Baby food website
The History of Baby Food - How Do We Feed Babies?
Eunoia, 6 months, eats egg.The invention of baby food
Baby food as it is traditionally known—jars of sweet potatoes and cans of rice cereal—didn’t really exist until the 1920s.
According to Amy Bentley, author of Inventing Baby Food, the first solid baby food to appear on the market was invented by a man named Harold Clapp. The story is that when his wife fell ill and couldn’t care for their baby, Clapp developed a soup made from beef broth, vegetables, and cereal.1 When Clapp saw how well his baby did on the soup, he began making big batches and eventually started selling it to other parents via local drugstores.2
The rise of industrial baby food
A few years after Clapp’s baby food went on sale in New York pharmacies, Frank and Dan Gerber (father and son) began experimenting with strained baby food at their cannery, the Fremont Canning Company.3 By 1933, Fremont produced more than 2 million cans of baby food, which included a variety of strained fruits and vegetables, as well as a beef vegetable soup. 4 Recognizing the tremendous opportunity, companies such as Heinz and Beech-Nut quickly followed suit. The Gerber’s line of canned baby food became so popular, in fact, that Fremont Canning eventually abandoned all of its other lines of canned food and changed its name to Gerber’s Baby Foods.
Campaign to persuade moms and doctors
While the concept of store-bought food specifically made for babies picked up some serious speed in the 1930s, many Americans were still suspicious of canned food, having lived through the days of spoiled and contaminated canned food.5 To overcome this, Gerber undertook an ambitious advertising campaign to convince moms, dieticians, and pediatricians that their processed baby food was not only nutritionally superior to homemade baby food, but safer.6 The ad campaign included research—funded by Gerber—that praised the benefits of canned food generally.
Meanwhile, American mothers began to rely more and more on the advice of doctors and pediatricians for feeding their children. Recognizing this shift, Gerber stepped up its advertising efforts to the medical community, offering their canned baby food free of charge to doctors who requested it.7
Recognizing this shift, Gerber stepped up its advertising efforts to the medical community, offering their canned baby food free of charge to doctors who requested it.7
Future ad campaigns would include messaging to convince moms that homemade baby food was not as safe as commercially-made baby food and that toiling away in the kitchen was not good for mothers…or their babies.
Importantly, many baby food advertisements also encouraged feeding solids at 3 months old, sometimes explicitly in the text, but also visually by the babies depicted in the ads themselves. Not surprisingly, by the 1950s, babies were being fed commercial solid food by just six weeks of age.8
From beef soup to caramel pudding
The first commercial baby food to hit the market was a vegetable soup with a beef broth base. Other common baby foods in the 1940s included liver, veal, and strained single-ingredient vegetables and fruits. By the 1950s, however, baby food companies increased their focus on taste, adding sugar and artificial flavors, as well as food that was a more consistent, smooth purée. 9 Whereas American babies fed in the 1940s were likely to get significant amounts of iron and protein—as well as some different textures—from commercial baby food, babies in the 1960s and beyond were more likely to experience a sweet, smooth purée. While there is no publicly available information for why baby food companies stopped producing foods like liver and veal, it’s not hard to imagine the increased return on investment of sweet purées. Not only were apples, bananas, and sweet potatoes cheaper than meat, they played to a baby’s preference for sweet foods.
9 Whereas American babies fed in the 1940s were likely to get significant amounts of iron and protein—as well as some different textures—from commercial baby food, babies in the 1960s and beyond were more likely to experience a sweet, smooth purée. While there is no publicly available information for why baby food companies stopped producing foods like liver and veal, it’s not hard to imagine the increased return on investment of sweet purées. Not only were apples, bananas, and sweet potatoes cheaper than meat, they played to a baby’s preference for sweet foods.
Baby food: a cultural boomerang
In 1880, babies were not commonly fed solid food until they were 11 months old, and by 1950, that age plummeted to just 6 weeks old.10 It wasn’t until the 1970s that the medical community began to realize that the early introduction of solid food was contributing to a displacement of breast milk and formula, which doctors were starting to recognize as more nutritious. 11
11
As of today, the American Academy of Pediatrics, U.S. National Institutes for Health, and World Health Organization all recommend waiting until a baby is at least 6 months old to introduce solids.
The impact of commercial baby food on American food culture has been enormous. Not only were babies fed solids earlier and earlier—displacing breast milk as the primary source of nutrition—they were exposed to textureless purées with refined sugar, salt, MSG, and other artificial flavors more than ever before, potentially impacting their flavor preferences for life.12
Perhaps most poignant in the cultural shift of feeding babies, however, is the boomerang effect the industry has had on moms in the last 100 years. The very products designed to make feeding babies easier for moms laid the foundation for a cultural expectation that moms should make organic, unprocessed baby food at home. Not surprisingly, the industry has responded with lines of pricey organic pouches, featuring everything from organic beets with super foods like chia seeds to wild-caught salmon purées. A close inspection of these modern products, however, show that most still contain the traditional sweeteners of sweet potatoes, carrots, apples, and pears.
A close inspection of these modern products, however, show that most still contain the traditional sweeteners of sweet potatoes, carrots, apples, and pears.
Rise of picky eating
Prior to the invention of perfectly smooth baby food, babies were exposed to a wider variety of textures. Further, because straining baby food was so labor intensive, it’s not hard to imagine that babies may have eaten finger foods earlier in their solid food journey than babies did in the 1950s as well.
In 2019, Solid Starts conducted an analysis of North American Google searches related to baby food. Interestingly, the results demonstrated that searches related to picky eating were among the most popular queries. While picky eating is nothing new, research shows that it has been on the rise for quite some time.13
Cultural shifts in eating are rarely linear. No single baby food company can be responsible for the sheer impact that commercial baby food has had. One has to factor in the rise of advertising, the increase of marketing to kids, the boom of snack foods, as well as the extended period of time in which babies were spoon-fed purées.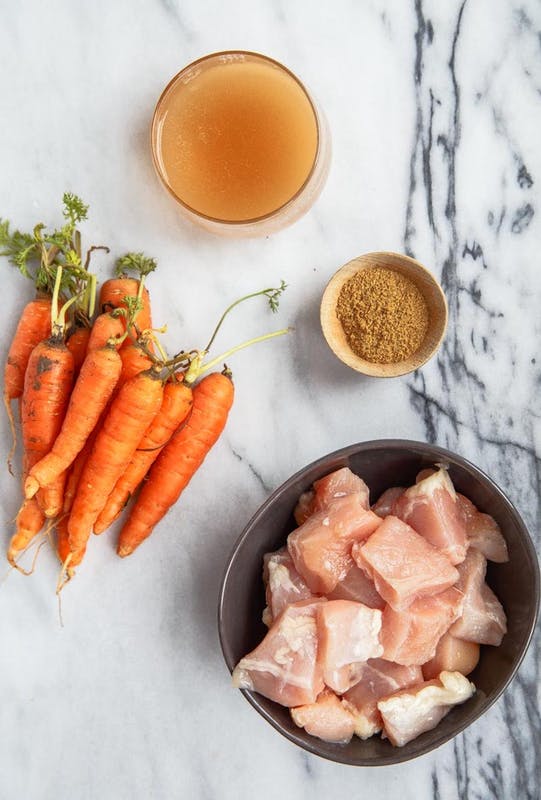 But once you put all those things together, it’s easy to see how picky eating has become the number one problem in feeding little ones.
But once you put all those things together, it’s easy to see how picky eating has become the number one problem in feeding little ones.
The future of feeding babies
Numerous studies have shown that the more variety of tastes, textures, colors, and mouth feels a baby is exposed to, the more likely those children are to accept new foods later on.14 Further, research studies have shown that babies fed diets of bland, textureless foods are more likely to prefer these foods later on.15
As the evidence builds for the benefits of introducing a variety of wholesome, real food to babies, feeding philosophies are shifting. Methods such as baby-led weaning (where purées and spoon-feeding are skipped in favor of finger foods) are quickly growing in popularity. For a detailed review of baby-led weaning, and why you might want to try it, hop over to our next section: What is Baby-Led Weaning?
- A. Bentley, Inventing Baby Food, University of California Press, 2014, p.
 30
30 - A. Bentley, Inventing Baby Food, University of California Press, 2014, p. 30.
- A. Bentley, Inventing Baby Food, University of California Press, 2014, p. 32.
- A. Bentley, Inventing Baby Food, University of California Press, 2014, p. 30, 32.
- A. Bentley, Inventing Baby Food, University of California Press, 2014, p. 33.
- A. Bentley, Inventing Baby Food, University of California Press, 2014, p. 33.
- A. Bentley, Inventing Baby Food, University of California Press, 2014, p. 35.
- A. Bentley, Inventing Baby Food, University of California Press, 2014, p. 59.
- A. Bentley, Inventing Baby Food, University of California Press, 2014, p. 80.
- A. Bentley, Inventing Baby Food, University of California Press, 2014, p. 80.
- A. Bentley, Inventing Baby Food, University of California Press, 2014, p. 125.
- L. Birch and J. Fisher, Development of Eating Behaviors Among Children and Adolescents, Semantic Scholar [website]https://pdfs.
 semanticscholar.org/c324/d4bf4fcebfff9fc80e11c233dfc497242dcf.pdf (retrieved November 5, 2019).
semanticscholar.org/c324/d4bf4fcebfff9fc80e11c233dfc497242dcf.pdf (retrieved November 5, 2019). - J. Traig. The Making of a Picky Eater, The Wall Street Journal, January 11, 2019.
- L. Birch and J. Fisher, Development of Eating Behaviors Among Children and Adolescents, Semantic Scholar [website]https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/c324/d4bf4fcebfff9fc80e11c233dfc497242dcf.pdf (retrieved November 5, 2019).
- A. Bentley, Inventing Baby Food, University of California Press, 2014, p. 158
What to do when baby won’t touch food
If you have just started solids and are not sure how to go about it, check out our course videos on starting solids, baby-led weaning and responsive spoonfeeding and consider downloading our Starting Solids bundle.
There are many reasons why a child may not be interested in eating, but what do you do when babies or toddlers aren’t interested in even touching their food?
Chase the whyIf a baby is not eating, they are trying to communicate something. For some babies, they simply might not have the interest, skill, or desire to eat at that moment; for others, it may be more complicated given their history (reflux, a bad gag, negative associations with the highchair, etc.) It’s imperative to listen to baby’s cues in any of these situations while guiding them to learn.
For some babies, they simply might not have the interest, skill, or desire to eat at that moment; for others, it may be more complicated given their history (reflux, a bad gag, negative associations with the highchair, etc.) It’s imperative to listen to baby’s cues in any of these situations while guiding them to learn.
The most important thing you can do is bring calm confidence to the table and believe that baby can learn the skills for eating. In other words, stay calm and don’t give up!
If baby is 6 months old or youngerYou’ve done all the reading about starting solids. You have the highchair, bib, and you know what food you want to introduce first. And then, in the blink of a camera, at the height of your anticipation, your bubble bursts. Baby doesn’t bring a single thing to their mouth.
Or maybe you started with spoon feeding and decided to make the switch to finger food. You cut the food just right, set the meal just so, but instead of enjoying it, baby doesn’t touch a thing.
At 6 months of age or younger, babies are often just not ready. Evaluate whether baby is truly ready for solids (see our page on readiness or check out our video) and make sure baby is truly meeting all of the developmental signs before starting solid food.
Consider waiting a week or two. If baby is less than or around 6 months old and showing signs of readiness, but doesn’t engage with food offered, try not to worry too much. Many babies at this age are just not cognitively ready to self-feed, even if they are showing the motor milestones for readiness. This is normal.
Even with spoon-feeding, many babies will turn away from the spoon when they are not ready. This is communication saying they are not interested or ready yet. Listen to what baby is telling you. Sometimes the youngest eaters just need another week or two to wrap their heads around eating.
Avoid feeding schedule changes. Encouraging or pushing baby to eat before they are ready can lead down a bumpy road of food refusal. At this age, avoid feeding schedule changes to make baby hungry enough to try solid foods. Remember: Baby’s primary nutrition should be from breast milk or formula until 12 months of age. Plus, an overly hungry young baby is not primed to learn. Babies who are too hungry and don’t yet have the skills to self-feed will end up melting down at the table. (Cue screaming for the breast or bottle.)
At this age, avoid feeding schedule changes to make baby hungry enough to try solid foods. Remember: Baby’s primary nutrition should be from breast milk or formula until 12 months of age. Plus, an overly hungry young baby is not primed to learn. Babies who are too hungry and don’t yet have the skills to self-feed will end up melting down at the table. (Cue screaming for the breast or bottle.)
Let baby watch you eat, often. Even before you start solids, bring baby to the table. Pull up the bouncing chair so baby can watch you eat or sit baby on your lap. Channel a dinner party vibe—laugh, smile, and enjoy your meal so baby can see the fun of eating. When baby is ready to start solids, pull baby’s highchair up to the table or put baby on your lap while YOU eat. Babies learn from watching us, and many young babies need more modeling to realize that food goes in our mouths.
Get baby’s attention. Tap their highchair tray or table with your fork or finger, call their name, and make eye contact. Once they are paying attention, bring the food to your mouth and smile. This is very important with spoon-fed babies. Spoon-fed babies learn that food comes on a spoon, it’s put in their mouth, and swallowed. Picking up food with their hands and bringing it to their mouth is an entirely different story—the concept that hands bring food to the mouth is brand new. See the tips below for helping baby pick up and bring food to their mouth or dive in to our video on transitioning from spoon feeding to self-feeding.
Once they are paying attention, bring the food to your mouth and smile. This is very important with spoon-fed babies. Spoon-fed babies learn that food comes on a spoon, it’s put in their mouth, and swallowed. Picking up food with their hands and bringing it to their mouth is an entirely different story—the concept that hands bring food to the mouth is brand new. See the tips below for helping baby pick up and bring food to their mouth or dive in to our video on transitioning from spoon feeding to self-feeding.
Talk to baby and describe the food: “This is delicious spaghetti with Grandma Mary’s famous sauce! It’s tangy and sweet at the same time!”
Model with your mouth open. Throw your manners out the window and chew with your mouth open so babe can see what you are doing. When you swallow, point to your stomach and say: “The spaghetti went all the way to my belly!” You may feel a bit silly, but modeling is a game-changer for many young babies.
Go BIG with food sizes. It may seem counter-intuitive, but for young babies, bigger is better. Watch how a 6- to 9-month-old baby interacts with toys, and you’ll notice they use all of their fingers and the palm of their hand to grasp things. Bigger pieces of food are much easier to grasp, hold, and control. Learning to chew is challenging work, and we want to help make everything else (i.e., reaching and grasping) as easy as possible. A baby struggling with a smaller piece of food may give up because they don’t have the skill to grab it yet.
Bigger pieces of food are also easier for baby to manage in their mouth. The brain more readily notices and registers big pieces. Young babies are more likely to explore and move big pieces around in the mouth successfully.
You want to provide just the right amount of challenge. Bigger pieces of food provide baby with a fun challenge but aren’t too difficult to reach, grasp, and move around with their tongue. When tasks are too hard, babies may give up and (in their own way) say, “No, thanks!” Fine motor control improves as baby gets closer to 9+ months, and they’ll start using their thumb and index finger to pinch smaller items. This is a great time to size down in food so they can utilize their new skill.
This is a great time to size down in food so they can utilize their new skill.
If baby is just starting to self-feed after a period of spoon-feeding, they might not know what to do with food in front of them. Remember, they’ve been practicing a specific eating skill (accepting a spoon) and need to learn a different way to eat.
Make sure baby comes to the table happy. If babe has a meltdown the minute you put them in the highchair, start there. Take a break from the highchair and serve a meal with baby sitting on your lap or have a picnic on the living room floor. Some babies love a little excitement on the way to the table—try dancing, twirling, or crawling! Set baby up for success and start the meal happy.
Model your daily eating routine. This is especially important if you are transitioning from spoon-feeding to baby-led weaning. Remember: Everything baby is doing is a new skill, and they need to see how it’s done to understand better.
Imitate baby’s facial expressions and encourage them to imitate you. Watching to learn is a huge part of infancy. Think about it this way—the more you enjoy something, the more interest your baby has in it. The more you look at your phone, the more baby wants to play with it, right? Enjoy eating your meal, and baby will want to participate in eating, too!
Bring baby’s attention to the food. Tap baby’s tray near the food to make sure they are visually attending to it, call their name, and say, “Look!” Sometimes a simple, single cue is all a baby needs to acknowledge and touch food on a tray. Note: While not common, a lack of sustained attention can be a sign of autism. If baby is not attending to the food after repeated attempts to get their attention to it, consult your health care professional.
Offer food vertically in the air. Make it easy for baby to pick the food up by offering it to them in the air. You can also try standing food upright to make it easier for baby to grasp. (Such as banana sticks in yogurt with the banana standing upright.) If baby is still not interested, try taking a bite of the food yourself and then offering that piece to baby in the air. If you offer something like yogurt, oatmeal, or other puree-type foods, you can load the spoon and hand it to your child or hold the spoon in your mouth and lean toward baby to grab.
(Such as banana sticks in yogurt with the banana standing upright.) If baby is still not interested, try taking a bite of the food yourself and then offering that piece to baby in the air. If you offer something like yogurt, oatmeal, or other puree-type foods, you can load the spoon and hand it to your child or hold the spoon in your mouth and lean toward baby to grab.
Offer the food from your own mouth. Put your manners aside and try this tried-and-true feeding therapy trick: hold the food between your teeth, lean toward baby, and let them take the food out of your mouth with their hands.
Remember: Step one is for baby to interact with the food; if they are reaching for and/or grasping the food items, you’re making progress! Patience is key. We don’t expect babies to roll from tummy to back consistently the first time they try. Likewise, we don’t expect babies to eat consistently in the beginning, either. Their primary nutrition source remains breast milk or formula until 12 months of age. Any table food they consume is a plus.
Any table food they consume is a plus.
Bring baby to the table a bit hungry. Consider offering breast or bottle 1.5-2 hours before mealtime, so they have a bit more hunger drive to eat the food on their tray.
However, if a 9- to 12-month-old baby tries to eat but appears frustrated and irritable at the table, it could be a sign that they are too hungry and want food but have yet to hone their fine motor or chewing skills—cue the hanger. This could be a sign that baby needs an appetizer, so they come to the table with a desire to eat, ready to learn and build skill, but aren’t hangry. Consider a small breast or bottle-feed 30-45 minutes before mealtime or offer easy-to-eat food to start the meal.
For toddlers 12 months old and upHere are some additional tips to encourage food exploration and new skills for toddlers resistant to touching foods or who have been spoon-fed and are now transitioning to self-feeding table foods.
Practice makes perfect. Toddlers learn by doing. They may need additional practice scooping with their hands and using containers. You can encourage and practice these skills by scooping water with cups in the bathtub or scooping dry items like rice or beans with spoons or their hands.
Toddlers learn by doing. They may need additional practice scooping with their hands and using containers. You can encourage and practice these skills by scooping water with cups in the bathtub or scooping dry items like rice or beans with spoons or their hands.
Let them practice feeding you. If the child is okay touching food but won’t feed themselves, ask them to feed you. Bring their attention to a piece of food, hand it to them, and ask them to put it in your mouth. If you have pets (and feel comfortable with little hands near the pup’s mouth), ask the toddler to feed the dog.
Pretend play! Feed stuffed animals or dolls and explain what’s happening: “You fed bunny a piece of cheese! It’s going to go all the way to her belly and help her grow big and strong!”
Model and narrate more. Toddlers still learn a lot from watching and modeling. Demonstrate feeding yourself and explicitly verbalize what’s happening: “Mama is putting this banana in her mouth! And then she’s going to chew it with her teeth! Watch!” Then point from your mouth to your belly and explain: “The banana is going all the way to my belly to help me feel strong!”
Engage in sensory play outside of mealtime. If the child does not want to touch certain textures (i.e., wet, cold, sticky), try sensory play outside of mealtime. Go for finger paints, shaving cream, or slime. If texture avoidance happens with more than just food, consider talking to a pediatrician. An occupational therapist trained in sensory integration may be able to help.
If the child does not want to touch certain textures (i.e., wet, cold, sticky), try sensory play outside of mealtime. Go for finger paints, shaving cream, or slime. If texture avoidance happens with more than just food, consider talking to a pediatrician. An occupational therapist trained in sensory integration may be able to help.
Explore different shapes, sizes, and props. Some toddlers respond well to making food more fun. Try serving food with a toothpick or cut food in a fun shape. Mango in bite size pieces on a plate may seem totally boring… but mango on toothpicks? Fun!
Stop spoon-feeding. If a toddler knows they will always be spoon-fed to meet their hunger need, they are less likely to try feeding themselves, which is more challenging for them to do. Tips for this transition:
- Start meals slightly earlier than usual so they are hungry but not starving or hangry.
- Use the modeling tips above and model for them to feed themselves.

- If you are confident they can chew foods, consider not spoon-feeding them and see if they self-feed. If they choose not to eat, allow them to learn that hunger is a natural consequence if they don’t feed themselves. This is age appropriate and should work rapidly. If you have any concerns, discuss a plan of action with a feeding therapist or health care provider.
- Offer a snack that they can self-feed a little bit later to help them solidify the skill.
For more support on transitioning babies and toddlers from spoon-feeding to self-feeding, see our video here.
If the child has not had the chance to learn how to chew foods and they appear to struggle with consistencies other than purees, consider talking to your pediatrician about a referral for feeding therapy with an occupational or speech therapist to help build chewing skills.
When baby will touch everything but wet foods like yogurtWill baby or toddler interact with everything except wet textures like yogurt, oatmeal, or sauces? Some kids are more sensitive to this type of texture and may need help learning to tolerate it.
Practice self-feeding with a spoon. This is a skill babies and toddlers need for life, so practicing with pre-loaded spoons or scooping with utensils are great options. Offer the spoon but don’t put it in baby’s mouth: stop a few inches away from their face and let baby reach for the spoon to pull it toward their mouth.
Provide opportunities for sensory play. There are many ideas online for “sensory bins” for babies and toddlers, but consider playing in wet grass, painting with ketchup, making edible slime or finger paints, or playing with sponges in the bath or at a water table.
Let baby feed you. Will they touch the food to bring it to your mouth? This can be an excellent gateway to touching the food for themselves.
Avoid over-cleaning their hands. Sometimes when babies and toddlers know that messy play ends with a wipe down, they altogether avoid the activity anticipating the ending. It’s tough watching kids get super messy, but there’s a massive benefit in letting them get sticky. Make clean-up fun and lighthearted. Go to the sink, turn the water on, and have a splashing party.
It’s tough watching kids get super messy, but there’s a massive benefit in letting them get sticky. Make clean-up fun and lighthearted. Go to the sink, turn the water on, and have a splashing party.
Generally, a lack of interest in touching food is not typically a concern; it’s often just a sign the child needs more exposure and practice. However, consult your pediatric health care professional if the child is:
- Gagging, retching, or vomiting at the sight or touch of food.
- Extremely sensitive to certain textures (like wet, sticky, etc.). They may need extra help with sensory processing. Talk to your health care professional for a referral for occupational therapy to help them better regulate their body.
- Not gaining weight well despite drinking breast milk or formula.
- Not consuming any solid foods after 8 months of age. Note: Spoon-fed babies and toddlers in transition to finger food and self-feeding may have a period of food refusal.
 See our video for tips on how to bridge this transition.
See our video for tips on how to bridge this transition.
- Not accepting any chewable foods after a couple of weeks of exposure to solid foods (9 months or older). If baby is younger than 9 months and not accepting chewable foods, employ the tips above for baby’s age and give it a bit more time.
- Swallows all chewable food whole without attempting to chew and is 12 months old or older.
- Not attending to the food on the tray after attempts to get their attention (calling their name, tapping the tray, etc.). While not common, a lack of sustained attention can be a sign of autism.
No matter the age of baby, remember the division of responsibility. There are certain things you can control and certain things you cannot:
You control what foods the child is offered, when food is offered, and how you show up to the meal (i.e., your attitude).
Your child is in control of whether they eat and how much.
No matter how hard you try, you cannot control if or how much your child will eat.
Trying to control their intake is a slow spiral down a rabbit hole of picky eating and food refusal. Try one or two strategies at the meal, and if your child is still not interested, enjoy your own meal, and move on. Tomorrow is another day.
How you show up to the meal is much more important than you probably realize. The literature on picky eating shows that parental concern about intake and pushing babies to eat when they are not interested consistently leads to picky or selective eating later.1 2 3 4
So, take a deep breath and try to have fun as kiddo instinctively fumbles through learning to eat.
If you are concerned about your child’s weight gain or ability to eat table foods, talk to your child’s pediatrician. A feeding therapist can provide new ideas and additional support.
Reviewed by:
Kary Rappaport, OTR/L, MS, SCFES, IBCLC
Kimberly Grenawitzke, OTD, OTR/L, SCFES, IBCLC, CNT
- Emmett, P.
 M., Hays, N. P., & Taylor, C. M. (2018). Antecedents of picky eating behaviour in young children. Appetite, 130, 163–173.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2018.07.032
M., Hays, N. P., & Taylor, C. M. (2018). Antecedents of picky eating behaviour in young children. Appetite, 130, 163–173.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2018.07.032 - Cardona Cano, S., Hoek, H. W., & Bryant-Waugh, R. (2015). Picky eating. Current Opinion in Psychiatry, 28(6), 448–454.
- Steinsbekk, S., Bonneville-Roussy, A., Fildes, A., Llewellyn, C. H., & Wichstrøm, L. (2017). Child and parent predictors of picky eating from preschool to school age. International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity, 14(1).
- Cole, N. C., An, R., Lee, S.-Y., & Donovan, S. M. (2017). Correlates of picky eating and food neophobia in young children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrition Reviews, 75(7), 516–532
Center for Children and Diet Nutrition - Official website of UIA CDDP
Center for Baby and Diet Nutrition - Official website of UIA CDDPThe first monument in the country to a school cook was erected in Ufa
The administration of Ufa reported that the day before the opening of the only monument in Russia took place in the city. ..
..
First, second and compote: all about modern school meals in Bashkiria – Vesti report
https://gtrk.tv/novosti/255451-pervoe-vtoroe-kompot-vse-sovremennom-shkolnom-pitanii-bashkirii-reportazh-vestey
MBOU "Lyceum No. 21"
On December 25, the Head of Bashkortostan visited one of the oldest educational institutions of the republic - MBOU "Lyceum No. 21"
Children's drawing competition "Winter Fairy Tale"
Children's drawing competition "Winter Fairy Tale" came to an end. The fact is that…
Two school canteens in Bashkiria became diploma winners of the All-Russian competition
The federal stage of the All-Russian competition “The Best School Canteen” organized by the Ministry of Education has ended in Moscow…
The results of the republican stage of the All-Russian competition "The Best School Canteen" were summed up
1. If a child leaves a kindergarten for a school located within…
For questions about payment, obtaining information.

For payment, inquiries and other questions, please contact…
Vacancies
Are you satisfied with the quality of food at primary school?
of the August meeting
On August 21, 2020, the second day of the annual… Take off”
Children are our future, and ensuring their healthy growth and development…
Master class “Pancakes Pancakes”
FOR THE FIRST TIME!!!
02/27/2020 in secondary school No. 131 of the Kalininsky district of the city of Ufa took place ...
February 23 - Lyceum No. 161
opening…
“Field kitchen for the 31st anniversary of the withdrawal of Soviet troops from Afghanistan”
On February 15, 2020, a solemn ceremony took place in the City Palace of Culture in Ufa…
“Russian Ski Track – 2020”
Ufa hosted the All-Russian sports event…
Dear parents!
In order to prevent an increase in the incidence of ARVI and influenza among students, in accordance with . ..
..
World of the family. Motherhood and Childhood”
“The World of the Family” is a useful exhibition for parents and children.
Family World. Motherhood and childhood”…
Happy Teacher's Day!
Dear teachers!!! Happy Teacher's Day to all of you!!! Your work cannot be evaluated by any measure...
Dear parents!
From 08/01/2019, the organization of meals for pupils of preschool institutions in the city of Ufa will be carried out by the Municipal ...
Elections!
Our Center actively participates in elections! Canteens for voters are organized in all schools,…
SMART POLY-LINGUAL multidisciplinary school in the Bright microdistrict!
One of the features of this school is the availability of specialized classes. Physicians will come out of the walls of the institution…
September 1!
Dear students, parents, dear teachers and colleagues of educational institutions!
With great pleasure we congratulate everyone on…
We continue to develop the production of baby food in Ufa.

In this matter, the capital has accumulated vast experience, which is already being extended to…
On July 16, 2019, the Republican Forum of Regional Catering Operators was held in the city of Neftekamsk.
On July 16, 2019, the Republican Forum of Regional Catering Operators was held in the city of Neftekamsk, which is dedicated to…
“Eat, Learn, Grow”
Under this motto, Ufa preschool and educational institutions are preparing for the renovation of a children’s…
| Main | School menu | About us | +7 (347) 255-30-03 |
| Documents | Kindergarten menu | Contacts | +7 (347) 255-44-48 |
| Vacancies | Results | Write to us | |
| Parents | Dairy kitchen | Personal account |
Scientific Research Institute of Baby Food
About the Institute
For 30 years the Institute has been the leading scientific organization in Russia in the field of intersectoral baby food industry. The Institute is engaged in fundamental, applied and experimental scientific research in the field of technology and technology of baby food, aimed at the creation and implementation of new progressive technological processes for the production of domestic high-quality specialized baby food products.
The Institute is engaged in fundamental, applied and experimental scientific research in the field of technology and technology of baby food, aimed at the creation and implementation of new progressive technological processes for the production of domestic high-quality specialized baby food products.
The Institute develops new innovative technologies for specialized food products: for baby food, including water for baby food and drinks, for dietary therapeutic and dietary preventive nutrition, for pregnant and lactating women, for gero-dietic and sports nutrition. As part of the scientific support of the intersectoral baby food industry, many developed products for the nutrition of children of various age groups, pregnant and lactating women have been successfully introduced and mastered by the industry.
Official documents
Conference
Educational activities
Awards
Scientific activity
Partners
institute
Research Institute of Baby Nutrition - a branch of the Federal State Budgetary Scientific Institution "Federal Research Center for Nutrition and Biotechnology" carries out creative cooperation with industry universities and a number of research institutes of the Russian Academy of Sciences.