Baby wren bird food
Kids' Inquiry of Diverse Species, Troglodytes aedon, house wren: INFORMATION
What do they look like?
House Wrens are small, squat birds that lack bold or characteristic markings. They have long, curved bills and are seen perching in the "wren posture" with the tail held up. Their heads, napes, and backs are almost uniformly brown with their throats and chests a uniform light grey. Some black, dark brown, or pinkish spots appear on their flanks, tails, and wings. There is a faint, white stripe above their eyebrows. They are usually 11 to 13 cm long and weigh between 10 and 12 g.
- endothermic
- bilateral symmetry
- sexes alike
-
- Range mass
- 10.
0 to 12.0 g
- 0.35 to 0.42 oz
-
- Range length
- 11.0 to 13.0 cm
- 4.33 to 5.12 in
Where do they live?
House Wrens are native to the Nearctic region. During the breeding season they live from southern Canada to southern Argentina, Chile and the Falkland Islands. They spend the winter in a narrower range; the southern limits of the United States, southwestern California east to Florida and south throughout the Gulf Coast and Mexico.
- nearctic
- native
What kind of habitat do they need?
In the wild House Wrens live in open, shrubby woodlands. However, they were named for their preference for small town and suburban backyards and human-made bird houses. Small wood-lots and forest edges are also well known habitats for these birds. Human farming and towns have created more good breeding habitat for the wren by fragmenting forests, which explains why the House Wren has expanded its range and numbers in North America. During the winter wrens live in thickets, shrubby and brushy areas, riparian forests, and savannas in the southern United States. In Mexico, they prefer tropical evergreen and semideciduous forests.
However, they were named for their preference for small town and suburban backyards and human-made bird houses. Small wood-lots and forest edges are also well known habitats for these birds. Human farming and towns have created more good breeding habitat for the wren by fragmenting forests, which explains why the House Wren has expanded its range and numbers in North America. During the winter wrens live in thickets, shrubby and brushy areas, riparian forests, and savannas in the southern United States. In Mexico, they prefer tropical evergreen and semideciduous forests.
- temperate
- tropical
- terrestrial
- chaparral
- forest
- scrub forest
How do they reproduce?
- monogamous
House Wren nest sizes range from 4 to 8 eggs, with one egg laid per day. Females develop single large incubation patches (bare areas of skin on their bellies) and will spend over half of their time incubating the eggs, once their entire clutch has been laid. Hatching begins about 12 days after the last egg is laid and occurs only during daylight hours. House Wrens are able to breed (have reached sexual maturity) when they are 1 year old, but some first time breeders skip the regular breeding time and choose instead to breed alongside the older birds who are attempting a second clutch in a season. House Wrens nest in tree cavities, such as old woodpecker holes. They preferring cavities closer to the ground with small entrances.
Females develop single large incubation patches (bare areas of skin on their bellies) and will spend over half of their time incubating the eggs, once their entire clutch has been laid. Hatching begins about 12 days after the last egg is laid and occurs only during daylight hours. House Wrens are able to breed (have reached sexual maturity) when they are 1 year old, but some first time breeders skip the regular breeding time and choose instead to breed alongside the older birds who are attempting a second clutch in a season. House Wrens nest in tree cavities, such as old woodpecker holes. They preferring cavities closer to the ground with small entrances.
- iteroparous
- seasonal breeding
- gonochoric/gonochoristic/dioecious (sexes separate)
- sexual
- fertilization
- internal
- oviparous
-
- How often does reproduction occur?
- Breeding occurs in late April to early May with the majority of nests started in mid to late May.
 Some females that start a nest early will sometimes make a second nest in late June to early July.
Some females that start a nest early will sometimes make a second nest in late June to early July.
-
- Breeding season
- Late April to July
-
- Range eggs per season
- 4.0 to 8.0
-
- Average eggs per season
- 7
- AnAge
-
- Average time to hatching
- 12.0 days
-
- Average time to hatching
- 14 days
- AnAge
-
- Range fledging age
- 15.
 0 to 17.0 days
0 to 17.0 days
-
- Average age at sexual or reproductive maturity (female)
- 1.0 years
-
- Average age at sexual or reproductive maturity (male)
- 1.0 years
The young are completely helpless and depend on their parents, who both care for the young. They fledge after about 15 to 17 days and all leave the nest within a few hours of each other.
- altricial
- male parental care
- female parental care
How long do they live?
The oldest House Wren has been known to live is 7 years. It is hard to keep track of the age of individual birds because they do not always return to the same spot every year.
It is hard to keep track of the age of individual birds because they do not always return to the same spot every year.
-
- Range lifespan
Status: wild - 7.0 (high) years
- Range lifespan
-
- Average lifespan
Status: wild - 108 months
- Bird Banding Laboratory
- Average lifespan
How do they behave?
House Wrens mostly hop while on the ground and have a direct, steady flight only about 1 meter above the ground in open areas. House Wrens are most active during the day. They migrate yearly between breeding and wintering areas. They are very territorial and are usually found alone, in pairs, or in immediate family groups. Males take primary responsibility for defending the territory and will chase away intruders. They usually only have one mate, and both parents help to raise the young.
Males take primary responsibility for defending the territory and will chase away intruders. They usually only have one mate, and both parents help to raise the young.
- diurnal
- motile
- migratory
- territorial
How do they communicate with each other?
House Wrens are widely known for their songs. While both sexes produce calls and songs, the males' songs are more complex. Altogether 130 different song types are known from House Wrens. Unmated males can sing for up to 10 minutes. Males with a mate are known to produce a "whispering song", where he sings without opening his bill to produce a very quiet song. This song type only occurs around the time of copulation. The purpose of the quiet song may be to not reveal the location of his fertile mate to other males. The female sings during the first days of pairing when she responds to her mate's song.
The purpose of the quiet song may be to not reveal the location of his fertile mate to other males. The female sings during the first days of pairing when she responds to her mate's song.
They will also communicate using body language. If a predator is approaching the male will crouch, droop his wings, erect his back feathers, and lower his fanned out tail.
- visual
- tactile
- acoustic
- chemical
What do they eat?
House wrens feed primarily on small, terrestrial insects. The independent young and adults consume mostly spiders, beetles, and bugs while the babies still in the nest (called nestlings) are fed mostly grasshoppers, crickets, and caterpillars. Adults will feed their young, and supplement their own diet, with sources of calcium such as mollusk shells.
Adults will feed their young, and supplement their own diet, with sources of calcium such as mollusk shells.
- carnivore
- eats non-insect arthropods
What eats them and how do they avoid being eaten?
Adults respond to predators by chasing and striking at the predators while giving a loud, harsh alarm call. Cats, rats, opossums, woodpeckers, foxes, owls, raccoons, squirrels, and various snakes are known predators of this species.
-
- Known Predators
-
- domestic cats
- rats
- Virginia opossums
- woodpeckers
- foxes
- owls
- raccoons
- squirrels
- snakes
What roles do they have in the ecosystem?
House Wrens help to control several insect populations. They also supply an abundant food source for many different types of animals.
They also supply an abundant food source for many different types of animals.
How do they interact with us?
House Wrens eat many insects that humans consider to be pests.
- controls pest population
Are they endangered?
House Wrens are a very abundant species. They live in semi-forested areas, which is a common habitat type so conservation management is not necessary. However, House Wrens are protected under the U.S. Migratory Bird Act. These birds are quite tolerant of habitat change and nest disturbance, allowing them to live and reproduce successfully even in human populated areas.
-
- IUCN Red List
- Least Concern
More information
There are roughly 30 different subspecies of House Wrens. These subspecies are divided into 5 groups: Northern House Wrens, Brown-throated Wrens, Southern House Wrens, Antillean House Wrens and Cozumel Wrens. Southern House Wrens have 20 of the subspecies in their category.
These subspecies are divided into 5 groups: Northern House Wrens, Brown-throated Wrens, Southern House Wrens, Antillean House Wrens and Cozumel Wrens. Southern House Wrens have 20 of the subspecies in their category.
Brown-headed Cowbirds sometimes lay their eggs in House Wren nests. These birds act as a parasite to House Wrens but, because Brown-headed Cowbirds usually are too big to enter House Wren's cavity nests, this is a very rare occurrence.
What Do Baby Wrens Eat?
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.
A Rare Blue-Colored WrenWrens are frequently encountered across North America. These birds construct their nests in a variety of unusual locations, including old boxes, discarded cans, and even within barns and garages. It’s not uncommon for humans to discover abandoned wren babies or youngsters who’ve fallen from the canopy. It’s difficult to care for a wild wren, but with the right tools and understanding of how it works, it becomes much easier.
If the baby wren is uninjured, return it to the nest. If you can’t find the nest, wrap some newspaper around a berry basket and conceal it among dense bushes. Take any injured bird to your local veterinarian or a wildlife conservation organization if possible. If the parents are not contacted for three hours after the bird is returned to the nest, assume they have abandoned it and take it to a veterinarian, an animal shelter, or an indoor facility where you can care for it.
Caring for a baby wren requires effort and consistency. In this article, we explain how you can help a baby wren in an effective manner.
What Do Baby Wrens Eat? Baby Wrens Eat GrasshoppersThe diet of a baby wren is exclusively small terrestrial insects. The young and adults eat mostly spiders, bugs, and beetles while the youngsters still in the nest are fed mostly grasshoppers, caterpillars, and crickets. Adult wrens will feed their young, as well as supplement their own diet, with mollusk shells.
Wrens eat a wide variety of foods, most of which are high in protein. If they’re unable to find any bugs nearby, Wrens will resort to consuming insects. If insects aren’t found either, then their alternative option will be to feed on berries. Mealworms, peanuts hearts, peanuts, suet, and occasionally snail shells are all used to provide digestive grit in baby wrens. Digestive grit refers to the grinding of food in their stomach, which is aided by the presence of larger particles. You may attract a house Wren to your yard by putting some peanut butter on a stump or hanging a suet feeder. Wrens are an important part of your yard. They can consume all of the bugs and they’re fascinating to watch. The House Wren eats berries and insects, making it an omnivore.
Beetles Are Consumed By Baby WrensWarmth is important for baby wrens, especially if they’re abandoned in the wild. Line a shoebox with newspaper or paper towels and fill it with hot water. Small holes should be cut in the box’s lid and the baby bird should be placed inside. Keep the box hidden from children and pets by keeping it covered and away from them. Use a desk lamp with a high-wattage incandescent bulb to provide warmth. Fluorescent lights, on the other hand, do not give enough heat.
Keep the box hidden from children and pets by keeping it covered and away from them. Use a desk lamp with a high-wattage incandescent bulb to provide warmth. Fluorescent lights, on the other hand, do not give enough heat.
Baby wrens should be fed on a regular basis. Baby birds require food every 15 to 20 minutes when the sun is shining. To create a thick liquid, combine one part protein, such as canned puppy pup food or dried beef baby food, with two parts high-protein baby cereal or powdered grain meal. Feed the infant via a syringe or eyedropper.
Baby Wrens Eat SpidersNow it’s time to teach the baby wren how to eat insects. Offer tiny crawling insects, such as mealworms, at each feeding when your youngster is younger. To encourage a feeding response, press an insect against the beak of the baby wren. Because feeding is natural, don’t worry if it takes some practice.
Peanuts Are Also A Part of a Baby Wren’s DietReplace the container with a larger box as the bird matures. Old birds will become claustrophobic in a shoebox and require more space. Take the pet outside in a cage or box on occasion to acclimate it to the outdoors. Do not allow the baby wren to fly about freely in its habitat.
Old birds will become claustrophobic in a shoebox and require more space. Take the pet outside in a cage or box on occasion to acclimate it to the outdoors. Do not allow the baby wren to fly about freely in its habitat.
Once the baby wren is released, turn on some music and start dancing. Place the cage or box in an outdoor space that you’re familiar with where no dogs or cats are allowed to roam. Leave the lid or door open, and watch the bird fly off on its own. Leave the wren in its cage for several weeks so it has time to get used to you, but don’t handle or talk to it. The wren will revert to being wild at some point.
How Much Do Baby Wrens Eat?Feed the baby wren every 15 to 20 minutes throughout the day. Soak the kibble in water until it is soft and pliable. Dry out the water before mixing in a kibble and baby cereal with a ratio of 1:2. This will create a fluid mixture. It must be a liquid state. Fill the dropper or syringe and press the food into the bird. Make sure the food does not end up under its tongue if you’re feeding a fledgling nestling since this might obstruct its airway.
Make sure the food does not end up under its tongue if you’re feeding a fledgling nestling since this might obstruct its airway.
Place newspaper on the shoe box and line it up. Place the baby bird inside and punch holes in the top of the shoe box. Cover the shoebox with the lid and shine the lamp on it. Turn on (insert the light bulb and turn it on).
Can Baby Wrens Be Kept As Pets?No, house wrens are not a good choice as pets. These little birds may be aesthetically appealing, but they do not function well in a living environment. These are wild birds that require ample area to fly and explore. It is illegal to keep one as a pet in most areas.
It is against the law to keep wild birds, and they must be released as soon as feasible. It’s critical that little human interaction occurs so that the bird does not become domesticated. When a wild bird is discovered, it is HIGHLY advised to turn it over to the proper authorities.
Put your finger in the baby bird’s feet to determine whether it is a nestling or a fledgling. A fledgling has a firm grip on your finger if it does. It is a nestling if there is no hold on your finger at all. Watch the birds‘ nest for two hours after you put the wren back in. Assume that the parents have died if there is no parental care and contact your local wildlife conservation. It’s a myth that parent birds would abandon their young if they come into touch with humans.
A fledgling has a firm grip on your finger if it does. It is a nestling if there is no hold on your finger at all. Watch the birds‘ nest for two hours after you put the wren back in. Assume that the parents have died if there is no parental care and contact your local wildlife conservation. It’s a myth that parent birds would abandon their young if they come into touch with humans.
The top portion of a wren is reddish-brown and has fine darker brown bars on the wings, tail, and rump. The lower sides are pale brown with numerous, heavier streaks across the shoulders and abdomen. They have a short chestnut-hued tail with dark brown streaked sides.
The crown of a wren is browner, with fewer streaks and a pale supercilium from the bill’s base to just beyond the eye. They have long, thin bills that are slightly downcurved and black on top, with yellow on the bottom. The eyes of wrens are dark brown, and their feet and legs are pale browns in color. Male and female wrens appear identical.
Male and female wrens appear identical.
The House Wren is tiny yet has a loud voice. This creature makes chatters, rattles, and scolds when it detects potential predators. The house wren is a mundane little brown bird whose plumage varies by gender. Because of the sound it creates, you may identify a House Wren if it’s male or female.
Another indication that you’re looking at a wren is because it has white dots on its back. The wrens have evolved to blend in with their surroundings, which aids them in hiding from predators while still feeding on food. The House Wren weighs approximately half an ounce. That’s the size of half of a slice of whole-wheat bread, which is about five to six inches long. They live for up to nine years. They are typically around four to five inches long. The House Wren’s wingspan is approximately 6 inches. The House Wren flies near to the ground in its airborne method of transport. They are bright and lively, just like their music. However, they may be rather territorial.
The head, nape, and neck of baby wrens are crimson with streaks, while the underparts are streaked with black.
What Are The Natural Predators of Baby Wrens?The Wren is vulnerable to a variety of predators, including cats, opossums, rats, and woodpeckers. The female will lay one egg each day until five or six eggs are laid after choosing and constructing the nest.
At 12 to 15 days, the nestlings remain in the nest for 12 to 15 days. The mother leaves the nest periodically to obtain food while she is incubating. The period of time when the baby remains in his or her parent’s nest is known as incubation.
House Wrens’ songs are very strident, as they are produced in periods of time. They frequently do so during the breeding season to bring in additional mates. The House Wren leaves for warmer climes during the winter, but the trip is hazardous. The Wrens live in the southern United States, and they are among the most distinctive birds. Because of how harsh winter is, only half survive. The House Wren is a fantastic creature with an amazing song.
The house wren is a tiny bird that commonly flies and nests low to the ground, thus it is consumed by a variety of predators. Rats, opossums, foxes, squirrels, raccoons, owls, kites, and snakes are among the many creatures that may be found in any environment. Woodpeckers, like wrens, can also take revenge on tiny birds for stealing their eggs. The pugnacious little songbird, on the other hand, does not shy away from attacking predators with its sharp beaks and claws.
Amazon and the Amazon logo are trademarks of Amazon.com, Inc, or its affiliates.
How to feed the found chick, how many times a day
If you find a chick, the first thing you need to do is determine its species. Feeding granivorous, insectivorous and predatory chicks have their own differences. But in the early stages of feeding, you can use the same feeding methods, and then, after finding out what kind of bird you found, transfer the chick to the appropriate feeding.
Here is one of the most common feeding options for granivorous and insectivorous chicks. This nutrient mixture is well used for feeding for chicks and fledglings from the passerine family. To prepare our mixture, we need the following products: Boiled egg, low-fat cottage cheese, raw carrots, meat (beef, chicken, turkey), greens (lettuce, dandelion leaves, wood lice), hamarus and daphnia, Calcium gluconate (shell from boiled eggs) glycerophosphate , children's dry dairy-free porridge or boiled millet (without salt and fat on the water). nine0003
Action one. Boil the egg, free from the shell. We free the shell from the shell film. Grind the egg as much as possible, you can use a grater with small holes.
Second step. Boiled meat, it is better to take the pulp from the breast of a turkey or chicken and also chop or divide into fibers. The mixture will require meat 40 (for granivorous) and 60 grams (for insectivorous).
Third step. Take washed carrots of a small size, grate them on a fine grater, then squeeze the juice and we will use the remaining pulp. nine0003
Fourth step. We take not sour and not fatty cottage cheese. Cottage cheese should have 0% fat content, anything above is considered fat for poultry. We need 90-110 grams of cottage cheese. Sour cottage cheese must be boiled twice changing the water and then it will be suitable.
Step five. You can use greens to add the mixture, but you can do without it for the chicks. And so you can take the greens listed above, chop and add 1.5 teaspoons to the mixture.
Action six. To the above ingredients, add 1.5 -2 tsp. dairy-free porridge or boiled millet (well boiled, without salt and fat in the water). nine0003
Step seven. To the mixture we add the shell from the boiled egg, which must first be ground in a coffee grinder, plus one fourth of the crushed tablet of glycerophosphate. If it is not possible to find glycerophosphate, then you can purchase bone meal and add one fourth tsp. in powder form. At the very least, the shells are enough for now.
Step eight. We take chopped hamarus and daphnia and add about 1 tsp to the resulting mixture. Then we mix everything, it turns out a very thick, crumbly porridge, it should not stick to the fingers. If the mixture is sticky, you can add dairy-free porridge or powdered cereals. nine0003
We take chopped hamarus and daphnia and add about 1 tsp to the resulting mixture. Then we mix everything, it turns out a very thick, crumbly porridge, it should not stick to the fingers. If the mixture is sticky, you can add dairy-free porridge or powdered cereals. nine0003
From the resulting mixture we roll small balls no larger than a small pea, focus on the size of the chick's beak. You can feed 2-5 balls at a time and after each feeding drink plain water from an insulin syringe with a removable needle (without a needle) 4-6 drops. A week-old chick should be fed every 1-1.5 hours, older than two weeks of age every 2-4 hours, at three and four weeks of age you can feed 3-4 times a day. Do not forget that the chick is growing and, accordingly, one-time portions of food are growing. A very important point, do not forget to warm the chicks, because at their age they themselves cannot maintain normal body temperature. Warming up promotes better assimilation of feed. Don't forget to control your chick's weight.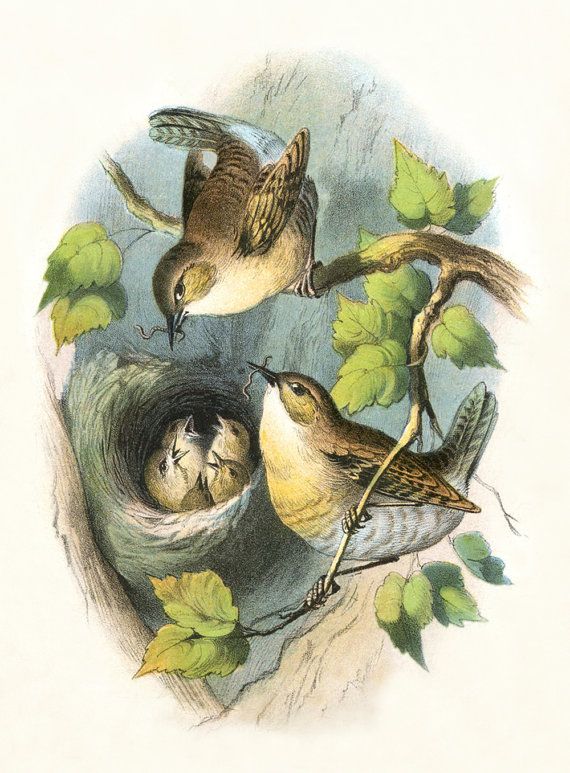 If possible, show the chick to a specialist. To control the work of the intestines, you can take the litter from the chick for a coprogram, this is an analysis of the digestibility of the feed. nine0003
If possible, show the chick to a specialist. To control the work of the intestines, you can take the litter from the chick for a coprogram, this is an analysis of the digestibility of the feed. nine0003
Take care and love your feathered friends and they will love you back.
Veterinarian ornithologist
Chuguevsky VV
Veterinary clinic Bambi.
You can ask an ornithologist on the forum.
How to save a chick that has fallen out of the nest | Encyclopedia of Animals
With the advent of warm weather, our forests and gardens are filled with bird songs, and people, in turn, try to spend as much time as possible outdoors. During outdoor recreation, helpless chicks are often found. Naturally, there is a desire to save the life of a baby, but not everyone knows how to save a chick that has fallen out of the nest. Let's see how we can help him. nine0003
To save or not to save - that is the question
The first thought that arises when looking at a fledgling and flightless chick is “fell out of the nest”, “lost” and even “parents abandoned and forgot”.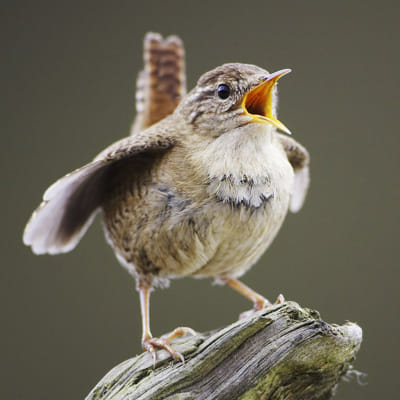 In fact, the chick is alone, no brothers, sisters, or adult birds are visible nearby, and it also screams loudly. How can you help here? But the fact of the matter is that help in 95% of cases in such situations is not needed.
In fact, the chick is alone, no brothers, sisters, or adult birds are visible nearby, and it also screams loudly. How can you help here? But the fact of the matter is that help in 95% of cases in such situations is not needed.
The fact is that in many birds (primarily small passerines) chicks leave the nest as half-fledged fledglings. During this period of life, they still do not know how to fly, but they are already actively exploring the surrounding space - they climb branches, clumsily flit. It is these rather active chicks that fall into the field of human vision. It is easy to determine the fledgling in appearance: it is feathered or covered with rudiments of unopened feathers; the chick is quite large (about 50-70% of the size of a sparrow), it is often active, that is, it opens its mouth and asks for food. Parents did not abandon this chick, but simply flew away for food. Of course, while you are standing next to the chick, they will not make themselves felt. And if you stay too long, then there is a chance that the parents will leave him out of concern. nine0003
Even if the chick looks too small and helpless, don't rush to classify it as an orphan. Birds such as warblers, warblers, larks, wagtails nest on the ground, their chicks spend their entire childhood on the grass. Your presence in this situation is also undesirable because magpies and crows track human behavior. Smart birds can check after you leave what you saw there, find and kill the chick. Hence the conclusion: do not "save" everything that catches your eye. If the chick is dry, warm, active, well feathered, then he does not need help. nine0003
What if the situation causes concern? Perhaps the chick is too weak or obviously fell out of the nest from a great height and cannot be returned to its parents. In this case, you can try to save him, but keep in mind that the likelihood of success will be directly proportional to your diligence, and you will have to put in a lot of work.
What to do first
- Quickly and carefully inspect the place where you found the chick, remember how it looks.
In some cases, this will help determine the type of bird. nine0055
- Pick up the chick (don't squeeze too hard!) and bring him home as soon as possible.
- On the way, inspect the chick for damage. If the bird has clearly visible fractures of the paws, wings, concussion (how to define it a little lower), then you can’t do without a veterinarian. It is highly desirable to seek help from a veterinarian who specializes specifically in the treatment of birds (unfortunately, such specialists are extremely rare). If there are no obvious signs of a fracture, and the general condition of the chick is satisfactory, then it is better not to torment him, but simply to provide good conditions - nature will do its job and he will recover. nine0055
- Providing a chick with food as soon as possible is even more important than furnishing a home for it.
Now a few words on how to define contusion. Usually, chicks get severe bruises either from hitting the ground or when they collide with cars. At the same time, the bird has no wounds on the outside, but a concussion is observed. True signs of this condition are bleeding from the nostrils, paralysis of both legs or paralysis of half of the body (paw and wing on one side), closure of one eye, or unequal degree of pupil dilation on the injured and healthy side of the body. nine0003
At the same time, the bird has no wounds on the outside, but a concussion is observed. True signs of this condition are bleeding from the nostrils, paralysis of both legs or paralysis of half of the body (paw and wing on one side), closure of one eye, or unequal degree of pupil dilation on the injured and healthy side of the body. nine0003
What to feed
You may think that feeding a chick is easy - crumble bread and crumble. But here you will find disappointment number 2. Chicks do not eat bread, crackers, porridge, cereals, seeds. They don't eat at all. Even the chicks of granivorous birds do not take dry food at first. And the reason is that the growing organism needs proteins, therefore, in nature, even granivorous birds feed their offspring with animal food and exceptionally soft food. You will have to do the same. Pigeons are the only exception. They feed the chicks with goiter secretions - bird's milk, and then with semi-digested grains. If you picked up a pigeon chick, then you can feed it with unsalted porridge, gradually reducing the degree of cooking. In other cases, the best food for the chick is mealworms, cockroaches, crickets, darkling larvae - zoophobus (all these foods are sold in pet stores), earthworms (you can dig up), caterpillars (you will have to collect), a boiled egg (only as an additional food, and not a substitute for anything and everything). Even if you have provided the chick with the listed food, it is recommended to periodically catch bugs, grasshoppers, butterflies, flies, mosquitoes and give these insects to him, because the more varied the diet, the healthier your ward will grow. Very weak chicks should be given glucose-sweetened water (not sugar syrup!), instead of solid food, for the first few hours. nine0003
In other cases, the best food for the chick is mealworms, cockroaches, crickets, darkling larvae - zoophobus (all these foods are sold in pet stores), earthworms (you can dig up), caterpillars (you will have to collect), a boiled egg (only as an additional food, and not a substitute for anything and everything). Even if you have provided the chick with the listed food, it is recommended to periodically catch bugs, grasshoppers, butterflies, flies, mosquitoes and give these insects to him, because the more varied the diet, the healthier your ward will grow. Very weak chicks should be given glucose-sweetened water (not sugar syrup!), instead of solid food, for the first few hours. nine0003
What not to feed chicks
- dead insects - no matter what species they belong to and wherever you find them. In nature, insects almost never live to old age, rather someone will eat them. If you find a dead cockroach behind the stove or a dead locust in the garden, do not rush to rejoice.
 Most likely, this individual died from an insecticide, which means that the poison from the feed can enter the body of the chick and greatly harm its already poor health; nine0055
Most likely, this individual died from an insecticide, which means that the poison from the feed can enter the body of the chick and greatly harm its already poor health; nine0055 - Colorado potato beetles - adults, larvae and eggs are poisonous in this species. They are not eaten by any species of birds, so this easily accessible resource will have to be forgotten;
- ladybugs - they secrete a moderately toxic liquid, in nature a bird that has caught such a bug by mistake will spit it out. In captivity, especially in the case of force-feeding the chick, he does not have the opportunity to refuse harmful food, so he can get poisoned;
- hairy caterpillars - firstly, they can be poisonous, and secondly, the villi during feeding can clog the chick's goiter and it will die. Although cuckoos and orioles can eat in the temperate hairy strip, it is still better to play it safe and not use this food;
- brightly colored bugs - in nature, many birds willingly peck at such insects, but this mainly concerns nondescript turtle bugs.
 The back of the bug, decorated with bright spots or stripes, is of a warning nature - "do not eat me, it will be worse for you." For safety net, it is not necessary to catch such specimens for the chick. nine0055
The back of the bug, decorated with bright spots or stripes, is of a warning nature - "do not eat me, it will be worse for you." For safety net, it is not necessary to catch such specimens for the chick. nine0055
How to feed
The main thing you should know from the very beginning is that birds have a very high metabolism, and small chicks have a huge metabolic rate. Any food eaten by the chicks is digested very quickly and they need to be fed again and again. In nature, parents jointly feed the brood 100-500 times a day! This means that every 10-15 minutes the chick needs to be fed. And don't expect to overtrain him! A chick deprived of food instantly weakens, a couple of hours of hunger is enough for it to die. You will have to provide the baby with constant supervision, feed him at first every 15 minutes, and when he grows up a little, after 20-30. But you need to take a break at night, but start the first feeding no later than 6 o'clock in the morning! Evening feeding is completed around sunset, that is, around 22.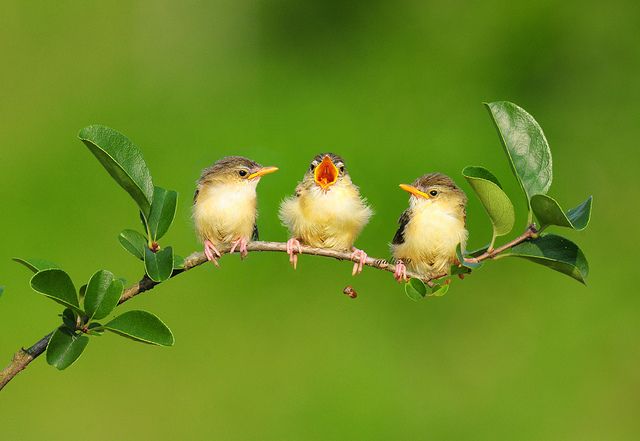 00. nine0003
00. nine0003
It is more convenient to bring food with tweezers. In general, tactile contact should be kept to a minimum, frequent touching is stressful for the tiny creature, and it worsens the condition of down and feathers. If the chick is very small and naked, then it is not necessary to give it a whole large insects. In this case, it is better to cut them with tweezers and feed them in pieces. It is also recommended to remove hard elytra from large beetles, long legs from grasshoppers and locusts. Often the chicks refuse to take any food. This happens because they do not recognize you as their mother, or they are so weak that they have lost their appetite. In this case, you will have to force-feed the ward. To do this, you need to crush the food and fill it with a syringe without a needle (you can add a couple of drops of water to dilute the mixture). Take the bird in your left hand and gently spread its beak with your fingers, insert a syringe into its mouth with your right hand and squeeze out about 1 cm³ of slurry. Do not overdo it! In tiny chicks, the beak is easily broken, and this is already a fatal injury. For greater convenience, a flexible tube can be put on the end of the syringe. nine0003
Do not overdo it! In tiny chicks, the beak is easily broken, and this is already a fatal injury. For greater convenience, a flexible tube can be put on the end of the syringe. nine0003
Where to house
If the first difficulties do not dampen your enthusiasm, then you should provide a shelter in your home for the chick. First of all, you need to make a nest.
Take a deep bowl or cardboard box with a rim about 10 cm high. Fill this container with sawdust, dry clean sand, hay, straw, scraps of cloth, make a recess in the middle that imitates the nest tray. Do not fill the container with fresh grass, raw material can cause hypothermia of the chick, because there is no one to warm it in an artificial house. By the way, if you are seriously engaged in rescue, you can purchase a small thermal mat at the pet store, it will to some extent replace the mother's warmth for your pupil. Also, cotton wool, yarn, fabrics with a rare weave of threads can be considered dangerous fillers. The paws of a chick are easily tangled in such material, and a tightened thread can even amputate the fingers of a feathered baby. Lay a paper napkin in the tray in 2-3 layers. Chicks defecate as often as they eat; in nature, their parents monitor their hygiene and take the litter out of the nest. You just need to change the napkin after each feeding. So, the nest is ready. nine0003
The paws of a chick are easily tangled in such material, and a tightened thread can even amputate the fingers of a feathered baby. Lay a paper napkin in the tray in 2-3 layers. Chicks defecate as often as they eat; in nature, their parents monitor their hygiene and take the litter out of the nest. You just need to change the napkin after each feeding. So, the nest is ready. nine0003
Now we need to think about security. In the house of the savior, stupid children, blind-sighted grandmothers, dogs, cats can live, and there are also curious neighbors who have dropped in for a minute. All these creatures threaten the life of a little chick: children can grab it and squeeze it in a fist (certain death), dogs and cats can arrange a hunt (you won’t even find feathers), a blind grandmother will sit by chance on a box (well, don’t execute the old woman for this), and noisy neighbors can accidentally knock it over (“Tanya, I’ll come to you for a second for salt, oh, it seems that something has fallen here!”). To prevent trouble, it is better to place the nest in a cage or an aquarium covered with gauze. In the cage, do not try to put the chick on the perch, do not place it in closed containers (jars, etc.). Don't nest on high ground. The fact is that a weak chick can get stronger and, unexpectedly for you, will go to explore the surrounding space. He is guaranteed to fall out of his shelter and, unlike the forest and the meadow, it will not be soft grass waiting for him at the bottom, but the floor. You should not put the box with the chick in the sun, so you will not warm it, and the helpless bird is guaranteed to get sunstroke and may die. Drafts are very dangerous. nine0003
To prevent trouble, it is better to place the nest in a cage or an aquarium covered with gauze. In the cage, do not try to put the chick on the perch, do not place it in closed containers (jars, etc.). Don't nest on high ground. The fact is that a weak chick can get stronger and, unexpectedly for you, will go to explore the surrounding space. He is guaranteed to fall out of his shelter and, unlike the forest and the meadow, it will not be soft grass waiting for him at the bottom, but the floor. You should not put the box with the chick in the sun, so you will not warm it, and the helpless bird is guaranteed to get sunstroke and may die. Drafts are very dangerous. nine0003
Do chicks need water?
In nature, chicks of passerines do not need water, as they get enough moisture with food. After all, adult birds do not bring them water in their beaks. At home, you can do without watering the chick if you follow the diet, that is, you give a variety of, and most importantly, “wet” food - earthworms, fatty juicy caterpillars. Flies, cockroaches, crickets (they are most often bought in a store) can be conditionally classified as “dry” food. They do not give the chick enough moisture. In this case, he can instill a few drops of liquid from a pipette, but do this not at every feeding, but a little less often. Please note that shell-shocked chicks should not be given water. nine0003
Flies, cockroaches, crickets (they are most often bought in a store) can be conditionally classified as “dry” food. They do not give the chick enough moisture. In this case, he can instill a few drops of liquid from a pipette, but do this not at every feeding, but a little less often. Please note that shell-shocked chicks should not be given water. nine0003
What to do next?
Fortunately, the chicks grow quickly and the period of trouble soon passes, in a week or two your ward may be completely stronger. In order for the feeding process to be completed successfully, do not forget to gradually accustom the chick to adult food. For granivorous birds, this can be porridge cooked without salt, small grains (millet, rice chaff). Chicks of insectivorous species will have to be supplemented with insects. No matter how hard you try, your chick will be weaker than its wild counterparts and completely unsuitable for independent living. There is nothing you can do to help him, so you have to take responsibility for his life.