Baby sick after feeding
Reflux in babies - NHS
Reflux is when a baby brings up milk, or is sick, during or shortly after feeding. It's very common and usually gets better on its own.
Check if your baby has reflux
Reflux usually starts before a baby is 8 weeks old and gets better by the time they're 1.
Symptoms of reflux in babies include:
- bringing up milk or being sick during or shortly after feeding
- coughing or hiccupping when feeding
- being unsettled during feeding
- swallowing or gulping after burping or feeding
- crying and not settling
- not gaining weight as they're not keeping enough food down
Sometimes babies may have signs of reflux but will not bring up milk or be sick. This is known as silent reflux.
Things you can try to ease reflux in babies
Your baby does not usually need to see a doctor if they have reflux, as long as they're happy, healthy and gaining weight.
Do
-
ask a health visitor for advice and support
-
get advice about your baby's breastfeeding position or how to bottle feed your baby
-
hold your baby upright during feeding and for as long as possible after feeding
-
burp your baby regularly during feeds
-
give formula-fed babies smaller feeds more often
-
make sure your baby sleeps flat on their back (they should not sleep on their side or front)
Non-urgent advice: See a GP if your baby:
- is not improving after trying things to ease reflux
- gets reflux for the first time after they're 6 months old
- is older than 1 and still has reflux
- is not gaining weight or is losing weight
Urgent advice: Ask for an urgent GP appointment or call 111 if your baby:
- has vomit that's green or yellow, or has blood in it
- is projectile vomiting (being sick with more force than usual)
- has blood in their poo
- has a swollen or tender tummy
- has a very high temperature or they feel hot or shivery
- keeps being sick and cannot keep fluid down
- has diarrhoea that lasts for over a week or has signs of dehydration
- will not stop crying and is very distressed
- is refusing to feed
Also call your GP or 111 if you have any other concerns about your baby.
Treatment for reflux in babies
A GP or specialist may sometimes recommend treatments for reflux.
If your baby is formula-fed, you may be given:
- a powder that's mixed with formula to thicken it
- a pre-thickened formula milk
If the thickening powder does not help or your baby is breastfed, a GP or specialist might recommend medicines that stop your baby's stomach producing as much acid.
Very rarely, surgery might be needed to strengthen the muscles to stop food or milk travelling back up. This is usually only after trying other things or if their reflux is severe.
Causes of reflux
Reflux usually happens because your baby's food pipe (oesophagus) has not fully developed, so milk can come back up easily.
Your baby's oesophagus will develop as they get older and the reflux should stop.
Page last reviewed: 13 December 2021
Next review due: 13 December 2024
Vomiting in babies | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
beginning of content5-minute read
Listen
From birth to 12 months, babies are known to vomit — it’s just one of their design features. However, as normal as vomiting is, it can also be worrying for parents. Occasionally, vomiting can be a sign of illness or complications, but for most babies, vomiting and reflux occurs simply because their guts are still developing.
What are the different types of vomiting
There are a few different types of vomiting and although the result is the same, the reasons are different:
- Possetting is the name for small amounts of milk brought up after a feed.

- Reflux happens when the valve at the top of a baby’s stomach is not tight enough to keep milk in there. A baby’s oesophagus (food pipe) is short, so when the valve opens and there’s only a short distance between it and their mouth, vomiting can occur.
- Projectile vomiting is vomiting with force. Projectile vomiting can be a symptom of a blockage at the outlet of a baby's stomach. If it's happening after most or all feeds, take your baby to a doctor.
What causes babies to vomit?
Generally, mild vomiting occurs because a young baby is still getting used to feeding on, digesting and eliminating milk. On average, a newborn baby’s stomach can hold around 20 millilitres, so it doesn’t take much milk for them to fill up and vomit the excess.
How can I tell if my baby is sick?
Vomiting by itself can be reassuring. However, if your baby has a temperature, is not feeding well, has diarrhoea or a rash, or experiences any other symptoms, your baby needs to see a doctor. If your baby seems healthy and well and is bright and alert, you may just want to monitor their vomiting to see when and how often it happens — but note that the amount that a baby vomits can be hard to work out and may seem larger than it really is.
If your baby seems healthy and well and is bright and alert, you may just want to monitor their vomiting to see when and how often it happens — but note that the amount that a baby vomits can be hard to work out and may seem larger than it really is.
What’s the difference between vomiting and reflux?
Vomiting caused by reflux generally occurs after feeding. It can seem effortless or cause pain. Some babies with reflux constantly 'spill' after and in-between their feeds. It’s important to think about how your baby’s vomiting affects them. If your baby seems happy, is thriving and gaining weight, you could simply try changing the frequency and amount of feeds you give them. If your baby seems to be in pain and/or not thriving, take them to a doctor. Sometimes medication is necessary for reflux.
Does breast or formula feeding cause more vomiting?
Breastfed babies can vomit as much as babies who are formula fed. There's no real difference between the two. Generally, the only difference is that feeding on formula makes a baby’s vomit smell and look different to that after feeding on breastmilk.
Can solids cause vomiting?
Some babies take time to adjust to digesting solid foods. They can vomit more when solids are introduced. This can occur because of overfeeding. Their stomachs are simply too small to accommodate extra volume. Start small when introducing solids — around 1-2 teaspoons of solids are ideal.
Is vomiting a sign of allergies?
Some allergies can cause vomiting, especially allergies to cow's milk. Your baby can react to particular foods or ingredients if they’re sensitive to them. Your doctor can help guide you to decide which foods are best for your baby.
How can I treat my vomiting baby?
Most babies recover quickly after vomiting and don't need any specialised care. They can seem hungry again straight away or take a while to want to feed again. However, if they vomit a lot and have other symptoms, a doctor needs to assess them.
Generally, babies are not given medication for vomiting unless they can’t keep any milk or fluids down. Dehydration is generally managed by giving intravenous fluids.
Dehydration is generally managed by giving intravenous fluids.
Sometimes changing feeding positions and frequency can reduce the likelihood of vomiting. It's still important to always follow the safe sleeping guidelines when settling your baby, even if they vomit. Back sleeping is protective against choking.
When should you see a doctor?
You should take your baby to see your doctor if:
- you are concerned about your baby's vomiting
- your baby is showing other signs of illness
- your baby seems lethargic, sleepy and not interested in feeding
- your baby is losing weight and not thriving
- there is blood or bile in their vomit
- their vomiting isn’t stopping or getting worse
Sources:
Raising Children (Vomiting), Red Nose Australia (Will baby choke if he/she vomits while sleeping on the back?), Safer Care Victoria (Vomiting in neonates), The Royal Australian College of General Practitioners (The vomiting child)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: September 2022
Back To Top
Related pages
- Vomiting in children
- Reflux
- How to know when your baby is well - video
- Knowing your baby is well - podcast
Healthdirect Australia acknowledges the Traditional Owners of Country throughout Australia and their continuing connection to land, sea and community. We pay our respects to the Traditional Owners and to Elders both past and present.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care.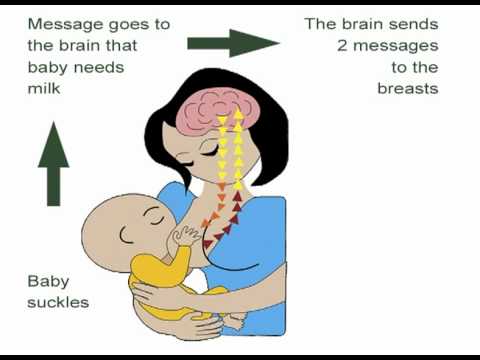 If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Feeding when sick | Medela
If you or your baby are unwell, you may wonder if it is safe to breastfeed. The great news is that breastfeeding when you're sick is most often good for both of you. Read more about this in our article.
The great news is that breastfeeding when you're sick is most often good for both of you. Read more about this in our article.
Share this information
Did you know that a breastfed baby is usually much less prone to illness? Although it is impossible to avoid them completely, the protective properties of breast milk help babies get sick less often 1 and recover faster than formula-fed babies.
Breast milk contains antibacterial and antiviral agents. 2 The longer you breastfeed your baby, the lower the risk of colds and flu, ear and respiratory infections, nausea and diarrhea. 1 Scientists are already exploring the use of breast milk to treat everything from conjunctivitis to cancer. 3.4
Should a sick baby be breastfed?
Yes. Breastfeeding promotes recovery and also helps to calm the baby. Breast milk contains antibodies, white blood cells, stem cells, and protective enzymes that help fight infections and help your baby recover faster. 1,5,6 In addition, the composition of breast milk (the balance of vitamins and nutrients) is constantly adjusted to the baby's body to help him recover as soon as possible. Thus, you will spend less time on sick leave and visit the doctor less often. 7
1,5,6 In addition, the composition of breast milk (the balance of vitamins and nutrients) is constantly adjusted to the baby's body to help him recover as soon as possible. Thus, you will spend less time on sick leave and visit the doctor less often. 7
“Breastfeeding gives the baby everything she needs when she is sick. This is his medicine, food, drink and comfort. For a baby, this is the best thing in the world,” says Sarah Beeson, a health visitor from the UK.
Surprisingly, when a child becomes ill, the composition of breast milk changes. When you come into contact with pathogens of bacterial and viral infections, your body begins to produce antibodies to fight them, which are then passed through milk to your baby. 8 When your baby is sick, your milk also spikes in immune-boosting cells (white blood cells). 5
In addition, breast milk is very easy to digest, making it ideal for babies with indigestion.
“At 12 months my daughter contracted norovirus and could only breastfeed,” recalls Maya, a mother of two in Spain. produce more milk. It was amazing. After 48 hours, I was able to meet the daily requirement for milk. It saved my baby from a drip."
produce more milk. It was amazing. After 48 hours, I was able to meet the daily requirement for milk. It saved my baby from a drip."
It should be taken into account that sometimes during an illness it is necessary to change the habitual breastfeeding regimen. For example, with a cold, a baby may want to eat more often, but little by little, both to calm down and because of nasal congestion, which makes it difficult to apply to the chest for a long time. If your baby has a stuffy nose, an upright breastfeeding position may be more comfortable, so don't be afraid to try different breastfeeding positions.
What should I do if my baby is seriously unwell and cannot breastfeed?
Occasionally, if a child feels unwell, they may not have an appetite or the strength to feed. If your baby is not eating well, seek advice from your healthcare provider, nurse practitioner, or lactation consultant to help prevent dehydration.
You may be asked to express milk to feed your baby with a bottle, a Soft Cup*, or other suitable method that requires minimal effort from the baby. Pumping on a regular breastfeeding schedule will also help keep your milk supply stable.
Pumping on a regular breastfeeding schedule will also help keep your milk supply stable.
You can express milk with one of our convenient breast pumps, such as the modern electronic Swing Flex** or the Harmony** manual breast pump. Rest assured, freshly expressed breast milk is just as good as breast milk, so your baby will get all the protection and support it needs.
If you have concerns about your baby's health or how much milk they are drinking, see your doctor as soon as possible.
Can I continue to breastfeed if I become ill myself?
You may not want to do this if you feel unwell, but in most cases it is best to continue breastfeeding. If you have a cold, runny nose, diarrhoea, vomiting, or mastitis, continue breastfeeding as normal with your doctor's approval. The baby is unlikely to become infected through breast milk. What's more, the antibodies in your milk will help reduce your baby's risk of contracting the same 13 virus.
“Breastfeeding when sick is not only safe most of the time, but also beneficial. Your baby is the least at risk of catching your upset stomach or cold, as he is already in close contact with you and receives a daily dose of protective antibodies from milk, ”says Sarah Beeson.
Your baby is the least at risk of catching your upset stomach or cold, as he is already in close contact with you and receives a daily dose of protective antibodies from milk, ”says Sarah Beeson.
If there is a risk of contracting a viral infection by airborne droplets, it is advisable to temporarily switch to expressing breast milk and bottle feeding.
In order not to lose the amount of milk produced when the body is still weakened by the disease, it is best to use the Swing Maxi Flex ** double breast pump, which helps to stimulate lactation, increase the amount of milk (by 18% on average) and increase its fat content (+1% ) 14 .
However, breastfeeding and pumping when sick can be very tiring. You need to take care of yourself so that you can take care of the baby. Try to drink more fluids, eat when you can, and get plenty of rest. Crawl under the covers for a few days and ask family or friends to help care for your baby if possible, so you can put all your energy into recovery.
“Don't worry about your milk supply, it will last. Most importantly, do not stop breastfeeding abruptly so that mastitis does not develop, ”adds Sarah.
Proper hygiene is very important to reduce the risk of spreading the disease. Wash your hands with soap and water before and after breastfeeding and pumping, preparing and eating food, using the toilet and changing diapers. Use a tissue when coughing and sneezing, or cover your mouth with the crook of your elbow (not your palm) if you don't have a tissue handy. Be sure to wash or sanitize your hands after coughing, sneezing, and blowing your nose.
Can I take medication while breastfeeding?
In agreement with the attending physician and compliance with the dosage, certain medications are allowed. 9.10
.
“When talking to a doctor or pharmacist for any reason, always state that you are breastfeeding,” she continues.
What about long-term treatment?
If you are on long-term treatment for diabetes, asthma, depression, or other chronic conditions, the benefits of breastfeeding may outweigh the risks. “Breastfeeding is often possible for almost any disease, with the exception of some very rare conditions,” Sarah says, “you will be very familiar with the drugs you are taking, and during pregnancy you can discuss them with your doctor or other specialist. There is guidance on the safe use of various medicines that all healthcare professionals use.” In any case, you should consult with your doctor.
“Breastfeeding is often possible for almost any disease, with the exception of some very rare conditions,” Sarah says, “you will be very familiar with the drugs you are taking, and during pregnancy you can discuss them with your doctor or other specialist. There is guidance on the safe use of various medicines that all healthcare professionals use.” In any case, you should consult with your doctor.
“I was on high doses of epilepsy medication, but I was still able to breastfeed,” recalls Nicola, a mother from the UK. “I saw a neurologist to ensure my son was safe and to minimize the risk of a seizure. Seizures can happen due to lack of sleep, and I fed day and night, but I took good care of myself, and my husband supported me. It was a positive experience."
What if I have to go to the hospital?
If you need to be hospitalized or urgently hospitalized, there are different ways to continue feeding your baby healthy breast milk so that you can return to normal breastfeeding after you are discharged.
“Express and freeze breast milk so that the caregiver can feed the baby. Practice at home ahead of time and be sure to let your doctors know that you are a breastfeeding mother, both before entering the hospital and while in it, ”recommends Sarah.
“If the baby is very small, you may be allowed to take him with you. Find out if the hospital has a supervising doctor or lactation consultant to contact. This specialist will support you, especially if you are in a general ward. If hospitalization is urgent, warn the doctors that you have a baby so that they take this into account.
Surgery under local or general anesthesia does not necessarily mean that breastfeeding will have to be stopped, or milk will need to be pumped and discarded. By the time you recover from surgery and can hold your baby, the amount of anesthetic in your breast milk will be minimal, so breastfeeding will be safe in most cases. 10 However, it is always best to consult your doctor or attending physician beforehand.
To ensure that the situation of treatment or departure does not affect the baby's diet, it is advisable to create a breast milk bank. This should be done daily by expressing one extra serving and freezing it in the handy, durable Medela Breast Milk Storage Bags. Even stored for several months and then thawed, your carefully prepared milk will still be incomparably healthier than formula.
For hygienic and easy pumping, use a breast pump with 2-Phase Expression technology for a fast, full flow of milk. For example, the ultra-comfortable Swing Flex** breastpump that adapts to the shape of your breasts and allows you to pump milk in a comfortable position, even lying back on the pillows 15 .
Don't forget to sterilize your breast pump with the Quick Clean microwave bags. Medela milk storage bags do not need to be handled as they are aseptically packaged and ready to use immediately.
Are there times when breastfeeding is not allowed?
In some cases, for the safety of the baby, breastfeeding should be stopped for a while, and instead, milk should be expressed and discarded to maintain milk production until the end of treatment. This includes radiotherapy and chemotherapy for cancer, herpes sores on the chest, and infections such as tuberculosis, measles, or blood poisoning that can be transmitted through breast milk. 11.12 Consult with a qualified professional about your condition to decide whether breastfeeding can continue in such cases.
This includes radiotherapy and chemotherapy for cancer, herpes sores on the chest, and infections such as tuberculosis, measles, or blood poisoning that can be transmitted through breast milk. 11.12 Consult with a qualified professional about your condition to decide whether breastfeeding can continue in such cases.
For quality lactation support during this period, you can use the dual electronic breast pump with innovative Flex technology or rent a Symphony Clinical Breast Pump** if possible. A list of cities where you can rent a breast pump can be found on the "Rent a Medela Clinical Breast Pump" page.
Literature
1 Victora CG et al. Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms, and lifelong effect. Lancet . 2016;387(10017):475-490. - Victor S.J. et al., "Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms and long-term effects". Lancet 2016;387(10017):475-490.
2 Lönnerdal B. Bioactive proteins in breast milk. J Pediatric Child Health. 2013;49 Suppl 1:1-7. - Lönnerdahl B., "Biologically active proteins of breast milk". F Pediatrician Child Health. 2013;49 Suppl 1:1-7.
Bioactive proteins in breast milk. J Pediatric Child Health. 2013;49 Suppl 1:1-7. - Lönnerdahl B., "Biologically active proteins of breast milk". F Pediatrician Child Health. 2013;49 Suppl 1:1-7.
3 Australian Breastfeeding Association [Internet]. Topical treatment with breastmilk: randomized trials. [ cited 2018 Apr 4]. Available from https://www.breastfeeding.asn.au - Australian Breastfeeding Association [Internet]. "Topical treatment with breast milk: a randomized trial". [cited 4 April 2018] See article at https://www.breastfeeding.asn.au
4 Ho JCS et al. HAMLET–A protein-lipid complex with broad tumoricidal activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;482(3):454-458. - Ho J.S.S. et al., "HAMLET - a protein-lipid complex with extensive antitumor activity". Biochem Biophys Res Comm. 2017;482(3):454-458.
2017;482(3):454-458.
5 Hassiotou F et al. Maternal and infant infections stimulate a rapid leukocyte response in breastmilk. Clin Transl Immunology . 2013;2(4): e 3. - Hassiot F. et al., "Infectious diseases of the mother and child stimulate a rapid leukocyte reaction in breast milk." Clean Transl Immunology. 2013;2(4):e3.
6 Hassiotou F, Hartmann PE. At the dawn of a new discovery: the potential of breast milk stem cells . Adv Nutr . 2014;5(6):770-778. - Hassiot F, Hartmann PI, "On the threshold of a new discovery: the potential of breast milk stem cells." Adv. 2014;5(6):770-778.
7 Ladomenou F et al. Protective effect of exclusive breastfeeding against infections during infancy: a prospective study. Arch Dis Child ./149272162-56a059825f9b58eba4b00130.jpg) 2010;95(12):1004-1008. - Ladomenu, F. et al., "The effect of exclusive breastfeeding on infection protection in infancy: a prospective study." Arch Dis Child. 2010;95(12):1004-1008.
2010;95(12):1004-1008. - Ladomenu, F. et al., "The effect of exclusive breastfeeding on infection protection in infancy: a prospective study." Arch Dis Child. 2010;95(12):1004-1008.
8 Hanson LA. Breastfeeding provides passive and likely long-lasting active immunity. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol . 1998;81(6):523-533. — Hanson, L.A., "Breastfeeding provides passive and likely long-term active protection against disease." Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1998;81(6):523-533.
9 Hale TW, Rowe HE. Medications and Mothers' Milk 2017. 17th ed. New York, USA: Springer Publishing Company; 2017. 1095 p . — Hale T.W., Rowe H.I., Medications and Breast Milk 2017. 17th edition. New York, USA: Publishing House Springer Publishing Company ; 2017. p. 1095.
10 Reece-Stremtan S et al. ABM Clinical Protocol# 15: Analgesia and anesthesia for the breastfeeding mother, Revised 2017. Breastfeed Med . 2017;12(9):500-506. - Rees-Stromtan S. et al., AVM Clinical Protocol #15: Analgesia and Anesthesia for Nursing Mothers, 2017 edition. Brestfeed Med (Breastfeeding Medicine). 2017;12(9):500-506.
ABM Clinical Protocol# 15: Analgesia and anesthesia for the breastfeeding mother, Revised 2017. Breastfeed Med . 2017;12(9):500-506. - Rees-Stromtan S. et al., AVM Clinical Protocol #15: Analgesia and Anesthesia for Nursing Mothers, 2017 edition. Brestfeed Med (Breastfeeding Medicine). 2017;12(9):500-506.
11 Lamounier JA et al. Recommendations for breastfeeding during maternal infections. J Pediatr 2004;80(5 Suppl ):181-188. - Lamunier J.A. et al., Guidelines for Breastfeeding during Maternal Infectious Diseases. J Pediatrician (Journal of Pediatrics) (Rio J). 2004;80(5 Suppl):181-188.
12 Hema M et al., Management of newborn infant born to mother suffering from tuberculosis: Current recommendations & gaps in knowledge. Indian J Med Res . 2014;140(1):32-39. - Hema M. et al., "Working with the Infant Born to a Mother with Tuberculosis: Current Recommendations and Gaps". Indian W Med Res. 2014;140(1):32-39.
2014;140(1):32-39. - Hema M. et al., "Working with the Infant Born to a Mother with Tuberculosis: Current Recommendations and Gaps". Indian W Med Res. 2014;140(1):32-39.
13 Lönnerdal B. Nutritional and physiologic significance of human milk proteins. Am JClin Nutr. 2003;77(6):1537S-1543S. Lönnerdahl B., "Biologically active proteins of breast milk". F Pediatrician Child Health. 2013;49 Suppl 1:1-7
14 Prime et al., Simultaneous Breast Expression in Breastfeeding Women Is More Efficacious Than Sequential Breast Expression, Breastfeed Med. Dec 2012; 7(6): 442–447. Prime DK and co-authors. "During the period of breastfeeding, simultaneous pumping of both breasts is more productive than sequential pumping." Brestfeed Med (Breastfeeding Medicine). 2012;7(6):442-447.
15 ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda MD: National Library of Medicine, USA, data on file: NCT03091985. Clinical Research.gov [Internet]. Bethesda MD: National Library of Medicine, USA, data on file: NCT03091985.
Read the instructions, Consult about possible contraindications with a specialist
* Ru FSZ 2010/07353 dated 07/19/10
** RU No. FCZ 2010/06525 dated 17/17/2021
9000
Breastfeeding when the mother is ill.
home
Articles
Nutrition
Stulova Maria Aleksandrovna Breastfeeding consultant
09.10.2013
Mom got sick! Nightmare! Grandmothers rush to the rescue, trying to protect the baby from infection and let the patient recover in peace.
However, good intentions and ignorance of physiology often lead to negative results.
Very important: if a nursing mother falls ill, it is necessary to choose medications that are compatible with breastfeeding*, and continue breastfeeding!!!
Contraindications to breastfeeding are the following diseases of the mother:
- eclampsia, severe bleeding during childbirth and in the postpartum period,
- open tuberculosis,
- a state of severe decompensation in chronic diseases of the heart, lungs, kidneys, liver,
- and hyperthyroidism,
- acute mental illness,
- especially dangerous infections (typhus, cholera, etc.
 ),
), - herpetic eruptions on the nipple of the mammary gland (before their follow-up treatment),
- HIV infection.
With such diseases of a nursing mother as rubella, chickenpox, measles, mumps, cytomegalovirus infection, herpes simplex, acute intestinal and acute respiratory viral infections, if they occur without severe intoxication, breastfeeding, subject to the rules of general hygiene, is not contraindicated.
The presence of hepatitis B and C in women is currently not a contraindication to breastfeeding, however, feeding is carried out through special silicone pads. In acute hepatitis A in the mother, breastfeeding is prohibited.
And if we are dealing with banal colds, flu or mastitis, then interrupting breastfeeding for the duration of the illness is NOT good for either the mother or the child.
Why?
Because by the time the mother has symptoms of the disease, the child may already be infected. He is in a state of “pre-disease”, but has the opportunity not to get sick or to suffer the disease in a mild / latent form.
To do this, it is necessary to help the baby's immune system and save the body's resources to fight infection. What can help the immune system are breast milk immunoglobulins, as well as a huge amount of vitamins and other biologically active substances from milk.
How to preserve the resources of the body - provide the child with the most easily digestible food (this is breast milk), which will save energy, reduce stressful situations (absence of a mother nearby, inability to habitually suckle the breast, the appearance of a new person in the house to care for the baby), save heat (avoid long walks in the cold season). Conclusion: the main help for the child's body is the preservation of the usual rhythm of breastfeeding and the usual contact with the mother.
If we decide to interrupt breastfeeding for the duration of the illness, then the child has to be transferred to artificial formula. What is NOT good for the child:
- The child is deprived of mother's milk immunoglobulins and many bioactive substances
- The load on the gastrointestinal tract increases, because the mixture is an indigestible product to which the body must adapt
- The risk of allergies increases and, accordingly, the body's resistance to infections decreases
- The child is deprived of habitual sucking and nutrition, and with it the necessary contact with the mother - this is a psychological stress for the baby, weakening the body's resources
- Often, when suckling the nipple, the child develops a mechanism of improper sucking, which prevents a further return to breastfeeding
What is NOT useful for a mother to interrupt breastfeeding during illness:
A change in the rhythm and quality of breast emptying, which in turn can provoke lactostasis, and then mastitis (especially if the mother has a bacterial infection).
During illness, the breast must be emptied very efficiently, sometimes giving the child to suck even more often than usual and from different positions. At the same time, many children themselves increase the rhythm of attachments during illnesses (mother's and / or their own) - they seem to “hang” on their chest for a couple of days. And grandmothers at this time can help mom around the house, take care of hygiene and the baby.
Usually safe, used in medium doses, are short courses of paracetamol, ibuprofen; most cough medicines; antibiotics - ampicillin and other penicillins, erythromycin. However, in the instructions for these drugs, you will most likely find a contraindication - breastfeeding. This is due to the fact that the manufacturer must conduct studies on the effect of the drug on the child through breast milk. Since it is very expensive and not every pharmaceutical company can conduct such studies, manufacturers are forced to write a warning. Studies by foreign companies show that the above drugs practically do not penetrate into breast milk (either due to the very large size of the molecules, or due to strong binding to blood proteins) and cannot harm the baby.