Formula fed baby feeding every 2 hours
Formula Feeding FAQs: How Much and How Often (for Parents)
Whether you plan to formula feed your baby from the start, want to supplement your breast milk with formula, or are switching from breast milk to formula, you probably have questions.
Here are answers to some common questions about formula feeding.
How Often Should I Feed My Baby?
Newborns and young babies should be fed whenever they seem hungry. This is called on-demand feeding.
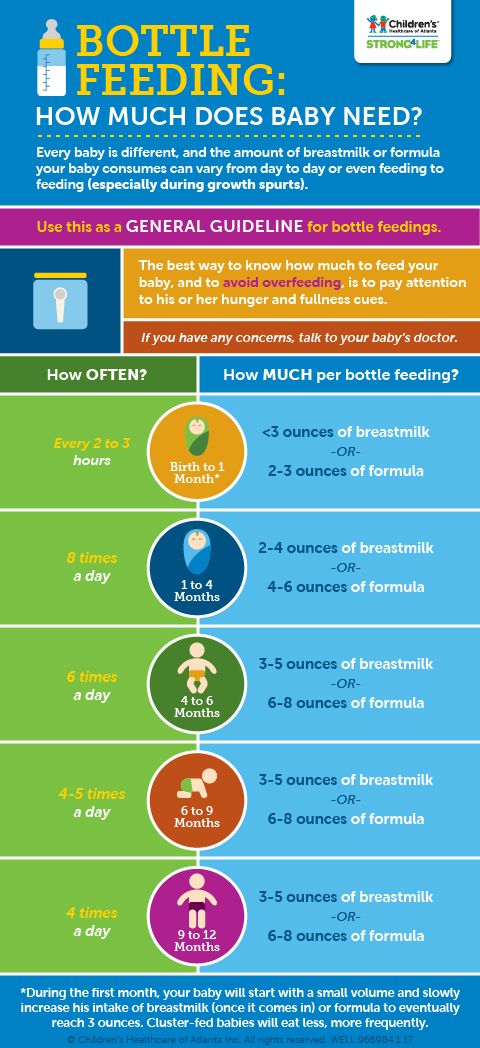
After the first few days of life, most healthy formula-fed newborns feed about every 2–3 hours. As they get bigger and their tummies can hold more milk, they usually eat about every 3–4 hours. As babies get older, they’ll settle into a more predictable feeding routine and go longer stretches at night without needing a bottle.
Talk to your doctor if you have concerns about feeding your baby, especially if your baby is very small, is not gaining weight, or was born early (prematurely).
How Can I Tell When My Baby Is Hungry?
Signs that babies are hungry include:
- moving their heads from side to side
- opening their mouths
- sticking out their tongues
- placing their hands, fingers, and fists to their mouths
- puckering their lips as if to suck
- nuzzling again their mothers' breasts
- showing the rooting reflex (when a baby moves its mouth in the direction of something that's stroking or touching its cheek)
Babies should be fed before they get upset and cry. Crying is a late sign of hunger. But every time your baby cries is not because of hunger. Sometimes babies just need to be cuddled or changed. Or they could be sick, tired, too hot or too cold, in pain, or have colic.
How Much Should My Baby Drink?
In the first few weeks, give 2- to 3-ounce (60- to 90-milliliter) bottles to your newborn. Give more or less depending on your baby’s hunger cues.
Here's a general look at how much your baby may be eating at different ages:
- On average, a newborn drinks about 1.5–3 ounces (45–90 milliliters) every 2–3 hours. This amount increases as your baby grows and can take more at each feeding.
- At about 2 months, your baby may drink about 4–5 ounces (120–150 milliliters) every 3–4 hours.
- At 4 months, your baby may drink about 4–6 ounces (120-180 milliliters) at each feeding, depending on how often they eat.
- By 6 months, your baby may drink 6–8 ounces (180–230 milliliters) about 4–5 times a day.
Watch for signs that your baby is hungry or full. Respond to these cues and let your baby stop when full. A baby who is full may suck with less enthusiasm, stop, or turn away from the bottle.
Why Does My Baby Seem Hungrier Than Usual?
As babies grow, they begin to eat more at each feeding and can go longer between feedings. Still, there may be times when your little one seems hungrier than usual.
Your baby may be going through a period of rapid growth (called a growth spurt). These can happen at any time, but in the early months are common at around:
- 7–14 days old
- between 3–6 weeks
- 4 months
- 6 months
During these times and whenever your baby seems especially hungry, follow their hunger cues and continue to feed on demand, increasing the amount of formula you give as needed.
Is My Baby Eating Enough?
At times, you may wonder whether your baby is getting enough nutrients for healthy growth and development. Babies who get enough to eat seem satisfied after eating and are regularly peeing and pooping.
Babies who get enough to eat seem satisfied after eating and are regularly peeing and pooping.
At your baby’s checkups, the doctor will review your baby’s growth chart, track your little one’s development, and answer any questions. Talk to your doctor if you have any concerns about your baby’s feeding and nutrition.
Reviewed by: Mary L. Gavin, MD
Date reviewed: November 2021
Newborn Feeding Every 2 Hours
Is your newborn feeding every 2 hours at night? Whether breastfed or formula-fed, lean how to stretch feedings and sleep a little longer.
Every 2 hours.
Almost on cue, your newborn will wake up after 2 hours screaming for yet another feeding. It doesn’t help when moms of other babies—even younger than yours—are stretching their feeds, sometimes up to five hours at night.
Yes, she’s still in the newborn stage, so you understand that her tummy is small and her sleep is erratic. But weeks, even months, into parenthood and your little one still wakes up every 2 hours on the dot.
But weeks, even months, into parenthood and your little one still wakes up every 2 hours on the dot.
And so, the questions pile on.
How can you get her to sleep in longer stretches? Is it normal for her to still feed so frequently, especially when others seem to go longer between feeds? Could you be doing something that’s holding her back instead of encouraging her to eat more?
How to handle your newborn feeding every 2 hours
Weeks and months after welcoming my first-born home, I still felt stuck.
Frequent feedings seemed more understandable in the early days, but when you’ve been doing this forever, it can feel depressing. I didn’t know when I’d ever get a full night of sleep again, and started to resent how often my baby nursed, especially at night.
In hindsight, I can see how short those weeks and months are compared to the grand scheme of things. But when you’re in that moment, every day can feel like an eternity, not knowing if or when life will feel normal again.
Rest assured mama, feeding every 2 hours is normal, not only in the newborn stage but I’d say throughout our lives. Think about it: even adults tend to eat in 2-3 hour chunks, with snacks eaten between meals.
But the biggest concern you likely have is the frequent feeding at night. Maybe you’re wondering when your baby will be able to eat mostly during the day and sleep at night. Because eventually, we all consume our calories during the day, even older infants. Why does it feel like yours is so far from that point?
First, an important note: a newborn isn’t going to sleep the whole night just yet. I sleep trained my kids to go 11-12 hours straight only once they were well past the newborn stage. That said, what do you do when your little one is still too young to sleep train, but you want to encourage her to go longer between feeds?
Take a look at these steps you can try:
1. Don’t keep your baby awake too long
As a first-time mom, I assumed babies would sleep when they were tired. So, it wasn’t unusual for me to keep my baby awake for long stretches, unaware that he needed help falling asleep.
So, it wasn’t unusual for me to keep my baby awake for long stretches, unaware that he needed help falling asleep.
Only later did I learn that keeping him awake led him to feeling overtired and cranky. The result? Frequent wake ups between feeds and a more difficult time settling him back down.
In other words, there’s a good chance your newborn is waking up every 2 hours not out of hunger, but from feeling overtired.
Try not to keep her awake too long—90 minutes at most, and sometimes she’ll need to sleep as soon as 45 minutes after waking up.
Free: Do you struggle with getting her to sleep? Her awake time just might be affecting how well she sleeps or not. Join my newsletter and get One Mistake You’re Making with Your Baby’s Awake Time—at no cost to you.
Don’t make the same mistakes I did—help her fall asleep with this one simple trick! Grab it below:
2. Feed often during the day
Feeding on demand is so important during the newborn stage, but tell that to any new mom and you might be met with dagger eyes. After all, it can be difficult to feel tied to your baby 24/7, especially if you’re the only one who can feed her.
After all, it can be difficult to feel tied to your baby 24/7, especially if you’re the only one who can feed her.
But feeding on demand, especially during the day, ensures that she’s getting all the food she needs. Don’t try to cap her off or put her on a schedule. Instead, follow her lead and feed as often as she wants during the day.
And hopefully, by having fed plenty the whole day, she’ll have less of a need to wake up often at night. Don’t expect her to sleep through the night yet, but at least you’re filling her up during the day when she’ll start to take in most of her feeds down the line.
How to handle a newborn constantly feeding.
3. Feed extra before bedtime
The first stretch of sleep after bedtime tends to be the longest. This is when you’ll likely grab five hours of uninterrupted sleep compared to, say, four o’clock in the morning. Help your baby sleep longer for that first stretch by offering her a bit of extra food for her bedtime milk.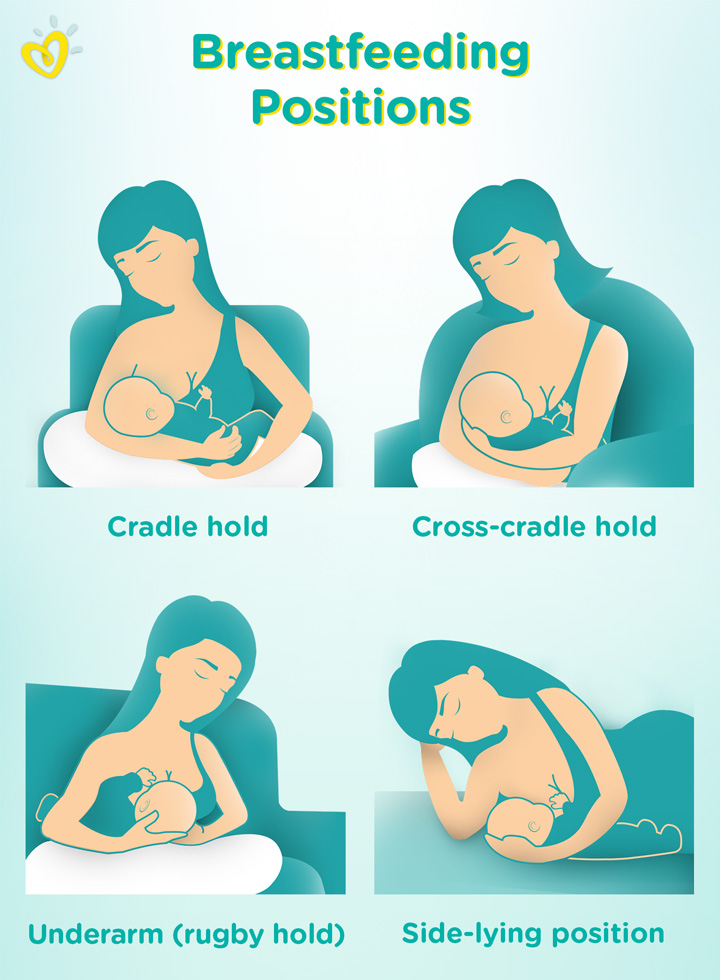
If you breastfeed, see if she’ll take a few extra minutes of nursing (or simply wait for her to pull away instead of putting a time limit). If you bottle-feed, try to add an extra ounce before setting her down for the night.
By topping her off with extra milk, you can ensure that she won’t wake up too soon after from hunger.
4. Dream feed
If you’re like most parents, you put your baby down for the night before your own bedtime. For instance, you might set her down at 7:30pm, then head to bed yourself at 10pm.
One trick that can pre-empt her first wake up is to offer a dream feed before you go to bed yourself. Let’s say you go to sleep at 10pm. Give her another feed at 9:30pm to top her off even further for the night. This allows you to feed her while you’re still awake and alert, and extends her feeding even more.
It’s okay if she’s groggy and half asleep as she feeds—there’s no need to wake her up all the way. This is more to give her a feed before she asks for it while you’re still awake.
Get more tips about dream feeding.
5. Make sure your baby is actually eating
Does it seem like your baby wakes up right after you had just fed her? There might be a chance she’s not even drinking at all, which could explain why she’s hungry so soon after feeding her. Instead of drinking, she might be half asleep and sucking for comfort, especially if she drifts off to sleep mid-feed.
How can you tell she’s eating? Listen for a swallowing sound—she should actually be gulping milk down. And look at her throat to see if it moves with each gulp. If you don’t hear a sound and her throat doesn’t move, she just might be moving her mouth and sucking.
If you suspect that she falls asleep, burp her mid-feed, talk to her, tickle her, and otherwise ensure that she stays awake while she feeds.
Learn how to stop your baby from snacking on the breast.
6. Give your baby a chance to settle
Newborns are notorious for making all sorts of sounds, even while they’re sound asleep. But back then, I’d sit up right away the minute my little guy made a peep (it didn’t help that he was in the same room as me). I felt compelled to scoop him up immediately, fearing that those sounds would escalate into full-on cries.
But back then, I’d sit up right away the minute my little guy made a peep (it didn’t help that he was in the same room as me). I felt compelled to scoop him up immediately, fearing that those sounds would escalate into full-on cries.
I’ve since learned that those sounds, and even the small whimpers and cries, can often settle on their own. The next time you hear your baby cry, try to discern the type of cry first. Does she sound like she’s complaining and whimpering, or is she angry and in need of your attention right away?
If it sounds like she might settle down, wait one minute. She might not be waking up out of hunger. This is also a little practice that will help her overcome small discomforts.
Conclusion
A newborn feeding every 2 hours isn’t always easy to handle. Your baby finally falls asleep, only to rest for a short while before he seems hungry again. How can you get him to sleep longer at a time?
Don’t keep him awake too long, as frequent wake ups could be a result of feeling overtired. Feed often during the day instead of capping him at a certain time or by a particular schedule. Give him extra milk before bedtime and take advantage of that long first stretch of sleep.
Feed often during the day instead of capping him at a certain time or by a particular schedule. Give him extra milk before bedtime and take advantage of that long first stretch of sleep.
Before heading to bed yourself, offer a dream feed to top him off for the night while you’re still awake and alert. Make sure he’s actually eating and not just sucking for comfort. And lastly, don’t feel compelled to respond right away—he might be asleep or making small sounds and eventually settle herself down.
You can do certain things to help you stretch those feedings at night—instead of waking up every 2 hours as if on cue.
Get more tips:
- How to Get Your Baby to Adjust Using a Newborn Schedule
- 4 Reasons Your Baby Never Seems Satisfied After Breastfeeding
- Baby Feeding Every Hour (And Not Sleeping, Either)?
- 11 Ways to Cope with Newborn Sleep Deprivation
- 12 Things to Do When Your Newborn Fights Sleep
Don’t forget: Join my newsletter and get One Mistake You’re Making with Your Baby’s Awake Time—at no cost to you:
feeding rules, types of mixtures, tips for breastfeeding mothers
If breastfeeding is not possible, do not be upset: modern technologies make it possible to achieve maximum compliance of artificial feeding with all healthy nutrition standards. We talk about the basic rules of artificial feeding and common mistakes.
We talk about the basic rules of artificial feeding and common mistakes.
Website editor
Tags:
Health
weight loss nine0003
Children
Nutrition
VOICE recommends
The health of a newborn is directly dependent on his nutrition.
⚡️⚡️⚡️ TO STAY CONNECTED NO matter what, LOOK FOR US IN Yandex.Zen, VK, Telegram, Odnoklassniki.
If you can breastfeed, great, it's the best food for your baby. But if for some reason natural feeding is not possible, this is not a reason to panic: there are now many healthy mixtures that can replace mother's milk. Study our rules for artificial feeding, and everything will work out! nine0003
When to switch to artificial feeding
- Inability to breastfeed for medical reasons.
 With some diseases, as well as when taking a number of medications, breastfeeding is prohibited, since milk can be dangerous for the baby due to the content of toxic substances. Sometimes the reason to stop breastfeeding may be the child's disease (for example, cleft lip or severe malformations).
With some diseases, as well as when taking a number of medications, breastfeeding is prohibited, since milk can be dangerous for the baby due to the content of toxic substances. Sometimes the reason to stop breastfeeding may be the child's disease (for example, cleft lip or severe malformations). - Cessation of lactation. If there is not enough milk or it has disappeared completely, there is nothing to do, it is necessary to supplement the baby with mixtures. As a rule, mixed and artificial feeding solve the problem. nine0034
- Impossibility of regular feeding. For example, you can go to work or end up in a hospital, and this is not a reason to starve a child, but a reason to switch to mixed or artificial feeding: the rules for feeding and portion sizes change somewhat.
- Inadequate nutritious milk from the mother. Sometimes the problem is solved by changing your diet, but if the milk remains watery and the baby is screaming with hunger, then it's time to supplement him with mixtures, and later switch to them completely.
 nine0034
nine0034 - The wish of the child's mother. No matter how pediatricians talk about the benefits of breastfeeding, sometimes women who have every opportunity to breastfeed still prefer to give their baby a bottle. Well, that's your right. Just learn first the rules of artificial feeding of infants!
Rules for artificial feeding of a child
It is best to consult a pediatrician, but in principle, if the baby is not lactose intolerant, any mixture approved by the Union of Pediatricians of Russia will do. It is great if the mixture contains Omega 3 and Omega 6 fatty acids, they contribute to the harmonious development of the nervous system. nine0003
For example, Nutricia's "Malyutka" formula meets all the standards and rules of artificial feeding, is produced according to European technologies with the strictest quality control and is recommended as an alternative to breast milk even for newborns. Nutricia regularly evaluates the quality and demand for its products among consumers and doctors, analyzing the results of independent surveys of pediatricians and mothers with children up to 24 months of age.Iodine, selenium, zinc, iron with enough vitamin C (for better absorption), choline, taurine, L-carnitine are modern ingredients, the amount of which is specially selected in formulas to meet the needs of children.The quality is monitored by the Dutch research center Numico, the milk base for formulas is made in the most environmentally friendly country - Ireland, and production is open in Russia, at a plant in Istra, which received the international ISO 22000 certificate - maximum food safety control who in. nine0003
Nutricia regularly evaluates the quality and demand for its products among consumers and doctors, analyzing the results of independent surveys of pediatricians and mothers with children up to 24 months of age.Iodine, selenium, zinc, iron with enough vitamin C (for better absorption), choline, taurine, L-carnitine are modern ingredients, the amount of which is specially selected in formulas to meet the needs of children.The quality is monitored by the Dutch research center Numico, the milk base for formulas is made in the most environmentally friendly country - Ireland, and production is open in Russia, at a plant in Istra, which received the international ISO 22000 certificate - maximum food safety control who in. nine0003
Bibikol New Zealand brand mix is made on the basis of wholesome goat milk. The range of the brand includes mixtures for the smallest and older children, and the quality of the products is confirmed by Russian pediatricians. As a rule, formula feeding does not cause serious side effects even during the adaptation period.
The Dutch brand Kabrita also makes milk formulas based on goat's milk, which is easier to digest than traditional cow's milk. The brand's products contain vitamins, microelements and other functional ingredients necessary for the development of the child. nine0003
The mixes of another Dutch brand, Friso, are considered among the best due to their high quality. The brand offers mixtures for both newborns and older children. Subject to the rules for artificial feeding, this is an excellent choice for babies of different ages.
2. How do I know if formula is right for my baby?
If possible, the transition to artificial feeding should be done according to the rules, gradually replacing breast milk with formula. Pediatricians believe that adaptation to a new diet in babies under the age of one year takes from 3 to 7 days. During this period, stool changes, gas formation are possible, and this should not be frightened. As a rule, after a week, the baby stops worrying about the tummy and gets used to the new mixture. If this does not happen, it is worth choosing another food for him. For example, instead of the usual milk mixture, offer a fermented milk analogue. Major brands, like Nutricia's Malyutka, always have both options in their product line. nine0003
As a rule, after a week, the baby stops worrying about the tummy and gets used to the new mixture. If this does not happen, it is worth choosing another food for him. For example, instead of the usual milk mixture, offer a fermented milk analogue. Major brands, like Nutricia's Malyutka, always have both options in their product line. nine0003
Formula milk can be used from birth
To improve digestion, a pediatrician can recommend cultured milk formula for formula feeding
3. How to choose a feeding bottle?
Feeding bottles come in plastic and glass, and each option has its own advantages, there are no strict rules for artificial feeding in this regard. Plastic ones are safer because they don't break. They are lighter, so it is convenient to take them with you for a walk. Glass is good because it can be sterilized many times, while plastic can deteriorate. Which bottle to choose for a newborn depends on the age of the baby. For the smallest, glassware is better, since sterility is in the first place. For older babies outside the home, it is better to use plastic bottles, but for home feeding, still leave glass bottles. nine0003
For the smallest, glassware is better, since sterility is in the first place. For older babies outside the home, it is better to use plastic bottles, but for home feeding, still leave glass bottles. nine0003
4. How to properly store baby food?
Prolonged exposure to non-standard temperatures, both low and high, can change the organoleptic properties of the product, affect its solubility, and cause swelling of the foil bag or the protective membrane of the can. In case of repeated heating and cooling of the mixture, especially in winter, further use of the product may cause a painful reaction in the child. Therefore, it is very important to observe temperature control from 0ºС to +25ºС. Formula feeding regulations do not recommend storing product near heat sources such as stoves, electric kitchen appliances, radiators, or on windowsills. nine0003
5. How long can I keep formula formula?
Less than an hour. If the baby has not finished eating, and you intend to finish feeding him in 15-20 minutes, you can not prepare a new mixture. But if the baby has eaten enough, and the feeding regimen for artificial feeding provides for the next feeding only after 2.5 - 4 hours, then the leftovers should be poured out, and a new portion should be prepared for the next time.
If the baby has not finished eating, and you intend to finish feeding him in 15-20 minutes, you can not prepare a new mixture. But if the baby has eaten enough, and the feeding regimen for artificial feeding provides for the next feeding only after 2.5 - 4 hours, then the leftovers should be poured out, and a new portion should be prepared for the next time.
6. Does my child need probiotic formula? nine0050
GOS/FOS prebiotics are natural dietary fibers similar in composition to breast milk prebiotics, they are added as high-quality mixtures to improve digestion. The child quickly and painlessly gets used to such a mixture, absorbs it well and encounters stool disorders less often. Rules for artificial feeding of newborns and older children recommend giving preference to such mixtures, although this is not a strict requirement.
7. How do you know if your baby is eating enough? nine0050
You can use the Shkarin formula: The volume of the mixture per day = 800 ml + 50 x (M-2), where M is the number of months of the child's life. But this method is only suitable for babies older than 2 months. For newborns, everything is very individual, since babies are born with different weights and heights, so if you are afraid that the baby is malnourished or overeating, consult a doctor before feeding the baby formula again.
But this method is only suitable for babies older than 2 months. For newborns, everything is very individual, since babies are born with different weights and heights, so if you are afraid that the baby is malnourished or overeating, consult a doctor before feeding the baby formula again.
8. Should I change my formula?
If there is no reason to doubt the quality of the mixture and its tolerance by the baby, you should not change your child's usual diet just because the new mixture seems more useful, modern, etc. to you. Replacing the mixture can be a real stress for the child's body. And there is no guarantee that a new diet will not cause any signs of intolerance. Replacing the mixture is justified when passing the next age limit, and even in this case, the rules for artificial feeding recommend remaining faithful to one manufacturer. nine0003
9. What is the correct way to mix?
According to the rules of artificial feeding, most mixtures are prepared as follows: cool boiled water to a temperature of 50-60 ° C (a higher temperature cannot be used, live bifidobacteria die and some vitamins are destroyed). Pour it into a bottle, add the exact amount of the dry mixture there. Close the bottle, mix the mixture thoroughly, shaking the contents of the bottle. Look at the light so that there are no lumps, the milk should turn out homogeneous. To check the temperature of the food - put a few drops on your wrist or elbow crease (the most sensitive place). The mixture should be slightly warmer than body temperature—i.e. practically not felt. nine0003
Pour it into a bottle, add the exact amount of the dry mixture there. Close the bottle, mix the mixture thoroughly, shaking the contents of the bottle. Look at the light so that there are no lumps, the milk should turn out homogeneous. To check the temperature of the food - put a few drops on your wrist or elbow crease (the most sensitive place). The mixture should be slightly warmer than body temperature—i.e. practically not felt. nine0003
10. Technique and rules of artificial feeding
How to formula feed correctly? In order to make it comfortable not only for the baby, who should be in a semi-vertical position, but also for the mother during feeding, you can use additional pillows by placing them under the back. The position of the mother's legs can be different: you can put your foot on the foot, you can put a low bench under your feet, you can feed the baby in the prone position, while gently holding the baby. To reduce air swallowing, tilt the bottle so that the milk fills the nipple and the air rises to the bottom of the bottle.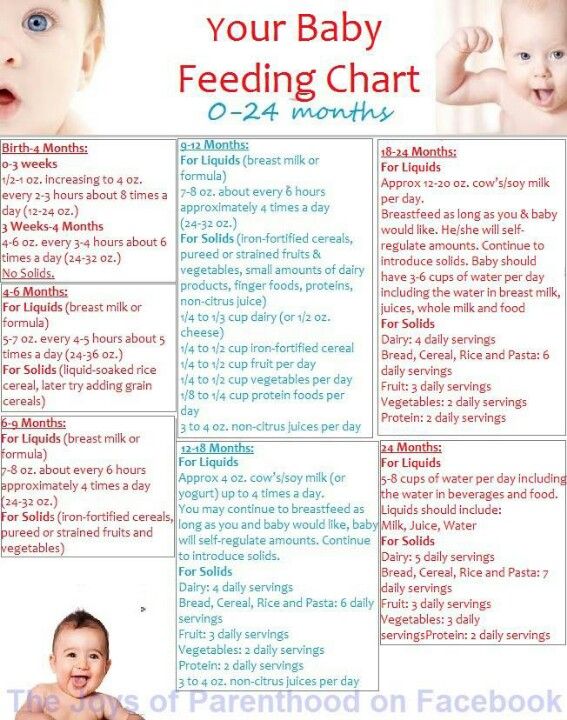 Hold your baby upright for a few minutes after feeding to reduce the chance of spitting up. nine0003
Hold your baby upright for a few minutes after feeding to reduce the chance of spitting up. nine0003
Mistakes in artificial feeding
- Blame yourself for being an "artificial" baby. Yes, mother's milk is considered the best food for babies, but if for some reason you cannot provide a child with them, this is not a reason to declare yourself a bad mother. Numerous children were bottle fed and did not experience any fatal consequences. Learn the rules of artificial feeding and follow them without blaming yourself needlessly.
- Feed on demand. Artificial feeding rules suggest feeding by the hour, not on demand. The mixture is digested longer than mother's milk, so it is important to withstand breaks between feedings. nine0034
- Ignore the rules for the introduction of complementary foods when artificially fed. Do not introduce complementary foods earlier than at 6 months, and be sure to consult with your pediatrician beforehand.

- Forgetting to drink water. For high-quality assimilation of mixtures, water is necessary! Be sure to let the baby drink.
- Feeding regular milk instead of formula. Neither cow's nor even wholesome goat's milk is suitable for children. Use only special formulas and follow all the rules of artificial feeding that we have talked about. nine0034
Breastfeeding and its benefits for the normal development of the infant.
Mother's milk is a natural biological product that provides physiologically adequate nutrition for babies. This is the "gold standard" of early childhood nutrition, and far from all aspects of its multifaceted influence have been studied.
A breastfed mother can follow different dietary patterns for her baby. Free feeding, or "on demand" feeding, is the diet of a child of the first year of life, when the mother puts the child to the breast as many times and at the time as the child requires, including at night. The duration of feeding is also determined by the child. It is more often carried out in the first months of life and with exclusive breastfeeding. Regulated feeding is such a diet of a child when feedings are carried out at more or less fixed hours, the frequency and volume of feedings is recommended by the doctor, taking into account the age, body weight, appetite and individual characteristics of the child. It is more often carried out after 1-2 months of life, especially with the option of mixed feeding. The duration of feeding of newborns ranges from 20 to 30 minutes, and for children older than 1 month - from 10 to 20 minutes. The water requirement of children in the first months of life is satisfied by breast milk with a sufficient level of lactation, so they do not need additional drinking. nine0003
The duration of feeding is also determined by the child. It is more often carried out in the first months of life and with exclusive breastfeeding. Regulated feeding is such a diet of a child when feedings are carried out at more or less fixed hours, the frequency and volume of feedings is recommended by the doctor, taking into account the age, body weight, appetite and individual characteristics of the child. It is more often carried out after 1-2 months of life, especially with the option of mixed feeding. The duration of feeding of newborns ranges from 20 to 30 minutes, and for children older than 1 month - from 10 to 20 minutes. The water requirement of children in the first months of life is satisfied by breast milk with a sufficient level of lactation, so they do not need additional drinking. nine0003
The criteria for a sufficient level of lactation are normal daily diuresis (600-700 ml), weight gain adequate to the age of the child and psychomotor development. If you suspect a lack of milk, you should determine the daily volume of lactation using control weighing and compare it with the calculated one, take measures to restore lactation or introduce supplementary feeding.
Breast milk is the most complex biologically active substance with unique properties:
- regulation of the processes of growth, development and differentiation of tissues;
- anti-infective protection;
- formation of immunological tolerance to dietary antigens;
- influence on the formation of the maxillofacial skeleton, speech, hearing;
- prevention of obesity, diabetes, atherosclerosis;
- beneficial effect on mental and behavioral responses, intelligence, learning ability and social adaptation;
- reduced risk of cancer in the mother, contraceptive effect in the first months of lactation. nine0034
Breast milk provides anti-inflammatory (antioxidants, enzymes that break down pro-inflammatory neurotransmitters, anti-inflammatory cytokines) and immunomodulatory substances (live CD4 and CD8 lymphocytes, nucleotides, IgA, cytokines IL-2, IL-10, IL-12, etc., soluble cytokine receptors). Breastfeeding and the state of the intestinal microflora play a key role in maintaining a balance in the Thh Th3, Th4 cytokine system. Thanks to the bifidogenic properties of human milk, a complete intestinal microbiota of the child is formed, innate immunity and protective mechanisms of the intestinal mucosa are activated, and the immune response matures. nine0003
Thanks to the bifidogenic properties of human milk, a complete intestinal microbiota of the child is formed, innate immunity and protective mechanisms of the intestinal mucosa are activated, and the immune response matures. nine0003
Digestive system:
- One of the main advantages of women's milk is the proximity of its proteins in terms of qualitative composition to blood serum proteins. Breast milk contains mainly finely dispersed, that is, consisting of the smallest particles, albumin proteins, which are easily absorbed in the child's digestive tract.
Digestibility, absorption completeness of women's milk proteins reaches 98-99%, for cow's milk proteins this figure is much less. The main protein component of cow's milk is casein, the content of which is up to ten times higher than that in human breast milk. Casein, being a large and aggressive soluble protein, is able to penetrate the intestinal walls, forcing the child's body to produce an endogenous inflammatory mediator - histamine. What can cause both intestinal bleeding, which is fraught with the subsequent development of anemia, and various kinds of allergic reactions. nine0003
What can cause both intestinal bleeding, which is fraught with the subsequent development of anemia, and various kinds of allergic reactions. nine0003
- The residence time of food in the gastrointestinal tract of the baby with natural and artificial feeding is also different. The child's stomach is freed from food after 2-3 hours with breastfeeding, and with artificial feeding - after 3-4 hours. Thus, artificial feeding puts a lot of stress on the digestive tract and on the baby's body as a whole.
- The activity of the enzyme lipase, which is responsible for the breakdown of fat in the gastrointestinal tract of the child, is much higher in human breast milk. Due to the activity of maternal lipase, a high degree of fat dispersion is achieved, which facilitates their further absorption and assimilation. As a result of the action of breast milk lipase, there is a significantly lower load on the pancreas and liver of the baby, the organs responsible for the digestion of fat
- Women's milk contains 5-6 times more linoleic acid. With a lack of this polyunsaturated fatty acid, a child may experience a delay in physical development, metabolism is disturbed, and adverse changes in the condition of the skin are possible.
With a lack of this polyunsaturated fatty acid, a child may experience a delay in physical development, metabolism is disturbed, and adverse changes in the condition of the skin are possible.
Immune system:
- The most important advantage of mother's milk in comparison with its artificial substitutes is the presence in it of a large group of substances that protect the child's body from infections. These are secretory immunoglobulin A - sIgA, interferon, lysozyme, lactoferrin, bifidus factor, cells of the immune system. nine0003
- Immunoglobulin A is contained in secrets (fluids) on the surface of mucous membranes in contact with the external environment - lungs, nasal cavity, gastrointestinal tract, urinary tract. Maternal secretory immunoglobulin A provides protection against infection of the vital organs and systems of the child.
- Human milk lactoferrin plays an exceptional role in protecting the baby from viral infections, preventing the penetration of viral particles through the cell membrane, thus preventing infection from entering the baby's body. In addition to the antiviral action, lactoferrin also has antibacterial properties. Many microorganisms contain receptors for lactoferrin on their surface, and the binding of lactoferrin to the corresponding receptor leads to the death of a foreign bacterial cell. Lactoferrin has a bactericidal effect against a large number of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. nine0003
- the bifidus factor of human milk is represented by a whole complex of various sugars (oligosaccharides) and their monomers: beta-lactose, galactooligosaccharides, D-glucose, D-galactose, N-acetylglucosamines, L-fucose and sialic acids. The bifidus factor of human milk stimulates the formation of the intestinal microflora, mainly consisting of bifidobacteria (B. Bifidum) and lactobacilli. Normal intestinal microflora lines the intestinal crypts like a blanket, creating a protective layer that prevents foreign bacteria and allergens from entering the baby's circulatory system. Also, bifido- and lactobacilli create a favorable intra-intestinal environment with a shift in the pH of the contents of the colon to the acid side, which inhibits the growth of pathogenic and conditionally pathogenic bacteria and promotes the absorption of iron, calcium, vitamin D and other micro- and macroelements; participates in the synthesis of vitamins B1, B2, B3, PP, B6, B12, folic acid, biotin. In addition, the normal intestinal microflora makes the baby's immunity stronger. nine0003
At present, using the latest scientific methods, the existence of oligosaccharides containing up to 32 sugar fragments and up to 15 fructose fragments has been established. This means that the number of different types of oligosaccharides in human breast milk can reach several tens of thousands of units. Naturally, even modern artificial mixtures containing prebiotics (industrial analogues of the bifidus factor) cannot be compared in quality and variety with breast milk.
Urinary system:
- The formation of the child's urinary system and the development of its functions takes place in the first year of life. In an infant at the time of birth, the plasma flow and the process of formation of primary urine by filtering plasma in the renal glomeruli are reduced, osmotic concentration of urine is not effective enough. The main indicators of kidney function come to the level of an adult by the beginning of the second year of life.
 Therefore, it is very important that the load on the kidneys, depending on the content of proteins and mineral salts in the food taken, be adequate to the physiological age of the child. nine0034
Therefore, it is very important that the load on the kidneys, depending on the content of proteins and mineral salts in the food taken, be adequate to the physiological age of the child. nine0034 - The protein level in women's milk averages from 0.8 to 1.2 g / 100 ml, while even in the adapted ready-made milk formula this figure is 40 - 70% higher and is 1.4 - 1, 6 g/100 ml. The increased content of proteins increases the load on the glomerular apparatus of the kidney.
- Another problem of milk mixtures is their normalization by mineral composition. Excess salt can overload the kidneys and cause thirst, which is reflected in the addition of water to formula-fed babies. nine0034
- Many pediatricians still recommend giving babies about 100 ml of water a day to avoid dehydration. However, at present, the World Health Organization and UNICEF insist that there is no need for supplementation and the introduction of any foreign liquids and products before the child reaches the age of 6 months.
- What is the basis for these recommendations? If breastfeeding is organized correctly (the mother feeds the baby on demand, approximately every 1.5 - 2 hours, keeping night feedings), then the baby receives enough water from milk in the first six months of life. nine0034
This section describes only the main advantages of breastfeeding.
Is there any benefit from breastfeeding for the mother and does this process affect the "usual" way of life?
The benefits for the mother can be divided into three groups:
1. Health benefits
- Breastfeeding within the first hour after birth significantly reduces the risk of postpartum uterine bleeding.
- Breastfeeding maintains a high level of hormones (oxytocin and prolactin) in the blood of the mother, which contributes to the formation of strong maternal feelings. nine0034
- If a woman breastfeeds her baby exclusively, then in the first 4-6 months after childbirth, the probability of pregnancy is reduced by 95%.

- Long-term breastfeeding reduces the risk of breast cancer by 50%, and if a mother breastfeeds multiple children, breastfeeding each child reduces the risk of ovarian cancer by 25%. Also, women who breastfeed for a long time are less likely to suffer from osteoporosis.\
2. Economic benefits
- You don't need to buy breast milk, you don't need additional accessories - nipples, sterilizers, heaters, breast pumps, which you still need to run around and choose exactly those that fit the size and shape of your breasts.
- Savings on artificial mixtures, which are not cheap at all.
3. Breastfeeding is convenient
From a practical point of view, breastfeeding makes life easier for mothers. Breast milk is always sterile, at the ideal temperature and composition, requires no preparation, and is always fresh and ready to drink. It is convenient that a mother can feed a child in any conditions: in transport, at a party, in nature - in those places where preparing baby food is difficult and dangerous due to infection.