Homemade baby bird food
This Is What To Feed Baby Birds — And How To Feed Them
If you’re wondering how to feed a baby bird, there are a few important things you need to know. Baby birds usually eat what their parents eat for dinner, since the parent has to burp its food into the mouth of its offspring. Birds cannot break down food at birth, so their parents must first partially digest the food to make it safe for chicks. Since baby birds are dependent on their parents not only for food but also for instructions on how to be a bird, it is essential that it stays with them. So, if you find a baby bird on the ground, try to bring it back to the nest rather than looking after it yourself. If you cannot return the bird to its nest, contact a rehabilitation center that can take care of it.
Contents
- Consult the experts if you think a baby bird isn’t being fed
- What to feed a baby bird
- What not to offer when feeding baby birds:
- DIY baby bird food
- How to feed a baby bird
Difficulty
Easy
Duration
15 minutes
What You Need
-
Dog or cat food, boiled eggs, or raw unseasoned liver
-
Small pieces of fruit or veggies
If you’re raising domestic birds or are licensed to take care of wild animals, however, then it’s important to know how and what to feed baby birds — and sometimes, even learn how to DIY baby bird food.
Consult the experts if you think a baby bird isn’t being fed
If you find a baby bird that does not seem to be fed, look for an hour or two to see if its parents provide food for it again. Note that the mother bird only needs a few seconds to feed its baby, so inattentive observers could miss several feeding cycles. However, if one parent bird has to look after several baby birds in different places, parental visits could be irregular. When the baby bird is fed, you can be sure that its parents have provided its needs, and there is no unnecessary intervention if the baby bird does not appear injured or sick.
Step 1: If the baby bird does not appear to be fed and becomes increasingly weak and lazy, the first step should be to find a licensed rehabilitator to provide, or guide you through, the appropriate care.
Step 2: If you have found a baby bird that needs to be fed but does not have contact with its parents or an animal rehabilitator, it is essential to know what a baby bird needs a portion of food similar to its natural diet. While each wild bird has its own diet, different types of food can serve as an emergency ration if necessary.
While each wild bird has its own diet, different types of food can serve as an emergency ration if necessary.
What to feed a baby bird
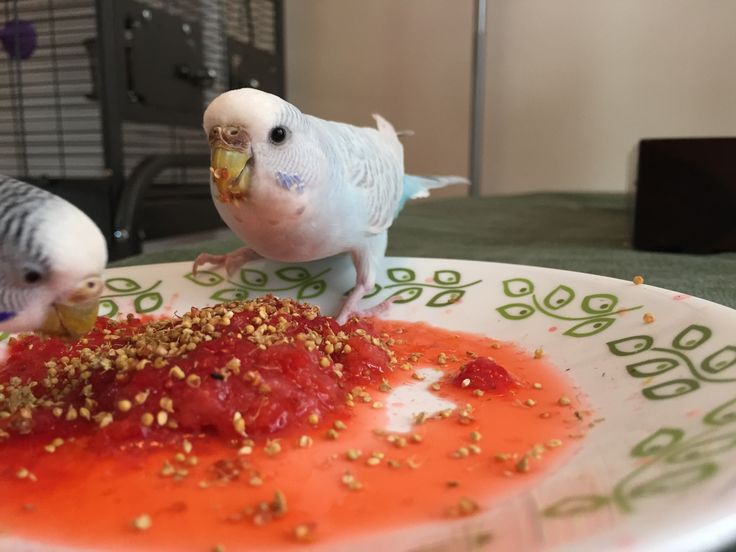
In nature, baby birds eat the same things that their parents eat: Worms, insects, and seeds. However, chicks can eat different types of food if they are taken care of by whoever found them. You could use puppy food soaked in water until it’s like a sponge. Moist dog or cat food can also be used in a jam when at room temperature. You can also use finely chopped fruits and vegetables (such as corn or peas) and even small insects.
It is equally essential to recognize that baby birds have very different nutritional needs than adult birds. What an adult bird eats can harm its young. As a baby bird grows, its diet can be adapted to more raw meat, giving them the protein that’s needed. As for water, a baby bird gets what it needs from the food it eats.
Food suitable for baby birds:
- Boiled eggs
- Moist dog food
- Wet cat food
- Raw liver (without seasoning)
What not to offer when feeding baby birds:
- Water
- Milk
- Bread and bakery products
- Kitchen waste
Unlike mammals, birds do not drink milk and their digestive systems won’t tolerate milk. Unfortunately, it’s a common misconception that mixing together bread and milk makes for an ideal feed for baby birds. Milk can be toxic to birds, so avoid feeding it entirely.
Unfortunately, it’s a common misconception that mixing together bread and milk makes for an ideal feed for baby birds. Milk can be toxic to birds, so avoid feeding it entirely.
When a baby bird is older, it can consume ”adult” bird foods without harming itself and the longer it can stay between strokes.
Cathy Hargreaves/Shutterstock.comDIY baby bird food
One easy recipe for feeding baby birds involves just two ingredients: pet food and water.
- Soaking dog biscuits or kibble in water will create a mushy consistency that’s easy to take and digest for young birds. This mimics the texture of the food given by mama birds in the wild and is also a high-protein option, which is extra important for nestlings.
- A classic biscuit treat like Milk-Bone is ideal for recipes like these. To forgo the mixing and mashing, a canned pet food like the Cesar brand is another great option. You still might want to stir in a tiny bit of water if your bird is particularly young, though.

How to feed a baby bird
Step 1: If you need to feed a wild baby bird, remember to offer foods that have a spongy consistency instead of dripping with water, which can suffocate or drown it. All dry food should be softened before offering it.
Step 2: Food should only be offered at room temperature, never heated or refrigerated.
Step 3: Keep food pieces small and proportional to the size of the bird — tiny birds need tiny bites. Cut or crush food properly to fit the size of the bird.
Step 4: When feeding the bird, be as careful as possible to minimize the risk of additional stress or injury. Never force a bird to eat its food.
Lastly, remember that feeding a baby bird should be only an emergency measure. If one is abandoned and needs care, it should be taken by a bird-rescue organization or an experienced rehabilitator as soon as possible. They can not only feed baby birds with a diet suitable for its type, but they also teach it to live independently, avoid predators, and master other skills to live in nature successfully.
Editors' Recommendations
- How to make a parrot’s perch with a natural branch (it’s easy!)
- Bird training classes are a thing – Here’s how to get your pet circus ready
- This is how to remove bird poop stains from clothes (tips that really work)
- Why do birds bob their heads? The answer is pretty complex
- Wondering how to take care of a hamster? Here are 8 pet hamster care tips that all beginners need to follow
What to Feed a Baby Bird
How to provide the right nutrition when wildlife rescues aren't an option
Reviewed by
Kathleen Miller
Reviewed by Kathleen Miller
Kathleen Miller is a highly-regarded Master Gardener and Horticulturist who shares her knowledge of sustainable living, organic gardening, farming, and landscape design. She founded Gaia's Farm and Gardens, a working sustainable permaculture farm, and writes for Gaia Grows, a local newspaper column. She has over 30 years of experience in gardening and sustainable farming.
She has over 30 years of experience in gardening and sustainable farming.
Learn more about The Spruce's Review Board
Fact checked by
Sarah Scott
Fact checked by Sarah Scott
Sarah Scott is a fact-checker and researcher who has worked in the custom home building industry in sales, marketing, and design.
Learn more about The Spruce's Editorial Process
The Spruce / Catherine Song
Every backyard birder has seen the "starving baby" act by fledgling birds, when they flutter their wings and call piteously for attention from seemingly hard-hearted, indifferent parents. The desire to nurture those fluffy balls of feathers can be strong, but it is important to understand the special needs of a fledgling's diet and know what to feed a baby bird for the best nutrition.
Do I Need to Feed This Baby Bird?
Baby birds have very demanding dietary needs. Depending on their age and species, baby birds may eat off and on for 12 to 14 hours per day, consuming a diet rich in insects for sufficient protein to ensure healthy growth. No human other than a licensed bird rehabilitator has the proper equipment, food supplements, or endurance to keep up that frantic feeding schedule. If you find a baby bird that appears to need feeding, the best thing to do is not to feed it, but to get it to an appropriate bird rescue organization. In many cases, the begging birds are not abandoned and the parent birds are nearby and tending to their babies as needed, even if they aren't seen.
No human other than a licensed bird rehabilitator has the proper equipment, food supplements, or endurance to keep up that frantic feeding schedule. If you find a baby bird that appears to need feeding, the best thing to do is not to feed it, but to get it to an appropriate bird rescue organization. In many cases, the begging birds are not abandoned and the parent birds are nearby and tending to their babies as needed, even if they aren't seen.
If you find a baby bird that seems to be unfed, watch the bird closely for a while to see if the parents return to feed it within the hour. Bear in mind that it may take just seconds for a parent bird to deliver a bite to its chick, and inattentive observers may miss several feeding cycles. As the chicks grow, feeding may also be less frequent, and one parent bird may be tending to several offspring in different locations, so parental visits may be uneven. If the baby is being fed, rest assured that the parent bird is able to keep up with its demands, and no intervention is necessary if the baby does not appear injured or ill in any other way.
If the baby bird is not being fed and appears to be growing weaker and more lethargic, the first step should be to find a licensed rehabilitator to provide it proper care. When contacting the rehabilitator, ask for their evaluation of the bird in question before attempting any emergency feeding. If it is recommended that you feed the baby bird, he or she might have specific suggestions in mind as an emergency measure, and those suggestions should be meticulously followed.
If Feeding Is Necessary
If you find a baby bird that needs to be fed but you are unable to contact a bird or wildlife rehabilitator, it is important to know what to feed a baby bird that will provide similar nutrition to its natural diet. While every wild bird has a different diet, several types of food can serve as emergency rations when necessary. At the same time, it is critical to understand that baby birds have very different nutritional needs than adult birds, and foods you would normally feed to your backyard birds are not appropriate for young fledglings.
Good Foods for Baby Birds
- Moist dog food
- Raw liver (no seasoning)
- Hard-boiled eggs
- Dog biscuits (moistened)
- Dog or cat kibble (moistened)
The Spruce / K. Dave
What Not to Feed Baby Birds
- Water
- Bread or bread products
- Whole birdseed
- Milk
- Pet bird food
- Worms
- Kitchen scraps
The more mature a baby bird is, the more "adult" food it can consume without harm, and the longer it can go between feedings.
The Spruce / K. Dave
Tips for Feeding Baby Wild Birds
If it is necessary for you to feed a baby bird, remember:
- Offer food that is spongy in texture, not dripping with water that could cause choking or drowning. All dry food should be softened before being offered to a baby bird.
- Food should be offered at room temperature only, never warmed or heated, and also never refrigerated or chilled.
- Keep bits of food small and in proportion to the bird's size; very small birds need very tiny bites.
 Cut or crush food appropriately to suit the bird's size.
Cut or crush food appropriately to suit the bird's size. - While feeding the bird, handle it as little as possible to minimize the risk of additional stress or injury. Never force the bird's bill open to eat.
Caring for Baby Birds
Remember that feeding a baby bird should be an emergency measure only. If a baby bird is abandoned and needs care, it should be taken to a bird rescue organization or experienced rehabilitator as soon as possible. Rehabilitators can not only feed it an appropriate diet for its species but can help it learn how to find its own food, evade predators, and learn other skills necessary for a successful life in the wild.
If there is no rescue organization or experienced rehab specialist available in your area, keep these tips in mind:
- Identify if the bird is a nestling (few or no feathers) or a fledgling (a feathered bird approaching adulthood). Nestlings will require much attention for a longer period than fledglings, which may be nearly ready for independence quite soon.
 An older fledgling can sometimes be fine if you simply place it high on a branch where its parents can find it. Nestlings, on the other hand, may require several weeks of attention (assuming a bird rehab organization is not available) to give them a chance for survival.
An older fledgling can sometimes be fine if you simply place it high on a branch where its parents can find it. Nestlings, on the other hand, may require several weeks of attention (assuming a bird rehab organization is not available) to give them a chance for survival. - Protect it from predators—including family pets. Normally, a simple cardboard box lined with a towel, placed high enough to be out of reach of pets, will suffice. If using a lidded container, make sure it is well-ventilated. Ordinary room temperature is normally fine, though a gentle heat lamp can be used if the room is very cold at night. But take care not to overheat the young bird—in most cases, no heat source is necessary.
- Give it a "nest" by using a small towel or cloth diaper formed into a concave shape and placed in the bottom of the box. This will help support the bird's body until it grows stronger.
- Small nestlings are best fed with moist, well-softened food from a syringe, offered very gently, in small drops.
 Even a kitchen baster may be too large to be useful. As a nestling grows older, you can offer it food by dangling it from tweezers in front of its beak.
Even a kitchen baster may be too large to be useful. As a nestling grows older, you can offer it food by dangling it from tweezers in front of its beak. - Never try to feed water directly to a baby bird. Nestlings will get their water needs met through moisture in food. A fledgling can be offered water in a shallow dish—if it's ready to consume water this way, it will drink on its own.
- When a fledgling bird has fully feathered out and is beginning to exercise its wings by flapping, it can be given time outdoors and encouraged to begin flying. Often, it is enough to simply set the bird's containment box outside in a safe location, open the lid and wait for nature to take its course.
But remember that raising a featherless nestling bird through the fledgling stage and into a mature adult bird is no easy matter. It's always better to leave this to professionals who are experienced in the practice.
Article Sources
The Spruce uses only high-quality sources, including peer-reviewed studies, to support the facts within our articles. Read our editorial process to learn more about how we fact-check and keep our content accurate, reliable, and trustworthy.
Read our editorial process to learn more about how we fact-check and keep our content accurate, reliable, and trustworthy.
Picking up baby birds can do more harm than good. Oregon State University.
diet in the first days of life, chicken feed norms
| The diet of chickens, especially small ones, is different from the diet of adult chickens. Many breeders who raise chickens in the household are interested in how and what to feed the chicks so that they develop properly. For healthy growth, chickens require a balanced diet in sufficient quantities. The composition of the products depends on the direction and age of the chicks. |
Content:
- What does healthy chicks eat?
- General rules for formulating rations
- What to feed chickens?
- General rules for feeding
- Feed for chickens of various ages
- Feeding frequency
- Feeding Features
- Farmer's Councils
What does a healthy chicken diet consist of?
Sources of proteins, vitamins, micro and macro elements are products of plant and animal origin, as well as substances synthesized in the laboratory. For the production of finished formulations in the factory, only high-quality proven raw materials are used. In feed for laying hens and broilers are introduced:
For the production of finished formulations in the factory, only high-quality proven raw materials are used. In feed for laying hens and broilers are introduced:
|
It is quite difficult to independently calculate the proportions and mix the components thoroughly without the appropriate equipment.
General dietary guidelines
The terms of growing meat breeds are 1.5-2 months, laying hens - up to six months. During this time, the bird should gain weight of 2.5-3 kg. To accelerate the growth of muscle mass in broilers, it is recommended to use specialized feed. It fully meets the needs of the bird in proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals. The composition and consumption of feed should be appropriate for the age of the chicks.
At 1-2 weeks of life, the foundation of the skeleton is laid in chickens, muscle mass increases at an average pace. At this time, it is necessary to introduce a sufficient amount of proteins, fiber, and mineral components into their diet.
In the growth phase, chickens are gaining weight intensively. They need as many amino acids and proteins as possible, which act as a building material for cells, as well as complex carbohydrates. The dose of vitamins and minerals received with food is increased.
At the finishing stage, the amount of carbohydrates is reduced so that the broilers gain more muscle mass, and not fat. At this stage, it is important to prevent weight loss. For these purposes, finishing compound feed is introduced into the diet.
What to feed chickens?
Cereals form the basis of the diet.
| Corn | One of the most useful and nutritious ingredients. Corn is the leader among grains in terms of protein content, while it contains less fiber than other cereals. The product is easily digested and well absorbed. The product is easily digested and well absorbed. |
|---|---|
| oats | Source of many amino acids. It is considered a dietary product, but contains a lot of fiber. In large quantities, it causes blockage of the intestines, so its share in the composition of the feed does not exceed 20%. Oats are given in a purified form, completely removing the film from the grains. The size of the fraction depends on the age of the bird. Sifted oatmeal is usually added to prestarter formulations. |
| Wheat | Contains a large amount of vitamin E, B. Feed wheat is usually used in bird feed. The percentage can be up to 30%. |
| Rye | It is a source of a number of useful proteins, but contains too much mucus, which negatively affects the digestive system of chickens. It is added to some feeds in small quantities. |
| Barley | Practically not inferior to oats in useful properties, but also contains a lot of fiber. It is introduced into the composition only in a purified and sifted form. It is introduced into the composition only in a purified and sifted form. |
| Buckwheat | Despite the fact that the product contains components useful for poultry, it is rarely used. Basically, it is added to granulated feed, because. in loose form, chickens do not peck it. |
| Bran | Products of processing grain crops are introduced to increase the caloric content of the diet. By themselves, they have no nutritional value, so they are rarely used. |
Peeled vegetables are used as succulent feed.
| Potato | Improves poultry digestion, promotes the absorption of nutrients. It is introduced in boiled dehydrated form. In the process of preparing food, it is unacceptable to use green potatoes, since poisonous solanine has formed in them. |
|---|---|
| Beet | It normalizes the work of the intestines, prevents its blockage, provides the needs of chickens for vitamin B2, carotene, sugar. It can be given both fresh and boiled. The content of beets in the diet is about 15%. It can be given both fresh and boiled. The content of beets in the diet is about 15%. |
| Pumpkin | It contains a lot of vitamins and microelements. The product is added in an amount not exceeding 15% of the total volume. |
Protein components provide the daily requirement for amino acids. Protein sources are also rich in vitamins and minerals. They can be of plant and animal origin. Amino acids are well absorbed by the body. Animal proteins are obtained from various types of flour:
- fish. This product makes up to 8% of the diet, but is not used in broiler feed so that the meat does not have a specific smell;
- bone. In terms of the amount of proteins, it is not inferior to cereals, and at the same time it is rich in fats (11%) and vitamins A and E. It is given to chickens from a month old;
- blood. The product is rich in essential amino acids, but in high concentrations it provokes indigestion.
 Its share in the diet should not exceed 4%;
Its share in the diet should not exceed 4%; - pen. This component is used as an available source of protein to balance the feed composition. It is added in small amounts (up to 2%).
Dairy products are also a source of well-digestible animal protein: cottage cheese or whey. Their inclusion in feed mixtures for laying hens increases the egg production and fertility of chickens.
Legumes are richest in vegetable proteins:
- soy in terms of percentage and qualitative composition of proteins and amino acids is practically not inferior to products of animal origin, it also contains vitamins and minerals;
- peas also provide protein requirements for poultry, although to a lesser extent; chickens do not eat it well because of the specific smell and taste, therefore, no more than 10% is introduced into the feed;
- soybean and sunflower meal and cake are an inexpensive, highly digestible source of amino acids. In compositions for adult chickens, their share is 15-17%, for chickens and young animals - 10%.

General feeding rules
| Each individual should consume approximately 15-30 g of food per day: how much depends on the breed, weight of the chicks, and the intensity of their development. In general, the amount of feed each time should be such that the young hens will eat it in 30 or 40 minutes. The remains must be removed from the feeders so as not to deteriorate, and the feeders themselves must be washed and dried. |
If the chicks do not eat the feed given to them often, then its rate should be reduced. If, on the contrary, the food is eaten quickly, then it is desirable to increase its volume.
Feed for chickens of various ages
| PC-2 | Designed for chicks under 7 weeks old. It is produced in the form of finely ground grains, designed for an insufficiently unformed digestive system, easily digestible, contains all the useful trace elements. |
|---|---|
| PC-3 | Balanced mix for young animals 8-20 weeks old. Promotes rapid growth and proper formation of the reproductive system. It is produced in the form of grains with medium-sized fractions. |
| PC-5 | Designed for broiler chickens from 2 weeks to 1 month of age. It consists of a complex of easily digestible components that stimulate a set of muscle mass. |
| PC-6 | It has similar characteristics, but is designed for broilers older than a month. |
All types of feed can be divided into three groups:
| carbohydrate | Protein | Vitamin |
|---|---|---|
Promote accelerated growth and muscle mass gain. Their composition is dominated by cereals and vegetables. Chickens digest foods high in carbohydrates well, which cause a slowdown in metabolism and rapid weight gain. Such feeds are designed for broilers and increase the average carcass weight. | Such compound feeds are developed mainly for laying hens. A large amount of protein increases the productivity of the bird, improves the palatability of the eggs, and makes the shell stronger. | Strengthen the immune system, help to survive the winter period. Usually produced in the form of concentrates, which enrich the main diet. |
According to the form of release, the compositions are of 2 types.
| Loose ones consist of fine-grained components. The disadvantage of such compositions is that they are worse absorbed. The chicken chooses tasty crumbs from the feed, and the less appetizing ingredients are thrown away. As a result, the bird receives less nutrients. In addition, a lot of dust remains in the feeder. However, it is impossible to completely abandon loose compositions. Chickens in the first weeks of life are not able to swallow and digest large granules, therefore they can peck only small grains. |
Expanded feed is produced by short-term heat treatment under high pressure. Nutrient mixtures are in the form of granules and contain liquid components in their composition. The advantages of expanded compositions include:
However, when heated, some of the vitamins are destroyed. |
Feeding frequency
The first time chickens are fed on the same day they are born. Then, until the age of 7 days, the chicks of meat breeds are fed 6-8 times a day, from the 2nd week of life - 6 times, from the 3rd - 4 times a day, by the age of one month, chickens are fed three times a day. Chicks of egg breeds up to 1.5 weeks are fed 5-6 times a day, and by the month they are gradually transferred to 3 meals a day.
Chicks of egg breeds up to 1.5 weeks are fed 5-6 times a day, and by the month they are gradually transferred to 3 meals a day.
When choosing a mixture, it is recommended to give preference to complete formulations. However, if the breeder has enough of his own food, you can limit yourself to concentrated additives to enrich it. Such compositions are marked with the QC marking. Concentrates for meat and egg-bearing breeds solve different problems:
| for broilers | for laying hens |
|---|---|
|
|
It is unacceptable to use concentrates as the main feed, since an excess of nutrients is no less harmful than their deficiency. BVMB is introduced into the composition of the mash, taking into account the age of the chickens.
BVMB is introduced into the composition of the mash, taking into account the age of the chickens.
Feeding Features
| 1st day of life | Feeding of chickens of egg breeds begins immediately after they dry out. The first food for newborn chickens should be a hard-boiled egg. It is cut as small as possible so that the chicks can swallow small crumbs and roll it in semolina to prevent pieces from sticking to the paws and fluff. In the brooder where they are, they put a drinker with clean, boiled and cooled water. Newly hatched chicks are also fed boiled eggs under the brood hen. |
|---|---|
| 2nd day | On the 2nd day, the chicks are already given a mash of eggs and homemade low-fat fresh cottage cheese (the ratio of ingredients is 1 to 1). The formula for feeding day-old chicks should be fresh and fed every 3 hours. |
| 1 Week | From the 3rd day, chickens are fed with a more varied mixture of cottage cheese, boiled eggs, crumbly porridge from corn, oat or wheat chips (the share of cereals should be 65%). Finely chopped greens and boiled red carrots grated on a fine grater are added to them. You can give germinated grain or grass flour at the rate of 2-3 g per chicken per day. More than 5 g of such flour cannot be fed due to the high content of fiber in it. Separately, a little skimmed milk or yogurt is poured into the container; it is better not to add them to the mixers. Twice a week, a few crystals of potassium permanganate are added to the water so that it becomes slightly pink. Keep it in drinkers for no more than 0.5 hours, and then replace it with clean water. This protects chickens from stomach diseases. You can feed the chicks with special industrial compound feed for chickens from the first days of life. It is made up of products that are easily absorbed by the body of small chickens and fully satisfy all their needs. Finely chopped greens and boiled red carrots grated on a fine grater are added to them. You can give germinated grain or grass flour at the rate of 2-3 g per chicken per day. More than 5 g of such flour cannot be fed due to the high content of fiber in it. Separately, a little skimmed milk or yogurt is poured into the container; it is better not to add them to the mixers. Twice a week, a few crystals of potassium permanganate are added to the water so that it becomes slightly pink. Keep it in drinkers for no more than 0.5 hours, and then replace it with clean water. This protects chickens from stomach diseases. You can feed the chicks with special industrial compound feed for chickens from the first days of life. It is made up of products that are easily absorbed by the body of small chickens and fully satisfy all their needs. |
| 2-4 weeks | From 1.5 weeks of life, a little sunflower or soybean meal (3-4% of the total food volume), chalk or shells, bone meal (5-7% of the feed amount or 2-3 g per 1 chick). Particles of top dressing should not be more than 1-2 mm. Very fine gravel or sand washed in water is placed in a separate container. After 10 days, eggs are removed from the diet, but other components are introduced, for example, root crops (boiled potatoes, etc.). Salt, rice, rye, wheat bran (up to 10%), herbal flour (6-10%) are introduced into the menu of two-week-old chickens. From 3 weeks old, chicks gradually begin to accustom themselves to whole grains. Particles of top dressing should not be more than 1-2 mm. Very fine gravel or sand washed in water is placed in a separate container. After 10 days, eggs are removed from the diet, but other components are introduced, for example, root crops (boiled potatoes, etc.). Salt, rice, rye, wheat bran (up to 10%), herbal flour (6-10%) are introduced into the menu of two-week-old chickens. From 3 weeks old, chicks gradually begin to accustom themselves to whole grains. |
| 1 month | At this age, the young are already quite strong, they can spend time walking, where they independently find greenery, seeds of various plants, worms and beetles. If the birds are in a closed aviary and cannot pluck the grass, then they need to be given it along with grain and vegetables. In general, the share of green grass in the diet of one-month-old young animals should be about 1/3 part, no less. Grain can be given both ground and whole: the birds are already able to peck it. It can be anything: wheat, barley, corn, oats, etc. At this age, legumes can also be fed: peas, chickpeas, small beans, etc. In addition to grain products, you can feed root crops, fresh or boiled, to monthly chickens, vegetables from the garden and their tops, kitchen waste of both plant and animal origin, bran, meal and cake, compound feed. From mineral additives - bone and fish meal, chalk or lime, shell rock, salt. In addition to food, young animals should always have clean water in drinking bowls and pebbles that the bird needs for normal digestion. At this age, legumes can also be fed: peas, chickpeas, small beans, etc. In addition to grain products, you can feed root crops, fresh or boiled, to monthly chickens, vegetables from the garden and their tops, kitchen waste of both plant and animal origin, bran, meal and cake, compound feed. From mineral additives - bone and fish meal, chalk or lime, shell rock, salt. In addition to food, young animals should always have clean water in drinking bowls and pebbles that the bird needs for normal digestion. |
Chickens of meat breeds differ from egg breeds in that they need more complete proteins and vitamins, so their diet should be tailored to this feature. Therefore, it is necessary to give more protein feed, such as legumes (grains and green mass), meat and bone and fish meal, fresh kitchen waste. It should also be borne in mind that they eat more, so they need to be fed more often, especially in the first days of life.
Farmer's councils
When changing nutrition, the sensitivity of chickens to changes in composition should be taken into account.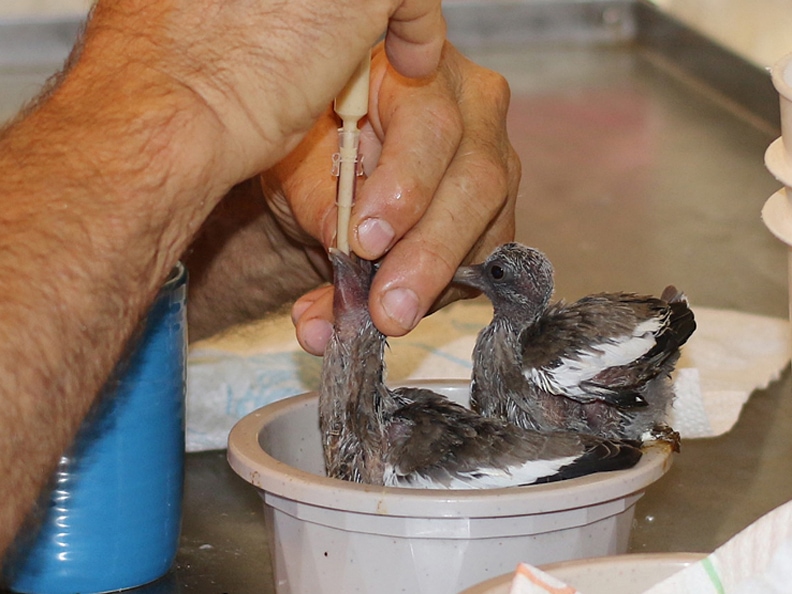 For this reason, birds should be transferred to a different diet gradually, over 3-5 days, daily adding new food to the usual food, gradually increasing its amount.
For this reason, birds should be transferred to a different diet gradually, over 3-5 days, daily adding new food to the usual food, gradually increasing its amount.
There should always be fresh water in the drinker, in which a little potassium permanganate is diluted - so much so that the liquid does not turn pink.
It is advisable to mix common salt (up to 5 g per 1 kg of the mixture) and ground egg shells into the feed.
The main disadvantage of self-prepared mixtures is the fragility of their storage. In contrast, prepared feed can be left in the feeder for as long as the chicks need to saturate.
In our company, you purchase safe, certified mixtures with high nutritional value. Products exceed the requirements of GOSTs in quality. At your request, it is possible to develop an individual recipe for specific chicken breeds.
The MEGAMIX company cooperates with a network of dealers in Moscow and regions. You can clarify the terms of the order and delivery by phone +7 (8442) 97-97-97 or on our website.
Free consultation
Ask a question to a specialist or order a price list
Telephone
Comment
I agree to the processing of personal data.
09.11.2020
Poultry food: how to feed it right
Successful breeding of poultry, both meat and egg, depends on the quality of the feed by 70%. A complete balanced diet (based on a complete poultry feed) provides rapid muscle growth, optimal average daily weight gain, increased egg production and excellent palatability of the final products. Compliance with feeding rules reduces the risk of poultry mortality due to mycotoxin poisoning and other diseases.
- Benefits of ready mixed feed
- What is included in compound feed for poultry?
- Compound feed and premixes "MEGAMIX" for feeding poultry
- Poultry Feeding Standards
- Feeding guidelines for various types of poultry
Benefits of prepared compound feed
The terms of growing birds of meat breeds are 1. 5–2 months, laying hens - up to six months. To accelerate the growth of muscle mass in chicks, it is recommended to use specialized feed for poultry. It fully meets the needs of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals. The composition and consumption of feed should correspond to the age of the bird.
5–2 months, laying hens - up to six months. To accelerate the growth of muscle mass in chicks, it is recommended to use specialized feed for poultry. It fully meets the needs of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals. The composition and consumption of feed should correspond to the age of the bird.
At 1-2 weeks of life, the skeleton of the chicks is laid, muscle mass increases at an average pace. For feeding, they need a sufficient amount of proteins, fiber, mineral components.
In the growth phase, the chicks are intensively gaining weight. They need as many amino acids and proteins as possible, which act as a building material for cells, as well as complex carbohydrates. The dose of vitamins and minerals received with food is increased.
At the finishing stage, the amount of carbohydrates is reduced so that the broilers gain more muscle mass, and not fat. At this stage, it is important to prevent weight loss. For these purposes, finishing compound feed is introduced into the diet.
To prevent coccidiosis, coccidiostatics are added to some feeds. They are absent in the final compositions. Medicines are administered only on the recommendations of veterinarians in a small dosage, so poultry meat is safe for humans. At home, it is difficult to calculate how much coccidiostatic can be added during the feeding of birds without harm to the end consumer.
In the process of mixing the components on our production line, the proportions specified in the recipe are strictly observed. Properly prepared compound feeds allow you to avoid the excess of some substances and the lack of others. An imbalance in the diet leads to improper formation of the bird and growth retardation.
A quality product almost always gives the maximum result and quickly pays off due to:
- Save time on formulating and mixing ingredients;
- strengthening the immunity of chickens and reducing the loss of livestock;
- increase the productivity of the poultry farm;
- improve the quality of meat and eggs.

In the long term, feeding ready-made complete feeds that provide all the nutritional requirements of poultry is better than using homemade products. Grain and herbal mixtures are very demanding on storage conditions. In case of violation of harvesting technologies, storage at high humidity and insufficient ventilation, the raw material begins to rot. Molds develop in it, releasing mycotoxins into the feed.
For the production of finished formulations at the feed mill, only high-quality proven raw materials are used. In compound feed for laying hens and meat breeds, the following are additionally introduced:
- amino acids,
- vitamins,
- minerals,
- probiotics,
- antioxidants,
- prebiotics,
- coccidiostats,
- mold inhibitors.
It is quite difficult to correctly calculate the proportions and mix the components thoroughly without the appropriate equipment.
What is included in the diet of poultry?
Sources of proteins, vitamins, micro and macro elements are products of plant and animal origin, as well as components synthesized in the laboratory. The optimal product for poultry of any kind is a balanced compound feed. It contains all the ingredients necessary for healthy growth.
The optimal product for poultry of any kind is a balanced compound feed. It contains all the ingredients necessary for healthy growth.
The basis of compound feed is cereals.
| Corn | One of the most useful and nutritious ingredients. It is the leader among grains in terms of protein content, while it has less fiber than other cereals. The product is easily digested and well absorbed. |
|---|---|
| oats | Source of many amino acids. It is considered a dietary product, but contains a lot of fiber. In large quantities, it causes blockage of the intestines, so its share in the composition of the feed does not exceed 20%. Oats are given in a purified form, completely removing the film from the grains. The size of the fraction depends on the age of the bird. Sifted oatmeal is usually added to prestarter formulations. |
| Wheat | It contains a large amount of vitamin E, as well as group B. |
| Rye | It is a source of a number of useful proteins, but contains too much mucus, which negatively affects the digestive system of chickens. It is added to some feeds in small quantities. |
| Barley | Practically not inferior to oats in useful properties, but also contains a lot of fiber. It is introduced into the composition only in a purified and sifted form. |
| Buckwheat | Despite the fact that the product contains components useful for poultry, it is rarely used. Basically, it is added to granulated feed, because. in loose form, chickens do not peck it. |
| Bran | Products of processing grain crops are introduced to increase the caloric content of the diet. By themselves, they have no nutritional value, so they are rarely used. |
Protein-rich legumes and oilseeds are also added to compound feed. Meal and cake of soybean and sunflower are an inexpensive, well-digestible source of amino acids. For example, in compositions for laying hens, their share is 15-17%, for chickens and young animals - 10%.
Animal products are a source of essential amino acids. In compound feeds, they are present in the form of flour of various types:
- fish. This product makes up to 8% of the diet, but is not used in broiler feed so that the meat does not have a specific smell;
- bone. In terms of the amount of proteins, it is not inferior to cereals and at the same time it is rich in fats (11%) and vitamins A and E. It is given to chickens from a month old;
- blood. The product is rich in essential amino acids, but in high concentrations it provokes indigestion. Its share in the diet should not exceed 4%;
- pen. This component is an available source of protein for balancing the composition of feed. It is added in small amounts (up to 2%).
In addition to compound feed, farmers use succulent feed. They enrich the diet with vitamins, which is especially important in winter or early spring. The addition of peeled vegetables reduces the consumption of compound feed, although it somewhat complicates the process of preparing feed mixtures.
| Potato | An important product for the normal digestion of poultry. Promotes the absorption of nutrients. It is introduced in boiled dehydrated form. In the process of preparing food, it is unacceptable to use green potatoes, since poisonous solanine has formed in them. |
|---|---|
| Beet | It normalizes the work of the intestines, prevents its blockage, provides the needs of chickens for vitamin B2, carotene, sugar. It can be given both fresh and boiled. The content of beets in the diet is about 15%. |
| Pumpkin | It contains a lot of vitamins and microelements. The product is added in an amount not exceeding 15% of the total volume. |
Dairy products are also a good source of animal protein: cottage cheese or whey. Farmers often add them to laying hen feed mixtures to increase egg production and fecundity of birds.
Compound feeds and premixes "MEGAMIX" for feeding poultry
Ready formulas are food mixtures designed specifically for laying hens or broilers to provide birds with exactly the nutrients they need most.
The company produces all types of complete feed:
- for broilers and layers,
- ducks,
- turkeys,
- quails.
Farmers who prefer to prepare their own feed mixtures can order from us
PMVA and premixes for enriching the diet of birds, as well as individual raw materials, coccidiostats and mycotoxin adsorbents.
The best digestible granulated feed. They are produced by short-term heat treatment under high pressure. Exposure to high temperatures destroys pathogens of infectious diseases (Salmonella, E. coli) and other pathogens. Each granule contains all the components of the feed. The bird cannot choose separate, tastier foods and refuse healthy, but insipid ingredients. Due to this, nutrients are better absorbed.
Feeding norms for poultry
When choosing a mixture, it is recommended to give preference to complete formulations. However, if the poultry farm has enough of its own feed, you can limit yourself to concentrated additives to enrich it. Such compositions are marked with the QC marking. Concentrates for meat and egg-bearing breeds solve different problems:
| for meat breeds | for laying hens |
|---|---|
|
|
Feeding recommendations for different types of poultry
There is currently no set standard. Breeders are guided by the recommendations of veterinarians and professional experience. If the bird eats food in less than half an hour, then this volume is not enough and you need to increase the rate. If after 40 minutes a lot of grain remains, the amount of product must be reduced. It is unacceptable to feed birds with concentrates as the main product, since an excess of nutrients is no less harmful than their deficiency. BVMB is introduced into the composition of the mixers, taking into account the age of the bird.
Daily consumption rates are calculated according to average indicators depending on the type, age and direction and are:
- for 1–3 months - 10–25 g;
- 4–8 months - 30–50 g;
- 9-16 months - 50–70 g;
- 16–20 months - 70–95 g;
- 20-30 months - 100–110 g;
- 30-45 months - 110-125 g;
- 45–65 months — 120–130 g.
The amount of finished feed is reduced if they are added to the mash.

 For broilers, loose compound feed can be introduced into the diet from the first days of life, and for laying hens - from the second week. When using dry mixes, it is important to provide the hens with sufficient drinking water.
For broilers, loose compound feed can be introduced into the diet from the first days of life, and for laying hens - from the second week. When using dry mixes, it is important to provide the hens with sufficient drinking water.