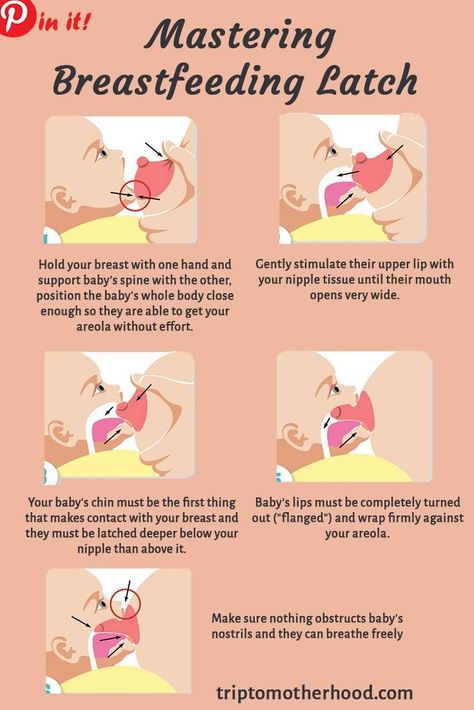
Baby spits up after feeding formula
Formula Feeding FAQs: Some Common Concerns (for Parents)
Whether you plan to formula feed your baby from the start, want to supplement your breast milk with formula, or are switching from breast milk to formula, you probably have questions.
Here are answers to some common questions about formula feeding.
Is it Normal for My Baby to Spit Up After Feedings?
Sometimes, babies spit up when they have eaten too much, burp, or drool.
Many infants will spit up a little after some — or even all — feedings or during burping because their digestive tracts are immature. That's normal.
As long as your baby is growing and gaining weight and doesn't seem uncomfortable with the spitting up, it's OK. The amount of spit-up often looks like more than it actually is.
But spitting up isn't the same as forcefully vomiting all or most of a feeding. Vomiting is a forceful ejection of stomach contents. Spitting up is a more gentle flow out the mouth or nose.
If you're concerned that your baby is vomiting, call your doctor. Keep a record of exactly how often and how much your baby is vomiting or spitting up. In rare cases, there may be an allergy, digestive problem, or other problem that needs medical care. The doctor should be able to tell you if it's normal or something of concern.
How Can I Keep My Baby From Spitting Up?
If the doctor says your baby's spitting up is normal, here are some things you can do to help lessen it:
- Burp your baby after your little one drinks 1–2 ounces from a bottle.
- Don't give the bottle while your baby is lying down, and keep your baby’s head above their feet.
- Keep your baby upright after feedings for at least 30 minutes. Holding your baby is best. The way your baby sits in an infant seat can make spitting up more likely.
- Don't jiggle, bounce, or actively play with your baby right after feedings.
- Make sure the hole in the nipple is the right size and/or flow for your baby.
 For example, fast-flow nipples can make babies gag or may give them more milk than they can handle at once. Many breastfed babies do well with a slow-flow nipple until they are 3 months old, or even older.
For example, fast-flow nipples can make babies gag or may give them more milk than they can handle at once. Many breastfed babies do well with a slow-flow nipple until they are 3 months old, or even older. - Raise the head of your baby's crib or bassinet. Roll up a few small hand towels or receiving blankets (or you can buy special wedges) to place under (not on top of) the mattress. Never use a pillow under your baby's head. Make sure the mattress doesn’t fold in the middle, and that the incline is gentle enough that your baby doesn’t slide down.
Most babies grow out of spitting up by the time they're able to sit up.
How Do I Know If My Baby Has an Allergy?
Some babies are allergic to the protein in cow's milk formula. Symptoms of an allergic reaction may include:
- vomiting
- diarrhea
- belly pain
- rash
- blood or mucus in the baby's poop
If your baby has any of these symptoms, tell your doctor. Also talk to the doctor before switching formulas.
Also talk to the doctor before switching formulas.
If your baby has symptoms of a severe allergic reaction — like sudden drooling, trouble swallowing, wheezing, or breathing problems — see a doctor right away.
Is Soy Formula Safe for My Baby?
Store-bought iron-fortified soy formula is safe and nutritionally complete. Doctors usually recommend soy-based formulas if:
- Parents don’t want their babies to eat animal protein.
- A baby has congenital lactase deficiency, a rare condition where babies are born without the enzyme needed to digest lactose. Lactose is the main sugar found in cow’s milk.
- A baby is born with galactosemia, a rare condition where babies can’t digest galactose. Lactose is made up of glucose and galactose.
Many babies who are allergic to cow's milk also are allergic to the protein in soy formulas, so doctors usually recommend hypoallergenic formulas for these infants.
Soy formula is a good alternative to cow's milk formula for full-term babies (those born at 39 weeks or later). Soy formulas are not recommended for premature babies. Talk to your doctor if you are considering a soy-based formula for your baby.
Soy formulas are not recommended for premature babies. Talk to your doctor if you are considering a soy-based formula for your baby.
Do not try to make your own formula at home. Online recipes may look healthy and promise to be nutritionally complete, but they can have too little — or too much — of important nutrients and cause serious health problems for your baby.
Is it OK to Switch to a Different Formula?
It’s probably OK to switch brands of the same kind of formula. For example, parents might buy another brand of cow’s milk formula because it’s on sale or to see if it helps with constipation, or switch to an organic formula because they’re concerned about pesticides.
But before switching formulas, talk to your doctor. Some parents may think that formula plays a part in a baby's fussiness, gas, spitting up, or constipation. But that’s not usually the case. Your doctor can help find out what may be causing these symptoms and recommend the right formula for your baby.
Do I Need to Give My Formula-Fed Baby Vitamins?
No. Commercial infant formulas with iron have all the nutrients your baby needs. Babies who are drinking less than about 1 quart (1 liter) of formula will need a vitamin D supplement.
Does My Baby Need Fluoride Supplements?
Babies do not need fluoride supplements during the first 6 months. Your doctor may recommend fluoride supplements when your baby is 6 months to 3 years old, but only if fluoride is not in your drinking water.
Is it OK to Prop a Bottle in My Baby's Mouth?
Never prop your baby’s bottle. Your baby can choke drinking from a propped bottle. Propping a bottle also can lead to ear infections and tooth decay. Always stay with and hold your baby during feedings.
It is OK to Let My Baby Sleep With a Bottle?
Never put your baby to bed with a bottle. Like propping a bottle, sleeping with a bottle can cause choking, ear infections, and tooth decay.
Reviewed by: Mary L. Gavin, MD
Gavin, MD
Date reviewed: November 2021
Why Babies Spit Up - HealthyChildren.org
By: Alejandro Velez, MD, FAAP & Christine Waasdorp Hurtado, MD, FAAP
All babies spit up. Some babies spit up more than others, or at certain times.
Typically, babies spit up after they gulp down some air with breastmilk or formula. A baby's stomach is small and can't hold a lot, after all. Milk and air can fill it up quickly.
With a full stomach, any change in position such as bouncing or sitting up can force the flap between the esophagus (food pipe) and stomach to open. And when that flap (the esophageal sphincter) opens, that's when some of what your baby just ate can make a return appearance.
So, what can you do―if anything―to reduce the amount of your baby's spit up? How do you know if your baby's symptoms are part of a larger problem? Read on to learn more.
Common concerns parents have about spit up
My baby spits up a little after most feedings.

Possible cause: Gastroesophageal reflux (normal if mild)
Action to take: None. The spitting up will grow less frequent and stop as your baby's muscles mature—especially that flap we talked about earlier. It often just takes time.
My baby gulps their feedings and seems to have a lot of gas.
Possible cause: Aerophagia (swallowing more air than usual)
Action to take: Make sure your baby is positioned properly during feeds. Also be sure to burp the baby during and after feeds. Consider trying a different bottle to decrease your baby's ability to suck in air.
My baby spits up when you bounce them or play with them after meals.
My baby's spitting up has changed to vomiting with muscle contractions that occur after every feeding. The vomit shoots out with force.
I found blood in my baby's spit-up or vomit.

Possible cause: Swelling of the esophagus or stomach (esophagitis or gastritis), or another health problem that requires diagnosis and treatment.
Action to take: Call you pediatrician right away so they can examine your baby.
Remedies for spitty babies
Regardless of whether or not your baby's spit up warrants watchful waiting or medical intervention, there are some simple feeding suggestions that can help you deal with the situation at hand.
5 tips to reduce your baby's spit up
Avoid overfeeding. Like a gas tank, fill baby's stomach it too full (or too fast) and it's going to spurt right back out at you. To help reduce the likelihood of overfeeding, feed your baby smaller amounts more frequently.
Burp your baby more frequently. Extra gas in your baby's stomach has a way of stirring up trouble.
 As gas bubbles escape, they have an annoying tendency to bring the rest of the stomach's contents up with them. To minimize the chances of this happening, burp not only after, but also during meals.
As gas bubbles escape, they have an annoying tendency to bring the rest of the stomach's contents up with them. To minimize the chances of this happening, burp not only after, but also during meals.Limit active play after meals and hold your baby upright. Pressing on a baby's belly right after eating can up the odds that anything in their stomach will be forced into action. While tummy time is important for babies, postponing it for a while after meals can serve as an easy and effective avoidance technique.
Consider the formula. If your baby is formula feeding, there's a possibility that their formula could be contributing to their spitting up. While some babies simply seem to fare better with one formula over another without having a true allergy or intolerance, an estimated 5% of babies are genuinely unable to handle the proteins found in milk or soy formula―a condition called Cow Milk Protein Intolerance/Allery (CMPI and CMPA).
 In either case, spitting up may serve as one of several cues your baby may give you that it's time to discuss alternative formulas with your pediatrician. If your baby does have a true intolerance, a 1- or 2-week trial of hypoallergenic (hydrolyzed) formula designed to be better tolerated might be recommended by your baby's provider.
In either case, spitting up may serve as one of several cues your baby may give you that it's time to discuss alternative formulas with your pediatrician. If your baby does have a true intolerance, a 1- or 2-week trial of hypoallergenic (hydrolyzed) formula designed to be better tolerated might be recommended by your baby's provider.If breastfeeding, consider your diet. Cow's milk and soy in your diet can worsen spit up in infants with Cow Milk Protein Intolerance/Allergy (CMPI and CMPA). Removing these proteins can help to reduce or eliminate spit up.
Try a little oatmeal. Giving babies cereal before 6 months is generally not recommended—with one possible exception. Babies and children with dysphagia or reflux, for example, may need their food to be thicker in order to swallow safely or reduce reflux. In response to concerns over arsenic in rice, the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) now recommends parents of children with these conditions use of oatmeal instead of rice cereal.
 See
Oatmeal: The Safer Alternative for Infants & Children Who Need Thicker Food for more information.
See
Oatmeal: The Safer Alternative for Infants & Children Who Need Thicker Food for more information.
Vomit vs. spit up: what's the difference?
There is a big difference between vomiting and spitting up:
Vomiting is the forceful throwing up of stomach contents through the mouth. This typically involves using the abdominal muscles and is often uncomfortable, leaving you with a crying child.
Spitting up is the easy flow of stomach contents out of the mouth, frequently with a burp. Spitting up doesn't involve forceful muscle contractions, brings up only small amounts of milk, and doesn't distress your baby or make them uncomfortable.
What causes vomiting?
Vomiting occurs when the abdominal muscles and diaphragm contract vigorously while the stomach is relaxed. This reflex action is triggered by the "vomiting center" in the brain after it has been stimulated by:
Nerves from the stomach and intestine when the gastrointestinal tract is either irritated or swollen by an infection or blockage (as in the stomach bug)
Chemicals in the blood such as drugs
Psychological stimuli from disturbing sights or smells
Stimuli from the middle ear (as in vomiting caused by motion sickness)
Always contact your pediatrician if your baby vomits forcefully after every feeding or if there is ever blood in your baby's vomit.
Remember
The best way to reduce spit up is to feed your baby before they get very hungry. Gently burp your baby when they take breaks during feedings. Limit active play after meals and hold your baby in an upright position for at least 20 minutes. Always closely supervise your baby during this time.
More information
- How to Keep Your Sleeping Baby Safe: AAP Policy Explained
- Gastroesophageal Reflux & Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Parent FAQs
-
How Much and How Often Should Your Baby Eat
About Dr. Velez
Alejandro Velez, MD, FAAP is a second-year gastroenterology fellow at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital who is interested in practicing general gastroenterology with a focus in motility and functional GI disorders, has a love for medical education at all levels, and harbors a passion for supporting and uplifting those that identify as unrepresented minorities in medicine. |
About Dr. Waasdorp
Christine Waasdorp Hurtado, MD, MSCS, FAAP is a member of the American Academy of Pediatrics and the North American Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology Hepatology and Nutrition. She is an Associate Professor of Pediatrics at the University of Colorado School of Medicine and practices in Colorado Springs. |
The information contained on this Web site should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician. There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
Baby spitting up formula | Nutrilak
11/17/2021 34420
Article content
- Up to what age is spitting up normal? nine0012 Why is the baby spitting up formula?
- Child spitting up formula in a fountain.
 What to do?
What to do? - Regurgitation after each feeding: normal or pathological?
- Anti-reflux mixtures and their types
Regurgitation occurs in both breastfed and bottle-fed babies. As a rule, they are not dangerous and do not affect the health of the baby. But sometimes regurgitation can be a symptom of a disease. nine0008
Until what age is regurgitation normal?
Until the age of three months, almost all children have regurgitation from time to time. By six months, the frequency of spitting up should decrease significantly, or they should go away altogether.
Regurgitation during the first half of the year and periodic single small volume of regurgitation at the age of 6 to 12 months are considered a variant of the norm, but in healthy children older than a year they should no longer be.
The child easily spits up formula or breast milk due to the structural features of the digestive tract. In newborns and young children, the esophagus and stomach are connected at a more obtuse angle than in adults, and the sphincter that blocks the entrance to the stomach is still weak and easily passes the contents back into the esophagus. In addition, the immature nervous system does not regulate the muscles well enough and does not have time to send a signal to reduce them in order to prevent regurgitation. nine0008
In newborns and young children, the esophagus and stomach are connected at a more obtuse angle than in adults, and the sphincter that blocks the entrance to the stomach is still weak and easily passes the contents back into the esophagus. In addition, the immature nervous system does not regulate the muscles well enough and does not have time to send a signal to reduce them in order to prevent regurgitation. nine0008
The baby can burp for the following reasons:
- When overeating - a large amount of the mixture does not fit in the stomach and is pushed back;
- When swallowing a large amount of air - the air bubble takes up a lot of space in the stomach, it does not remain for the mixture;
- With tight swaddling or a sharp pressure on the tummy - when the stomach is squeezed, food is thrown back into the esophagus and flows out of the baby's mouth;
nine0012 From a sudden change of position: when the child turned over on his own or was inadvertently picked up by an adult; the child may burp during the game after feeding, if he is disturbed, thrown up.

Such regurgitation does not affect the well-being of the baby. Usually, to prevent them, it is enough to hold the baby in a column after feeding until he burps the air swallowed with the mixture, and then for about half an hour do not lay him on his stomach, do not throw him up, do not put on squeezing clothes. nine0008
Child spitting up formula in a fountain. What to do?
If a child spits up a fountain, this is not the norm. We need to find the reason why the mixture is not absorbed. It is difficult to do this on your own, because the reasons can be very different - from an inappropriate mixture or a banal SARS to allergies and neurological disorders.
A single spit-up can be the result of overfeeding, incorrect positioning of the baby during feeding, or sudden movement. You need to watch the baby: if he behaves as usual, he has a normal temperature, there are no other alarming symptoms - most likely, this is an accidental situation and there is no reason for alarm. If regurgitation with a fountain is repeated, diarrhea or stool retention has appeared, the temperature has risen, the child has become more restless or, on the contrary, lethargic, you need to urgently consult a doctor. nine0008
If regurgitation with a fountain is repeated, diarrhea or stool retention has appeared, the temperature has risen, the child has become more restless or, on the contrary, lethargic, you need to urgently consult a doctor. nine0008
Regurgitation after each feeding: norm or pathology?
If the child spit up after each feeding with the mixture, then this is more of a pathology than the norm, especially if the regurgitation is plentiful, more than the volume of a teaspoon.The age feature of a particular baby and the norm of regurgitation after each feeding can only be recognized if there are no other alarming symptoms: the child is gaining enough weight, he has no digestive disorders, good appetite, sound sleep. nine0008
If the frequency of regurgitation does not decrease or even increases, the baby does not gain weight well against the background of regurgitation, you need to figure out what is behind this together with the doctor. Often a child can spit up due to improper selection of the mixture, allergies to cow's milk proteins, functional digestive disorders (such as colic, increased gas formation, constipation), metabolic disorders, as well as due to congenital diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and neurological disorders. Do not try to cure regurgitation on your own, on the advice of friends and recommendations from the Internet. A suitable treatment should be selected by a doctor after an examination and an accurate diagnosis. nine0008
Do not try to cure regurgitation on your own, on the advice of friends and recommendations from the Internet. A suitable treatment should be selected by a doctor after an examination and an accurate diagnosis. nine0008
Anti-reflux mixtures and their types
If the child spit up after feeding and the reason for this is an improperly selected mixture or age-related features of the digestive tract, the doctor may advise switching to an anti-reflux mixture (reflux is the throwing of stomach contents into the esophagus, “anti-reflux” means preventing the reverse flow of food).
Anti-reflux mixture is similar in composition to the standard. Its main difference from the standard mixture is the presence of a thickener, which makes the mixture more dense and does not allow it to freely pour out of the stomach back into the esophagus and mouth of the child. nine0028 The thickener can be starch or locust bean gum. Anti-reflux mixtures with starch should only be used if the child is prone to loose stools: starch thickens the stool and can cause constipation. If a child already has spitting up with constipation, then a mixture with natural locust bean gum, such as, for example, Nutrilak Premium Antireflux, will help get rid of these conditions.
If a child already has spitting up with constipation, then a mixture with natural locust bean gum, such as, for example, Nutrilak Premium Antireflux, will help get rid of these conditions.
Ingredients Nutrilak Premium Antireflux close to breast milk. It does not contain palm and rapeseed oils, which can cause constipation and loss of calcium in the baby's stool. nine0008
The mixture contains natural milk fat, necessary for the development of the baby's brain and proper metabolism, it is easily digested and provides energy for active growth. Omega-3 (DHA) fatty acids are indispensable for the development of intelligence and maintaining visual acuity, while nucleotides help the formation of the immune system and the maturation of the gastrointestinal tract.
It is important that natural locust bean gum is used as a thickener in Nutrilak Premium Antireflux: it is a prebiotic, stimulates the growth of beneficial bacteria in the intestines and thereby helps to eliminate increased gas formation and colic.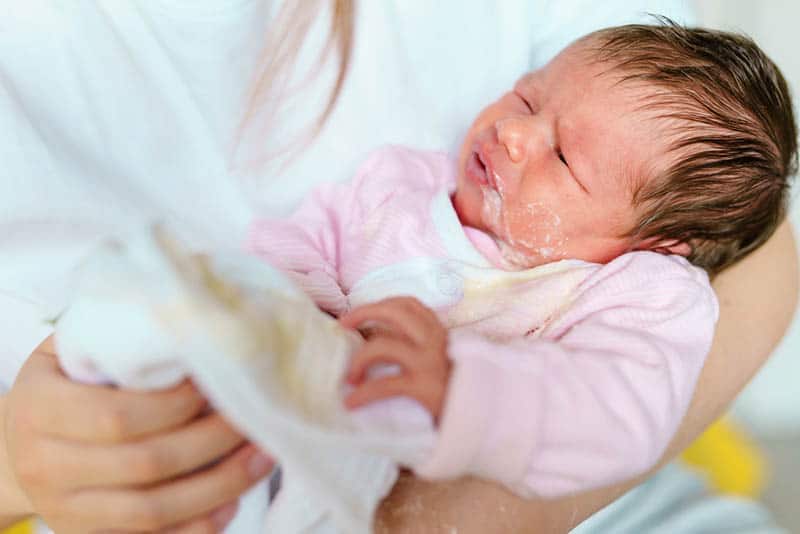 Dietary gum fibers actively stimulate intestinal motility, make stools regular and soft. nine0008
Dietary gum fibers actively stimulate intestinal motility, make stools regular and soft. nine0008
So:
- Periodic spitting up after a feed is normal during the first year of a baby's life.
- The child spit up the mixture due to the peculiarities of the structure of the digestive tract and the immaturity of the nervous system.
- If the child spit up a fountain, you need to see a doctor and look for the cause of profuse reflux.
- Frequent regurgitation after each feeding also requires medical attention and treatment. nine0028
- Properly selected anti-reflux mixture will help to save your baby from spitting up.
(4 ratings; article rating 3.0)
Neonatal regurgitation after formula feeding
01/01/1970 Rassadina Zinaida Vladimirovna
Articles
Neonatal regurgitation after formula feeding
Spitting up in a newborn baby is a common occurrence, but it is very frightening for new mothers. Should I be worried? How to get rid of this phenomenon? Read the answers to these and other questions in the article.
Should I be worried? How to get rid of this phenomenon? Read the answers to these and other questions in the article. At least 80% of babies under the age of six months regurgitate some amount of food just eaten. This happens for various reasons, and most often it is a variant of the norm.
But since the biggest aspiration of parents during this period is weight gain in the baby, spitting up often causes real panic. The child appears to be malnourished. nine0008
Let's figure it out: what is the norm, and in what cases you need to run to the doctor.
Causes of regurgitation
First, consider the causes of regurgitation, which happens in most babies and should not cause concern to parents:
- Immaturity of the digestive system . In an adult, a special muscular valve or sphincter is located between the stomach and esophagus. It's called Cardia. This valve prevents food from being thrown back into the esophagus.
 In babies up to six months, it is not sufficiently developed. Therefore, any contraction of the walls of the stomach causes regurgitation or reverse reflux. This is the absolute norm for all children. Most often, by the age of 6 months, everything passes. In rare cases, it continues until the age of one. nine0013
In babies up to six months, it is not sufficiently developed. Therefore, any contraction of the walls of the stomach causes regurgitation or reverse reflux. This is the absolute norm for all children. Most often, by the age of 6 months, everything passes. In rare cases, it continues until the age of one. nine0013 - Overeating . Toddlers do not always eat as much as they need, often they eat as much as they like. And the body already regulates the required amount of food, belching the excess. This cause of regurgitation is typical for artificial children. The mixture comes through the nipple more easily than from the breast. The baby eats faster than the feeling of fullness sets in. So overeating happens.
- Swallowing air with food . In this case, the air goes back along with the milk, and the baby spits up. nine0013
- Gas and colic . They can also cause reflux. Air bubbles press against the walls of the intestines and stomach and help food return to the esophagus.

- Increased nervous excitability . When the baby is worried, the walls of the stomach begin to contract and return of the milk eaten occurs.
Alarming symptoms that are the reason for an immediate visit to the doctor are most often accompanied by violations in weight gain, since the milk eaten is not absorbed by the body: nine0008
- Frequent vomiting fountain . It can be an indicator of lactase deficiency - in other words, indigestibility of milk. Read more about lactase deficiency in our article. Fountain regurgitation can also occur due to improper development of the baby's digestive system.
- Regurgitation of yellowish or greenish milk . May be an indicator of an infectious disease. Or occur as a result of the reflux of bile into the stomach. The baby is likely to behave restlessly, because bile irritates the walls of the stomach. nine0013
But how to determine the cause of reverse reflux? In fact, this is not necessary! There is only one indicator that is important to monitor - this is weight gain. If your child is gaining weight normally and you are not experiencing warning signs, then there is no cause for concern. The regurgitation will stop on its own as the child grows.
If your child is gaining weight normally and you are not experiencing warning signs, then there is no cause for concern. The regurgitation will stop on its own as the child grows.
Regurgitation after formula feeding
This is not to say that regurgitation after formula feeding is more common than with breast milk. However, it happens that the mixture did not fit the baby due to the characteristics of the composition. nine0028 In any case, remember that if abundant regurgitation occurs with a fountain after the mixture, then there is an indication to consult a doctor. And this must be done immediately.
The pediatrician will determine the cause. And if she is in the mixture, she will prescribe a different or special anti-reflux mixture.
How to reduce regurgitation
It will not be possible to completely get rid of the natural process of returning food, but this process can be facilitated for the baby and parents. nine0008
- Carry your baby upright in a "column" position after feeding.
 So the air that he swallowed during feeding will come out faster.
So the air that he swallowed during feeding will come out faster. - Make sure that the baby completely captures the circumference of the nipple. Then the air will not penetrate when sucking.
- Use anti-colic nipples when formula feeding. They are designed in such a way as to prevent air from getting inside.
- After feeding, do not entertain the baby, let him rest for a while. nine0013
- Try to feed a little less time to avoid overeating.
- Give your baby a pacifier before bed to stimulate digestive activity for some time after the meal.
- Provide your baby with more movement: exercise, massage, swimming, tactile contact, walking in the fresh air. To develop the muscular system more actively. Along with it, all internal organs will develop. nine0022
There is no drug that will reduce regurgitation. Because it is not a disease, it is either a symptom of it, or a natural process.
The only thing that can affect the amount of food returned is the use of anti-colic drugs, which reduce gas formation in the intestines.