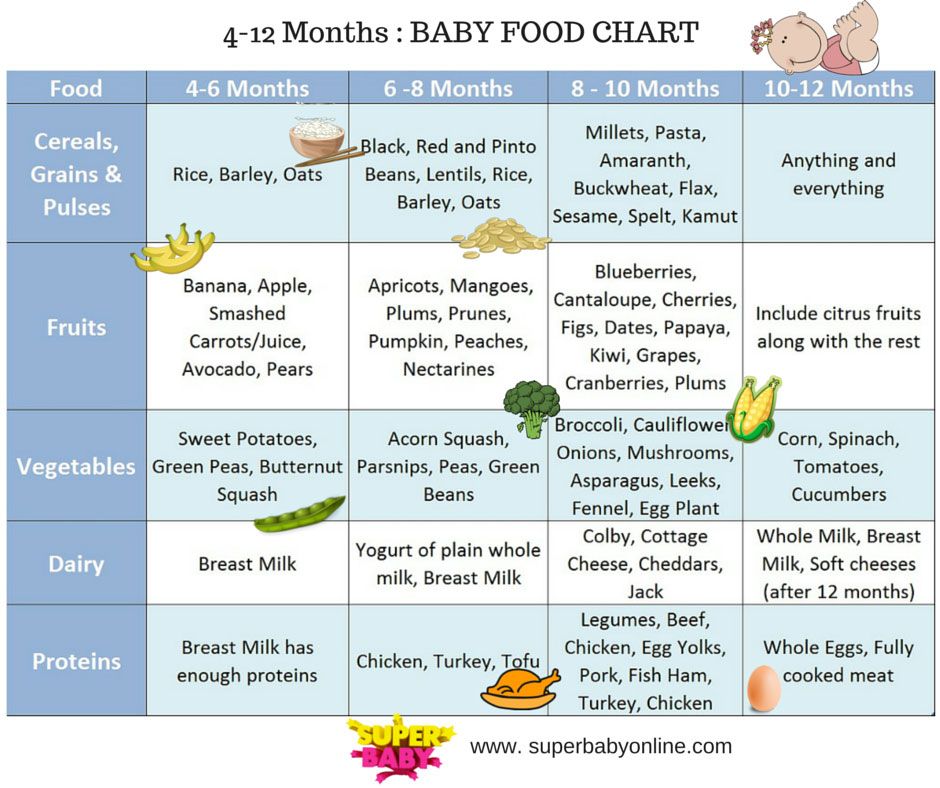
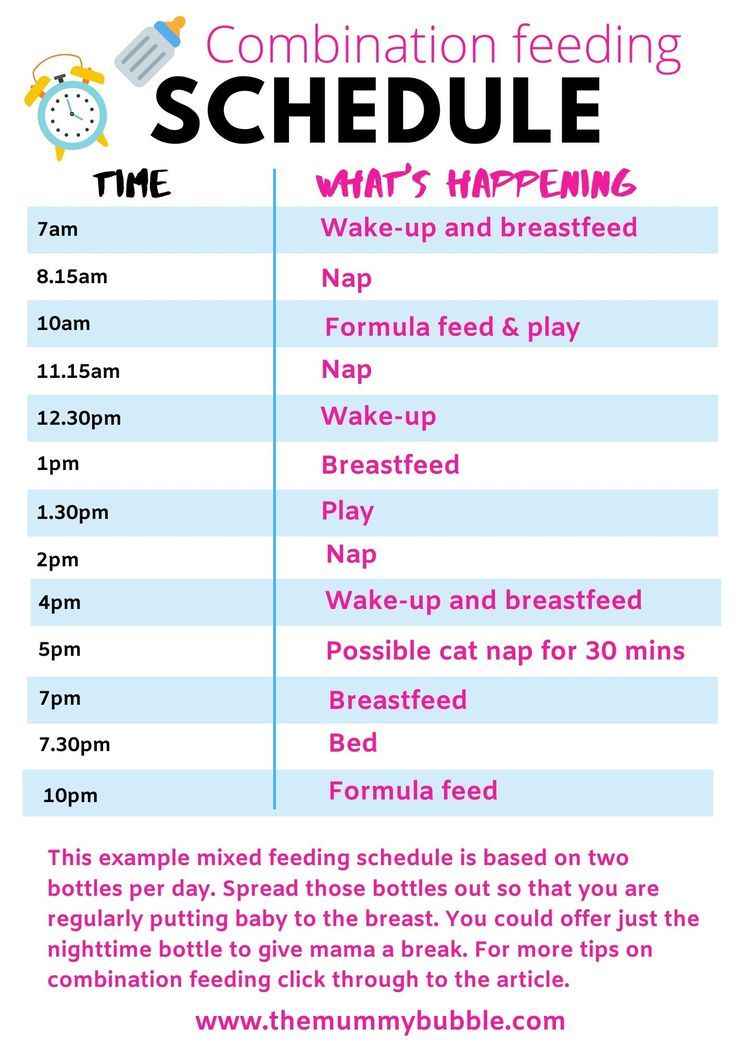
Second month baby feeding schedule
Breastfeeding FAQs: How Much and How Often (for Parents)
Breastfeeding is a natural thing to do, but it still comes with its fair share of questions. Here's what you need to know about how often and how long to breastfeed your baby.
How Often Should I Breastfeed?
Newborn babies should breastfeed 8–12 times per day for about the first month. Breast milk is easily digested, so newborns are hungry often. Frequent feedings helps stimulate your milk production during the first few weeks.
By the time your baby is 1–2 months old, he or she probably will nurse 7–9 times a day.
In the first few weeks of life, breastfeeding should be "on demand" (when your baby is hungry), which is about every 1-1/2 to 3 hours. As newborns get older, they'll nurse less often, and may have a more predictable schedule. Some might feed every 90 minutes, whereas others might go 2–3 hours between feedings.
Newborns should not go more than about 4 hours without feeding, even overnight.
How Do I Count the Time Between Feedings?
Count the length of time between feedings from the time your baby begins to nurse (rather than at the end) to when your little one starts nursing again. In other words, when your doctor asks how often your baby is feeding, you can say "about every 2 hours" if your first feeding started at 6 a.m., the next feeding was around 8 a.m., then 10 a.m., and so on.
Especially at first, you might feel like you're nursing around the clock, which is normal. Soon enough, your baby will go longer between feedings.
How Long Does Nursing Take?
Newborns may nurse for up to 20 minutes or longer on one or both breasts. As babies get older and more skilled at breastfeeding, they may take about 5–10 minutes on each side.
How long it takes to breastfeed depends on you, your baby, and other things, such as whether:
- your milk supply has come in (this usually happens 2–5 days after birth)
- your let-down reflex (which causes milk to flow from the nipple) happens right away or after a few minutes into a feeding
- your milk flow is slow or fast
- the baby has a good latch, taking in as much as possible of your areola (the dark circle of skin around your nipple)
- your baby begins gulping right away or takes it slow
- your baby is sleepy or distracted
Call your doctor if you're worried that your baby's feedings seem too short or too long.
When Should I Alternate Breasts?
Alternate breasts and try to give each one the same amount of nursing time throughout the day. This helps to keep up your milk supply in both breasts and prevents painful engorgement (when your breasts overfill with milk).
You may switch breasts in the middle of each feeding and then alternate which breast you offer first for each feeding. Can't remember where your baby last nursed? It can help to attach a reminder — like a safety pin or small ribbon — to your bra strap so you'll know which breast your baby last nursed on. Then, start with that breast at the next feeding. Or, keep a notebook handy or use a breastfeeding app to keep track of how your baby feeds.
Your baby may like switching breasts at each feeding or prefer to nurse just on one side. If so, then offer the other breast at the next feeding. Do whatever works best and is the most comfortable for you and your baby.
How Often Should I Burp My Baby During Feedings?
After your baby finishes on one side, try burping before switching breasts. Sometimes, the movement alone can be enough to cause a baby to burp.
Sometimes, the movement alone can be enough to cause a baby to burp.
Some infants need more burping, others less, and it can vary from feeding to feeding.
If your baby spits up a lot, try burping more often. While it's normal for infants to "spit up" a small amount after eating or during burping, a baby should not vomit after feeding. If your baby throws up all or most of a feeding, there could be a problem that needs medical care. If you're worried that your baby is spitting up too much, call your doctor.
Why Is My Baby Hungrier Than Usual?
When babies go through a period of rapid growth (called a growth spurt), they want to eat more than usual. These can happen at any time. But in the early months, growth spurts often happen when a baby is:
- 7–14 days old
- 2 months old
- 4 months old
- 6 months old
During these times and whenever your baby seems extra hungry, follow your little one's hunger cues. You may need to breastfeed more often for a while.
How Long Should I Breastfeed My Baby?
That's a personal choice. Experts recommend that babies be breastfed exclusively (without formula, water, juice, non–breast milk, or food) for the first 6 months. Then, breastfeeding can continue until 12 months (and beyond) if it's working for you and your baby.
Breastfeeding has many benefits for mom and baby both. Studies show that breastfeeding can lessen a baby's chances of diarrhea, ear infections, and bacterial meningitis, or make symptoms less severe. Breastfeeding also may protect children from sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), diabetes, obesity, and asthma.
For moms, breastfeeding burns calories and helps shrink the uterus. In fact, breastfeeding moms might return to their pre–pregnancy shape and weight quicker. Breastfeeding also helps lower a woman's risk of diseases like:
- breast cancer
- high blood pressure
- diabetes
- heart disease
It also might help protect moms from uterine cancer and ovarian cancer.
2-Month-Old Baby: Milestones, Sleep & Feeding Schedule
Have you noticed that your tiny newborn isn't so tiny anymore? There are many exciting growth and developmental milestones to look forward to once your baby turns 2 months old, and we’re providing a preview of some of the ones you’ll definitely want to watch for. We also cover how to deal with common health concerns like diaper rash and coughs. If you’re returning to work soon, we also have a section on things to keep in mind so that this transition goes smoothly for both you and your baby.
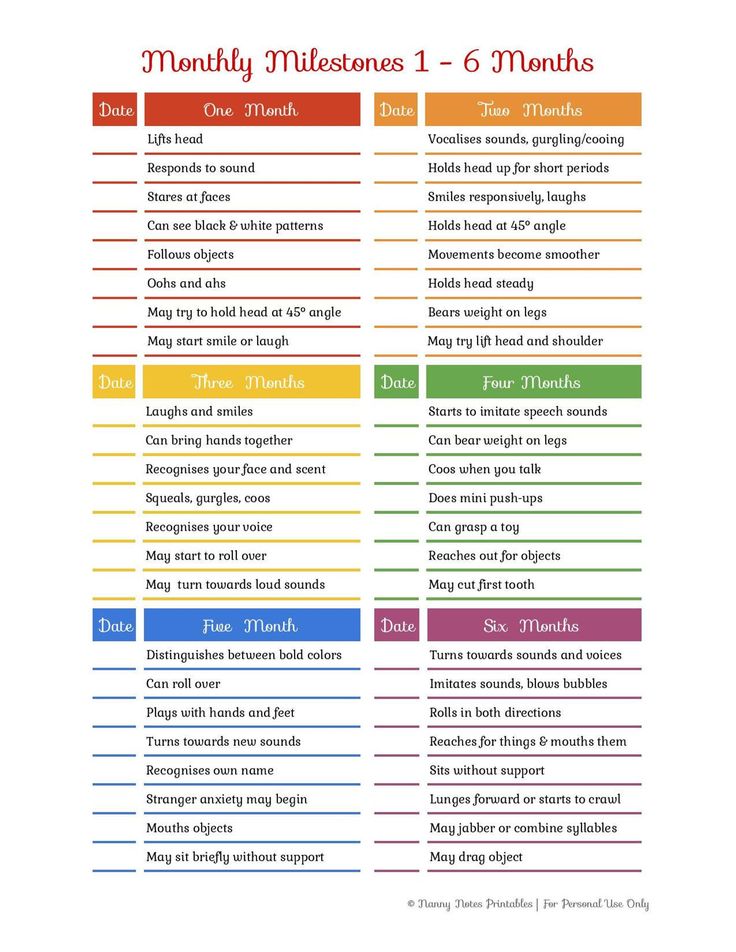
Baby Development Milestones
This month will be full of discovery for your baby, as he becomes more and more aware of the world around him. Here are some of the baby development milestones your 2-month-old baby may be approaching.
Growth and Physical Development: The Mani-Pedi Routine
During these early months, babies tend to grow about 1 to 1 ½ inches in length and gain about 1 ½ to 2 pounds in weight each month. Your healthcare provider will monitor your baby's growth rate at each checkup, noting your 2-month-old baby's weight, length, and head circumference to make sure he's on track and doing well. Read more about how baby growth charts are used in your baby's first 24 months.
Your healthcare provider will monitor your baby's growth rate at each checkup, noting your 2-month-old baby's weight, length, and head circumference to make sure he's on track and doing well. Read more about how baby growth charts are used in your baby's first 24 months.
Speaking of growth, you may have noticed that your baby's nails seem to grow at the speed of light. You'll likely have to clip or file your baby's fingernails about once a week, and his toenails about twice a month. You may not have to worry about reminding yourself — you'll know it's time when you or your baby get scratched! Here are some tips on how to care for your baby's nails:
Use baby nail scissors or clippers, or a soft nail file.
Clip your baby's nails while he's asleep or after a relaxing bath, as his hands will be less of a moving target.
Push down on the skin of the fingertip so you can safely clip just the nail, not the skin.
File any rough edges after clipping the nails.

If you're still unsure about how to safely cut your baby's nails, ask the healthcare provider to show you how.
For even more “growing news,” the soft spots on your baby's head, called the fontanelles, will begin to harden as the bones of your baby's head fuse together.
Senses: Seeing the World in Color
Your baby will start to recognize objects and will love to look at familiar human faces best of all, especially mom's and dad's. In earlier weeks, your baby may have been drawn to simple patterns with straight lines, but soon he'll start to notice circular shapes and patterns such as bull's-eyes and spirals. Your little one is starting to see colors better, too.
As you take your baby out for walks he'll enjoy looking out from the stroller or the baby carrier. Help him learn by saying the names of different objects aloud, in particular naming anything that catches his eye.
Movement: Baby Squats
Although many of your baby's movements are still reflexive, he'll gradually learn to control more of what he does. For a while he may seem less active as some of his early reflexes fade, but new movements will start appearing that are more purposeful. The kicks he may have started practicing last month will start to gather force, as you might well learn from experience if he accidentally kicks you. In the coming weeks, he'll start controlling bending and straightening his knees. If you hold him upright with his feet on the ground, he might crouch down and then “stand” — and he'll soon realize he can bounce.
For a while he may seem less active as some of his early reflexes fade, but new movements will start appearing that are more purposeful. The kicks he may have started practicing last month will start to gather force, as you might well learn from experience if he accidentally kicks you. In the coming weeks, he'll start controlling bending and straightening his knees. If you hold him upright with his feet on the ground, he might crouch down and then “stand” — and he'll soon realize he can bounce.
Your baby's hand and finger skills are also developing. He may be spending more and more time with his hand unclenched, and he'll likely be fascinated by his hands as they pass by in front of him. He'll slowly develop the ability to bring his hand to his mouth — initially it might happen by accident, but eventually he will place his hands in his mouth on purpose as sucking his knuckles will be soothing. If you put a rattle in his hand he might hold onto it and even shake it, but — watch out! — he'll drop it when he gets bored.
All that tummy time he's been putting in (with you closely supervising) will slowly start to pay off. Around this month or next, your baby will be able to push up off his arms, and briefly hold his chest and head up. This is big news because it's a step toward greater independence for your little one. Gaining this skill will mean being able to look around at whatever interests him, even when he's lying on his tummy.
related baby tool
Keep an eye on your baby’s average growth by tracking height, weight, and head circumference with our simple tool.
Fill out your baby's details*:
What is your child*
Boy Girl
This is a mandatory field.
Age (between 0 and 24 months)
This is a mandatory field.
Weight (lbs.)
This is a mandatory field.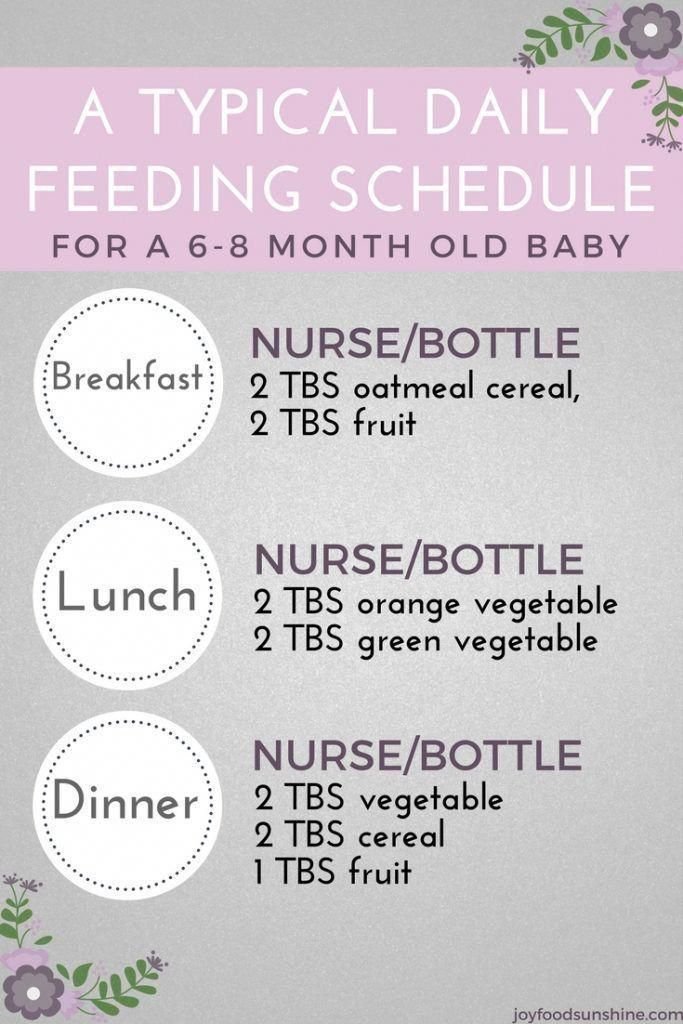
Height (in.)
This is a mandatory field.
Head circumference (in.)
This is a mandatory field.
*Input details of your baby’s last measurements. **Source: World Health Organization
Personality: Muh-muh-muh-muh
Your baby's personality will reveal itself more and more each day. It will start to show in the way he communicates using facial expressions, vocalizations, and even gestures. For example, if you smile at him and he feels happy he might smile right back at you. Around this time, he might start to happily amuse himself by making all kinds of strange new sounds. You might hear muh-muh and bah-bah, and aahs and oohs. Have conversations with him repeating these sounds back to him. “Baby talk” is important at this stage, but add in real words, too. All along, he will be learning that conversation is a two-way street where each person takes turns, and each contribution is important. As the weeks progress, your baby will be more alert to your tone of voice and will be able to get an idea of your mood by how you talk to him. Your voice also helps signal what's to come, so tell him what you're doing when you're changing his diaper, taking him out for a walk, or bathing him.
As the weeks progress, your baby will be more alert to your tone of voice and will be able to get an idea of your mood by how you talk to him. Your voice also helps signal what's to come, so tell him what you're doing when you're changing his diaper, taking him out for a walk, or bathing him.
Soon your baby won't just be smiling: he'll be squealing or laughing in delight. But don't be surprised if your baby isn't as responsive to strangers. Mom and Dad are his favorites, as are his siblings, and probably other regular visitors. Just like adults, your little one has his preferences, too!
How to Support Your Baby’s Development
Playing and interacting with you both have a huge role in your baby's brain development and early learning. Here are some activities you could do together:
Read to your baby. Even if he doesn't fully understand all the words, your baby is listening to the sounds you're making, and he's learning about tone and pacing, for example.
 Don't hesitate to read the same book over and over — babies love repetition. For more tips on reading to your baby, watch this short video on language development through “baby talk”.
Don't hesitate to read the same book over and over — babies love repetition. For more tips on reading to your baby, watch this short video on language development through “baby talk”.Have a “chat.” Respond to your baby's coos and aahs, and initiate conversation by telling him what you're up to. When he “talks,” try not to interrupt or look away. Your attention tells him that his voice is important too and helps build trust.
Tummy time. Continue to give your baby short periods of tummy time each day to help strengthen his neck, arm, and shoulder muscles. Tummy time involves laying your baby on his tummy on a firm surface like the floor — just make sure you're watching.
Introduce a variety of sounds. Play your baby music or give him toys that make different sounds when touched. Let him listen to the sounds of everyday life, too. For example, have him safely nearby as you do household chores — the sound of you tidying will probably fascinate him.
Feeding Your 2-Month-Old Baby
Feed your baby whenever he’s hungry — which will be often, as 2-month-old babies usually eat about six to eight times a day. He’ll show you he's ready to eat by making sucking motions, moving his hand to his mouth, whimpering, or flexing his arms and hands. Avoid overfeeding your baby by keeping an eye out for the signs he’s had enough, such as slowing down or stopping sucking or turning away. You can probably tell your baby is generally eating well if he dozes off after a feed but seems alert, content, and active between feeds. At this stage, you might be able to leave out one middle-of-the-night feed; as your baby’s stomach capacity grows he may not be hungry again until early morning.
Tracking wet and dirty diapers: The number of diapers you change gives you clues about whether your baby is healthy and is getting enough to eat. Keep in mind, each baby is unique and may pee anywhere from once every couple of hours to only once every four to six hours.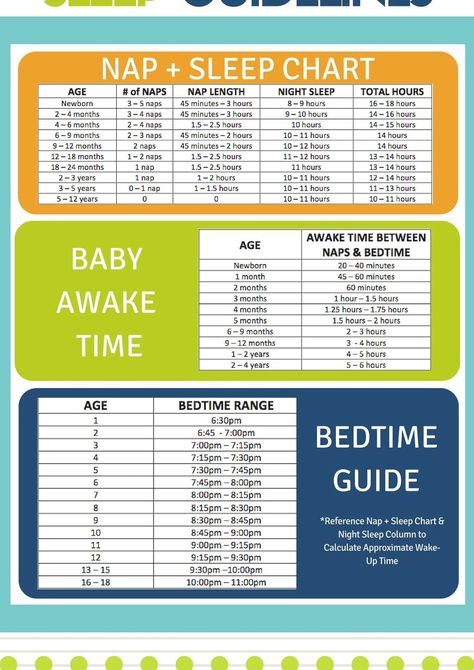 Fewer than six wet diapers may be a sign of mild dehydration. Pay attention to how many diapers your baby typically goes through. If there is a significant drop in the number of wet diapers or your baby’s mouth seems dry, he may be dehydrated. If you’re in any doubt, consult your baby’s healthcare provider. There is no “right” number when it comes to poopy diapers either. Two-month-old babies can poop anywhere from several times a day to only once a week. If your baby is pooping less than normal but the stools are soft and your baby is otherwise well, there may not be cause for concern. Still, if you’re worried, your baby’s healthcare provider will be able to check whether everything is OK.
Fewer than six wet diapers may be a sign of mild dehydration. Pay attention to how many diapers your baby typically goes through. If there is a significant drop in the number of wet diapers or your baby’s mouth seems dry, he may be dehydrated. If you’re in any doubt, consult your baby’s healthcare provider. There is no “right” number when it comes to poopy diapers either. Two-month-old babies can poop anywhere from several times a day to only once a week. If your baby is pooping less than normal but the stools are soft and your baby is otherwise well, there may not be cause for concern. Still, if you’re worried, your baby’s healthcare provider will be able to check whether everything is OK.
As you’ve no doubt realized, your baby’s getting through plenty of diapers. If you haven’t already, don’t forget to download the Pampers Club app so you can get great rewards for all those diapers you’re buying.
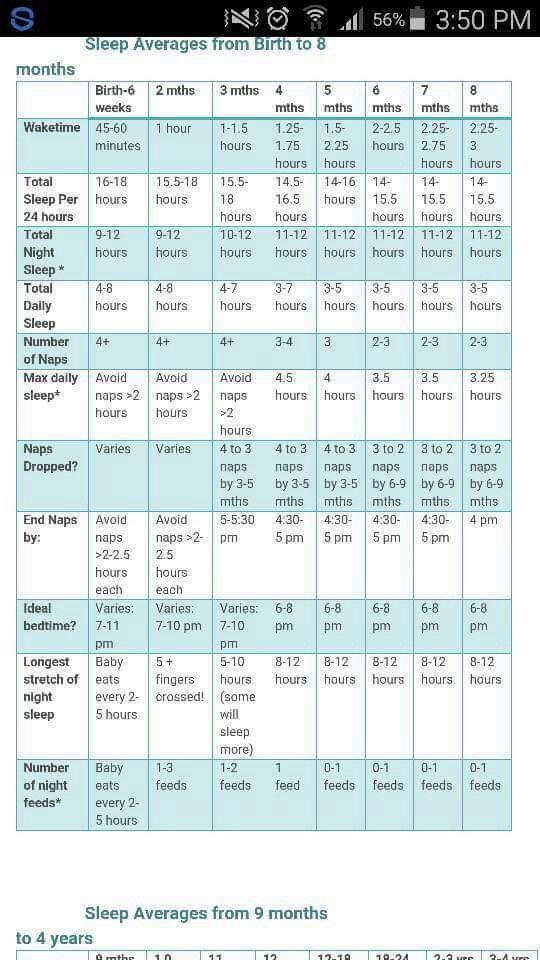
How Much Sleep Does a 2-Month-Old Baby Need?
At 2 months old, your baby may be getting about 14 to 17 hours of sleep over a 24-hour period.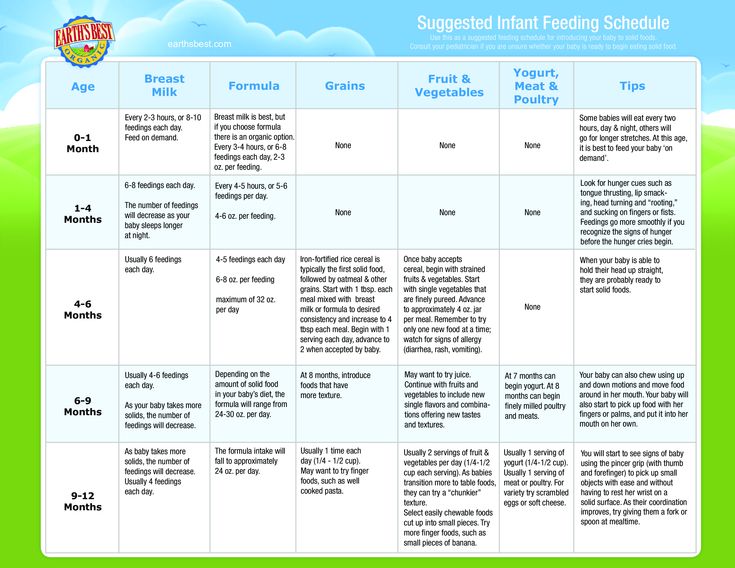 She may spend more time alert and awake during the day, and although she may want fewer naps they might be a little longer in duration. At this stage, some (but not all) babies even manage to sleep through the night, meaning about six to eight hours in one stretch.
She may spend more time alert and awake during the day, and although she may want fewer naps they might be a little longer in duration. At this stage, some (but not all) babies even manage to sleep through the night, meaning about six to eight hours in one stretch.
Good sleep routines — regular bedtimes and naptimes, and restful sleeping periods — give your little one a great start in life, contributing to her general health and wellbeing. Although it can take a while for evening routines to become established, you can help your baby head in the right direction by making nighttime feeds as quiet as possible. For example, keep the lighting low, don’t speak much or loudly, and after the feeding and a quick diaper change put her right back to sleep on her back. For more on this, watch these great tips for a good night’s sleep.
Don’t miss these must-watch sleep tips from the Smart Sleep Coach pediatric sleep consultant:
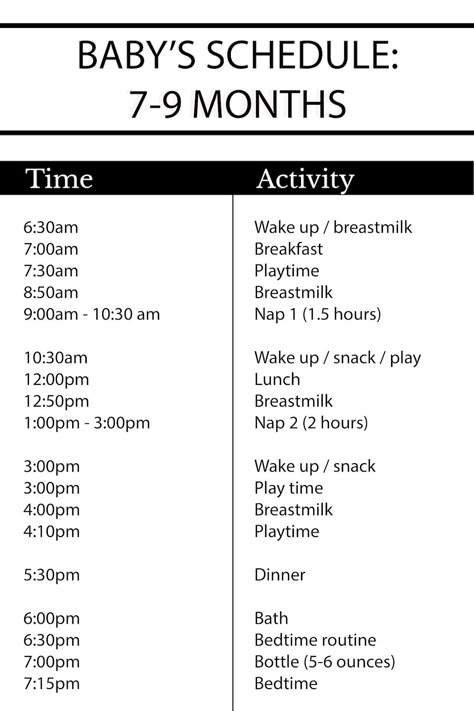
A Day in the Life of Your Baby
Your 2-month-old baby’s daily schedule may include simple routines for sleeping, feeding, bathing, and playing. Here’s one example of what a typical day might look like:
Here’s one example of what a typical day might look like:
Your Baby’s Health: Dealing With Diaper Rash
Skin conditions:
Diaper rash. A wet or soiled diaper that touches baby skin for too long can cause a red rash on the diaper area. To combat diaper rash, change wet or poopy diapers as soon as possible, clean the area with wipes at each change, and expose your baby’s bottom to air whenever possible. These steps will help the rash clear up and help prevent it from reoccurring. Watch our short video on diaper rash treatment and prevention for even more tips.
Heat rash. These tiny, red bumps typically occur in hot and humid weather, usually on the neck, arms, legs, or diaper area. Don’t apply skin ointments; instead, cool the area with water, then completely dry the skin, dress your baby in cool, dry clothing, and try to keep her out of the heat. With this kind of care, heat rash typically goes away after a few days.
Eczema. If your baby has red, itchy, scaly patches of skin in the crooks of her elbows and knees, it could be eczema. Your baby’s healthcare provider can make a diagnosis and will recommend treatment options. It may help to use mild, unscented baby soaps on your baby and her clothes and sheets, to dress her in soft clothes that don’t prickle, and to bathe her three times a week at the most.
Coughing. If you notice your 2-month-old baby coughing, it’s a sign that her airways are irritated. Coughs can be triggered by many kinds of respiratory illnesses, from the common cold to pneumonia. It’s a good idea to reach out to your baby’s healthcare provider if your little one is coughing; but if coughing is accompanied by fever or a difficulty in breathing take your baby to the doctor right away for treatment or advice.
Allergies. Potential signs of a food allergy or sensitivity include if your baby seems fussy or cries excessively, vomits up most of her food, has very watery or bloody poops, or develops a rash.
 Your baby’s healthcare provider will need to explore potential causes and make a diagnosis.
Your baby’s healthcare provider will need to explore potential causes and make a diagnosis.
Your Life as a Parent: Returning to Work
Depending on your situation, different factors may come into play as you decide if and when to go back to work, including your finances, maternity leave options, and general family considerations. If you can, allow yourself some flexibility as you may change your mind about your return to work when the time comes. Whenever you do return to work, it’s natural to feel sad, anxious, or concerned about how your baby will adjust. If your partner is not staying home with your baby, the key is to find child care that you feel comfortable with and that your baby thrives under. You might also consider getting additional help at home so you can spend that precious home time with your baby without additional distractions.
Establish a routine
A couple of weeks before you return to work, start mapping out what your typical workday will look like. Consider things like what time you will need to wake up in order to be ready to leave the house in time, how long will your commute take when you take into account dropping your baby off at day care, or perhaps you are getting a nanny, what time will they need to arrive? How about evenings, if you are nursing when do you plan on pumping etc? Be sure to include your baby’s naps and feeding times, and of course don’t forget to make sure you have time for those all-important baby snuggles!
To help you establish a consistent routine, check out the Smart Sleep Coach by Pampers™. Co-developed with pediatric sleep experts and packed with articles that explain your baby’s development, the Smart Sleep Coach also has a powerful sleep tracking tool that suggests the best times for your baby to nap and sleep. Plus, the Smart Sleep Coach’s exclusive algorithm customizes sleep coaching approaches based on your input and your baby’s unique sleep patterns – all to help you help your baby grow well while giving you more free time and sleep time, too.
Consider things like what time you will need to wake up in order to be ready to leave the house in time, how long will your commute take when you take into account dropping your baby off at day care, or perhaps you are getting a nanny, what time will they need to arrive? How about evenings, if you are nursing when do you plan on pumping etc? Be sure to include your baby’s naps and feeding times, and of course don’t forget to make sure you have time for those all-important baby snuggles!
To help you establish a consistent routine, check out the Smart Sleep Coach by Pampers™. Co-developed with pediatric sleep experts and packed with articles that explain your baby’s development, the Smart Sleep Coach also has a powerful sleep tracking tool that suggests the best times for your baby to nap and sleep. Plus, the Smart Sleep Coach’s exclusive algorithm customizes sleep coaching approaches based on your input and your baby’s unique sleep patterns – all to help you help your baby grow well while giving you more free time and sleep time, too.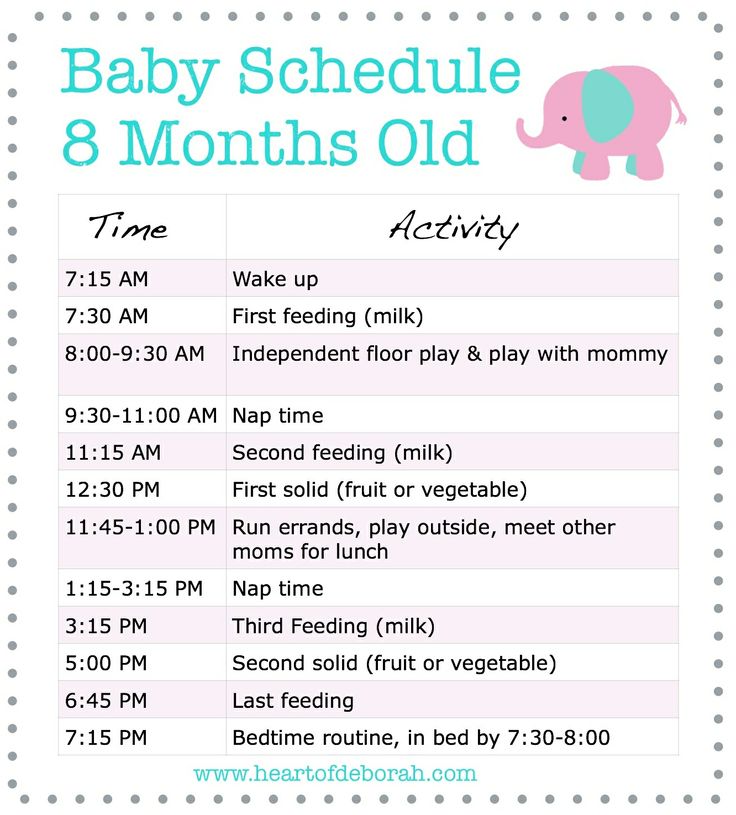 Once you have this draft schedule you have a rough idea of what you may need to try to adjust to make the return to work as smooth as possible for all of you. It’s a good idea to start to adjust your daily routine at least a week before going back to work so that you and your baby are already used to the new timeline.
Obviously at just 2-months old your baby still needs to be fed frequently and it may seem challenging to ‘get them on a schedule’. A lot of working parents try to adjust things they can control to help here. Things like waking up 30mins before your baby so you can shower and get ready first.
Babies thrive in a routine, and once routine is established it is scientifically proven that they will fall asleep faster and stay asleep longer. You’ve got this!
Once you have this draft schedule you have a rough idea of what you may need to try to adjust to make the return to work as smooth as possible for all of you. It’s a good idea to start to adjust your daily routine at least a week before going back to work so that you and your baby are already used to the new timeline.
Obviously at just 2-months old your baby still needs to be fed frequently and it may seem challenging to ‘get them on a schedule’. A lot of working parents try to adjust things they can control to help here. Things like waking up 30mins before your baby so you can shower and get ready first.
Babies thrive in a routine, and once routine is established it is scientifically proven that they will fall asleep faster and stay asleep longer. You’ve got this!
Organizing Child Care
You may have multiple sources and forms of child care, which you could consider, including
your parents or other relatives
a babysitter
a day care center
in-home care, either solely for your baby or in a group with other children
a nanny
or a combination of the above.
As you search for child care, keep in mind that the most important thing is to make sure your baby is happy and developing well under the care you select. Ask other parents or your baby’s healthcare provider for referrals. Speak to potential caregivers at length, observe them with your baby for a day or two, check their references and do background checks, and trust your instincts. You should always keep a watchful eye that your baby is doing well, and reevaluate your choice if need be.
Expressing Breast Milk at Work
Returning to work can be stressful for some women and may reduce your breast milk supply (as may other sources of stress), particularly if you are not able to pump as much as you would like. By law, your employer must allow you time and a space — other than a bathroom — for you to express breast milk until your baby turns 1 year old. If you are concerned your milk supply may be running low, read up on how to increase breast milk supply and contact your healthcare provider or lactation consultant for help.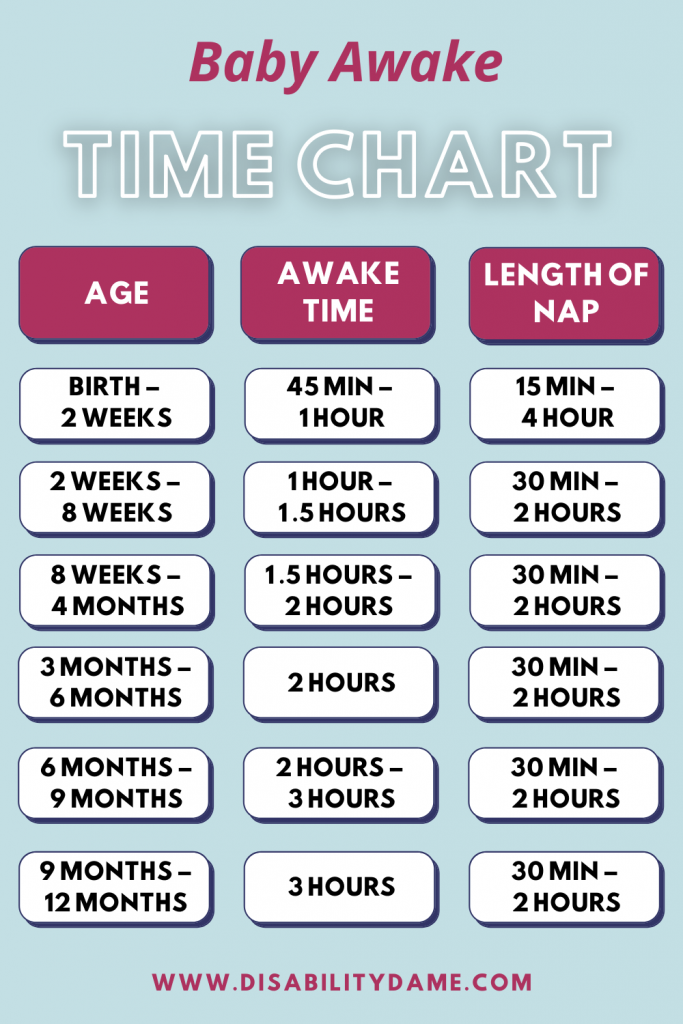
Finding Help at Home
As you return to work — or simply because you need an extra pair of helping hands — you may need help with cooking, household chores, or errands. Here are some things to keep in mind:
Make sure you have someone you trust who will relieve the load, not add to it.
Figure out when you’ll need help and make sure the helper can reliably commit to this schedule.
Be clear about what you need help with and consider having it in writing.
Ask for enough warning if the helper can’t make it or if they are sick.
Have a plan B like a babysitter or neighbor you can call to jump in at the last minute.
Consider getting a background check and checking for a valid driver’s license.
If the person’s role includes caring for your baby, ask the caregiver to complete a baby first aid course.
Child's regimen at 2 months
06/29/2022 Reading time: 5 min 10357
Article contents
- Sleep pattern
- Feeding schedule
- Walk mode
- What can you do to keep your baby awake at 2 months
At two months, the main period of adaptation for both the mother and the child is behind.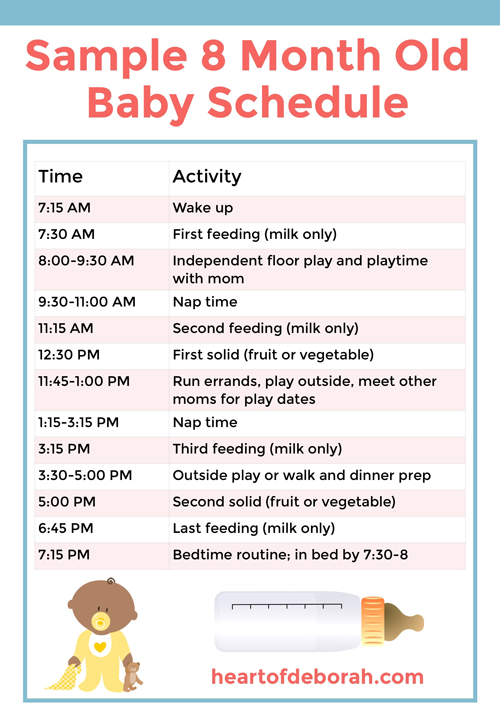 Mom has already learned to recognize the condition and needs of the crumbs by special signals. The kid got used to the new world around him and began to show interest in him. The two-month-old regimen is still taking shape, but a certain rhythm can already be seen in it.
Mom has already learned to recognize the condition and needs of the crumbs by special signals. The kid got used to the new world around him and began to show interest in him. The two-month-old regimen is still taking shape, but a certain rhythm can already be seen in it.
Sleep mode
At two months, the baby is already more likely to fall asleep at the same time every day. Night sleep, as in one month, can be interrupted by feedings. Although periods of wakefulness are getting longer, sleep still takes up most of the day.
Sleep norms in two months - 15-17 hours a day. This is an average of 5-6 daytime sleeps of 2-2.5 hours and about 6 hours of night sleep. If a child sleeps less than 11 hours a day or more than 19 hours, this is a reason to consult a doctor.
At night the child usually eats almost in his sleep. He quickly calms down and goes back to sleep. If the baby is active at night, does not fall asleep after feeding, his daily routine may be disturbed. During the day, the baby can sleep too much, and then meet the night cheerful and full of energy. In this case, it is worth switching to a sleep mode for the next age level: reduce one daytime sleep, make wakefulness more active, regularly ventilate the children's room and walk longer in the fresh air.
During the day, the baby can sleep too much, and then meet the night cheerful and full of energy. In this case, it is worth switching to a sleep mode for the next age level: reduce one daytime sleep, make wakefulness more active, regularly ventilate the children's room and walk longer in the fresh air.
Feeding schedule
The daily routine of a 2-month-old child receiving breast milk and a child receiving formula corresponds to the scheme: feeding - wakefulness - sleep.
Breastfeeding provides a less strict feeding schedule. If in the first month of life the child received a breast on demand, then during the second month a more or less well-established scheme of alternating sleep, wakefulness and nutrition is gradually established. The intervals between feedings should gradually lengthen. On average, a two-month-old baby eats every 3 to 3.5 hours.
If everything is in order with lactation, the baby is gaining weight well, then try to at least roughly adhere to this time and not to breastfeed until you are sure that the source of crying is precisely hunger. If you suspect that the baby is not full, and your fears are confirmed by insufficient weight gain of the child, then apply it to the breast more often, including at night, and use other ways to maintain and restore lactation. Do not supplement with formula without consulting your pediatrician.
If you suspect that the baby is not full, and your fears are confirmed by insufficient weight gain of the child, then apply it to the breast more often, including at night, and use other ways to maintain and restore lactation. Do not supplement with formula without consulting your pediatrician.
For a bottle-fed baby, the feeding schedule is still strict, according to the schedule. The daily volume of the mixture, calculated taking into account the weight and age of the child, is divided into 6-7 feedings. This is how a single portion is determined. If a 2-month-old baby wakes up at night and makes it clear by crying that he is hungry, keep the night feeding. If he sleeps calmly - do not wake him up, then he does not need additional night food.
Approximate feeding schedule for a 2-month-old baby
06:00 - 1st feeding;
09:30 - 2nd feeding;
13:00 - 3rd feeding;
16:30 - 4th feeding;
20:00 - 5th feeding;
23:30 - 6th feeding;
03:00 - 7th, night, feeding - if necessary.
Walk mode
The daily routine of a two-month-old child must necessarily include outdoor walks. Pediatricians recommend spending 5-6 hours outside in cool weather, dividing them into two walks, and walking as much as possible in the summer.
Try to go for a walk at the same time every day. For a two-month-old baby, it is still worth planning for nap time. A measured swaying will quickly lull the baby to sleep, but he still won’t be able to become interested in the surrounding landscape, since you won’t see much while lying in a stroller.
Adjust the duration and number of walks every day, based on the weather outside, the mood of the baby and your well-being. If any of these components leaves much to be desired, replace the walk with sleeping on the balcony or terrace.
What can keep a child awake at 2 months
At 2 months, the baby can be awake for up to an hour and a half. Of course, just lying in his bed for so long will be boring for him. Wake periods can be used for physical activity, play and age-appropriate activities.
Wake periods can be used for physical activity, play and age-appropriate activities.
In the second month of life, the child begins to make attempts to raise and hold his head. Be sure to put it on your tummy half an hour to an hour before meals or two hours after. This exercise will not only help strengthen the baby's muscles, but will also serve as a prevention of regurgitation, colic and constipation.
At this age, the baby is already able to focus on objects and faces, listens with interest to sounds. Attach a musical mobile to the crib or hang a rattle at the level of the baby's chest at a distance of 30-40 cm. Fix contrasting images on the side of the bed or on the wall - where the child will see them well. The pictures can be animals, plants or just clear patterns - there is not much difference. The kid will not study the world around these images, as long as it is enough that he focuses his eyes and examines the lines.
The main need of a baby at 2 months is the presence of his mother.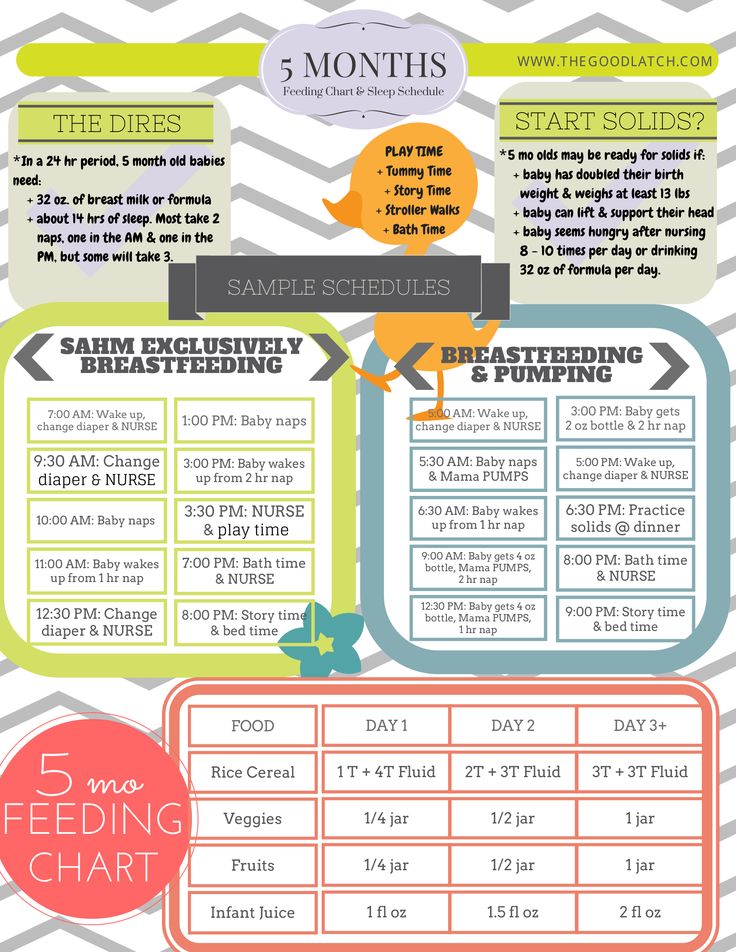 Use your waking hours to communicate with your baby: talk, sing songs and nursery rhymes, tell poems and fairy tales: it does not matter that their content is not yet available to the child. Walk with the baby in your arms around the rooms, talk about objects and events around. Your voice will calm the baby, he will listen to the rhythm of speech and form a passive vocabulary.
Use your waking hours to communicate with your baby: talk, sing songs and nursery rhymes, tell poems and fairy tales: it does not matter that their content is not yet available to the child. Walk with the baby in your arms around the rooms, talk about objects and events around. Your voice will calm the baby, he will listen to the rhythm of speech and form a passive vocabulary.
List
- At 2 months the child sleeps 15-17 hours a day, 5-6 times during the day.
- There is no strict feeding schedule at GV, although an approximate regimen is beginning to take shape. On the IV, feeding continues by the hour.
- In cold weather, the baby is walked twice a day for 2.5-3 hours. In summer, the more the better.
- When you are awake, you can do gymnastics with your baby, give him a massage, put him on his tummy. Hang a musical mobile or rattles in the crib, fix black and white pictures. Talk to your child a lot.
(0 ratings; article rating 0)
The daily routine of a child at 2 months: development, sleep, feeding The baby becomes more active, his sense organs develop, his sleep and wakefulness change.
 We tell you what you need to consider when shaping the daily regimen of two-month-old children on breastfeeding and artificial feeding.
We tell you what you need to consider when shaping the daily regimen of two-month-old children on breastfeeding and artificial feeding.
Sleep at night
By 2 months you will notice that your baby's sleep patterns are changing. The biological rhythms of the baby continue to form, and the duration of night sleep gradually increases. The child will begin to go into the night earlier - at 22.00-23.00 hours. But for the time being, bedtime is not as important as whether the baby gets enough sleep. Many babies sleep for about 9-10 hours at night with waking up for feedings. How long you should be between night feeds is best discussed with your pediatrician. The time of the morning rise is also not yet constant and not always at 7 in the morning.
Daytime naps
The duration and time of daytime naps are still different, as well as the time of wakefulness between them. In general, a two-month-old baby sleeps approximately 4-5 hours during the day. And sleep segments are now usually from 30-40 minutes to an hour. During the day, the child sleeps from 4 to 6 times - depending on the time of getting up and leaving at night.
And sleep segments are now usually from 30-40 minutes to an hour. During the day, the child sleeps from 4 to 6 times - depending on the time of getting up and leaving at night.
Baby can be active for up to 1 hour or 1 hour and 15 minutes. But you should not allow overwork and focus also on the signs of fatigue and the duration of the previous sleep.
If a two-month-old baby calms down, loses interest in surrounding objects, starts rubbing his eyes, directs his eyes to one point, for no reason starts to get nervous and asks for food, then he wants to sleep and it's time to go to bed.
How many hours of sleep is needed in general? A newborn needs 14-16 hours of sleep a day.
By this age, you already understand your baby better, and it will be easier to follow a more or less understandable schedule. Although the exact daily routine has not yet been organized.
Why can a two-month-old baby not sleep?
If bedtimes are long and it is difficult for the child to fall asleep during the day, the causes of sleep disturbances should be found out and, if possible, eliminated:
-
At this age, the baby begins to be distracted by the surrounding objects, so be sure to darken the room.
 Darkness will help calm the baby and set him to sleep. This is especially important if you have trouble falling asleep in the evening. From 2.5 months, the sleep hormone melatonin begins to be produced. Therefore, remember that bright light destroys it, and darkness, on the contrary, contributes to the formation of melatonin in the child's body.
Darkness will help calm the baby and set him to sleep. This is especially important if you have trouble falling asleep in the evening. From 2.5 months, the sleep hormone melatonin begins to be produced. Therefore, remember that bright light destroys it, and darkness, on the contrary, contributes to the formation of melatonin in the child's body. -
At 2 months, the senses are actively developing in babies. Now the child reacts to any rustle. And those sounds that he did not notice before can now wake him up during sleep. The use of a white noise generator will help here to protect the baby from extraneous noise. It is not recommended to buy special white noise toys that are placed in the crib, as this is unsafe.
-
Even an extra 5-10 minutes can affect the child's well-being this month and lead to more overwork. If this happens, use different ways to calm the baby and put him to bed.
Now is the time to introduce a ritual that will help set the baby up for sleep. Daily repetition of activities facilitates the process of falling asleep and improves night sleep. Start by bathing, lightly massage your baby, swaddle, feed in dim light, walk with your baby upright to ease spitting up.
Daily repetition of activities facilitates the process of falling asleep and improves night sleep. Start by bathing, lightly massage your baby, swaddle, feed in dim light, walk with your baby upright to ease spitting up.
At the end, read a story or sing a lullaby. Separating feeding and falling asleep will help your baby learn to fall asleep on his own in the future, not relying only on the breast. Gradually, food will become part of the ritual, and not the only way for the child to fall asleep.
Sleepy, but awake, put the baby in the crib, stroking the head and tummy if necessary.
If it’s hard to adjust the baby’s sleep and routine on your own, come to the Club REGIME FROM A TO Z.
How to avoid confusion between day and night
.
When you are awake, take your baby outside, turn on the lights and open the curtains. Let the child be surrounded by familiar everyday sounds while playing.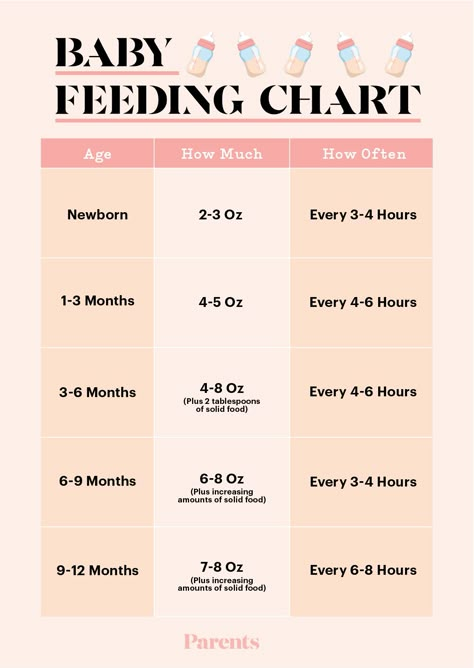
Avoid bright lights at night, feed and change diapers with minimal light if possible. If the baby wakes up at night, be quiet and do not play with him.
In the table you will find the norms of sleep and wakefulness of a child at 2 months
Feeding and daily routine of a child of 2 months
The daily routine of a 2-month-old baby on breastfeeding and on artificial feeding is almost the same. The only difference is the feeding schedule. Since the mixture is digested more slowly, meals will be less frequent. The feeding regimen should be discussed with the doctor observing the child. As in the case if the baby was born prematurely or does not gain weight.
At two months, the number of attachments with natural feeding during the day is about 6-9, at night - from 2 to 4 times. For a two-month-old baby, about 800-900 ml is enough. milk or 700-750 ml. mixture per day. The menu should not include other fluids while breastfeeding. Feeding on demand usually occurs at 2 months for 15-20 minutes.
Feeding on demand usually occurs at 2 months for 15-20 minutes.
A baby of the second month of life has a need for contact with the outside world. He begins to be distracted by environmental stimuli during breastfeeding and eats less milk or formula during the day than he needs. Have you noticed this with your child?
Therefore, offer breasts during sleep and after waking up. And during feeding, retire with the baby in a quiet place, darken the room so that nothing distracts the baby, and offer him the breast in a calm environment.
Baby development at 2 months
At this age, babies develop a reflex that makes them look at their outstretched arms when they wave them. The child gets used to his body and learns it. Surely, your baby loves to take his fingers in his mouth and touch his legs with his hands! And now you will notice the first smile - smile and you will respond in order to establish contact with the child.