Proper baby feeding
Feeding Your Newborn (for Parents)
How you feed your newborn is the first nutrition decision you make for your child. These guidelines on breastfeeding and bottle feeding can help you know what's right for you and your baby.
Breast or Bottle?
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommends that babies be breastfed exclusively for about the first 6 months. After they start on solid foods, babies should breastfeed through the first year of life and even beyond, if desired.
But breastfeeding isn't possible or preferable for all new moms. Deciding to breastfeed or bottle feed a baby is usually based on the mother's comfort level with breastfeeding and her lifestyle. In some cases, breastfeeding may not be recommended for a mom and her baby. If you have any questions about whether to breastfeed or formula feed, talk to your pediatrician.
Remember, your baby's nutritional and emotional needs will be met whether you choose to breastfeed or formula feed.
Benefits of Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding your newborn has many benefits. Perhaps most important, breast milk is the perfect food for a baby's digestive system. It has the nutrients that a newborn needs, and it’s easily digested. Commercial formulas try to imitate breast milk, and come close, but can't match it exactly.
Breast milk has
antibodiesthat help protect babies from many infections, including diarrhea and ear and lung infections. Breastfed babies are less likely to develop medical problems such as diabetes, high cholesterol, asthma, and allergies. Breastfeeding also might make a child less likely to become overweight.
Breastfeeding is great for moms too. It burns calories, so can help nursing moms lose the weight gained during pregnancy. Breastfeeding also may offer protection from breast cancer and ovarian cancer.
Some moms find breastfeeding easier and quicker than formula feeding — it needs no preparation, and you don't run out of breast milk in the middle of the night. Also, breastfeeding costs little. Nursing mothers do need to eat more and may want to buy nursing bras and pads, a breast pump, or other equipment. But these expenses are generally less than the cost of formula.
Also, breastfeeding costs little. Nursing mothers do need to eat more and may want to buy nursing bras and pads, a breast pump, or other equipment. But these expenses are generally less than the cost of formula.
Breastfeeding meets a variety of emotional needs for both moms and babies. The skin-to-skin contact can enhance the emotional connection, and providing complete nourishment can help new moms feel confident in their ability to care for their newborn.
Limitations of Breastfeeding
With all the good things known about breastfeeding, why doesn't every mother choose to breastfeed?
Breastfeeding requires a big commitment from a mother. Some new moms feel tied down by the demands of a nursing newborn. Because breast milk is easily digested, breastfed babies tend to eat more often than babies who are fed formula. This means moms can be in demand as often as every 2 or 3 hours in the first few weeks. This can be tiring, but it's not long before babies feed less often and sleep longer at night.
Some new mothers need to get back to work outside the home or separate from their babies from time to time for other reasons. Some opt for formula feeding so other caregivers can give the baby a bottle. Mothers who want to continue breastfeeding can use a breast pump to collect breast milk to be given in a bottle, so their babies still get its benefits even when mom isn't there to breastfeed.
Fathers and other family members may want to share in feeding the baby. When mom is breastfeeding, dad or siblings may want to stay close by. Helping mom get comfortable, or providing a burp cloth when needed, will let them be part of the experience.
When breastfeeding is going well, other family members can help by giving the baby pumped breast milk in a bottle when mom needs a break.
Some moms may feel embarrassed or worried about breastfeeding. These feelings usually end after a successful breastfeeding process is set. It can help to get advice from those who've gone through the experience. Most hospitals and birthing centers offer in-depth instruction on breastfeeding to new moms. Your pediatrician, nurse practitioner, or nurse can answer questions or put you in touch with a lactation consultant or a breastfeeding support group.
Most hospitals and birthing centers offer in-depth instruction on breastfeeding to new moms. Your pediatrician, nurse practitioner, or nurse can answer questions or put you in touch with a lactation consultant or a breastfeeding support group.
In some cases, a mother's health may affect her ability to breastfeed. Moms getting chemotherapy for cancer and those who have HIV should not breastfeed, for example.
If you have a medical condition or take any medicines regularly, talk with your doctor about whether it's OK to breastfeed. If you have to stop nursing temporarily, continue to pump breast milk to maintain milk production. If you or your baby are sick, continue to breastfeed if you can. Talk to the doctor if you have any concerns.
In some situations, it may not possible to breastfeed, such as when a baby is very sick or born early. Mothers should talk with their baby's doctor about expressing and storing milk. Often, a baby who can't breastfeed can get breast milk through a feeding tube or bottle.
Some moms who have inverted nipples may have trouble breastfeeding, but a lactation consultant usually can help them overcome this. Likewise, women who have had plastic surgery on their breasts should be able to successfully breastfeed. Talk with your doctor if you have any concerns.
Hold off on pacifiers or bottles until your baby has gotten used to and is good at breastfeeding. Lactation professionals recommend waiting until a baby is about 3–4 weeks old before offering artificial nipples of any kind (including pacifiers).
Benefits of Formula Feeding
Commercially prepared infant formula is a nutritious alternative to breast milk. Bottle feeding can offer more freedom and flexibility for moms, and make it easier to know how much the baby is getting.
Because babies digest formula more slowly than breast milk, a baby who is getting formula may need fewer feedings than one who breastfeeds. Formula feeding also can make it easier to feed the baby in public, and lets the father and other family members help feed the baby, which can enhance bonding.
Limitations of Formula Feeding
Just as breastfeeding has its unique demands, so does bottle feeding. Bottle feeding takes organization and preparation, especially if you want to take your baby out. Store-bought formula can be pretty expensive, but do not try to make your own formula at home.
It's important to make sure that you have enough formula on hand, and bottles that are clean and ready to be used.
Here are a few guidelines for formula feeding:
- Carefully follow directions on the label when preparing formula. Do not add more water than directed.
- Bottles left out of the refrigerator longer than 1 hour and any formula left in the bottle that a baby doesn't finish should be discarded.
- Prepared bottles of formula can be stored in the refrigerator up to 24 hours and carefully warmed just before feeding. You don't have to warm formula, but most babies prefer it.
- A bottle of formula can be warmed by holding it in running warm water or setting it in a pan of warm water.
 A bottle of formula (or breast milk) should never be warmed in a microwave. The bottle can heat unevenly and leave "hot spots" that can burn a baby's mouth.
A bottle of formula (or breast milk) should never be warmed in a microwave. The bottle can heat unevenly and leave "hot spots" that can burn a baby's mouth.
How Often Do Newborns Eat?
Your newborn will nurse about 8 to 12 times per day during the first weeks of life. In the beginning, mothers may want to try nursing 10–15 minutes on each breast, then adjust the time as needed.
Breastfeeding should be on demand (when your baby is hungry), which is generally every 1–3 hours. As newborns get older, they'll nurse less often and have longer stretches between feedings. Newborn babies who are getting formula will likely take about 2–3 ounces every 2–4 hours. Newborns should not go more than about 4–5 hours without feeding.
Signs that babies are hungry include:
- moving their heads from side to side
- opening their mouths
- sticking out their tongues
- placing their hands and fists to their mouths
- puckering their lips as if to suck
- nuzzling against their mothers' breasts
- crying
A feeding schedule is not necessary — you and your baby will get into a routine.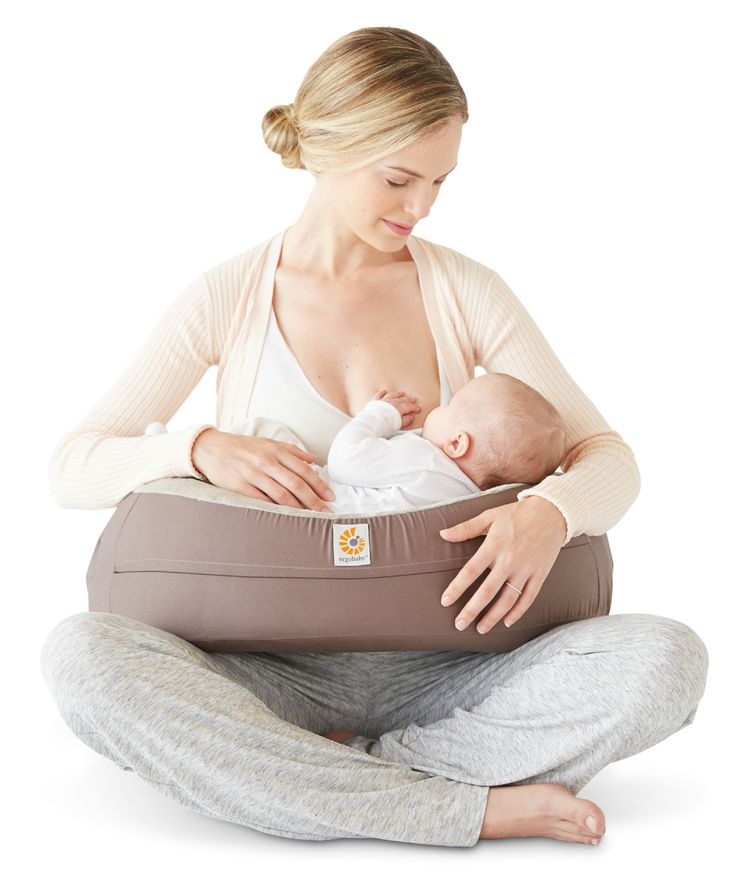 Babies know (and will let their parents know) when they're hungry and when they've had enough. Watch for signs that your baby is full (slowing down, spitting out the bottle or unlatching from breast, closing the mouth, turning away from the breast or bottle) and stop the feeding when these signs appear.
Babies know (and will let their parents know) when they're hungry and when they've had enough. Watch for signs that your baby is full (slowing down, spitting out the bottle or unlatching from breast, closing the mouth, turning away from the breast or bottle) and stop the feeding when these signs appear.
As babies grow, they begin to eat more at each feeding and can go longer between feedings. There may be other times when your infant seems hungrier than usual. Continue to nurse or feed on demand. Nursing mothers need not worry — breastfeeding stimulates milk production, and your supply of breast milk will adjust to your baby's demand for it.
Is My Newborn Getting Enough to Eat?
New parents often worry about whether their babies are getting enough to eat.
Babies are getting enough to eat if they:
- seem satisfied
- have about 6–8 wet diapers a day
- have regular bowel movements (poops)
- sleep well
- are alert when awake
- are gaining weight
A baby who is fussing, crying, seems hungry, does not appear satisfied after feeding, and has fewer wet diapers may not be getting enough to eat. If you're concerned that your baby isn't getting enough to eat, call your doctor.
If you're concerned that your baby isn't getting enough to eat, call your doctor.
Most infants "spit up" a small amount after eating or during burping, but a baby should not vomit after feeding. Vomiting after every feeding might be a sign of an allergy, digestive problem, or other problem that needs medical care. If you have concerns that your baby is spitting up too much, call your doctor.
Should Newborns Get Nutritional Supplements?
Breast milk has the right combination of vitamins and easily absorbed iron for newborns. A healthy infant being nursed by a healthy mother doesn't need extra vitamins or nutritional supplements, with the exception of vitamin D. Breastfed babies should begin vitamin D supplements within the first few days of life, continuing until they get enough vitamin D-fortified formula or milk (after 1 year of age).
Breastfeeding mothers who follow vegetarian diets that do not include animal products need vitamin B12 supplements.
Iron-fortified formula has the right blend of vitamins and minerals for a baby, so supplements usually aren't needed. Infants drinking less than 1 liter, or about a quart, of formula a day may need a vitamin D supplement.
Water, juice, and other foods usually aren't necessary during a baby's first 6 months. Breast milk and formula provide everything babies need nutritionally until they start eating solid foods. Talk to your doctor if you have any questions about feeding your newborn.
Reviewed by: Mary L. Gavin, MD
Date reviewed: February 2021
How to Bottle-Feed a Baby
Whether you’re breastfeeding, formula-feeding or doing a combination of both, chances are you’ll eventually use a bottle with your infant. No big deal, right? But while images of a parent blissfully holding a bottle make the process look easy, there’s a learning curve when it comes to proper bottle-feeding. Here, everything you need to know about how to bottle-feed a baby safely and happily.
In this article:
How to choose the right bottle and nipple
How to make a baby bottle
Best bottle-feeding positions
What is pace feeding?
How to get baby to take a bottle
When to wean baby off the bottle
How to Choose the Right Bottle and Nipple
When it comes to figuring out how to bottle-feed a baby, selecting an appropriate bottle and nipple is step one. If people gifted you a bunch of bottles at your baby shower, you may want to hold off before opening and sterilizing them until baby is born, or at least take out just a few to try in the early days of feeding. Why? Because you won’t know what kind of bottle is best until you figure out what baby’s feeding needs are.
“Certain bottles work better for certain babies,” explains Jamie O’Day, BSN, RN, CLC, a registered nurse, certified lactation consultant and cofounder of Boston NAPS, a pre- and postnatal resource center in the Boston area. “For example, some babies who have issues with gas may do better with a bottle that has a filtration system, like a Doctor Brown’s style bottle, while babies who are used to being breastfed may have more success drinking from a bottle that aims to mimic the shape and feel of a mother’s breast, like the Comotomo.”
That said, O’Day has a universal tip for all parents: Look for a bottle that’s easy to take apart and clean. That generally means a nice wide neck and the fewest parts possible. “Proper cleaning is so important, so I always tell parents to choose the simplest bottle, which may just have a nipple, bottle and collar,” she says. If your child seems happy and easily takes the bottle, then there’s no need to switch.
Of course, it’s not just the bottle that you have to consider. It’s also important to pay attention to the flow of the nipple, which varies based on infant age. Generally speaking, young babies need a slower flow, while older babies who’ve mastered the art of bottle-feeding can handle a faster flow. The nipple may be called “slow flow,” “medium flow” or “fast flow” or may be numbered from one to three, with one being the slowest flow. There is no standard of flow between different brands, but most newborns should begin on level one or slow flow.
So how can you tell when it’s time to change the nipple size? That depends. Some infants happily use the same flow nipple throughout their infancy, while others may need a faster flow nipple. “If you notice your child taking a long time to finish a bottle, or losing interest midway through feedings, a faster flow nipple may be needed,” O’Day says, adding that this might happen at around 3 or 4 months of age, with another potential upgrade around 6 or 7 months.
If your infant finishes a bottle quickly (say, under five minutes), seems gassy or cranky, or spits up a lot of milk right after feedings, it may be time to go back to a slower-flow nipple. Your pediatrician can also help determine if it may be time to switch the flow of the nipple.
How to Make a Baby Bottle
If you’re wondering how to bottle-feed a baby, you’re probably new to prepping baby bottles. Take a new skill, add in sleep deprivation and sprinkle in some very real safety concerns and you’ve got the somewhat daunting process of making a baby bottle (at least at first). Don’t despair. By reading directions, following the advice of a pediatrician and making sure to err on the side of caution, you’ll get the hang of it in no time.
How to make a baby bottle with formula
Baby formula comes in three different forms: ready-to-feed, concentrate and powder. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends that babies under 3 months start off with ready-to-feed formula because of the small but real risk of cronobacter, a bacteria that can live in powdered infant formula.
• Preparing ready-to-feed formula: These require very little prep, since they come ready to be poured into a bottle and fed to an infant. Some ready-to-feed formulas come in bottles that can accomodate disposable nipples—all you need to do is screw a nipple on, feed and discard.
• Preparing concentrate formula: To prepare a baby body with this liquid formula, you’ll need to add water. It’s important to read the directions to learn the right ratio of water to concentrate. As for what type of water should you use, that depends on where you live, your pediatrician’s recommendation and your own wishes. If your tap water is safe, feel free to use it—just run it for several minutes before you fill the bottle to remove any trace contaminants in the water. You can also use filtered water, bottled water or boiled (and cooled) tap water.
• Preparing powdered formula: Just like concentrate, it’s important to follow directions on the right ratio of scoops of powder to ounces of water, says Carmen Baker-Clark, an International Board Certified Lactation Consultant (IBCLC) in Hoboken, New Jersey. When using powdered formula, make sure to shake well so the liquid isn’t clumpy. “Some parents notice powdered formulas may make their infant more gassy, more prone to spit-up or more constipated. A lot of this is due to the bottle preparation. For example, not shaking enough can create uneven consistency that may be harder for baby to digest,” Baker-Clark explains.
Regardless of what kind of formula you choose, Baker-Clark recommends sticking with the same brand or being deliberate as you try new ones, instead of just using whatever formula is on sale. While all infant formulas are regulated by the FDA and must pass the same nutrient tests, babies may react differently to various brands of formula. If an infant has frequent reflux, crying episodes or seems uncomfortable after a feeding, speak with your pediatrician. Your child may have an allergy or intolerance and may need a special formula.
Whether you warm the bottle up is up to you. “Many infants have no problem taking a cold bottle and the advantage is that you then don’t need to warm a bottle when you’re on the go,” Baker-Clark says. Once a formula bottle has been made and the nipple has touched baby’s lips, the bottle is good for an hour. But if the bottle isn’t used, a bottle may be refrigerated for a day, O’Day says. Some parents like to prepare and refrigerate a bottle in advance to make middle-of-the-night feedings easier, while others may prepare a pitcher to use during the day.
How to make a baby bottle with breast milk
Preparing a bottle of breast milk is of course much more straightforward, since the milk itself is ready to go. But when grabbing a bag of breast milk to use, it’s important to keep an eye on when it was pumped and how it’s been stored since. According to breast milk storage guidelines, it’s safe to use freshly pumped milk that’s been stored at room temperature for up to four hours, in the fridge for up to four days or in the freezer for up to 12 months. Always use the oldest milk first. If baby doesn’t finish a bottle, you can offer it again within two hours of the last feeding.
Before giving baby the bottle, you can warm the milk up by placing the bottle (or milk storage bag) in a cup of warm water for a few minutes, or pop the bottle into a bottle warmer. Whatever you do, steer clear of the microwave, which can cause dangerous hot spots.
Best Bottle-Feeding Positions
How you hold your little one during a feeding is a crucial part of knowing how to bottle-feed a baby properly. Chances are, you’ve come across loads of images of parents bottle-feeding babies—but the positions you sometimes see in photos or on TV may not actually be the best for baby. For one, forget about laying baby across your lap. “Have you ever easily drank something while you lay on your back?” O’Day asks. (Answer: no.) “It’s the same for baby.” Not only can a back position lead to reflux, but it may also cause ear infections. Try these bottle-feeding positions instead:
• Cradle baby in your arms. This is the classic position you probably think of when you imagine giving baby a bottle. In this bottle-feeding position, baby’s head rests in the crook of your arm as you hold her head and chest at a slight incline—close to your chest is great.
• Hold baby upright. Instead of lying down, baby should be almost in a seated position, with his head on your chest or in the crook of your arm. “This position can work especially well for infants who have reflux,” Baker-Clark says. Tilt the bottle so the milk completely fills the nipple, since a nipple filled only halfway with milk may lead to baby gulping some air, which can lead to gassiness or reflux.
• Use a pillow. A nursing pillow can be helpful in keeping baby’s chest and head propped up at an angle. Bonus: It can give your arms a break too as you cradle baby in your lap.
• Switch sides. Regardless of whether you’re breastfeeding or bottle-feeding exclusively, switching baby from one side to another can help prevent your little one from developing a side preference and can give your arms a break. Switching sides can also naturally pace a feeding session and can give baby a chance to decide whether or not he’s full before the bottle is finished.
As baby gets older, she may toy with holding the bottle. That’s fine, if she wants to, but it’s not a developmental milestone. “She may want to hold the bottle at 6 months, so you can let her, but you should still be close by, holding her and supervising her,” O’Day says. And if baby doesn’t show any interest in holding her bottle? As long as she’s reached other developmental milestones, like reaching or grasping for toys, it’s totally normal if your older infant wants his bottle served to him.
What is Pace Feeding?
You may have heard of “pace feeding” and wondered how to bottle-feed a baby using this method. “Paced bottle-feeding is where you follow baby’s cues and allow for breaks,” Baker-Clark says. “Taking the bottle away and re-offering it benefits both breastfed and exclusively bottle-fed babies.”
Pace feeding helps babies learn to regulate their hunger and allows ample time for digestion. It can also cue you into baby’s biorhythm, O’Day says. You may find baby doesn’t uniformly eat the same size bottle at each time of day. For example, maybe he’s extra hungry in the morning and drinks 8 ounces, but prefers 4-ounce bottles post-nap. Paying attention to baby’s cues can help you clue into her unique needs and natural schedule.
Plus, paced bottle-feeding makes a feeding session—which can last about 15 to 20 minutes—a great time for baby and his caregiver to bond. Here, some tips for how to pace feed:
• Hold the bottle at a horizontal angle. When the bottle is held horizontally, baby has to work to pull milk from the bottle, instead of the milk dripping into her mouth.
• Give baby some breaks. Instead of pulling the bottle away from baby’s mouth, lean the bottle back so the milk leaves the nipple. That way, baby has a chance to catch his breath. If he seems like he’s still rooting for milk, offer him more.
• Burp mid-feed. “If baby is pulling away, seems fussy or seems to be playing with the nipple with her mouth, give her a burp,” O’Day says. Then offer the bottle again.
How to Get Baby to Take a Bottle
Even if you’re planning to exclusively breastfeed, at some point you’ll likely need some pointers on how to get baby to take a bottle. “I tell my clients to introduce baby to a bottle once breastfeeding has been established, which depends on each mother-baby dyad, but on average, it’s around one month,” O’Day says. “Even if they’re not planning to regularly bottle-feed, doing so can give peace of mind if an emergency comes up, and can also be a way for mom to get a break.”
Some babies take a bottle no problem—after all, sucking is an instinctive reflex, which is why bottle-fed babies tend to get the hang of it in the first few days of life. But other breastfed babies may initially be reluctant to take a bottle. And sometimes breastfed babies have no issue taking a bottle when they’re one month old, but if a bottle hasn’t been regularly offered, by 3 or 4 months of age, they’re less happy to accept a bottle. Bottle resistance is pretty common, but luckily there are some tried-and-true tips for what to do when baby is refusing a bottle.
• Offer often. Even if you’re breastfeeding, O’Day recommends giving baby at least one bottle a week, once breastfeeding has been established. “That way it’s part of their routine, so they’re less likely to resist it,” she says.
• Don’t offer it when baby is starving. If you’re regularly nursing your infant, O’Day suggests offering a bottle in between nursing sessions. “If they’re too hungry, they may be too worked up to take a bottle. If they’re calm and not super hungry, they may take it,” she explains.
• Let others try bottle-feeding. Some moms have success leaving the house and allowing their partner to try feeding baby a bottle. Again, try it at a time that’s not baby’s “must-feed” time.
• Don’t get frustrated. If baby isn’t taking the bottle, O’Day suggests putting it down and trying again later rather than forcing it, which can make both you and baby upset.
• Ask for help. A lactation consultant can suggest some techniques to help get even the most resistant bottle-feeders to accept a bottle. They may check your infant’s mouth and tongue for any latch problems that could contribute to the difficulty, suggest the best bottle for your infant, troubleshoot any behavioral issues or offer alternate nutritive methods, such as cup- or syringe-feeding.
When to Wean Baby Off the Bottle
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends parents stop offering bottles by 18 months due to tooth decay concern, but it’s smart to talk with your pediatrician about exactly when baby should wean from the bottle around the 9-month mark, O’Day says. “How and when to wean depends on how much table food baby is eating, any developmental concerns and your pediatrician’s assessment,” she says. Note, though, that cow’s milk shouldn’t be introduced until baby is 12 months old.
When baby is around 6 months old, offer a sippy cup or straw cup for water, O’Day says, since learning to drink from cups can help make the transition from bottles seamless. Some babies have no problem giving up the bottle, while others may require more time to make the transition, but looping in your pediatrician or lactation consultant can help make sure you’re all on the right track.
Whether you’re breastfeeding and offering the occasional bottle, combo-feeding or exclusively bottle-feeding, you might hit some bumps along your bottle-feeding journey. But there are ways to navigate through any problems that arise. If you’re struggling to find the best baby bottle for your child, need some pointers on how to bottle-feed a baby in an optimal position or encounter a full-on bottle strike, reach out to your pediatrician or lactation consultants for guidance.
Published August 2018
Please note: The Bump and the materials and information it contains are not intended to, and do not constitute, medical or other health advice or diagnosis and should not be used as such. You should always consult with a qualified physician or health professional about your specific circumstances.
Plus, more from The Bump:
14 Best Bottles for Every Feeding Need
Pumping 101: How to Pump Breast Milk
The Best Baby Formulas for Your Child’s Needs
Breastfeeding rules
Breastfeeding rules and techniques.
Every woman can breastfeed her baby.
All troubles arise from ignorance of the rules and techniques of feeding.
The first rule is very important - early contact of the mother with the child in the maternity hospital, in the first minutes after birth.
Psychological benefits of breastfeeding.
Breast milk has a positive effect on the formation of the emotional and intellectual sphere, the development of creative abilities.
- emotional connection from both mother and child:
- close, loving relationship between mother and child;
- - emotional satisfaction of mother and child;
- - the child cries less, positive emotions are formed;
- - the mother becomes more affectionate, attachment to the child appears, self-confidence; : - less likely that the child will be abandoned or offended; breast milk also protects against the occurrence of neuroses.
- Development: the child shows the best results of intellectual development and creative abilities at an older age.
No less important is the correct laying of the baby to the breast, because this is a powerful stimulus to provide the right amount of milk - galactopoiesis.
- The position of the mother during feeding should be comfortable. It is better to feed the baby either from a lying or sitting position.
- Take the chest in the palm of your hand with 4 fingers from below and 1 from above.
- Touch the nipple to the baby's lips so that he opens his mouth.
- The baby should capture not only the nipple, but also the halo.
- If the mother felt pain in her chest while feeding the baby, this means that the baby did not take the breast correctly. In this case, it is necessary to carefully touch the child's lips with a finger so that he opens his mouth, and not pull it by force. Try to apply to the chest again.
- Feed the baby on demand. In the first days up to 10-14 times a day. After the formation of lactation (after approximately 2-3 weeks), the regimen is established independently and is 6-7 feedings per day.
7, It is not recommended to take night breaks in feeding.
- Frequent feeding, including night feeding, contributes to the development of the prolactin and oxytocin reflex.
Produced BEFORE and DURING breastfeeding causes milk to DROP
Sensory suction impulses
- Promotes uterine contractions
- No additional food other than breast milk should be given to a baby under 3-4 months of age.
- It must be remembered that during the day the baby sucks out different amounts of milk.
- Negative emotions block the oxytocin reflex, spasm occurs and milk is poorly excreted.
- The positive psychological attitude of the mother, the desire to breastfeed her child and the belief that breast milk is the best food for children are important.
- It is important to observe the rules of personal hygiene (clean linen, hands, mother's chest).
- The duration of feeding is currently not limited.
The most important factors in the development of full lactation in the early days are:
- Skin to skin contact;
- Early breastfeeding;
- Joint stay of mother and child in a maternity hospital;
- Feeding the baby "on demand";
- Application to both mammary glands;
- Exclusion of pre-lactation feeding and supplementation; • Exclusion of devices imitating mother's breasts (nipples, pacifiers).
There are certain rules to follow with an infant:
- There should not be co-sleeping with an infant!!!
- forbid yourself to take a baby to bed !!!!!!!
- the baby is not a place in bed with other family members, also do not put him to sleep with each other, in order to avoid harm in a dream;
- do not overheat the baby, there is no need to wrap him in a large amount of clothes;
- no need to swaddle the baby tightly. He should be able to change the position of the head and body in case of lack of air;
- the surface of the bed should be pretty flat, without extra pillows, duvets, blankets. These items can accidentally cut off the oxygen supply to the baby. But even under the weight of your body, it should not fall through, otherwise there is a high probability that the child will get there on his face and strangulation may occur;
- there is no need to put the child to sleep between you and the back of the sofa, even if it is soft, so that it does not become sandwiched between the fabric and the body of an adult;
- consider measures that will protect your baby from an unexpected fall from your bed.
Feeding technique Bottle feeding
Feeding technique Bottle feeding is not really difficult. However, there are a few feeding rules you should remember to avoid baby tears, food spills, and other problems.
The position taken by the feeder should resemble the natural position of the mother during breastfeeding:
- The child's head should rest on the left hand.
- The nipple that enters the baby's mouth must always be full of milk or formula - otherwise the baby will swallow air which can cause colic.
- The appearance of bubbles in the bottle means that the child is eating incorrectly and you need to help him, change the position, tilt the bottle in a different way.
- Do not leave a child alone with a bottle and do not let the baby sleep with a bottle in his mouth - in both cases this can lead to choking.
- It is best to feed your baby when he is in your arms - babies feel safest in their parents' arms.
- Remember that the baby's head should always be slightly higher than his torso.
- Make sure that the baby does not tilt the head too far back or forward - if the head is in the wrong position, it becomes more difficult for the baby to eat, the wrong head position can also cause food to enter the respiratory tract.
- When a baby eats from a bottle, he swallows air with nutrition, so he may feel full, despite the fact that he has eaten little.
- Take breaks every 5 minutes during feeding so that the baby has the opportunity to burp.
- After he has let out air and some nourishment, he will feel hungry again.
- In order for the baby to burp, you need to change his position: put the baby's head on your shoulder and support his back with your hands.
- The child must be in an upright or semi-upright position. If the baby does not burp between feedings, the accumulated air will lead to the formation of painful gases.
- The sitting position is the most classic feeding position. With this feeding, the baby sits on your hips with his booty, his back leans against your left hand, and his head is in the crook of the elbow of his left hand.
- Handling the bottle from the side is convenient if the baby suffers from gastroesophageal reflux or has a runny nose. In this option, the child lies on his side (according to the recommendations of doctors, it is better for the child to lie on his left side), and you are nearby and can also take a position lying on your side, turning to face him.
- Clean and sterilize all parts before each use.
- Do not use abrasive cleaners or antibacterial cleaners on bottles and teats.
- While inspecting the nipple, pull it in all directions to make sure it is intact.
- Throw away bottles and nipples at the first sign of damage, wear and scratches.
- Change nipples and cups every 3 months.
- Do not heat milk in the microwave as it may heat unevenly and cause burns to the baby during bottle feeding.
- Always check the milk temperature before feeding.
How to breastfeed correctly - "Healthy child's Internet office"
Ksenofontova Olga Leonidovna
Deputy chief physician of MBU "EKPC"
It would seem that there is such a difficult thing - put it on the chest and feed. It turns out that attachment is also a kind of science. In the first three months, the baby learns to suckle properly, so the task of the mother is to help him in this difficult task.
It is important to find a comfortable position. If you are seated, try to sit up straight with good back support. Use pillows that can be used to support your back or arm in your lap to help hold your baby.
Position the child correctly near the chest: you need to turn the child towards you with the whole body “belly to stomach”, press the legs. Nose at nipple level. When the baby opens his mouth wide, his head will tilt back slightly and the nipple will look at the sky.
Support the chest with your hand - with four fingers from below and a thumb from above, squeezing a little, the fingers should be parallel to the baby's lips and away from the nipple so as not to interfere with capturing most of the areola. Point the nipple up.
After you sat down comfortably and correctly positioned the baby - touch the baby's lips with the nipple, you can express a drop of colostrum so that he feels the taste of milk and begins to actively look for the breast and open his mouth wider. Wait until the baby opens his mouth as wide as possible (at first he may lick the nipple and open his mouth not very wide), lower the tongue down, and push it to the chest (not the chest to the baby) and insert the breast as deep as possible. The lower lip should touch the first breast and away from the nipple, the lower edge of the areola (for a medium-sized areola).
If the child took the breast correctly: his mouth is wide open, the lips are turned outward, the chin rests on the chest, when feeding, the tongue is sometimes visible (the breast is located on it), the areola is captured from below more than from above. After feeding, the nipple is extended forward and of the correct rounded shape, not flattened, not squeezed, not beveled.
If you feel pain during feeding or notice signs of improper attachment, remove the breast (to do this, place the little finger in the corner of the baby's mouth and slightly press the lower jaw down) and feed it again.
Breastfeeding in various positions
In feeding, it is very important that the breast is well emptied, all the lobules work in the same way, so the position of breastfeeding must be changed. If we remember that the share to which the child's chin is directed is emptied to the maximum, we will be able to ensure a uniform outflow of milk from the entire mammary gland. If you find a seal in your chest, use this rule and deal with stagnation much faster.
Do not use pacifiers or bottles with teats
Strange as it may seem at first glance, bottle feeding and pacifier sucking can lead to early termination of breastfeeding. But mothers do not always take this recommendation seriously. In fact, the technique of sucking a bottle (pacifier) and the technique of breast sucking are very different: different muscle groups are worked, the breast is taken in different ways. For example, when sucking a bottle, the baby works more with sponges, draws in his cheeks, tightens his tongue, and when sucking the breast, the lower jaw works, the chest lies on the tongue, so when combining such different sucking methods, some babies begin to take the breast incorrectly (which worsens its stimulation), and others may refuse to breastfeed altogether.
If you need to feed your baby with expressed milk, then do it from a cup, from a spoon, from a syringe.
Nighttime baby feedings
Night feedings by a breast - stimulants of our lactation. The hormone prolactin is produced at night in the largest amount, so you should not offer your baby a breast replacement at night - feed, as in the daytime, on demand. By the way, at the end of breastfeeding, night feedings are most often removed last.
Baby does not need water for the first six months
Breast milk consists of 87% water, so giving your baby extra water in the first six months is not worth it. The presence of another liquid can reduce milk production, since the baby’s satiety and thirst quenching centers are very close, and a portion of water is perceived as food. Do not worry that milk is fatty and it is difficult for a child to digest it. It has enough liquid (especially in the foremilk) and enzymes that help the milk "digest itself".