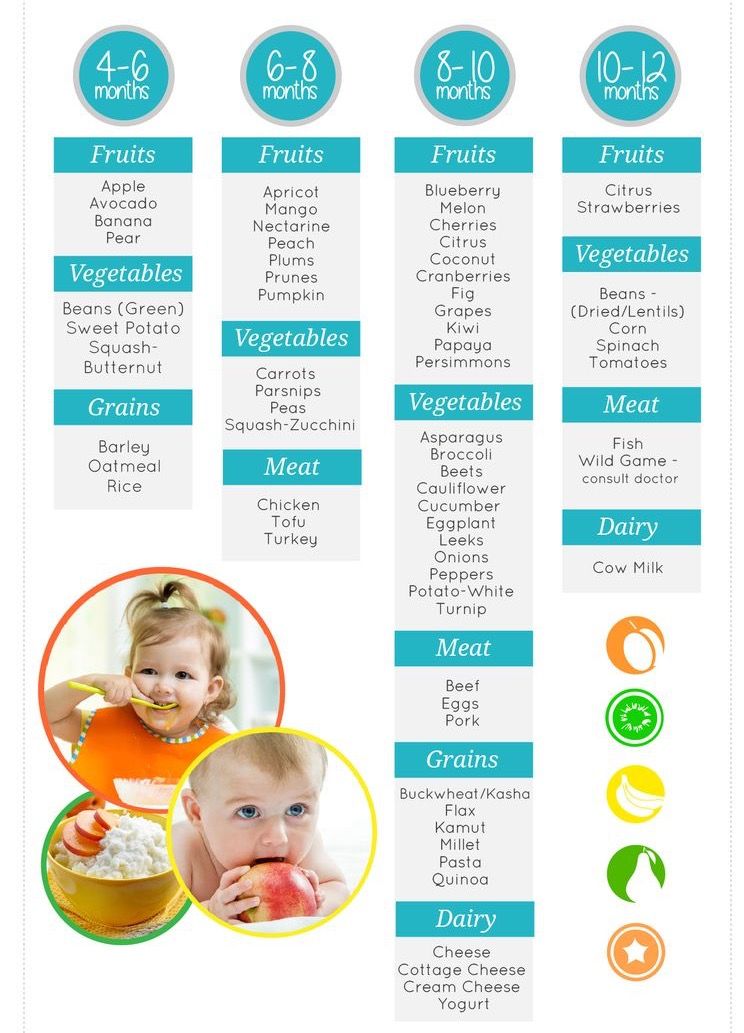
Feeding multiple babies
Feeding multiple babies | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
Feeding multiple babies | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content7-minute read
Listen
Feeding multiple babies can be a challenge at first.
Midwives, lactation consultants (health professionals that help you with breast feeding) or community health nurses will help you.
The links in this article will provide further advice and resources. You can also ask for help from family and friends. Make sure to rest as much as you can.
When feeding multiple babies, it's important to treat each baby as an individual. Try not to compare siblings. Decisions about their feeding patterns and how they are growing depend on:
- the sex of each baby
- the weight of each baby
- when each baby was born
Many multiple babies are premature and born very small, so you may need help with feeding them.
If they are in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU), they may be fed at first through a tube. This tube runs through the nose, and carries the milk straight to their stomach.
When feeding, using different positions, pillows and other equipment can make it easier to feed twins, triplets or other multiples. It may also be helpful to keep records of every feed, especially at first.
Breastfeeding multiple babies
Breastfeeding is a natural way to feed your baby. Breast milk contains all the nutrients your baby needs to develop and grow for their first 6 months. It is easily digested, it's convenient and it's economical. Breast milk is especially important for low weight or premature babies. This is because it also helps them to fight infection.
Your babies may not be able to breastfeed at first. You may choose to express and store your breast milk to feed them later.
Breastfeeding and expressing helps to release the hormone oxytocin. This helps bonding between mother and baby. This is especially important if you're separated from your babies for a while.
This is especially important if you're separated from your babies for a while.
Mothers of multiple babies often worry that they can’t make enough milk. But it is possible to breastfeed multiple babies. Breastfeeding works on 'supply and demand'. The more often your babies feed (or you express), the more milk you will produce. Keep up a good supply by alternating babies between each breast.
How to breastfeed 3 or more babies
Breastfeed your babies as soon as you can. It is possible to breastfeed twins at the same time. There are different positions that can help with feeding 2 babies at once.
- You can use the 'twin football hold', with one baby under each arm.
- The 'laid back' position may be used as well. This is where you lie back and have both babies lying on your tummy.
- You can use the parallel hold as they get older. This is where both babies lie in the same direction across your body.
Your lactation consultant can advise you about different positions. You can experiment with different positions to find out what you are most comfortable with.
You can experiment with different positions to find out what you are most comfortable with.
Some women choose to breastfeed their babies separately, especially at the beginning.
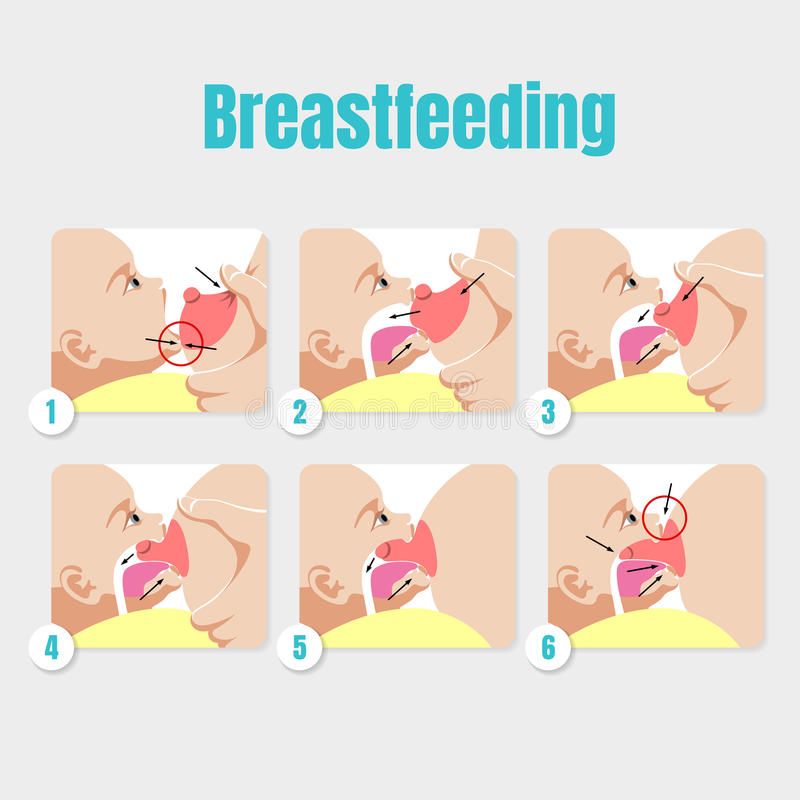
It’s important to make sure each baby is feeding well and attached properly to the breast. When a baby attaches and sucks deeply, it helps them drain the breast and it helps avoid sore nipples.
Breastfeeding 3 or more babies is a little trickier. You will have to learn how to express milk and will ideally need someone else to help you.
Focus on mastering the ability to feed 2 babies at the same time. Then, the third and/or fourth baby can be bottle fed.
Bottle feeding can be done with expressed breast milk or with formula. This can be done when you’ve finished feeding the first 2. Otherwise, someone else can feed them at the same time. Rotate the order of the babies for the next feed, to have time to bond with each baby.
Breastfeeding 3 or more babies can take a lot of time and patience. Accept all the support you can. Remember, even if you don’t breastfeed for long, some breastmilk is better than none for your babies.
Accept all the support you can. Remember, even if you don’t breastfeed for long, some breastmilk is better than none for your babies.
Formula feeding multiple babies
Many parents of multiple babies introduce formula feeding at some stage. It may also be necessary if you don’t produce enough breast milk or if you have trouble breastfeeding one or more of your babies.
Some parents decide to use a combination of breast and formula feeding. Introducing formula feeds can affect your breastmilk supply. If you decide to stop breastfeeding altogether, it is hard to go back later.
There is a range of different formulas available. There are formulas that are suitable for small or premature babies. Follow the directions on the label and ensure to keep all the equipment sterile. Have separate, clearly labelled bottles for each baby. This way, you can keep track of how much formula they are taking.
Timing multiple babies' feeds
Feeding multiple babies is a skill that takes time to learn. It will become easier, and you may be able to feed your babies at the same time if you would like. Some mothers choose to feed them separately, especially at night.
It will become easier, and you may be able to feed your babies at the same time if you would like. Some mothers choose to feed them separately, especially at night.
Each baby will have their own feeding patterns. Some mothers feed the baby that wakes up first. Then, they gently wake up the next baby to feed them. But sometimes a sleepy baby may not feed so well.
An alternative is to breastfeed one baby, then use expressed breastmilk or formula for the next baby. This means that someone else can bottle feed them while you rest.
Multiple babies often have different birth weights and nutritional needs. You may need to adjust your feeding schedule to suit one or more of the babies. This is because as they grow, their needs change. You can be advised about this by your:
- midwife
- lactation consultant
- community nurse
There is no right or wrong way to time feeds for multiple babies. You will eventually find a routine that works for you, your babies and your support network.
Looking after yourself
Feeding multiple babies can be hard work, especially at first. It is normal for parents of multiples to feel constantly exhausted and stressed. Mothers of multiples are much more likely to suffer postnatal depression than mothers of single babies.
Make sure you look after yourself by:
- eating healthily
- resting whenever you can
- finding and accepting support
For more information on postnatal depression or anxiety, help and support, call the Perinatal Anxiety and Depression Australia (PANDA) helpline on 1300 726 306.
The Australian Multiple Birth Association sells equipment for feeding multiples. They can also put you in touch with other mothers in a similar situation.
The Australian Breastfeeding Association sells books and CDs on breastfeeding multiples.
For help with breastfeeding, contact your midwife or lactation consultant. You can also call the Breastfeeding Helpline on 1800 mum 2 mum (1800 686 268).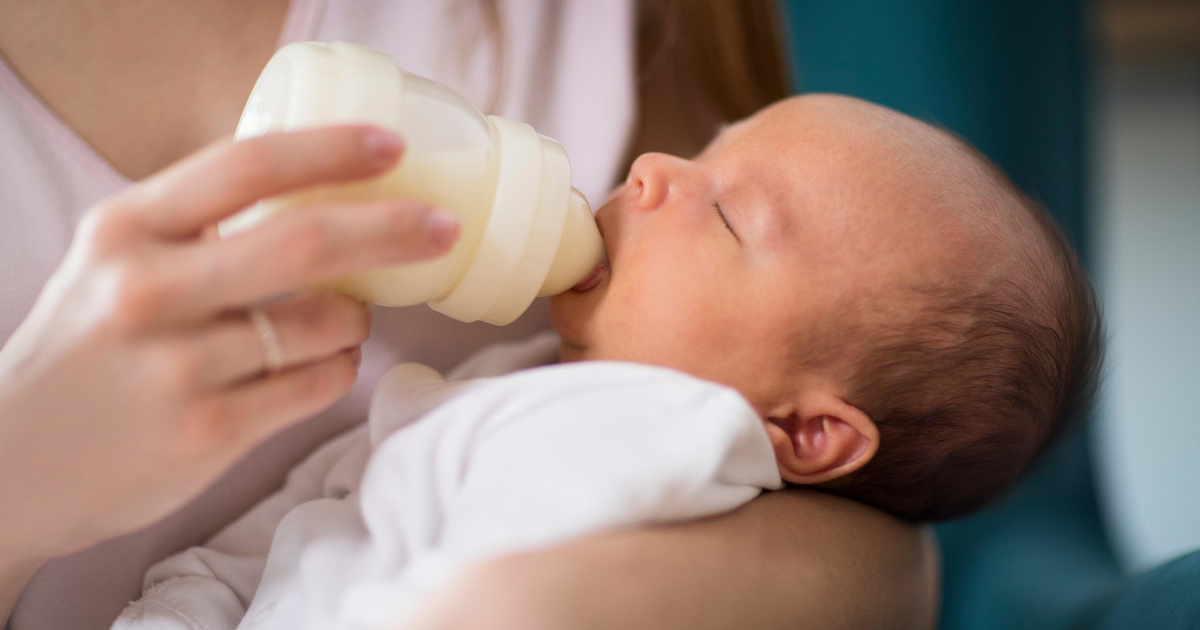
Speak to a maternal child health nurse
Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436 or video call. Available 7am to midnight (AET), 7 days a week.
Sources:
Australian Multiple Birth Association (Feeding multiples), Australian Breastfeeding Association (Breastfeeding twins), The Royal Hospital for Women (Formula feeding for a neonate), The Royal Women’s Hospital (Breast milk fortifier), Breastfeeding Twins and Triplets UK (Combination Feeding Twins and Multiples)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: June 2022
Back To Top
Related pages
- Twins, triplets and multiples
Need more information?
Multiple pregnancy (triplets or more)
Learning you're pregnant with triplets or more can be a shock, but overall, most parents find having multiple babies to be a positive experience.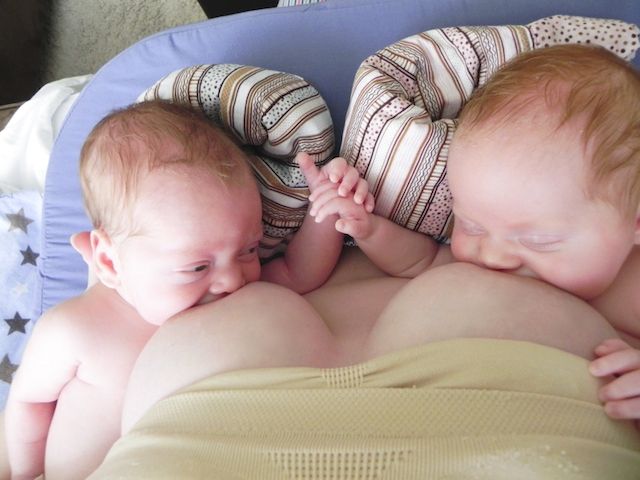
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Multiple birth - triplets or more
If you are pregnant with triplets or more, the birth will need careful planning. The main risk is that your babies will be born prematurely. Find out more here.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Neonatal intensive care unit (NICU)
Learn about the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU), where premature or very ill babies are admitted for highly specialised hospital care.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
Need further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Subscribe to newsletters
- Sign in
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.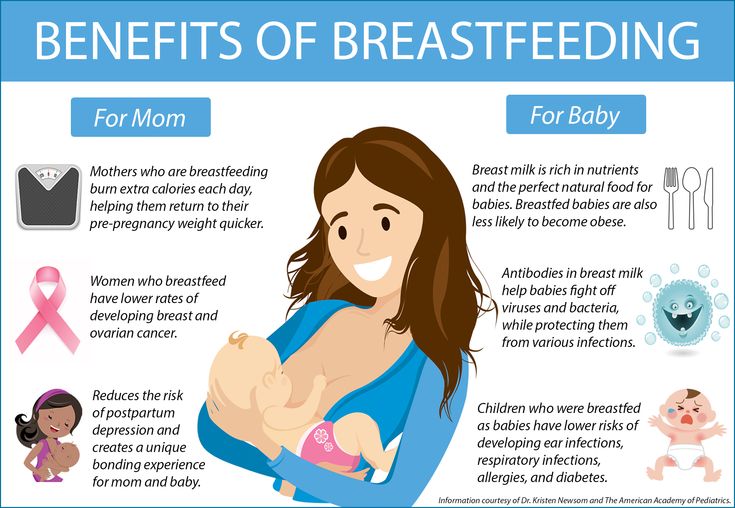
Healthdirect Australia acknowledges the Traditional Owners of Country throughout Australia and their continuing connection to land, sea and community. We pay our respects to the Traditional Owners and to Elders both past and present.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.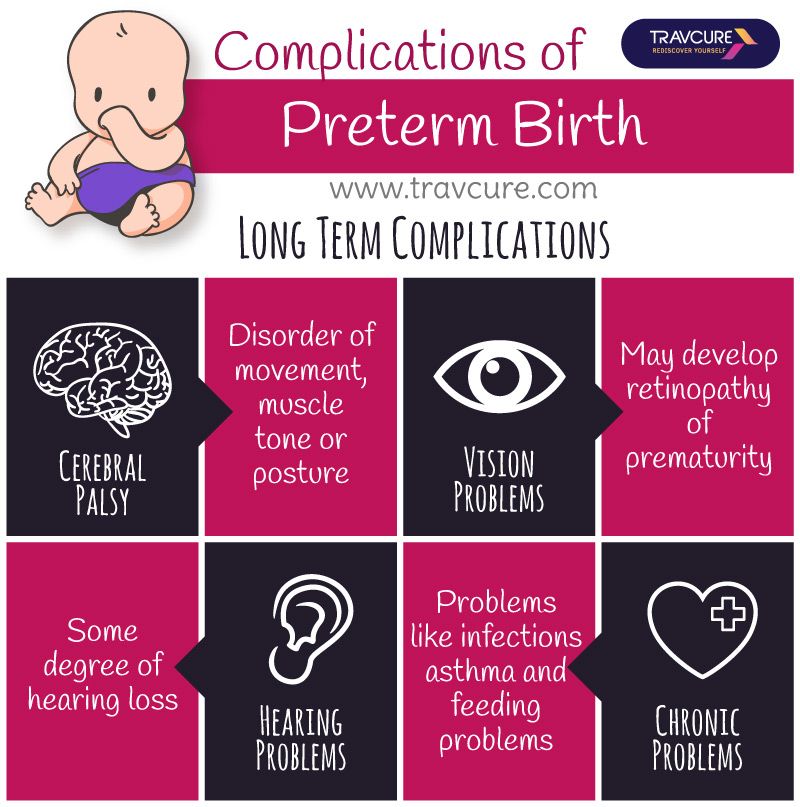
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Feeding twins and multiples - NHS
Feeding will take up a lot of your time in the first few months of your babies' lives.
Whether you breastfeed or formula feed, you'll need to create a routine that suits you and your babies.
Some mothers can feed 2 babies at the same time, while some prefer to feed 1 after the other.
Others feed whenever their babies seem hungry (on demand).
If one baby seems to be feeding more or less than the other, or you have any other concerns about your babies, talk to your health visitor.
Your health visitor can tell you where to find your nearest baby clinic.
Some health visitors will visit you regularly at home to keep an eye on your babies' progress.
Breastfeeding twins or more
It's important not to be put off breastfeeding because you're having more than 1 baby.
Breastfeeding is a great way to soothe your babies and helps you build a strong bond with them.
It's perfectly possible to breastfeed twins, triplets or more. Lots of twins are breastfed until they start eating solid foods.
You may like to try a few breastfeeding positions to see which suits you best.
You'll get support with breastfeeding at the hospital and also when you take your babies home.
The benefits of breast milk for your babies are the same as for single babies.
But as multiple babies are more likely to be born prematurely, there are extra benefits.
Breastfeeding premature twins
Breast milk is better for premature babies as their gut is immature and it's easier for them to tolerate and digest.
Breast milk also contains proteins and antibodies to protect your babies against infections.
If your babies are very tiny or sick when they're born, you may need to express your breast milk to begin with.
Your expressed milk may be fed to your babies through a thin tube that passes through the nose and into the stomach.
Visit the Twins Trust charity's website for more information on breastfeeding twins or more.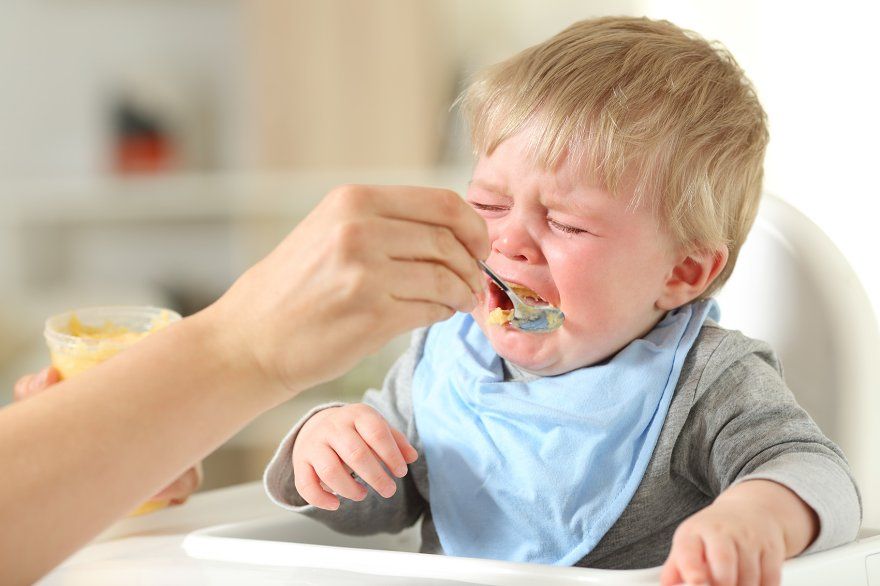
Formula feeding multiples
You may need to combine formula feeding with breastfeeding if, for example, you have triplets or more, or you may choose to only formula feed your babies.
Formula feeding is more expensive than breastfeeding when you have twins or more.
But it does mean that other people can help with feeding your babies.
As with breastfeeding, you'll need to decide whether you're going to feed your babies together or separately.
Bottles need to be freshly prepared for each feed. This can be quite time consuming with twins or more, so you may want to ask your partner or someone else to help with this.
As with breastfeeding, formula feeding your babies can help you build a close and loving bond.
Hold your babies close during feeds, look into their eyes and talk to them.
Learn to notice their cues when they want to be fed and when they have had enough.
Visit the Twins Trust website for more information on formula feeding twins or more.
Weaning twins on to solids
When your babies are around 6 months old, you can give them their first solid foods.
It's not unusual for 1 baby to be ready to begin solids before the other.
If your babies were born prematurely, your health visitor can give you advice on the best time to start solids.
Find out more about your baby's first solid foods
Visit the Multiple Births Foundation website for a publication about feeding twins, triplets or more.
Video: breastfeeding twins
In this video, a breastfeeding support specialist gives advice on how to breastfeed twins.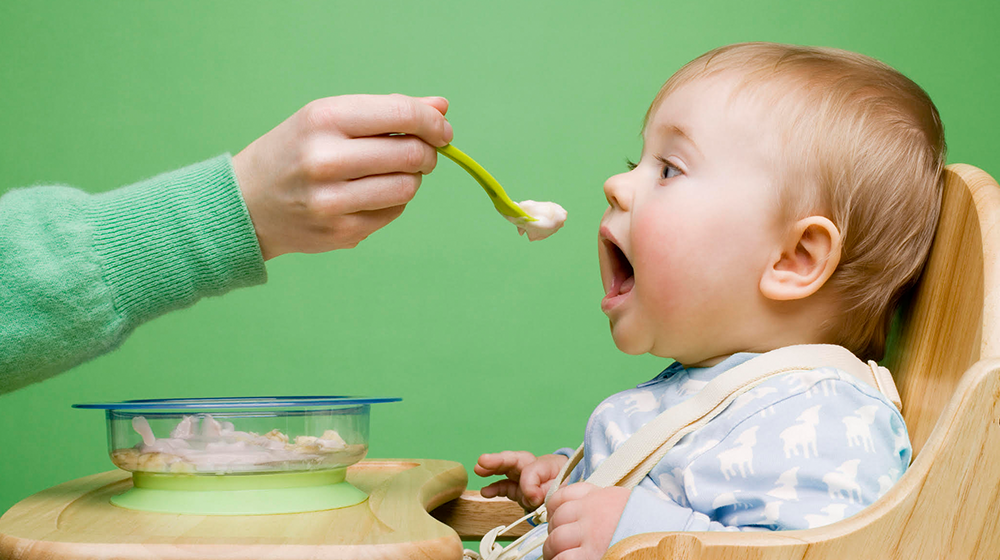
Media last reviewed: 1 September 2021
Media review due: 1 September 2024
Page last reviewed: 30 November 2022
Next review due: 30 November 2025
Tandem feeding
Reviewer Kovtun Tatiana Anatolievna
3359 views
November 10, 2021
What if the mother finds out about the pregnancy, when the older baby is still breastfeeding?! If earlier this question had an unequivocal answer - we wean the baby from the breast, now there are more and more supporters of tandem feeding.
What is tandem feeding
Tandem feeding is the breastfeeding of two children with a small difference in age, most often of the same age.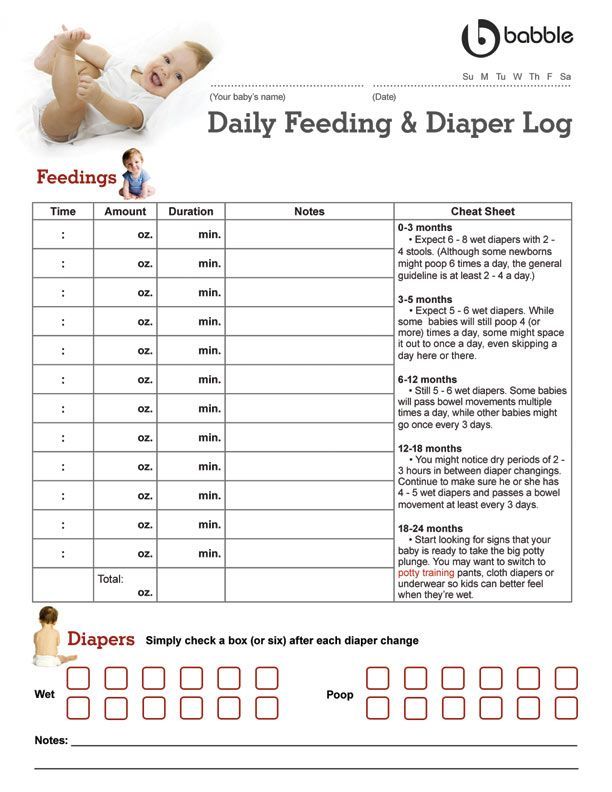
The trend of tandem feeding is due to the fact that the popularity of long-term breastfeeding has increased. And if earlier the baby was weaned from the mother's breast a year, now more and more mothers give their milk to the baby up to 2 and even up to 3 years.
It may seem that it is impossible to feed two or even three children of different ages at the same time, or at least very difficult, but in fact it is not. Lactation persists even with the onset of a new pregnancy.
When deciding whether to continue breastfeeding during pregnancy, you should first consult with an obstetrician-gynecologist. The doctor will tell you if there are currently any contraindications to continuing breastfeeding on the part of the health of the mother and the unborn child. If there are no contraindications, then everything is in your hands.
Organization of feeding
If the difference between the children is 2 years or less, then they need to be fed as twins, without highlighting the firstborn as the eldest.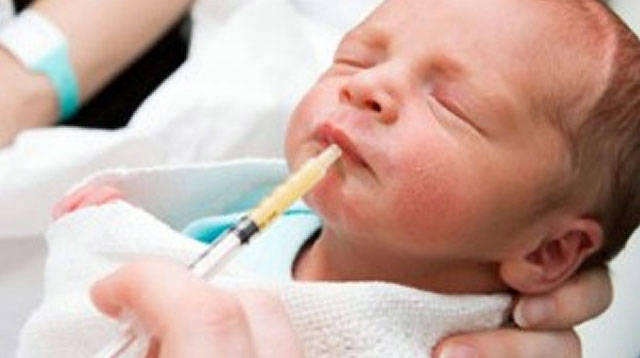 After the birth of a brother or sister, he may regress in his development and behavior for a while, begin to hang on his chest for a long time, ask for hands, and so on - and it is very important not to deprive him of your care and milk, so as not to provoke jealousy and aggression towards junior.
After the birth of a brother or sister, he may regress in his development and behavior for a while, begin to hang on his chest for a long time, ask for hands, and so on - and it is very important not to deprive him of your care and milk, so as not to provoke jealousy and aggression towards junior.
Benefits of tandem feeding
- You don't deprive your older baby of milk.
- No abrupt weaning.
- The older child will help to easily cope with the stagnation of milk and prevent lactostasis.
- The degree of childish jealousy is decreasing.
- No fight for mom.
- Children get sick less.
Disadvantages of tandem feeding
- A big load on the mother's body, it is necessary to eat well and get enough rest, take a multivitamin complex for pregnant and lactating women on the recommendation of a doctor.
- It is difficult to prioritize the feeding of children if the age difference is large.

- Mom is practically "attached" to children.
Lifehacks
If you do not want to feed the children at the same time, then organize a place for feeding the youngest child in such a way that you can safely play with the older one at this time. While the little one is eating, you can read a book with the older one, collect puzzles or work out with sorters and pyramids. It is important that the older child does not feel abandoned when the younger one is feeding. Then he will not interfere and will know that this is a special time when his mother plays with him, and how long it will last depends on him and his behavior.
Always feed the youngest child first and then the oldest. This sequence is important so that the newborn receives enough milk and, accordingly, the nutrients he needs.
If the eldest at the time of the birth of the youngest child is more than 2 years old, then a number of restrictions can be safely introduced:
- his mother does not feed him on the street and in public places;
- only feedings after waking up, at night and before bedtime, including daytime ones, are saved;
- the breast is not used as a consolation if the baby has fallen or is upset;
- all attempts to touch or play with the chest must be stopped.

The older child is already able to switch and calm down without a mother's breast. Teach him to be distracted, mother's breasts are not a toy and not an activity when you are bored.
With tandem feeding, it is very important to pay attention to each of the babies. Every child should have a time when he is alone with his mother. Agree with your husband or grandmother that every day they work with the youngest for an hour and a half, while you walk or play with the older fidget.
Tandem feeding is very exhausting, especially in the first 3-4 months after the birth of the youngest child. Such mothers are more likely to experience postpartum depression, which requires correction. Carefully monitor your condition, do not refuse the help of loved ones, find time for yourself.
Tandem Feeding Rules
- Follow the order - first the youngest, then the oldest.
- Do not let an older child empty a full breast.
- Offer to the elder first the breast that the newborn suckled before.

- Create rules for the firstborn and follow them.
Deciding on a tandem is very difficult, it is important to understand that this is both a physiologically and psychologically difficult process that will last not a day or two, but if you feel the strength to feed the weather, and your doctor has nothing against it, then you will definitely succeed.
Reviewer Kovtun Tatiana Anatolievna
Scientific adviser to PROGRESS JSC, Candidate of Medical Sciences
All expert articles
Breast milk feeding on demand
You can often hear from a nursing mother: "I feed on demand, my baby requires a breast every 3.5 hours." Or: “I have always fed on demand. In a year, we already had 1 feeding in the evening, and my child calmly refused to breastfeed.
Before talking about the demand of the child, it is necessary to find out what modern women mean when they say - "I breastfeed."
Modern mothers consider breastfeeding necessary for feeding their baby. Just for feeding. Breast milk is food, the mother supplies the baby with the nutrients necessary for growth and development. When a baby suckles at the breast, he eats. Breastfeeding makes sense only as a process of supplying proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and microelements.
During suckling, the baby receives the nutrients it needs with mother's milk. This is the absolute truth. There is another unconditional truth, which is not given any importance in modern society, it is not taken into account and is not considered. Breastfeeding for a child is communication with the mother. We need to figure out how the child understands feeding on demand? Can he understand anything at all? Is there any difference for him how he is fed, for 15-20 minutes after 3. 5 hours or in some other way?
5 hours or in some other way?
What is on-demand feeding
On-demand feeding of a newborn baby means putting it to the breast for every squeak or search. Squeak and search movements in newborns, even as early as the second or third day of life, begin to appear much more often than after 3.5 or 2.5 hours. The need for attachments increases rapidly, and by the 10-12th day of life, the need to attach to a child may occur 15-16 or more times a day. Applications vary in duration. The baby can fall asleep and sleep while sucking for, for example, 1.5-2 hours. Can release the breast after 1-2 minutes. And then ask her again. Why does a child need such frequent contact with his mother's breast?
That's why. Being in the mother's belly, in a calm, familiar environment, listening to the noises of the mother's body, being in a warm, cramped, confined space, the baby sucked his fist, fingers, loops of the umbilical cord, swallowed amniotic fluid. Learned to suck and swallow. After birth, experiencing discomfort for any, the most insignificant reason, the baby tries to get rid of it. You can get rid of discomfort by getting into the usual conditions of a comfortable stay. The only place where the baby after birth can feel the sensations familiar to him is in the arms of the mother. The only familiar action is sucking. The only familiar taste and smell is the taste and smell of milk and lube in the areola. Milk and lubricant have an odor and taste similar to the taste and smell of amniotic fluid. Therefore, experiencing discomfort, the baby squeaks, or begins to look for an object to suck with his mouth. Ideally, it is immediately applied to the chest. The baby becomes warm, cramped, he hears the beating of his mother's heart, breathing, grumbling in the intestines, he sucks and feels the familiar taste and smell. If such an action happens constantly, the baby gains confidence, no matter what happens, he will solve all his problems with his mother. The place of comfort is now under the breast, and you can suck on the breast.
After birth, experiencing discomfort for any, the most insignificant reason, the baby tries to get rid of it. You can get rid of discomfort by getting into the usual conditions of a comfortable stay. The only place where the baby after birth can feel the sensations familiar to him is in the arms of the mother. The only familiar action is sucking. The only familiar taste and smell is the taste and smell of milk and lube in the areola. Milk and lubricant have an odor and taste similar to the taste and smell of amniotic fluid. Therefore, experiencing discomfort, the baby squeaks, or begins to look for an object to suck with his mouth. Ideally, it is immediately applied to the chest. The baby becomes warm, cramped, he hears the beating of his mother's heart, breathing, grumbling in the intestines, he sucks and feels the familiar taste and smell. If such an action happens constantly, the baby gains confidence, no matter what happens, he will solve all his problems with his mother. The place of comfort is now under the breast, and you can suck on the breast.
This whole process is justified from a biological point of view. A newborn child does not feel the feeling of hunger, this feeling is not formed in him. It will begin to form at about two months of age. How to feed a creature that does not experience hunger ?! How to encourage him to take some action to get food? This can be done only at the expense of some other incentives. This stimulus for the newborn is constant bodily discomfort, thanks to which he wants to suckle all the time! The most intense, frequent and prolonged sucking in infants is observed in the first two or three months of life. It is in these first months that the main weight gain of the baby occurs.
Feeding in the first month
Baby falls asleep with the breast in his mouth, sleeps sucking for a while. Falling asleep deeply, lets go of the chest. After sleeping for a while, he wakes up, and is applied on waking. After sleep, he can stay awake for some time, for example, an hour and a half. During wakefulness, he may feel discomfort 2-3 times, for example, from a completely natural desire to pee, and having called his mother for help, having kissed for a couple of minutes, he will do his deeds.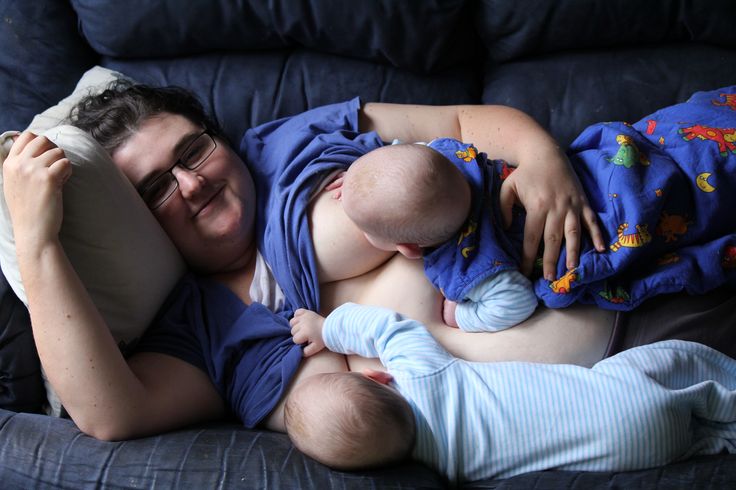 Then he will want to sleep, feel discomfort and, kissing his chest, will again fall asleep sucking. After some time, he will wake up and attach again. Then again a little "walk". And after some time, he will fall asleep at the chest again.
Then he will want to sleep, feel discomfort and, kissing his chest, will again fall asleep sucking. After some time, he will wake up and attach again. Then again a little "walk". And after some time, he will fall asleep at the chest again.
The daytime naps of a one-month-old infant feeding on demand vary in duration and number. There can be 4-6 dreams during the day, and they can last from 5-15 minutes to 2-2.5 sometimes 3 hours. "Around" each dream, the baby is applied to the chest, and applied between dreams several times. At night, the child falls asleep at the breast. Usually in the early morning hours, he begins to fuss and apply. In the morning, he almost never fully wakes up. The baby sleeps, from time to time, sucking on his mother's breast. Waking up in the morning, the baby is again applied to the chest. If you count all the attachments that have happened in a baby of one month of age, then approximately 16-20 attachments are obtained. This is how a newborn human cub behaves if it is given the opportunity to behave in accordance with physiological and psychological needs, which, by the way, are genetically determined. The child of the first months of life does not separate his personality from the personality of the mother and from her breast. Mom and her breasts, and everything connected with them, are the universe of the baby and himself.
The child of the first months of life does not separate his personality from the personality of the mother and from her breast. Mom and her breasts, and everything connected with them, are the universe of the baby and himself.
In most cases, a modern woman, being afraid to “accustom a child to hands”, strives to limit his requests for sucking. A pacifier and a bottle of tea or water come to her aid in this matter. They, too, can be sucked ... The need for sucking seems to be satisfied. But only the need for communication with the mother during suckling is not satisfied, the peculiar chain of mutual assistance and cooperation between mother and baby is destroyed, the formation of maternal affection and concentration is disrupted. Is the difference in the two actions noticeable to the reader: the baby cried, the mother took him, put him to her chest and started rocking him, or gave him a pacifier and started rocking the stroller, even with the words “Why are you crying, my sun?”
The modern woman who gives a pacifier and pumps a stroller is not a bad person deliberately harming an infant.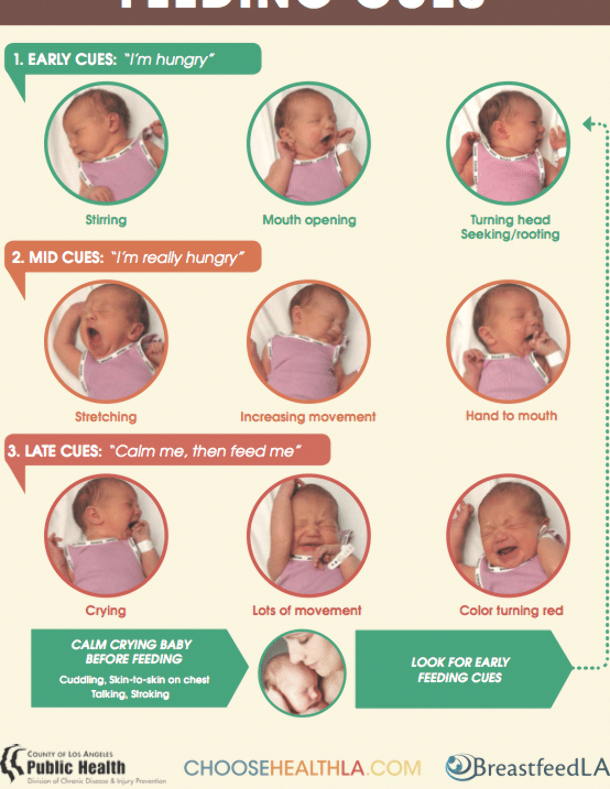 She is simply in captivity of prejudices regarding the relationship between mother and baby. She does not know how to behave correctly, does not know what to do in accordance with the natural needs of the child. If you tell her what the child really needs, she will exclaim in horror: “What is it, don’t let him get away with?!” Indeed, the child of the first months of life must not be let off the hook. For a woman who does not know how to comfortably carry a baby, and who does not know how to feed him in various positions (sitting, lying, standing and even moving), this can be very difficult. Especially if she is not sure of the correctness of her actions.
She is simply in captivity of prejudices regarding the relationship between mother and baby. She does not know how to behave correctly, does not know what to do in accordance with the natural needs of the child. If you tell her what the child really needs, she will exclaim in horror: “What is it, don’t let him get away with?!” Indeed, the child of the first months of life must not be let off the hook. For a woman who does not know how to comfortably carry a baby, and who does not know how to feed him in various positions (sitting, lying, standing and even moving), this can be very difficult. Especially if she is not sure of the correctness of her actions.
An action that should become automatic for the mother of a newborn: when the baby cries or shows other signs of anxiety, put the baby to the breast.
What's next?
The baby is growing. A fairly stable rhythm of daytime sleep begins to form in him, and a 3-4-month-old baby behaves quite differently from a newborn. Feeding on demand at this age looks something like this...
Feeding on demand at this age looks something like this...
- At three months, the baby has 10-12 feeds during the day and 2-4 at night. There are frequent applications for a short time, but their number is reduced. There may be a long night break in feedings, about 5 hours, but this is very rare. Much more often the night break is 2.5-3.5 hours. By this age, the baby's body is noticeably rounded.
- At four months, the baby begins to breastfeed noticeably less frequently. The main feedings are associated with sleep: the baby suckles before bedtime, during awakening and during sleep, both daytime and nighttime. In this regard, he has a fairly accurate feeding regimen. And many babies stop breastfeeding when they wake up after daytime sleep, sometimes as early as 2.5-3 months.
- At five months, the baby has 8-10 daytime feedings and 2-3 nighttime, attachments as well as in the fourth month of life, are organized around dreams - the baby eats when going to bed and some babies suck during awakening.
- At six months, the feeding regimen changes. The most active sucking shifts to the last 2-3 hours before waking up from a night's sleep. The period of daytime wakefulness can be divided into two periods: in the morning, when the baby sucked during the night is rarely applied to the breast, and in the evening, when attachments become very frequent. In total, there can be 7-10 day applications and 3-4 night applications. At this age, the baby begins a period of acquaintance with new food - pedagogical complementary foods. Sometimes there are attachments associated with the introduction of complementary foods, the baby “washes down” samples of new food with mother's milk. But many children do not want to drink complementary foods. When complementary foods are introduced to an on-demand baby, it is never meant to replace feedings with complementary foods. This is practically impossible, because the main feedings of the baby are associated with sleep, and mother's breakfasts, lunches and dinners, during which the baby gets acquainted with new food, are located between the baby's dreams, during his wakefulness.

- At seven months, the frequency of application is about the same.
- At eight months, the feeding regimen changes. Since the baby shows high motor activity and is very busy exploring the surrounding space, in the daytime he forgets to breastfeed. In this regard, the number of daily feedings can be reduced to 6-8 times. The baby compensates for the reduction in daytime feedings by increasing the frequency and duration of nighttime feedings up to 6 times.
- In the second half of the year, babies who stopped breastfeeding when waking up after daytime naps recall this habit again. The baby’s daytime sleep in the second half of life, as well as in the region of a year and older, looks something like this: the baby falls asleep sucking, sleeps quietly for a while, for example 1-1.5 hours, then starts tossing and turning, fiddling, worrying, at this moment the mother lies down next to , gives him a breast and the baby can fill up 10-15-30 minutes sucking. Mom may well use this time for her own rest - lie down, read, while the baby sleeps while sucking.
 I know my mother, a lover of embroidery, who used this time specifically for embroidery ...
I know my mother, a lover of embroidery, who used this time specifically for embroidery ... - Breastfeeding becomes more frequent at nine to ten months. In the daytime, this is 4-6 full feedings and about the same number of attachments for various reasons. The baby has new reasons for attachment. If, during active actions to master the world, the baby fills a bump or gets scared, he calms down with his mother's breast. There may be situations when you can comfort the baby by sitting next to him and hugging him. At night, 4-6 feedings remain, the baby begins to suckle more actively in the morning between 3 and 8 hours.
- At eleven months, a baby can already have 2-3 complete complementary foods. Initiation to adult food in the mind of a child is not associated with breastfeeding: attachment to the mother's breast is something other than the desire to get enough of the product they like. As a rule, after the baby has eaten, he feels the need to attach himself to the breast.
 The number of daily feedings remains the same in the child, but the number of short-term attachments increases. There are active mid-morning feedings between 4 and 8 o'clock in the morning.
The number of daily feedings remains the same in the child, but the number of short-term attachments increases. There are active mid-morning feedings between 4 and 8 o'clock in the morning. - At ten or twelve months, the baby, if he is already walking, can sometimes breastfeed every time he comes to his mother, i.e. about every 15-30 minutes. Attachments around dreams and night sucking persist. Therefore, if a mother says that a child suckles once or twice a day, this means that there is no feeding at the request of the child. There are restrictions imposed by the mother, with which the baby has come to terms. He treats breast sucking like food, sucks on a pacifier or a finger to fall asleep or soothe, or falls asleep just like that, without calming down.
- At twelve months, the baby is applied in about the same way.
- At the age of one and a half years, there may already be one daytime nap, so there are fewer attachments associated with sleep. Preserved for morning sucking.
 The baby is very free with his mother's breasts. Sometimes it happens that he comes up to suck just for fun. For example, like this: he comes up, climbs on his knees, looks into his mother’s face, smiles, starts to swarm in his shirt, gets breasts, smiles at his breasts, sucks for 30 seconds and leaves.
The baby is very free with his mother's breasts. Sometimes it happens that he comes up to suck just for fun. For example, like this: he comes up, climbs on his knees, looks into his mother’s face, smiles, starts to swarm in his shirt, gets breasts, smiles at his breasts, sucks for 30 seconds and leaves.
As for the number of feedings per day when feeding a child on demand, their number is almost never less than 12. A newborn has 12 or more attachments, basically they are all associated with dreams. And a child, say 1.5-2 years old, can also have about 12 attachments, only 3-4 are associated with sleep, and the rest are short-term attachments for various reasons. I suggest to all mothers reading this text - do not count the application, do not notice their duration. Breastfeed your baby as often as he asks, when you feel the need to.
Mothers who do not think about breastfeeding without looking back at the clock may get the impression that when feeding on demand, the mother can do nothing but feed the baby.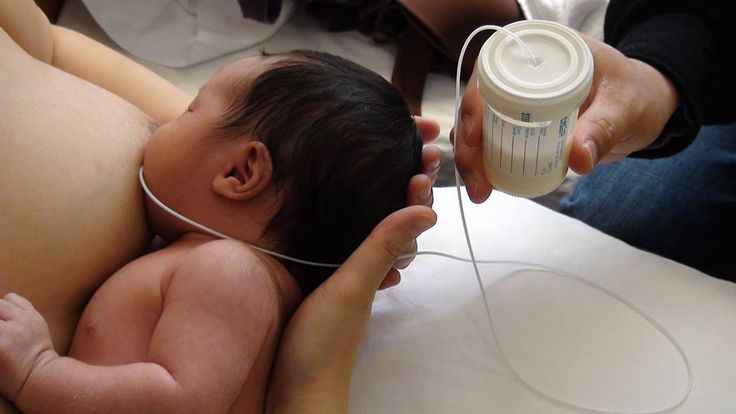 This is wrong. After the birth of a baby, a mother begins another life, she is called life with a baby. That's all. The child is with the mother, not the mother with the child! Feel the difference! You need to be able to organize your life in a different way, in the first months, of course, the help of loved ones is very necessary. In the tradition of many peoples, it was customary for the first 40 days after childbirth to remove a woman from any housework and household chores, she was engaged only in a child. In some nations, objects that the mother of a newborn touched were considered “unclean”, therefore, they preferred to protect the mother from the rest of the household, allocating her a separate “corner” of the house, where no one bothered her and she did not interfere with anyone. Among the Slavs, such a restrictive custom was called a six-week. By 1.5-2 months, the rhythm of daytime dreams begins to form, and the baby has a kind of “regime”, the mother becomes more free.
This is wrong. After the birth of a baby, a mother begins another life, she is called life with a baby. That's all. The child is with the mother, not the mother with the child! Feel the difference! You need to be able to organize your life in a different way, in the first months, of course, the help of loved ones is very necessary. In the tradition of many peoples, it was customary for the first 40 days after childbirth to remove a woman from any housework and household chores, she was engaged only in a child. In some nations, objects that the mother of a newborn touched were considered “unclean”, therefore, they preferred to protect the mother from the rest of the household, allocating her a separate “corner” of the house, where no one bothered her and she did not interfere with anyone. Among the Slavs, such a restrictive custom was called a six-week. By 1.5-2 months, the rhythm of daytime dreams begins to form, and the baby has a kind of “regime”, the mother becomes more free.
For a mother who can't imagine breastfeeding without looking back at the clock, and who is sure that the “right” baby is the baby lying quietly in her crib all the time, feeding on demand will be a complete hassle. It will be much easier for such a mother if she stops looking at the clock and ties the baby to herself with a large scarf or uses a patchwork holder (sling). It will become easier for her if she stops running between the nursery and the kitchen, but takes the baby with her to the kitchen and carries him around the house with her, doing housework, in a box, a cradle, a special chair, if she tries not to put him off often, and pick up as soon as possible, postponing the baby only in case of emergency and not for long.
It will be much easier for such a mother if she stops looking at the clock and ties the baby to herself with a large scarf or uses a patchwork holder (sling). It will become easier for her if she stops running between the nursery and the kitchen, but takes the baby with her to the kitchen and carries him around the house with her, doing housework, in a box, a cradle, a special chair, if she tries not to put him off often, and pick up as soon as possible, postponing the baby only in case of emergency and not for long.
Breastfeeding is not the same as house arrest. In the conditions of modern society, it is possible to organize the exit of a nursing mother to work from about 6 months of age of the baby. If necessary, you can start working from the age of 4 months, but, of course, it is better not every day of the week and not full time. It is the responsibility of a breastfeeding consultant to help a mother organize her return to work.
Sometimes, when I advise mothers on breastfeeding, I suggest that they forget for a second that they are already living in the 21st century. I propose to return, for example, to the cave and ask what they will do if the child woke up at night, how to calm him down? If you are walking through the forest and trying not to attract the attention of predators, how to make the baby silent? If the child is thirsty, what will you give him? What is the baby used to, for thousands of years of its existence? To the fact that he sleeps on his mother while she wanders through the forest with a digging stick in search of roots, and wakes up when mother stops. Since mom stopped, then there is time to wake up and suck. Therefore, even now the child sleeps well, tied to the mother with a patchwork holder, wakes up when the mother, having done a few household chores, sits in a chair to take care of the baby.
I propose to return, for example, to the cave and ask what they will do if the child woke up at night, how to calm him down? If you are walking through the forest and trying not to attract the attention of predators, how to make the baby silent? If the child is thirsty, what will you give him? What is the baby used to, for thousands of years of its existence? To the fact that he sleeps on his mother while she wanders through the forest with a digging stick in search of roots, and wakes up when mother stops. Since mom stopped, then there is time to wake up and suck. Therefore, even now the child sleeps well, tied to the mother with a patchwork holder, wakes up when the mother, having done a few household chores, sits in a chair to take care of the baby.
Some mother, reading about the cave, will be offended, saying that she is a civilized creature. But please think. Man, mother's breast and mother's milk have been created by evolution over millions of years. They are made for each other. Baby food has created progress and more recently. The skills of motherhood and breastfeeding have also been lost by our society quite recently. A person is not physiologically adapted to artificial feeding and a pacifier. The mother's breast will not produce enough milk at 6-7 feedings per day. Nature did not know, when creating man as a mammal, that the time would come when the need for breastfeeding would be satisfied by some kind of pacifiers and nipples.
Baby food has created progress and more recently. The skills of motherhood and breastfeeding have also been lost by our society quite recently. A person is not physiologically adapted to artificial feeding and a pacifier. The mother's breast will not produce enough milk at 6-7 feedings per day. Nature did not know, when creating man as a mammal, that the time would come when the need for breastfeeding would be satisfied by some kind of pacifiers and nipples.
Changes that occur during the formation of the personality of a child who did not have full contact with the mother during prolonged breastfeeding are noted by modern research by psychologists and sociologists. These are changes with a minus sign. It would be better if they were not, these changes.
Breastfeeding is not only important for the baby, it is also important for the mother. During on-demand feeding, the woman's feelings change, a stronger attachment to the baby is formed, the woman becomes more sensitive to the needs of the baby.