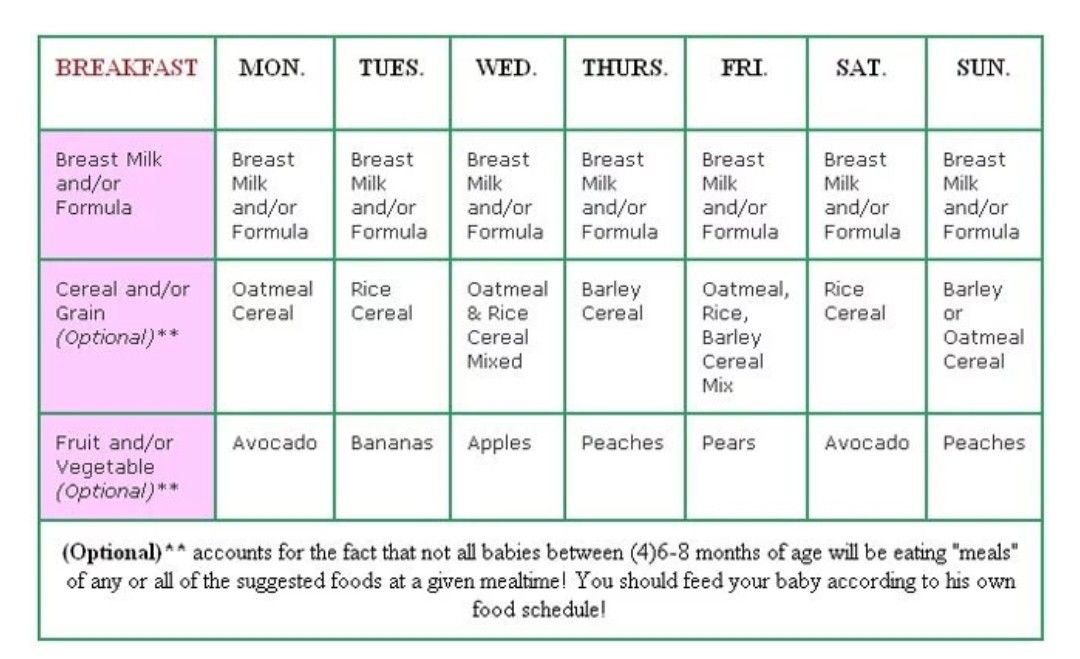
Feed baby cereal first time
When, What, and How to Introduce Solid Foods | Nutrition
For more information about how to know if your baby is ready to starting eating foods, what first foods to offer, and what to expect, watch these videos from 1,000 Days.
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend children be introduced to foods other than breast milk or infant formula when they are about 6 months old. Introducing foods before 4 months old is not recommended. Every child is different. How do you know if your child is ready for foods other than breast milk or infant formula? You can look for these signs that your child is developmentally ready.
Your child:
- Sits up alone or with support.
- Is able to control head and neck.
- Opens the mouth when food is offered.
- Swallows food rather than pushes it back out onto the chin.
- Brings objects to the mouth.
- Tries to grasp small objects, such as toys or food.
- Transfers food from the front to the back of the tongue to swallow.
What Foods Should I Introduce to My Child First?
The American Academy of Pediatrics says that for most children, you do not need to give foods in a certain order. Your child can begin eating solid foods at about 6 months old. By the time he or she is 7 or 8 months old, your child can eat a variety of foods from different food groups. These foods include infant cereals, meat or other proteins, fruits, vegetables, grains, yogurts and cheeses, and more.
If your child is eating infant cereals, it is important to offer a variety of fortifiedalert icon infant cereals such as oat, barley, and multi-grain instead of only rice cereal. Only providing infant rice cereal is not recommended by the Food and Drug Administration because there is a risk for children to be exposed to arsenic. Visit the U.S. Food & Drug Administrationexternal icon to learn more.
How Should I Introduce My Child to Foods?
Your child needs certain vitamins and minerals to grow healthy and strong.
Now that your child is starting to eat food, be sure to choose foods that give your child all the vitamins and minerals they need.
Click here to learn more about some of these vitamins & minerals.
Let your child try one single-ingredient food at a time at first. This helps you see if your child has any problems with that food, such as food allergies. Wait 3 to 5 days between each new food. Before you know it, your child will be on his or her way to eating and enjoying lots of new foods.
Introduce potentially allergenic foods when other foods are introduced.
Potentially allergenic foods include cow’s milk products, eggs, fish, shellfish, tree nuts, peanuts, wheat, soy, and sesame. Drinking cow’s milk or fortified soy beverages is not recommended until your child is older than 12 months, but other cow’s milk products, such as yogurt, can be introduced before 12 months. If your child has severe eczema and/or egg allergy, talk with your child’s doctor or nurse about when and how to safely introduce foods with peanuts.
How Should I Prepare Food for My Child to Eat?
At first, it’s easier for your child to eat foods that are mashed, pureed, or strained and very smooth in texture. It can take time for your child to adjust to new food textures. Your child might cough, gag, or spit up. As your baby’s oral skills develop, thicker and lumpier foods can be introduced.
Some foods are potential choking hazards, so it is important to feed your child foods that are the right texture for his or her development. To help prevent choking, prepare foods that can be easily dissolved with saliva and do not require chewing. Feed small portions and encourage your baby to eat slowly. Always watch your child while he or she is eating.
Here are some tips for preparing foods:
- Mix cereals and mashed cooked grains with breast milk, formula, or water to make it smooth and easy for your baby to swallow.
- Mash or puree vegetables, fruits and other foods until they are smooth.
- Hard fruits and vegetables, like apples and carrots, usually need to be cooked so they can be easily mashed or pureed.
- Cook food until it is soft enough to easily mash with a fork.
- Remove all fat, skin, and bones from poultry, meat, and fish, before cooking.
- Remove seeds and hard pits from fruit, and then cut the fruit into small pieces.
- Cut soft food into small pieces or thin slices.
- Cut cylindrical foods like hot dogs, sausage and string cheese into short thin strips instead of round pieces that could get stuck in the airway.
- Cut small spherical foods like grapes, cherries, berries and tomatoes into small pieces.
- Cook and finely grind or mash whole-grain kernels of wheat, barley, rice, and other grains.
Learn more about potential choking hazards and how to prevent your child from choking.
Top of Page
How to Get Started – The Baby's Brew
I will always remember feeding each of my babies their first foods. After months of only breastfeeding and bottles, my husband and I couldn’t wait to introduce the next milestone to each of our babies. But with the first baby at least, there was also apprehension. Our pediatrician had recommended we start with a single-grain baby cereal such as rice cereal, but I didn’t know which one to get and I wanted to make sure I fed my baby the right way!
After months of only breastfeeding and bottles, my husband and I couldn’t wait to introduce the next milestone to each of our babies. But with the first baby at least, there was also apprehension. Our pediatrician had recommended we start with a single-grain baby cereal such as rice cereal, but I didn’t know which one to get and I wanted to make sure I fed my baby the right way!
So to get you started off on the right food with baby feeding 101, I’ve put together this guide to giving your baby cereal for the first time. And it will only get more exciting as you introduce other foods to your little one.
Choosing a First Baby CerealBefore you actually feed your baby, you have to choose what you want to give them from the array of cereals and other options available.
Most parents reach for the rice cereal to give their baby as their first food. I know I did as a new mom! It’s an easy choice and one that doctors suggest due to its benefits. It's easy to such as its digest, won’t trigger an allergic reaction and is tolerated well by babies who’ve only been fed breastmilk or formula. It’s also iron-fortified, which babies need as their iron stores start to deplete around 6 months of age.
It’s also iron-fortified, which babies need as their iron stores start to deplete around 6 months of age.
Though rice cereal has traditionally been suggested as the best first food for your baby, even many doctors may still give this recommendation, it has gotten a bit of a bad rap in recent years due to the arsenic that’s found in rice - causing parents to look at other options. (This article from Healthy Children explains how you can ensure rice cereal can be used in a healthy diet for your baby.)
If you do choose rice cereal, you’ll want to start introducing other solids to your baby shortly so that’s not all that they are getting, as recommended by the FDA.
Other Cereal Options Besides RiceFortunately, if you want to skip the rice cereal completely, you can! There is no need to feel like this is the only first food for your baby. Many experts share that any iron-fortified single-grain baby cereal is a great choice, such as baby oatmeal or barley. You can even start with other pureed foods which we discuss later on in this article.
You can even start with other pureed foods which we discuss later on in this article.
Several years ago the recommendation was that parents could feed their babies at four months if they showed readiness signs. But medical advice evolves and this is a guideline that medical experts have changed to give babies the healthiest start possible.
It’s now suggested that it’s best to wait til closer to your baby’s ½ birthday to introduce solids, especially if he is breastfed. There’s really no reason to rush it!
But it’s not just age you want to pay attention to as we know that all babies develop at different rates.
Here are signs to look for that will let you know your baby is ready for solid foods:
- able to sit up supported in a high chair
- has proper head control
- no more tongue thrust
- eager to take a spoon
- are interested in the food that you are eating
If your baby isn’t yet showing these signs, you’ll want to wait a bit longer before starting baby cereal or other solid foods. No need to worry - all babies are ready in their own time! Your baby will continue to get the nutrition they need from their breastmilk or formula so you don’t need to be concerned that they are missing out on important nutrients. If you do have concerns, it’s always best to talk to your pediatrician.
No need to worry - all babies are ready in their own time! Your baby will continue to get the nutrition they need from their breastmilk or formula so you don’t need to be concerned that they are missing out on important nutrients. If you do have concerns, it’s always best to talk to your pediatrician.
Even though your well-meaning grandma may suggest that you mix cereal into your baby’s bottle to help fill them up so they can sleep better, this practice is actually not safe according to the CDC. In fact, they share that it won’t help your baby sleep better anyway. This practice puts your baby at risk for choking or overfeeding and also may encourage parents to start solid foods long before they are ready.
Instead, follow the guideline to not feed your baby solid foods until he or she is at least 5-6 months in age and watch for the other readiness signs mentioned above. At this point you can feed your baby with a spoon and introduce finger foods as they are ready.
RELATED: Starting Solid Foods With Your Baby
How to Introduce Cereal to Your BabyBreastmilk and formula will continue to be your baby’s primary source of nutrition until the age of one, but cereal is a great way to get them started with supplemental nutrition and transition them to solid foods. So how do you go about it?
Here are the steps to follow to give your baby her first single-grain cereal:
- Make sure they meet the recommended readiness signs. This will not only make for a safe feeding experience for your little guy or gal, but it will also be a lot more enjoyable for you.
- Plan to feed your little one after they’ve had a full feeding of breastmilk or formula. This way their tummy will mostly be full which means they’ll likely be happy to try a little cereal. (If you try to introduce solids to a hungry baby they will most likely be uncooperative!) Initially you’ll only feed your baby once per day, and it’s up to you when you want that time to be.
 We recommend choosing a time that your baby is usually in good spirits!
We recommend choosing a time that your baby is usually in good spirits! - Follow the directions on the label of your chosen baby cereal. You don’t need much to start! 1 tablespoon of cereal mixed with breastmilk or formula until it’s a runny consistency will be plenty for those first couple of feedings. If your baby is used to drinking warm milk or formula, you’ll want to use that same temperature of milk to mix with your baby’s food. (This is why we love the Baby’s Brew portable bottle warmer...you can choose your baby’s milk temperature with the push of a button!)
- Be sure your baby is sitting upright. Ideally this would be in a highchair, but they could also be sitting on your lap. You’ll want them to be wearing a bib as a lot your little one’s food won’t make it into their mouth initially.
- Use an infant spoon to feed your baby. Do your best to get the spoon into their open mouth, but just know it’s going to be a bit messy at first as they get the hang of what’s going on.
 It won’t be long before they are opening wide at mealtime!
It won’t be long before they are opening wide at mealtime! - Watch for cues from your baby that show that they are full (or are just are no longer interested). If your baby turns their head, is fussy or won’t open their mouth to eat, it’s time to be “all done!”
And that’s it! You can do another feeding the next day (or you can just do every other day) with the same type of cereal. Be sure to wait three - five days before introducing another food so you can keep an eye out for any allergic reactions. This is the recommendation given by the CDC.
After a couple weeks to a month of successfully feeding your baby once per day you can move to twice per day.
Does cereal have to be your baby’s first food?Some parents choose to start with a different food or may take baby cereal out of their little one’s diet altogether. Starting with other pureed foods instead is totally fine and may even work better for some babies. WebMD shares that both pureed vegetables or fruits are good starter foods and that there’s no rule saying that baby cereals must be first.
Some great first foods, if you want to skip the cereal route, include:
- Avocados
- Bananas
- Blended Red Meat (great source of iron)
- Squash
- Sweet Potatoes
- Pears
Just remember that these all need to be pureed and made into a runny consistency that’s easy for your baby to eat. Mixing with your baby’s warmed breastmilk or formula will help to bring this to a consistency that your baby can manage. You’ll also want to avoid giving your baby any of the top allergen foods such as the ones listed here unless you’ve been given different advice from your doctor. These are best introduced when your baby gets a little older.
Still not sure which food to start with? It can be a bit overwhelming! This is a great conversation to have with your doctor before your baby turns 6 months and they can help guide you on what would be the best option. Whatever you choose, it is sure to be an exciting time for your family as your little guy or gal begins his journey of eating "real" food!
Nursing nipple care | Breast Care
Breastfeeding is good for you and your baby, but it can be a real challenge for the nipples. Check out our tips and tricks to help reduce the pain.
Check out our tips and tricks to help reduce the pain.
Share this information
Sioned Hilton, health visitor, neonatal nurse and lactation consultant:
A mother of three, Sioned Hilton has been supporting families with newborns and young children for over 30 years. She provides advice on breastfeeding and pumping, both in clinics and at home. In addition, Schoned writes articles for parenting magazines, attends conferences, and conducts seminars for attending physicians. nine0003
New mothers often hear: "Breastfeeding doesn't have to be painful." However, in the early days, many are faced with the opposite.
In most women during pregnancy, the nipples enlarge and become more sensitive. When a newborn baby begins to suckle, it creates a certain pressure, and this is a completely new and unfamiliar sensation for a woman (at least for a first-time mother).
Feedings can be prolonged for a long time, sometimes up to an hour, and the child may ask to be breastfed up to 13 times a day. nine0016 1 This sucking, pressure and saliva of the baby can cause sore nipples.
nine0016 1 This sucking, pressure and saliva of the baby can cause sore nipples.
Remember how your lips crack in the wind and sun. The more often you lick them, the more they will dry and become inflamed. Therefore, lips require good hydration to soften, protect and speed up the healing of cracks. The same thing happens with nipples.
However, sore nipples usually don't last more than a couple of weeks and go away as your baby and your breasts get used to breastfeeding. It is important to start nipple care as early as possible to prevent the situation from worsening. Therefore, if your nipples become very inflamed, crack or bleed, contact your doctor as soon as possible. nine0016 2
Prevention is better than cure, so check out our tips.
Check your baby's latch-on
Correct latch is the key to pain-free breastfeeding. When putting the baby to the breast, point the nipple towards his palate. This will allow him to grab the nipple and the part of the areola (the darker skin around the nipple) underneath. When the nipple and part of the breast is in the baby's mouth, feeding is taking place correctly. 3
When the nipple and part of the breast is in the baby's mouth, feeding is taking place correctly. 3
For the first few days, see a lactation consultant or specialist to check for proper latch. He will be able to give you advice on how to solve problems and recommend other feeding positions that will make it less painful for you to feed your baby. nine0003
Check tongue tie
Tongue tie (ankyloglossia) occurs in 4-11% of
newborns. 4 At the same time, the strip of skin that attaches the tongue to the bottom of the mouth - the so-called frenulum - is too short. A child with a shortened frenulum will not be able to open his mouth wide enough to latch onto the breast well, and his tongue will not cover the lower gum when sucking. As a result, the baby will be nervous, and your nipples may become inflamed.
The doctor or lactation consultant must examine the baby to make this diagnosis. The problem of a shortened bridle is solved by a simple undercutting procedure. It is performed by a doctor, and is usually done without blood and does not require anesthesia. Cutting the bridle allows you to restore the normal feeding mechanism almost instantly. nine0016 5
It is performed by a doctor, and is usually done without blood and does not require anesthesia. Cutting the bridle allows you to restore the normal feeding mechanism almost instantly. nine0016 5
Less common in children is a short frenulum of the upper lip. In this case, it is necessary to dissect the skin that connects the upper lip to the gum. A shortened frenum of the tongue or upper lip in a newborn is not always detected during the examination conducted immediately after birth, so if you think that this is what is causing your nipples pain, seek medical advice as soon as possible. 4
Breastfeeding Tips
- Wash your breasts with water only when you shower or bathe. Small bumps on the areola (Montgomery's glands) secrete oil that moisturizes and protects your nipples. Soaps and shower gels can strip away this natural defense, causing dryness and irritation. 6
- Pat the nipples gently with a soft towel or simply let them air dry.
 In the past, women were often advised to rub their nipples to make them stiffer, but thankfully, such advice is a thing of the past! nine0056
In the past, women were often advised to rub their nipples to make them stiffer, but thankfully, such advice is a thing of the past! nine0056 - Do not wash breasts or nipples before feeding. The bacteria found on the surface of the breast actually help the baby's intestinal microflora to develop. 7
- Fresh breast milk helps to heal cracked nipples, 8 so rub a few drops of milk into them before and after feeding.
- Change your bra pads often if they get wet. This will reduce the risk of bacterial and fungal infections, including thrush. nine0016 6
- It is not necessary to increase the intervals between feedings to give the nipples a "rest". For a baby to be healthy and grow well, it needs to be fed on demand. Remember, frequent feeding stimulates and maintains milk production, so keep feeding despite the pain. 9
Healthy teat care products
- Pure lanolin teat cleaner, a natural product derived from sheep's wool.
 It moisturizes and promotes healing of the nipples. This cream is safe for the baby, so it does not need to be washed off before feeding. nine0056
It moisturizes and promotes healing of the nipples. This cream is safe for the baby, so it does not need to be washed off before feeding. nine0056 - Hydrogel Pads* can be applied to sore nipples to relieve pain while feeding and help promote healing. They can even be stored in the refrigerator to enhance the soothing cooling effect.
- Breast pads* fit into the bra. They help prevent nipple irritation from clothing and have air holes to help nipples heal.
- Nursing Bras** are made from breathable material such as cotton or a special fabric that dries quickly and wicks moisture away from sore nipples. nine0056
- Nursing pads* are special silicone pads that fit over the nipples. They have small holes through which milk flows when you are breastfeeding. The pads help to protect the skin underneath and help the baby to better latch on to the nipple by making the nipple stiffer. Do not use nursing pads for a long time. If you have problems or pain, contact your healthcare professional or lactation consultant.
 nine0056
nine0056
When to Seek Medical Care
The soreness should go away as your nipples and baby get used to breastfeeding. It is worth repeating that the main cause of sore nipples is improper grip. If your lactation consultant has not been able to resolve your pain while feeding, see another specialist and a third if necessary.
If nipple pain persists or if you notice unusual symptoms, talk to your doctor. The appearance of white spots or flakes on the nipples may be a sign of thrush, whitish or bluish nipples may indicate a circulation disorder such as Raynaud's disease (vasospasm), and pus and redness indicate an infection. nine0016 2
Literature
1 Kent JC et al. Volume and frequency of breastfeedings and fat content of breast milk throughout the day. Pediatrics. 2006;117(3): e 387-395. - Kent J.S. et al., "Amount and frequency of breastfeeding and fat content of breast milk during the day." Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 2006;117(3):e387-95.
2 Berens P et al. Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine. ABM Clinical Protocol#26: Persistent pain with breastfeeding. Breastfeeding Medicine. 2016;11(2):46-53. - Behrens, P. et al., Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine, AVM Clinical Protocol #26: Persistence of Breastfeeding Pain. Brestfeed Med (Breastfeeding Medicine). 2016;11(2):46-53.
3 Cadwell K. Latching - On and Suckling of the Healthy Term Neonate: Breastfeeding Assessment. J Midwifery & Women's Health. nine0102 2007;52(6):638-42. — Cadwell, K., "Latching and sucking in healthy newborns: evaluation of breastfeeding." F Midwifery Women Health. 2007;52(6):638-642.
4 Segal LM et al. Prevalence, diagnosis, and treatment of ankyloglossia: methodological review. Canadian Family Physician. 2007;53(6):1027-1033. - Segal L.M. et al., Incidence, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Ankyloglossia: A Methodological Review. Canadian Family Physic. 2007;53(6):1027-1033. nine0102
Canadian Family Physic. 2007;53(6):1027-1033. nine0102
5 O'Shea JE et al. Frenotomy for tongue - tie in newborn infants. The Cochrane Library. 2017. - O'Shea J.I. et al., "Dissection of the frenulum in the newborn", The Cochrane Labrery (Cochrane Library), 2017.
6 Jacobs A et al. S3-guidelines for the treatment of inflammatory breast disease during the lactation period. Geburtshilfe und Frauenheilkunde. 2013;73(12):1202-1208. - Jacobs A. et al., "Recommendations S -3 for the treatment of inflammatory diseases of the breast during breastfeeding. Geburtskhilfe und Frauenheilkünde. milk bacterial communities and establishment and development of the infant gut microbiome JAMA pediatrics 2017;171(7):647-654 - P. S. Pannaraj et al. development of the neonatal gut microbiome." JAMA pediatric. 2017;171(7):647-654.
8 Mohammadzadeh A et al. The effect of breast milk and lanolin on sore nipples. Saudi medical journal. 2005;26(8):1231-1234. — Mohammedzade A. et al., "Effects of breast milk and lanolin on sore nipples." Saudi Medical Journal. 2005;26(8):1231-1234.
The effect of breast milk and lanolin on sore nipples. Saudi medical journal. 2005;26(8):1231-1234. — Mohammedzade A. et al., "Effects of breast milk and lanolin on sore nipples." Saudi Medical Journal. 2005;26(8):1231-1234.
9 Kent JC et al. Principles for maintaining or increasing breast milk production. J Obstet , Gynecol , & Neonatal Nurs . 2012;41(1):114-121. - Kent J.S. et al., "Principles for Maintaining and Increasing Milk Production". J Obstet Ginecol Neoneutal Nurs. 2012;41(1):114-121.
Read instructions before use. Consult a specialist about possible contraindications.
* RC № № ФСЗ 2010/07352 dated 19.07.2010
** RU No. ФСЗ 2009/05592 dated 11/25/2009
Breastfeeding in the first month: what to expect
Not sure how to achieve lactation and increase milk production? If you need help, support, or just want to know what to expect, read our first month breastfeeding advice
Share this information
The first weeks of breastfeeding are a very stressful period. If at times you feel like you can't handle it, know that you are not alone. Feeding your baby all day long is completely natural and helps produce breast milk, but can be quite tiring at times. Be patient, think about yourself and remember: after the first month, when milk production stabilizes, it will become easier. nine0003
If at times you feel like you can't handle it, know that you are not alone. Feeding your baby all day long is completely natural and helps produce breast milk, but can be quite tiring at times. Be patient, think about yourself and remember: after the first month, when milk production stabilizes, it will become easier. nine0003
How often should a baby be breastfed?
Babies are born with a small stomach that grows rapidly as milk production increases: in the first week it is no larger than an apricot, and after two weeks it is already the size of a large hen's egg. 1.2 Let the child eat as much as he wants and when he wants. This will help him quickly regain the weight lost after birth and grow and develop further.
“Be prepared to feed every two to three hours throughout the day. At night, the intervals between feedings can be longer: three to four or even five hours, says Cathy Garbin, a recognized international expert on breastfeeding. Some eat quickly and are satiated in 15 minutes, while others take an entire hour to feed. Do not compare your breastfeeding regimen with that of other mothers - it is very likely that there will be nothing in common between them. nine0003
Do not compare your breastfeeding regimen with that of other mothers - it is very likely that there will be nothing in common between them. nine0003
At each feed, give your baby a full meal from one breast and then offer a second one, but don't worry if the baby doesn't take it. When the baby is full, he lets go of his chest and at the same time looks relaxed and satisfied - so much so that he can immediately fall asleep. The next time you feed, start on the other breast. You can monitor the order of the mammary glands during feeding using a special application.
Why does the child always ask for a breast?
The first month is usually the hardest time to breastfeed. But do not think that because the baby is constantly hungry and asks for a breast almost every 45 minutes, then you do not have enough milk. nine0003
In the first month, the baby needs to eat frequently to start and stimulate the mother's milk production. It lays the foundation for a stable milk supply in the future. 3
3
In addition, we must not forget that the child needs almost constant contact with the mother. The bright light and noise of the surrounding world at first frighten the baby, and only by clinging to his mother, he can calm down.
Sarah, mother of three from the UK, confirms: “Crying is not always a sign of hunger. Sometimes my kids just wanted me to be around and begged for breasts to calm them down. Use a sling. Place the cradle next to the bed. Don't look at the clock. Take advantage of every opportunity to relax. Forget about cleaning. Let those around you take care of you. And not three days, but six weeks at least! Hug your baby, enjoy the comfort - and trust your body." nine0003
Do I need to feed my baby on a schedule?
Your baby is still too young for a strict daily routine, so
forget about breastfeeding schedules and focus on his needs.
“Volumes have been written about how to feed a baby on a schedule, but babies don't read or understand books,” Cathy says. - All children are different. Some people can eat on a schedule, but most can't. Most often, over time, the child develops his own schedule.
- All children are different. Some people can eat on a schedule, but most can't. Most often, over time, the child develops his own schedule.
Some mothers report that their babies are fine with scheduled feedings, but they are probably just the few babies who would eat every four hours anyway. Adults rarely eat and drink the same foods at the same time of day - so why do we expect this from toddlers?
Offer your baby the breast at the first sign of hunger. Crying is already the last stage, so be attentive to early signs: the baby licks his lips, opens his mouth, sucks his fist, turns his head with his mouth open - looking for the breast. nine0016 4
What is a “milk flush”?
At the beginning of each feed, a hungry baby actively sucks on the nipple,
thereby stimulating the milk flow reflex - the movement of milk through the milk ducts. 5
“Nipple stimulation triggers the release of the hormone oxytocin,” Cathy explains. “Oxytocin is distributed throughout the body and causes the muscles around the milk-producing glands to contract and the milk ducts to dilate. This stimulates the flow of milk. nine0003
This stimulates the flow of milk. nine0003
If the flushing reflex fails, milk will not come out. This is a hormonal response, and under stress it may not work at all or work poorly. Therefore, it is so important that you feel comfortable and calm when feeding.
“Studies show that each mother has a different rhythm of hot flashes during one feed,” Kathy continues, “Oxytocin is a short-acting hormone, it breaks down in just 30-40 seconds after formation. Milk begins to flow, the baby eats, the effect of oxytocin ends, but then a new rush of milk occurs, the baby continues to suckle the breast, and this process is repeated cyclically. That is why, during feeding, the child periodically stops and rests - this is how nature intended. nine0003
The flow of milk may be accompanied by a strong sensation of movement or tingling in the chest, although 21% of mothers, according to surveys, do not feel anything at all. 5 Cathy explains: “Many women only feel the first rush of milk.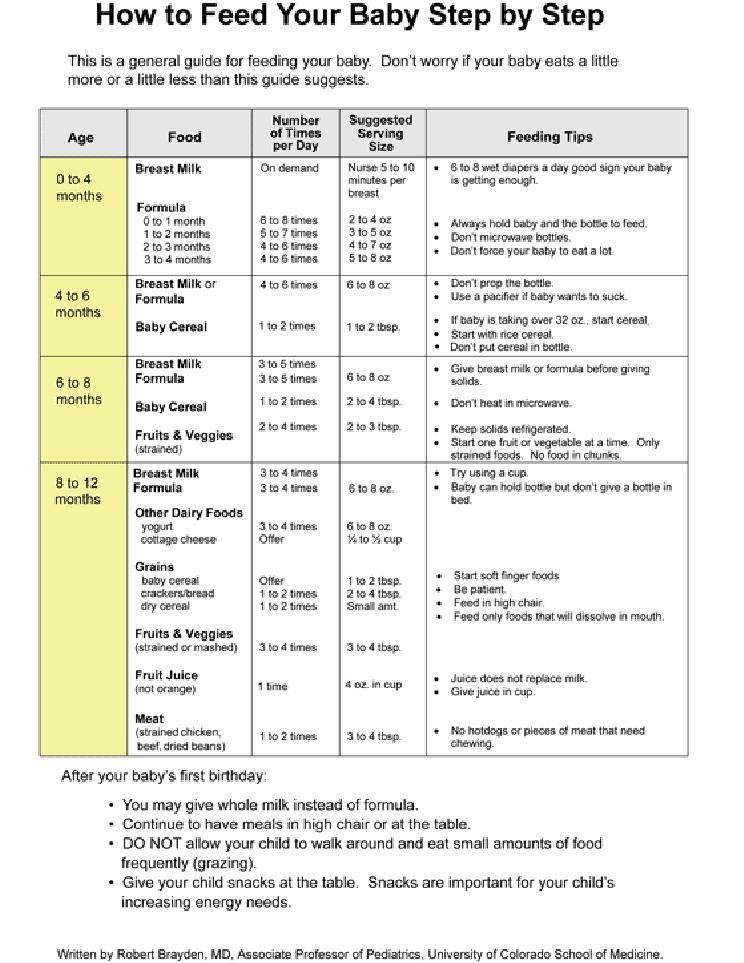 If you do not feel hot flashes, do not worry: since the child eats normally, most likely, you simply do not understand that they are.
If you do not feel hot flashes, do not worry: since the child eats normally, most likely, you simply do not understand that they are.
How can you tell if your baby is getting enough milk?
Since it is impossible to track how much milk a baby eats while breastfeeding, mothers sometimes worry that the baby is malnourished. Trust your child and your body. nine0003
After a rush of milk, the baby usually begins to suckle more slowly. Some mothers clearly hear how the baby swallows, others do not notice it. But one way or another, the child himself will show when he is full - just watch carefully. Many babies make two or three approaches to the breast at one feeding. 6
“When a child has eaten, it is noticeable almost immediately: a kind of “milk intoxication” sets in. The baby is relaxed and makes it clear with his whole body that he is completely full, says Katie, “Diapers are another great way to assess whether the baby is getting enough milk. During this period, a breastfed baby should have at least five wet diapers a day and at least two portions of soft yellow stool, and often more.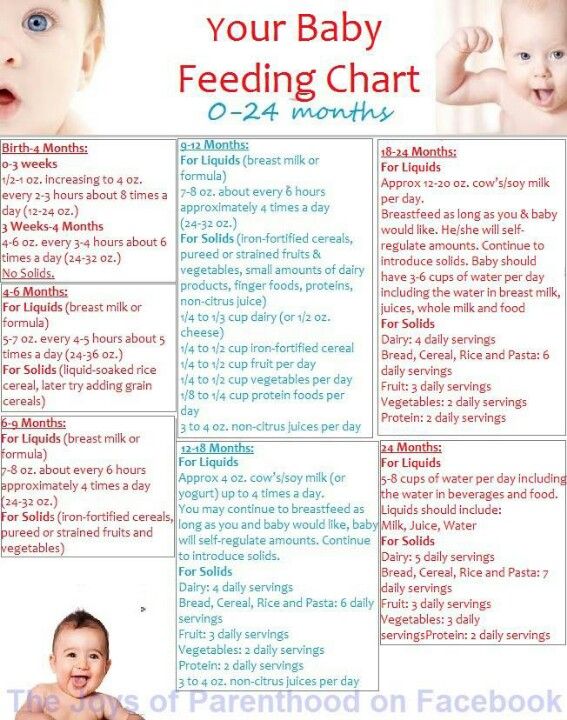 ” nine0003
” nine0003
From one month until weaning at six months of age, a baby's stool (if exclusively breastfed) should look the same every day: yellow, grainy, loose, and watery.
When is the child's birth weight restored?
Most newborns lose weight in the first few days of life. This is normal and should not be cause for concern. As a rule, weight is reduced by 5-7%, although some may lose up to 10%. One way or another, by 10–14 days, almost all newborns regain their birth weight. In the first three to four months, the minimum expected weight gain is an average of 150 grams per week. But one week the child may gain weight faster, and the next slower, so it is necessary that the attending physician monitor the health and growth of the baby constantly. nine0016 7.8
At the slightest doubt or signs of dehydration, such as
dark urine, no stool for more than 24 hours, retraction of the fontanel (soft spot on the head), yellowing of the skin, drowsiness, lethargy, lack of appetite (ability to four to six hours without feeding), you should immediately consult a doctor. 7
7
What is "cluster feeding"?
When a baby asks for a breast very often for several hours, this is called cluster feeding. nine0016 6 The peak often occurs in the evening between 18:00 and 22:00, just when many babies are especially restless and need close contact with their mother. Most often, mothers complain about this in the period from two to nine weeks after childbirth. This is perfectly normal and common behavior as long as the baby is otherwise healthy, eating well, gaining weight normally, and appears content throughout the day. 9
Cluster feeding can be caused by a sharp jump in the development of the body - during this period the baby especially needs love, comfort and a sense of security. The growing brain of a child is so excited that it can be difficult for him to turn off, or it just scares the baby. nine0016 9 If a child is overworked, it is often difficult for him or her to calm down on his own and adult assistance is needed.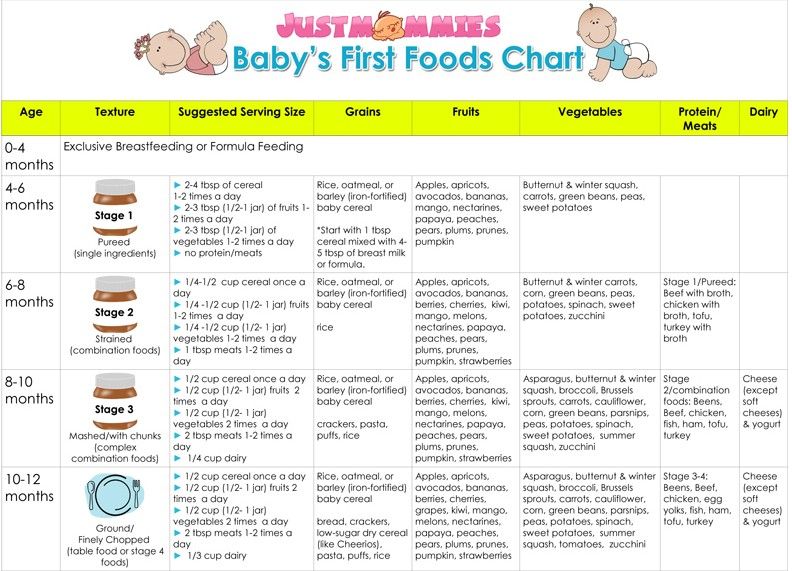 And breastfeeding is the best way to calm the baby, because breast milk is not only food, but also pain reliever and a source of happiness hormones. 10
And breastfeeding is the best way to calm the baby, because breast milk is not only food, but also pain reliever and a source of happiness hormones. 10
“Nobody told me about cluster feeding, so for the first 10 days I just went crazy with anxiety - I was sure that my milk was not enough for the baby,” recalls Camille, a mother from Australia, “It was a very difficult period . I was advised to pump and supplement until I finally contacted the Australian Breastfeeding Association. There they explained to me what was happening: it turned out that it was not about milk at all. nine0003
Remember, this is temporary. Try to prepare dinner for yourself in the afternoon, when the baby is fast asleep, so that in the evening, when he begins to often breastfeed, you have the opportunity to quickly warm up the food and have a snack. If you are not alone, arrange to carry and rock the baby in turns so that you have the opportunity to rest. If you have no one to turn to for help and you feel that your strength is leaving you, put the baby in the crib and rest for a few minutes, and then pick it up again. nine0003
nine0003
Ask your partner, family and friends to help you with household chores, cooking and caring for older children if you have any. If possible, hire an au pair. Get as much rest as possible, eat well and drink plenty of water.
“My daughter slept a lot during the day, but from 23:00 to 5:00 the cluster feeding period began, which was very tiring,” recalls Jenal, a mother from the USA, “My husband tried his best to make life easier for me - washed, cleaned, cooked, changed diapers, let me sleep at every opportunity and never tired of assuring me that we were doing well. nine0003
If you are concerned about the frequency of breastfeeding, it is worth contacting a specialist. “Check with a lactation consultant or doctor to see if this is indicative of any problems,” recommends Cathy. “Resist the temptation to supplement your baby with formula (unless recommended by your doctor) until you find the cause. It may not be a matter of limited milk production at all - it may be that the child is inefficiently sucking it.
When will breastfeeding become easier? nine0028
This early stage is very special and does not last long. Although sometimes it seems that there will be no end to it, rest assured: it will get easier soon! By the end of the first month, breast milk production will stabilize, and the baby will become stronger and learn to suckle better. 2.3 Any problems with latch on by this time will most likely be resolved and the body will be able to produce milk more efficiently so inflammation and leakage of milk will start to subside.
“The first four to six weeks are the hardest, but then things start to get better,” Cathy assures. It just needs to be experienced!” nine0003
The longer breastfeeding continues, the more benefits it brings, from saving on formula and improving sleep quality 11-13 to boosting your baby's immune system 14 and reducing your risk of developing certain types of cancer. 15
“When you feel like you're pushing yourself, try to go from feed to feed and day to day,” advises Hannah, a UK mom. “I was sure I wouldn’t make it to eight weeks. And now I have been breastfeeding for almost 17 weeks, and I dare say it is very easy.” nine0003
“I was sure I wouldn’t make it to eight weeks. And now I have been breastfeeding for almost 17 weeks, and I dare say it is very easy.” nine0003
Read the resource Breastfeeding After the First Month: What to Expect Readings 1 Naveed M et al. An autopsy study of relationship between perinatal stomach capacity and birth weight. Indian J Gastroenterol .1992;11(4):156-158. - Navid M. et al., Association between prenatal gastric volume and birth weight. Autopsy. Indian J Gastroenterol. 1992;11(4):156-158. 2 Neville MC et al. Studies in human lactation: milk volumes in lactating women during the onset of lactation and full lactation . Am J Clinl Nutr . 1988;48(6):1375-1386. at the beginning and at the peak of lactation." Am F Clean Nutr. 1988;48(6):1375-1386. 3 Kent JC et al. 4 Australian Breastfeeding Feeding cues ; 2017 Sep [ cited 2018 Feb ]. - Australian Breastfeeding Association [Internet], Feed Ready Signals; September 2017 [cited February 2018] 5 Kent JC et al. Response of breasts to different stimulation patterns of an electric breast pump. J Human Lact . 2003;19(2):179-186. - Kent J.S. et al., Breast Response to Different Types of Electric Breast Pump Stimulation. J Human Lact (Journal of the International Association of Lactation Consultants). 6) Kent JC et al . Volume and frequency of breastfeedings and fat content of breast milk throughout the day. Pediatrics. 2006;117(3): e 387-395. - Kent J.S. et al., "Amount and frequency of breastfeeding and fat content of breast milk during the day." Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 2006;117(3):e387-95. 7 Lawrence RA, Lawrence RM. Breastfeeding: A guide for the medical profession. 7th ed. Maryland Heights MO, USA: Elsevier Mosby; 2010. 1128 p . - Lawrence R.A., Lawrence R.M., "Breastfeeding: A guide for healthcare professionals." Seventh edition. Publisher Maryland Heights , Missouri, USA: Elsevier Mosby; 2010. P. 1128. 8 World Health Organization. [Internet]. Child growth standards; 2018 [cited 2018 Feb] - World Health Organization. 9 Australian Breastfeeding Association . [ Internet ]. Cluster feeding and fussing babies ; Dec 2017 [ cited 2018 Feb ] - Australian Breastfeeding Association [Internet], Cluster Feeding and Screaming Babies; December 2017 [cited February 2018]. nine0102 10 Moberg KU, Prime DK. Oxytocin effects in mothers and infants during breastfeeding. Infant . 2013;9(6):201-206.- Moberg K, Prime DK, "Oxytocin effects on mother and child during breastfeeding". Infant. 2013;9(6):201-206. 11 U.S. Department of Health & Human Services [Internet]. Surgeon General Breastfeeding factsheet; 2011 Jan 20 [cited 2017 Feb] - Department of Health and Human Services [Internet], "Breastfeeding Facts from the Chief Medical Officer", Jan 20, 2011 [cited Feb 2017] 12 Kendall-Tackett K et al. 13 Brown A, Harries V. Infant sleep and night feeding patterns during later infancy: Association with breastfeeding frequency, daytime complementary food intake, and infant weight. Breast Med . 2015;10(5):246-252. - Brown A., Harris W., "Night feedings and infant sleep in the first year of life and their association with feeding frequency, daytime supplementation, and infant weight." Brest Med (Breastfeeding Medicine). 2015;10(5):246-252. 14 Hassiotou F et al. Maternal and infant infections stimulate a rapid leukocyte response in breastmilk. Principles for maintaining or increasing breast milk production. 2012;41(1):114-121. - Kent J.S. et al., "Principles for Maintaining and Increasing Milk Production". J Obstet Ginecol Neoneutal Nurs. 2012;41(1):114-121. nine0102
Principles for maintaining or increasing breast milk production. 2012;41(1):114-121. - Kent J.S. et al., "Principles for Maintaining and Increasing Milk Production". J Obstet Ginecol Neoneutal Nurs. 2012;41(1):114-121. nine0102  2003;19(2):179-186.
2003;19(2):179-186.  [Internet]. Child Growth Standards 2018 [cited February 2018]. nine0102
[Internet]. Child Growth Standards 2018 [cited February 2018]. nine0102 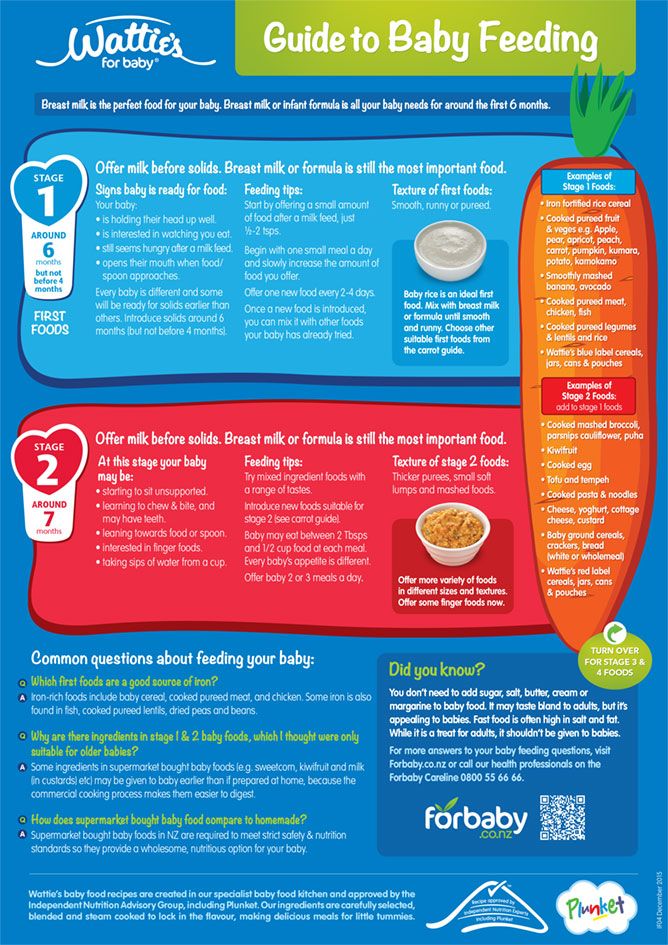 The effect of feeding method on sleep duration, maternal well-being, and postpartum depression. clinical lactation. 2011;1;2(2):22-26. - Kendall-Tuckett, K. et al., "Influence of feeding pattern on sleep duration, maternal well-being and the development of postpartum depression." Clinical Lactation. 2011;2(2):22-26.
The effect of feeding method on sleep duration, maternal well-being, and postpartum depression. clinical lactation. 2011;1;2(2):22-26. - Kendall-Tuckett, K. et al., "Influence of feeding pattern on sleep duration, maternal well-being and the development of postpartum depression." Clinical Lactation. 2011;2(2):22-26. 











