How much baby food is equal to formula
How Much Baby Food Your Baby Should Be Eating- A Guide
You’re wondering about the above statement aren’t you? Ask the vast majority of pediatricians and they will all say, “Feed your baby as much as your baby will eat”.
One of the caveats when feeding your baby solid foods is that that you ensure that your baby is still receiving proper amounts of breast milk and/or formula. Solid foods in the early stage are meant for practice. Solids are not meant to provide for baby’s nutrition as breast milk and/or formula are.
How much solid food a baby will be eating depends on a variety of different things.
Don’t forget that your baby is a little human being, and like all of us, she has her own appetite. This will influence to how much solid foods she will be eating. As with adults, some babies will eat more than others due to their individual appetites. Below are a few key points to remember when feeding your baby.
- A baby who began solid foods at 4 months of age will most likely be eating more solid foods than the baby who began to eat solid foods at 6 months old.
- A baby who is eating soft diced foods as beginner foods may seem to eat less than the baby who is being spoon-fed purées.
- A baby who is ill or teething may eat less than what has been typical for a few days and then suddenly the typical appetite comes roaring back.
- An infant who is busy exploring the carpet or the new soft-book she has received may be miffed when she is put into a high chair and offered food.
The natural slow down of growth that babies go through will also influence how much they eat. They may be ravenous for a few days or a week or two and then suddenly, they are barely eating. Babies who are coming out of a growth spurt will tend to eat less than they were during the growth spurt.
How do I know if my baby is eating enough solid food?
As all pediatricians will tell you ” Your baby will never starve himself or herself! ” The majority of healthy babies will eat just the right amount of foods that they need. Resist the urge to offer “just one more bite” when baby indicates she’s finished. You do not want to accidentally override your baby’s developing ability to self-regulate his or her feeding by continuing to try and feed your baby. It is important to pay close attention to your baby’s cues as your baby’s feeding patterns will change daily and may be affected by the goings-on around him.
Resist the urge to offer “just one more bite” when baby indicates she’s finished. You do not want to accidentally override your baby’s developing ability to self-regulate his or her feeding by continuing to try and feed your baby. It is important to pay close attention to your baby’s cues as your baby’s feeding patterns will change daily and may be affected by the goings-on around him.
Offering a well balanced diet of solid foods will help ensure that your baby is eating the right amount of the right nutritious foods.
Example feeding “schedule” of solid foods
REMEMBER: 1 ounce equals approximately 2 tablespoons
Before 4 Months:- According to the CDC, babies before 4 months of age should not be fed solid baby foods. Infants should be able to sit up on their own and take food off the spoon before being introduced to solids
- Why can’t we give baby younger than 4 months solids? According to Dr.
 Alice Kuo of UCLA, “Introducing solid foods early means that the baby gets less breast milk over the course of their infancy, and that decreases the ability to get optimal benefits, like protection against infection,”
Alice Kuo of UCLA, “Introducing solid foods early means that the baby gets less breast milk over the course of their infancy, and that decreases the ability to get optimal benefits, like protection against infection,”
What to Feed Baby:
- Breast milk or formula
Breastfeed every 1-3 hours or Formula 18-40 ounces
4-6 Months:
If baby can sit up on their own and still seems hungry after breastfeeding, baby may be ready to start eating solids! Baby should be able to hold their head up, close their mouth around a spoon and “move” the food to the back of their mouth.
What to Feed Baby:
- Breast milk or formula AND
- 1-3 tablespoons of food at 1 or 2 “meals”
Click here to learn what foods you can introduce to a 4-6 month baby
6-8 Months:
Formula and/or Breast Milk is still most important at this age and stage.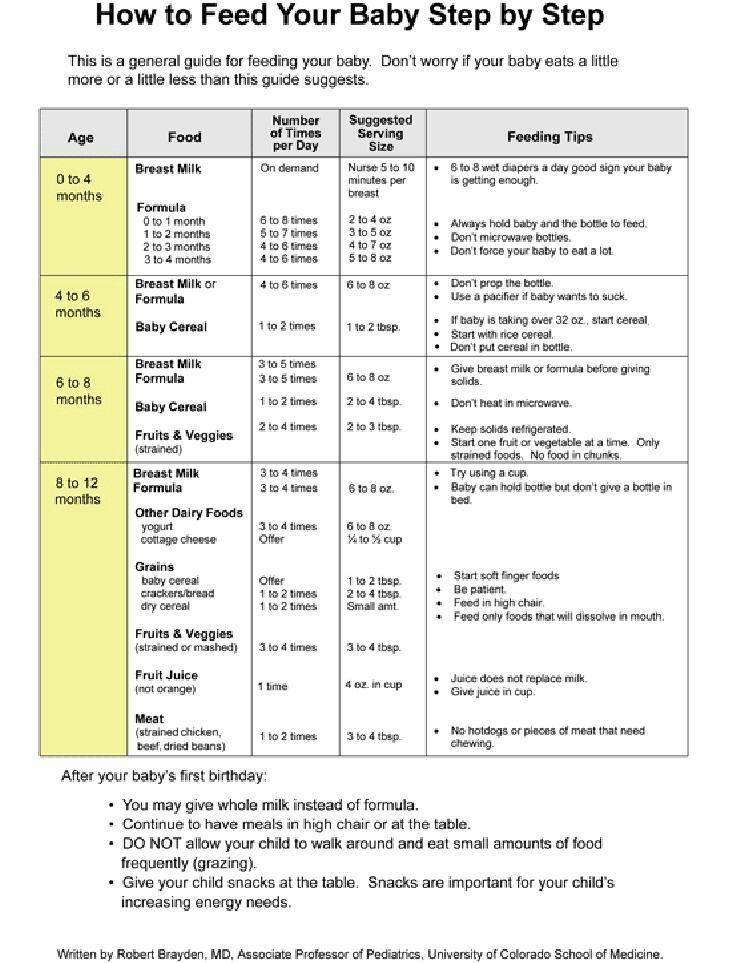 Babies in this range may be just starting solids so the above for 4-6 Months would apply. Some babies may be eating up to 8 ounces of solid foods between 2-3 “meals” during a day.
Babies in this range may be just starting solids so the above for 4-6 Months would apply. Some babies may be eating up to 8 ounces of solid foods between 2-3 “meals” during a day.
What to Feed Baby:
- Breast milk or formula AND
- Foods in this chart for solids OK to give baby 6-8 months, 2-3 “meals” a day
Click here to learn what solid foods you can introduce to a 6-8 month baby
8 to 10 months:
Many babies will be eating 3 “meals” per day at this stage; including a grain, fruit, veggie and a meat or protein source such as eggs.
Again, pay close attention to your baby’s cues as your baby’s feeding patterns will change daily and may be affected by the goings-on around him. Your baby will eat just the right amount for YOUR baby.
What to Feed Baby:
- Breast milk or formula AND
- Foods in this chart for solids OK to give baby 6-8 months, 3 “meals” a day
Click here to lean what solid foods you can introduce to a 8 to 10 month baby
10 to 12 months:
Many babies will be eating 3 “meals” per day at this stage; including a grain, fruit, veggie and a meat or protein source such as eggs.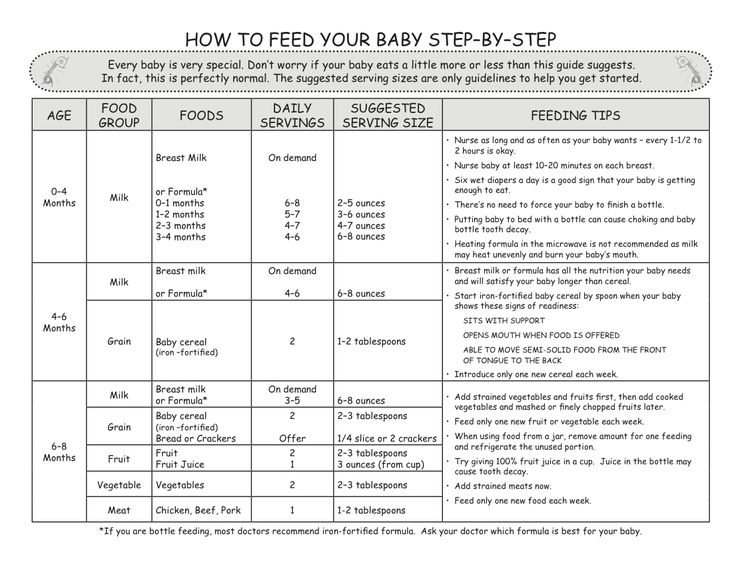
Again, pay close attention to your baby’s cues as your baby’s feeding patterns will change daily and may be affected by the goings-on around him. Your baby will eat just the right amount for YOUR baby.
What to Feed Baby:
- Breast milk or formula AND
- Foods in this chart for solids OK to give baby 10-12 months, 3 “meals” a day
Click here to lean what solid foods you can introduce to a 10 to 12 month baby
Here are a few things to watch for to ensure that you are not over or under feeding your baby:
Signs that baby may want to continue to eat- Leaning in for the spoon
- Opening the mouth
- Grabbing for food and trying to put it in the mouth
- Closing of the mouth as the spoon comes close
- Spitting out the food that is being fed
- Turning the head away as the spoon comes closer
A healthy well-fed baby should be producing wet diapers regularly as well as producing a bowel movement or two during the day.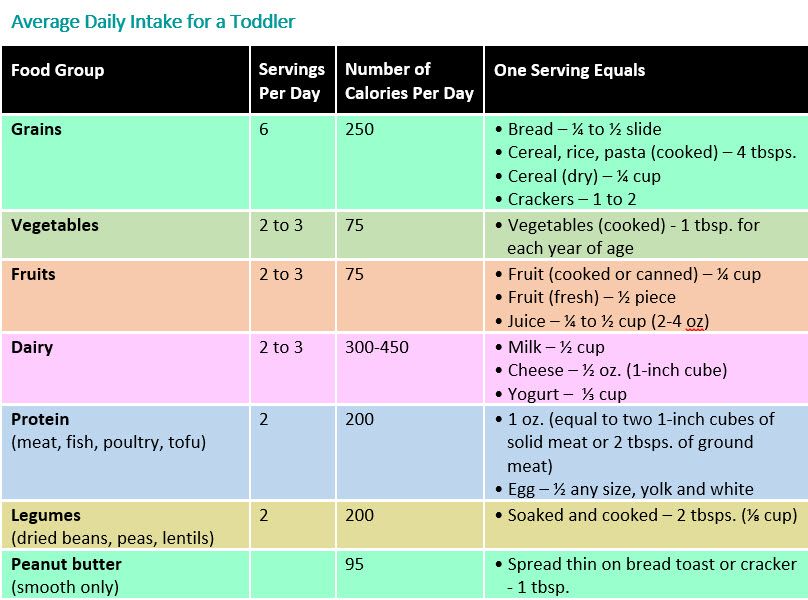
Ensure that you take your baby to the well-child visits as scheduled so that your pediatrician may weigh and measure baby to ensure that your baby has good sustained growth.
If you are ever uncertain about the foods and the amount of solid foods you are feeding your baby, always consult your baby’s pediatrician. Your pediatrician should be able to assist you in validating your feeding routines and also help allay your fears.
Remember, always consult with your pediatrician regarding introducing solid foods to your baby and specifically discuss any foods that may pose allergy risks for your baby.
No two babies will eat the exact same amounts (or foods!) The amount that each eats is just right for that baby!
Suggested Daily “Milk” Intakes for Babies age 0 to 12 months
- 0-3 Months of age:
Breastfeed every 1-3 hours or Formula 18-40 ounces - 4-5 Months of age:
Breastfeed every 2-4 hours or Formula 24-45 ounces - 6-8 Months of age:
Breastfeed every 3-4 hours or Formula 24-37 ounces - 9-12 Months of age:
Breastfeed every 4-5 hours or Formula 24-31 ounces
Whole Cow Milk, as a drink, should not be introduced until 12 months of age. Learn about Introducing Yogurt and Feeding Cheese to your baby.
Learn about Introducing Yogurt and Feeding Cheese to your baby.
Table compiled from Merck Source
Follow Your Baby’s Cues When Feeding Your Baby Solid Foods
Following your baby’s cues during feeding time will ensure that your baby is eating the proper amounts of food for him or her.
There is no “set-in-stone” guideline or chart of exactly how many jars of baby food or how many 8 ounce bottles of formula each baby should be receiving. This is simply because each and every baby is different. Babies will eat as much food and drink as much breast milk and/or formula as they need.
For example: You may wonder how it is possible that your friend’s 7 month old baby is eating 2 whole jars of baby food (8-9 oz) in one day while your 7 month old baby barely manages to eat 3 or 4 baby food cubes (3-4 oz) of food per day. You may also wonder why your baby nurses every 2 hours at 7 months old while your friend’s baby may only nurse every 3 or 4 hours. Again, each baby has different food and milk needs and these needs are just right for the individual baby.
Again, each baby has different food and milk needs and these needs are just right for the individual baby.
Read More About Solid Foods for Baby Food
Ask the vast majority of pediatricians and they will all say, “Feed your baby as much as your baby will eat”.
- Is My Baby Ready for Solid Foods?
- Baby Food Combinations
- Baby Food Allergies
- Iron and Your Baby
- Yogurt for Baby
- Travel with Homemade Baby Food
- Constipation and Your Baby
Remember, always consult with your pediatrician regarding introducing solid foods to your baby and specifically discuss any foods that may pose allergy risks for your baby.
This site complies with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information:
verify here.
SHARE ON FACEBOOK SHARE ON PINTEREST
Formula Feeding FAQs: Starting Solids and Milk (for Parents)
Whether you plan to formula feed your baby from the start, want to supplement your breast milk with formula, or are switching from breast milk to formula, you probably have questions.
Here are answers to some common questions about formula feeding.
When Can My Baby Try Solid Foods?
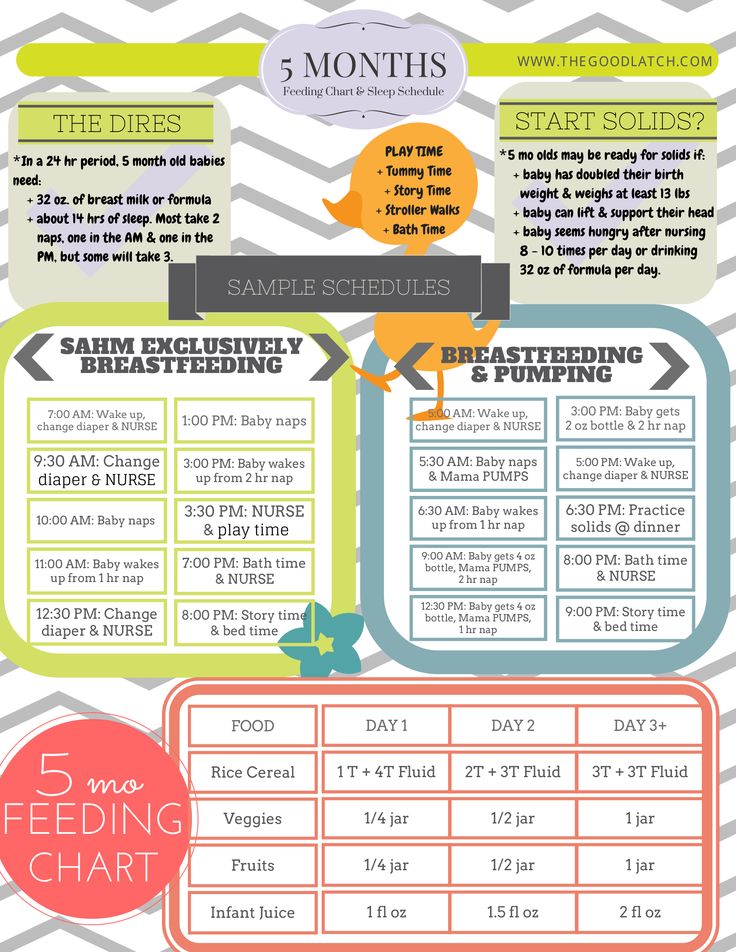
Doctors recommend waiting until your baby is about 6 months old to start solid foods. Some babies may be ready for solids sooner than 6 months, but wait until your baby is at least 4 months old.
Babies who are ready to eat solids foods:
- are interested in foods (for example, they may watch others eat, reach for food, and open their mouths when food is near)
- hold up their heads well, and sit up with little or no help
- don't push food of their mouth (which is a natural tongue reflex that disappears when babies are 4–6 months old)
- usually weigh twice their birth weight, or close to it
Talk to your doctor about the right time to start solid foods.
How Do I Introduce Solid Foods?
When the time is right, start with a single-grain, iron-fortified baby cereal. Start with 1 or 2 tablespoons of cereal mixed with breast milk, formula, or water.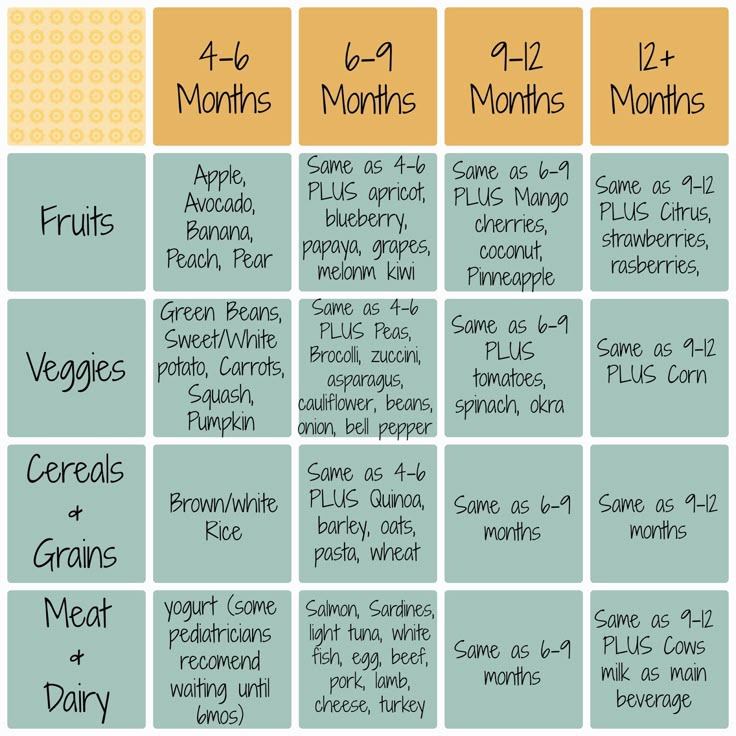 Feed your baby with a small baby spoon. Don’t add cereal to a baby's bottle unless your doctor recommends it.
Feed your baby with a small baby spoon. Don’t add cereal to a baby's bottle unless your doctor recommends it.
When your baby gets the hang of eating the first food, introduce other foods from all food groups, such as puréed meats, fruits, vegetables, grains, beans, and yogurt. Wait a few days between introducing new foods to make sure your baby doesn't have an allergic reaction.
You can include foods that are more likely to cause allergies — such as peanuts, eggs, cow’s milk, seafood, nuts, wheat, and soy — among the foods you introduce to your infant. Waiting to start these foods does not prevent food allergies.
Talk to your doctor before giving foods that contain peanuts if your baby has severe eczema or an egg allergy, as these conditions make an allergy to peanuts more likely. Eating peanut-containing foods early on may lower a child’s chances of developing a peanut allergy. But your doctor will need to decide if you can give peanuts to your baby, and the safest way to do it. Usually, this requires allergy tests.
Usually, this requires allergy tests.
Should We Avoid Some Foods?
Yes, don’t give your baby:
- foods with added sugars or no-calorie sweeteners
- high-sodium foods
- honey until after the first birthday. It can cause botulism in babies.
- unpasteurized juice, milk, yogurt, or cheese
- regular cow's milk or soy beverages instead of breast milk or formula before 12 months. It’s OK to offer pasteurized yogurt and cheese.
- foods that may cause choking, such as hot dogs, raw carrots, grapes, popcorn, and nuts
Always supervise your child when eating. Make sure your child is sitting up in high chair or other safe place.
When Can My Baby Have Cow's Milk?
Before their first birthday, babies still need the nutrients in breast milk or formula. But after that, they’re ready to switch to cow's milk.
Most kids under age 2 should drink whole milk. If a toddler is overweight or there is a family history of obesity, high cholesterol, or heart problems, your doctor might recommend switching to reduced fat (2%) milk.
If your child can’t drink cow’s milk, choose an unsweetened soy beverage fortified with calcium and vitamin D. Other milk alternatives, like almond, oat, rice, or coconut milk, have less protein and may not be fortified.
How Do We Switch to Cow’s Milk?
You can switch your baby from formula to whole milk by replace bottles of formula with bottles — or sippy cups — of milk. By 1 year old, your baby should be eating a variety of solid foods and drinking about 16 to 24 ounces (480–720 milliliters) of milk per day.
When Can I Start Giving My Baby Water and Other Drinks?
In their first 6 months, healthy babies drinking enough formula usually don't need extra water. Once your baby is eating solid foods, you can offer a small amount of water between feedings, up to 4–8 ounces a day.
Water that has fluoride helps prevent tooth decay. If your water does not have fluoride, talk to your doctor or dentist about fluoride drops.
Do not give juice to babies younger than 12 months. After your child’s first birthday, limit 100% fruit juice to no more than 4 ounces a day. Always serve juice in a cup, not in a bottle. Don’t give your child sugar-sweetened beverages, including soda, juice drinks, sports drinks, and flavored milks.
After your child’s first birthday, limit 100% fruit juice to no more than 4 ounces a day. Always serve juice in a cup, not in a bottle. Don’t give your child sugar-sweetened beverages, including soda, juice drinks, sports drinks, and flavored milks.
Reviewed by: Mary L. Gavin, MD
Date reviewed: November 2021
How much formula should be given to a child depending on age,
- Polina Alexandrovna, when might a baby need powdered milk formula?
— There are several situations when a mother is physically unable to breastfeed her child and switches to artificial or mixed feeding (covers the child's nutritional needs partly from breast milk, partly from formula):
- Contraindications to breastfeeding by mother and / or child.
- Lack of milk is true hypogalactia.
- Psychological reasons why a mother is not ready to breastfeed.
- The child needs a special medical formula.

- What determines the amount of formula that a child eats, and how to calculate how much formula a child needs?
- Often mothers think that the amount of formula depends only on age, but the weight of the child is also an important factor . Each age has its own formulas for calculating the mixture for one meal.
Important! The weight of children of the same age, especially the first months of life, can be radically different. Accordingly, the volume of the milk mixture for them will be different.
On mixed feeding, the total amount of milk nutrition per day that the child should consume depends on the amount of breast milk. The main part of the mother gives breast milk, and the amount that is not enough for the daily norm, replenishes, feeding the mixture.
- Let's talk about how much formula a child needs and what a baby can do at different periods of development. Let's start from the first days of the baby: how much formula should a newborn baby receive?
- The stomach of a newborn holds about 10 ml per feeding. With each subsequent day, the volume of the stomach and nutrition increases by 10 ml, that is, on the second day of life it is 20 ml, on the third - 30 ml, by the seventh day - 70 ml. Formula-fed baby receives power at intervals of three hours.
With each subsequent day, the volume of the stomach and nutrition increases by 10 ml, that is, on the second day of life it is 20 ml, on the third - 30 ml, by the seventh day - 70 ml. Formula-fed baby receives power at intervals of three hours.
The volume of the mixture on artificial feeding up to 1 month:
- the amount of food per day - 500-700 ml,
- the number of feedings in one day is 8-10.
Read also
- how to calculate the nutrition of a newborn
HOW MUCH FORMULA SHOULD BE GIVED IN 1 MONTH
- By one month, the child has a feeding regimen. By this age, the baby begins to open his eyes more often and fix his eyes on his mother, especially at the time of feeding (the distance at which the baby can focus his eyes is 20 cm, this is the distance from the mother’s chest to her eyes). Some babies gradually learn to hold their heads: it doesn’t work out completely, but they are already trying.
The volume of the mixture on artificial feeding from 1 to 2 months:
- the amount of food per day - 600-900 ml,
- the number of feedings in one day is 7-8.
HOW MUCH FORMULA DOES A 3 MONTH BABY NEED
- The baby continues to grow and gain weight. He raises his head more confidently. She can smile at her mother and start laughing closer to four months.
Volume formula for bottle-fed 3 to 4 months:
- the amount of food per day - 750-950 ml,
- the number of feedings in one day is 6-7.
HOW MUCH FORMULA DOES A 4 MONTH BABY NEED
- The baby recognizes his mother very well. At this age, a “complex of revival” appears - when mom or dad, a close relative, comes into the room, the baby comes to life (begins to walk, move arms and legs). In physical development, this is the period of the first attempts to roll over, and some babies begin to roll over from their tummy to their back.
Volume formula formula fed 4 to 5 months:
- food volume per day - 850-1000 ml,
- the number of feedings in one day is 5-6.
HOW MUCH FORMULA DOES A 5 MONTH BABY NEED
- The baby recognizes his mother very well. At this age, a “complex of revival” appears - when mom or dad, a close relative, comes into the room, the baby comes to life (begins to walk, move arms and legs). In physical development, this is the period of the first attempts to roll over, and some babies begin to roll over from their tummy to their back.
Volume formula for formula-fed 5 to 6 months:
- food volume per day - 850-1000 ml,
- the number of feedings in one day is 5-6.
RECOMMENDED AMOUNT OF BREAST-MILK SUBSTITUTE FOR FORMULATION FEEDING
HOW MUCH FORMULA DOES A 6 MONTHS BABY NEED
- Some babies can crawl or are just learning to do so. Others follow a different scenario and learn to sit - they begin to sit down and hold in this position. Usually a child does one thing: either learns to sit and then begins to crawl, or begins to crawl and from this position begins to sit.
Others follow a different scenario and learn to sit - they begin to sit down and hold in this position. Usually a child does one thing: either learns to sit and then begins to crawl, or begins to crawl and from this position begins to sit.
HOW MUCH FORMULA DOES A 6-12 MONTHS BABY NEED
- The baby becomes more mobile and can move wherever he wants. Begins to be interested in subjects that were previously inaccessible to him. Gradually preparing for walking - learned to crawl, began to get on his knees and then fully on his legs, move, holding the handles on the supports, then walk by one handle. At about 12 months, the baby takes its first steps.
HOW MUCH FORMULA DOES A 12 MONTH BABY NEED
— The kid is mature enough and independent. There is an active development of walking, speech. The child becomes a smaller copy of an adult with his own desires and needs.
After 6 months, children receive complementary foods, and this happens differently for different babies, so it is not possible to specify the total amount of food for all. At this age, everything is calculated individually, and the amount of supplementary feeding with a mixture depends on the amount of complementary foods , which the child receives.
At this age, everything is calculated individually, and the amount of supplementary feeding with a mixture depends on the amount of complementary foods , which the child receives.
- How to work out the optimal frequency of feeding?
- It is advisable to focus on the indicators of the table. For example, on the packaging of each formula of the MAMAKO ® Premium mixture, there is a feeding table that is averagely suitable for babies of different ages. If the child eats little and often, then this can become a problem at the stage of complementary feeding (the child gets used to eating every hour, but he will not be given complementary foods on demand). By the time complementary foods are introduced, it is desirable that the child has established 5 meals a day (maximum 6 meals a day), not counting night feedings.
How to determine how much formula your baby needs
- Polina Alexandrovna, is it worth focusing on the behavior of the child and considering that his body "knows how best", or should we try to do everything clearly according to the standards?
“Parents need to follow the rules. If you know the norm of the amount of food, you can assess how much the child, following his desires, consumes this norm - whether he has enough, whether he eats less or asks for food in excess. If you focus only on the wishes of the child, you will not be able to assess how normal the situation is.
If you know the norm of the amount of food, you can assess how much the child, following his desires, consumes this norm - whether he has enough, whether he eats less or asks for food in excess. If you focus only on the wishes of the child, you will not be able to assess how normal the situation is.
Usually, if the baby does not eat enough food, he does not gain weight and is slightly behind in development. Nothing good comes out of this, just like if a child goes over the norm. We must try to stay within the norm. However, sometimes it is permissible to deviate from the rules for a short time (the baby is sick and has a poor appetite).
- How to understand that the child has enough formula and does not need to try to supplement?
- According to the signs that are noticeable to the mother or that can be assessed:
- behavior - the child is calm, active, in a good mood - he is unlikely to be malnourished;
- appearance — the child gains weight well or, on the contrary, began to look thinner;
- weighing - if the child gains weight and height within the normal range, we can say that the food is sufficient
See also
- what to do if the baby is not gaining weight well
— How does underfeeding manifest itself?
- Underfeeding is primarily manifested by the behavior of the child - he becomes whiny, irritable, can be constantly excited. Outwardly, it is noticeable that the child is not gaining weight well or has lost weight.
Outwardly, it is noticeable that the child is not gaining weight well or has lost weight.
Important! The child is constantly lethargic and sleepy, there are long breaks between feedings - this may indicate extreme underfeeding and is a reason to see a doctor.
— How does overfeeding manifest itself?
- If overfeeding is one-time, then most often the child spits up an excessive amount of formula milk or breast milk. If a child is regularly fed more than normal, then the main indicator of overfeeding will be excessive weight gain - growth will continue to increase evenly, but the weight will not correspond to growth.
— Polina Alexandrovna, is it possible to distinguish a child's anxiety from hunger from other problems?
- It is necessary to objectively assess at what time the child is worried.
- If the child is worried 2.5 hours after feeding, it can be assumed that he cannot stand the three-hour interval between feedings and is hungry before the due date.

- If the child is worried 15-20 minutes after feeding, then most likely the reason is not hunger. Wet diaper, wants to sleep, high body temperature, environmental conditions become uncomfortable, tired of lying on one side and wants to roll over - you always need to evaluate the situation objectively.
Advice to mom: at the first worry of the child, you should not assume that he is hungry and try to feed him. The reasons for concern can be varied.
MAMACO ® 1 Premium with 2'-FL human milk oligosaccharides is an important step in the evolution of baby nutrition.
- How to supplement if the child does not eat his norm for feeding?
- First you need to determine whether the norm is adequate for the age and weight of the child.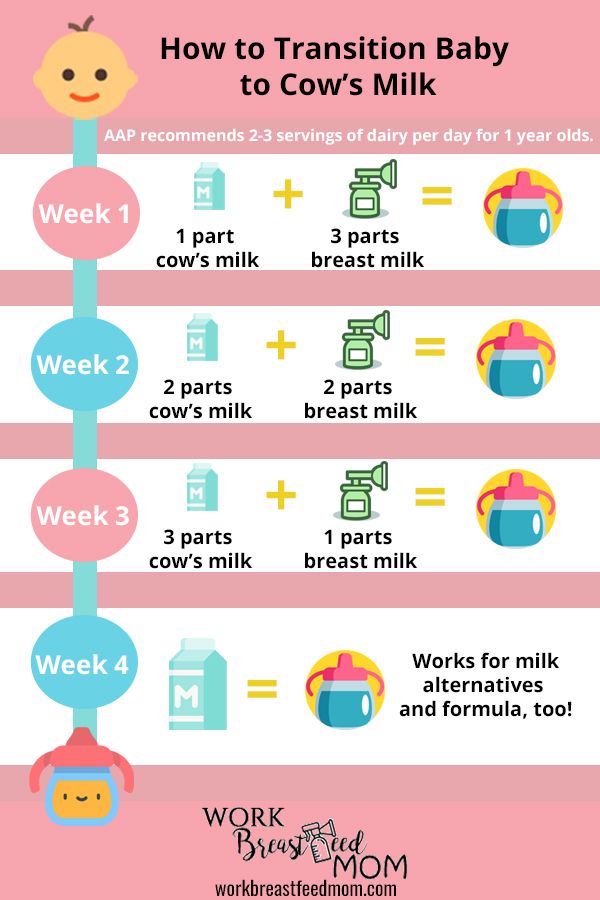 Mothers think that a child needs one amount of food, but according to his weight, it may be less. If the child is undernourished and there is insufficient weight gain and growth, then it makes sense to supplement him during sleep, add night feedings.
Mothers think that a child needs one amount of food, but according to his weight, it may be less. If the child is undernourished and there is insufficient weight gain and growth, then it makes sense to supplement him during sleep, add night feedings.
Feeding around dreams is feeding during sleep, when the baby is not awake and cannot stop eating.
— What to do if the child has eaten his norm and continues to ask for food?
- A child who has eaten his norm and is worried, most likely, is not so acutely hungry that he should be supplemented. Try to distract the baby, switch his attention and see how he behaves further. At the same time, you need to be sure of the relevance of the nutritional norm calculated for the child, and always check it for compliance with the age and weight of the baby.
At each age, each child has his own rate of consumption of milk formula. How many milliliters of formula a child should eat, the doctor calculates, taking into account the age and weight of your baby.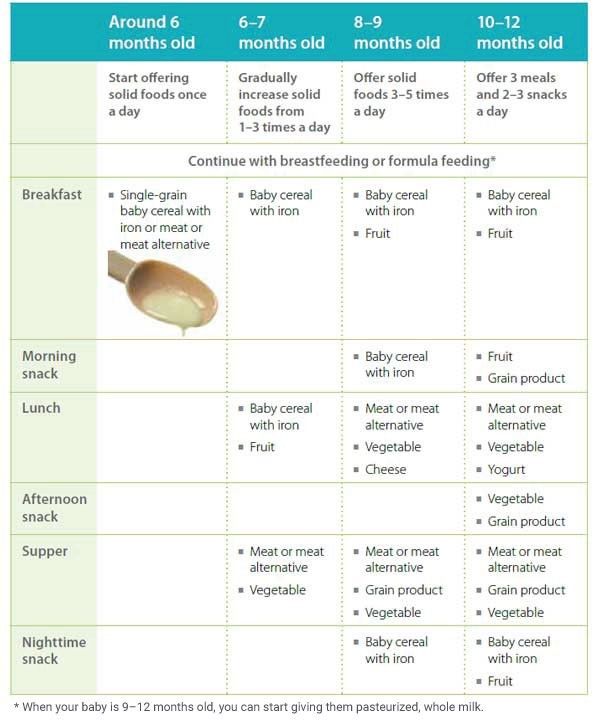 In order to properly build a diet, you need to ensure that there are adequate intervals between feedings. And by learning to listen to your baby's cues, you'll know if he's getting the right amount of formula. If you are concerned that your baby is eating too little or too much formula, talk to your doctor.
In order to properly build a diet, you need to ensure that there are adequate intervals between feedings. And by learning to listen to your baby's cues, you'll know if he's getting the right amount of formula. If you are concerned that your baby is eating too little or too much formula, talk to your doctor.
* Breast milk is the best food for babies. WHO recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months of a child's life and continued breastfeeding after complementary foods are introduced until the age of 2 years. Before introducing new products into the baby's diet, you should consult with a specialist. The material is for informational purposes and cannot replace the advice of a healthcare professional. For feeding children from birth. The product is certified.
How to dilute the mixture correctly | Nutrilak
Kuznetsova Anna
Published: 01/16/2023
Reading time: 7 minutes
1828
Consult your pediatrician before giving formula to your baby for the first time.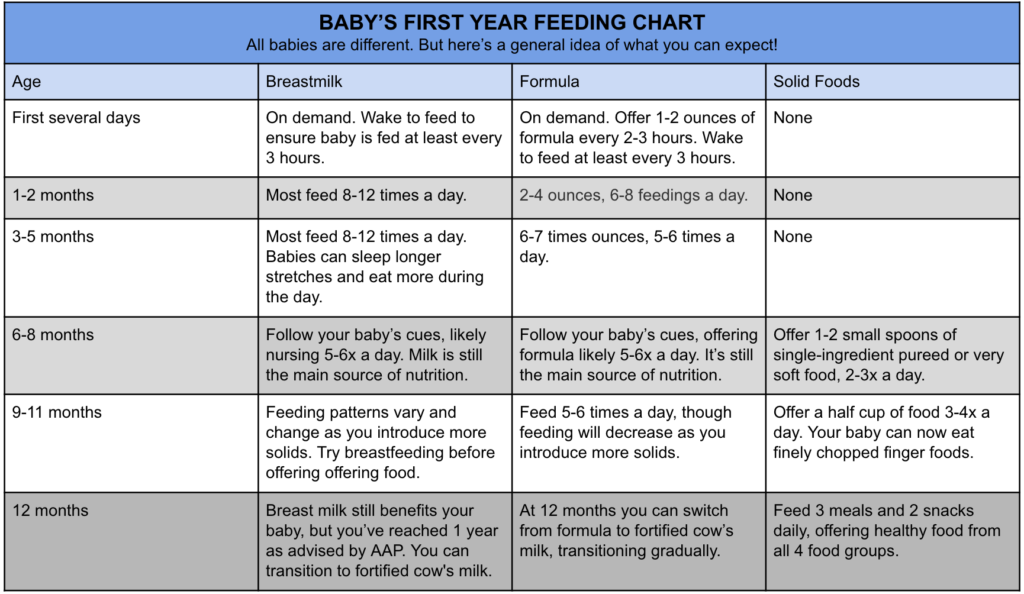 He will help you choose the type of mixture - after all, there are many of them, and without experience and the necessary medical knowledge, it will be difficult for a young mother to figure them out on her own.
He will help you choose the type of mixture - after all, there are many of them, and without experience and the necessary medical knowledge, it will be difficult for a young mother to figure them out on her own.
Also, the doctor will help you determine the daily volume of the mixture and a single serving. Each package of baby food has a table that shows the proportions of water and dry product, depending on the age of the child. You can focus on it, but these recommendations do not take into account the weight of the baby, but it is also important. Therefore, still ask your doctor to make more accurate calculations.
How to reconstitute infant formula
- Wash your hands with soap and water immediately before reconstituting formula.
- Prepare a sterile bottle, nipple and measuring spoon You can treat feeding utensils in a special sterilizer or in boiling water for 5-10 minutes.
- Heat bottled baby water to about 40 degrees or boil and cool regular water to this temperature.
 Special baby water is preferable. It undergoes strict quality control and according to the chemical composition corresponds to the age needs of the baby.
Special baby water is preferable. It undergoes strict quality control and according to the chemical composition corresponds to the age needs of the baby. - Pour the correct amount of water into the bottle in measured intervals.
This is important!
First, water is poured into the bottle, and only then the mixture is poured. If you do the opposite, it will be difficult to measure the desired volume of liquid.
- Add as many scoops as required. Dial the mixture without a slide. The excess mixture can be brushed off with a knife so that the powder is flush with the edges of the spoon.
- Do not shake the bottle to mix the dry mix with water, otherwise there will be a lot of foam. Roll the bottle between your palms or, more simply, take a sterile long-handled silicone spoon and gently stir the mixture in a circular motion.
- Before feeding, check the temperature of the finished product. It should be approximately equal to body temperature - 36-37 degrees.
 The easiest way is to drip from a bottle on your wrist. If you feel comfortable warmth, everything is in order. It turned out hotter than it should be - cool. You can put the bottle in a container of cold water, stir after a few minutes and check again. If the mixture is not warm enough, you can also warm it in a bottle in a container, but with hot water. Drinking from a bottle to check the temperature of the mixture is unhygienic and therefore unacceptable.
The easiest way is to drip from a bottle on your wrist. If you feel comfortable warmth, everything is in order. It turned out hotter than it should be - cool. You can put the bottle in a container of cold water, stir after a few minutes and check again. If the mixture is not warm enough, you can also warm it in a bottle in a container, but with hot water. Drinking from a bottle to check the temperature of the mixture is unhygienic and therefore unacceptable.
This is important!
Mixture must not be heated in the microwave. Firstly, it warms up unevenly, it is easy to burn a child. Secondly, not all ingredients of the mixture can tolerate high temperatures, this will affect the properties and quality of the heated milk food.
Why it is important to dilute the mixture correctly
Nature endowed breast milk with the ideal chemical composition for the baby, the right consistency, fat content and calorie content.
The formula, while not having all of these characteristics, provides the baby with essential nutrients for healthy growth and development, is safe and tastes good.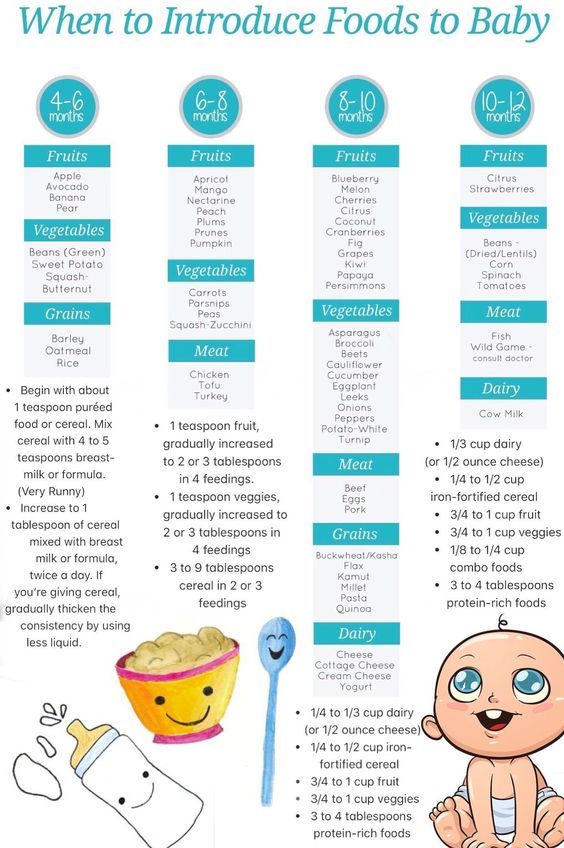
If the mixture is diluted not according to the instructions, but by eye, then the proportions of water and dry product will be violated. The finished mixture will be either liquid or thick. In the first case, the child will not receive enough proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals, in the second case there will be more of them than the baby needs, but there will not be enough liquid. If this is done constantly, then the deficit or surplus will accumulate, and the problems caused by this will grow.
This is important!
Follow the manufacturer's instructions that recommend using the formula either immediately after feeding, within an hour or two.
How long to keep reconstituted infant formula
Formula should be prepared immediately before use. The best option is not to store the diluted mixture at all. After dilution in milk nutrition, oxidation processes begin, in other words, the mixture gradually turns sour and soon becomes unsafe for the child.
The prepared mixture is a nutrient medium for microorganisms, including pathogenic ones; long-term storage of the prepared mixture increases the risk of food poisoning.
If the baby has not yet eaten from a bottle, you can leave it at room temperature for up to an hour. In the refrigerator - for 3-4 hours. After refrigeration, the mixture can only be reheated once. The second time to put the heated mixture in the refrigerator to feed the child later is unacceptable.
If the baby is simply not finished eating, throw away the rest of the mixture. Saliva got into it, which means bacteria. This product will not be stored under any circumstances.
Conclusions:
- You can learn how to properly dilute the Nutrilak formula and other breast milk substitutes from the instructions on the package, but it’s more correct to check with your doctor.
- It is important to follow these recommendations in order for the mixture to meet manufacturer's specifications.