How many ounces in a small jar of baby food
How Much Baby Food Your Baby Should Be Eating- A Guide
You’re wondering about the above statement aren’t you? Ask the vast majority of pediatricians and they will all say, “Feed your baby as much as your baby will eat”.
One of the caveats when feeding your baby solid foods is that that you ensure that your baby is still receiving proper amounts of breast milk and/or formula. Solid foods in the early stage are meant for practice. Solids are not meant to provide for baby’s nutrition as breast milk and/or formula are.
How much solid food a baby will be eating depends on a variety of different things.
Don’t forget that your baby is a little human being, and like all of us, she has her own appetite. This will influence to how much solid foods she will be eating. As with adults, some babies will eat more than others due to their individual appetites. Below are a few key points to remember when feeding your baby.
- A baby who began solid foods at 4 months of age will most likely be eating more solid foods than the baby who began to eat solid foods at 6 months old.
- A baby who is eating soft diced foods as beginner foods may seem to eat less than the baby who is being spoon-fed purées.
- A baby who is ill or teething may eat less than what has been typical for a few days and then suddenly the typical appetite comes roaring back.
- An infant who is busy exploring the carpet or the new soft-book she has received may be miffed when she is put into a high chair and offered food.
The natural slow down of growth that babies go through will also influence how much they eat. They may be ravenous for a few days or a week or two and then suddenly, they are barely eating. Babies who are coming out of a growth spurt will tend to eat less than they were during the growth spurt.
How do I know if my baby is eating enough solid food?
As all pediatricians will tell you ” Your baby will never starve himself or herself! ” The majority of healthy babies will eat just the right amount of foods that they need. Resist the urge to offer “just one more bite” when baby indicates she’s finished. You do not want to accidentally override your baby’s developing ability to self-regulate his or her feeding by continuing to try and feed your baby. It is important to pay close attention to your baby’s cues as your baby’s feeding patterns will change daily and may be affected by the goings-on around him.
Resist the urge to offer “just one more bite” when baby indicates she’s finished. You do not want to accidentally override your baby’s developing ability to self-regulate his or her feeding by continuing to try and feed your baby. It is important to pay close attention to your baby’s cues as your baby’s feeding patterns will change daily and may be affected by the goings-on around him.
Offering a well balanced diet of solid foods will help ensure that your baby is eating the right amount of the right nutritious foods.
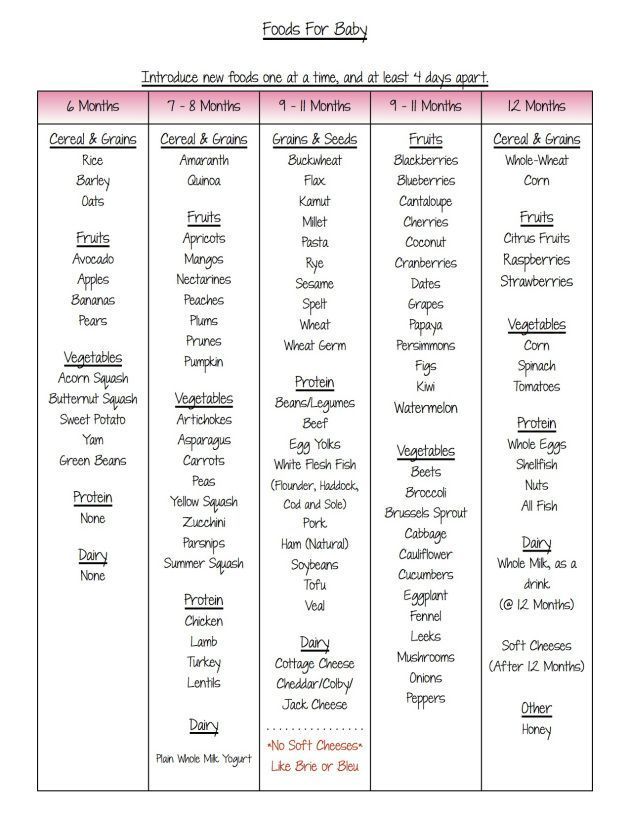
Example feeding “schedule” of solid foods
REMEMBER: 1 ounce equals approximately 2 tablespoons
Before 4 Months:- According to the CDC, babies before 4 months of age should not be fed solid baby foods. Infants should be able to sit up on their own and take food off the spoon before being introduced to solids
- Why can’t we give baby younger than 4 months solids? According to Dr.
 Alice Kuo of UCLA, “Introducing solid foods early means that the baby gets less breast milk over the course of their infancy, and that decreases the ability to get optimal benefits, like protection against infection,”
Alice Kuo of UCLA, “Introducing solid foods early means that the baby gets less breast milk over the course of their infancy, and that decreases the ability to get optimal benefits, like protection against infection,”
What to Feed Baby:
- Breast milk or formula
Breastfeed every 1-3 hours or Formula 18-40 ounces
4-6 Months:
If baby can sit up on their own and still seems hungry after breastfeeding, baby may be ready to start eating solids! Baby should be able to hold their head up, close their mouth around a spoon and “move” the food to the back of their mouth.
What to Feed Baby:
- Breast milk or formula AND
- 1-3 tablespoons of food at 1 or 2 “meals”
Click here to learn what foods you can introduce to a 4-6 month baby
6-8 Months:
Formula and/or Breast Milk is still most important at this age and stage. Babies in this range may be just starting solids so the above for 4-6 Months would apply. Some babies may be eating up to 8 ounces of solid foods between 2-3 “meals” during a day.
Babies in this range may be just starting solids so the above for 4-6 Months would apply. Some babies may be eating up to 8 ounces of solid foods between 2-3 “meals” during a day.
What to Feed Baby:
- Breast milk or formula AND
- Foods in this chart for solids OK to give baby 6-8 months, 2-3 “meals” a day
Click here to learn what solid foods you can introduce to a 6-8 month baby
8 to 10 months:
Many babies will be eating 3 “meals” per day at this stage; including a grain, fruit, veggie and a meat or protein source such as eggs.
Again, pay close attention to your baby’s cues as your baby’s feeding patterns will change daily and may be affected by the goings-on around him. Your baby will eat just the right amount for YOUR baby.
What to Feed Baby:
- Breast milk or formula AND
- Foods in this chart for solids OK to give baby 6-8 months, 3 “meals” a day
Click here to lean what solid foods you can introduce to a 8 to 10 month baby
10 to 12 months:
Many babies will be eating 3 “meals” per day at this stage; including a grain, fruit, veggie and a meat or protein source such as eggs.
Again, pay close attention to your baby’s cues as your baby’s feeding patterns will change daily and may be affected by the goings-on around him. Your baby will eat just the right amount for YOUR baby.
What to Feed Baby:
- Breast milk or formula AND
- Foods in this chart for solids OK to give baby 10-12 months, 3 “meals” a day
Click here to lean what solid foods you can introduce to a 10 to 12 month baby
Here are a few things to watch for to ensure that you are not over or under feeding your baby:
Signs that baby may want to continue to eat- Leaning in for the spoon
- Opening the mouth
- Grabbing for food and trying to put it in the mouth
- Closing of the mouth as the spoon comes close
- Spitting out the food that is being fed
- Turning the head away as the spoon comes closer
A healthy well-fed baby should be producing wet diapers regularly as well as producing a bowel movement or two during the day.
Ensure that you take your baby to the well-child visits as scheduled so that your pediatrician may weigh and measure baby to ensure that your baby has good sustained growth.
If you are ever uncertain about the foods and the amount of solid foods you are feeding your baby, always consult your baby’s pediatrician. Your pediatrician should be able to assist you in validating your feeding routines and also help allay your fears.
Remember, always consult with your pediatrician regarding introducing solid foods to your baby and specifically discuss any foods that may pose allergy risks for your baby.
No two babies will eat the exact same amounts (or foods!) The amount that each eats is just right for that baby!
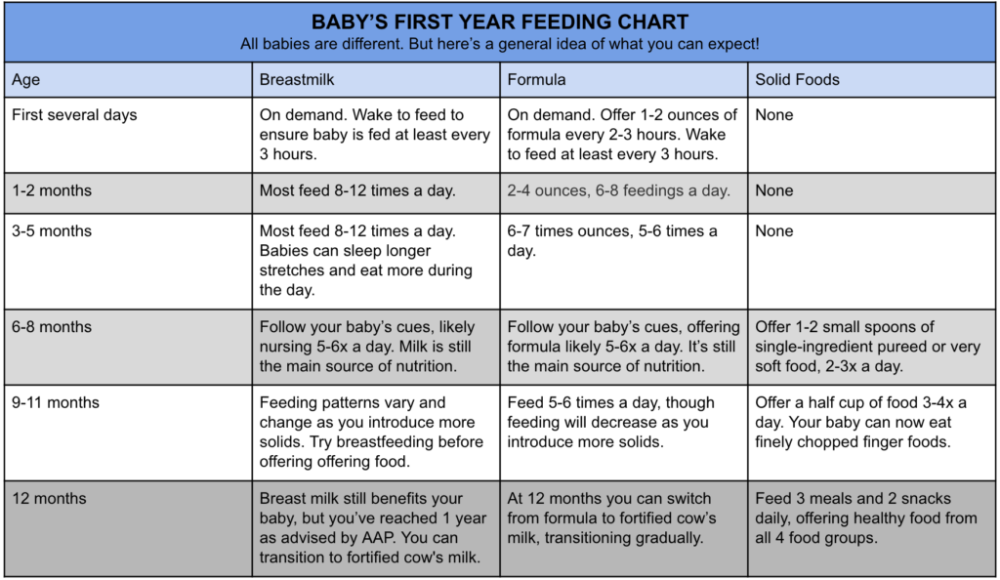
Suggested Daily “Milk” Intakes for Babies age 0 to 12 months
- 0-3 Months of age:
Breastfeed every 1-3 hours or Formula 18-40 ounces - 4-5 Months of age:
Breastfeed every 2-4 hours or Formula 24-45 ounces - 6-8 Months of age:
Breastfeed every 3-4 hours or Formula 24-37 ounces - 9-12 Months of age:
Breastfeed every 4-5 hours or Formula 24-31 ounces
Whole Cow Milk, as a drink, should not be introduced until 12 months of age. Learn about Introducing Yogurt and Feeding Cheese to your baby.
Learn about Introducing Yogurt and Feeding Cheese to your baby.
Table compiled from Merck Source
Follow Your Baby’s Cues When Feeding Your Baby Solid Foods
Following your baby’s cues during feeding time will ensure that your baby is eating the proper amounts of food for him or her.
There is no “set-in-stone” guideline or chart of exactly how many jars of baby food or how many 8 ounce bottles of formula each baby should be receiving. This is simply because each and every baby is different. Babies will eat as much food and drink as much breast milk and/or formula as they need.
For example: You may wonder how it is possible that your friend’s 7 month old baby is eating 2 whole jars of baby food (8-9 oz) in one day while your 7 month old baby barely manages to eat 3 or 4 baby food cubes (3-4 oz) of food per day. You may also wonder why your baby nurses every 2 hours at 7 months old while your friend’s baby may only nurse every 3 or 4 hours. Again, each baby has different food and milk needs and these needs are just right for the individual baby.
Again, each baby has different food and milk needs and these needs are just right for the individual baby.
Read More About Solid Foods for Baby Food
Ask the vast majority of pediatricians and they will all say, “Feed your baby as much as your baby will eat”.
- Is My Baby Ready for Solid Foods?
- Baby Food Combinations
- Baby Food Allergies
- Iron and Your Baby
- Yogurt for Baby
- Travel with Homemade Baby Food
- Constipation and Your Baby
Remember, always consult with your pediatrician regarding introducing solid foods to your baby and specifically discuss any foods that may pose allergy risks for your baby.
This site complies with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information:
verify here.
SHARE ON FACEBOOK SHARE ON PINTEREST
Baby Food Puree in Glass Jars
Filter
Filter
Puree Type
- Jar 39items
- Tub
- Pouch
- Natural 17items
- Organic 12items
- 1st Foods 13items
- 2nd Foods 22items
- 3rd Foods 8items
Milestones
- Pregnancy
- Newborn
- Supported Sitter 12items
- Sitter 22items
- Crawler 8items
- Toddler
- Preschooler
Ingredients
- Apple 13items
- Apricot
- Avocado
- Banana 8items
- Beef 2items
- Blueberry 3items
- Carrot 8items
- Cereal
- Chicken 1item
- Corn 1item
- Green Bean 1item
- Ham 1item
- Kale 2items
- Mango 2items
- Oatmeal
- Pea 3items
- Peach 2items
- Pear 6items
- Pineapple 1item
- Pumpkin
- Raspberry 1item
- Rice 2items
- Spinach 2items
- Squash 2items
- Strawberry 3items
- Sweet Potato 4items
- Turkey 2items
- Zucchini 2items
Needs
- Colic
- Crying
- Fussiness
- Gas
- Mild Spit-Up
- Uncomfortable Poops
- Teething
- Vitamin D
- On the Go 2items
- Iron
- Starting Solids 2items
- Expanding Textures 5items
- Probiotics
- DHA
- Prebiotics/2’-FL HMO
CLEAR ALL
Price - Low to High Price - High to Low Newest On Sale Top Sellers
| Information about the educational organization Basic | 1. 2. Potato chips, especially cooked not from whole potatoes, but from mashed potatoes. It's essentially a mixture of carbs and fat plus artificial flavors. 3. Sweet bars. The combination of big amount of sugar and various chemical additives provides the highest calories and the desire to eat them again and again. 4. Sausages, sausages, boiled sausage, pates and other products with so-called hidden fats. They contain fat interior fat, pork skin occupy up to 40% of the weight, but are disguised as meat, in including with the help of flavoring additives. 5. Fatty meats, especially fried. These products are widely distributed, no one can imagine life without them. And yet, if you have become a supporter of a healthy, proper diet from the following must be abandoned. At least for a while! Salt In an ideal diet, salt is almost never used, and also pickled cucumbers, tomatoes, mushrooms, etc. Sugar Sugar and all products containing it - confectionery products, preserves, jams, compotes, ice cream, sweetened juices, etc. in principle, herbal tea with sugar or jam as a separate meal sometimes can be allowed, but in combination with other food, sweets are decidedly contraindicated. Eaten with starches or proteins, sugar causes putrefaction. fermentation, with fruit it acidifies the blood. Fruit is a powerful source of alkali, but with sugar they become equally powerful sources of acid. One small a jar of Coca-Cola contains 10 teaspoons of sugar. Jar per day throughout 10 years old and you are guaranteed diabetes. The risk of developing obesity increases by about 50% with each additional a portion of a sweet carbonated drink per day. Honey in moderate amounts does not cause such reactions, little by little honey can be added to many dishes. Margarine, artificial fats, vegetable fat If you care about your health, then the use of eating the above foods should be limited. Margarine Presents a mixture of animal and vegetable fats subjected to hydrogenation - saturation fatty acid molecules with hydrogen atoms. Transisomers (mutated molecules fatty acids), the share of which in hydrogenated margarine reaches 40%, increase the level of cholesterol in the blood, disrupt the normal functioning of cellular membranes, contribute to the development of vascular diseases, adversely affect on sexual potency.
Canned food These are dead products. Chemical drinks On the shelves of stores - a variety of sparkling water with many flavors. Regardless of the price category, they are equally destructive affect the body. Remember, the best of all drinks is pure water! food dyes, preservatives contained in "neon" drinks - source xenobiotics (persistent and stubborn substances). Their accumulation in cells especially fat is the cause of chronic fatigue syndrome, reduced immunity, leads to functional disorders of the body systems - constipation, skin diseases, tumors of the stomach, cancer of the esophagus. Deeply processed meat products These include all sausages, as well as smoked fish, ham, smoked brisket. Perhaps many will agree that boiled sausage today it is difficult to even call it a product. Sausages are slightly better in quality, but they cannot serve as tolerable food. There are many irritating substances in smoked meats and salt, they quite noticeably "hit" the digestive and excretory organs and very strongly acidify the blood. Fried foods All fried. Roasting produces poisonous and carcinogens (especially when fat from a frying pan is used in repeatedly). Many toxic compounds are obtained by heating all vegetable oils other than corn. If, as an exception, one still has to fry something, it is better to do it only in ghee. Ruddy crusts, so appetizing and tasty, are extremely difficult to digest and contribute to gastritis, colitis, ulcers, diseases of the liver and kidneys. Spices Vinegar, peppers, tomato sauces, mustard, marinades and others spicy or sour seasonings. Sluggish, stale vegetables Not only are they not useful, they may even cause poisoning. The same applies to yesterday's salads. Already cooked salad loses half its value after half an hour. Moreover, it starts microorganisms develop intensively (especially if seasoned with sour cream or mayonnaise) and nitrates are actively converted into nitrites. Therefore never prepare a five-liter pot of salad for the future, it is better to prepare additives than scoop a harmful mixture from the pan. Mayonnaise Product of the middle category of "harmfulness". 1 tablespoon mayonnaise provides more than 50% of the daily requirement of the human body in vitamin E and almost 70% in polyunsaturated fatty acids. Reheated or stale food Reheating also loses almost all valuable substances. Calories and products of bacterial activity remain (after all, microbes develop even in the refrigerator, although much more slowly than at room temperature. temperature). Dried fruits treated with preservatives and bleaches Nutritionists do not recommend dried fruits processed sulfuric acid solution or sulfur dioxide. And according to technology similar we process apples, pears and most of the apricots. Dried apricots without sulfur dioxide has a darker, almost brown, to brown color. It is advisable to soak the processed dried fruits for several minutes in a slightly warm water, then most of the sulfur dioxide will go into solution. | Support for families with families Single number 8-800-700-2404 |
Can I take food on the plane?
Perhaps not everyone knows about it, but you can take food on board the aircraft, and not only what was bought in Duty Free before landing.
Knowledgeable tourists take with them not only chocolates and cookies, but also sandwiches and other homemade preparations. There are only restrictions on drinks, but flight attendants carry them anyway, unless you fly on low-cost airlines, where you have to pay for tea or juice.
There are several guidelines to follow when choosing food.
It is advisable to take protein-rich foods with you: chicken, beef, cheese, nuts. Choose products that do not have a strong smell, which will not crumble much and will not deteriorate during several hours of flying and waiting at the airport. For a snack, a mix of nuts and dried fruits, sandwiches or a salad in a container are perfect.
For a snack, a mix of nuts and dried fruits, sandwiches or a salad in a container are perfect.
Avoid strongly smelling and gassy foods (onions, garlic, fish, beans, broccoli, eggs) and fatty foods. You can ruin your stay on the plane not only for yourself, but also for numerous neighbors.
Please note that liquids, including creams and gels, are prohibited from carriage .
Unless they comply with the regulations:
- The volume of the containers must not exceed 100 ml.
- All containers should be stored in the same resealable, clear plastic container. The total capacity should not exceed 1 liter.
- Each passenger is only allowed to carry one such package.
- Containers containing liquids must be presented separately at the Security Control Desk.
Which of the products are liquids and gels? The list is not very large, it includes: yogurt, sauces (for example, for salad), cottage cheese, peanut butter, jam, jam, jelly, soup, pate.
Over 100 ml you can take baby food , provided that you are flying with a child under 2 years old and this food is only for the duration of the flight.
In your checked baggage, you can carry any amount of liquid. Restrictions are only on the amount of alcohol.
Is it possible to take caviar in hand luggage?
Yes, you can take caviar in glass or tin factory packaging. On domestic flights in Russia, they may also let you in with plastic containers (if you bought caviar by weight). But pay attention to the volume, it should not exceed 100 ml, because. caviar is considered liquid.
On domestic flights, the volume of cans of caviar is more tolerant, and sometimes containers larger than 100 ml are skipped. But if you are flying with luggage, then it is better to hand over the caviar.
A bit more complicated with overseas flights. Here it is necessary to take into account not only restrictions on the liquid, but also customs rules.
According to Russian legislation, it is allowed to export from the Russian Federation no more than 250 grams of sturgeon caviar (black caviar - beluga, sturgeon and stellate sturgeon). Before leaving, be sure to familiarize yourself with the customs regulations of the country where you are going. For example, the EU and the US are allowed to import no more than 125 grams of sturgeon caviar per passenger.
Red caviar is salmon caviar, you can take it out up to 5 kg. Please note that the standard factory packaging of red caviar is 140 gr, which is more than the allowed 100 ml for hand luggage. Therefore, always put caviar in your luggage.
What exactly can I take from the products in hand luggage?
- cookies, chips, dryers, gingerbread, crackers, wafers, etc.
- pastries
- sweets, chocolate bars and chocolates
- fruits and vegetables - in the amount necessary for a snack on board. It is not always possible to carry a couple of kilos of tomatoes on an international flight.

- sandwiches and sandwiches
Products subject to the 100 ml limit:
- Drinkable yoghurt
- Baby food (mashed potatoes and pâtés) if you are traveling without a child. If you have a child under 2 years old with you, then you can take more than allowed, but on the condition that this is the food that the child will need during the flight, and not with a supply for the entire period of rest.
- Alcohol. It's even more difficult for him. More and more airlines are introducing “prohibition”. those. a ban on the sale and consumption of alcohol on board the aircraft. Only alcohol purchased from the Dute Free store and unopened is allowed to be transported. The rules for drinking alcohol should be checked with a particular airline.
- Honey
- Soft cheese, including brie, camembert, mozzarella, ricotta, feta, etc.
- Canned food. Even if 99% of the content is solid. The security service will focus only on the volume of the jar, it should be up to 100 ml, if more, then check it in your luggage.


 Sugary carbonated drinks. Created at all not to quench thirst, but to evoke it. Huge content sugar: in one glass of it at least five teaspoons.
Sugary carbonated drinks. Created at all not to quench thirst, but to evoke it. Huge content sugar: in one glass of it at least five teaspoons.  are minimized, excluded crisps, salted crackers, some cheeses, and other salty ones products. Sauerkraut with a minimum of salt is allowed when there are no others sources of vitamins.
are minimized, excluded crisps, salted crackers, some cheeses, and other salty ones products. Sauerkraut with a minimum of salt is allowed when there are no others sources of vitamins.  Preparations from berries with sugar much less harmful than just sugar. The point is that during storage enzymes of berries and fruits convert part of the sugar into fructose, moreover, similar mixtures contain many vitamins. But still, jams, jams and other "live" products based on sugar - foods that you need to eat little by little, in the form of a treat.
Preparations from berries with sugar much less harmful than just sugar. The point is that during storage enzymes of berries and fruits convert part of the sugar into fructose, moreover, similar mixtures contain many vitamins. But still, jams, jams and other "live" products based on sugar - foods that you need to eat little by little, in the form of a treat. 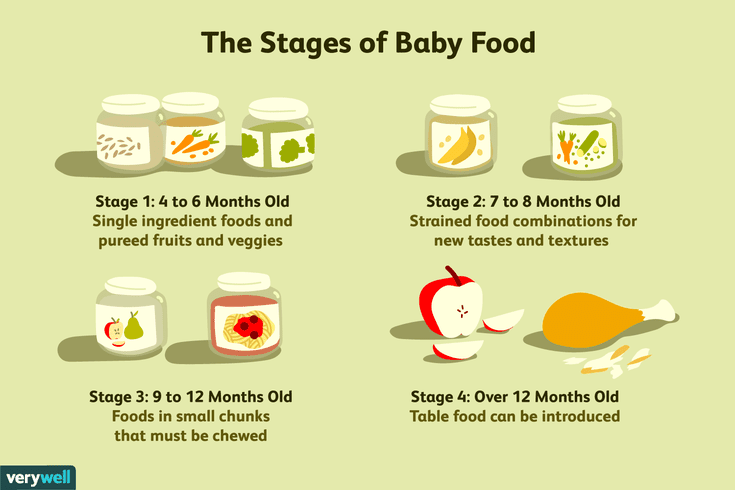 Canned meat and fish loaded with salt and preservatives. Canned vegetables are sometimes edible. Fruit and vegetable purees for baby food are often acceptable as well. But they are suitable only for the most extreme cases, when it is impossible to find anything fresh. So, most canned food - products of particular hazard. And even those rare representatives that are not very harmful are usually not useful. Can, however, make fruit and vegetable preparations yourself. But better, if possible, keep everything fresh. Cabbage, potatoes, carrots, beets are preserved until spring itself, greens can be grown or bought.
Canned meat and fish loaded with salt and preservatives. Canned vegetables are sometimes edible. Fruit and vegetable purees for baby food are often acceptable as well. But they are suitable only for the most extreme cases, when it is impossible to find anything fresh. So, most canned food - products of particular hazard. And even those rare representatives that are not very harmful are usually not useful. Can, however, make fruit and vegetable preparations yourself. But better, if possible, keep everything fresh. Cabbage, potatoes, carrots, beets are preserved until spring itself, greens can be grown or bought. 
 These products are designed to "improve" the taste dishes. Yes, they do an excellent job with the task, but at the same time they are very irritate the digestive and excretory organs, interfere with their normal functioning and contribute to many diseases. Such irritants are permissible to use only in microdoses and, of course, not constantly.
These products are designed to "improve" the taste dishes. Yes, they do an excellent job with the task, but at the same time they are very irritate the digestive and excretory organs, interfere with their normal functioning and contribute to many diseases. Such irritants are permissible to use only in microdoses and, of course, not constantly.  However, it should be remembered that mayonnaise is a high-calorie product, more than 65% made up of fat. It is high in sodium and cholesterol. An excess of sodium reduces the supply of nutrients to the cell, slows down the release of metabolic products, reduces cell activity. Cholesterol is known to be a major risk factor for arteriosclerosis.
However, it should be remembered that mayonnaise is a high-calorie product, more than 65% made up of fat. It is high in sodium and cholesterol. An excess of sodium reduces the supply of nutrients to the cell, slows down the release of metabolic products, reduces cell activity. Cholesterol is known to be a major risk factor for arteriosclerosis.