Newborn babies feeding habits
How Often and How Much Should Your Baby Eat?
By: Sanjeev Jain, MD, FAAP
One of the most common questions new parents have is how often their baby should eat. The best answer is surprisingly simple: in general, babies should be fed whenever they seem hungry.
How do I know when my baby is hungry?
For babies born
prematurely or with certain medical conditions, scheduled feedings advised by your pediatrician are best. But for most healthy, full-term infants, parents can look to their baby rather than the clock for hunger cues. This is called feeding on demand, or
responsive feeding.
Hunger cues
A hungry baby often will cry. But it's best to watch for hunger cues before the baby starts crying, which is a late sign of hunger and can make it hard for them to settle down and eat.
Some other typical hunger cues in babies:
Licking lips
Sticking tongue out
Rooting (moving jaw and mouth or head in search of breast)
Putting his/her hand to mouth repeatedly
Opening her mouth
Fussiness
Sucking on everything around
It is important to realize, however, that every time your baby cries or sucks it is not necessarily because he or she is hungry. Babies suck not only for hunger, but also for comfort; it can be hard at first for parents to tell the difference. Sometimes, your baby just needs to be cuddled or changed.
General guidelines for baby feeding
It is important to remember all babies are different―some like to snack more often, and others drink more at one time and go longer between feedings. However, most babies will drink more and go longer between feedings as they get bigger and their tummies can hold more milk:
Most newborns eat every 2 to 3 hours, or 8 to 12 times every 24 hours. Babies might only take in half ounce per feeding for the first day or two of life, but after that will usually drink 1 to 2 ounces at each feeding. This amount increases to 2 to 3 ounces by 2 weeks of age.
At about 2 months of age, babies usually take 4 to 5 ounces per feeding every 3 to 4 hours.
At 4 months, babies usually take 4 to 6 ounces per feeding.

At 6 months, babies may be taking up to 8 ounces every 4 to 5 hours.
Most babies will increase the amount of formula they drink by an average of 1 ounce each month before leveling off at about 7 to 8 ounces per feeding. Solid foods should be started at about 6 months old.
Concerns about overfeeding or underfeeding your baby
Too full?
Babies are usually pretty good at eating the right amount, but they can sometimes take in more than they need. Infants who are bottle feeding may be more likely to overfeed, because drinking from a bottle may take less effort than breastfeeding.
Overfed babies can have stomach pains, gas, spit up or vomit and be at higher risk for obesity later in life. It's better to offer less, since you can always give more if your baby wants it. This also gives babies time to realize when they're full.
If you are concerned your baby wants to eat
all the time―even when he or she is full―talk with your pediatrician. Pacifiers may be used after feeding to help sooth healthy-weight babies who like to suck for comfort, rather than nutrition. For babies who are breastfed, it's best to wait to offer pacifiers until around 3 to 4 weeks of age, when breastfeeding is well-established.
Pacifiers may be used after feeding to help sooth healthy-weight babies who like to suck for comfort, rather than nutrition. For babies who are breastfed, it's best to wait to offer pacifiers until around 3 to 4 weeks of age, when breastfeeding is well-established.
Trouble gaining weight?
Most babies will double their birth weight by 5 months of age and triple their birth weight by their first birthday. If your baby is having trouble gaining weight, don't wait too long between feeding―even if it means waking your baby. Be sure to talk with your pediatrician about how often and how much to feed your baby.
How do I know if my baby is getting enough to eat?
Daily diapers
A newborn's
diaper is a good indicator of whether he or she is getting enough to eat. In the first few days after birth, a baby should have 2 to 3 wet diapers each day. After the first 4 to 5 days, a baby should have at least 5 to 6 wet diapers a day. Stool frequency is more variable and depends whether your baby is
breastfed or formula fed.
Growth charts
During regular health check-ups, your pediatrician will check your baby's weight and plot it on a growth chart. Your baby's progress on the growth chart is one way to tell whether or not they are getting enough food. Babies who stay in healthy growth percentile ranges are probably getting a healthy amount of food during feedings.
Remember
Talk with your pediatrician if you have any questions or concerns about your baby getting the right amount to eat.
More information:
- Making Sure Your Baby is Getting Enough Milk
- Amount and Schedule of Formula Feedings
- Is Your Baby Hungry or Full? Responsive Feeding Explained (Video)
- Remedies for Spitty Babies
- Ask the Pediatrician: With the baby formula shortage, what should I do if I can't find any?
- Ask the Pediatrician: How should we feed our baby if we're running low on money?
-
Airplane Choo Choo: A Feeding Guide for Children (National Dairy Council)
About Dr.
 Jain:
Jain:
Sanjeev Jain, MD, FAAP, is a Clinical Associate Professor of General Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine at the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health. Within the American Academy of Pediatrics, he is a member of the Section on International Child Health and the Wisconsin State Chapter.
The information contained on this Web site should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician. There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
Feeding patterns and diet - babies and infants Information | Mount Sinai
Babies and infants - feeding; Diet - age appropriate - babies and infants; Breastfeeding - babies and infants; Formula feeding - babies and infants
Recommendations
During the first 6 months of life, your baby needs only breast milk or formula for proper nutrition.
- Your baby will digest breast milk more quickly than formula. So if you breastfeed, your newborn may need to nurse 8 to 12 times per day, or every 2 to 3 hours.
- Be sure you empty your breasts regularly by feeding or using a breast pump. This will prevent them from becoming overly full and achy. It will also allow you to continue producing milk.
- If you feed your baby formula, your baby will eat about 6 to 8 times per day, or every 2 to 4 hours. Start your newborn with 1 to 2 ounces (30 to 60 mL) at every feeding and gradually increase the feedings.
- Feed your baby when they seem hungry. Signs include smacking lips, making suckling movements, and rooting (moving their head around to find your breast).
- Do not wait until your baby cries to feed them. This means they are very hungry.
- Your baby should not sleep more than 4 hours at night without feeding (4 to 5 hours if you are feeding formula). It is OK to wake them up to feed them.
- If you are breastfeeding exclusively, ask your pediatrician if you need to give your baby supplemental vitamin D drops.

You can tell your baby is getting enough to eat if:
- Your baby has several wet or dirty diapers for the first few days.
- Once your milk comes in, your baby should have at least 6 wet diapers and 3 or more dirty diapers a day.
- You can see milk leaking or dripping while nursing.
- Your baby starts to gain weight; about 4 to 5 days after birth.
If you are concerned your baby is not eating enough, talk with your pediatrician.
You should also know:
- Never give honey to your infant. It may contain bacteria that can cause botulism, a rare but serious illness.
- Do not give your baby cow's milk until age 1 year. Babies under age 1 have a difficult time digesting cow's milk.
- Do not feed your baby any solid food until 4 to 6 months old. Your baby will not be able to digest it and may choke.
- Never put your child to bed with a bottle. This can cause tooth decay. If your baby wants to suck, give them a pacifier.

There are several ways you can tell that your infant is ready to eat solid foods:
- Your baby's birth weight has doubled.
- Your baby can control their head and neck movements.
- Your baby can sit up with some support.
- Your baby can show you they are full by turning their head away or by not opening their mouth.
- Your baby begins showing interest in food when others are eating.
When to Call the Doctor
Call the health care provider if you are concerned because your baby:
- Is not eating enough
- Is eating too much
- Is gaining too much or too little weight
- Has an allergic reaction to food
American Academy of Pediatrics, Section on Breastfeeding; Johnston M, Landers S, Noble L, Szucs K, Viehmann L. Breastfeeding and the use of human milk. Pediatrics. 2012;129(3):e827-e841. PMID: 22371471 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22371471/.
Breastfeeding and the use of human milk. Pediatrics. 2012;129(3):e827-e841. PMID: 22371471 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22371471/.
HealthyChildren.org website. How often and how much should your baby eat? www.healthychildren.org/English/ages-stages/baby/feeding-nutrition/Pages/How-Often-and-How-Much-Should-Your-Baby-Eat.aspx. Updated October 29, 2020. Accessed December 6, 2021.
Parks EP, Shaikhkhalil A, Sainath NN, Mitchell JA, Brownell JN, Stallings VA. Feeding healthy infants, children, and adolescents. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 56.
Last reviewed on: 8/10/2021
Reviewed by: Neil K. Kaneshiro, MD, MHA, Clinical Professor of Pediatrics, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Features of nutrition of newborns - Articles about baby nutrition from pediatricians and experts MAMAKO
- Polina Alexandrovna, can we talk about the influence of the type of birth on the nutrition of the baby?
— The nutrition of a child in the first month of life is tied to breastfeeding, this is conceived by nature and does not depend on the method of delivery and on the baby himself. An exception is situations when a newborn, for health reasons, cannot take a breast, for example, due to deep prematurity, in which the sucking reflex is very little or not expressed at all. Such a child is simply physically unable to suck milk. Then the mother resorts to pumping, which allows you to maintain the amount of milk at some optimal level. nine0005
An exception is situations when a newborn, for health reasons, cannot take a breast, for example, due to deep prematurity, in which the sucking reflex is very little or not expressed at all. Such a child is simply physically unable to suck milk. Then the mother resorts to pumping, which allows you to maintain the amount of milk at some optimal level. nine0005
— You can often hear from doctors about the oxytocin reflex. What is the role of the hormone oxytocin in lactation and the condition of a woman?
- The hormone oxytocin is responsible for the process of starting lactation. Oxytocin affects the work of the muscle walls that line the milk ducts - they help milk from the thickness of the mammary gland to get into the baby's mouth. Simply put, this hormone makes it easier for the baby to get milk from the breast.
Oxytocin also affects the contraction of the uterus: the more hormone, the more it contracts, which reduces the risk of postpartum hemorrhage. Therefore, the first attachment to the breast in the delivery room is important not only for the newborn and the beginning of lactation, but also for the health of the mother.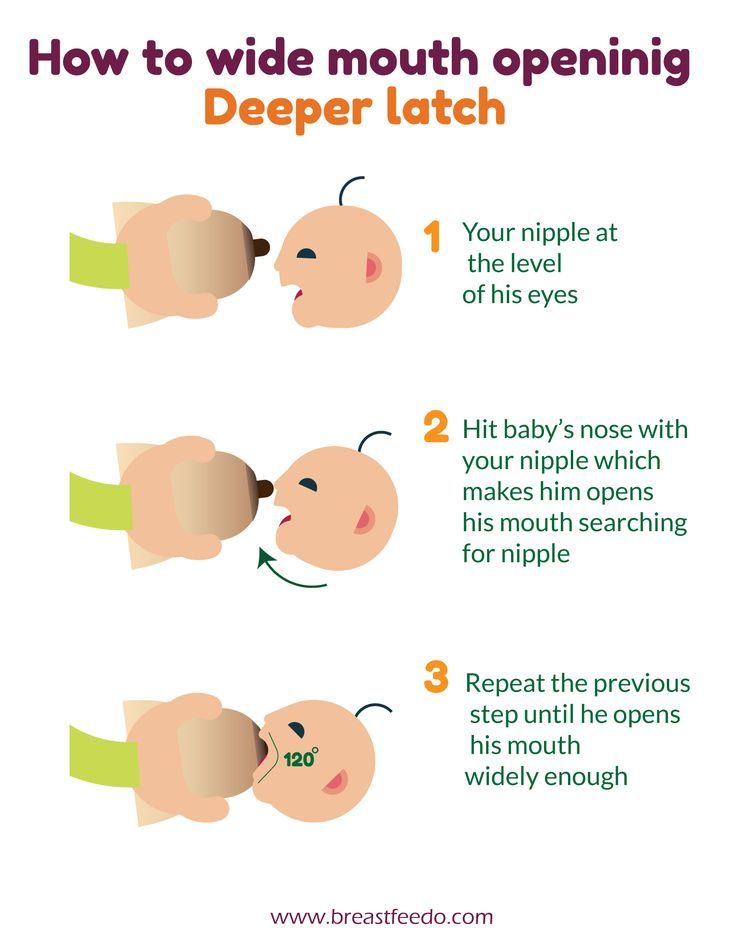 nine0005
nine0005
— In the early days, the mother does not have a large supply of milk and “milk rivers”, which are often talked about. How to establish breastfeeding after childbirth?
- Milk in a sufficiently large amount can come by the end of the first day, by the second and fourth days. The more difficult the birth and the more difficult the condition of the mother, the more time it may take to produce milk. In the meantime, this has not happened, colostrum is secreted from the breast. There is very little of it, but per unit volume the amount of nutrients and biological substances in it is higher than in milk. Therefore, the child will not be left without nutrition: with colostrum, he will receive everything he needs. nine0005
— When does lactation return to normal?
- The process of milk production is quite regular. It is believed that mature lactation is established by the end of the first month of a baby's life. By this time, the female body is able to adapt to the needs of the baby and increase the flow of milk by the expected feeding time..jpg)
We recommend breastfeeding at least every 2-2.5 hours, or more often if requested. After the first month, the intervals between feedings will be about 3 hours. If the newborn is sleeping, you can not wake him up, but you definitely need to feed him. A small child can sleep and eat at the same time. nine0005
To start lactation, the first attachment to the breast in the delivery room is important. In response, the hormone oxytocin will be produced and milk will flow. And the more often the baby suckles the breast, the more actively lactation will be established. The hormone prolactin is responsible for the amount of milk.
- Sometimes formula is included in feeding from birth. What are the reasons for transferring a child to artificial feeding? And how to establish artificial feeding of a newborn?
— When you need to add milk formula and according to what scheme, the doctor will decide based on the health of the newborn. In some cases, supplementary feeding is enough, and in some cases, a complete rejection of breastfeeding and a transition to a mixture adapted to the needs and age of the child is needed. Infant formula, like a caesarean section, is not something to strive for, but sometimes it saves lives. nine0005
Infant formula, like a caesarean section, is not something to strive for, but sometimes it saves lives. nine0005
Reasons for transferring a child to mixed feeding
Reasons for transferring a child to artificial feeding
— Polina Alexandrovna, if a newborn after a caesarean section does not require special nutrition, then how to feed a premature baby?
- Everything is very individual. There are different degrees of prematurity, different degrees of maturity of babies.
Feeding options for a premature baby
— Feeding habits of a baby in the first month of life are the most important. When premature babies gain their weight, the differences between natural birth and caesarean section level out. Children begin to eat "on knurled". They either remain on breastfeeding, or gradually transition from artificial feeding to breastfeeding, or continue to receive therapeutic nutrition. nine0005
— When to start complementary foods for preterm and term babies?
— According to WHO recommendations, complementary foods are introduced from 6 months. Recent scientific evidence suggests that it is possible to start complementary foods earlier. As for premature babies, it all depends on the degree of prematurity and how actively the growth and development of a particular child takes place. The deeper the prematurity, the more the doctor will focus on the gestational age, and not on the date of birth. The lower the degree of prematurity, the less attention should be paid to it. There is no difference in complementary feeding patterns for preterm and full-term babies, or for babies born by caesarean section who have gone through vaginal delivery. nine0005
Recent scientific evidence suggests that it is possible to start complementary foods earlier. As for premature babies, it all depends on the degree of prematurity and how actively the growth and development of a particular child takes place. The deeper the prematurity, the more the doctor will focus on the gestational age, and not on the date of birth. The lower the degree of prematurity, the less attention should be paid to it. There is no difference in complementary feeding patterns for preterm and full-term babies, or for babies born by caesarean section who have gone through vaginal delivery. nine0005
Breast sucking stimulates the production of hormones. Oxytocin allows the child to drink milk freely, and prolactin helps the mother to produce the right amount of it. If breastfeeding is not suitable for you and your baby, then expressed breast milk or adapted formula will be your baby food. Remember, a newborn baby can always receive adequate nutrition for growth and development, regardless of the type of birth and type of feeding.
* Breast milk is the best food for babies. WHO recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months of a child's life and continued breastfeeding after complementary foods are introduced until the age of 2 years. Before introducing new products into the baby's diet, you should consult with a specialist. The material is for informational purposes and cannot replace the advice of a healthcare professional. For feeding children from birth. The product is certified. nine0063
Newborn nutrition
Breastfeeding is by far the best way to feed your newborn. It is a natural continuation of physiological processes such as conception, pregnancy and childbirth. No other food can fully replace breast milk for a baby. This is due to the fact that in the milk of a nursing mother there are more than 500 nutrients necessary for the normal development of the baby's body.
Breastfeeding of newborns in the first days after birth
Even during pregnancy, certain hormones in a woman's body prepare her mammary glands for breastfeeding. When a baby is born, the breast secretes colostrum - the first milk is orange-yellow. It contains proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals that are useful for the baby, which help the newborn to adapt in the extrauterine environment. Colostrum is perfectly absorbed by the child's body, and also cleanses the intestines of meconium (the first stool), which reduces the risk of developing jaundice. nine0005
When a baby is born, the breast secretes colostrum - the first milk is orange-yellow. It contains proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals that are useful for the baby, which help the newborn to adapt in the extrauterine environment. Colostrum is perfectly absorbed by the child's body, and also cleanses the intestines of meconium (the first stool), which reduces the risk of developing jaundice. nine0005
Important!
It is recommended to attach the baby to the mother's breast in the first hours of life. This will help both mother and child get used to new sensations, to each other, to establish an inextricable bond between them.
The newborn may be sleepy after delivery. Despite this, in the first days of life, it is important to keep him close to the breast and try to start feeding. Attachment will cause a sucking reflex in the baby and relieve heaviness in the chest.
In the first days, the frequency of breastfeeding reaches 10-15 times, and the mother should breastfeed the baby at the first sign of anxiety. Subsequently, the number of attachments decreases, because the woman sensitively catches the hungry cry of the child and distinguishes it from crying for other reasons. The frequency of feeding is reduced to 5-7 times a day. nine0005
Subsequently, the number of attachments decreases, because the woman sensitively catches the hungry cry of the child and distinguishes it from crying for other reasons. The frequency of feeding is reduced to 5-7 times a day. nine0005
Good to know
The transition from free to regime feeding is individual and ranges from 10–15 days to 1.5 months.
During the first feedings, the baby swallows very little colostrum. Between the second and fifth days, the body of a nursing mother begins to produce transitional milk - lighter and not so thick, but no less healthy and nutritious. Day by day, the milk will become more and more white, transparent and liquid, its quantity will begin to increase rapidly. The more often a mother puts her baby to her breast, the more milk her body produces. nine0005
Frequency of feeding newborns with breast milk
At first, the baby eats little and often, but this is enough for him. The frequency of breastfeeding a baby is different for everyone, because each nursing mother and child have individual characteristics of the body. The golden rule of breastfeeding a newborn in the first months of life is not to limit the duration of breastfeeding and the number of attachments. Do not worry that he will consume more milk than necessary. The kid himself controls what he needs. nine0005
The golden rule of breastfeeding a newborn in the first months of life is not to limit the duration of breastfeeding and the number of attachments. Do not worry that he will consume more milk than necessary. The kid himself controls what he needs. nine0005
Important!
Make sure that the baby grasps the nipple correctly . If you see that he is uncomfortable, try changing the position for feeding.
A newborn may breastfeed more than eight times in 24 hours. This means that milk production has adapted well to the needs of the baby. At first, it is worth satisfying the baby's need at the first sign of hunger.
It is extremely important that the baby latch on the nipple correctly. The older he gets, the lower the average feeding figure. Gradually, the number of attachments to the chest decreases to five or six times. However, at the same time, each feeding lasts a longer time, becoming much more effective than in the first days of a baby's life. nine0005
nine0005
Night breastfeeding: pros and cons
Baby asks for food at certain hours of the day and night. You need to remember the approximate time of each feeding in order to better understand the rhythm of sleep, awakening and nutrition of the baby.
Important!
Do not torture your baby and stick to a strict feeding schedule. Breastfeeding on demand is more comfortable and healthier for your baby.
The baby eats not only in the daytime. Almost all breastfeeding women face night feedings . This process is undoubtedly important for the child and for the mother. At night, the mother's body produces the hormone prolactin, which plays a huge role in maintaining lactation. It promotes the formation of milk in the mammary glands in sufficient quantity for the child, and this milk is characterized by increased density and is tastier for the baby. Although, of course, milk production is carried out during the day.
Breastfeeding newborns is the most effective way to soothe your baby. Within six months after birth, the active phase of sleep dominates in newborns during sleep, and vice versa in adults, so the baby can wake up more often and be naughty. The child feels hunger, fear and loneliness from the first months of life. Only his mother's breast can calm him down, and night feedings temporarily become the norm. nine0005
Within six months after birth, the active phase of sleep dominates in newborns during sleep, and vice versa in adults, so the baby can wake up more often and be naughty. The child feels hunger, fear and loneliness from the first months of life. Only his mother's breast can calm him down, and night feedings temporarily become the norm. nine0005
Important!
A mother needs to learn to distinguish between her baby's hungry cries and other types of cries. Remember that breastfeeding with any disturbance can lead to overfeeding!
Breastfeeding and menstruation: is there a danger to the baby?
Women who continue to breastfeed will start menstruating when their baby is about 8-10 months old. It is normal that at first there is no menstruation, because the body needs to recover after pregnancy and childbirth .
Menstruation while breastfeeding does not bring any negative consequences. The only thing is that milk production may decrease slightly during the cycle, so it needs to be increased by various methods of increasing lactation. Some mothers note that during menstruation, the child is reluctant to breastfeed, probably due to a change in the taste of milk during this period.
Some mothers note that during menstruation, the child is reluctant to breastfeed, probably due to a change in the taste of milk during this period.
When to wean a baby from breastfeeding: advice to a nursing mother
Often young mothers are interested in the question, until what age should they breastfeed their baby. The duration of feeding depends on many characteristics of the body - both mother and child. WHO experts advise to continue breastfeeding up to 12 months. Subsequently, breastfeeding is valuable for mother and baby from a psychological point of view. But the baby is able to receive nutrients after a year from other foods. Many experts and experienced parents believe that breastfeeding after a year is not the main element of a child's nutrition. nine0005
Important!
Complementary foods are recommended to be introduced at the age of six months. You should start with cereals and vegetable purees, then meat purees are added to the diet.
The older the child gets, the less he needs to feed on mother's milk. For some children, breastfeeding lasts up to three years, while for others it stops after a year of the baby's life. There are practically no easy ways to wean from the breast, it is always a certain stress for the crumbs. However, the end of breastfeeding is an integral part of the growing up of the child. The beginning of breastfeeding causes certain difficulties for some mothers. The best approach is to trust your body and follow your instincts. If the process of breastfeeding is debugged at the very beginning of feeding, in the future, the mother will have no problems either with feeding the child or with finishing it when the baby grows up. nine0005
Breastfeeding helps the baby grow and develop, but not only: mother's milk protects the baby from infections and viruses . Learn about the "magic" ingredients that provide a reliable immune barrier against various diseases.
BREAST MILK OLIGOSACCHARIDES
Breast milk oligosaccharides are special bioactive compounds that are found only in breast milk and they are one of the most widely distributed components of breast milk and are responsible for the formation of the child's immunity. The main action of HMO is carried out at the level of the intestine. nine0005
The main action of HMO is carried out at the level of the intestine. nine0005
BENEFICIAL BACTERIA
Breast milk naturally contains various types of beneficial bacteria that help maintain the balance of the intestinal bacterial flora. Scientists have found that breastfed babies have more beneficial bacteria in their gut.
PROTEINS
Breast milk contains high quality proteins necessary for the growth and development of the baby, especially whey proteins. During the first six months, the concentration of proteins in breast milk gradually decreases, adjusting to the needs of the child. nine0005
ANTIBODIES
Breast milk, which is produced during the first days after birth (colostrum), contains a large amount of antibodies. Every time you breastfeed your baby, you give him protection against a wide range of infections.
The benefits of breastfeeding do not end in infancy. Breastfed children are less likely to develop health problems as adults. Thus, breastfeeding today is a concern for the future of your child. nine0005
Thus, breastfeeding today is a concern for the future of your child. nine0005
Breastfeeding is a type of feeding in which a child up to 6 months receives only mother's milk.
There are 3 types of mother's milk.
- Colostrum is a sticky thick liquid of yellow color,
appears after the birth of a child and is excreted up to 4-5 days. - Transitional milk is produced from 4 - 5 days of life and up to 2 - 3 weeks
has an intermediate composition between colostrum and
mature milk. nine0178 Mature milk is produced from 2 - 3 weeks of a child's life and
has a complete biological similarity with the child's body.
Composition of breast milk (see 10 benefits of breast milk).
Breastfeeding benefits:
- Breast milk contains all the necessary ingredients in optimal ratios B:L:U=1:3:6
- There is more protein in cow's milk, but it is coarsely dispersed (casein), so it is difficult to break down and digest, while breast milk protein is finely dispersed, practically does not require enzymes for splitting and, accordingly, is very well absorbed, therefore, allergic reactions develop much less often in infants
- Human milk proteins contain all essential amino acids
- Human milk contains protective antibodies against various infections
- Contains significantly more unsaturated fatty acids that increase resistance to infections
- More milk sugar (lactose), which promotes brain development, normalization of intestinal microflora
- Less mineral salts compared to the composition of cow's milk (salts overload the kidneys, contribute to the further development of hypertension)
- Optimal amount of vitamins, trace elements, enzymes
- Breast milk is sterile (lower risk of intestinal infections)
- Contains lecithin, which promotes the reproduction of brain cells
- An increased need for food is fixed on artificial feeding - the risk of obesity at an older age.
- Physical (biological maturation and aging) and sexual development are faster in artificers, and mental vice versa (intelligence, talent - breastfeeding for at least 6 months is necessary for their implementation)
- The child accumulates (deposits) in the subcutaneous fat the best components of breast milk and then uses them for several years (for brain function)
- Sucking promotes correct articulation, correct formation of the maxillofacial skull. Infants are less likely to have speech disorders.
Until now, a huge amount of nutrients in breast milk has not been deciphered (for example, taurine is needed for brain development, the formation of the retina of the eye, it is not found in cow's milk because calves do not need to go to school). nine0005
It is impossible to create a full-fledged substitute for women's milk also because, depending on the age of the child, the composition of women's milk changes, reflecting the changing needs of a growing organism, and feeding with donor milk will still be not natural, but pseudo-natural.
Benefits of early breastfeeding within the first 30 minutes after birth:
For the mother:
1. Promotes rapid contraction of the uterus, reducing the risk of bleeding, and rapid recovery; nine0005
2. Stimulates prolonged lactation;
3. Reduces the risk of developing mastitis
4. Early contact stimulates the feeling of motherhood.
For a child:
1. Promotes the formation of normal intestinal microflora
2. Reliable immunological protection is formed (on the second day of a child’s life, the number of antibodies in mother’s milk decreases by 2 times)
3. Stimulation of the sucking reflex
.Close psychological and emotional contact with the mother in the first hours after the stress - birth
Rules for first breastfeeding.
For the first time, the child is laid on the mother's stomach naked and covered with a sterile sheet before the end of the umbilical cord pulsation (if the state of health of the child and mother allows)
Recommendations for breastfeeding mothers:
- Correct daily routine: sleep at least 8 hours a day, daytime sleep 1.
 5 - 2 hours, walks in the fresh air, moderate exercise, positive emotional attitude, avoidance of stressful situations
5 - 2 hours, walks in the fresh air, moderate exercise, positive emotional attitude, avoidance of stressful situations - The amount of liquid in the diet is increased by about 1 liter
- The calorie content of the daily ration should be increased by 50% compared to the diet of a non-nursing woman of this age. Meat and (or) fish, dairy products (cottage cheese, cheese), vitamins are needed daily. Nutrition 4-5 times a day (as many times as the child feeds), in small portions, to stimulate milk production, drink a glass of tea with milk and cheese 10-15 minutes before feeding. nine0178 Refrain from taking products that change the smell and taste of milk (fresh onion, garlic)
- No medication before consulting a doctor
- Do not abuse gas-forming (cucumbers, grapes), laxative (plums, beets) and fixing (nuts, pears), allergenic (strawberries, pineapple, red fish, eggs, honey) and tonic (strong tea, coffee, chocolate) products
- Duration, usefulness of lactation significantly depend on the anamnesis of feeding of the woman herself.
 nine0180
nine0180
Breastfeeding rules:
- Wash breasts under running water, remove long hair
- Get into a comfortable position - sitting, lying on your side
- Make sure that the child is in a comfortable environment, and nothing distracts him from the feeding process (clean, dry, warmly dressed)
- Check that the child's nasal breathing is free (if necessary, remove crusts from the nose)
- Make sure that when suckling, the child grabs not only the nipple, but also the areola and that it does not rest with the nose against the mammary gland
- In case of greedy suckling and/or active flow of milk, periodically hold the baby upright for several minutes, and then reattach to the breast
- In case of sluggish sucking, the child falls asleep during feeding, wake him up (stroke the cheek, tickle the heels)
- The duration of the first feedings is usually 30-40 minutes (this is the period of formation of lactation), then it takes an average of 20 minutes (in the first 5 minutes of feeding, the baby sucks 50% of the milk volume)
- If the amount of milk in one breast is not enough to meet the needs of the child, then it is applied to the other, and the sequence is changed at the next feeding
- Hold baby upright for 3-5 minutes after feeding to prevent regurgitation
- Breast wash
Currently, free feeding is recommended for a newborn baby and children of the first months of life - the baby is applied to the breast at the first sign or demand (up to 12-16 times a day). This is done because in the first weeks after birth, the process of adapting the body of the nursing mother to the needs of the child takes place and frequent application solves the problem of the child's hunger and stimulates lactation in the mother. Up to 3-4 days of a child's life, the mammary glands secrete very little milk, but it contains a large amount of protein and fat in order to somehow satisfy the needs of the child. This milk is called colostrum. Then lactation gradually increases and the composition of milk (transitional) approaches the composition of mature milk: protein - about 2.5 g, fat - an average of 3 g, carbohydrates - 7 g. her nutrition, emotional state, hereditary characteristics of lactation. Nobody knows the norms of milk. For each “mother-child” pair, it is individual (in the “final” milk, fat is up to 17%, so it is impossible to calculate). All nutrition correction should go through mother's milk (nutrition of a nursing woman)
This is done because in the first weeks after birth, the process of adapting the body of the nursing mother to the needs of the child takes place and frequent application solves the problem of the child's hunger and stimulates lactation in the mother. Up to 3-4 days of a child's life, the mammary glands secrete very little milk, but it contains a large amount of protein and fat in order to somehow satisfy the needs of the child. This milk is called colostrum. Then lactation gradually increases and the composition of milk (transitional) approaches the composition of mature milk: protein - about 2.5 g, fat - an average of 3 g, carbohydrates - 7 g. her nutrition, emotional state, hereditary characteristics of lactation. Nobody knows the norms of milk. For each “mother-child” pair, it is individual (in the “final” milk, fat is up to 17%, so it is impossible to calculate). All nutrition correction should go through mother's milk (nutrition of a nursing woman)
Difficulty in breastfeeding:
On the part of the child :
- Rhinitis with impaired nasal breathing (secret suction, removal of crusts from the nose, use of vasoconstrictor drops before feeding)
- Thrush (candidiasis stomatitis) - treatment of the oral mucosa with a 2% solution of baking soda after each feeding
- Lack of sucking reflex (premature) - spoon or tube feeding
Maternal side
- Flat, inverted nipple (special pads are used to make it easier for the baby to latch on)
- Nipple abrasions and cracks (correct attachment to the breast so that the baby presses on the areola and does not pull the nipple, special ointments - bipanthen)
- Milk stasis - correct feeding and expression of milk, use of a breast pump
- Hypogalactia
Hypogalactia - a decrease in lactation, a very common problem of lactating women at present. nine0005
nine0005
Possible signs of hypogalactia:
- The child has become restless, sleeps poorly, cannot stand the interval between feedings
- Decreased daily diuresis (became less likely to urinate)
- Low weight gain, flat weight curve
- Subjective sensation of an "empty" breast in a woman
Diagnosis of hypogalactia - carrying out control feeding, when the child is weighed before and after breastfeeding, the difference in weight is compared with the nutritional norm obtained for this child according to formula
Prevention and treatment of hypogalactia :
- Breastfeeding promotion, psychotherapy
- Prevention of cracks and mastitis
- Compliance with diet and daily routine, support for other family members
- Nettle decoction (20 g of dry leaves per liter of boiling water, leave for 45 minutes and drink 1 tbsp 3 times a day), anise, dill, oregano fruits, lactogenic herbs
- Medications: vitamins E, A, PP, C, gendevit, aevit, prenatale, materna, dry brewer's yeast, apilac, microdoses of iodine
- More frequent latching, latching on both breasts in one feeding
Quartz irradiation, UHF, massage, acupuncture
Mixed feeding
Mixed feeding is a type of feeding in which the child receives breast milk and supplementary feeding in the form of milk mixtures.
The effectiveness of mixed feeding depends on breast milk in the daily diet of the child:
- if the amount of mother's milk is half the daily
diet (2/3, 3/4), then the effectiveness of mixed feeding
is close to natural; - if the amount of mother's milk is less than half of the
daily ration (1/3, 1/4), then the effectiveness of mixed feeding
is close to artificial;
Additives.
Supplements are dosed meals that are included in the diet as sources of vitamins, minerals, trace elements and as additional sources of the main ingredients (proteins, fats, carbohydrates). nine0005
A distinction is made between vitamin and protein supplements such as :
- Fruit juices (puree) - apple, white cherry, white currant, apricot, peach, pear, plum (given in order of preference). They begin to introduce into the diet with drops, gradually increasing the amount to 40-60 ml.
 It is desirable that the first juices of the child be natural and fresh (home-made)
It is desirable that the first juices of the child be natural and fresh (home-made) - Cottage cheese (calcined) is also desirable home-made - 1-2 tablespoons of CaCl 9 are added to 200 ml of milk at the time of boiling0409 2 , then leans back on gauze, or milk cuisine, special baby food. Begin to introduce into the diet with grains and bring up to 40 grams per day
- Egg yolk of a hard-boiled egg. From grains to 1/12 - 1/8 added to milk or vegetable puree (use with caution in the diet of allergy sufferers)
Supplementary
Complementary foods are meals that replace breast milk (milk formulas).
The reason for the introduction of supplementary food is hypogalactia, which in the mother leads to malnutrition of the child. nine0005
Signs of starvation:
- Flattening and then decreasing weight curve
- Restlessness, restless and interrupted sleep.
- Decreased daily diuresis and frequency of urination.

- Violation of the stool (constipation, diarrhea).
If all signs are present, then the mother and child are invited to the children's clinic in the healthy child's room for control feeding.
How to help latch on the nipple? nine0005
1. First grasp your breast with your thumb above the nipple and with your index finger below the nipple, then lightly rub your baby's lower lip with the nipple. This may be enough to stimulate the innate reflex: the baby will turn his head to the nipple and open his mouth.
- When the baby opens its mouth wide, move the baby towards you (but do not move towards the baby). If the baby has grasped the nipple correctly, his lower lip will drop down. The lips of the baby should wrap around the nipple as much as possible along the contours of the areola. If the baby latch on the nipple correctly, you will hear a few sucking sounds, then a pause, followed by a swallowing sound. nine0180
- With the correct latch on the nipple, the baby holds the mother's breast firmly.
 If you want to release the breast or transfer the baby to another breast, gently insert your finger between the baby's jaws to interrupt the suckling. Fingernails should be neatly trimmed so as not to scratch the lips of the child.
If you want to release the breast or transfer the baby to another breast, gently insert your finger between the baby's jaws to interrupt the suckling. Fingernails should be neatly trimmed so as not to scratch the lips of the child.
Criteria and timing for the introduction of complementary foods . Complementary foods - the introduction of a new food, more concentrated, gradually and consistently replacing breastfeeding. The need to introduce complementary foods is due to the growing needs of an actively growing child's body for energy, proteins, fats, and micronutrients. In addition, the child needs to take more dense food to stimulate the further development of the masticatory apparatus, motor and enzymatic functions of the gastrointestinal tract. Complementary foods are necessary for the introduction of new nutrients that are not found in milk and are necessary for the full growth and development of the child (vegetable protein, dietary fiber, fatty acids, etc. ). nine0005
). nine0005
When introducing complementary foods, it is necessary to take into account the individual characteristics of the child as much as possible. European baby nutrition experts say that the first complementary foods can be introduced no earlier than 4 months and no later than 6 months. Early introduction of complementary foods reduces the frequency and intensity of breastfeeding, which leads to a decrease in maternal lactation. In addition, early introduced complementary foods can lead to food sensitization, the development of dyspeptic manifestations due to the immaturity of the gastrointestinal tract. nine0074 The first complementary food in the form of milk porridge is introduced during the second morning feeding . Complementary foods are always given before breastfeeding. It is necessary to gradually increase the volume of porridge and reduce the amount of breast milk. Gluten-free cereals (rice, buckwheat, corn) should be used as the first cereal food. Cereals such as oatmeal, barley, semolina are introduced later, as these cereals contain gluten, which is not always well tolerated by infants. Complementary foods are introduced once a day, sometimes 10-15 attempts are needed for the child to perceive new food for him. Usually the first meal in the form of porridge is preferred for underweight children. For children who are overweight, as well as with a tendency to constipation, it is better to introduce the first complementary foods in the form of vegetable puree with the addition of vegetable oil. It should be remembered that complementary foods can only be introduced to a healthy child, and industrial dishes have advantages. nine0005
Complementary foods are introduced once a day, sometimes 10-15 attempts are needed for the child to perceive new food for him. Usually the first meal in the form of porridge is preferred for underweight children. For children who are overweight, as well as with a tendency to constipation, it is better to introduce the first complementary foods in the form of vegetable puree with the addition of vegetable oil. It should be remembered that complementary foods can only be introduced to a healthy child, and industrial dishes have advantages. nine0005
A new type of complementary food is introduced after assimilation of the full volume of the previous complementary food in 10–14 days.
The second food is vegetable puree. Vegetable puree must be monocomponent (from one type of vegetable). Preference is usually given to squash puree, cabbage of various varieties. Within 7-10 days, the volume of feeding is brought to the age norm. In the future, you can use multi-component vegetable purees. This type of complementary food is introduced in the third feeding. nine0074 Meat is introduced 2 weeks after the introduction of vegetable puree, but no later than 7 months. Meat must be added to vegetable puree. You can use different types of meat or canned meat (lean beef, turkey meat, horse meat, lean pork, chicken). Canned meat containing by-products (tongue, liver, heart) are introduced into the child's diet no earlier than 8 months. Meat broths are prohibited for infants. From 8 months, 1-2 times a week instead of meat, fish (fish puree) is included in the child's diet, it is an important source of complete protein, rich in phosphorus, fluorine, iodine. The age norm of fish at 11–12 months is 100–150 g. Salmon, pink salmon, chum must not!!! be included in the diet of a child of the first year of life due to the high content of fat and salt.
This type of complementary food is introduced in the third feeding. nine0074 Meat is introduced 2 weeks after the introduction of vegetable puree, but no later than 7 months. Meat must be added to vegetable puree. You can use different types of meat or canned meat (lean beef, turkey meat, horse meat, lean pork, chicken). Canned meat containing by-products (tongue, liver, heart) are introduced into the child's diet no earlier than 8 months. Meat broths are prohibited for infants. From 8 months, 1-2 times a week instead of meat, fish (fish puree) is included in the child's diet, it is an important source of complete protein, rich in phosphorus, fluorine, iodine. The age norm of fish at 11–12 months is 100–150 g. Salmon, pink salmon, chum must not!!! be included in the diet of a child of the first year of life due to the high content of fat and salt.
In accordance with modern concepts of nutrition, fruit juices and fruit purees should be introduced into the diet after the introduction of the main complementary foods - cereal, vegetable puree, meat. Fruit purees are introduced, like all complementary foods, gradually. The approximate volume of fruit puree is 10 ml for 1 month of life, but not more than 100 ml per day and is divided into 2 feedings. Fruit juices and fruit purees contain a diverse set of vitamins and minerals. Preference is given to industrial products. nine0005
Fruit purees are introduced, like all complementary foods, gradually. The approximate volume of fruit puree is 10 ml for 1 month of life, but not more than 100 ml per day and is divided into 2 feedings. Fruit juices and fruit purees contain a diverse set of vitamins and minerals. Preference is given to industrial products. nine0005
From the age of 7–8 months, the yolk of a hard-boiled chicken egg is introduced into the child’s diet as a source of vitamins A and D, protein, etc. Begin the introduction of the yolk from a small amount and gradually bring it up to ½ yolk by 8–9 months life. From the age of 7 months, biscuits or crackers from white bread in the amount of 5 g can be introduced into the child's diet.
By the year the daily norm of bread is 10-15 g. From 8 months you can use wheat bread in the same amount. Rye bread is not recommended for infants due to its high salt content. Kefir and cow's milk are non-adapted dairy products, have a low content of essential food components, are highly allergenic and have an excessive osmotic load on the kidneys of an infant.