Baby retching when feeding
Breastfeeding FAQs: Spitting Up, Gagging, and Biting (for Parents)
Breastfeeding is natural, but it takes practice to get it right. Here's what you need to know about spitting up, gagging, and other concerns during breastfeeding.
Is it Normal for My Baby to Spit Up After Feedings?
Sometimes, babies spit up when they eat too much, or when they burp or drool. Many infants will spit up a little after some — or even all — feedings or during burping because their digestive systems are immature. That's perfectly normal.
As long as your baby is growing and gaining weight and doesn't seem uncomfortable with the spitting up, it's OK. The amount of spit-up often looks like more than it actually is. But spitting up isn't the same as forcefully vomiting all or most of a feeding.
What’s the Difference Between Spitting Up and Vomiting?
Vomiting is a forceful projection of stomach fluids. Spitting up is a more gentle "flow" of fluids that come up. Babies don’t usually react to spitting up, but a vomiting baby will usually look upset or cry.
If you're concerned that your baby is vomiting, call your doctor. In rare cases, there may be an allergy, digestive problem, or other problem that needs medical care. It helps to keep track of how often and how much your baby is vomiting or spitting up.
How Can I Keep My Baby From Spitting Up?
If the doctor says your baby's spitting up is normal, here are some things you can do to help lessen it:
- Burp your baby after each feed from each breast. Sometimes giving smaller feeds more often can help, rather than giving larger-volume feeds.
- Keep your baby upright after feedings for at least 30 minutes. Holding your baby is best, since the way your baby sits in an infant seat may actually make spitting up more likely.
- Don't jiggle, bounce, or actively play with your baby right after feedings.
- Keep your baby's head above the feet while feeding. Don't hold your baby in a dipped-down position when feeding.
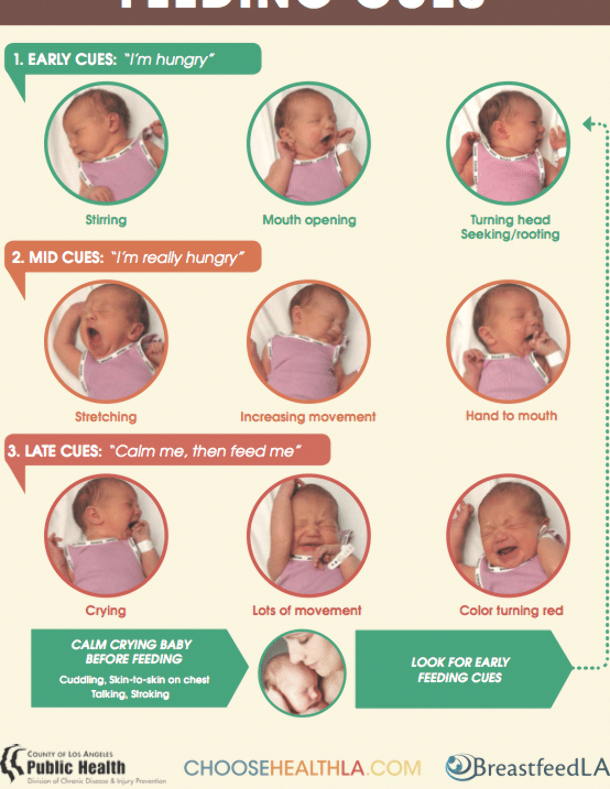
- Raise the head of your baby's crib or bassinet. Roll up a few small hand towels or receiving blankets (or you can buy special wedges) to place under — not on top of — the mattress. Never use a pillow under your baby's head. Make sure the mattress doesn’t fold in the middle, and that the incline is gentle enough that your baby doesn’t slide down.
If your baby also gets bottles of breast milk or infant formula supplements:
- Burp after your baby drinks 1–2 ounces from a bottle.
- Don't give the bottle while your little one is lying down.
- Make sure the hole in the nipple is the right size and/or flow for your baby. For example, fast-flow nipples may cause babies to gag or may give them more milk than they can handle at once. Many breastfed babies do well with the slow-flow nipple until they are 3 months old, or even older.
Many babies outgrow spitting up by the time they're sitting up.
How Can I Keep My Baby From Gagging?
Sometimes the force of your milk (especially when it “lets down”) is so strong that it can cause your baby to gag and pull off of the breast. If this happens during feeding:
- Try nursing your baby in a more upright position (head above the breast). This may ease the force of the milk.
- Nurse in a side-lying position, which also might help slow the flow of milk.
- Make sure your breasts are not engorged or over-full. Nursing every 2–3 hours can help prevent engorgement. If your breasts are too full and you’re concerned about a forceful letdown, express or pump a little bit of milk a few minutes before feeding time to avoid a strong letdown.
If your baby is pulling off and gagging or coughing during feeding, sit your baby up in a seated burp position. Gently pat the back to help your baby calm down before continuing feeding. If you’ve tried the steps above and this continues to happen, talk to your doctor or lactation consultant.
If your baby sometimes gags or chokes while taking a bottle of breast milk:
- Try a different nipple with a slower flow.
- Practice “paced” bottle feeding. This is where you slow down the milk flow from the bottle by holding it at less of an angle and allowing your baby to pause for breaks.
My Baby Bites During Breastfeeding. What Can I Do?
Babies will often play with their mothers' nipples with their gums, not meaning to cause any harm. But once they start teething, a baby might bite down, not knowing this is hurting mom.
Sometimes you can tell when your baby's about ready to bite down — usually when satisfied and starting to pull away from the breast. When you sense that your baby is finished feeding and may be bored or feeling playful, end the feeding. Break the suction by slipping your finger into the corner of your baby’s mouth.
If your baby is already biting down, pull your baby closer to you to make it more difficult to pull off easily. Then, break the suction. React calmly without raising your voice.
Then, break the suction. React calmly without raising your voice.
Here are more ways to make baby less likely to bite:
- Before a feed, give your baby something to chew on. Make sure it's big enough that it can't be swallowed or choked on and that it can't break into small pieces. A wet washcloth placed in the freezer for 30 minutes makes a handy teething toy. Be sure to take it out of the freezer before it becomes rock hard — you don't want to bruise those already swollen gums. Wash after each use.
- Say, "Mommy is not for biting. You can bite this." Then, offer your little one a teething toy or ring.
- Praise your baby — with a hug, kiss, or cuddle — whenever they nurse without biting or trying to bite.
Usually this is enough to stop the biting, but if your baby continues, talk to your doctor or lactation consultant for advice.
Reviewed by: Jamila H. Richardson, BSN, RN, IBCLC
Date reviewed: January 2021
Why babies gag themselves, and what to do if your baby's gagging on food
It's normal for babies to gag. They may gag when they're first getting used to eating, taste something they don't like, or have too much to eat. Gagging is different from choking: Gagging resolves on its own, but a choking baby needs help. You can tell a baby is choking if they're unable to cry, talk, or cough. If your newborn is gagging, try slowing the flow of milk by changing nursing positions or changing the bottle nipple. If your baby gags on food, they may not be ready for solids yet – or you may need to keep trying.
They may gag when they're first getting used to eating, taste something they don't like, or have too much to eat. Gagging is different from choking: Gagging resolves on its own, but a choking baby needs help. You can tell a baby is choking if they're unable to cry, talk, or cough. If your newborn is gagging, try slowing the flow of milk by changing nursing positions or changing the bottle nipple. If your baby gags on food, they may not be ready for solids yet – or you may need to keep trying.
We all have a gag reflex – it's a lifelong automatic response that helps prevent choking.
Gagging is normal for babies as they learn to eat solids, whether they're spoon-fed or you're doing baby-led weaning. Gagging brings food forward into your baby's mouth to help them learn how to chew.
Until your baby's around 6 months old, they also have a reflex that causes them to thrust their tongue forward whenever the back of their throat is stimulated. This tongue-thrust reflex can make early solid feedings a bit of a challenge, so it's best to wait until the reflex is gone to try solid feeding. Still, gagging on or pushing out those first spoonfuls of pureed food isn't uncommon.
Still, gagging on or pushing out those first spoonfuls of pureed food isn't uncommon.
Prodding your baby to eat more than they want can cause them to gag, as can having too much food (or food they don't like) in their mouth. Some babies will even gag on their own fingers until they figure out how far they can put things in their mouths. And until they get the rhythm of sucking, some infants will gag while breastfeeding or bottle-feeding, especially if it's flowing too quickly for them.
The difference between gagging and choking
Gagging is different from choking. Choking means your child's airway is partially or completely blocked, which prevents breathing. Here's how to recognize the difference between gagging and choking:
A child who's gagging may push their tongue forward or out of their mouth and do a retching movement to try to bring food forward. Their eyes may water. They may cough or even vomit. Let your child continue to gag and cough – it means their airway isn't completely blocked.
Coughing can usually effectively clear their airway. Don't pat them on the back or reach into their mouth to try to grab the object. Doing either can cause whatever they're gagging on to go farther down their airway. It's best to calmly stay with them and make sure they completely recover.
A child who's choking is unable to talk, cry, or cough because their airway is blocked. They may gasp or wheeze, make odd noises, or make no sound at all while opening their mouth. They may grab at their throat or appear panicked. A choking child might turn blue because they aren't getting oxygen. They may need first aid for choking – back blows and chest thrusts (or, for children over age 1, abdominal thrusts) – to dislodge the blockage.
This is best done by someone who's trained, so it's a good idea to learn first aid for choking and infant CPR in case you ever need it. BabyCenter offers a virtual Infant CPR and Choking course led by a top pediatric ER doctor.
Advertisement | page continues below
If your child is unable to breathe, talk, or make noise, call 911 immediately.
Newborn gagging
Newborns might have their gag reflex stimulated if the breast milk or formula they're fed comes out too quickly, especially when they're first getting used to eating.
Try to get your baby to relax during feedings and don't push them to eat more than they want.
If you're breastfeeding, the flow of milk coming out (the "letdown") can be strong – especially in the early weeks – and cause your baby to gag. Try nursing your baby with them in more of an upright position, so they aren't lying down. This might help slow the flow as it enters their mouth. You can also try nursing in a side-lying position (with both of you lying on your sides) to slow the milk flow as well.
If you create a lot of milk, or it's been a little longer than usual since you last nursed your baby and your breasts feel engorged, you can try pumping or hand-expressing milk for just a few minutes to get past the initial forceful letdown before nursing your baby. Then, the milk flow will be a little slower.
If your baby is bottle-fed, make sure the nipple is the right size. Nipples with faster flow have more holes, and can allow too much breast milk or formula to come out at once, causing babies to gag.
What if your baby's gagging on food?
It's scary when your baby gags on food, but it's part of the normal process of learning to eat. Try not to worry when it happens, as hard as that might be.
From birth to around 7 to 9 months, the gag reflex is actually triggered closer to the front of the mouth. Because of this, gagging might be more common when first starting solids and lessen once your baby gets older (around 9 to 12 months), when the gag reflex moves more to the back of the mouth.
If you're starting to introduce solid foods and your baby gags, here's what you can do.
Make sure your baby is ready for solid food before you introduce it. This usually happens around 6 months old, once your baby is able to sit upright, has good head control, grasps, turns away when full, and shows an interest in food, leaning forward and opening their mouth when food comes near.
When you think your baby's ready, start by putting a small amount of food on a spoon. Tip the spoon to get a bit of the food on the front of their tongue, rather than putting the whole spoonful in their mouth, which may trigger the gag reflex.
If your baby pushes the food out with their tongue, it doesn't necessarily mean that they don't like it – they're probably just trying to figure out this new way of eating. Feed them slowly while they get the hang of it.
After a few tries, they'll start using their tongue to move the food to the back of their mouth. If your baby is still pushing food out of their mouth or having trouble swallowing food after a week of trying, they may not be ready for solids yet.
If you're introducing your baby to solid food through baby-led weaning, gagging is also a normal part of the process. Your baby's learning to feed themself, and that's naturally going to come with some bumps along the way. Let your baby work out the gagging on their own, but keep an eye on them to make sure they're not choking.
To help keep your baby from gagging on finger foods, feed them soft, easy-to-swallow food that's cut into bite-size pieces once they develop the pincer grasp, at around 8 or 9 months old. If you're doing baby-led weaning, you'll give them large pieces of soft foods to grab and gnaw on. These foods should pass the squish test – they should squish easily between your thumb and forefinger or between your tongue and the roof of your mouth – so they're easy for your baby to eat.
Don't give them foods that are choking hazards, like whole grapes, hot dogs, nuts, raw vegetables, large chunks of meat or cheese, popcorn, or other cylindrical foods that can block the airway (like pieces of sausage or hot dog).
If your baby gags because they don't like the texture of solid food, try giving them different types of food – and remember that it's normal to have to give a baby a new food many times before they'll accept it.
If your baby turns away or cries, they're done eating. Resist the urge to push extra food on them or make them eat more once they're done.
Your baby will most likely gag less as they get more meals under their belt and as they get older, though some kids do have an overactive gag reflex. If your baby is still gagging about a month after starting solids, mention it to their doctor. Your baby's doctor can give you input and check for problems, or may even suggest seeing a specialist, just to be sure.
Why does the baby spit up after feeding?
search support iconSearch Keywords
Regurgitation is a common condition in newborns and infants and is most often a normal variant. However, it is not uncommon for parents to worry if their baby is spitting up frequently, believing that it is due to nutritional or health problems in general. Sometimes these fears are not unfounded, and regurgitation really has a pathological origin. What is its cause and when should you really consult a doctor about this? nine0003
Regurgitation - Return of a small amount of food (uncurdled or partially curdled milk) from the stomach up the digestive tract: into the esophagus and further into the oral cavity. According to statistics, at least 1 time during the day, at least 50% of babies from 0 to 3 months old can spit up, more than 60% of children 3-4 months old, and in 5% of children spit up continues up to the year 1 .
Regurgitation in newborns is considered a physiological process. It is caused by a number of factors, including:
- Features of the structure of the upper digestive tract in babies
- In newborns and infants up to a year of life, the stomach has a spherical shape. It holds a small amount of food, besides, the release from it into the duodenum is slower in comparison with children after the year 2 .
- Weakness of the lower esophageal sphincter that separates the esophagus from the stomach
- Normally, the lower esophageal sphincter should tightly "close" the esophagus, allowing food to pass into the stomach and not allowing it to enter back into the upper digestive tract. However, in young children (up to a year), the muscles of the esophageal sphincter are poorly developed, and it does not do its job very well 2 .
- Slow movement of food through the gastrointestinal tract
- The neuromuscular system of newborns is immature. It does not ensure the proper movement of food through the esophagus, causing regurgitation.
One of the important risk factors contributing to regurgitation in newborns is aerophagia. This is the swallowing of large amounts of air during feedings. This happens when the baby is not properly attached to the breast, the mother has a lack of breast milk, or the bottle is in the wrong position in the child who receives the mixture. The size of the opening in the nipple also matters - if it is too large, the newborn swallows a lot of air 3 .
With aerophagia, the baby becomes capricious, restless immediately after feeding. Noticeable bloating. If the baby spits up immediately after a feed, the milk (or formula) remains practically fresh, uncurdled 3 .
Promotes regurgitation after feeding and a predominantly horizontal position of the baby during the day, combined with relatively high intra-abdominal pressure 4 . Therefore, the correct position of the baby after feeding is so important. To avoid regurgitation of an excessive amount of stomach contents, after feeding, it is necessary to hold the baby in an upright “column” position for some time (10-20 minutes), lightly patting on the back and allowing excess air to “exit”. nine0003
Therefore, the correct position of the baby after feeding is so important. To avoid regurgitation of an excessive amount of stomach contents, after feeding, it is necessary to hold the baby in an upright “column” position for some time (10-20 minutes), lightly patting on the back and allowing excess air to “exit”. nine0003
Regurgitation in many newborns can be provoked by other situations in which pressure in the abdominal cavity increases and stomach contents are thrown into the esophagus, in particular 3 :
- tight swaddling;
- stool disorders, in particular constipation;
- long, forced cry and some others.
Want to avoid common feeding problems? nine0069
Start with a baby bottle with an anti-colic system that helps you avoid common feeding problems such as colic, gas and spitting up*
How can you tell the difference between normal spitting up and vomiting?
Sometimes regurgitation is considered a manifestation of disorders in the digestive tract of children. Due to the constant reflux of acidic stomach contents into the upper sections, inflammation and other complications may develop, including growth retardation, a decrease in hemoglobin levels, and others. Therefore, it is important for parents to understand where the line is between physiological and pathological regurgitation 1 .
Due to the constant reflux of acidic stomach contents into the upper sections, inflammation and other complications may develop, including growth retardation, a decrease in hemoglobin levels, and others. Therefore, it is important for parents to understand where the line is between physiological and pathological regurgitation 1 .
If the mother is worried that her baby is spitting up, keep track of when this happens and count the total number of spit ups per day. Normally, regurgitation usually occurs after eating (the child burps after each feeding), lasts no more than 20 seconds and repeats no more than 20-30 times a day. With pathology, the problem manifests itself at any time of the day, regardless of when the baby was fed. Their number can reach 50 per day, and sometimes more 1 .
The amount of discharge during regurgitation also matters. With normal, physiological regurgitation, it is approximately 5 - 30 ml. If this volume fluctuates between 50 and 100 ml, it is already defined as profuse vomiting. When the range of the jet of vomit is up to 50 cm, doctors talk about "vomiting a fountain." A variant of atonic vomiting is possible, when the contents of the stomach flow "sluggishly". It occurs with atony of the stomach (decrease in muscle tone of the stomach wall) and disruption of the esophagus 1 .
When the range of the jet of vomit is up to 50 cm, doctors talk about "vomiting a fountain." A variant of atonic vomiting is possible, when the contents of the stomach flow "sluggishly". It occurs with atony of the stomach (decrease in muscle tone of the stomach wall) and disruption of the esophagus 1 .
Vomiting in babies is a warning sign. Doctors are especially alarmed by repeated vomiting, a fountain, with an admixture of bile, in combination with constipation. Vomiting can lead to the development of dehydration, acid-base imbalance and other consequences, therefore, if it occurs, you should urgently contact a pediatrician to find out the cause and begin treatment. A doctor's consultation is necessary if the child is spitting up a lot (more than 15-30 ml at a time), with a frequency of more than 50 episodes per day 1.3 .
Physiological regurgitation: symptoms
Regurgitation in newborns, which is considered a normal variant and does not cause concern to pediatricians 3 :
- usually continues for a certain period of time;
- is characterized by slow, "passive" leakage; if the baby spits up a fountain, it is better to consult a doctor;
- has a sour smell of curdled milk;
- occurs without the participation of muscles - the baby does not strain during regurgitation;
- does not affect the general well-being of the baby.

How to help a newborn who spit up often?
If the baby is healthy, no medication is prescribed for spitting up. To help the child allow simple measures based on lifestyle changes and feeding.
- Frequent feeding of the baby
It is known that the baby is more prone to spit up if his stomach is full. To improve the situation, it is recommended to feed the baby more often, avoiding oversaturation, best of all - on demand 5 .
- Correct feeding technique
Every feeding, the mother must ensure that the baby does not swallow too much air during suckling. When sucking, there should be no loud, smacking, clicking sounds. You also need to control that the baby captures the nipple along with the areola.
- Choosing the right bottle and nipple
If the newborn is bottle-fed and receiving formula, it is important to choose the right bottle and nipple. The hole in it should be such that the milk flows out in drops, and not in a stream. The nipple must not be filled with air
The hole in it should be such that the milk flows out in drops, and not in a stream. The nipple must not be filled with air New Anti-colic bottle with AirFree valve
The AirFree valve prevents air from entering the baby's stomach.
- Baby standing upright after eating
To allow air that has entered the digestive tract during meals to escape, it is important to keep the newborn upright for 10-20 minutes after feeding 4 .
- Ensure the correct position of the baby during sleep
To reduce the negative impact of the acidic contents of the stomach on the esophagus, it is necessary to put the baby to sleep in the supine position. The side or prone position, which many pediatricians used to recommend, is no longer recommended. It was found to be associated with an increased risk of sudden infant death syndrome 5 .
If parents notice alarming symptoms, such as spitting up too often or large volume, etc.
 , it is important to consult a pediatrician without delay. This will allow you to identify the real problem in time and help the baby grow up healthy and happy. nine0003
, it is important to consult a pediatrician without delay. This will allow you to identify the real problem in time and help the baby grow up healthy and happy. nine0003
References1 Zakharova I. N., Andryukhina E. N. Regurgitation and vomiting syndrome in young children // Pediatric pharmacology, 2010. V. 7. No. 4.
Nagornaya 2900 V., Limarenko M. P., Logvinenko N. G. Experience with the use of domperidone in suspension in young children with regurgitation syndrome // Child Health, 2013. No. 5 (48).
3 Zakharova IN Regurgitation and vomiting in children: what to do? //Pediatrics. Supplement to Consilium Medicum, 2009. No. 3. S. 58-67.
4 Zakharova I. N., Sugyan N. G., Pykov M. I. Regurgitation syndrome in young children: diagnosis and correction // Effective pharmacotherapy, 2014. No. 3. P. 18-28.
5 Vandenplas Y. et al. Pediatric gastroesophageal reflux clinical practice guidelines: joint recommendations of the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (NASPGHAN) and the European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (ESPGHAN) //Journal of pediatric gastroenterology and nutrition.
 2009; 49(4): 498-547.
2009; 49(4): 498-547. You are leaving the Philips Healthcare (“Philips”) official website. Any links to third party websites that may be included on this site are provided solely as a convenience to you. Philips makes no warranties regarding any third party websites or the information they contain.
I understand
You are about to visit a Philips global content page
Continue
You are about to visit the Philips USA website. nine0003
I understand
How to help the baby when regulating
Support Support iconKeywords for searching
Home Home ›!! How to help a child in sprinkling
Home Home ›!!
Breastfeeding is a very special time for a mother and her newborn baby. Together with the feeling of closeness and affection that feeding brings, understanding its nuances cannot but raise many questions, including the question of how to help an infant spit up. Regurgitation in a newborn is by no means always the result of a simple pat on his back. nine0013
Regurgitation in a newborn is by no means always the result of a simple pat on his back. nine0013 In this article, we'll talk about the basics of helping a newborn spit up, as well as other questions you may have about spitting up.
Why do babies spit up?Let's get this straight: Why do newborns need to burp in the first place? During feeding, children usually swallow extra air - this is called aerophagia. Spitting up helps prevent this air from entering the intestines, as well as vomiting, gas, and crankiness in the baby. To avoid the return of milk after feeding, you should give the baby the opportunity to burp more often. nine0003
How to help a newborn spit up?
During the first six months, the baby should be kept upright in a column for 10-15 minutes after each feed. This will help keep the milk in his stomach, but if the baby occasionally burps anyway, parents need not worry. While carrying your baby in an upright position, you can put a baby diaper or wipes on your shoulder to keep your clothes clean.
We've already seen why spitting up is important, now let's find out how to help your baby spit up. Parents should gently pat the baby on the back with a hand folded in a handful until he burps. Folding your hand into a handful is important because clapping with a flat palm may be too strong for an infant.
Every baby is different and there is no one right position for spitting up. To get started, you can try the following options:
- Sitting position with the baby on the chest. In this position, the parent puts the baby's head with his chin on his shoulder and with one hand supports the baby under the back. With the other hand, you can gently pat the baby on the back. This method is most effective in a rocking chair or when the baby is gently rocking. nine0017
- Holding a child upright on one's legs. With one hand, parents can hold the baby by the back and head, supporting his chin and placing his palm on the baby’s chest, with the other hand, you can gently pat him on the back.
 At the same time, it is important to be careful: do not press the child on the throat, but only gently support his chin.
At the same time, it is important to be careful: do not press the child on the throat, but only gently support his chin. - Holding a baby lying on his tummy in his lap. Make sure his head is above his chest and gently pat your baby on the back until he burps. nine0013
Here are some tips on how best to help your newborn spit up:
- Let your baby spit up while feeding. If the baby is restless or has swallowed air, it is worth giving him the opportunity to burp during feeding, and not just after.
- When bottle feeding, let the newborn burp after every 50-60 ml.
- When breastfeeding, let the baby burp at every breast change. nine0013
It is important to let your baby spit up after eating, even if he spit up during feeding!
If your baby is gassy, spit up more often. Also, if he vomits frequently or suffers from gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), have him spit up after every 30 ml bottle-feeding or every five minutes while breastfeeding.

How long should a baby be held for it to burp? It's different for everyone, but generally keeping a newborn upright for 15 to 20 minutes after a feed helps the milk stay in the baby's stomach. nine0003
Minimize the amount of air you swallow. Gas production and regurgitation result from aerophagia during feeding. The baby will inevitably swallow air, but there are ways to prevent it from swallowing too much. Whether you bottle feed your baby or combine breastfeeding with bottle feeding, the Philips Avent anti-colic bottle with AirFree valve is designed so that the nipple is always filled with milk without excess air, even in a horizontal position, thus preventing the baby from swallowing excess air during feeding. nine0013
Reducing the amount of air your baby swallows can help reduce your baby's risk of colic, gas, and spitting up.
Breastfeeding is a wonderful time to strengthen the bond between parent and baby. Every mom and every baby is different, so learning to help your newborn burp properly can take time and practice.