Gassy baby food
How to Help Baby or Toddler With Gas – Foods to Avoid
Dr. Deena Blanchard
All people pass gas! In fact, it is normal to pass gas anywhere from six to twenty times a day. Additional gassiness is typically not related to a serious health problem and will often resolve without any intervention. When gas becomes painful or bothersome for your little one, it is important to get in touch with your pediatrician.
Gas when Starting Solids
As your little one gets older and you start to introduce solid foods, you may find that certain foods increase gassiness. It is important to differentiate between gas that is painful and gas that is not. If your little one is passing gas frequently but seems happy and playful and without abdominal pain then there is no reason to intervene or make changes.
Foods that break down more slowly, such as beans, cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, cauliflower, kale, etc..), and other high fiber containing foods can cause additional gas. These foods are rich in nutrients and fiber and an important part of your little one’s diet. It may take some time for your little one’s digestive system to adjust to these foods and that is okay. If your baby is in pain, vomiting, irritable or has blood in the stool you should always call your pediatrician.
Making sure your little one is well hydrated as you introduce solid foods and particularly high fiber foods, can minimize gassiness and prevent constipation.
Gas in the Older Infant and Toddler Diet
Common culprits for increasing gas in older children are:
- Fried and fatty foods.
- Beans.
- Vegetables such as artichokes, asparagus, broccoli, brussels sprouts, cabbage, cauliflower, cucumbers, green peppers, onions, peas, radishes, and raw potatoes.
- Fruits such as apricots, bananas, melons, peaches, pears, prunes, and raw apples.
- Wheat and wheat bran.
Keeping a food and symptom log can help determine if specific foods are increasing your child’s symptoms. Symptoms of gas can include, passing gas, bloating, mild abdominal discomfort, and belching. If you are finding certain foods are causing your child to have these symptoms or feel uncomfortable, it is best to discuss this with their pediatrician.
Symptoms of gas can include, passing gas, bloating, mild abdominal discomfort, and belching. If you are finding certain foods are causing your child to have these symptoms or feel uncomfortable, it is best to discuss this with their pediatrician.
Drinking lots of water and getting regular exercise and movement can help decrease symptoms of gas and bloating. Avoiding carbonated beverages and drinks containing sorbitol or xylitol is another helpful way to prevent gas build up. As always, if you have any concerns and before making dietary changes it is best to talk to your pediatrician.
Sources
American Gastroenterological Association http://www.gastro.org/wmspage.cfm?parm1=689
The American College of Gastroenterology http://www.acg.gi.org/patients/gihealth/belching.asp
American Academy of Pediatrics: “Abdominal Pain.”
American Academy of Family Physicians: “Feeding Problems in Infants and Children.”
Published: February 10, 2020
Last modified: February 10, 2020
What You Can Do To Help Your Gassy Breastfed Baby
What are some common culprits behind your baby's gassiness? Learn the signs, foods that may cause gassiness in your baby, and how to soothe and relieve his or her symptoms.
Share this content
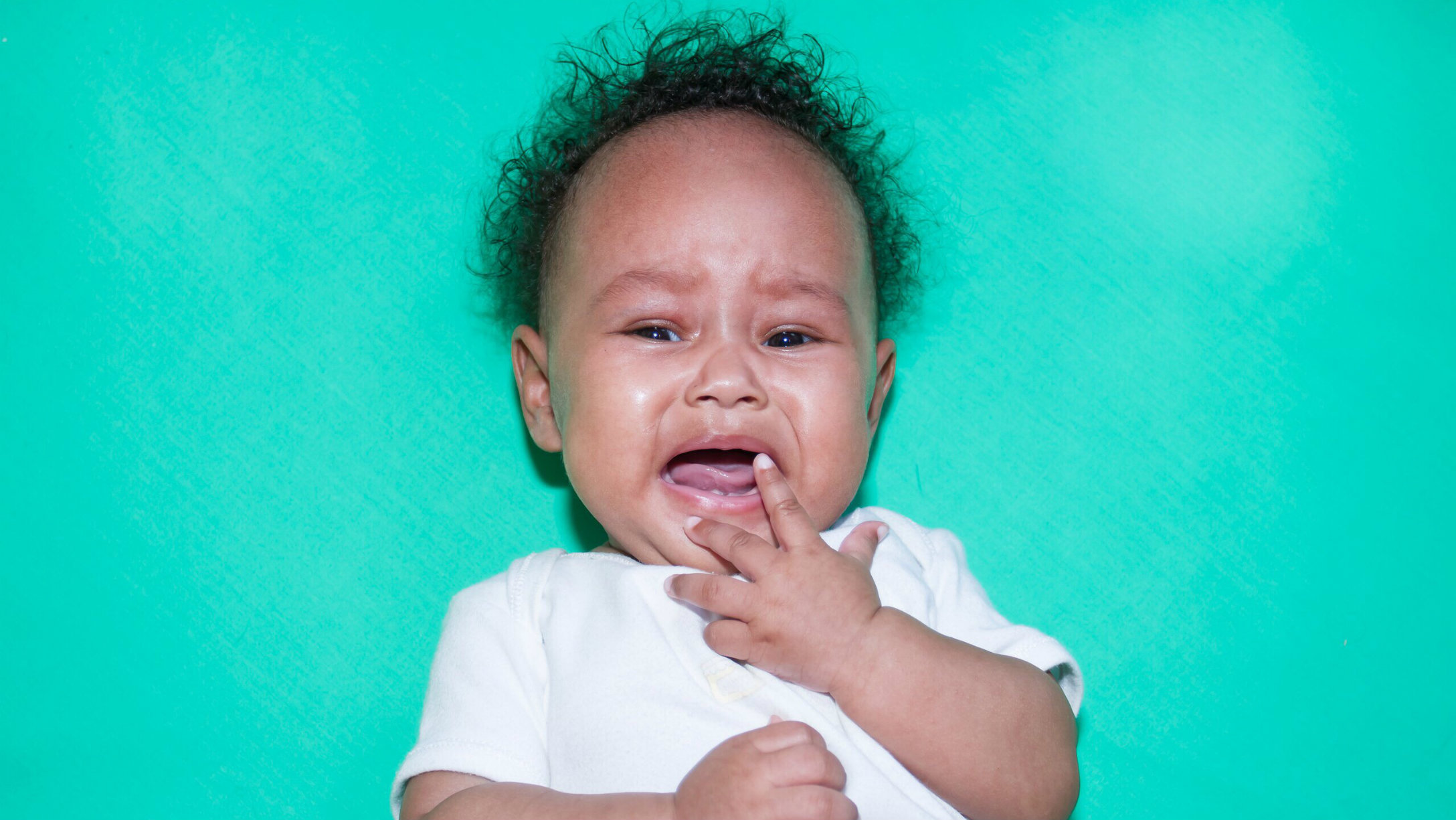
As a new parent, it can be stressful and upsetting to see and hear your baby cry. That’s especially true if you've checked off all the usual suspects— dirty diaper, empty belly, discomfort, or over-tiredness —and you still can’t seem to soothe your little one.
Gas is something that many newborns experience, and it can be painful for them! It isn't always the first thing that parents remember to consider, since it's not something easily visible.
Signs Your Breastfed Baby is Gassy
If you suspect excess gas could be the culprit causing your baby’s fussiness, there are several signs that may indicate you are correct:
- Burping. It’s possible your baby has swallowed too much air while nursing or crying for a long period.
- Spitting up. While spitting up is perfectly normal, gas that’s trapped in the stomach can push breast milk back up and cause your baby to spit up.
- Bloated tummy.
 This could be a sign that gas has built up in your baby’s stomach.
This could be a sign that gas has built up in your baby’s stomach. - Flatulence. Every baby toots, but if they’re doing so excessively, it could mean they have excess gas.
- Arched back, legs drawn toward the tummy. The discomfort from gas pains will make a baby try to adjust to alleviate it.
Gassy Baby Causes
Gas in a breastfed baby is not uncommon and can be attributed to several factors:
- Gulping while feeding. If your milk let-down reflex is strong, your baby may gulp your milk to keep up and swallow extra air in the process. If that’s the case, your little one may do better nursing in a more upright position, so he or she has better control over milk intake and flow.
- Introducing a bottle. If your baby is used to the breast and you begin feeding with a bottle, it may take some getting used to at first. As a result, he or she may swallow too much air while eating.

- Constipation. When your baby is constipated, they may have gas trapped in their tummies that they’re having a hard time releasing.
- Crying. If your baby has been crying for a long time, they may be gulping in air in the process.
- Mom’s diet. Food that you’ve eaten can make your baby gassy as well. Certain foods such as dairy, soy or wheat may contribute to gassiness in your little one. Keep a food journal of what you eat to see if you can pinpoint the culprit in your diet.
Foods That Make Breastfed Babies Gassy
Though a baby’s gas is not commonly linked to mom’s diet, there are certain gas-inducing foods that could give both a breastfeeding mom and her baby gas. These include:
- Fiber. Foods like bran, beans, and whole grains.
- Fruit. Citrus fruits, prunes, plums, peaches, or apricots.
- Vegetables. Broccoli, cabbage, and Brussel sprouts.

- Garlic. Garlic-seasoned foods like pasta dishes or garlic bread.
- Dairy. Yogurt, ice cream, or milk products.
- Carbonated beverages. If they make you burp, they could make your baby gassy too.
It’s not necessary to give up all your favorite foods when pregnant and/or breastfeeding. Health experts recommend only making dietary changes if you see a direct connection between something you’ve eaten and your baby's gassiness.
Additionally, if you’re still breastfeeding after your little one begins solids or finger foods, it’s easier to detect what food might be the culprit and then eliminate it.
Relieving Gassy Babies
There are several effective ways to help relieve your baby’s gas pains and soothe them. Try a combination of these to find what works best for your little one.
- Burp twice. Try to coax two burps out of your baby instead of just one.
- Sit upright.
 Hold your baby in an upright position while burping. This makes it easier to expel gas.
Hold your baby in an upright position while burping. This makes it easier to expel gas. - Tummy time. Laying your baby on their tummy will help to push gas out.
- Bicycle exercises. Put your baby on his or her back and move their legs in a pedaling motion, similar to cycling on a bike. This helps with constipation as well.
- Massage the tummy. A gentle massage can help move gas out.
- Adjust baby’s latch. Make sure your baby is latching correctly to avoid swallowing too much air.
Don't worry, mama - Gas is typically a normal occurrence and most babies experience gassiness from time to time! With some minor adjustments, you can soothe your little one and help them get through the discomfort of gas.
about baby food production technology - 1 answers
I found an article where it is written how baby food is divided. it was interesting for me to read it, because it is an acute question to give jars or cook it yourself.
The general operations include the preparatory cycle operations associated with the acceptance of raw materials in terms of quantity and quality, inspection, preliminary preparation for processing, etc.
In the production of fruit and vegetable-based canned food, fruit and vegetable raw materials are sorted, which makes it possible to form batches of products that are homogeneous in quality by rejecting defective products by dividing them into quality gradations. Sorting includes inspection (visual inspection) of a batch of raw materials, removal of non-standard specimens - unripe, with signs of microbial spoilage, with a damaged surface, etc. does not affect the quality of the finished product.
Purification of raw materials consists in the removal of inedible or nutritionally low-value parts - skins, seeds, seeds, stalks, seed chambers, etc., thereby increasing the amount of the edible part. Chemical, steam-thermal, pneumatic, refrigeration and mechanical cleaning methods are used.
The peel of fruits and vegetables is chemically removed, for which the raw materials are processed in a hot (80-90 ° C) solution of caustic soda. In this case, the connection between the skin and adjacent parenchymal tissues is weakened, the skin is easily removed. Potatoes and root crops are processed by the steam-thermal method, which consists in processing raw materials with live steam under pressure. The moisture under the skin boils, as it were, as a result of which the skin is torn and partially separated. Finally, the skin is separated in a washing machine. At the same time, partial losses of vitamins are observed, mainly due to the skin rich in these substances. At the same time, enzymes are inactivated and biochemical processes leading to the loss of nutrients are stopped.
Root crops and potatoes are also peeled mechanically on root peelers with an abrasive surface. This method is the least economical due to the increased amount of waste, but does not affect the composition of the raw material.
The refrigeration method of cleaning is based on the instantaneous sharp freezing of the skin and subcutaneous layer of the fruit with a refrigerant and the subsequent removal of the exfoliated skin in a brush washer. At the same time, vitamins are well preserved, but expensive equipment is required. Therefore, this method is rarely used.
The pneumatic method is used when peeling onions with compressed air. The scales are removed by means of conical rotating rollers, the upper and lower knives installed in the machine cut off the neck and lower part of the bulb.
Washing of raw materials is carried out in order to remove contaminants, pesticides, impurities and microorganisms in washing machines, followed by control of the degree of microorganism contamination of clean raw materials. The contamination should not exceed the maximum allowable level for vegetables 5 * 104, for apples - 1 * 103 per 1 g of raw materials.
For highly contaminated vegetable raw materials (carrots, beets), a preliminary washing is carried out in hydraulic conveyors using brushes, vibrating vibrations, ultrasound and water turbulence. Water consumption for washing should be 1 m3 per 1 ton of raw materials.
Water consumption for washing should be 1 m3 per 1 ton of raw materials.
The new method of washing with carbon dioxide gas is based on the fact that carbon dioxide is bubbled into the water in a washing bath. In this case, partial acidification of water and its turbulization occur. As a result of the resulting flotation effect, contaminants are completely removed. This washing method was developed at VNIIKOP.
In the production of meat and vegetable-based canned food, then mechanical processing of raw materials is carried out, which includes cutting, grinding (crushing), rubbing, pressing, filtering, homogenization, deaeration.
In the production of meat-based canned food, the general operations of the preparatory cycle are external inspection, toilet, deboning, trimming, sorting. Frozen meat is thawed in the air. At the same time, all inedible and nutritionally invaluable parts are removed - bones, cartilage, connective tissues. Bird carcasses are inspected, the remaining hemp, oil gland, internal organs, and veterinary marks are removed. Then they are washed from the outside and inside, first with warm, then with cold water. The offal is inspected, cleaned of the contents, and also washed first with warm, then cold water. Further, the prepared raw material is sent for mechanical processing.
Then they are washed from the outside and inside, first with warm, then with cold water. The offal is inspected, cleaned of the contents, and also washed first with warm, then cold water. Further, the prepared raw material is sent for mechanical processing.
Preparation of auxiliary raw materials is as follows: the butter is cleaned from staff; salt is sieved; onions and root crops are cleaned and washed; starch and casecite are sifted and mixed with meat broth. The casecit emulsion is prepared immediately before use. Long-term storage is not allowed. Spice extracts (celery, parsley, dill) are mixed with prepared salt in proportions according to the recipe.
Preparation of fish includes defrosting frozen fish, sorting by size and quality, washing, removing parts that are inedible and of little nutritional value (scales, skin, fins, viscera), cutting into pieces weighing 80-100 g. At the same time, auxiliary materials and the main vegetable raw materials. These operations are carried out in the same way as in the production of canned meat with vegetables.
Mixing of components is used in the production of combined canned meat and fish - with vegetables, cereals, etc. In the production of fish-based canned food, mixing of the components is carried out according to the recipe. First, minced fish and carrots are loaded, then oatmeal, oatmeal, starch and milk powder are added until a homogeneous mass is obtained. After that, butter, salt and water or pasteurized milk are introduced and mixed again. The resulting mass is transferred to deaeration and heating.
In addition, blanching, homogenization, deaeration, packaging, sealing, sterilization are common to all canned food. However, it is advisable to consider them in a certain technological sequence, so they will be considered in a number of specific operations.
Specific technological operations include the processing of raw materials, including cutting, blanching, grinding, rubbing, separating, filtering.
Cutting the raw material facilitates its further processing, and the shape and size of the particles depend on the type of finished product.
Blanching is the treatment of raw materials with live steam under pressure or hot water to inactivate enzymes. Thus, protoplasmic proteins coagulate in vegetable raw materials when heated, which facilitates the extraction of cell sap. There is a partial hydrolysis of protopectin and its transition to soluble pectin. As a result, the tissues of the fruits soften, the process of rubbing the fruits is facilitated, which is accompanied by a change in the volume and mass of the raw material as a result of the removal of air and water or moisture absorption. In this case, there are losses of volatile substances, as well as partial losses of coloring substances.
In the production of canned meat and fish, blanching is carried out with live steam or boiling water. The duration of blanching for beef and tongues is 10-15 minutes, brains - 5, chicken carcasses - 9-11, and canned fish 5-7 minutes. In this case, there is a partial hydrolysis of the connective tissue, coagulation of proteins, hydrolysis of collagen, which passes into soluble glutin, as a result of which the structure of the product and its digestibility improve. In fish raw materials during blanching, muscle tissue and skin are destroyed, the integrity of muscle cells is violated, which contributes to the release of fat, moisture and extractive nitrogenous substances from fish meat. At the same time, there is no significant improvement in the taste and nutritional properties of fish meat. The resulting broth is centrifuged or filtered through a cloth, and then used in the production of canned food.
In fish raw materials during blanching, muscle tissue and skin are destroyed, the integrity of muscle cells is violated, which contributes to the release of fat, moisture and extractive nitrogenous substances from fish meat. At the same time, there is no significant improvement in the taste and nutritional properties of fish meat. The resulting broth is centrifuged or filtered through a cloth, and then used in the production of canned food.
Grinding (crushing) in the production of juices allows to destroy the tissue structure and increase the yield of juice. In the production of puree, the fruit mass is wiped. To prevent the destruction of biologically active substances, grinding is carried out in an atmosphere of steam (CO2) or inert gases, since the activity of oxidizing enzymes is activated in the crushed raw materials.
Grinding of fish raw materials is carried out to facilitate the heat treatment of raw materials and accelerate the partial destruction of connective and muscle tissue proteins. In the production of puree products, the minced meat is immediately sent for mixing, while homogenized products are subjected to homogenization and then fed into the mixer.
In the production of puree products, the minced meat is immediately sent for mixing, while homogenized products are subjected to homogenization and then fed into the mixer.
Poultry-based PDP is produced in the same way as meat-based. If, for example, according to the recipe, other products (onions, carrots, butter) are included in the chicken soup puree, they are crushed and thoroughly mixed with chopped chicken meat, homogenized, deaerated and heated. When hot, the mass is packed in 100 g cans or 200 g glass jars, and then sterilized according to the generally accepted scheme.
Rubbing is carried out after heat treatment of fruit and vegetable raw materials on special rubbing machines in the production of puree products and juices with pulp. It is carried out after heat treatment, when oxidative enzymes are inactivated. Three times rubbing of raw materials gives finer grinding and helps to reduce waste. In this case, the diameter of the sieve openings in the first machine should be 1. 5-2 mm, in the second - 0.8-1, in the third - 0.4-0.5 mm.
5-2 mm, in the second - 0.8-1, in the third - 0.4-0.5 mm.
In the production of canned meat, meat previously boiled for 5-6 hours at a low boil is separated from bones and fat, and then filtered on mesh filters with holes with a diameter of 0.7-0.8 mm.
Separation is carried out to clean juices produced without pulp from large suspended particles. For this purpose, disc separators are used, as well as horizontal screw centrifuges with a conical drum - decanters, on which juice with a high content of suspended matter can be clarified.
Pressing is used in the production of pulp-free baby food juices. It is carried out immediately after
pressed when heated to 85-90°C and immediately cooled to 35-40°C. At the same time, oxidative enzymes are inactivated and protein substances are coagulated, which facilitates the process of juice clarification and prevents its darkening.
Filtration produces clear liquids. As a filtering material, a filter cardboard, microporous plates or a membrane made of polymeric materials are used.
And now let's continue the consideration of operations common for the production of all types of canned food: homogenization (except for fish-based canned food), deaeration, packaging, capping (sealing) and sterilization.
Homogenization - fine grinding of the pulp to a particle size of 10-30 microns. To do this, various types of homogenizers are used in the production of puree products - plunger, rotary-pulsation, ultrasonic, etc. Homogenized products are well absorbed by the child's body. Thus, in fruit-and-berry and vegetable-based preserves, due to homogenization in juices with pulp, a homogeneous consistency of the product is created, and its delamination is prevented. A new method is homogenization using liquid carbon dioxide. In this case, the raw material is first saturated with CO2 under pressure, then, along the path of movement of the raw material, the pressure decreases, CO2 boils, the particles of the raw material are crushed to a size of 50–60 microns. The method was developed by VNIIKOP.
In the production of meat-based canned food, blanched meat is homogenized, previously ground on a microcutter to a particle size of 0.15-0.20 m/km, which makes it possible to obtain a homogeneous finely ground mass saturated with air.
Deaeration - removal of air from the product - is carried out at different stages of the technological cycle in order to prevent the oxidation of labile components by atmospheric oxygen. So, in the production of canned food based on fruit, berries and vegetables, the product is heated and air is sucked off, thereby creating a vacuum for 10-20 minutes. For this, continuous deaerators are used. In such devices, the juice is passed in a continuous stream through a chamber in which a deep vacuum is maintained. The juice is fed into the chamber in a thin layer or sprayed, due to which its surface increases sharply, which contributes to the removal of air.
In the production of meat-based canned food, deaeration is carried out by spraying in a vacuum chamber when heated to 80°C for 30-40 seconds. At the same time, the main part of microorganisms is destroyed, which further facilitates the sterilization of the product.
At the same time, the main part of microorganisms is destroyed, which further facilitates the sterilization of the product.
In the production of canned fish, the resulting mass is deaerated in a vacuum dispenser in the same way as in the production of canned meat, then heated to 80 ° C and immediately packed tightly in aluminum cans of cues in cans of lacquered tinplate with a capacity of up to 200 g. Filled cans sealed under vacuum and transferred to sterilization.
Depending on the type of canned food for baby food, the following methods of thermal preservation are used: sterilization in hermetically sealed containers, pasteurization, hot filling and aseptic preservation.
Sterilization - heat treatment of the product at a temperature above 100°C. As a result of this, the development of PDPs that meet the requirements of industrial sterility is ensured. Canned foods are considered industrially sterile if they do not contain pathogens of sticking, pathogenic and toxic forms of bacteria, as well as other microorganisms that can develop under normal storage conditions and cause spoilage of canned food or form products of their vital activity hazardous to health.
Sterilization in hermetically sealed containers is used in the production of liquid and puree semi-finished products packed in large containers. So, sterilization of meat-based canned food is carried out at t = 120-125°C in horizontal autoclaves of various types. At the same time, it is important to observe the sterilization regimes - temperature and duration of treatment. There is an inverse relationship between them: with an increase in temperature, the necessary “deadly” time decreases, but the loss of valuable nutrients increases.
Pasteurization - heat treatment of the product at a temperature below 100°C. Various types of pasteurizers are used for processing canned food, giving a temperature of 90-95 ° C, and more stringent requirements are imposed on the PDP from the point of view of industrial sterility.
During industrial sterilization and pasteurization, systematic monitoring of the presence of residual spore-forming mesophilic aerobic microflora is carried out. Before sterilization, the contamination should not exceed 2-102 in 1 g. Spore anaerobic microorganisms should not be detected in 0.5 g of the product. In an already sterile product, the number of thermophilic microorganisms should not exceed 3 per 1 g of the product.
Before sterilization, the contamination should not exceed 2-102 in 1 g. Spore anaerobic microorganisms should not be detected in 0.5 g of the product. In an already sterile product, the number of thermophilic microorganisms should not exceed 3 per 1 g of the product.
Hot filling (product temperature 97-98°C) is typical only for fruit and vegetable-based preserves. It is carried out in continuously operating heat exchangers with automatic temperature control. With this method, vitamins and other useful substances are destroyed to a somewhat lesser extent. At this temperature, the product is packaged in a hot container and sealed immediately. In this way, juices are packed in jars with a capacity of more than 2 dm3, and semi-finished purees - 10 dm3.
Aseptic preservation - sterilization of the product by rapid heat treatment followed by cooling, its packaging in sterile containers of various capacities under sterile conditions and storage in hermetically sealed containers, which excludes the possibility of microorganisms from entering from outside. Aseptic preservation is used in the preparation of puree and liquid semi-finished products used for the manufacture of canned food for baby food.
Aseptic preservation is used in the preparation of puree and liquid semi-finished products used for the manufacture of canned food for baby food.
Other methods of heat treatment of raw materials include blanching, frying, boiling.
Frying in the production of canned food for PDP, as a rule, is replaced by boiling the crushed raw materials, such as zucchini, followed by boiling in a vacuum apparatus. This allows you to get a product with a more delicate texture, which contributes to its better digestibility by the child's body. To increase the nutritional value add butter, sour cream, milk, vegetable oil.
Boiling is carried out in order to increase the concentration of solids, for example, in the production of concentrated juices.
taken from here link
Experts: The content of benzapyrene in food is allowed only in microdoses
July 29, 2013, 16:37 /ITAR-TASS/. The content of benzapyrene in food products is acceptable, but in extremely small, strictly regulated doses. Such data were presented to ITAR-TASS by a number of interviewed experts in connection with the ban on the import of Ukrainian sweets from Roshen / "Roshen" / into Russia, introduced by Rospotrebnadzor 29July 2013.
Such data were presented to ITAR-TASS by a number of interviewed experts in connection with the ban on the import of Ukrainian sweets from Roshen / "Roshen" / into Russia, introduced by Rospotrebnadzor 29July 2013.
Benzopyrene was found in the products of this enterprise, which, along with a number of other claims, was the reason for the introduction of supply restrictions.
To date, the Russian agency has not provided accurate data on the amount of the detected substance in the products of the Ukrainian company, while the company itself has not received any notifications. In this regard, it is quite difficult to determine the level of danger of imported products, experts say.
Benzopyrene content in products: to be or not to be?
According to Vladimir Dadali, professor of the Department of Biological and General Chemistry at the Mechnikov North-Western State Medical University, "there are no absolutely pure products", that is, the same benzapyrene can be found in some types of food, including fried or those that are sold on the streets. The fact is that benzapyrene is actively present in the exhaust gases of motor vehicles. It is with this that scientists often associate the presence of this substance in vegetable oil, if the sunflower grew near roads, or in milk, if cattle were fed grass or grain, which also absorbed this substance. Despite the fact that benzapyrene is a carcinogen, some regulatory documents establish its permissible value.
The fact is that benzapyrene is actively present in the exhaust gases of motor vehicles. It is with this that scientists often associate the presence of this substance in vegetable oil, if the sunflower grew near roads, or in milk, if cattle were fed grass or grain, which also absorbed this substance. Despite the fact that benzapyrene is a carcinogen, some regulatory documents establish its permissible value.
Roshen representatives explained that the products supplied to the territory of Russia were manufactured in accordance with the technical regulations of the Customs Union /CU/ on food safety /TR CU 021/2011/, which establishes standards for the content of benzapyrene in baby food, food for pregnant women and lactating women. At the same time, the requirements for the content of this substance in chocolate products have not been established not only in Ukraine and the Russian Federation, but also in the EU countries, the company emphasized. In addition, Roshen had doubts about "the correctness of sampling for conducting the necessary analyzes, confirming the compliance of products with the requirements of the regulatory documentation of the Russian Federation. "
"
According to Yury Morozov, executive director of the Fat and Oil Union of Russia, the technical regulation of the Customs Union for fat and oil products /TR TS 024/2011, which came into force on July 1, 2013/, strictly determines the dose of this substance. The regulation specifies a limit value of 0.002 mg per 1 kg. Meanwhile, in the CU regulation on food safety mentioned by the Ukrainian side, this indicator for bakery and flour confectionery products is even lower - 0.0002 mg per 1 kg, or "not allowed." According to Morozov, it is still worth figuring out how the substance got into the sweets: from the soil, when the ingredients were stored on asphalt, or otherwise.
Experts agree that benzapyrene is extremely dangerous for humans, especially for children. "This substance can penetrate the skin, if doses exceed the maximum permissible values, it can cause serious consequences," says Dadali.
And according to a member of the expert council at Rospotrebnadzor, deputy director of the Institute of Child Nutrition Vyacheslav Isaev, the degree of danger of this substance is so high that even its slight presence in food is unacceptable. "This is a heavy toxic substance that causes intractable occupational diseases. It should not be in the products," he concluded.
"This is a heavy toxic substance that causes intractable occupational diseases. It should not be in the products," he concluded.
Substance of the first hazard class
Benzopyrene (otherwise - benzpyrene, benzopyrene, benz / a / pyrene / - a chemical compound, a member of the family of polycyclic hydrocarbons, a substance of the first hazard class, which is formed during the combustion of hydrocarbon liquid, solid and gaseous fuel.
The chemical bond of benzpyrene with the nucleotides of DNA molecules can lead to severe types of defects and deformities in newborns. Benzopyrene is the most typical chemical environmental carcinogen, it is dangerous to humans even at low concentrations, since it has the property of biological accumulation. Being chemically relatively stable, it can migrate from one object to another for a long time. As a result, many environmental objects and processes that themselves do not have the ability to synthesize benzapyrene become its secondary sources.