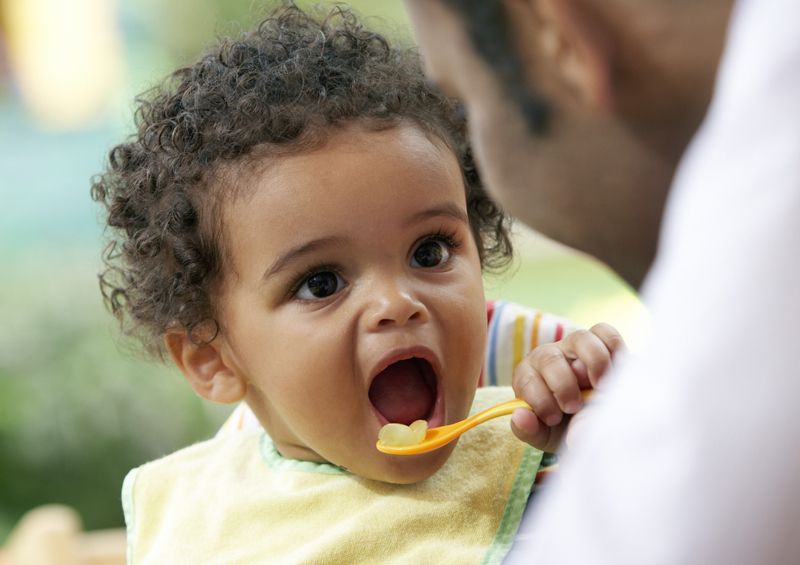
Feeding my baby solids
When, What, and How to Introduce Solid Foods | Nutrition
For more information about how to know if your baby is ready to starting eating foods, what first foods to offer, and what to expect, watch these videos from 1,000 Days.
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend children be introduced to foods other than breast milk or infant formula when they are about 6 months old. Introducing foods before 4 months old is not recommended. Every child is different. How do you know if your child is ready for foods other than breast milk or infant formula? You can look for these signs that your child is developmentally ready.
Your child:
- Sits up alone or with support.
- Is able to control head and neck.
- Opens the mouth when food is offered.
- Swallows food rather than pushes it back out onto the chin.
- Brings objects to the mouth.
- Tries to grasp small objects, such as toys or food.
- Transfers food from the front to the back of the tongue to swallow.
What Foods Should I Introduce to My Child First?
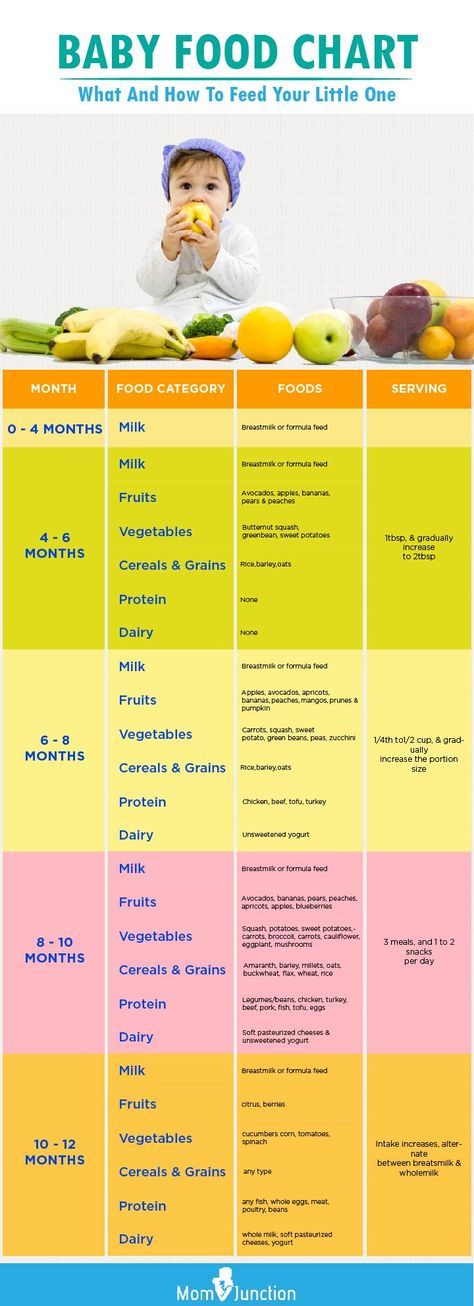
The American Academy of Pediatrics says that for most children, you do not need to give foods in a certain order. Your child can begin eating solid foods at about 6 months old. By the time he or she is 7 or 8 months old, your child can eat a variety of foods from different food groups. These foods include infant cereals, meat or other proteins, fruits, vegetables, grains, yogurts and cheeses, and more.
If your child is eating infant cereals, it is important to offer a variety of fortifiedalert icon infant cereals such as oat, barley, and multi-grain instead of only rice cereal. Only providing infant rice cereal is not recommended by the Food and Drug Administration because there is a risk for children to be exposed to arsenic. Visit the U.S. Food & Drug Administrationexternal icon to learn more.
How Should I Introduce My Child to Foods?
Your child needs certain vitamins and minerals to grow healthy and strong.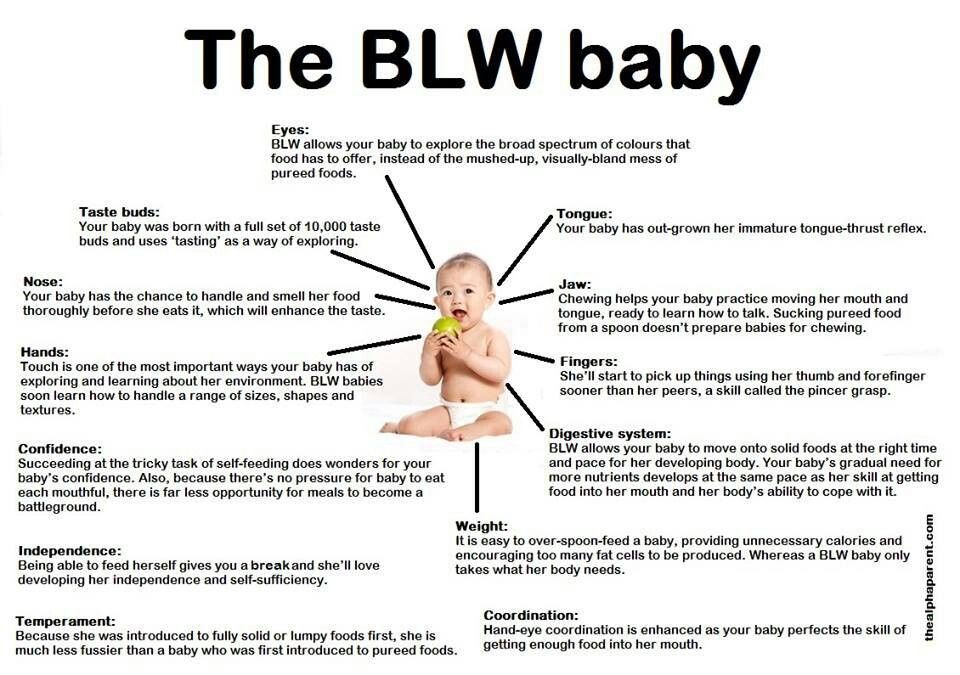
Now that your child is starting to eat food, be sure to choose foods that give your child all the vitamins and minerals they need.
Click here to learn more about some of these vitamins & minerals.
Let your child try one single-ingredient food at a time at first. This helps you see if your child has any problems with that food, such as food allergies. Wait 3 to 5 days between each new food. Before you know it, your child will be on his or her way to eating and enjoying lots of new foods.
Introduce potentially allergenic foods when other foods are introduced.
Potentially allergenic foods include cow’s milk products, eggs, fish, shellfish, tree nuts, peanuts, wheat, soy, and sesame. Drinking cow’s milk or fortified soy beverages is not recommended until your child is older than 12 months, but other cow’s milk products, such as yogurt, can be introduced before 12 months. If your child has severe eczema and/or egg allergy, talk with your child’s doctor or nurse about when and how to safely introduce foods with peanuts.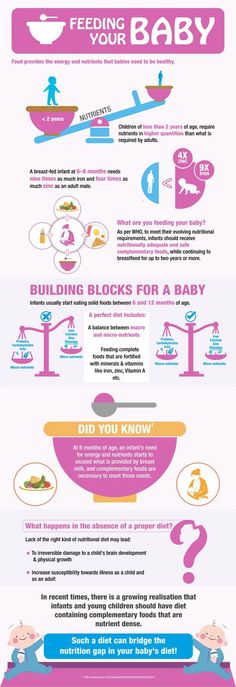
How Should I Prepare Food for My Child to Eat?
At first, it’s easier for your child to eat foods that are mashed, pureed, or strained and very smooth in texture. It can take time for your child to adjust to new food textures. Your child might cough, gag, or spit up. As your baby’s oral skills develop, thicker and lumpier foods can be introduced.
Some foods are potential choking hazards, so it is important to feed your child foods that are the right texture for his or her development. To help prevent choking, prepare foods that can be easily dissolved with saliva and do not require chewing. Feed small portions and encourage your baby to eat slowly. Always watch your child while he or she is eating.
Here are some tips for preparing foods:
- Mix cereals and mashed cooked grains with breast milk, formula, or water to make it smooth and easy for your baby to swallow.
- Mash or puree vegetables, fruits and other foods until they are smooth.

- Hard fruits and vegetables, like apples and carrots, usually need to be cooked so they can be easily mashed or pureed.
- Cook food until it is soft enough to easily mash with a fork.
- Remove all fat, skin, and bones from poultry, meat, and fish, before cooking.
- Remove seeds and hard pits from fruit, and then cut the fruit into small pieces.
- Cut soft food into small pieces or thin slices.
- Cut cylindrical foods like hot dogs, sausage and string cheese into short thin strips instead of round pieces that could get stuck in the airway.
- Cut small spherical foods like grapes, cherries, berries and tomatoes into small pieces.
- Cook and finely grind or mash whole-grain kernels of wheat, barley, rice, and other grains.
Learn more about potential choking hazards and how to prevent your child from choking.
Top of Page
Helpful Resources | Nutrition | CDC
If you would like more information on topics related to feeding your baby or toddler, here are some resources:
General
CDC’s Infant and Toddler Nutrition microsite syndication
CDC offers a free Web Content Syndication service that gives public health partners the opportunity to syndicate CDC content directly to their sites without having to monitor or copy updates. To search the CDC infant and toddler nutrition website available for syndication as well as other resources you can share, visit the CDC Public Health Media Library and browse or search for “infant and toddler nutrition”. Learn more about content syndication and how to add CDC syndicated content on your site.
To search the CDC infant and toddler nutrition website available for syndication as well as other resources you can share, visit the CDC Public Health Media Library and browse or search for “infant and toddler nutrition”. Learn more about content syndication and how to add CDC syndicated content on your site.
CDC’s Child and Teen Resources
This collection of resources provides parents and caregivers, health care providers, and partners with tools and information to help children and teens maintain a healthy weight and prevent obesity.
CDC’s Child Development Positive Parenting Tips (Infants)
This CDC website provides information about infants’ development, as well as tips for positive parenting and promoting the safety and health of infants.
CDC’s Learn the Signs. Act Early.
This website includes tools to track children’s milestones and resources about children’s development.
CDC’s Parent Information
This CDC website provides resources and information on pregnancy, infants and toddlers, children, and teens. Learn how to handle common parenting challenges through interactive activities, videos, and more. Healthcare professionals and researchers can also find information on children’s health and safety.
Learn how to handle common parenting challenges through interactive activities, videos, and more. Healthcare professionals and researchers can also find information on children’s health and safety.
CDC’s Division of Oral Health
Tooth decay (cavities) is one of the most common chronic diseases of childhood in the United States. Untreated tooth decay can cause pain and infections that may lead to problems with eating, speaking, playing, and learning. CDC’s Division of Oral Health provides information on what parents and caregivers can do to ensure good oral health for your child.
Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2020–2025 pdf icon[PDF-30.6MB]external icon
These guidelines provide science-based advice for Americans on what to eat and drink to promote health, reduce chronic disease, and meet nutrient needs. The 2020–2025 edition provides recommendations for all life stages, including infants and toddlers.
Feeding Guidelines for Infants and Young Toddlers: A Responsive Parenting Approachexternal icon
This report presents recommendations for promoting healthy nutrition and feeding patterns for infants and toddlers from birth to 24 months, with an emphasis on dietary quality, portion sizes, and mealtime environment.
Healthy Childrenexternal icon
This website was developed by the American Academy of Pediatrics for parents. It features thousands of articles in English and Spanish on children’s health and safety, as well as interactive tools.
United States Department of Agriculture Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC)external icon
The WIC Program provides support to low-income pregnant, postpartum, and breastfeeding women, babies, and children up to age 5. WIC provides nutritious foods, information on healthy eating, breastfeeding promotion and support, and referrals to health care.
United States Department of Agriculture Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP)external icon
SNAP provides benefits to low-income individuals and families and provides economic benefits to communities.
Feeding and Beverage Recommendationsexternal icon
Healthy Eating Research, a national program of the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, offers science-based recommendations for parents and caregivers.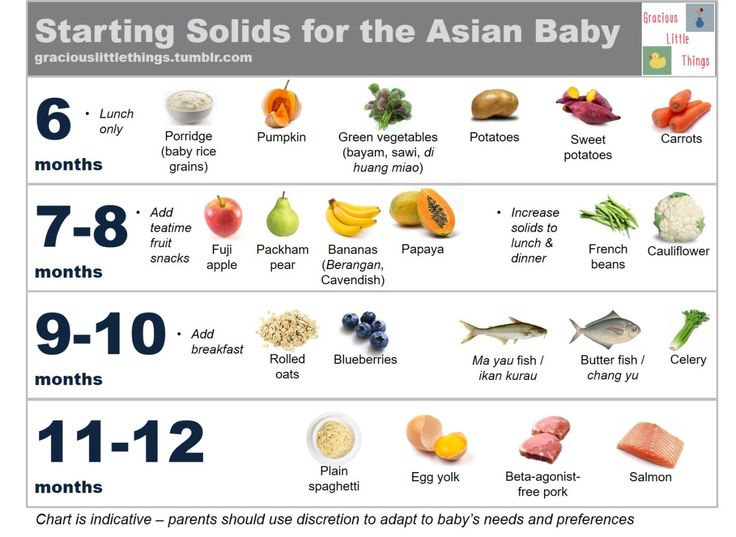 Tips are available for feeding children from birth through 24 monthsexternal icon and beverages for children from birth through 5 yearsexternal icon. Tips for older children are also available.
Tips are available for feeding children from birth through 24 monthsexternal icon and beverages for children from birth through 5 yearsexternal icon. Tips for older children are also available.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) Advice About Eating Fishexternal icon
The U.S. FDA and EPA provide advice regarding eating fish. This advice can help people make informed choices when it comes to the types of fish that are nutritious and safe to eat. It is especially important for those who might become pregnant, who are pregnant, or who are breastfeeding, as well as for parents and caregivers who are feeding children. This advice supports the recommendations of the Dietary Guidelines for Americans.
Top of Page
Breastfeeding
CDC’s Breastfeeding Information
CDC’s Division of Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Obesity (DNPAO) is committed to increasing breastfeeding rates throughout the United States. CDC provides information for public health professionals and others to help support breastfeeding mothers, such as managing breastfeeding during various maternal and infant illnesses and conditions, any precautions for vaccines during breastfeeding, and recommendations for proper storage and handling of expressed human milk.
CDC provides information for public health professionals and others to help support breastfeeding mothers, such as managing breastfeeding during various maternal and infant illnesses and conditions, any precautions for vaccines during breastfeeding, and recommendations for proper storage and handling of expressed human milk.
International Lactation Consultant Association (ILCA)external icon
ILCA is the member association for professionals who care for breastfeeding families. ILCA’s “Find a Lactation Consultant Directory” can help you find a lactation consultant to get the breastfeeding support you need.
United States Lactation Consultant Association (USLCA)external icon
USLCA is a professional association for International Board Certified Lactation Consultants (IBCLCs) and other health care professionals who care for breastfeeding families. USLCA’s “Find an IBCLC” can help you find a lactation consultant to get the breastfeeding support you need.
WIC, the Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children—Breastfeeding Support external icon
The United States Department of Agriculture Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC) Breastfeeding Support website includes resources for expectant and current mothers about breastfeeding, overcoming common challenges, and thriving to make breastfeeding work for their families.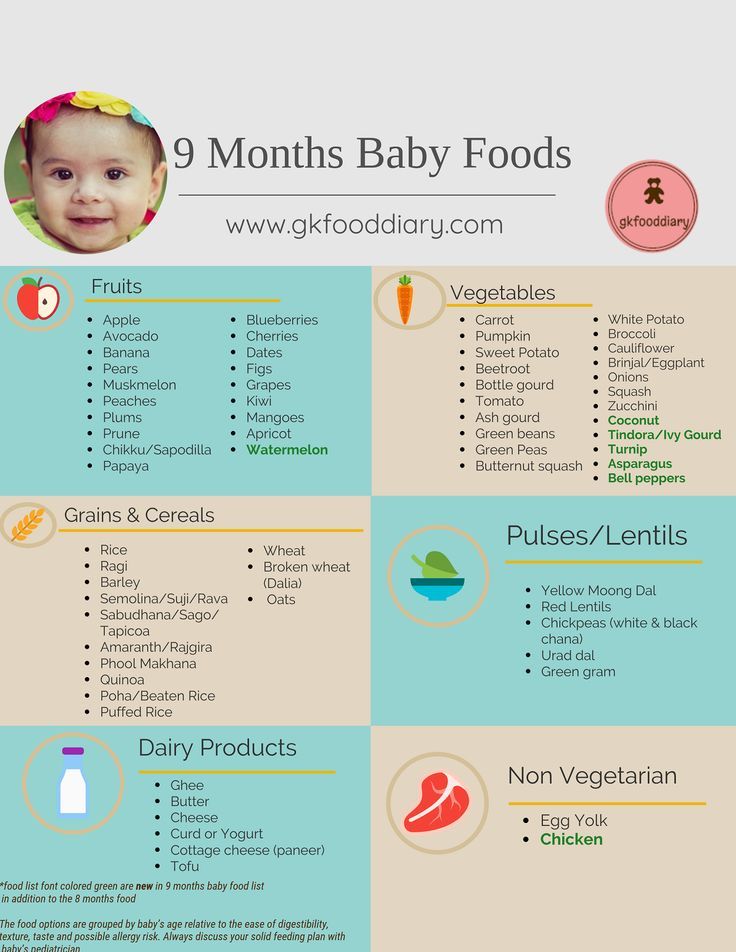
La Leche League USAexternal icon
La Leche League USA helps mothers to breastfeed through mother-to-mother support, encouragement, information, and education and promotes a better understanding of breastfeeding as an important element in the healthy development of the baby and mother.
Office on Women’s Healthexternal icon
The Office on Women’s Health’s vision is for all women and girls to achieve the best possible health outcomes. They provide information on breastfeeding to help women make infant feeding decisions and to guide mothers through the breastfeeding process.
Top of Page
Infant Formula
Questions & Answers for Consumers Concerning Infant Formulaexternal icon
The U.S. Food & Drug Administration regulates infant formula and has a list of questions and answers about infant formula.
Infant Formula Do’s and Don’tsexternal icon
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration provides information on infant formula preparation and storage, as well as other tips on how to keep infant formula safe.
Top of Page
Food Safety
Food Safety Concerns for Children Under Fiveexternal icon
Food safety is particularly important for young children. Foodsafety.gov provides information on safely preparing food for your child.
Top of Page
Meal Time
Fruits & Veggies—Have a Plant Movementexternal icon
A resource designed to help spread the word about the health benefits of adding more fruits and veggies to your diet.
USDA MyPlate Kitchenexternal icon
This online tool features a large collection of recipes and resources to support building healthy and budget-friendly meals. Site features include:
- Extensive search filters on cuisine, cooking equipment, nutrition content, and more.
- Detailed nutrition information.
- Cookbooks to browse and download or build your own.
- Recipe star ratings, review comments, and sharing on social networks.
Video Series on How to Introduce Solid Foods
1,000 Days has developed helpful videos about introducing solid foods to your baby. Topics include:
Topics include:
- Is your baby ready to start eating foods?
- What is a good first food for your baby?
- What to expect when introducing first foods
- How much should I feed my baby?
- How to win at mealtimeexternal icon
- What foods should my baby avoid?
- What should your baby eat in the first year?
Top of Page
Vitamins and Minerals
Vitamin and Mineral Fact Sheetsexternal icon
The National Institutes of Health’s Office of Dietary Supplements has fact sheets for consumers and health professionals about vitamins, minerals, and dietary supplements.
Top of Page
Solid food 9 to 12 months
In the previous period, your main task was to introduce the child to solid food - to prepare him for the transition from liquid food to solid food, to teach him to take food in his mouth and chew it. Many children do not bring food to their mouths, spilling or spilling it along the way, and as a result, they get very little of what was intended.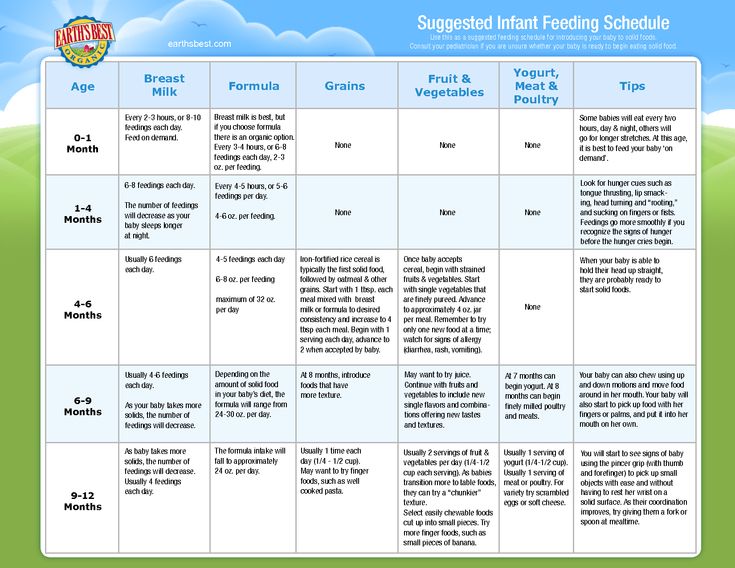 Breast milk and/or formula make up about 90% of their diet.
Breast milk and/or formula make up about 90% of their diet.
In the last period of the first year of life, the development of the swallowing mechanism is completed in children. The protective "pushing out" reflex gradually weakens, the child chokes on food less, and swallowing becomes more coordinated. This allows you to gradually move from mashed and liquid food to minty, coarser and lumpy. The structure of solid food also changes. But be careful. If you delay this process, then deprive the child of the chance to experiment with different food structures and increase the period when he eats only pureed food. If you hurry too much, the child will refuse new food with an unfamiliar structure for a long time because of the fear of choking and suffocating.
New skills - new food
At this age, children receive more varied food, and the amount of it increases. Solid food becomes the main source of nutrition for the child, making up about 50% of his diet by the year (for most breastfed children, milk remains the main food by 80-90% even a year). There is a development of new skills, which entails acquaintance with new types of food. Improved "tweezer grip" - the ability to pick up objects with the thumb and forefinger, so the child can take and put small pieces in his mouth. Interest in small objects develops; use this new passion of the child by giving him small pieces of food during feeding.
There is a development of new skills, which entails acquaintance with new types of food. Improved "tweezer grip" - the ability to pick up objects with the thumb and forefinger, so the child can take and put small pieces in his mouth. Interest in small objects develops; use this new passion of the child by giving him small pieces of food during feeding.
Handling food
Encourage your child to take food with his fingers. Teach him to put food in his mouth, and not to scatter, smear it on the table or plate. Place small pieces of boiled carrots, rice biscuits, or soft fruits in front of it. Babies use solid food to "scratch" their gums when they start teething. Hard food, especially for teething teeth, should soften in the mouth, dissolving easily as it is chewed. We found that our children were very interested in the various shapes of boiled pasta that we placed in front of them. Baby's new skill of grasping and holding small objects can be used during feeding. This makes it possible to keep the attention of the child at the table much longer. During the performance of such \"captures \" some part of the food still gets into his mouth. If you are afraid of allergies, do not give your baby, who is not yet a year old, wheat products (butter biscuits, pasta, etc.). If your baby is prone to allergies, you can buy cookies made not from wheat flour, but, for example, from rice.
This makes it possible to keep the attention of the child at the table much longer. During the performance of such \"captures \" some part of the food still gets into his mouth. If you are afraid of allergies, do not give your baby, who is not yet a year old, wheat products (butter biscuits, pasta, etc.). If your baby is prone to allergies, you can buy cookies made not from wheat flour, but, for example, from rice.
The child's ability to take food with his hands has its downside. Food, as well as utensils, become interesting objects to study - they can be grabbed, knocked with them, they can be dropped and thrown. Of course, this does not mean that you should stop such feedings, but only speaks of the natural and normal need of the child to identify all new opportunities for using newly acquired skills.
Let the baby dip the pieces of food
At 9 months. Toddler starts using his index finger (a new skill!) to stick it somewhere or point them at something. Children are happy to dip their fingers in food, taste it. Use this new skill when feeding. The reflection in the nutrition and feeding of the child of everything that he masters along the way of his development has its funny sides. As soon as your baby starts using his finger to dip it in food and then suck on it, expect him to soon start painting himself or his chair with the food you feed him. Be lenient about this and treat the young researcher with understanding.
Children are happy to dip their fingers in food, taste it. Use this new skill when feeding. The reflection in the nutrition and feeding of the child of everything that he masters along the way of his development has its funny sides. As soon as your baby starts using his finger to dip it in food and then suck on it, expect him to soon start painting himself or his chair with the food you feed him. Be lenient about this and treat the young researcher with understanding.
Give your child a bone
Over time, when giving a chicken bone to a child, you can leave pieces of meat on it (but without a thin sharp bone). Let him play (bites, knocks, swings, shifts from one hand to another), and at this time you can eat relatively calmly yourself. In addition, the child will probably get some chicken meat.
Using a spoon
Toward the end of the 1st year, the child wants and tries to eat with a spoon on his own. Usually this leads to the fact that everything around is dirty, and the food goes anywhere but in his mouth.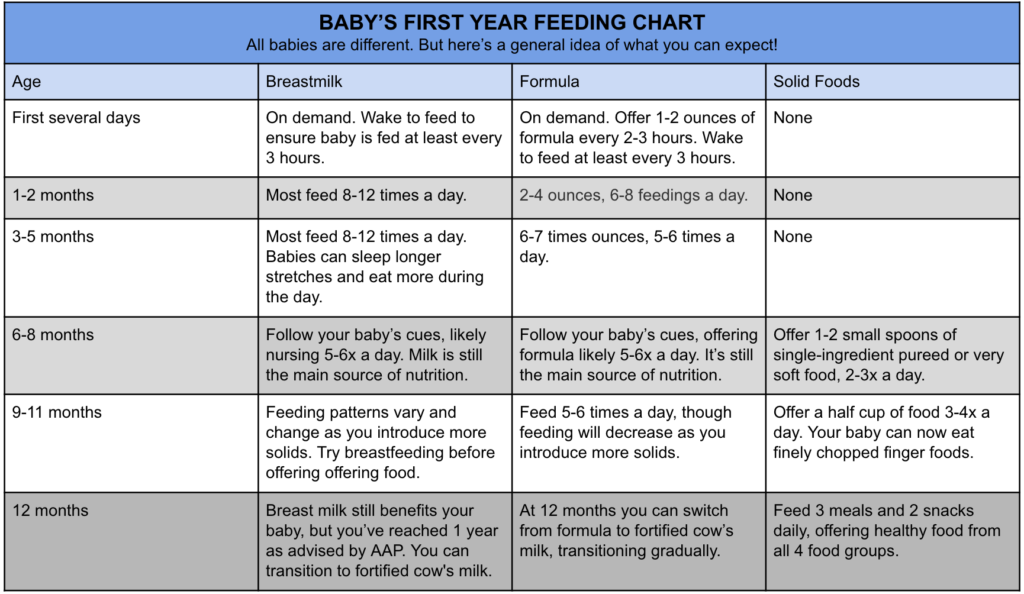 It seems to you that it is easier to feed the baby than to let him eat with a spoon. At the age of about a year, the child begins a period of independence ("I myself \"). To somewhat limit this independence, you can hold a spoon with food, but allow the child to hold on to it, or let the baby hold the spoon himself, and you "tweak" it into his mouth.
It seems to you that it is easier to feed the baby than to let him eat with a spoon. At the age of about a year, the child begins a period of independence ("I myself \"). To somewhat limit this independence, you can hold a spoon with food, but allow the child to hold on to it, or let the baby hold the spoon himself, and you "tweak" it into his mouth.
Food Safety Precautions:
- Do not give your child fibrous foods
- Choose fish bones carefully before giving them to your child. In canned salmon, knead the bones
- do not give white bread; it turns into a tight lump in the mouth that a child can choke on
- cut meat and chicken across the grain and into very small pieces
- do not give the child large pieces. The baby's front teeth are for biting only. Molar teeth - chewing - appear only after a year. Children press their gums more than they chew
- Feed children only in your presence and only when the child is sitting, not lying down or playing
- Put only a few pieces of food on a plate. When a child sees a whole mountain of food in front of him, he will try to shove it all into his mouth rather than chewing each piece
When a child sees a whole mountain of food in front of him, he will try to shove it all into his mouth rather than chewing each piece
- sausages do not have a special nutritional value and, moreover, can be dangerous for infants. Putting a whole sausage in your mouth can suffocate your child. Nitrate-free and nitrite-free sausages can be given to children after a year, but even then they should be cut lengthwise into thin narrow strips. Even these "healthy" sausages can be high in sodium, so don't overdo it.
Safe food:
- porridge - rice biscuits (unsalted)
- carrots (boiled)
- whole wheat bread toast (without crust)
- scrambled eggs without egg yolk 9000 9000 squirrels
- boiled peas (shelled)
- pear slices (very ripe)
- apple slices (boiled)
- pasta (boiled)
- green beans (well cooked, without fibers)
- pulp or slices of avocado
food, which can be choked with nuts:
- seeds
- corn
- sausages (entirely or large pieces) solid beans
- hard candy
- raw carrots
- Raw apples
- Grapes
- Unripe pears
- Fibrous food
- Large cuts of meat
Attitude towards food and feeding process
Your task is not only to provide the child with healthy, wholesome food, but also to form in him the right attitude towards the very process of eating. This chapter tells you how to help your baby enjoy food and you can help him enjoy feeding.
This chapter tells you how to help your baby enjoy food and you can help him enjoy feeding.
Table manners
Children are born artists. When they drop dishes or food on the floor, every adult immediately reacts to this. The child understands this as a game and begins to lay out food anywhere, but not in the mouth. Lunch time becomes a familiar game for him. Sometimes he is very impatient, picks up a handful of food and stuffs it all into his mouth, smearing half of it on his face. And such antics will continue until you react the way he expects. Laughter not only reinforces this habit, but can be very dangerous: when a child laughs with a full mouth, he takes a deep breath of air and may choke.
Soon the baby realizes that he is able to evoke the reaction he wants in the adult. Responding to the child's pranks too quickly and explicitly, we only encourage him to continue this domestic performance. Whether you laugh or scold, the child perceives it as an artist - he sees the reaction of the audience, and the performance continues. Not reacting is the best way to get this little clown off the stage. If he doesn't stop being naughty, you have to assume that he is not hungry and stop feeding. Don't expect your little one to sit quietly at the table like older children. At the same time, already at this early age, children learn to behave with a goal by the example of others. If a child sees that other children (and adults) are laughing with a full mouth or throwing food, knocking a cup, and they are having a lot of fun, the little parrot will do the same. And at the same time, do not forget to praise him for his good manners.
Not reacting is the best way to get this little clown off the stage. If he doesn't stop being naughty, you have to assume that he is not hungry and stop feeding. Don't expect your little one to sit quietly at the table like older children. At the same time, already at this early age, children learn to behave with a goal by the example of others. If a child sees that other children (and adults) are laughing with a full mouth or throwing food, knocking a cup, and they are having a lot of fun, the little parrot will do the same. And at the same time, do not forget to praise him for his good manners.
If the child is reluctant to eat
For the child who withdraws your hand with a spoon, place toys with suction cups on the chair (otherwise you will have to constantly pick them up from the floor) and, while he is playing with toys, try to feed him using any a trick to get the spoon into his mouth. We played spoon-airplane: \"Look, here is a plane flying\", - the spoon is approaching and right into the open mouth. If your baby constantly flaps his arms like a windmill while eating, use 3 plastic spoons: one for each of his arms and one for you to feed him. And don't forget that maybe the baby just doesn't want solid food. You must be sure that you do not overstep or force the introduction of this type of food, otherwise the child may develop a negative attitude towards food.
If your baby constantly flaps his arms like a windmill while eating, use 3 plastic spoons: one for each of his arms and one for you to feed him. And don't forget that maybe the baby just doesn't want solid food. You must be sure that you do not overstep or force the introduction of this type of food, otherwise the child may develop a negative attitude towards food.
Overcoming fear of solid foods
Some children have a fear of solid foods, and this is quite normal. Don't be surprised if your child wants to explore a new food first before eating it. You can help him get to know her: before you start feeding such a wary baby, put some food on the baby's index finger and put it in his mouth.
How to teach your baby to chew: teaching your baby to chew solid food
Glinskikh Elena
Published: 01/15/2023
Reading time:
1696
What are the difficulties
When a small child appears in a family, parents face a difficult task: not just to raise and educate, but also to instill in the baby all the necessary skills. For example, young parents are often concerned about the question of how to teach a child to chew. We have collected tips for you from well-known Russian and foreign pediatricians who will help you find the best solution.
For example, young parents are often concerned about the question of how to teach a child to chew. We have collected tips for you from well-known Russian and foreign pediatricians who will help you find the best solution.
For adults, the process of chewing food seems to be something completely natural. But the child has only a sucking reflex, and even liquid puree becomes an unusual and unfamiliar food for him. In addition, other reflex reactions are characteristic of the same period, due to which solid pieces of food that have fallen into the mouth are rejected. They weaken by 4 months, but it is not necessary to wean a child at this age: mother's milk "adjusts" to the needs of the baby, its composition changes over time.
When to introduce the first complementary foods
Exactly at this time - in the period from 4-6 months. Depending on various factors, this can be a monocomponent vegetable puree or dairy-free porridge from a single cereal. It is worth considering the weight, height, state of the digestive system and other features of the child's health.
How to tell if your baby is ready for solid food
Your baby will usually let you know that he is interested in updating his diet. This can be seen from his behavior:
- At 6–7 months, tiny particles up to 0.3 mm are acceptable. Shredded vegetables are ideal
- At 8-9 months, food with particles up to 1.5 mm can be added to the diet. These can be cereal flakes in cereals, tiny pieces of well-cooked vegetables
- At 9–12 months, the child can already cope with chewing food with pieces up to 3 mm.
- At 1 year of age and beyond, teach the child to chew solid food independently
Common mistakes
Young parents may inadvertently make mistakes. This is normal and should not cause panic: the first child is always difficult. If the baby refuses solid food, there are several reasons.
Solids too large . The child has a protective reflex, due to which he often spits out food. And if the piece is very large, the baby may begin to vomit.
And if the piece is very large, the baby may begin to vomit.
Complementary foods started very late . Some "specialists" and "experienced relatives" convince young mothers that they need to breastfeed their baby for up to a year, without giving him any other food. The kid gets used to such food, and the chewing reflex is not formed in him. You should not be afraid, it is difficult, but you can fix it.
The child does not like the taste . Yes, he is already an independent person who has his own preferences. So the baby can easily eat broccoli and refuse a baked pear. Or vice versa. You should not forcefully stuff the child with what he does not like, or force him to finish eating the entire portion.
Negative associations . Some psychologists believe that the refusal to eat from a spoon may be due to the fact that the child associates food with medicine (manifested in cases where the baby was given tasteless potions).
Too many new products . Don't try to include a wide variety of foods in your diet. As Ellyn Satter writes in Feeding and Feeding Your Child with Love and Common Sense, it's best to add "scary and unfamiliar" foods to what your child already loves, and in very small portions.
Don't try to include a wide variety of foods in your diet. As Ellyn Satter writes in Feeding and Feeding Your Child with Love and Common Sense, it's best to add "scary and unfamiliar" foods to what your child already loves, and in very small portions.
The child is fed like an adult . Larisa Surkova writes in the book “How cool it is with a child from 1 to 3 years old: a generator of useful tips”, you should not deny your baby tactile sensations. If he wants to crush food, sniff, smear on the table - let him do it. In the end, the table can be covered with oilcloth (and the floor, by the way, too).
No Foods
To avoid food allergies and digestive problems, never give a child under four years of age:
- lollipops, caramel, toffee
- nuts and any seeds
- hard pieces of meat
- whole grapes
- large pieces of hard fruits and vegetables
a one-year-old baby cannot chew food and constantly chokes on small pieces.
 This means that the chewing reflex is not fully formed, and parents will have to act very delicately:
This means that the chewing reflex is not fully formed, and parents will have to act very delicately: - Prepare thick creamy soups and purees for your child, but leave a few tiny pieces of cooked vegetables while blending
- Later vegetables can be chopped with a fork, the pieces will become larger, but not hard enough for the child to choke
- Foods that your child likes will help you achieve the best results. It can be baked apples and pears, bananas, children's cookies
- 0160
If, during the learning process, the child continues to choke and is unable to swallow solid food, this is an occasion to consult a doctor who will find the cause of the problem.
Game process
The child needs to be interested. A game plot for eating is an absolute norm. In the process, the baby can be told an interesting story in which he will be involved. The well-known “airplane” flying to the “hangar” is a real way to feed a child without nerves and tantrums.