How do you know when to feed your baby solids
When, What, and How to Introduce Solid Foods | Nutrition
For more information about how to know if your baby is ready to starting eating foods, what first foods to offer, and what to expect, watch these videos from 1,000 Days.
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend children be introduced to foods other than breast milk or infant formula when they are about 6 months old. Introducing foods before 4 months old is not recommended. Every child is different. How do you know if your child is ready for foods other than breast milk or infant formula? You can look for these signs that your child is developmentally ready.
Your child:
- Sits up alone or with support.
- Is able to control head and neck.
- Opens the mouth when food is offered.
- Swallows food rather than pushes it back out onto the chin.
- Brings objects to the mouth.
- Tries to grasp small objects, such as toys or food.
- Transfers food from the front to the back of the tongue to swallow.
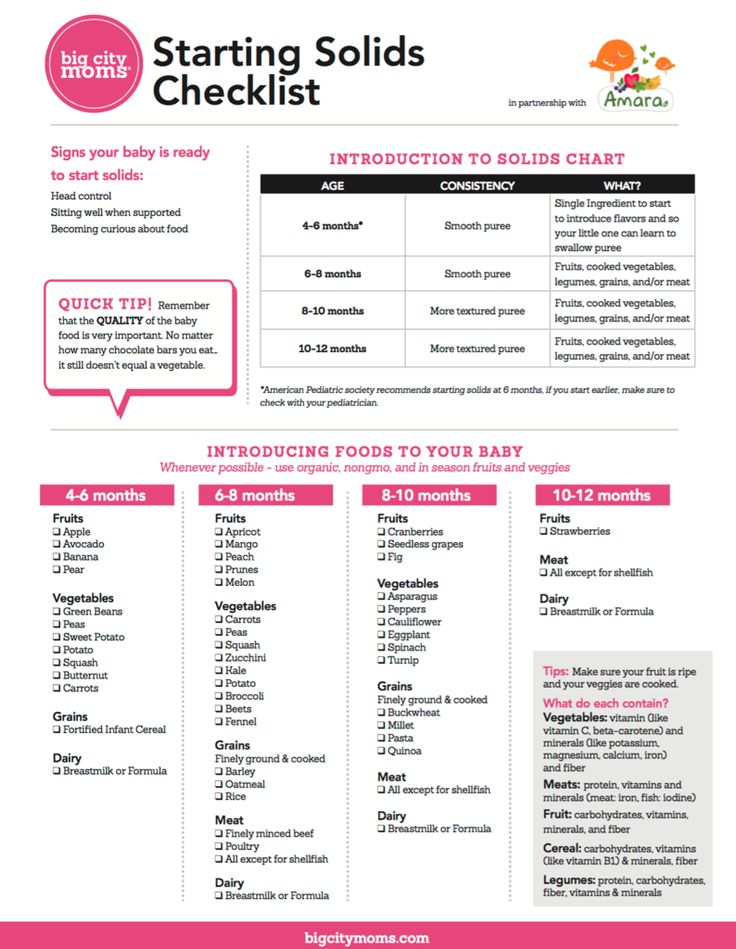
What Foods Should I Introduce to My Child First?
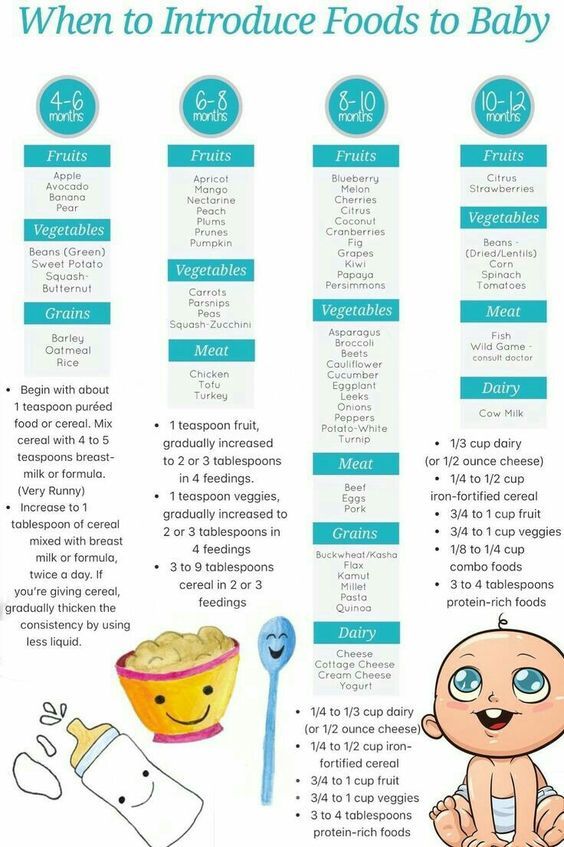
The American Academy of Pediatrics says that for most children, you do not need to give foods in a certain order. Your child can begin eating solid foods at about 6 months old. By the time he or she is 7 or 8 months old, your child can eat a variety of foods from different food groups. These foods include infant cereals, meat or other proteins, fruits, vegetables, grains, yogurts and cheeses, and more.
If your child is eating infant cereals, it is important to offer a variety of fortifiedalert icon infant cereals such as oat, barley, and multi-grain instead of only rice cereal. Only providing infant rice cereal is not recommended by the Food and Drug Administration because there is a risk for children to be exposed to arsenic. Visit the U.S. Food & Drug Administrationexternal icon to learn more.
How Should I Introduce My Child to Foods?
Your child needs certain vitamins and minerals to grow healthy and strong.
Now that your child is starting to eat food, be sure to choose foods that give your child all the vitamins and minerals they need.
Click here to learn more about some of these vitamins & minerals.
Let your child try one single-ingredient food at a time at first. This helps you see if your child has any problems with that food, such as food allergies. Wait 3 to 5 days between each new food. Before you know it, your child will be on his or her way to eating and enjoying lots of new foods.
Introduce potentially allergenic foods when other foods are introduced.
Potentially allergenic foods include cow’s milk products, eggs, fish, shellfish, tree nuts, peanuts, wheat, soy, and sesame. Drinking cow’s milk or fortified soy beverages is not recommended until your child is older than 12 months, but other cow’s milk products, such as yogurt, can be introduced before 12 months. If your child has severe eczema and/or egg allergy, talk with your child’s doctor or nurse about when and how to safely introduce foods with peanuts.
How Should I Prepare Food for My Child to Eat?
At first, it’s easier for your child to eat foods that are mashed, pureed, or strained and very smooth in texture. It can take time for your child to adjust to new food textures. Your child might cough, gag, or spit up. As your baby’s oral skills develop, thicker and lumpier foods can be introduced.
Some foods are potential choking hazards, so it is important to feed your child foods that are the right texture for his or her development. To help prevent choking, prepare foods that can be easily dissolved with saliva and do not require chewing. Feed small portions and encourage your baby to eat slowly. Always watch your child while he or she is eating.
Here are some tips for preparing foods:
- Mix cereals and mashed cooked grains with breast milk, formula, or water to make it smooth and easy for your baby to swallow.
- Mash or puree vegetables, fruits and other foods until they are smooth.

- Hard fruits and vegetables, like apples and carrots, usually need to be cooked so they can be easily mashed or pureed.
- Cook food until it is soft enough to easily mash with a fork.
- Remove all fat, skin, and bones from poultry, meat, and fish, before cooking.
- Remove seeds and hard pits from fruit, and then cut the fruit into small pieces.
- Cut soft food into small pieces or thin slices.
- Cut cylindrical foods like hot dogs, sausage and string cheese into short thin strips instead of round pieces that could get stuck in the airway.
- Cut small spherical foods like grapes, cherries, berries and tomatoes into small pieces.
- Cook and finely grind or mash whole-grain kernels of wheat, barley, rice, and other grains.
Learn more about potential choking hazards and how to prevent your child from choking.
Top of Page
Introducing solids: why, when, what & how
Solid foods: why babies need them
As babies get older, they need solid food to get enough nutrients for growth and development. These essential nutrients include iron, zinc and others.
These essential nutrients include iron, zinc and others.
For the first 6 months of life, babies use iron stored in their bodies from when they were in the womb. They also get some iron from breastmilk and/or infant formula. But babies’ iron stores go down as they grow. By around 6 months, babies need to start having solid food.
Introducing solids is also important for helping babies learn to eat, giving them experience of new tastes and textures from a range of foods. It develops their teeth and jaws, and it builds other skills that they’ll need later for language development.
Signs that it’s time to introduce solids
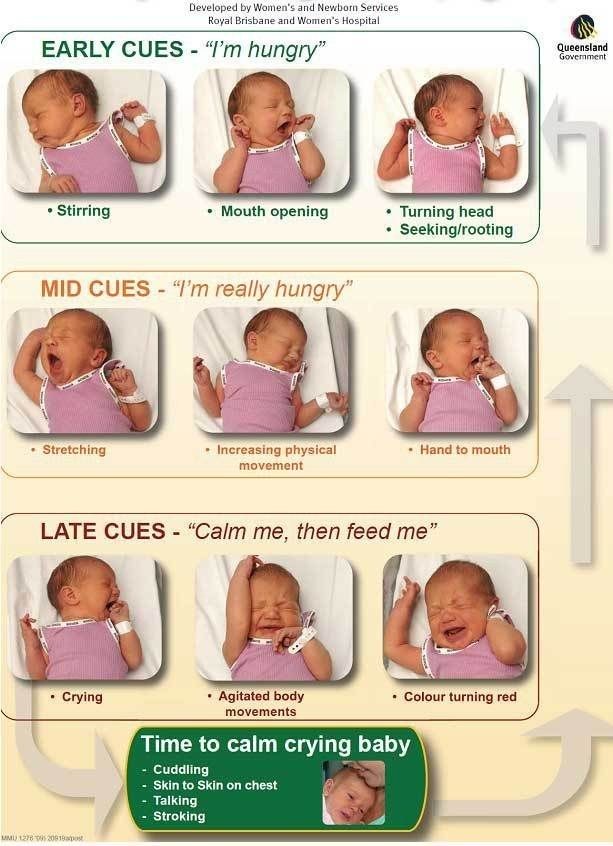
Signs your baby is ready for solids include when your baby:
- has good head and neck control and can sit upright when supported
- shows an interest in food – for example, they look at what’s on your plate
- reaches out for your food
- opens their mouth when you offer them food on a spoon.
Most babies start to show these signs by around 6 months, although this can vary.
It’s recommended not to introduce solids before 4 months.
If your baby is nearing 7 months of age and hasn’t started solids, you might like to get some advice from your child and family health nurse or GP.
The best times of day to introduce solids
When you’re first introducing solids, it’s good to offer solids when you and your baby are both happy and relaxed.
This is often after a feed of breastmilk or formula. Babies will still have room in their tummies for a taste of new foods after a feed of breastmilk or formula. But if they’re really hungry before a feed, they just want the breastmilk or formula that they know satisfies their hunger.
As time passes, you’ll learn when your baby is hungry or full, not interested or tired.
Signs of hunger include your baby:
- getting excited when they see you getting their food ready
- leaning towards you while they’re sitting in the highchair
- opening their mouth as you’re about to feed them.

Signs your baby is no longer interested include:
- turning their head away
- losing interest or getting distracted
- pushing the spoon away
- clamping their mouth shut.
Your baby’s appetite can vary from day to day.
How much food to offer when introducing solids
When you’re first introducing solids, try offering 1-2 teaspoons of food once a day. At first, your baby might have only a small taste and probably won’t swallow much.
As your baby grows, you can increase the amount according to your baby’s appetite and signs.
By 12 months, your baby should be eating around 3 small meals a day, plus breastmilk or infant formula.
The right textures for first foods
When your baby is ready for solids, first foods might be smooth or finely mashed, depending on what baby likes. Over the next weeks and months, your baby can move on to roughly mashed or minced foods and then chopped foods.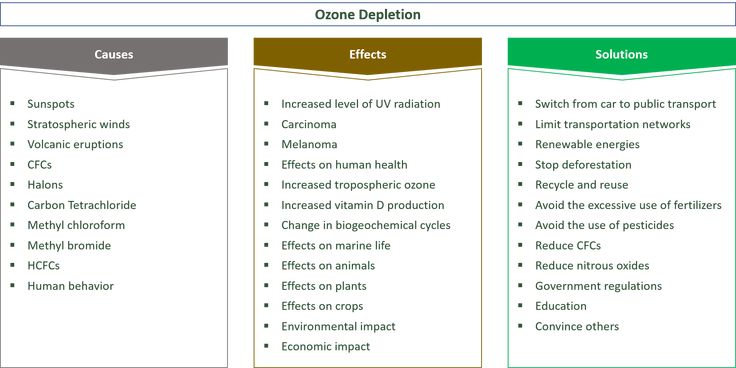 All foods should be very soft.
All foods should be very soft.
Your baby needs a variety of food textures. This helps your baby learn how to chew, and chewing helps with speech development and self-feeding. It also helps to prevent feeding difficulties as your baby develops. Babies can chew even before they get their first teeth.
By the time your baby is 12 months old, they should be eating the same foods that the rest of the family is eating. But you might still need to chop some foods into smaller pieces and cook vegetables until they’re soft.
To prevent choking, always supervise babies and young children while they’re eating solid food. Avoid nuts, take special care with pieces of meat and check fish for small bones, because these are choking hazards. And if your baby can move around, make sure baby is sitting down while they’re eating. If you sit with your baby while they’re eating, baby is less likely to move around.
Types of food to offer when introducing solids
All new foods are exciting for your baby.
The key is to include iron-rich foods of the right texture in your baby’s first foods. Iron-rich foods include:
- iron-fortified infant cereal
- minced meat, poultry and fish
- cooked tofu and legumes
- mashed, cooked egg (avoid raw or runny egg).
To these iron-rich foods, you can add other healthy foods of the right texture like:
- vegetables – for example, cooked potato, pumpkin, sweet potato, carrot, broccoli or spinach
- fruit – for example, banana, apple, pear, melon or avocado
- grains – for example, oats, bread, rice and pasta
- dairy foods – for example, yoghurt and full-fat cheese.
You can introduce any number of new foods at a time and in any order. When you offer your baby a variety of foods, they can try plenty of new tastes and get a range of nutrients.
Read our tips for introducing solid foods to learn how to get your baby interested in new foods and manage mealtime mess and play.
Breastmilk and infant formula while introducing solids
You should keep breastfeeding or using infant formula until at least 12 months.
When you start introducing solids, breastmilk or infant formula should still be the main source of your baby’s nutrition. Over the next few months, your baby will start having more solids and less milk or formula. The rate that this happens will vary.
By around 9 months, babies have generally developed enough chewing and swallowing skills to move from having milk before solids to having milk after solids.
Here are some signs that your baby is getting enough nutrition from both solids and breastmilk or formula during this time. Your baby:
- has plenty of wet nappies – at least 6-8 wet cloth nappies or 5 very wet disposables in 24 hours
- is alert and mostly happy after and between feeds
- is gaining weight at about the right rate – your child and family health nurse will weigh your baby at your regular check-ups.
From 12 months onwards, solids should be the main source of your baby’s nutrition. Your baby doesn’t need infant formula after 12 months, but you can keep breastfeeding for as long as you and your baby like.
If solid food replaces breastmilk and/or infant formula too quickly, babies can miss out on important nutrition. If you have any concerns about your baby’s feeds or weight, talk to your midwife, child and family health nurse, lactation consultant or GP.
Introducing water
Once your baby has reached 6 months, you can start to offer baby cooled, boiled water in a cup at mealtimes and at other times during the day. This is so your baby can practise drinking from a cup, but baby still doesn’t really need fluids other than breastmilk or formula at this age.
Once your baby has reached 12 months, you can offer fresh tap water without boiling it.
Foods and drinks to avoid while introducing solids
There are some foods to avoid until your baby is a certain age:
- Honey until 12 months – this is to avoid the risk of infant botulism.
- Raw or runny eggs and foods containing raw eggs like home-made mayonnaise until 12 months – bacteria in raw eggs can be harmful to babies.
- Reduced-fat dairy until 2 years – babies need full-fat dairy for growth.
- Whole nuts and similar hard foods until 3 years – these are choking hazards.
There are some drinks to avoid until your baby is a certain age:
- pasteurised full-fat cow’s milk as a main drink until 12 months
- dairy alternatives like soy, goat’s, sheep’s, rice, oat, almond and coconut milk until 2 years, unless your GP or child and family health nurse has recommended these for a particular reason
- unpasteurised milks at all ages
- tea, coffee or sugar-sweetened drinks at all ages
- fruit juice – this should be limited at all ages (whole fruits are better because they have fibre and help babies develop chewing and feeding skills).
Your baby doesn’t need added salt or sugar. Processed or packaged foods with high levels of fat, sugar and/or salt aren’t good for babies and children. These foods include cakes, biscuits, chips and fried foods.
Processed or packaged foods with high levels of fat, sugar and/or salt aren’t good for babies and children. These foods include cakes, biscuits, chips and fried foods.
Food allergy and introducing solids
Introducing allergenic foods early can reduce the risk of your child developing food allergy. Allergenic foods are foods that might cause allergies.
All babies, including babies with a high allergy risk, should try solid foods that might cause allergies from around 6 months of age. These foods include well-cooked egg, peanut butter and other nut butters, wheat (from wheat-based breads, cereals and pasta) and cow’s milk (but not as a main drink).
Once you’ve introduced an allergenic food, it’s a good idea to regularly include it in your baby’s diet.
It’s a good idea to get advice from your GP, child and family health nurse, dietitian, paediatrician or allergy and immunology specialist for the following reasons:
- Your baby already has a food allergy.

- Your baby has severe eczema.
- Your family has a history of food allergy and you’re concerned about starting solids.
- You’re worried about reactions to foods.
How to properly feed your 7-month-old baby with solid food
Learn how to make a menu, what to include and what to avoid when you introduce solid food into your baby's diet.
Carolina Plavina
Рixabay
Collected detailed information about what and how much to feed a 7-month-old baby. Also included are some interesting recipes that allow you to diversify the complementary foods menu.
Content of article
Do not self-medicate! In our articles, we collect the latest scientific data and the opinions of authoritative health experts. But remember: only a doctor can diagnose and prescribe treatment.
How do you know when a 7-month-old baby is ready for solid foods?
The signs below will help you determine if your baby is able to digest solid foods:
- He holds his head well.
- Can sit upright on a high chair or feeding seat (no or little support).
- Tries to reach out (leans forward) for solid food.
- Opens mouth and willingly eats solid food when offered.
- Fingers capable of grasping objects.
Delaying the introduction of solid foods may affect a child's healthy weight gain. Therefore, encourage your child to eat solid food as soon as he shows signs of readiness.
A 7-month-old baby's diet can include a variety of healthy foods such as grains, legumes, meat, fish, poultry, fruits, and vegetables. With constant breast or milk feeding, children can consume these products in the form of a well-cooked puree or gruel.
How often should I feed my baby when weaning?
Feed 7-month-old babies nutritious foods and drinks every two to three hours to support proper growth and development. If on some days the baby eats less than usual, refrain from force feeding. We have a separate article on maternal nutrition during breastfeeding.
We have a separate article on maternal nutrition during breastfeeding.
Remember that the main source of nutrition even for a seven-month-old baby is breast milk or formula. They can get solid food, but in small amounts, as they need time to get used to the taste, texture, and digestibility of weaning food.
How much food should a 7-month-old baby eat?
The Association of American Pediatricians recommends that mothers continue breastfeeding until at least 12 months of age. Therefore, the baby can be given alternately both breast milk and solid food.
Portion sizes per day
At 7 months, a baby needs a portion of food per day, which is equal to about ⅛ of body weight. This is 1000-1200 ml of food, excluding water, juices, children's tea. Divide this amount by 5 feedings and you will get an estimated amount of food per meal - 200-210 ml.
7-month-old meal options
Traditionally, parents start with single-grain cereal or vegetables and fruits (blended, pureed, or cooked soft). When your baby is seven to nine months old, you can include a variety of foods from different food groups in your diet.
Vegetables
Broccoli, cauliflower, peas, spinach, asparagus, parsnips, peppers, carrots, cabbage, avocados, green beans and squash.
Fruit
Banana, apple, mango, blueberry, kiwi, pear, strawberry, papaya, melon, peach, plum and orange.
Starchy foods
Potatoes, sweet potatoes, rice, porridge, oatmeal, oats, corn, millet, quinoa, cornmeal and bread.
Protein-rich foods
Meat (chicken, lamb, boneless fish), eggs, legumes, lentils, beans.
Dairy products
Pasteurized full fat kefir, curd without sugar or sweeteners.
What is the right way to cook food for a 7 month old baby?
Boil and mash hard fruits such as apples before serving them to a child. You can mix fruit and vegetable purees with formula or breast milk. When choosing meat, you can also consider serving meat broth.
All foods must be soft so that the baby does not choke. Make sure your child eats slowly and in small portions.
Recipes for complementary foods for 7-month-old children
omelet with onions
You will need:
1 Small bulb, peeled and chopped
1 Egg
½ ½ teaspoon
How to prepare:
How to prepare:
How to prepare:
egg. Cut the onion into small pieces and add it to the egg. Whip them together.
Cut the onion into small pieces and add it to the egg. Whip them together.
Place the butter in a frying pan. When the pan is hot, add the mixture and let it cook through.
Let the omelet cool down. Cut it into thin slices and serve to the child.
Berry porridge
You will need:
2 tablespoons of oatmeal
¼ banana
Frozen blueberries (you can use fresh blueberries)
1 tablespoon of yogurt
Water 9000
how to prepare: 9000
How oatmeal and water in a saucepan. Cook until the mixture thickens and becomes soft.
Top with finely chopped or pureed bananas and blueberries before serving.
Spicy chicken fingers
You will need:
skinless chicken breast
juice of ½ lemon
How to cook:
Take the skinless chicken breast and cut into medium-sized pieces.
Preheat oven to 200°C (approx. 400°F).
Place the chicken pieces on a baking sheet and squeeze a few drops of lemon juice onto them.
Roast the chicken for 25 minutes. Once baked, it can be crumbled or given as finger food.
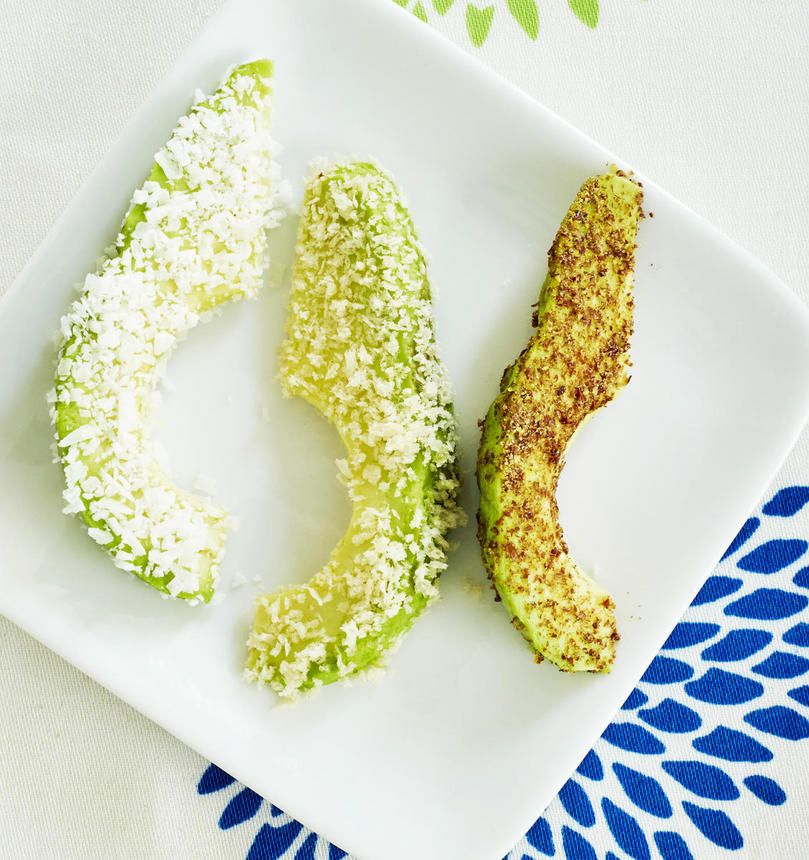
Avocado and banana puree
You will need:
½ avocado
1 banana, peeled
How to make:
Remove the avocado from the pan Add a banana to it and make a puree.
You can also add formula or breast milk to the puree and mix before serving.
Sample menu for the day
Breakfast (morning). Solid food :
● Porridge for infants
Liquid :
● Breast milk or formula
Snack (late morning).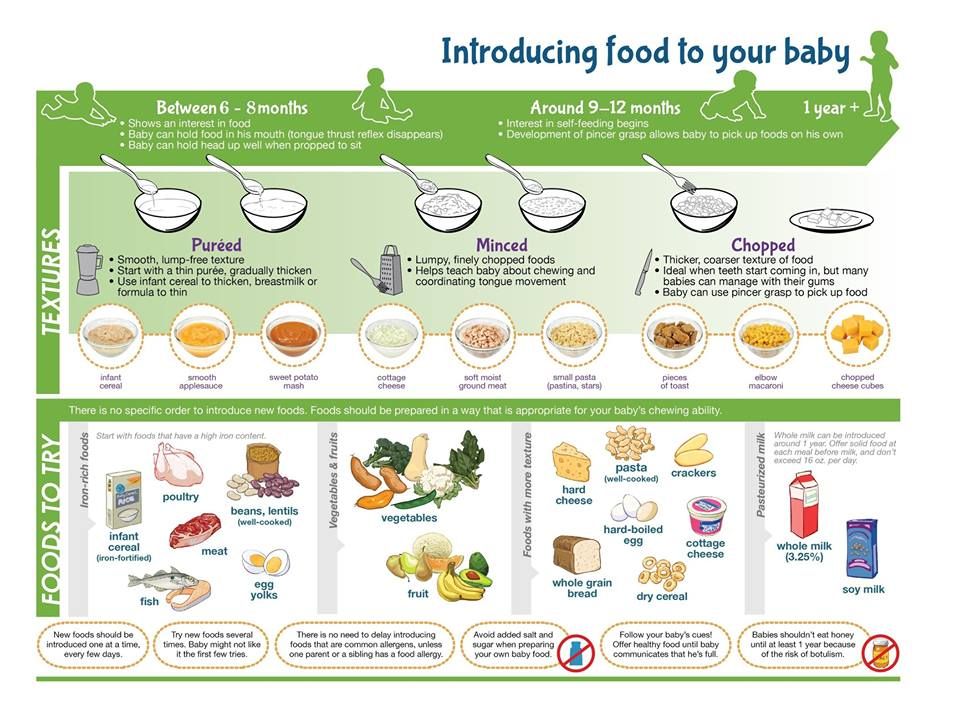 Solid food :
Solid food :
● Fruit puree such as banana, kiwi, strawberry, boiled apple, boiled pear with unsweetened yogurt (low fat).
Liquid :
● Breast milk or formula
Lunch. Solid food :
● Boiled and finely chopped chicken,
● Cooked and mashed vegetables such as pumpkin, potatoes, spinach, squash, etc. with cooked and mashed rice.
Liquid :
● Breast milk or formula
Snack (evening). Solid food :
● Boiled and mashed pear
● Boiled and finely chopped carrots or mashed beans.
● Plain yogurt or kefir
● Whole grain cracker
Liquid :
● Breast milk or formula
Dinner.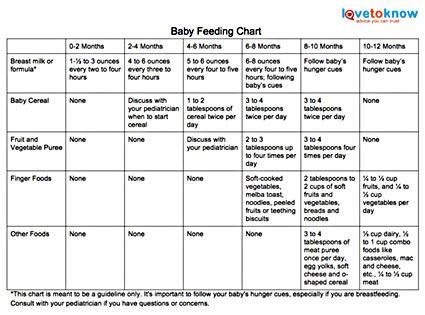 Solid food :
Solid food :
● Boiled vegetables.
Liquid:
● Breast milk or formula
Start with one or two tablespoons of food and see if your baby shows signs of hunger or satiety. Remember that their tummies are still small! You can alternate between solids and liquids depending on your child's hunger signals. You can learn more about breastfeeding here.
Try to include foods with a variety of colors and textures in your child's diet. By the end of seven months, you can also slowly start introducing finger foods to develop the habit of self-feeding.
Baby's meal plan at seven months
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), complementary foods (foods other than breast milk) can be given to babies between six and eight months of age up to two to three times a day. In addition, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends giving your child something to drink or eat every two to three hours, or about five to six times a day (10).
Feeding precautions for a 7 month old baby
Here are a few things to keep in mind when feeding your baby.
- add one ingredient at a time. Give this product for three to five days, during which time do not give any other new food. Monitor your child for signs of an allergy.
- Gradually increase the variety and quantity of food ingredients; start with a teaspoon and then move on to a tablespoon.
- You can also try finger food if your child seems ready. Your child may begin to grasp objects with his fingers when he is ready for finger food. Make sure you are present during meals to avoid the danger of choking.
- Wash, peel, remove seeds and seeds before giving fruits and vegetables to your child.
- Use a spoon to feed your baby. Make sure that during feeding the child sits on a chair with a table. Observe and respond to your child's hunger cues. Try to develop a predictable schedule for your child for all meals and snacks, and limit the time of each meal to 15-20 minutes.
- Avoid adding salt, sugar and butter when preparing baby food at home. Also, avoid cow's milk and honey until your baby is at least 12 months old.
How to teach your baby to chew: teaching your baby to chew solid food
Glinskikh Elena
Published: 01/15/2023
Reading time:
723
What are the difficulties
When a small child appears in a family, parents face a difficult task: not just to raise and educate, but also to instill in the baby all the necessary skills. For example, young parents are often concerned about the question of how to teach a child to chew. We have collected tips for you from well-known Russian and foreign pediatricians who will help you find the best solution.
For adults, the process of chewing food seems to be something completely natural. But the child has only a sucking reflex, and even liquid puree becomes an unusual and unfamiliar food for him. In addition, other reflex reactions are characteristic of the same period, due to which solid pieces of food that have fallen into the mouth are rejected. They weaken by 4 months, but it is not necessary to wean a child at this age: mother's milk "adjusts" to the needs of the baby, its composition changes over time.
In addition, other reflex reactions are characteristic of the same period, due to which solid pieces of food that have fallen into the mouth are rejected. They weaken by 4 months, but it is not necessary to wean a child at this age: mother's milk "adjusts" to the needs of the baby, its composition changes over time.
When to introduce the first complementary foods
Exactly at this time - in the period from 4-6 months. Depending on various factors, it can be a monocomponent vegetable puree or dairy-free porridge from a single cereal. It is worth considering the weight, height, state of the digestive system and other features of the child's health.
How do you know when your baby is ready for solid food? This can be seen from his behavior:
- stops sucking food from a spoon, removing it with lips
- .

This usually happens no earlier than 6-8 months - that's when you can start giving the baby cereals and other foods with small dense particles.
How to choose a diet for young children
- At 6-7 months, tiny particles up to 0.3 mm are acceptable. Shredded vegetables are ideal
- At 8-9 months, food with particles up to 1.5 mm can be added to the diet. These can be cereal flakes as part of cereals, tiny pieces of well-cooked vegetables
- At 9-12 months, the child can already cope with chewing food with pieces up to 3 mm.
- At 1 year of age and beyond, teach the child to chew solid food independently
Common mistakes
Young parents may inadvertently make mistakes. This is normal and should not cause panic: the first child is always difficult. If the baby refuses solid food, there are several reasons.
Solids too large . The child has a protective reflex, due to which he often spits out food.
 And if the piece is very large, the baby may begin to vomit.
And if the piece is very large, the baby may begin to vomit. Complementary foods were introduced very late . Some "specialists" and "experienced relatives" convince young mothers that they need to breastfeed their baby for up to a year, without giving him any other food. The kid gets used to such food, and the chewing reflex is not formed in him. You should not be afraid, it is difficult, but you can fix it.
The child does not like the taste . Yes, he is already an independent person who has his own preferences. So the baby can easily eat broccoli and refuse a baked pear. Or vice versa. You should not forcefully stuff the child with what he does not like, or force him to finish eating the entire portion.
Negative associations . Some psychologists believe that the refusal to eat from a spoon may be due to the fact that the child associates food with medicine (manifested in cases where the baby was given tasteless potions).
Too many new products .
 Don't try to include a wide variety of foods in your diet. As Ellyn Satter writes in Feeding and Feeding Your Child with Love and Common Sense, it's best to add "scary and unfamiliar" foods to what your child already loves, and in very small portions.
Don't try to include a wide variety of foods in your diet. As Ellyn Satter writes in Feeding and Feeding Your Child with Love and Common Sense, it's best to add "scary and unfamiliar" foods to what your child already loves, and in very small portions. The child is fed like an adult . Larisa Surkova writes in the book “How cool it is with a child from 1 to 3 years old: a generator of useful tips”, you should not deny your baby tactile sensations. If he wants to crush food, sniff, smear on the table - let him do it. In the end, the table can be covered with oilcloth (and the floor, by the way, too).
No Foods
To avoid food allergies and digestive problems, never give a child under four years of age:
- lollipops, caramel, toffee
- nuts and seeds of any kind
- hard pieces of meat
- whole grapes
- large pieces of hard fruits and vegetables
a one-year-old baby cannot chew food and constantly chokes on small pieces.
 This means that the chewing reflex is not fully formed, and parents will have to act very delicately:
This means that the chewing reflex is not fully formed, and parents will have to act very delicately: - Prepare thick creamy soups and purees for the child, but leave a few tiny, boiled pieces of vegetables while blending with a blender
- Later, the vegetables can be chopped with a fork, the pieces will become larger, but not hard enough for the child to choke
- The best effect will help to achieve products that taste like a child. These can be baked apples and pears, bananas, children's cookies
- 0022
If, during the learning process, the child continues to choke and is unable to swallow solid food, this is an occasion to consult a doctor who will find the cause of the problem.
Game process
The child needs to be interested. A game plot for eating is an absolute norm. In the process, the baby can be told an interesting story in which he will be involved. The well-known “airplane” flying to the “hangar” is a real way to feed a child without nerves and tantrums.












