Baby throws up every feeding
Vomiting (0-12 Months)
Is this your child's symptom?
- Vomiting (throwing up) stomach contents
- Other names for vomiting are puking, barfing and heaving
Causes of Vomiting
- Viral Gastritis. Stomach infection from a stomach virus is the most common cause. Also called stomach flu. A common cause is the Rotavirus. The illness starts with vomiting. Watery loose stools may follow within 12-24 hours.
- Food Allergy. Vomiting can be the only symptom of a food reaction. The vomiting comes on quickly after eating the food. Uncommon in infants, but main foods are eggs and peanut butter.
- Coughing. Hard coughing can also cause your child to throw up. This is more common in children with reflux.
- Serious Causes. Vomiting alone should stop within about 24 hours. If it lasts over 24 hours, you must think about more serious causes. An example is a kidney infection.
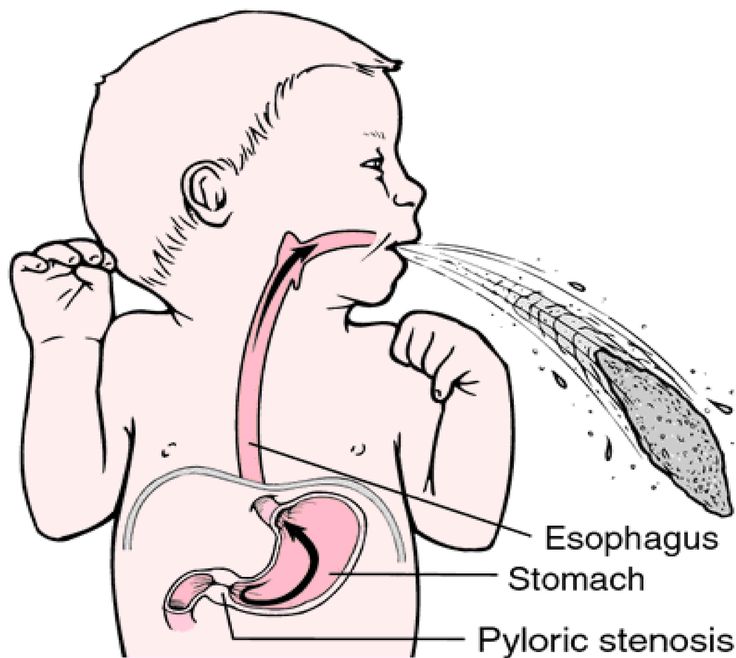
A serious cause in young babies is pyloric stenosis. See below for more on this.
Pyloric Stenosis (Serious Cause)
- The most common cause of true vomiting in young babies.
- Onset of vomiting is age 2 weeks to 2 months
- Vomiting is forceful. It becomes projectile and shoots out.
- Right after vomiting, the baby is hungry and wants to feed. ("hungry vomiter")
- Cause: The pylorus is the channel between the stomach and the gut. In these babies, it becomes narrow and tight.
- Risk: Weight loss or dehydration
- Treatment: Cured by surgery.
Vomiting Scale
- Mild: 1 - 2 times/day
- Moderate: 3 - 7 times/day
- Severe: Vomits everything, nearly everything or 8 or more times/day
- Severity relates even more to how long the vomiting goes on for. At the start of the illness, it's common for a child to vomit everything.
 This can last for 3 or 4 hours. Children then often become stable and change to mild vomiting.
This can last for 3 or 4 hours. Children then often become stable and change to mild vomiting. - The main risk of vomiting is dehydration. Dehydration means the body has lost too much fluid.
- The younger the child, the greater the risk for dehydration.
Dehydration: How to Tell
- The main risk of vomiting is dehydration. Dehydration means the body has lost too much water.
- Vomiting with watery diarrhea is the most common cause of dehydration.
- Dehydration is a reason to see a doctor right away.
- Your child may have dehydration if not drinking much fluid and:
- The urine is dark yellow and has not passed any in over 8 hours.
- Inside of the mouth and tongue are very dry.
- No tears if your child cries.
- Slow blood refill test: Longer than 2 seconds. First, press on the thumbnail and make it pale. Then let go. Count the seconds it takes for the nail to turn pink again. Ask your doctor to teach you how to do this test.

When to Call for Vomiting (0-12 Months)
Call 911 Now
- Can't wake up
- Not moving
- You think your child has a life-threatening emergency
Call Doctor or Seek Care Now
- Dehydration suspected. No urine in over 8 hours, dark urine, very dry mouth and no tears.
- Stomach pain when not vomiting. Exception: stomach pain or crying just before vomiting is quite common.
- Age less than 12 weeks old with vomiting 2 or more times. Exception: normal spitting up.
- Vomited 3 or more times and also has diarrhea
- Severe vomiting (vomits everything) more than 8 hours while getting Pedialyte (or breastmilk)
- Head injury within the last 24 hours
- Weak immune system. Examples are sickle cell disease, HIV, cancer, organ transplant, taking oral steroids.
- Vomiting a prescription medicine
- Fever over 104° F (40° C)
- Fever in baby less than 12 weeks old. Caution: Do NOT give your baby any fever medicine before being seen.

- Your child looks or acts very sick
- You think your child needs to be seen, and the problem is urgent
Contact Doctor Within 24 Hours
- All other infants (age less than 1 year) with vomiting. See Care Advice while waiting to discuss with doctor.
Seattle Children's Urgent Care Locations
If your child’s illness or injury is life-threatening, call 911.
- Bellevue
- Everett
- Federal Way
- Seattle
- Virtual Urgent Care
Care Advice for Vomiting
- What You Should Know About Vomiting:
- Most vomiting is caused by a viral infection of the stomach.

- Vomiting is the body's way of protecting the lower gut.
- The good news is that stomach illnesses last only a short time.
- The main risk of vomiting is dehydration. Dehydration means the body has lost too much fluid.
- Here is some care advice that should help.
- Most vomiting is caused by a viral infection of the stomach.
- Formula Fed Babies - May Give Oral Rehydration Solution (ORS) for 8 Hours:
- If vomits once, give half the regular amount of formula every 1 to 2 hours.
- If vomits formula more than once, offer ORS for 8 hours. If you don't have ORS, use formula until you can get some.
- ORS is a special fluid that can help your child stay hydrated. You can use Pedialyte or the store brand of ORS. It can be bought in food stores or drug stores.
- Spoon or syringe feed small amounts. Give 1-2 teaspoons (5-10 mL) every 5 minutes.
- After 4 hours without throwing up, double the amount.
- Return to Formula. After 8 hours without throwing up, go back to regular formula.

- Breastfed Babies - Reduce the Amount Per Feeding:
- If vomits once, nurse half the regular time every 1 to 2 hours.
- If vomits more than once, nurse for 5 minutes every 30 to 60 minutes. After 4 hours without throwing up, return to regular nursing.
- If continues to vomit, switch to pumped breastmilk. (ORS is rarely needed in breastfed babies. It can be used if vomiting becomes worse).
- Spoon or syringe feed small amounts of pumped milk. Give 1-2 teaspoons (5-10 mL) every 5 minutes.
- After 4 hours without throwing up, return to regular feeding at the breast. Start with small feedings of 5 minutes every 30 minutes. As your baby keeps down the smaller amounts, slowly give more.
- Pumped Breastmilk Bottle-Fed Infants - Reduce the Amount per Feeding:
- If vomits once and bottle-feeding breastmilk, give half the regular amount every 1-2 hours.
- If vomits more than once within last 2 hours, give 1 ounce (30 mL) every 30 to 60 minutes.
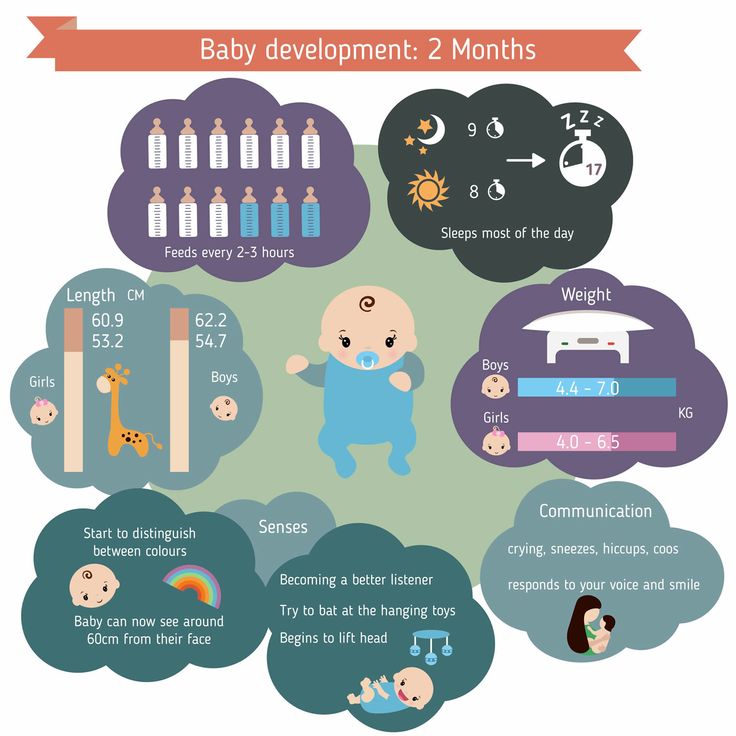
- If continues to vomit, give 1-2 teaspoons (5-10 mL) every 5 minutes. Only if not tolerating breastmilk, switch to ORS (e.g., Pedialyte) for every 5 minutes for a few hours.
- After 4 hours without vomiting, return to regular feedings. Start with 1 ounce (30 mL) every 30 minutes and slowly increase as tolerated.
- Stop All Solid Foods:
- Avoid all solid foods and baby foods in kids who are vomiting.
- After 8 hours without throwing up, gradually add them back.
- If on solid foods, start with starchy foods that are easy to digest. Examples are cereals, crackers and bread.
- Do Not Give Medicines:
- Stop using any drug that is over-the-counter for 8 hours. Reason: Some of these can make vomiting worse.
- Fever. Mild fevers don't need to be treated with any drugs. For higher fevers, you can use an acetaminophen suppository (such as FeverAll). This is a form of the drug you put in the rectum (bottom).
 Ask a pharmacist for help finding this product. Do not use ibuprofen. It can upset the stomach.
Ask a pharmacist for help finding this product. Do not use ibuprofen. It can upset the stomach. - Call your doctor if: Your child vomits a drug ordered by your doctor.
- Try to Sleep:
- Help your child go to sleep for a few hours.
- Reason: Sleep often empties the stomach and removes the need to vomit.
- Your child doesn't have to drink anything if his stomach feels upset and he doesn't have any diarrhea.
- Return to Child Care:
- Your child can return to child care after the vomiting and fever are gone.
- What to Expect:
- For the first 3 or 4 hours, your child may vomit everything. Then the stomach settles down.
- Vomiting from a viral illness often stops in 12 to 24 hours.
- Mild vomiting and nausea may last up to 3 days.
- Call Your Doctor If:
- Vomits clear fluids for more than 8 hours
- Vomiting lasts more than 24 hours
- Blood or bile (green color) in the vomit
- Stomach ache present when not vomiting
- Dehydration suspected (no urine in over 8 hours, dark urine, very dry mouth, and no tears)
- You think your child needs to be seen
- Your child becomes worse
And remember, contact your doctor if your child develops any of the 'Call Your Doctor' symptoms.

Disclaimer: this health information is for educational purposes only. You, the reader, assume full responsibility for how you choose to use it.
Last Reviewed: 03/04/2023
Last Revised: 12/30/2022
Copyright 2000-2023 Schmitt Pediatric Guidelines LLC.
Infant Vomiting - HealthyChildren.org
My baby vomits a lot. Is this a sign of a problem?
Because many common childhood illnesses can cause vomiting, you should expect your child to have this problem several times during these early years. Usually it ends quickly without treatment, but this doesn’t make it any easier for you to watch. That feeling of helplessness combined with the fear that something serious might be wrong and the desire to do something to make it better may make you tense and anxious. To help put your mind at ease, learn as much as you can about the causes of vomiting and what you can do to treat your child when it occurs.
Vomiting vs Spitting Up
First of all, there’s a difference between real vomiting and just spitting up. Vomiting is the forceful throwing up of stomach contents through the mouth. Spitting up (most commonly seen in infants under one year of age) is the easy flow of stomach contents out of the mouth, frequently with a burp.
Vomiting is the forceful throwing up of stomach contents through the mouth. Spitting up (most commonly seen in infants under one year of age) is the easy flow of stomach contents out of the mouth, frequently with a burp.
Vomiting occurs when the abdominal muscles and diaphragm contract vigorously while the stomach is relaxed. This reflex action is triggered by the “vomiting center” in the brain after it has been stimulated by:
Nerves from the stomach and intestine when the gastrointestinal tract is either irritated or swollen by an infection or blockage
Chemicals in the blood (e.g., drugs)
Psychological stimuli from disturbing sights or smells
Stimuli from the middle ear (as in vomiting caused by motion sickness)
Causes of Vomiting
The common causes of spitting up or vomiting vary according to age. During the first few months, for instance, most infants will spit up small amounts of formula or breastmilk, usually within the first hour after being fed. This “cheesing,” as it is often called, is simply the occasional movement of food from the stomach, through the tube (esophagus) leading to it, and out of the mouth. It will occur less often if a child is burped frequently and if active play is limited right after meals. This spitting up tends to decrease as the baby becomes older, but may persist in a mild form until ten to twelve months of age. Spitting up is not serious and doesn’t interfere with normal weight gain.
This “cheesing,” as it is often called, is simply the occasional movement of food from the stomach, through the tube (esophagus) leading to it, and out of the mouth. It will occur less often if a child is burped frequently and if active play is limited right after meals. This spitting up tends to decrease as the baby becomes older, but may persist in a mild form until ten to twelve months of age. Spitting up is not serious and doesn’t interfere with normal weight gain.
Occasional vomiting may occur during the first month. If it appears repeatedly or is unusually forceful, call your pediatrician. It may be just a mild feeding difficulty, but it also could be a sign of something more serious.
Persistent Vomiting
Between two weeks and four months of age, persistent forceful vomiting may be caused by a thickening of the muscle at the stomach exit. Known as hypertrophic pyloric stenosis, this thickening prevents food from passing into the intestines. It requires immediate medical attention. Surgery usually is required to open the narrowed area. The important sign of this condition is forceful vomiting occurring approximately fifteen to thirty minutes or less after every feeding. Anytime you notice this, call your pediatrician as soon as possible.
It requires immediate medical attention. Surgery usually is required to open the narrowed area. The important sign of this condition is forceful vomiting occurring approximately fifteen to thirty minutes or less after every feeding. Anytime you notice this, call your pediatrician as soon as possible.
GERD
Occasionally the spitting up in the first few weeks to months of life gets worse instead of better—that is, even though it’s not forceful, it occurs all the time. This happens when the muscles at the lower end of the esophagus become overly relaxed and allow the stomach contents to back up. This condition is known as gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD. This condition usually can be controlled by doing the following:
Thicken the milk with small amounts of baby cereal as directed by your pediatrician.
- Avoid overfeeding or give smaller feeds more frequently.
- Burp the baby frequently.
- Leave the infant in a safe, quiet, upright position for at least thirty minutes following feeding.
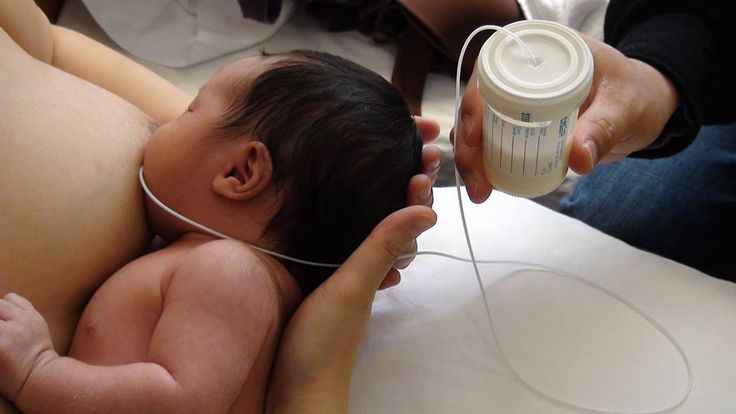
If these steps are not successful, your pediatrician may refer you to a gastrointestinal (GI) specialist.
Infection
After the first few months of life, the most common cause of vomiting is a stomach or intestinal infection. Viruses are by far the most frequent infecting agents, but occasionally bacteria and even parasites may be the cause. The infection also may produce fever, diarrhea, and sometimes nausea and abdominal pain. The infection is usually contagious; if your child has it, chances are good that some of her playmates also will be affected.
Rotaviruses are a leading cause of vomiting in infants and young children, with symptoms often progressing to diarrhea and fever. These viruses are very contagious, but are becoming less common than in the past, due to the availability of a vaccine that can prevent the disease. The rotavirus is one of the viral causes of gastroenteritis, but other types of viruses—such as noroviruses, enteroviruses, and adenoviruses—can cause it as well.
Occasionally infections outside the gastrointestinal tract will cause vomiting. These include infections of the respiratory system, infections of the urinary tract otitis media, meningitis , and appendicitis. Some of these conditions require immediate medical treatment, so be alert for the following trouble signs, whatever your child’s age, and call your pediatrician if they occur.
Blood or bile (a green-colored material) in the vomit
Severe abdominal pain
Strenuous, repeated vomiting
Swollen or enlarged abdomen
Lethargy or severe irritability
Convulsions
Signs or symptoms of dehydration, including dry mouth, absent tears, depression of the "soft spot", and decreased urination
Inability to drink adequate amounts of fluid
Vomiting continuing beyond twenty-four hours
The information contained on this Web site should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician. There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
Why does the baby spit up after feeding?
search support iconSearch Keywords
Regurgitation is a common condition in newborns and infants and is most often a normal variant. However, it is not uncommon for parents to worry if their baby is spitting up frequently, believing that it is due to nutritional or health problems in general. Sometimes these fears are not unfounded, and regurgitation really has a pathological origin. What is its cause and when should you really consult a doctor about this?
Regurgitation - Return of a small amount of food (uncurdled or partially curdled milk) from the stomach up the digestive tract: into the esophagus and further into the oral cavity. According to statistics, at least 1 time during the day, at least 50% of babies from 0 to 3 months old can spit up, more than 60% of children 3-4 months old, and in 5% of children spit up continues up to the year 1 .
Regurgitation in newborns is considered a physiological process. It is caused by a number of factors, including:
- Features of the structure of the upper digestive tract in babies
- In newborns and infants up to a year of life, the stomach has a spherical shape. It holds a small amount of food, besides, the release from it into the duodenum is slower in comparison with children after the year 2 .
- Weakness of the lower esophageal sphincter that separates the esophagus from the stomach
- Normally, the lower esophageal sphincter should tightly "close" the esophagus, allowing food to pass into the stomach and not allowing it to enter back into the upper digestive tract. However, in young children (up to a year), the muscles of the esophageal sphincter are poorly developed, and it does not do its job very well 2 .
- Slow movement of food through the gastrointestinal tract
- The neuromuscular system of newborns is immature.
 It does not ensure the proper movement of food through the esophagus, causing regurgitation.
It does not ensure the proper movement of food through the esophagus, causing regurgitation.
One of the important risk factors contributing to regurgitation in newborns is aerophagia. This is the swallowing of large amounts of air during feedings. This happens when the baby is not properly attached to the breast, the mother has a lack of breast milk, or the bottle is in the wrong position in the child who receives the mixture. The size of the opening in the nipple also matters - if it is too large, the newborn swallows a lot of air 3 .
With aerophagia, the baby becomes capricious, restless immediately after feeding. Noticeable bloating. If the baby spits up immediately after a feed, the milk (or formula) remains practically fresh, uncurdled 3 .
Promotes regurgitation after feeding and a predominantly horizontal position of the baby during the day, combined with relatively high intra-abdominal pressure 4 . Therefore, the correct position of the baby after feeding is so important. To avoid regurgitation of an excessive amount of stomach contents, after feeding, it is necessary to hold the baby in an upright “column” position for some time (10-20 minutes), lightly patting on the back and allowing excess air to “exit”.
Therefore, the correct position of the baby after feeding is so important. To avoid regurgitation of an excessive amount of stomach contents, after feeding, it is necessary to hold the baby in an upright “column” position for some time (10-20 minutes), lightly patting on the back and allowing excess air to “exit”.
Regurgitation in many newborns can be provoked by other situations in which pressure in the abdominal cavity increases and stomach contents are thrown into the esophagus, in particular 3 :
- tight swaddling;
- stool disorders, in particular constipation;
- long, forced cry and some others.
Want to avoid common feeding problems?
Start with a baby bottle with an anti-colic system that helps you avoid common feeding problems such as colic, gas and spitting up*
How can you tell the difference between normal spitting up and vomiting?
Sometimes regurgitation is considered a manifestation of disorders in the digestive tract of children. Due to the constant reflux of acidic stomach contents into the upper sections, inflammation and other complications may develop, including growth retardation, a decrease in hemoglobin levels, and others. Therefore, it is important for parents to understand where the line is between physiological and pathological regurgitation 1 .
Due to the constant reflux of acidic stomach contents into the upper sections, inflammation and other complications may develop, including growth retardation, a decrease in hemoglobin levels, and others. Therefore, it is important for parents to understand where the line is between physiological and pathological regurgitation 1 .
If the mother is worried that her baby is spitting up, keep track of when this happens and count the total number of spit ups per day. Normally, regurgitation usually occurs after eating (the child burps after each feeding), lasts no more than 20 seconds and repeats no more than 20-30 times a day. With pathology, the problem manifests itself at any time of the day, regardless of when the baby was fed. Their number can reach 50 per day, and sometimes more 1 .
The amount of discharge during regurgitation also matters. With normal, physiological regurgitation, it is approximately 5 - 30 ml. If this volume fluctuates between 50 and 100 ml, it is already defined as profuse vomiting. When the range of the jet of vomit is up to 50 cm, doctors talk about "vomiting a fountain." A variant of atonic vomiting is possible, when the contents of the stomach flow "sluggishly". It occurs with atony of the stomach (decrease in muscle tone of the stomach wall) and disruption of the esophagus 1 .
When the range of the jet of vomit is up to 50 cm, doctors talk about "vomiting a fountain." A variant of atonic vomiting is possible, when the contents of the stomach flow "sluggishly". It occurs with atony of the stomach (decrease in muscle tone of the stomach wall) and disruption of the esophagus 1 .
Vomiting in babies is a warning sign. Doctors are especially alarmed by repeated vomiting, a fountain, with an admixture of bile, in combination with constipation. Vomiting can lead to the development of dehydration, acid-base imbalance and other consequences, therefore, if it occurs, you should urgently contact a pediatrician to find out the cause and begin treatment. A doctor's consultation is necessary if the child is spitting up a lot (more than 15-30 ml at a time), with a frequency of more than 50 episodes per day 1.3 .
Physiological regurgitation: symptoms
Regurgitation in newborns, which is considered a normal variant and does not cause concern to pediatricians 3 :
- usually continues for a certain period of time;
- is characterized by slow, "passive" leakage; if the baby spits up a fountain, it is better to consult a doctor;
- has a sour smell of curdled milk;
- occurs without the participation of muscles - the baby does not strain during regurgitation;
- does not affect the general well-being of the baby.

How to help a newborn who spit up often?
If the baby is healthy, no medication is prescribed for spitting up. To help the child allow simple measures based on lifestyle changes and feeding.
- Frequent feeding of the baby
It is known that the baby is more prone to spit up if his stomach is full. To improve the situation, it is recommended to feed the baby more often, avoiding oversaturation, best of all - on demand 5 .
- Correct feeding technique
Every feeding, the mother must ensure that the baby does not swallow too much air during suckling. When sucking, there should be no loud, smacking, clicking sounds. You also need to control that the baby captures the nipple along with the areola.
- Choosing the right bottle and nipple
If the newborn is bottle-fed and receiving formula, it is important to choose the right bottle and nipple. The hole in it should be such that the milk flows out in drops, and not in a stream. The nipple must not be filled with air
The hole in it should be such that the milk flows out in drops, and not in a stream. The nipple must not be filled with air New Anti-colic bottle with AirFree valve
The AirFree valve prevents air from entering the baby's stomach.
- Baby standing upright after eating
To allow air that has entered the digestive tract during meals to escape, it is important to keep the newborn upright for 10-20 minutes after feeding 4 .
- Ensure the correct position of the baby during sleep
To reduce the negative impact of the acidic contents of the stomach on the esophagus, it is necessary to put the baby to sleep in the supine position. The side or prone position, which many pediatricians used to recommend, is no longer recommended. It was found to be associated with an increased risk of sudden infant death syndrome 5 .
If parents notice alarming symptoms, such as spitting up too often or large volume, etc.
 , it is important to consult a pediatrician without delay. This will allow you to identify the real problem in time and help the baby grow up healthy and happy.
, it is important to consult a pediatrician without delay. This will allow you to identify the real problem in time and help the baby grow up healthy and happy.
References1 Zakharova I. N., Andryukhina E. N. Regurgitation and vomiting syndrome in young children // Pediatric pharmacology, 2010. V. 7. No. 4.
Nagornaya 2900 V., Limarenko M. P., Logvinenko N. G. Experience with the use of domperidone in suspension in young children with regurgitation syndrome // Child Health, 2013. No. 5 (48).
3 Zakharova IN Regurgitation and vomiting in children: what to do? //Pediatrics. Supplement to Consilium Medicum, 2009. No. 3. S. 58-67.
4 Zakharova I. N., Sugyan N. G., Pykov M. I. Regurgitation syndrome in young children: diagnosis and correction // Effective pharmacotherapy, 2014. No. 3. P. 18-28.
5 Vandenplas Y. et al. Pediatric gastroesophageal reflux clinical practice guidelines: joint recommendations of the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (NASPGHAN) and the European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (ESPGHAN) //Journal of pediatric gastroenterology and nutrition.
 2009; 49(4): 498-547.
2009; 49(4): 498-547. You are leaving the Philips Healthcare (“Philips”) official website. Any links to third party websites that may be included on this site are provided solely as a convenience to you. Philips makes no warranties regarding any third party websites or the information they contain.
I understand
You are about to visit a Philips global content page
Continue
You are about to visit the Philips USA website. 9Ol000
Breastfeeding is a very special time for a mother and her newborn baby. Together with the feeling of closeness and affection that feeding brings, understanding its nuances cannot but raise many questions, including the question of how to help an infant spit up. Regurgitation in a newborn is by no means always the result of a simple pat on his back.
In this article, we'll talk about the basics of helping a newborn spit up, as well as other questions you may have about spitting up.

Why do babies spit up?Let's get this straight: Why do newborns need to burp in the first place? During feeding, children usually swallow extra air - this is called aerophagia. Spitting up helps prevent this air from entering the intestines, as well as vomiting, gas, and crankiness in the baby. To avoid the return of milk after feeding, you should give the baby the opportunity to burp more often.
How to help a newborn spit up?
During the first six months, the baby should be kept upright in a column for 10-15 minutes after each feed. This will help keep the milk in his stomach, but if the baby occasionally burps anyway, parents need not worry. While carrying your baby in an upright position, you can put a baby diaper or wipes on your shoulder to keep your clothes clean.
We've already seen why spitting up is important, now let's find out how to help your baby spit up. Parents should gently pat the baby on the back with a hand folded in a handful until he burps.
 Folding your hand into a handful is important because clapping with a flat palm may be too strong for an infant.
Folding your hand into a handful is important because clapping with a flat palm may be too strong for an infant.
Every baby is different and there is no one right position for spitting up. To get started, you can try the following options:
- Sitting position with the baby on the chest. In this position, the parent puts the baby's head with his chin on his shoulder and with one hand supports the baby under the back. With the other hand, you can gently pat the baby on the back. This method is most effective in a rocking chair or when the baby is gently rocking.
- Holding a child upright on one's legs. With one hand, parents can hold the baby by the back and head, supporting his chin and placing his palm on the baby’s chest, with the other hand, you can gently pat him on the back. At the same time, it is important to be careful: do not press the child on the throat, but only gently support his chin.
- Holding a baby lying on his tummy in his lap.
 Make sure his head is above his chest and gently pat your baby on the back until he burps.
Make sure his head is above his chest and gently pat your baby on the back until he burps.
Here are some tips on how best to help your newborn spit up:
- Let your baby spit up while feeding. If the baby is restless or has swallowed air, it is worth giving him the opportunity to burp during feeding, and not just after.
- When bottle feeding, let the newborn burp after every 50-60 ml.
- When breastfeeding, let the baby burp at every breast change.
It is important to let your baby spit up after eating, even if he spit up during feeding!
If your baby is gassy, spit up more often. Also, if he vomits frequently or suffers from gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), have him spit up after every 30 ml bottle-feeding or every five minutes while breastfeeding.
How long should a baby be held for it to burp? It's different for everyone, but generally keeping a newborn upright for 15 to 20 minutes after a feed helps the milk stay in the baby's stomach.
Minimize the amount of air you swallow. Gas production and regurgitation result from aerophagia during feeding. The baby will inevitably swallow air, but there are ways to prevent it from swallowing too much. Whether you bottle feed your baby or combine breastfeeding with bottle feeding, the Philips Avent anti-colic bottle with AirFree valve is designed so that the nipple is always filled with milk without excess air, even in a horizontal position, thus preventing the baby from swallowing excess air during feeding.
Reducing the amount of air your baby swallows can help reduce your baby's risk of colic, gas, and spitting up.
Breastfeeding is a wonderful time to strengthen the bond between parent and baby. Every mom and every baby is different, so learning to help your newborn burp properly can take time and practice.
Articles and tips from Philips Avent
Baby+ app
Download the app and track your child's development and growth with trackers, and save those special moments forever.