How to feed 6 months baby schedule
6-month-old feeding schedule: Timetable
A baby’s 6-month birthday marks an important transition as many infants are ready to start trying solids at this point.
While breast milk or formula should still form the core of a 6-month-old’s diet, some caregivers find that a child’s feeding schedule shifts as they begin eating purees and other solids.
Share on PinterestWhen a baby reaches 6 months of age, purees and other solid foods can usually become part of their diet.Babies typically need to eat every 2–3 hours, five to six times during the day.
It is normal for a baby’s schedule to change from day to day, or for babies to eat different amounts of food each day.
Caregivers can follow a baby’s cues, even if they have established a schedule already. A parent or caregiver does not need to deny food to a baby just because it has already eaten.
Introducing solids
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) advise that parents exclusively breastfeed infants for about 6 months if possible. By the time a baby hits their half birthday, they may be ready to try solids.
A baby may be ready for solids at 6 months if:
- they have good head control
- they can hold their head up for extended periods
- they can sit up with no or very little assistance
- they no longer have the tongue thrust reflect to push food out of the mouth with the tongue
- they show interest at mealtime and lean toward food if a caregiver offers it
At this age, breast milk or formula is still a baby’s most important form of nutrition and solids are an addition.
Not all 6-month-olds are ready for solids. If a baby shows no interest, a caregiver can wait a few weeks and try again.
Giving a baby 1–2 tablespoons of iron fortified cereal or fruit or vegetable purees per feeding can be a good place to start.
Gradually increasing this as the baby’s interest and appetite increase can follow.
To ensure a baby eats sufficient food, the adult can breastfeed or give a bottle before offering solids.
Caregivers can give solid food as a supplement each time they nurse the baby or give a bottle. Or, they can include the baby in family meals by giving solids at mealtime.
At 6 months of age, when an infant may begin to want solids, a caregiver can offer these just once per day.
Choosing a time of day when the caregiver is relaxed and not pressed for time, and the baby is not overly hungry, fussy, or tired often works best.
Once a baby is enjoying their once-a-day solids, the frequency can increase to two and then three times a day.
There is no “right” schedule, but caregivers should plan to increase the number of solids babies get gradually.
At 6 months, the goal is not to introduce new foods and eating habits. Similarly, there is no need to force a baby to eat solids or restrict new food if a baby indicates they want more.
Regardless of their size and eating habits, babies need access to an expanding variety of solid foods.
Most babies will need to try new foods several times before they feel comfortable eating them. It is fine to let a child eat at their own pace, in the way that feels right to them.
It is fine to let a child eat at their own pace, in the way that feels right to them.
It is acceptable at this age for a baby to play with their food since this is a way of exploring new things.
Breast milk and formula
Breast milk or formula remains the most important food at 6 months of age. The easiest way to ensure a baby eats enough is to nurse or formula feed them on demand when they show signs of hunger.
Research supports the value of feeding on demand.
A longitudinal study of 10,419 children found better academic achievement and a four-point Intelligent Quotient (IQ) advantage at 8 years old among children whose caregivers fed them on demand.
However, the caregivers of these children got less sleep and had lower overall well-being.
These results may point to adults finding a happy medium, such as steadily shaping the baby’s preferred schedule into one that works for them.
In general, caregivers should plan to breastfeed babies 3 to 5 times per day, and sometimes more. However, babies vary greatly and every 3–4 hours is common, which can amount to up to eight times in 24 hours.
However, babies vary greatly and every 3–4 hours is common, which can amount to up to eight times in 24 hours.
Some babies prefer cluster feedings, during which they nurse several times in a short period. Growing or sick babies may also nurse more frequently.
If a baby has formula, giving 24–32 ounces of iron fortified formula spread over five or six feeds per day is typical. While some babies sleep through the night at 6 months, others will still wake or want to feed.
A nighttime “dream feed” around the time caregivers retire for the evening may help babies sleep longer.
Other liquids
Babies do not need juice at 6 months. The extra calories can decrease a baby’s appetite, and the sugar may damage a child’s developing teeth. Soda and other drinks are not healthful for babies.
Babies can have water beginning at 6 months, or when caregivers introduce solids, whichever is later. Introducing a cup of water along with solid meals may be helpful.
Around 6 months old, some babies begin transitioning from three or four daily naps to two. The baby might take a midmorning nap and a midafternoon nap. At this age, most babies need 12–15 hours of sleep per day, and naps usually last 1–3 hours.
The baby might take a midmorning nap and a midafternoon nap. At this age, most babies need 12–15 hours of sleep per day, and naps usually last 1–3 hours.
Caregivers are best finding a schedule that works for them and the child. Some children are used to falling asleep by nursing or with a bottle. Others happily doze off on their own.
A caregiver can follow the baby’s cues and work to adapt their needs to the family’s schedule slowly.
These feeding tips may help:
- Babies may be hungrier after waking from a long nap. This can be a good time to try solids after offering formula or breast milk to ease their initial hunger.
- There is no evidence that adding cereal to a bottle helps babies sleep longer. Doing so can increase their risk of choking.
- Babies must never have food without close supervision. nor have solids, even very thin purees, in bed.
Deciding what, when, and how to feed a baby can be challenging, especially during the transition to solids.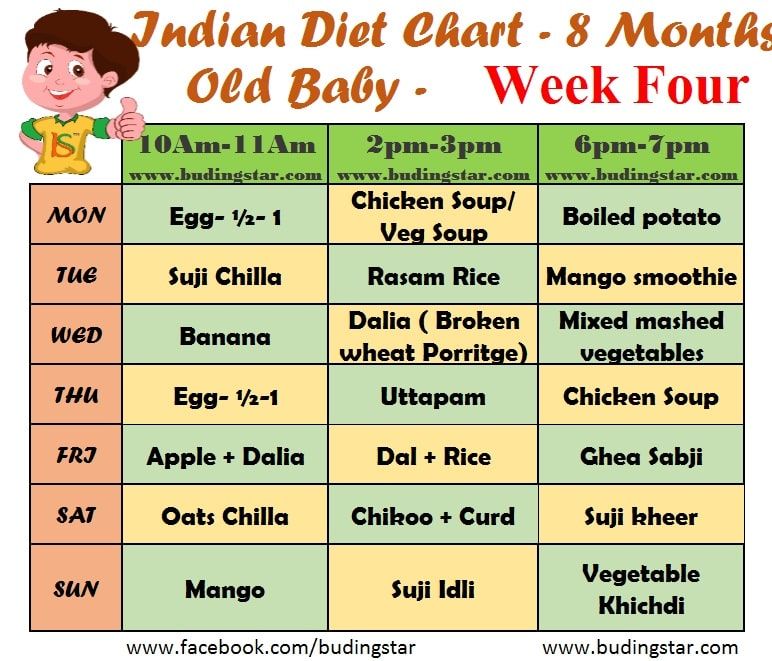 As long as babies get regular breast milk or formula, caregivers do not need to rush the transition to solids or worry that babies are not eating enough.
As long as babies get regular breast milk or formula, caregivers do not need to rush the transition to solids or worry that babies are not eating enough.
Some babies take longer than others to embrace solids, while some will eagerly eat anything. The right schedule is one that works for the baby and family. This schedule may change over time which is also fine.
Example 6 Month Old Feeding Schedule
As you make the transition to introducing solid foods around six months, life starts to change!
The thought of introducing new foods on top of breast milk or formula and naps can leave even the calmest of new parents apprehensive.
Here are some things to keep in mind as you start to introduce those first foods to your baby, and a sample schedule to help you wrap your head around what to do!
More: For more help with baby led weaning and how to help your baby succeed with eating, be sure to check out this article with a comprehensive guide to baby led weaning and first baby foods!
6 month old baby’s feeding schedule pointers
Before we get to the actual schedule, here are a few things to keep in mind.
When to Start Solid Foods With Baby
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends starting solid foods around 6 months. In this case solid food means traditional baby food or baby led weaning style finger foods. Really, anything other than breast milk or infant formula!
The best way to tell if your baby is ready to start solid foods is by following their developmental signs of readiness.
Once they are ready for foods, grab a good high chair, take a look at the schedule below, and you can start them with some modified table foods or a baby cereal and pureed foods.
Learn How to Set The Best Foundation For Feeding Your Baby!
Learning what to feed your baby is helpful. But what about all the rest?! Things like how they should be positioned for eating, what you should say at meals, and how to set up an environment that fosters a positive feeding relationship-for life!
These are the things your parents and friends don't have the answers for, and they're the things that make the biggest difference!
Grab the Foundations course where I walk you through it all.
Breast Milk or Formula Is Still Their Primary Source of Nutrition
A 6 month old baby’s main source of nutrition is still going to be breast milk or formula. Introducing food is to help them get used to it, form a positive association with food, and to start getting some additional nutrients that they start to need right around that 6-month mark.
But your baby’s needs don’t all of a sudden change to where they need an additional three meals a day and a ton of food and eating opportunities!
The idea is to start slowly and follow your baby’s cues as you introduce more food and eating opportunities.
Keep giving breast milk or formula as you were before. That can mean on demand if you’re breastfeeding, or following the same general schedule you were before for formula-fed babies and breastfed babies.
Their amount of formula or breastmilk won’t necessarily change. The average baby at this time is usually going to be nursing 5-6 times a day, or taking 24-32 ounces of formula.![]() In many cases, it might actually increase because they are having growth spurts and will start to need more!
In many cases, it might actually increase because they are having growth spurts and will start to need more!
After you give them their breast milk or formula, add in a meal 30-60 minutes later. This doesn’t need to be set in stone, as what works for your baby might differ from someone else’s!
The general idea is to offer breast milk or formula first, give them a bit of a break, and then offer them solid foods.
Your 6 Month Old Baby Won’t Eat That Much!
At the beginning, babies take time to learn how to eat. Most babies will need to get the handle of how to get food to their mouth and down their throat. They won’t really be eating solid meals for several weeks in most cases.
Don’t panic if you’re a few weeks in and they still aren’t getting much solid food down. Give it some time. Remember, their primary source of nutrition is still their breast milk or formula!
And if you aren’t sure what to expect when it comes to solid foods, make sure to grab the Starting Solids course to help prepare you and give you confidence in feeding and to help you set up a great foundation for your feeding relationship with them.
Sample Feeding Schedule For A 6-Month-Old Baby
The biggest thing to keep in mind is that every baby is going to be different. I generally shy away from giving out specific schedules, because different things work for different babies.
But after many parents have asked consistently for it, here is an example schedule for your 6 month old to help you with a place to start for your daily routines.
I’m giving specific times to help you visualize it, but think of this more as a spacing example for your day than an exact example of when you should be doing these things.
A Note On Your Baby’s Sleep Schedule
All babies will have different sleep schedules. This is especially true for the first year of your baby’s life. Some babies will have a short nap in the morning, while others will take a long nap.
Sometimes that happens no matter how hard you try to maximize the hours of sleep your baby gets!
The best thing you can do is to be consistent in your wake windows. Meaning if your baby gets up at 7 am, you want to be consistent with something like a 2 hour wake window. This means that they will go back down for their first nap 2 hours after waking up.
Meaning if your baby gets up at 7 am, you want to be consistent with something like a 2 hour wake window. This means that they will go back down for their first nap 2 hours after waking up.
Follow this same pattern for their later naps and plan to put them down based on when they woke up, not necessarily the time the clock says.
As the day goes on, their wake window might get slightly longer. And as they grow, they will generally start to take longer naps and lengthen their wake time between naps.
Sample 6 Month Old Feeding Schedule With Breakfast
Here is an example of how I might space my day if I was planning to feed my baby solid foods at breakfast time. When they are first starting to eat and for the first several weeks of solid foods, they really do only need one meal a day.
Daily Schedule With Breakfast
- 6:30 am: Wake-up, then nurse or bottle
- 7:30-8:00 am: Breakfast (Head to this article for specific help with what to serve your baby at meals.
 )
) - 8:30 am: First morning nap
- 10:30 am: Nurse or bottle
- 12:00 pm: Second nap
- 1:30 pm: Nurse or bottle
- 4:00 pm: Third nap
- 5:00 pm: Nurse or bottle
- 6:30 pm: Nurse or bottle, then bedtime routine and sleep
Sample Feeding Schedule With Dinner
Here is a sample feeding schedule with dinner as your meal for the day. Again, this is just an example. To serve a different meal, simply aim to have the food 30-60 minutes after you have given them breast milk or formula.
You do not need to serve food at the same meal every day, or exactly at the same time. If your baby sleeps through your normal lunch time when you were planning to feed them, just plan to feed them at dinner.
I do recommend aiming to get in at least one meal a day once you start giving them solid foods to help them get in the practice that they need.
Daily Schedule With Dinner
- 6:30 am: Wake-up, then nurse or bottle
- 8:30 am: First morning nap
- 10:30 am: Nurse or bottle
- 12:00 pm: Second nap
- 1:30 pm: Nurse or bottle
- 4:00 pm: Third nap
- 5:00 pm: Nurse or bottle
- 5:30 pm: Dinner (Here are some dinner ideas for babies)
- 6:30 pm: Nurse or bottle, then bedtime routine and sleep
These Schedules Are Just Starting Places!
This is just a final reminder for you that these really are just places for you to start. Every baby and family will find a different flow that works for them.
Being consistent in wake windows is the most important thing at this age. Sleeping really is primary!
Sleeping really is primary!
A tired baby isn’t going to want to sit at the table and focus on learning how to eat. So do your best to let sleeping and breast milk or formula be the main concerns, and add in meals in between those.
As your baby gets older, the feeding schedule for 7 month olds really doesn’t change much.
They might drop a nap, have longer wake windows, and will likely start wanting to have more meals.
To increase meals to 2 a day, simply keep the same things in mind and add a meal 30-60 minutes after breast milk or formula when they are awake.
Looking for help on a feeding schedule for your toddler or 1-year-old? Check out this article with a sample 1 year old feeding schedule!
Child's daily routine, nutrition, development at 6 months
04/19/2019
29
Approximate daily routine of a child
6 months
The daily routine of a 6 month old child is becoming more and more stable:
Some babies are comfortable with two naps during the day, others sleep three times a day until 8-9 months.
It is worth paying attention to the duration of daytime sleep - morning and afternoon sleep should be at least 1-1.5 hours long so that the child's body has a good rest. The third dream may remain short, it is better to start it between 15.00-16.00. Make sure that it does not end too late, otherwise the time for evening bedtime will shift. Morning and afternoon naps are recommended to be done at home, the third nap can be spent outside in a stroller.
When going to bed early, the best time to wake up in the morning is 06.30-07.00.
- Regular bedtime appears
A six-month-old baby is already physiologically ready for early bedtime. The optimal time for leaving at night will be between 18.00-20.00. You will have a clear bedtime ritual that will help the child relax and make the process of bedtime easier. The ritual must be repeated daily. It takes 20-30 minutes to complete it.
The ritual must be repeated daily. It takes 20-30 minutes to complete it.
- The period of wakefulness of the child increases
Now, when forming the daily routine, one should focus primarily on the recommended waking time - in six months it increases to 2.5 hours with an established regimen with three daytime sleeps. Signs of fatigue in a child are already harder to notice, so you can miss the moment when the baby is ready for bed.
Total amount of sleep
Now the child needs to sleep 13-14 hours a day. Night sleep is 11-12 hours with awakenings for 2-3 feedings while breastfeeding. The number of night awakenings in formula-fed babies will be less. The total duration of daytime sleep at this age is about 2.5-4 hours.
Monitor your baby's condition and follow the main recommendations of the table to understand how many hours of sleep he needs and correctly build a daily routine that will suit your six-month-old baby.
A table on the sleep and wakefulness of a child at 6 months will help you with this:
You can adjust the regime and adapt it as your baby grows in the Club MODE FROM A TO Z - read more.
What affects baby's sleep:
1. By 6 months, your baby has already learned to roll over from back to stomach and back. Now he is gradually mastering new skills: he learns to pull himself up at the support, get on all fours, sit on his own and actively prepare for crawling. The baby can continue to practice new skills both during the day and in the crib during sleep. At such moments, he often wakes up and sleeps restlessly. This is part of the natural development of the child.
To help him quickly get used to the new possibilities of his body, practice new skills while awake. Show how you can lie back down from a sitting position. And if earlier the child did not mind spending a lot of time in the stroller, now he needs time and space for active play during wakefulness. After 7-14 days, the child's sleep will improve.
After 7-14 days, the child's sleep will improve.
2. Skipping naps and going to bed too late at this age can lead to overtiredness, protests before bed and frequent nighttime awakenings. To prevent this from happening, try to follow a clear daily routine.
3. At six months, the baby may show the first signs of separation anxiety. Having become more independent, he realizes that he is not one with her. And the baby develops fear and anxiety that the mother will leave and will not return. If you find your baby won't let go of you during bedtime, extend the ritual to include carrying, massages, hugs, and kisses. Offer your child a sleep toy that smells like you and "guards" their sleep. It is also worth spending more time with the child one on one, without being distracted by other things.
4. Teething is another factor that affects the sleep of children of this age. In the acute period, help the baby in every possible way, use teething toys and anesthetic gel as recommended by your pediatrician.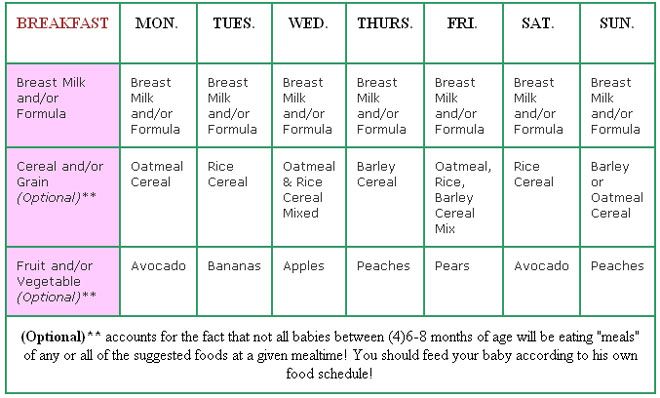 As soon as the acute period passes, return to the previous sleep conditions and daily routine.
As soon as the acute period passes, return to the previous sleep conditions and daily routine.
Watch the free workshop MY BABY SLEEPING BADLY AT NIGHT: 3 SOLUTIONS if your child is having trouble sleeping at night.
Child's diet
6 months
Breast milk and infant formula are still your baby's main complete food, from which he gets important nutrients.
But at 5-6 months you will notice that he has begun to show interest in adult food - watching you eat, following the spoon with his eyes, opening his mouth and smacking his lips. At six months, it is important to maintain this food interest in him, gradually expanding the child's nutrition. For this purpose, complementary foods are introduced. It is from the age of six months that WHO recommends including adult food in the diet of a breastfed child.
Complementary foods can be started with vegetable puree. Choose zucchini, cauliflower, broccoli.
Then gluten-free cereals are introduced. If the child is not gaining weight, then complementary foods usually begin with cereals.
Water is also added to the diet from 6 months. But modern pediatricians do not recommend giving juices to a child in the first year of life.
The volume of complementary foods is small - in the first days, half a teaspoon of puree is enough for a baby, then the serving volume gradually increases over 10 days to the required norm. Feed one food and see how your baby reacts. The best feeding time is the first half of the day.
By the age of 6 months, the feeding regimen is formed. The child eats on awakening and shortly before bedtime up to 5-6 times a day. Attachments to the breast are short, as the child is often distracted during feeding. The most frequent feedings are in the evening and active sucking is shifted to the last 2-3 hours before waking up.
The amount and frequency of feedings should be discussed with the pediatrician.
Development of the child
Thinking
The baby now distinguishes well between friends and strangers and can show his displeasure, being left without a mother.
Be prepared that the child will not want to let you go if you want to leave him with his grandparents.⠀
Communication
The baby is already turning around at his name, listening to the voice of an adult and pronouncing syllables in response to your voice.
Say his name as often as possible and name toys when communicating with your baby to develop his vocabulary.⠀
Physical development
Most likely your baby has already learned to roll over, master the skill of sitting and getting ready to crawl. Also, the child begins to transfer weight to the legs and can stand with the support of both hands. He stretches both hands to his mother, expressing a desire that she take him to her.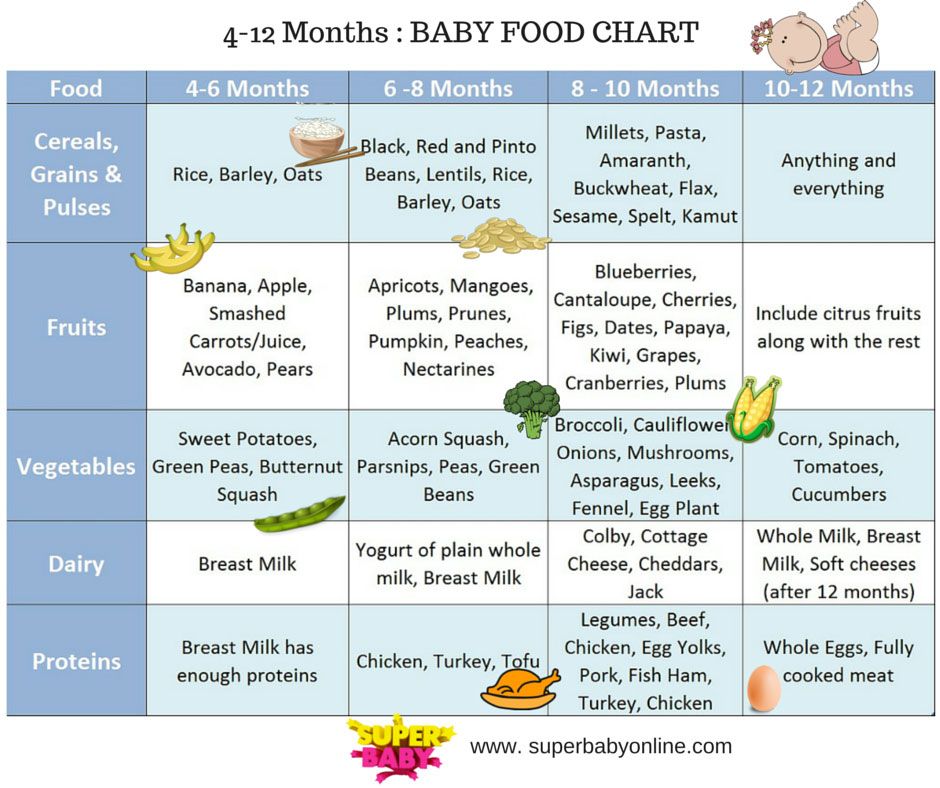 You may also notice that during feeding, the child rests on you with his arms and pushes away. This behavior is normal - he is testing his new bodily capabilities.
You may also notice that during feeding, the child rests on you with his arms and pushes away. This behavior is normal - he is testing his new bodily capabilities.
While playing with your baby, clap your hands, squeeze toys, use taps. He will repeat after you and improve motor skills, wielding a toy.
Share in the comments, what questions and difficulties did you encounter when organizing a baby regimen at 6 months?
Like this article? Rate:
Votes: 330
diet for a 6-month-old baby with breast and artificial feeding, an approximate menu for a week in the table, a diet for day
Published: 02/10/2021
Reading time: 4 min.
Number of reads: 184190
Author of the article: Ponomareva Yuliya Vladimirovna
Pediatrician, Candidate of Medical Sciences, allergist-immunologist
Changes in a child in the first year of life are very rapid, and each month is not like another. The 6-month milestone is very important, it is largely evaluative and transitional. By this age, most babies have doubled their birth weight, are about 15 cm tall, and some babies have already erupted their teeth. The age of 6 months is also transitional in terms of nutrition. Breast milk or an adapted formula is still the basis of the diet, but with the beginning of the second half of life, all children, without exception, should begin to receive complementary foods. Despite the general graph of growth and weight gain and indicators of psychomotor development, the status and diet of children at 6 months can be very different. 9Ol000 If the baby is healthy and breastfed, and his mother eats a full and varied diet, exclusive breastfeeding is possible until this age. Cereal complementary foods in this case are preferable to start. This is due to the high energy and nutritional value of cereals, the ability to significantly enrich the baby's diet with a delayed start of the introduction of complementary foods.
The 6-month milestone is very important, it is largely evaluative and transitional. By this age, most babies have doubled their birth weight, are about 15 cm tall, and some babies have already erupted their teeth. The age of 6 months is also transitional in terms of nutrition. Breast milk or an adapted formula is still the basis of the diet, but with the beginning of the second half of life, all children, without exception, should begin to receive complementary foods. Despite the general graph of growth and weight gain and indicators of psychomotor development, the status and diet of children at 6 months can be very different. 9Ol000 If the baby is healthy and breastfed, and his mother eats a full and varied diet, exclusive breastfeeding is possible until this age. Cereal complementary foods in this case are preferable to start. This is due to the high energy and nutritional value of cereals, the ability to significantly enrich the baby's diet with a delayed start of the introduction of complementary foods.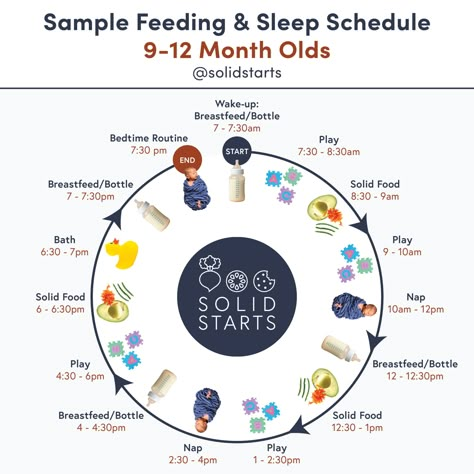
However, the rate of expansion of the child's diet in this situation will be accelerated. Before the 8th month of life, it is necessary to introduce all basic food groups into the baby’s menu, since in the second half of the year the need for additional intake of nutrients and micronutrients is very high. Another reason explaining the importance of the rapid introduction of complementary foods is the formation of immunity of the immune cells of the intestine to ordinary food. If a child is introduced to these foods at the age of 4-8 months, the risk of developing food allergies has been proven to be reduced.
Complementary feeding starts at 4-5 months
In modern life, the nutrition of a nursing mother, unfortunately, is not always complete. Therefore, for most breastfed babies, complementary foods already need to be introduced from 5 months in order to prevent deficient conditions.
If a child is bottle-fed, then by the 4th month of life, the baby will not have enough adapted formula alone, and in this group of children, the timing of the introduction of complementary foods usually shifts a month earlier than in breast-fed babies.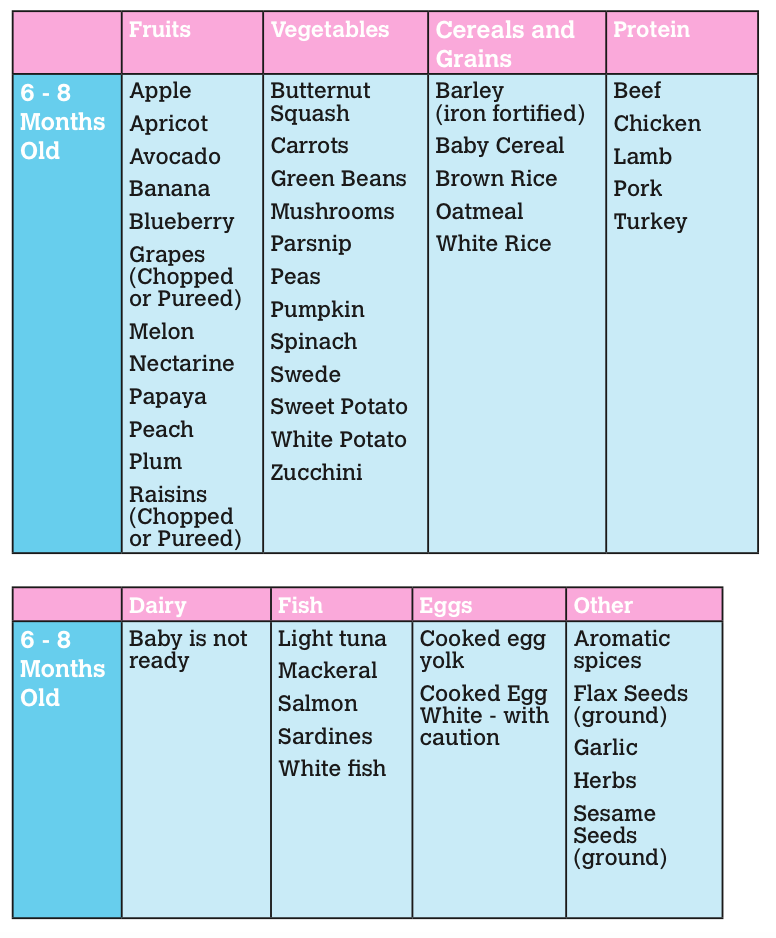 Accordingly, by 6 months, children will have vegetable puree and gluten-free porridge (buckwheat, corn and rice) in their diet. In the first half of life, monocomponent meals are used (that is, from one type of grain and vegetables), prepared on the basis of water, breast milk or an adapted mixture.
Accordingly, by 6 months, children will have vegetable puree and gluten-free porridge (buckwheat, corn and rice) in their diet. In the first half of life, monocomponent meals are used (that is, from one type of grain and vegetables), prepared on the basis of water, breast milk or an adapted mixture.
Fruit puree and juice can be another possible complementary food for children under 6 months of age without allergy symptoms. In a child with a risk of developing or manifesting allergies, the timing of the introduction of fruit complementary foods is shifted to the 8th month.
Second six months of life
Children over 6 months of age can supplement their diet with cereals containing gluten. First of all, these are oatmeal and wheat porridge, and then multi-cereal dishes with the addition of other cereals (millet, barley, rye). If the child does not have any manifestations of allergies, milk porridge can be included in the menu at this age. Bebi Premium industrial baby food products include specially prepared milk that is safe to use in healthy babies in the first year of life.
From the age of 6 months, the baby's diet is expanded with such important products as meat and cottage cheese. These products are a source of high-quality protein, fats, and are also rich in minerals such as iron, calcium, and phosphorus. Pediatricians and nutritionists recommend introducing meat and cottage cheese as part of combined dishes based on a fruit and vegetable and / or grain component in a ratio of 1 (cottage cheese / meat): 4–5 (fruits / vegetables / cereals).
To enrich the diet with polyunsaturated fatty acids in the second half of the year, the menu includes vegetable oil in the amount of 3–5 grams per day, which can be added to the complementary food dish. The volume of each feeding is approximately 150-170 ml, and the child can already stand up to 3.5 hours between meals.
In the table below, we offer a menu of 6 months for a week for a child who started receiving complementary foods at the age of 4-5 months, and by the time the second half of life begins, dairy-free gluten-free cereals, vegetable and fruit purees have already been introduced into his diet.