One day old baby not feeding
Breastfeeding sleepy and reluctant babies
Go backExplore this article's topics:
Feeding Breastfeeding Common breastfeeding challenges
There are lots of reasons why your baby may be reluctant to feed. It doesn’t mean you aren’t doing a good job as a mum. Don’t put too much pressure on yourself to know all the answers straight away and speak to your midwife or health visitor if you have any questions or concerns, or are looking for ways to make feeding more comfortable.
How often should my baby feed?
All babies are different, but it's very common for babies not to feed all that much in the first 24-48 hours, and some don't attach at all. However, from day 2-3 days babies should become much more awake and feed in more frequent (but probably irregular) bursts at least 6 times in 24 hours.
How do I know if my baby's getting enough milk?
Photo of a baby breastfeeding
Breastfeeding at first can be really hard to get used to and you might find yourself wondering if your baby has had enough milk - it can be very hard to judge how much breastmilk your baby has had, but they are clever wee things and you have to have some faith that your baby knows whether it needs more milk. There are signs to look out for if you think your baby isn't getting enough milk.
Why are some babies reluctant to feed?
This happens most often when babies don't get skin-to-skin contact with mum soon enough or for long enough after the birth. Ideally, you want skin-to-skin contact with your baby straight away and for as long as it takes for your baby to want to feed. If you don’t have any complications, your midwife will help you get skin-to-skin with your baby quickly after they are born. Some reluctant babies are just too tired, sore, or sedated to feed after birth, and others can't because they are premature, ill or jaundiced.
What if I miss my baby's signs that they're hungry?
New mums sometimes miss or don't understand their baby's feeding signs – our page about learning your baby's cues explains what you should be looking for. Don’t worry if it takes a while to get used to when your baby wants a feed – it's something you are both learning together and it's baby steps for both of you. It's completely understandable to be worried about how much milk your baby is getting if they're not feeding in the early hours and days. It might help to know that babies are born with several days' supply of fluid and stored fat to get them by until they're ready to feed.
It's completely understandable to be worried about how much milk your baby is getting if they're not feeding in the early hours and days. It might help to know that babies are born with several days' supply of fluid and stored fat to get them by until they're ready to feed.
What's the solution?
Your midwife will check in on you to make sure your baby is well and to help you spot the signs that they're ready to feed – remember you can ask your midwife (in the hospital or at home) to help show you how to get in a comfortable position to help get your baby feeding. This video shows just this – very often all it takes is some help with positioning, skin-to-skin contact and a little patience!
Top tips to encourage a reluctant or sleepy baby to breastfeed
Tip #1: Hand expressing to keep your milk supply up
Start hand-expressing your colostrum – this is the first milk you make, and helps protect your baby from illness and infection. You can give this to your baby by syringe, spoon, dropper or cup. Expressing helps to build a good milk supply for when your baby is ready to feed. If this is your first time breastfeeding, it will take some time to get used to expressing your milk. You can find out more about expressing here.
You can give this to your baby by syringe, spoon, dropper or cup. Expressing helps to build a good milk supply for when your baby is ready to feed. If this is your first time breastfeeding, it will take some time to get used to expressing your milk. You can find out more about expressing here.
In the first couple of days you only make small amounts of colostrum so don’t become disheartened if it is difficult or takes time. It will get easier as each day and week goes by.
Tip #2: Try lots of skin-to-skin contact
Aim for lots of skin contact and being close to soothe your baby and give them the opportunity to feed.
Tip #3: Try to find a comfortable feeding position
Biological 'laid back' breastfeeding positions can help encourage babies to feed. Your midwife will be able to show you comfortable ways to feed. You can find out more about feeding positions here.
Tip #4: Get your baby ready for a feed
Massaging your baby's skin, changing their nappy and expressing a little milk for them to taste can help get your baby interested in feeding.
Tip #5: Don’t force your baby to feed
Don’t push your baby by the head or try to force them to feed as this could put them off completely.
Getting to know your baby
Learning your baby's cues
Signs your baby isn't getting enough milk
Refusing the breast
Looking after yourself with a newborn
The Scotland wide donor milk bank
This article was created as part of
Last updated: 31 May, 2022
Feeding Your Newborn (for Parents)
How you feed your newborn is the first nutrition decision you make for your child. These guidelines on breastfeeding and bottle feeding can help you know what's right for you and your baby.
These guidelines on breastfeeding and bottle feeding can help you know what's right for you and your baby.
Breast or Bottle?
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommends that babies be breastfed exclusively for about the first 6 months. After they start on solid foods, babies should breastfeed through the first year of life and even beyond, if desired.
But breastfeeding isn't possible or preferable for all new moms. Deciding to breastfeed or bottle feed a baby is usually based on the mother's comfort level with breastfeeding and her lifestyle. In some cases, breastfeeding may not be recommended for a mom and her baby. If you have any questions about whether to breastfeed or formula feed, talk to your pediatrician.
Remember, your baby's nutritional and emotional needs will be met whether you choose to breastfeed or formula feed.
Benefits of Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding your newborn has many benefits. Perhaps most important, breast milk is the perfect food for a baby's digestive system. It has the nutrients that a newborn needs, and it’s easily digested. Commercial formulas try to imitate breast milk, and come close, but can't match it exactly.
It has the nutrients that a newborn needs, and it’s easily digested. Commercial formulas try to imitate breast milk, and come close, but can't match it exactly.
Breast milk has
antibodiesthat help protect babies from many infections, including diarrhea and ear and lung infections. Breastfed babies are less likely to develop medical problems such as diabetes, high cholesterol, asthma, and allergies. Breastfeeding also might make a child less likely to become overweight.
Breastfeeding is great for moms too. It burns calories, so can help nursing moms lose the weight gained during pregnancy. Breastfeeding also may offer protection from breast cancer and ovarian cancer.
Some moms find breastfeeding easier and quicker than formula feeding — it needs no preparation, and you don't run out of breast milk in the middle of the night. Also, breastfeeding costs little. Nursing mothers do need to eat more and may want to buy nursing bras and pads, a breast pump, or other equipment.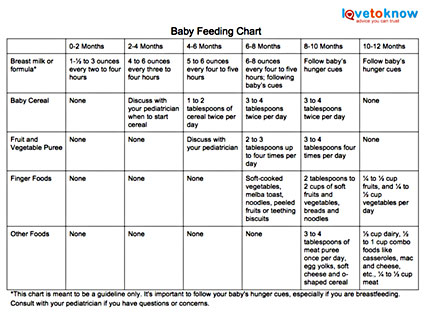 But these expenses are generally less than the cost of formula.
But these expenses are generally less than the cost of formula.
Breastfeeding meets a variety of emotional needs for both moms and babies. The skin-to-skin contact can enhance the emotional connection, and providing complete nourishment can help new moms feel confident in their ability to care for their newborn.
Limitations of Breastfeeding
With all the good things known about breastfeeding, why doesn't every mother choose to breastfeed?
Breastfeeding requires a big commitment from a mother. Some new moms feel tied down by the demands of a nursing newborn. Because breast milk is easily digested, breastfed babies tend to eat more often than babies who are fed formula. This means moms can be in demand as often as every 2 or 3 hours in the first few weeks. This can be tiring, but it's not long before babies feed less often and sleep longer at night.
Some new mothers need to get back to work outside the home or separate from their babies from time to time for other reasons.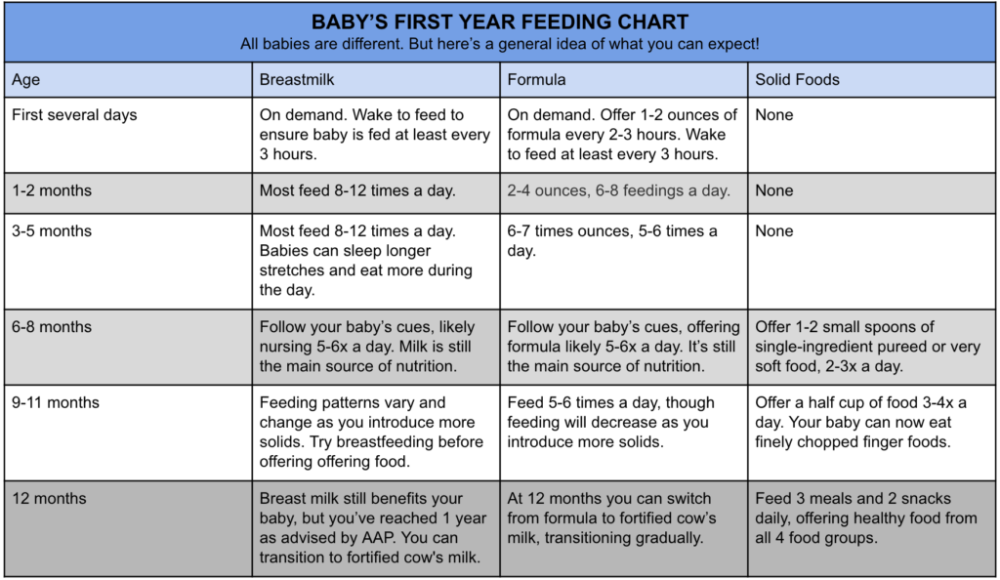 Some opt for formula feeding so other caregivers can give the baby a bottle. Mothers who want to continue breastfeeding can use a breast pump to collect breast milk to be given in a bottle, so their babies still get its benefits even when mom isn't there to breastfeed.
Some opt for formula feeding so other caregivers can give the baby a bottle. Mothers who want to continue breastfeeding can use a breast pump to collect breast milk to be given in a bottle, so their babies still get its benefits even when mom isn't there to breastfeed.
Fathers and other family members may want to share in feeding the baby. When mom is breastfeeding, dad or siblings may want to stay close by. Helping mom get comfortable, or providing a burp cloth when needed, will let them be part of the experience.
When breastfeeding is going well, other family members can help by giving the baby pumped breast milk in a bottle when mom needs a break.
Some moms may feel embarrassed or worried about breastfeeding. These feelings usually end after a successful breastfeeding process is set. It can help to get advice from those who've gone through the experience. Most hospitals and birthing centers offer in-depth instruction on breastfeeding to new moms. Your pediatrician, nurse practitioner, or nurse can answer questions or put you in touch with a lactation consultant or a breastfeeding support group.
In some cases, a mother's health may affect her ability to breastfeed. Moms getting chemotherapy for cancer and those who have HIV should not breastfeed, for example.
If you have a medical condition or take any medicines regularly, talk with your doctor about whether it's OK to breastfeed. If you have to stop nursing temporarily, continue to pump breast milk to maintain milk production. If you or your baby are sick, continue to breastfeed if you can. Talk to the doctor if you have any concerns.
In some situations, it may not possible to breastfeed, such as when a baby is very sick or born early. Mothers should talk with their baby's doctor about expressing and storing milk. Often, a baby who can't breastfeed can get breast milk through a feeding tube or bottle.
Some moms who have inverted nipples may have trouble breastfeeding, but a lactation consultant usually can help them overcome this. Likewise, women who have had plastic surgery on their breasts should be able to successfully breastfeed. Talk with your doctor if you have any concerns.
Talk with your doctor if you have any concerns.
Hold off on pacifiers or bottles until your baby has gotten used to and is good at breastfeeding. Lactation professionals recommend waiting until a baby is about 3–4 weeks old before offering artificial nipples of any kind (including pacifiers).
Benefits of Formula Feeding
Commercially prepared infant formula is a nutritious alternative to breast milk. Bottle feeding can offer more freedom and flexibility for moms, and make it easier to know how much the baby is getting.
Because babies digest formula more slowly than breast milk, a baby who is getting formula may need fewer feedings than one who breastfeeds. Formula feeding also can make it easier to feed the baby in public, and lets the father and other family members help feed the baby, which can enhance bonding.
Limitations of Formula Feeding
Just as breastfeeding has its unique demands, so does bottle feeding. Bottle feeding takes organization and preparation, especially if you want to take your baby out. Store-bought formula can be pretty expensive, but do not try to make your own formula at home.
Store-bought formula can be pretty expensive, but do not try to make your own formula at home.
It's important to make sure that you have enough formula on hand, and bottles that are clean and ready to be used.
Here are a few guidelines for formula feeding:
- Carefully follow directions on the label when preparing formula. Do not add more water than directed.
- Bottles left out of the refrigerator longer than 1 hour and any formula left in the bottle that a baby doesn't finish should be discarded.
- Prepared bottles of formula can be stored in the refrigerator up to 24 hours and carefully warmed just before feeding. You don't have to warm formula, but most babies prefer it.
- A bottle of formula can be warmed by holding it in running warm water or setting it in a pan of warm water. A bottle of formula (or breast milk) should never be warmed in a microwave. The bottle can heat unevenly and leave "hot spots" that can burn a baby's mouth.

How Often Do Newborns Eat?
Your newborn will nurse about 8 to 12 times per day during the first weeks of life. In the beginning, mothers may want to try nursing 10–15 minutes on each breast, then adjust the time as needed.
Breastfeeding should be on demand (when your baby is hungry), which is generally every 1–3 hours. As newborns get older, they'll nurse less often and have longer stretches between feedings. Newborn babies who are getting formula will likely take about 2–3 ounces every 2–4 hours. Newborns should not go more than about 4–5 hours without feeding.
Signs that babies are hungry include:
- moving their heads from side to side
- opening their mouths
- sticking out their tongues
- placing their hands and fists to their mouths
- puckering their lips as if to suck
- nuzzling against their mothers' breasts
- crying
A feeding schedule is not necessary — you and your baby will get into a routine. Babies know (and will let their parents know) when they're hungry and when they've had enough. Watch for signs that your baby is full (slowing down, spitting out the bottle or unlatching from breast, closing the mouth, turning away from the breast or bottle) and stop the feeding when these signs appear.
Babies know (and will let their parents know) when they're hungry and when they've had enough. Watch for signs that your baby is full (slowing down, spitting out the bottle or unlatching from breast, closing the mouth, turning away from the breast or bottle) and stop the feeding when these signs appear.
As babies grow, they begin to eat more at each feeding and can go longer between feedings. There may be other times when your infant seems hungrier than usual. Continue to nurse or feed on demand. Nursing mothers need not worry — breastfeeding stimulates milk production, and your supply of breast milk will adjust to your baby's demand for it.
Is My Newborn Getting Enough to Eat?
New parents often worry about whether their babies are getting enough to eat.
Babies are getting enough to eat if they:
- seem satisfied
- have about 6–8 wet diapers a day
- have regular bowel movements (poops)
- sleep well
- are alert when awake
- are gaining weight
A baby who is fussing, crying, seems hungry, does not appear satisfied after feeding, and has fewer wet diapers may not be getting enough to eat. If you're concerned that your baby isn't getting enough to eat, call your doctor.
If you're concerned that your baby isn't getting enough to eat, call your doctor.
Most infants "spit up" a small amount after eating or during burping, but a baby should not vomit after feeding. Vomiting after every feeding might be a sign of an allergy, digestive problem, or other problem that needs medical care. If you have concerns that your baby is spitting up too much, call your doctor.
Should Newborns Get Nutritional Supplements?
Breast milk has the right combination of vitamins and easily absorbed iron for newborns. A healthy infant being nursed by a healthy mother doesn't need extra vitamins or nutritional supplements, with the exception of vitamin D. Breastfed babies should begin vitamin D supplements within the first few days of life, continuing until they get enough vitamin D-fortified formula or milk (after 1 year of age).
Breastfeeding mothers who follow vegetarian diets that do not include animal products need vitamin B12 supplements.
Iron-fortified formula has the right blend of vitamins and minerals for a baby, so supplements usually aren't needed.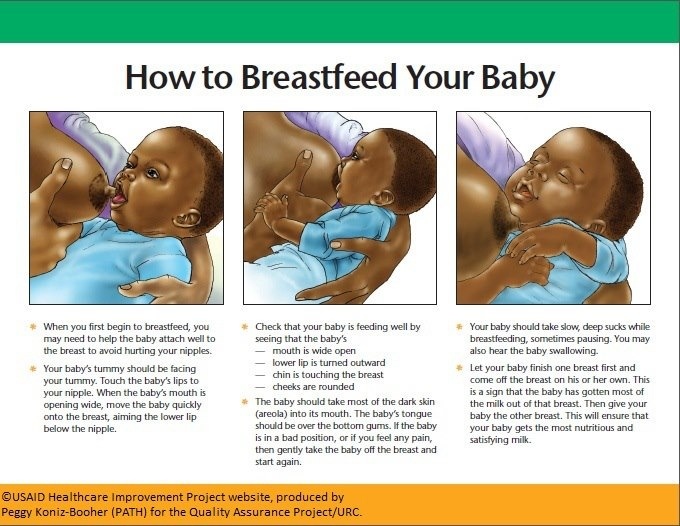 Infants drinking less than 1 liter, or about a quart, of formula a day may need a vitamin D supplement.
Infants drinking less than 1 liter, or about a quart, of formula a day may need a vitamin D supplement.
Water, juice, and other foods usually aren't necessary during a baby's first 6 months. Breast milk and formula provide everything babies need nutritionally until they start eating solid foods. Talk to your doctor if you have any questions about feeding your newborn.
Reviewed by: Mary L. Gavin, MD
Date reviewed: February 2021
If the child does not eat well: what to do and what not to do
What to do if the child does not want to eat.
- Malyusik, well, one more spoon - and that's it! Last! I ate only two, let's have a little more, here's the most delicious piece for you! - says the average mother, offering a spoon with one hand, playing the accordion with the other, showing the trick with the disappearance of the handkerchief with the third, turning the cutlets over with the fourth, while doing somersaults on one leg.
Sound familiar?
Every dad has an instinct to bring home food, and mom has to feed the baby food. And if he refuses to eat, a signal is triggered - "I'm a bad mother" or "the child is sick."
And if he refuses to eat, a signal is triggered - "I'm a bad mother" or "the child is sick."
In this case, the most important thing for a parent to understand is whether the child DOES NOT WANT or CANNOT eat?
If the baby is running around, having fun and looking good, without showing any signs of illness, then most likely he does not want to eat. There can be many reasons:
- A breastfeeding child prefers milk and dairy products, intuitively understanding that he needs calcium, and now milk is healthier for him than soup.
- The child wants a cookie, not vegetables.
- He really wasn't hungry. For example, his metabolism is slow, breakfast has not yet been digested, and lunch is already being offered. Or the child was sitting in front of the TV after breakfast and his appetite had not yet had enough time to play out. Compared to the boy next door who was outside all day.
- If a child is not genetically destined to become Uncle Styopa, then he can eat much less than his peer, who has tall parents.
- Psychological problems. If earlier you accidentally gave your child a bitter cucumber, then he may refuse any green food. Or you yell at the child during the meal, and for him the food is perceived as a trauma.
If your child is lively, but at the same time he has a "bad appetite", then this is not his problem, but yours - the psychological problem of an unsatisfied instinct. If a child jumps, jumps, he has healthy nails, hair, etc., think less about what he lacks. Better think about something nice))
An active child = not a hungry child.
Wait for the natural desire and correctly distribute energy costs - walk more often, send the child to the sports section, or simply say: “If you don’t want to, take a walk, dinner is not earlier than seven and no snacks.” That is, if your child simply does not want to eat, normalize feeding - strictly at a certain time and without snacks. The body will get used to secrete gastric juice strictly according to the schedule.
And one more thing. There are no rules about how much a child should eat. He can eat a kilo (and make you very happy) and 9Send 00 grams to the toilet. Or eat 100 g and learn everything.
But it is much more difficult if the child CANNOT eat.
Causes:
- If you are breastfeeding, you may have “tight breasts”, when it is very difficult for the baby to suck milk.
- The child has a runny nose, and when he eats, he begins to choke.
- Food hot, cold, sour, bitter.
- He has sores in his mouth (for example, from toys), and they hurt when food gets on them.
- Teeth are cut, gums hurt.
- Bowel problems. The stomach starts to hurt while eating.
- The child simply fell ill (cold, SARS, poisoning, influenza, etc.). If the child is sick, and he is not dystrophic, then you should not force him to eat. The body fights infections better when it's hungry. But be sure to drink.
If a child at first shows appetite and interest in food, but refuses to eat through a spoon or two, then, most likely, the process of eating causes him certain difficulties.
If the baby CANNOT eat and you can't identify or eliminate the cause, the best thing to do is contact your pediatrician. The doctor will accurately determine the problem and give the necessary recommendations.
Our clinic has a wonderful pediatrician Yuliya Vladimirovna Sinyagina with 17 years of experience! You can sign up to her))
Bon appetit everyone! As well as strength, patience and satisfied instincts!
Back to the list of articles
five ways to make life easier for a baby with constipation0001
Why it's so important to go potty early in the morning and how dried fruit can help your bowels.
Constipation is delayed, difficult or systematically insufficient bowel movement. And constipation in children is a problem that parents often face. About whether it is worth worrying if the baby rarely goes to the potty, in which cases it is important to consult a doctor, and in which it is possible to solve the problem on your own, says the famous pediatrician, candidate of medical sciences, TV presenter Evgeny Komarovsky.
Evgeny Komarovsky
famous pediatrician, candidate of medical sciences, TV presenter
“Very often, constipation is not an independent disease, but only a symptom of peptic ulcer, hemorrhoids, pancreatitis, cholecystitis, dysfunction of the thyroid gland”
– When it comes to about children of the first year of life, then in one case for several thousand constipation may be the result of the so-called Hirschsprung's disease, continues Evgeny Komarovsky. - This is a congenital disease in which nerve cells are not developed in one of the sections of the intestine, which is why peristalsis is disturbed and fecal masses accumulate in the intestine. In this case, there is only one way out - an operation.
In a word, the child's constant problems with stool should encourage parents to contact a gastroenterologist, who would rule out diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
It is normal for babies to hold stools
Every baby has a different bowel movement frequency, which depends on many factors. And here it is important to remember this:
And here it is important to remember this:
- In infants, a rare bowel movement almost always indicates that the food that the child eats is of high quality, suits him perfectly and is almost completely absorbed, - says Evgeny Komarovsky. - And if the baby is fed breast milk or an adapted formula, if you introduce the right complementary foods on time, but the baby does not poop for up to six days in a row, this is normal. Provided, of course, that this does not cause him discomfort and does not affect his well-being and development.
The better the food is digested, the less often the baby goes to the potty.
That is why the problem is most often not in the child, but in his environment.
– Grandmothers, having learned that the baby has not gone to the potty for two days, immediately begin to lament about this, advise him to “treat” him with folk methods, and mothers worry and look longingly into an empty pot, says Evgeny Olegovich. - In this case, the cause of stool retention may be, for example, excessive mother's care. Judge for yourself. Let's say mom has two potatoes. She can cook them in uniform and give them to a child, while he will absorb 80% of this dish, the rest will come out naturally. Or mom can cook them, clean them, knead them properly, add milk and butter. It will turn out a liquid puree, which will be absorbed almost entirely. There is simply nothing to leave the body!
Judge for yourself. Let's say mom has two potatoes. She can cook them in uniform and give them to a child, while he will absorb 80% of this dish, the rest will come out naturally. Or mom can cook them, clean them, knead them properly, add milk and butter. It will turn out a liquid puree, which will be absorbed almost entirely. There is simply nothing to leave the body!
Five rules for treating constipation
If your doctor is sure that constipation is not a symptom of something serious, you can try to manage it yourself. What do you need to pay attention to?
1. The child must not be dehydrated.
Lack of fluid is one of the most common causes of constipation in children. At the same time, stool masses become thick, slowly move along the intestines, scratch its walls, which causes pain and colic. Yes, and the urge to go to the toilet occurs only when the accumulated masses begin to put pressure on the walls of the rectum, while water helps to increase their volume, and the baby poops faster. So we give more to drink and moisturize the nursery!
So we give more to drink and moisturize the nursery!
2. There must be enough potassium in the body.
With a lack of potassium, intestinal contractions (the so-called peristalsis) are sharply weakened, and this may well be the cause of constipation. Most potassium in raisins, dried apricots, prunes, figs, which, by the way, can be added to compotes or eaten simply steamed.
3. Complete diet rich in fiber.
For constipation, foods rich in protein, such as chocolate, cottage cheese, nuts, are undesirable. Yogurts, one-day kefir and yogurt are desirable. Black bread is better than white bread. Apple juice is better than a whole apple. Meat is better to limit. In general, fiber is an excellent prevention of constipation. This means that the child needs to be given more fruits and vegetables, as well as cereals, preferably slightly undercooked.
If lactulose and glycerin suppositories do not help, see a doctor.
4. Safe medicines.
Safe medicines.
There are only two drugs that can be used even in infants and without a doctor's prescription. The first is lactulose syrup, which is sold under various commercial names in any pharmacy. It increases the volume of feces, retaining water in the intestines, does not cause "addiction", you can take it for as long as you like. True, at the first dose, the baby may form gaziki - as a reaction to the drug, so it is better to increase the dose gradually. The second is candles with glycerin. Their advantage is that glycerin is not absorbed by the body, but is released along with the contents of the intestine, while such suppositories act much softer than an enema.
If the cause of constipation is cracks in the anus (appeared, for example, after passing lumps of hard feces), because of which the child simply does not want to go to the potty, fearing pain, suppositories with sea buckthorn oil will help.
5. Daily routine.
It happens that the urge to go out to eat, the child feels it, but ignores it - for example, he is very busy or simply does not want to go to the toilet in the garden or at school, preferring to wait until he gets home. If this behavior becomes systematic, then the rectum begins to stretch from excess feces, and in order to feel the urge to go to the toilet, the child needs more and more time. Hence - constipation, which has to be treated for a very long time.
If this behavior becomes systematic, then the rectum begins to stretch from excess feces, and in order to feel the urge to go to the toilet, the child needs more and more time. Hence - constipation, which has to be treated for a very long time.
In order to prevent this, it is important to teach your baby to systematic bowel movements from childhood. Better - at the same time and in the same familiar environment. Let him go potty before bed or after breakfast, before leaving the house.
If all of the above do not help, seek medical attention. It is important to understand that specialists have a much larger set of constipation treatment regimens than parents.
Know!
- Constipation and iron
Constipation is a common side effect of iron supplements prescribed for low hemoglobin. Solution: start taking iron at a dose 2-4 times less than according to the instructions, and gradually increase it.
- Prunes will help
Evgeny Komarovsky talks about products that in 25% of cases help to cope with constipation in a child without any medication.