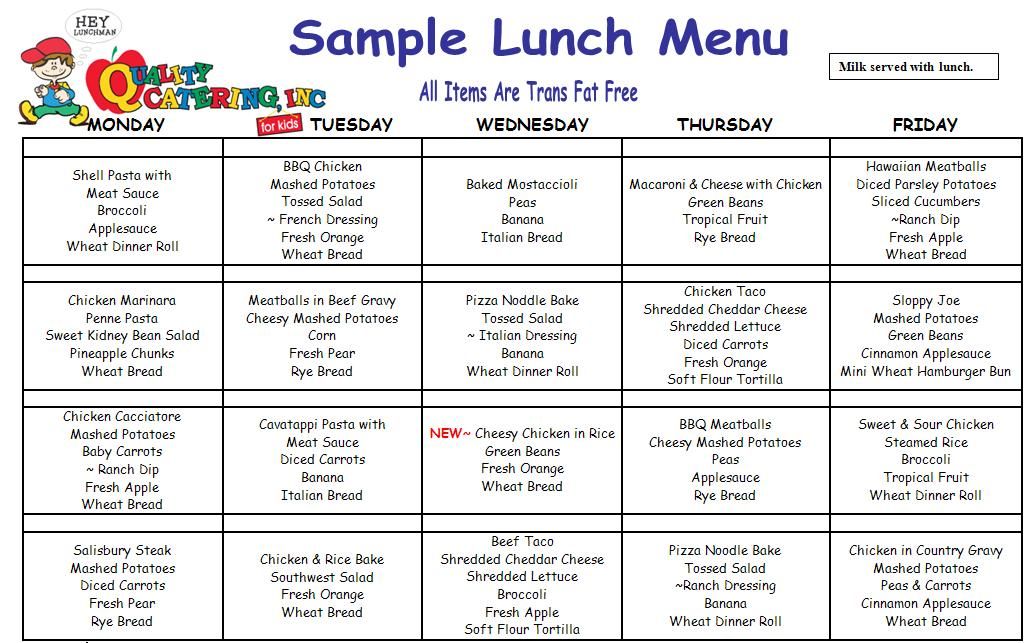 The oil should not be the fattest - the optimal fat content is from 72.5 to 82%.
The oil should not be the fattest - the optimal fat content is from 72.5 to 82%.
Vegetable oils are rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids, which are necessary for maintaining the health of both children and adults. It is enough for a one-year-old child to eat 10-15 ml of vegetable oil daily. In addition to the popular sunflower oil, the baby's diet may include corn oil, olive and sesame oil.
Important! Both butter and vegetable oil should be added to ready-made dishes, they should not be subjected to heat treatment.
How to cook for a 9 year old baby0005
After a year, a very important stage should begin in the child's nutrition - a gradual transition to solid food. It is now very important for a baby to learn to chew food, so he will develop chewing muscles, improve the ability to voluntarily control the movements of the organs of articulation.
To begin with, try to offer your child vegetable stew, just thoroughly mashed with a fork, instead of “airy” puree. A little later, you don’t need to knead the vegetables, it will be enough to chop them finely. Start cooking cereals from ordinary, not ground, cereals. Make salads with finely chopped fruits and vegetables.
A little later, you don’t need to knead the vegetables, it will be enough to chop them finely. Start cooking cereals from ordinary, not ground, cereals. Make salads with finely chopped fruits and vegetables.
An important principle in the preparation of children's food is to preserve the beneficial substances contained in the products as much as possible. Therefore, use gentle technologies: boil, bake, stew, steam.
Remember that a significant part of the vitamins is destroyed by heat and exposure to moisture and air. Never peel vegetables ahead of time - just before putting them in the pot. The water should be boiling by now. To preserve minerals in vegetables, boil them in salted water. The rule does not apply to beets - boiling in salted water worsens their taste.
Prepare baby soup without toasting. If the soup is meat, be sure to drain the first broth.
Is it possible to use salt and spices
Food for a one year old child can be slightly salted. To an adult, children's food should seem undersalted.
To an adult, children's food should seem undersalted.
It is acceptable to use spices, but in very small quantities - only until a light shade of taste is achieved. Bay leaves, basil, cumin, thyme, coriander, marjoram, rosemary, allspice, vanilla, cinnamon can be added to the dishes of a child from one to three years old. Spices such as red and black pepper, horseradish, mustard are too hot and are not suitable for children's dishes.
What about sweets
In our culture it is customary to treat children with candy, and this is completely wrong. Sweets increase allergic reactions, lead to overweight and provoke the appearance of caries, so the later the baby gets to know them, the better.
You can sweeten food only if the baby refuses to eat unleavened food - cottage cheese, porridge, etc. But first, try to improve the taste with berries, fruits or dried fruits.
If you still can't wait to pamper your child with something sweet, let it be marshmallows, marshmallows, marmalade, jam, marmalade, jam or children's cookies.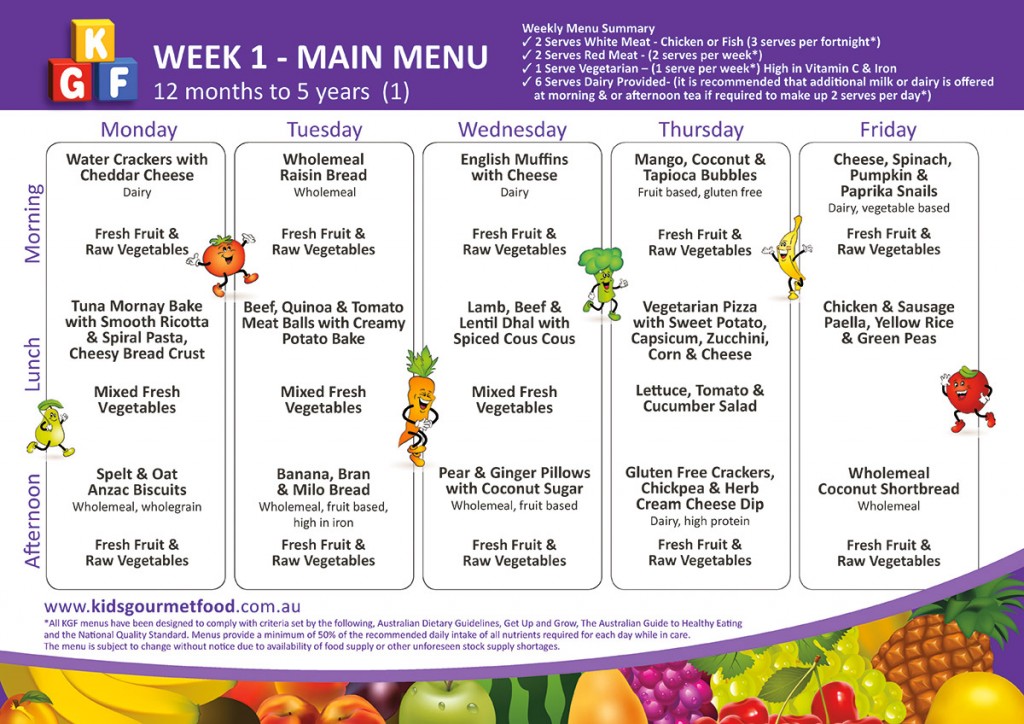 But only after the main meal.
But only after the main meal.
What you can and cannot drink
For a child, as well as for an adult, the ideal drink is ordinary water. You can offer the baby boiled water from the tap or buy a special one - in a bottle marked "for baby food".
Compotes from vegetables, fruits and dried fruits diversify the drinking diet. Try to cook them without sugar, most likely, the baby will be delicious anyway. Vegetable and fruit juices are also better to make yourself. However, it is often not worth giving them to a child to drink: there are no dietary fibers in them, but there is plenty of sugar and acids.
At the age of one year, the child can already be given weak herbal and fruit teas. It is useful to drink cocoa, it contains proteins, carbohydrates, fats and a biologically active component that can stimulate the activity of the cardiovascular and nervous systems. Sometimes you can treat your baby to surrogate coffee, which is made from barley, oats, rye, chicory, soybeans, chestnuts, etc.
Do not give your child tea, cocoa, or surrogate coffee after fish or meat dishes. These drinks contain substances that prevent the absorption of certain nutrients, such as iron.
Do not treat your baby to carbonated drinks, even mineral water - the carbon dioxide contained in them irritates the gastric mucosa.
How to make a menu for a 1 year old baby
Experts advise you to make a menu for a child for a week in advance. This makes it easier to ensure that the baby's nutrition is balanced. It is important to immediately build a regular meal schedule and, if possible, do not deviate from it for more than 30 minutes. Thanks to the regime, the child develops a conditioned food reflex, and this helps to digest and assimilate food well.
A one-year-old child is recommended to be fed five times a day. three main meals: breakfast, lunch, dinner and two additional ones: afternoon tea and bedtime feeding.
A child from one to one and a half years old needs about 1000-1200 ml of food per day, from one and a half to three years - 1200-1500 ml.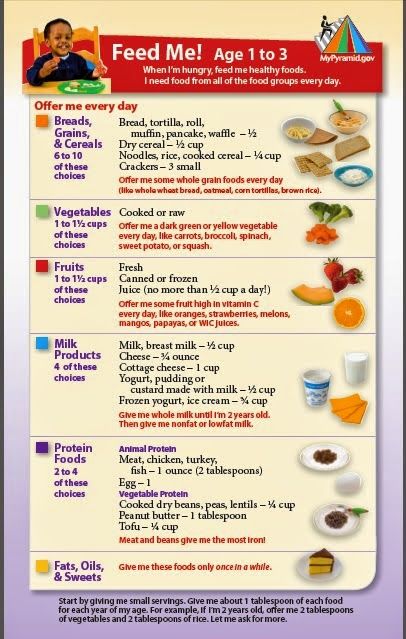 The volume of food in one feeding should not exceed 300-350 ml.
The volume of food in one feeding should not exceed 300-350 ml.
The total calorie content of meals should now be approximately 1300 kcal. A child's menu per year may look something like this:
- Breakfast: porridge with milk 180 ml, fruit 30 g.
- Lunch: vegetable soup 120 ml, meat soufflé 50 g, rice garnish 80 g, compote 100 ml.
- Snack: fermented milk drink 150 ml, fruit 100 g.
- Dinner: vegetable stew 150 g, steamed chicken cutlet 50 g.
- At bedtime: breast milk or infant formula.
— share with your friends!
Read more
- Fish menu for a child: when to introduce fish into the diet and 5 healthy recipes
- Doctors created a petition against the high amount of sugar in the diet DOW
- When everything around is in food: the diet of a child at 8-12 months. Recommendations from a nutritionist from Germany
Menu for a child up to a year (tables)
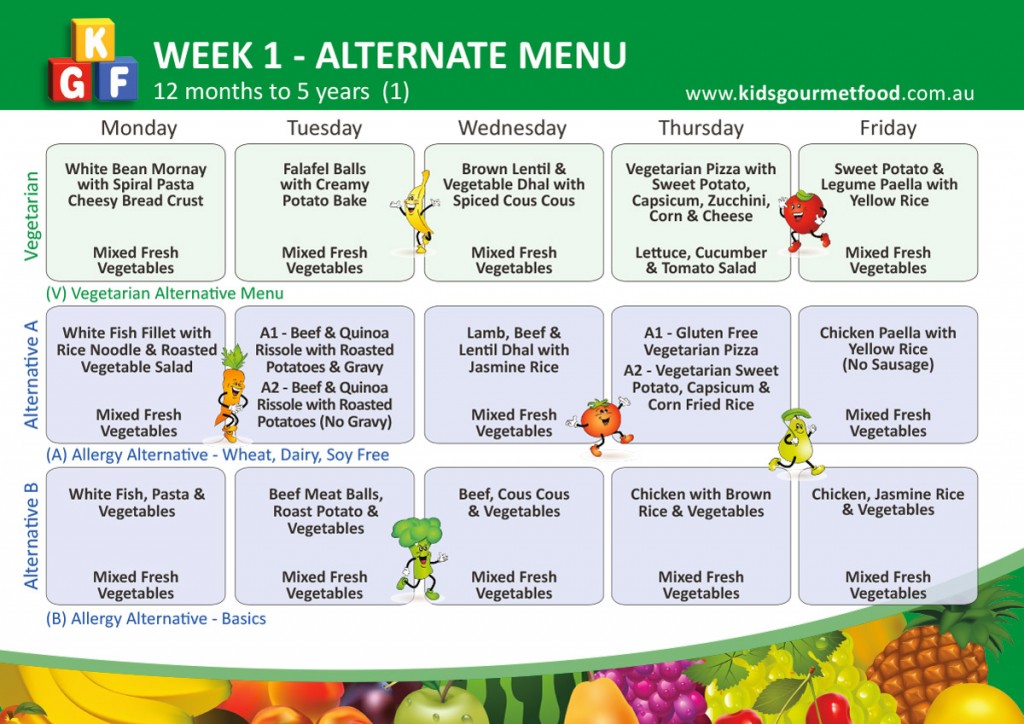
Approximately by 9 months the child develops a stable feeding schedule: frequency, time, dosage.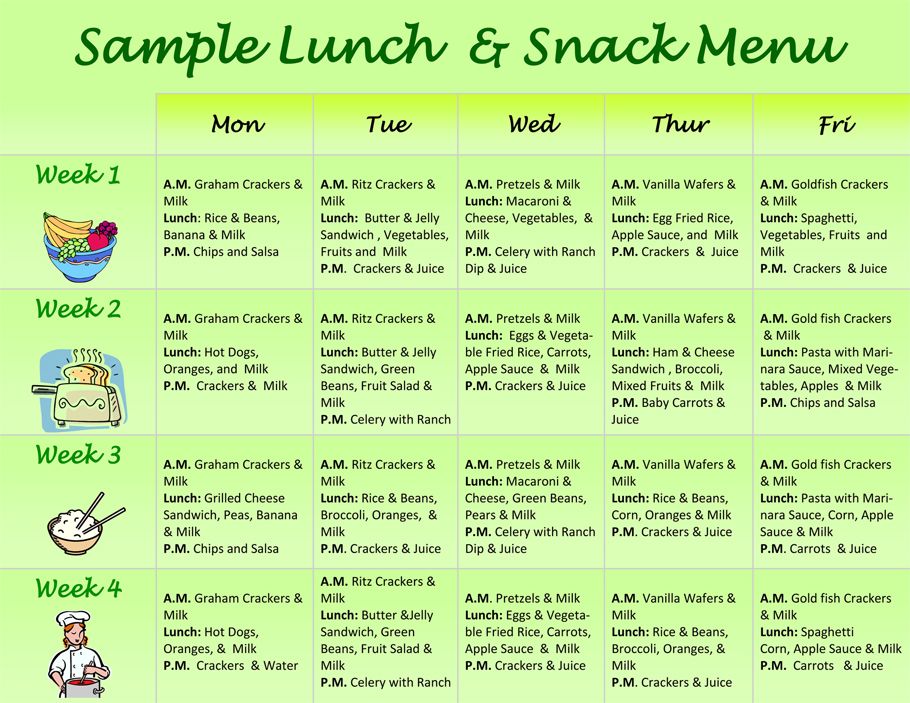 All basic complementary foods have already been introduced, but breast milk or formula is still the mainstay of nutrition. Still, mothers are lost in what sequence, in what quantity of products to give to child aged up to year . Here are several options for an approximate menu for children aged 9 months to 1 year in tables . With the help of convenient tables, it will be easier for mothers to draw up a nutrition plan for the baby, taking into account age characteristics and individual preferences. Learn, choose, apply.
All basic complementary foods have already been introduced, but breast milk or formula is still the mainstay of nutrition. Still, mothers are lost in what sequence, in what quantity of products to give to child aged up to year . Here are several options for an approximate menu for children aged 9 months to 1 year in tables . With the help of convenient tables, it will be easier for mothers to draw up a nutrition plan for the baby, taking into account age characteristics and individual preferences. Learn, choose, apply.
Weekly menu for a child from 9 months to 1 year
Menu of our mothers and grandmothers: from the book "Mother and Child", 1954, authors B. A. Arkhangelsky and G. N. Speransky - members of the Academy of Medical Sciences of the USSR. The approximate menu is designed for 5 main feedings per day (click on the table to enlarge it)
Features of the menu for children under 1 year old
- 1-3 month old baby eats only breast milk or milk formula.
- In the menu of a 4 - 5 month old baby - artificial, the first complementary foods are introduced.
- The menu of breastfed children under 6 months does not include additional meals. By this time, breast milk no longer fulfills the nutritional needs of the growing baby.
- A child of 6-7 months eats 4-5 times a day, the menu becomes varied and looks something like this:
Variants of the daily menu for a child up to a year (table)
- Table "Child's menu 6-7 months «
- Children's menu 8-9 months
From 8 - 9 months of age, meat, fish, cottage cheese, kefir are added to the menu:
At the age of 10-11 months in the evening feeding, milk can be replaced with kefir, gradually weaning the baby from the breast. Kids menu 10-11 months must contain:
- breast milk or formula
- milk oatmeal
- rice or buckwheat porridge
- vegetable broth
- meat dishes
- vegetable puree
- fruit purees
- vermicelli
- egg yolk
- kefir
- juices
- kissel
Number of breastfeeds up to one year
Approximate diet for children up to one year - NUTRICIA
Feeding scheme for a child up to a year
The numbers in the center of scheme indicate the hours of feeding.