How to feed baby vitamin d drops
Do Babies Really Need Vitamin D Supplements? – Cleveland Clinic
When you’re loading up the cart with baby essentials, like diapers and wipes, make sure to throw in some vitamin D drops.
A daily dose of vitamin D is important for your baby’s health for several reasons. Pediatrician Kylie Liermann, DO, explains why and how to give this vitamin to your newborn or infant.
Why is vitamin D important for babies?
Vitamin D is crucial for the health of your baby’s bones and teeth. “Severe vitamin D deficiency can lead to a brittle bone disease called rickets,” says Dr. Liermann. “Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium and utilize it to form and strengthen bones. Without vitamin D, a child is more prone to fractures and growth problems.”
The body also needs vitamin D for brain development and immune system health. “Vitamin D is necessary for so many functions, and it’s hard to get enough without a supplement,” says Dr. Liermann.
Do breastfed babies really need vitamin D?
We often hear that breast milk is a complete food, containing everything your baby needs. But tests have shown that breast milk is lacking in vitamin D.
“Infants should get vitamin D drops starting in the first few days of life,” Dr. Liermann says. “It’s especially important in breastfed babies because they get minimal, if any, vitamin D from breast milk.”
Infant formula contains vitamin D, but it’s not enough for younger babies. “Formula-fed babies need a vitamin D supplement until they are taking 32 ounces of formula every day,” says Dr. Liermann. “This usually happens after the first few months of life, but is different in every baby. Newborns, in the first few months of life, don’t consume enough formula to get the recommended daily amount of vitamin D.”
Advertising Policy
Can you raise vitamin D levels in breast milk?
What if a breastfeeding mom takes vitamin D? Does that change levels in her breast milk?
“One study found that mothers could safely supplement 6400 IU/day and adequately supply their breast milk to satisfy the infant requirement,” says Dr. Liermann. “But mothers should discuss with their pediatrician to determine if this is the right option for them.”
Liermann. “But mothers should discuss with their pediatrician to determine if this is the right option for them.”
How much vitamin D do babies need?
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends a daily intake of 400 IU for babies. Most infant vitamin D supplements contain this amount in one dose. But the dose could be different, depending on which brand of drops you buy.
“Some supplements have 400 IU in one drop, but others have 400 IU in a dropperful,” says Dr. Liermann. “Whatever supplement you choose, be sure it says it’s for infants. Follow the dosing instructions carefully. If you don’t know which kind to use, ask your child’s pediatrician.”
Can babies get vitamin D from sunlight?
Our bodies make vitamin D when we’re exposed to the sun. So can you just spend time outside with your baby and skip the supplement?
“UV rays from the sun are damaging to the skin at any age,” says Dr. Liermann. “It’s better to take the supplement than to risk skin damage from the sun. When your baby is outside, cover them with a hat, clothing, or a shade over their stroller or baby carrier. Once they’re 6 months old, you can use sunscreen, but you should still keep them out of the sun as much as possible.”
When your baby is outside, cover them with a hat, clothing, or a shade over their stroller or baby carrier. Once they’re 6 months old, you can use sunscreen, but you should still keep them out of the sun as much as possible.”
Advertising Policy
How do you give vitamin D drops to baby?
Infant vitamin D drops are concentrated, so you only need a small amount to get 400 IU. To give it to your baby, you can:
- Place the dose directly in her mouth when she’s relaxed, such as during her bath or while holding her. Aim for the inside of her cheek, not the back of her throat.
- Mix the vitamin D drops in with baby’s formula or expressed breastmilk in a bottle.
- Put the drop directly on your nipple before breastfeeding. This works best if the dose is only one drop.
Always use the dropper that came with the drops and fill it as prescribed. You may not need to fill the entire dropper.
When can babies stop getting vitamin D drops?
Once your baby is drinking one liter of formula or fortified whole milk every day, they are getting enough vitamin D without drops. For formula-fed infants this could be within a few months of life but for infants who are exclusively breast fed this is not until they reach 1 year of age and are able to start drinking fortified whole milk. Ask your pediatrician when to stop giving your child vitamin D drops.
For formula-fed infants this could be within a few months of life but for infants who are exclusively breast fed this is not until they reach 1 year of age and are able to start drinking fortified whole milk. Ask your pediatrician when to stop giving your child vitamin D drops.
Signs of vitamin D deficiency in babies
Vitamin D deficiency isn’t easy to spot in babies, partly because they can’t tell you how they’re feeling. And fatigue and muscle pain, symptoms of vitamin D deficiency, are common symptoms of several other conditions. In addition, signs of vitamin D deficiency may not show up until months or years later.
But doctors may check your baby’s vitamin D levels if your baby has:
- Frequent illnesses or infections.
- Poor growth.
- Frequent bone fractures.
“Don’t wait to see if your baby has symptoms of vitamin D deficiency,” Dr. Liermann says. “Supplement Vitamin D regularly to prevent deficiency. And if you have any concerns about your baby’s health, talk to your pediatrician. ”
”
Vitamin D Drops for Your Baby
NutritionNewbornPediatrics
Reviewed By Vicki A. Herrman, M.D.
Vitamin D is a fat soluble vitamin produced by natural exposure to sunlight that helps your new baby with their development and growth of the body and bones by absorbing calcium and phosphorus. Normal development for your baby relies on the sufficient amount of daily vitamin D.
What are vitamin D drops and does my baby need them?
A mother's breast milk is the best source of nutrients for a baby but the amount of vitamin D in breast milk may not be enough which may lead to your baby to have Rickets – a softening and weakening of the bones. Correcting the proper amount of vitamin D will generally solve most Rickets cases. While sun exposure is an important source of vitamin D, it is not recommended for babies younger than 6 months to be exposed to too much sun. This is why liquid vitamin D drops are so beneficial in the early stages of your newborn baby.
Vitamin D drops usage and benefits:
New lifestyle changes for mothers due to concerns with UV ray exposure and risks of cancer over the recent years show the benefits of the liquid drops in helping prevent vitamin D deficiency in infants – especially with mothers that tend to spend less time in the sun and use sunscreen more frequently than mothers in the past.
- If you're breast-feeding or partially breast-feeding your baby, the American Academy of Pediatrics suggests giving your baby 400 international units (IU) of liquid vitamin D a day starting the first few days after birth.
- Continue giving your baby the drops unless he or she can successfully drink 32 ounces (about 1 liter) per day of vitamin D-fortified formula.
- Formula generally has vitamin D added in the formula so additional drops would not need to be added as a supplement.
- Not all formulas are the same (be sure to check the nutrition facts).
- As your baby becomes older, your baby can meet the daily vitamin D requirements in their solid foods such as oily fish, eggs and fortified foods.

- Most babies will not consistently be able to meet the daily requirements on the solid food alone as they might not like the food or do not eat the food consistently. This is especially true during the early years and having formula to drink with the meal can still be beneficial.
When giving your baby liquid vitamin D drops, it is important to remember an excessive dosage is not beneficial to the baby and can be just as harmful as a deficiency. Be sure to carefully read the instructions that come with the supplement and use only the dropper that's provided. Chewable and gummy vitamins that contain vitamin D are also available for older children.
If you have questions about your baby's need for vitamin D supplements, consult your baby's pediatrician. Be sure to ask your pediatrician before taking any vitamin supplements and learn about the correct amount of dosage for your baby because every baby and child is unique in their growth and development.
Nutrition;Newborn Pediatrics
It looks like your browser does not have JavaScript enabled. Please turn on JavaScript and try again.
It looks like your browser does not have JavaScript enabled. Please turn on JavaScript and try again.
Why vitamin D is important for an infant and a nursing mother - symptoms of vitamin D deficiency in a child, the consequences of rickets
Vitamin D plays a key role in metabolic processes occurring in bone tissue. In the body of a newborn child, there are no reserves of it, and the metabolism is imperfect. This is why sun exposure and breastfeeding are so important. But it happens that the family lives in a region with mostly cloudy weather, and mother's milk does not contain the required amount of vitamin D. Then the deficiency must be filled with appropriate supplements.
Benefits of vitamin D for lactating women
Breastfeeding women have an increased need for vitamins and microelements, a significant amount of these substances, along with milk, is transferred to a newborn child. Therefore, they need to be replenished daily. Studies show that, on average, a nursing mother loses 4 times more vitamin D than during pregnancy.
The benefit of the vitamin for women is to maintain bone mineral density. After the birth of a child, the secretion of the hormone prolactin increases in a nursing mother. It suppresses ovarian function and the production of estrogens, which are involved in maintaining calcium in the bones. At the same time, prolactin stimulates the synthesis of parathyroid hormone. It activates osteoclast cells in tubular bones and increases the flow of calcium into the blood by destroying tissue.
After the birth of a child, the secretion of the hormone prolactin increases in a nursing mother. It suppresses ovarian function and the production of estrogens, which are involved in maintaining calcium in the bones. At the same time, prolactin stimulates the synthesis of parathyroid hormone. It activates osteoclast cells in tubular bones and increases the flow of calcium into the blood by destroying tissue.
Women who take vitamin D at the daily dosage recommended for breastfeeding maintain physiological calcium levels and may avoid pain in the limbs and deterioration of the teeth.
The role of vitamin D in the development of the infant
The required concentration of this substance in the body is reached a few months after birth. In premature babies, its supply is even less, so it takes longer to recover.
Sufficient vitamin D provides:
- normal calcium-phosphorus metabolism;
- growth and development of bone tissue;
- muscle development;
- strong immunity;
- thyroid support;
- normal blood clotting;
- regulation of heart contractions.

It also prevents the occurrence of autoimmune diseases. It is also important for mental development. Vitamin D is responsible for the formation of cognitive functions and their further maintenance. If during the period of active growth the body receives less of this substance, the child will suffer from rickets. This is a violation of osteogenesis (bone development), associated with a lack of minerals - mainly calcium and phosphorus.
Symptoms begin at three to four months of age. Parents pay attention to:
- general restless behavior;
- sleep disorders;
- heightened reactions to loudness and brightness;
- skin redness;
- sweating;
- itching of the scalp;
- decreased appetite;
- digestive disorders.
Running rickets slows down the development of the musculoskeletal system. The child later than peers begins to hold his head, sit and walk. Delayed teething. The disease also affects the appearance of the baby.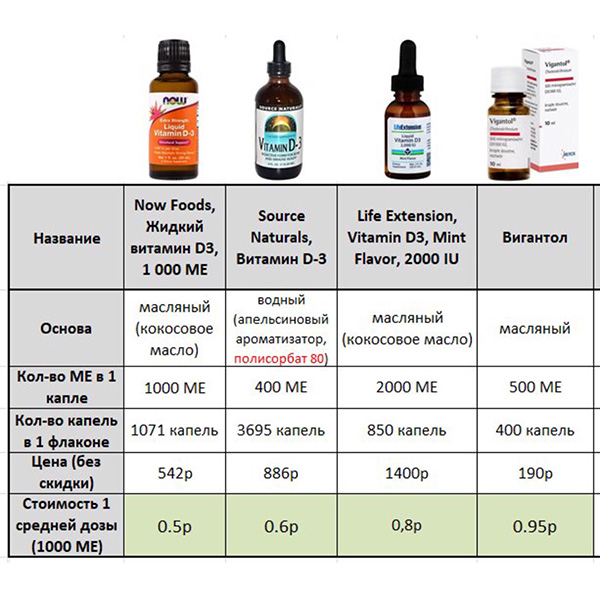 The most famous symptom is a fontanel that does not grow in time. The child may have a flat back of the head and a wide forehead, crooked legs, thickening on the arms and a deformed chest.
The most famous symptom is a fontanel that does not grow in time. The child may have a flat back of the head and a wide forehead, crooked legs, thickening on the arms and a deformed chest.
Vitamin D requirement
Vitamin D requirements vary depending on initial blood levels, type of diet and time spent in the sun. Infants under 6 months of age are recommended to take 400 mg per day, but the maximum allowable dose is 1000 mg. Children after 6 months The recommended dose of the vitamin does not change, but the maximum amount has been increased to 1500 mg. For lactating women, the intake of 800 mg is considered normal, the maximum dosage per day, bordering on toxic, is 4000 mg.
To determine the need for calciferol, a special blood test can be taken. The normal indicator of vitamin D content for an adult is 60-100 ng / ml, when using other measurement methods - 150-250 nmol / l. If you do not adhere to the recommended norms, the child will suffer first of all in a nursing woman. He will have the consequences of rickets for the rest of his life.
He will have the consequences of rickets for the rest of his life.
The musculoskeletal system of an adult person will be fragile and weakened. This causes difficulty in walking, pain in the limbs, brittle bones. Rickets is also reflected in body composition:
- short stature;
- incorrect posture;
- pronounced parietal and frontal tubercles;
- laterally flattened chest;
- narrowed small pelvis.
Wrist bulges may disappear as you get better. But problems with movement can only get worse with age. In especially severe cases, patients stop walking due to severe pain. Untreated rickets is fraught with seizures in adolescence and adulthood. Sometimes they cause respiratory arrest.
When to take vitamin D
A pregnant woman should take at least 800 IU of vitamin D per day to ensure an adequate supply for her baby. But not everyone has this opportunity. The reasons may be different:
- little sun in the region;
- dark skin, immune to its rays;
- gestational diabetes;
- overweight;
- malnutrition.

Breastfeeding should be continued as long as possible if possible. If an infant is diagnosed with vitamin D deficiency, the pediatrician will prescribe an additional dose. Most often, the vitamin is obtained from fish oil or milk mixtures. A nursing mother should consult a therapist to select the appropriate dosage for herself.
A pediatrician may prescribe an aqueous vitamin solution for a newborn if he notices the first signs of a calciferol deficiency. This can be done without analysis. It is recommended to drink drops when sweating of the back of the head appears in a child, a slow pace of fontanel closure, which does not correspond to age, and a manifestation of increased irritability of the baby.
Better when baby gets it naturally. His body itself produces a useful substance when the skin comes into contact with the sun's rays. Therefore, you need to walk with babies every day and at least an hour.
The baby's face and hands do not need to be protected from the sun. But at the same time, one should not allow overheating and go out on a summer afternoon under direct rays. At a comfortable temperature, full-body sunbathing is recommended.
But at the same time, one should not allow overheating and go out on a summer afternoon under direct rays. At a comfortable temperature, full-body sunbathing is recommended.
The second natural source of vitamin D is mother's milk. But it should be enough in a woman's body to provide for both herself and the child. You need to take care of this even during pregnancy:
- walk in the sun;
- eat fish, cereals, eggs, cheese;
- drink milk and orange juice;
- take fish oil.
It is better for a woman to start from the very first trimester, while all the main body systems of the future baby are being laid. By the third trimester, his skeleton will actively accumulate calcium - you need to be ready for this. Otherwise, a deficiency of vitamin D will be created in the mother's body. This is dangerous not only for the child, but also for herself.
How to take vitamin D while breastfeeding
Vitamin D is sold as a fat and water solution. It can have a different structure, on which its solubility in lipids depends. Vitamin D2 is predominantly fat-soluble, so it can be taken as fish oil. But this form of the drug can be dangerous. In a solution of fats, the vitamin enters the liver, where it can be deposited and gradually released into the blood. Sometimes its concentration reaches the limit values, it is impossible to control this process. Therefore, overdose symptoms easily occur.
It can have a different structure, on which its solubility in lipids depends. Vitamin D2 is predominantly fat-soluble, so it can be taken as fish oil. But this form of the drug can be dangerous. In a solution of fats, the vitamin enters the liver, where it can be deposited and gradually released into the blood. Sometimes its concentration reaches the limit values, it is impossible to control this process. Therefore, overdose symptoms easily occur.
Breastfeeding women and young children are advised to take vitamin D3 in an aqueous solution or in the form of Aquadetrim tablets. For some women with calcium deficiency, a doctor may prescribe a special complex.
Take the vitamin in a daily dosage 1 time per day. It can be taken by all women who live in the middle climate zone from September to April. During this period, there is not enough sunlight, and the activity of the sun is low, so that the skin synthesizes its own calciferol.
It is also allowed to take the vitamin complex in the summer if there are changes in the analysis of cuts or other signs of deficiency. But in this case, careful dosage control is necessary so as not to cause complications and side effects.
But in this case, careful dosage control is necessary so as not to cause complications and side effects.
Contraindications and side effects
Nursing mothers must follow the dosage of the vitamin prescribed by the doctor. Otherwise, its excess can lead to side effects or toxic effects on the newborn. Discussing the need to take the drug is necessary if there are the following contraindications:
- blood test shows increased calcium concentration;
- in the analysis of urine calcium excretion is increased;
- hypersensitivity to the drug or its individual components was observed;
- diagnosed with urolithiasis, especially oxalate stones;
- have acute or chronic liver and kidney disease;
- confirmed renal failure, regardless of the form;
- diagnosed with sarcoidosis - non-infectious inflammation of muscle tissue;
- in a lactating woman with pulmonary tuberculosis or other localization in an active form.

But even compliance with the dosage does not guarantee that there will be no side effects of the drug. Some women may have intolerance to auxiliary components, which manifests itself in allergic reactions. Most often, these are rashes on the skin of the face, neck, elbows, and abdomen.
In case of hypersensitivity to the drug or hypervitaminosis, appetite may disappear, nausea, vomiting appear. A woman feels headaches and muscle pain, discomfort and aching joints. Often there are violations of the stool in the form of prolonged constipation. Hypervitaminosis causes dry mouth, thirst, copious urine. Large amounts of calcium are lost in the urine.
High doses of the vitamin damage the kidneys, protein appears in the urine, as a reaction to inflammation - leukocytes, and in severe cases - blood. If the drug is not canceled, body weight falls, sleep disturbances, depression and other mental disorders occur. Elevated calcium concentrations can cause calcification of blood vessels, lungs and kidneys, which further worsens the condition of the body and requires emergency medical attention.
Vitamin D is vital for the developing fetus, newborn baby and his mother. But it must be taken with caution and only after consulting a doctor.
Vitamin D3 for children and newborns | Which vitamin D3 is better | Dosage (Daily Value) of Vitamin D3
Vitamin D3 is an important component for the healthy development of children. It helps to form strong bones and teeth, healthy nails and hair, and muscle tissue. In addition, it is involved in maintaining immunity.
At the same time, people living in central Russia and to the north are at risk of developing a shortage of this substance due to the small number of sunny days. Its deficiency is very dangerous for infants and toddlers of the first year of life, especially those born from October to March.
In what doses to give it to newborns and older babies, what forms and preparations exist, we will consider in this article. The recommendations are based on the National Program of the Ministry of Health, released in 2018 - "Vitamin D deficiency in children and adolescents of the Russian Federation: modern approaches to correction. "
"
What is vitamin D3 for
It regulates the absorption of phosphorus and calcium in our body. Parents most often know that it is essential for bone growth. However, its benefit also lies in the following:
- regulates the timely teething,
- is responsible for muscle growth,
- improves skin condition and reduces the likelihood of its diseases,
- is involved in tuning the immune and endocrine systems,
- reduces the risk of inflammation,
- reduces the likelihood of oncology and autoimmune conditions.
D or D3 - what's the difference
Vitamin D (calciferol) is a whole group of substances, but it is the D3 form that is produced by the body on its own and is the component that helps to absorb calcium and phosphorus. Therefore, speaking further about vitamin D, we will mean its form D3 or cholecalciferol.
Vitamin D3 sources
The peculiarity of this substance is that our body receives it from two sources:
- First, it is produced in our skin under the influence of ultraviolet rays.
 That is why it is so useful to walk on sunny days. It does not have to be under the scorching sun. In the shade of trees will have the same effect. Just 20 minutes of walking with an open face and palms is enough to provide yourself with cholecalciferol for several days.
That is why it is so useful to walk on sunny days. It does not have to be under the scorching sun. In the shade of trees will have the same effect. Just 20 minutes of walking with an open face and palms is enough to provide yourself with cholecalciferol for several days. - Secondly, the source of this substance is food. It is found in significant quantities in fish, caviar and eggs.
Reasons for shortages
When the intake of a vitamin from food or its production by the body is limited, its deficiency develops. Main reasons:
- Long absence of sun exposure
- Putting to bed on a glazed balcony – ultraviolet does not penetrate the glass.
- Genetically poor ability to absorb cholecalciferol
- Vegetarian diet for nursing mothers
- Prematurity - the baby's body did not have time to get enough of the necessary substances. This process takes place during the last two months of pregnancy.
Deficiency symptoms
D3 deficiency in babies of the first year is fraught with the occurrence of rickets. In our country, the practice of making this diagnosis “by eye” is very common. In fact, rickets is a very rare disease. In developed countries, it occurs in 1 in 200,000 children. Diagnosis is based on x-ray and blood tests.
In our country, the practice of making this diagnosis “by eye” is very common. In fact, rickets is a very rare disease. In developed countries, it occurs in 1 in 200,000 children. Diagnosis is based on x-ray and blood tests.
Possible symptoms of rickets:
- Softening and thinning of the skull bones
- Enlargement of frontal and parietal tubercles
- Late teething with poor enamel
- Rachitic rosary - indurations on bones, on ribs, e.g.
- Decreased muscle tone or change in bone sensitivity
- Slowdown
These are just possible symptoms. You can not draw a conclusion only on their basis. The diagnosis is made only after an X-ray examination of the bones, analyzes of the content of phosphorus, calcium, vitamin D and some hormones.
Symptoms that are not symptoms of rickets:
- Increased sweating
- Erased hair on the back of the head
- Anxiety
- Capriciousness
- Crooked legs
- Hypertonus
In children who are breastfed, rickets almost never occurs, because the baby receives the necessary dose of the substance with mother's milk. Here, it is much more important for a mother to monitor its amount in her body and take care of how to replace the lack of sun.
Here, it is much more important for a mother to monitor its amount in her body and take care of how to replace the lack of sun.
Formula-fed babies used to be at risk, but now in almost all mixtures of this substance there is a sufficient amount to prevent the development of the disease.
You should check with your pediatrician if you have any doubts that your baby is getting enough vitamin D.
Daily requirement and how to take
A child from one month to a year needs 1000 IU (international units) of vitamin D. A pediatrician can prescribe the drug from the first days of life. Healthy full-term newborns are prescribed 500 IU until they reach the age of one month.
The National Program of the Ministry of Health recommends the following dosages for healthy babies:
| Age | Prophylactic daily dose | Daily dose for residents of the European North of Russia |
| term newborn | 500 IU | 500 IU |
| 1 - 6 months | 1000 IU | 1000 IU |
| 6 to 12 months | 1000 IU | 1500 IU |
| 1 to 3 years | 1500 IU | 1500 IU |
| 3 to 18 years old | 1000 IU | 1500 IU |
Modern mixtures, as well as breast milk, contain vitamin D, which, however, is not enough to prevent deficiency among Russians. Therefore, the indicated dosages are prescribed for babies, regardless of the type of feeding.
Therefore, the indicated dosages are prescribed for babies, regardless of the type of feeding.
You can get acquainted with the recommended dosages for premature babies, children at risk and therapeutic dosages in the National Program.
Overdose symptoms
An overdose leads to a violation of the absorption of calcium and is the cause of allergic reactions. However, it is incorrect to talk about an allergy to cholecalciferol. Allergies are the consequences of its overabundance.
Other symptoms are increased nervous excitability and, as a result, sleep disturbance.
Taking prophylactic doses does not lead to an excess of vitamin D. In accordance with the National Program, the drug is recommended to be taken continuously, including the summer months.
Vitamin D oil or water based
Calciferol is a fat-soluble substance, therefore, special additives are used to dissolve it in water. You can find a list of them in the composition of excipients in the instructions for the drug. Stabilizers are also added to such preparations so that the solution retains its shape and preservatives, which most often is ethyl alcohol. Auxiliary components are contained in scanty doses, so you should not be afraid of this. Store the aqueous solution in the refrigerator.
Stabilizers are also added to such preparations so that the solution retains its shape and preservatives, which most often is ethyl alcohol. Auxiliary components are contained in scanty doses, so you should not be afraid of this. Store the aqueous solution in the refrigerator.
There are cases when only an aqueous solution is suitable for children. These are babies with diseases of the intestines and pancreas, which do not absorb fats well.
The oil solution contains only oil and cholecalciferol. In this case, oil acts as a natural preservative. Oil-based preparations are stored at room temperature.
A healthy, non-allergic child is given any option to prevent deficiency of this substance. In any case, the questions: which vitamin D is better - on a water or oil basis, how to give and up to what age, and what is the correct dosage, your pediatrician should answer.
Zinaida Rassadina
Pediatrician, experience - 14 years
Israeli children's vitamin D3
On our website you can buy an oil-based drug from two Israeli manufacturers.