Side effects of bottle feeding baby
Baby Formula Side Effects | Benefits and Risks of Baby Formulas
Formula-fed babies are more likely to have respiratory infections and food allergies than breastfed babies. Common baby formula side effects include eczema, upset stomach and runny nose. In rare cases, formula may cause necrotizing enterocolitis, or NEC, in premature babies.
Common Baby Formula Side Effects
Common baby formula side effects are typically caused by food allergies, contaminated formula or using a formula that was made improperly.
For example, many baby formulas are made with cow’s milk, and cow’s milk allergy is one of the most common childhood allergies. About seven percent of babies younger than 12 months of age are allergic to the protein in cow’s milk, according to the UK’s National Health Service.
fact
Symptoms of cow’s milk allergy include: Skin reactions, stomach problems, stuffy nose and eczema. Severe allergies may cause swelling and difficulty breathing.
Source: National Health Service
Feeding baby formula made incorrectly can also harm your baby. The CDC warns parents not to use homemade infant formula or buy imported formula online from third party sellers because of problems like insufficient nutrition, dangerous electrolyte imbalances or contamination.
All baby formula legally sold in the US follows the FDA’s guidelines for safety and nutrition. For example, in August 2021, the FDA announced a baby formula recall for formulas made by Able Groupe because the formulas didn’t contain enough iron. Iron-deficiency anemia in infants could lead to irreversible cognitive and functional-development problems.
Serious Baby Formula Side Effects
Baby formulas rarely cause serious side effects. But food allergies, nutrient deficiency or baby formula contamination can lead to serious health problems if left unchecked.
Premature babies may also develop a serious condition called necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) when drinking cow’s milk baby formulas such as Enfamil or Similac. NEC affects about one in 1,000 infants born prematurely. The risk is highest in babies who weigh less than two pounds at birth.
The risk is highest in babies who weigh less than two pounds at birth.
Life-threatening food allergy symptoms such as swelling of the mouth or throat, hives and vomiting are a medical emergency. These are rare and can happen within days to weeks after starting cow’s milk baby formula. Babies may also be allergic to soy protein formula. Seek emergency medical attention right away.
fact
Baby formula has all the nutrition needed by a baby, but studies show formula-fed babies may have a greater risk of respiratory infections, allergies, sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), obesity, cognitive development issues and other health risks compared to breastfed babies.
Source: Italian Journal of Pediatrics
Rarely, baby formula may be contaminated with a type of bacteria called Cronobacter. This can happen during manufacturing, home preparation or during feeding if bottles aren’t properly cleaned.
In February 2022, Abbott issued a baby formula recall for certain lots of its Similac, Alimentum and EleCare formulas after a few babies got sick from Cronobacter infections and some died.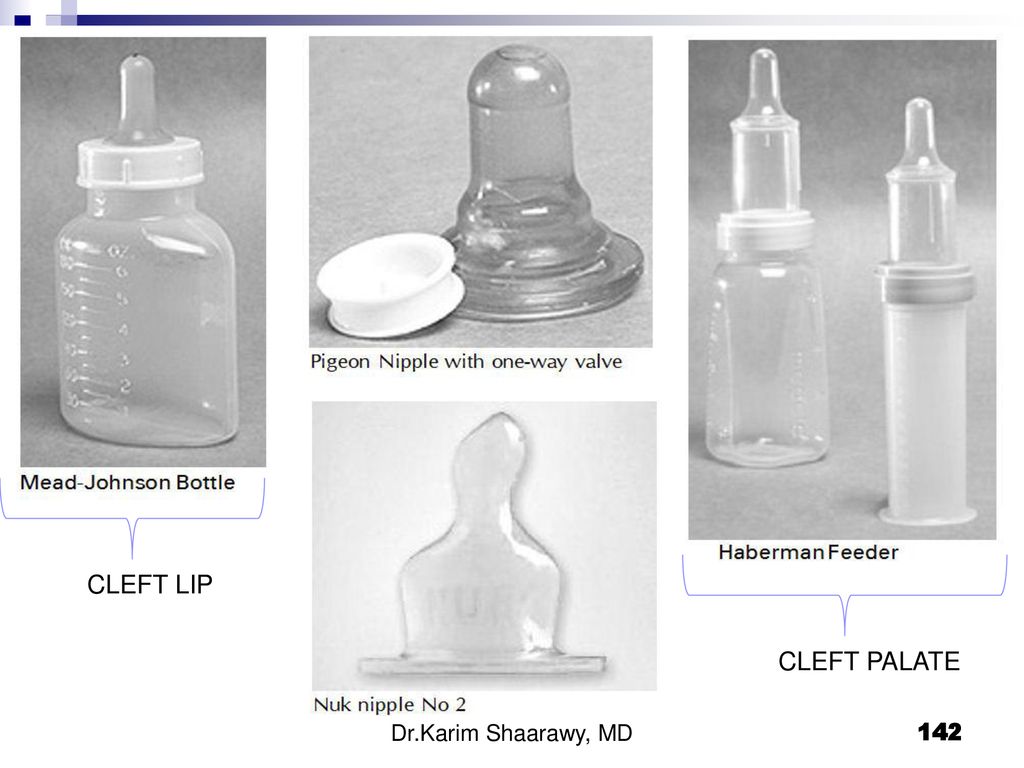 In March 2022, FDA inspectors observed several places that were positive for the presence of Cronobacter in the Abbott factory that manufactured the affected formulas.
In March 2022, FDA inspectors observed several places that were positive for the presence of Cronobacter in the Abbott factory that manufactured the affected formulas.
Babies younger than three months or with weakened immune systems are especially susceptible to bacterial infections, and Cronobacter can cause serious and potentially fatal infections. Make sure to prepare infant formula in a clean, sanitized area and keep your hands clean.
Michelle Llamas, BCPA | 0:49 What is NEC?
Senior Writer Michelle Llamas discusses what necrotizing enterocolitis is and how it has been linked to baby formula.
What Is Necrotizing Enterocolitis (NEC)?
Necrotizing enterocolitis is a gastrointestinal disease that usually affects infants. It’s fatal in up to 50% of all cases, according to a 2022 article. NEC causes inflammation that can cause tissues in the intestine and colon to die. It may lead to holes in the intestine, sepsis and death.
It may lead to holes in the intestine, sepsis and death.
NEC symptoms include lack of appetite, tenderness or swelling in the abdomen, bloody stools, vomiting and sluggishness. It typically affects babies between three and 12 days after birth but can occur many weeks after.
Studies show that premature babies fed cow’s milk formula alone or as a supplement to breastfeeding are more likely to develop NEC. One of the first studies to link cow’s milk formula to NEC was a 1990 study that showed that NEC was up to 10 times more common in formula-fed premature babies.
Parents of premature babies that developed NEC are filing baby formula lawsuits against the makers of Enfamil and Similac for failing to warn them of the risk.
Lawsuit Information
Lawsuits are being filed by parents whose children were diagnosed with necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) after consuming cow's milk-based formula. Learn more.
View Lawsuits
Side Effects of Changing Baby Formulas
Sometimes, your baby’s pediatrician may recommend changing baby formulas. It may be because of food allergies, formula intolerance or other medical concerns. Some babies may have side effects from switching baby formulas, but they are usually mild digestive issues, such as changes in stool.
It may be because of food allergies, formula intolerance or other medical concerns. Some babies may have side effects from switching baby formulas, but they are usually mild digestive issues, such as changes in stool.
Signs a baby isn’t tolerating a type of formula well include: Diarrhea, constipation, gassiness or frequent throwing up. More serious intolerance issues include: Bloody stools, congestion or wheezing after eating.
It can be a shock to a baby’s sensitive digestive system if you change formulas too quickly. Parents should transition a baby to the new formula by slowly adding it into feeding times. Make sure to consult your pediatrician on how to properly transition your baby and how long to test a new formula to avoid side effects.
Baby Formula Side Effects Facts
Please seek the advice of a medical professional before making health care decisions.
TELL US WHAT YOU THINK
Did You Find Drugwatch Helpful?
Yes No
Thank you for your feedback.
 Do you have any thoughts you'd like to share about Drugwatch.com?
Do you have any thoughts you'd like to share about Drugwatch.com?This article changed my life!
This article was informative
I have a question
How can we improve this page?
This article contains incorrect information
This article doesn't have the information I'm looking for
I have a question
How can we improve this page?
Thank You for Your Feedback
We appreciate your feedback. One of our content team members will be in touch with you soon.
We appreciate your feedback. One of our content team members will be in touch with you soon.
Bottle-feeding babies: giving the bottle
About bottle-feeding
If your baby can’t always feed directly from your breast, you might choose to bottle-feed with expressed breastmilk. Or you might need to feed your baby infant formula, which is the only safe alternative to breastmilk.
Before you bottle-feed your baby, it’s important to know how to clean and sterilise bottle-feeding equipment, as well as how to prepare, store and warm bottles of formula. This will help to keep your baby safe from infection and make sure baby is getting the right nutrition.
This will help to keep your baby safe from infection and make sure baby is getting the right nutrition.
Getting the right flow when bottle-feeding
To test the flow of the formula or breastmilk, hold the bottle upside down when it’s filled with liquid at room temperature. The liquid should drip steadily from the teat but not pour out.
If you have to shake the bottle vigorously to see the drip, the flow is too slow. Your baby might go to sleep before drinking what they need.
When you feed your baby, you might see a little leakage at the corners of your baby’s mouth. This doesn’t mean the flow is too fast. It’s nothing to worry about. It will stop as your baby gets older.
If you have trouble finding a teat with a flow to suit your baby, try a faster teat rather than a slower one. You might need to try a few different teats before you find one that suits.
Giving baby the bottle
Make yourself comfortable and cuddle your baby close to you, holding baby gently but firmly. It’s better for your baby to be on a slight incline so any air bubbles rise to the top, making burping easier.
It’s better for your baby to be on a slight incline so any air bubbles rise to the top, making burping easier.
Put the teat against your baby’s lips. Your baby will open their mouth and start to suck. Keep the neck of the bottle at an angle so it’s filled with formula or breastmilk.
When your baby stops sucking strongly or when about half of the formula or breastmilk has gone, gently remove the bottle and see whether baby wants to burp. Once you’ve tried burping your baby, you can offer the bottle again.
Paced bottle-feeding
Babies who are normally breastfed might find it hard to pace themselves when bottle-feeding, particularly if they’re premature. This is because they’re used to controlling the flow of breastmilk. Sometimes these babies can drink too much too quickly.
Paced feeding can sometimes help. This involves holding your baby in an upright position and letting them rest every few minutes. If you’re interested in paced bottle-feeding, it’s best to get help from your child and family health nurse or a lactation consultant.
Holding, cuddling and talking to your baby during feeding will help baby develop and grow. It’s also a great opportunity to bond with your baby.
When baby doesn’t finish the bottle or goes to sleep while feeding
Don’t worry if your baby doesn’t finish the bottle. Babies are very good at judging how much they need, so you can let your baby decide when they’ve had enough formula or breastmilk.
If your baby goes to sleep during a feed, put baby over your shoulder, rub their back, and stroke their head, legs and tummy. This can help your baby to wake up. A nappy change is a good way to wake up your baby if that doesn’t work.
Wait until your baby is properly awake before offering the rest of the formula or breastmilk.
If there’s any formula or breastmilk left in the bottle, throw it away after one hour. When your baby drinks from a bottle of formula or breastmilk, bacteria from their mouth get into the milk. The bacteria can grow and make your baby sick if you give your the baby the half-finished bottle later.
When baby refuses the bottle
Babies sometimes refuse a bottle altogether. Here are things to try if this happens:
- Try a new feeding position or change the feeding environment. For example, move around while you’re feeding, find a quieter place to feed, or play some relaxing background music.
- Try again later when your baby is more settled. For example, give your baby a bath and then try again.
- Ask your partner or another family member to give your baby the bottle.
- Try using a different teat. If the flow of formula or breastmilk is too slow, it might frustrate your baby.
- Let your baby open their mouth for the bottle when they’re ready, rather than putting the teat into their mouth.
- Offer the formula or breastmilk from a small cup or spoon. To do this, sit your baby up and offer them small sips.
If your baby is regularly refusing the bottle, you could try adjusting your routine.
If you think your baby is refusing the bottle because they’re unwell, treat your baby’s symptoms or take your baby to see your GP.
How much do bottle-feeding babies drink?
Newborn babies commonly have 6-8 feeds every 24 hours, but there’s no set amount of food or number of feeds your baby should have. Different babies drink different amounts of formula or breastmilk. Some might have feeds close together and others further apart. And it can change from day to day.
Just feed your baby whenever they’re hungry. You’ll see baby cues that say ‘I’m hungry’ – for example, your baby will make sucking noises or start turning towards the breast or bottle. If your baby stops sucking or turns their head away from the bottle, you’ll know they’ve had enough.
As your baby eats more and more solid food, the total amount of breastmilk or formula they take in a day will decrease. The amount of breastmilk or formula will also decrease as your baby starts to drink from a cup instead of a bottle.
Some babies never drink the ‘recommended amount’ for their age and size, and others need more. Plenty of wet nappies, consistent healthy weight gains, and a thriving, active baby mean all is well. If you’re concerned about how much breastmilk or formula your baby is taking, talk to your child and family health nurse or GP.
Plenty of wet nappies, consistent healthy weight gains, and a thriving, active baby mean all is well. If you’re concerned about how much breastmilk or formula your baby is taking, talk to your child and family health nurse or GP.
Bottle-feeding in bed: issues and risks
Sleep associations
If your baby gets used to falling asleep with a bottle in bed, they might depend on it to get to sleep. This can make it more difficult for your child to fall asleep or settle for sleep independently.
Bottle-feeding in bed also has several risks for your baby.
Choking
Babies who fall asleep while bottle-feeding can draw liquid into their lungs. They might then choke on it or inhale it.
Tooth decay
Babies have less saliva in their mouths to protect their teeth during sleep. If your baby falls asleep with a bottle, the lactose in the milk can build up on your baby’s teeth, putting your baby at risk of tooth decay.
Ear infections
If your baby drinks while lying flat, milk can flow into the ear cavity, which can cause ear infections.
It’s best to put your baby to bed without a bottle or to take the bottle away after your baby has finished feeding.
Using a feeding cup
When your baby is around 6 months old, you can help your baby start leaning to drink from a cup. It’s best to stop using bottles by the time your baby is 12 months old.
You should continue to thoroughly wash and sterilise feeding cups containing infant formula or breastmilk until your baby is 12 months old.
newborn diet on IV, how to properly feed a baby with formula from a bottle
The desire for a child to grow up strong and healthy is natural for mothers. And the health of a newborn begins with proper nutrition. Mother's milk has always been considered the best option for feeding - the most healthy and nutritious food for infants. However, in some cases, breastfeeding is not possible.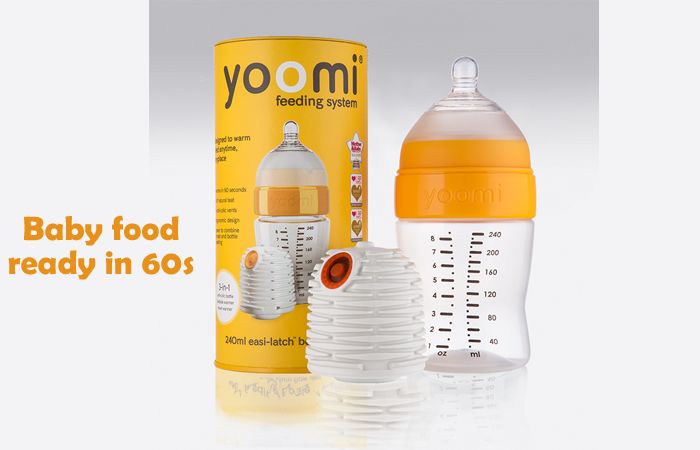 And then mixtures come to the aid of mothers.
And then mixtures come to the aid of mothers.
Contents: Hide
- In what cases is the transition to artificial feeding
- How to choose a mixture of
- Basic artificial feeding rules
- The main errors for artificial feeding
In what cases is required the transition to artificial feeding 9,0002 Medical medical contrasts to breastfeeding. There are a number of diseases in which breast milk is prohibited. On the mother's side, these are HIV, an open form of tuberculosis, dangerous infections, and a serious state of health. On the part of the child, these are leucinosis, galactosemia, and individual food intolerance. It is not necessary to take tests after hearing the terrible names of diseases. All newborns are checked in maternity hospitals for their presence. But allergies are not so easy to identify. Many newborns have skin rashes and redness, which may be due to a reaction to an aggressive environment. Only a strict diet for the mother can help here, so that her milk does not contain allergens, monitoring the baby and consulting a doctor.

Lack of lactation or its complete cessation. This is the second objective reason for transferring a child from breast milk to formula. Lactation does not always come in the right amount and it can be increased. It happens that milk disappears a few days after the birth of the crumbs. This often depends on the individual characteristics of the mother's body. So that the child does not starve, he is first transferred to mixed, and then completely to artificial feeding.
Insufficient nutritional value of mother's milk. Usually this problem can be solved without resorting to the transition to IoT, but this is not always possible. A woman may have a lot of milk, but it will be like water in both color and consistency. In such cases, doctors give advice to the mother on nutrition in order to increase the fat content of milk and its usefulness. If the milk remains watery, the child stops eating, cries of hunger, loses weight. The only way out in this situation is the transition to the mixture.
Impossibility of regular feeding. Children who, for a number of reasons, are separated from their mother for long periods of time are transferred to artificial feeding: the woman is in a hospital, going to work or study, business trips, etc. If the break in breastfeeding is one-time, then restoring lactation and breastfeeding is still possible . However, more often in such cases, breastfeeding has to be abandoned.
Mother's personal wish. Unfortunately, there are cases when a woman, having every opportunity to breastfeed her baby, refuses to breastfeed for various subjective reasons. In this case, lactation is interrupted, and the baby is transferred to the mixture.
Read also: Newborn weight gain by month
How to choose a formula
If you are going to transfer your baby to artificial feeding, then the first thing you will encounter will be the choice of nutrition. Today there are a large number of different mixtures: adapted and non-adapted, dairy and sour-milk, dry and liquid. There are mixtures against regurgitation, hypoallergenic, for premature babies, etc. How to choose the optimal replacement for mother's milk from such a variety?
There are mixtures against regurgitation, hypoallergenic, for premature babies, etc. How to choose the optimal replacement for mother's milk from such a variety?
- Make your choice only after consulting a pediatrician. The doctor will examine the baby and give all the necessary recommendations.
- Monitor your child. When adapting to a new diet, the child may have small rashes, but they disappear if the body begins to absorb the mixture normally. The baby eats with appetite, he has a normal stool and no colic. Otherwise, the mixture must be changed.
- If it is necessary to replace the mixture with a thicker formula (anti spit up), choose the same brand of food that was previously used.
- Consider the age of the baby. All mixtures have a gradation by months of life.
- Prefer adapted formulas, they are usually easier to digest
Basic rules for artificial feeding save you a lot of problems.
1. Choose proven blends.![]() This applies not only to the choice of brand, but also to the packaging itself. Look at its integrity, check the expiration date.
This applies not only to the choice of brand, but also to the packaging itself. Look at its integrity, check the expiration date.
2. Observe the storage conditions for opened packaging at home (in a dry and cool place, but in no case in the refrigerator, the mixture must not become damp). Remember that the open mixture is stored for three weeks. After this period, it can no longer be used.
3. Strictly follow the instructions when preparing meals. It is indicated on the packaging. Water for the preparation of the mixture must be purified and boiled. The optimal temperature for preparing the mixture is 36–37 °C. You can cook food right in the bottle. This is quite convenient, since baby bottles have a volume scale that makes it easier to calculate the right amount of scoops. The mixture must be stirred until completely dissolved, and then cooled to an acceptable temperature so that the baby can drink without burning himself. You can check if the milk is hot by dropping it on your wrist - there the skin is most tender and sensitive. If the temperature is almost not felt, then the mixture can be given to the child.
If the temperature is almost not felt, then the mixture can be given to the child.
4. Sterilize baby dishes. Baby bottles and nipples should be thoroughly rinsed using a special brush so that no food residue remains. You can use children's dishwashing detergents. Do not wash bottles with common cleaning products that you are used to using, no matter how good they are. After washing, be sure to place the dishes in boiling water. This helps to kill harmful bacteria. It is recommended to sterilize children's dishes during the entire first year of a baby's life. Then you can limit yourself to just a thorough wash.
5. Hold the bottle in a semi-vertical position when feeding. The milk should completely fill the nipple. This prevents the child from swallowing air. After feeding, it is necessary to hold the baby in a column for several minutes to avoid spitting up.
6. Monitor the amount of formula consumed and the feeding schedule. Maintaining a balance is extremely important for the healthy and full development of the baby.
- Calculate the amount of formula to be prepared based on the baby's weight. It is body weight, and not the age of the crumbs, that is the main indicator when calculating the daily nutritional intake. You can find out the required volume of the mixture for feeding either at a pediatrician’s appointment, or on your own (it is recommended to use Maslov’s caloric method when calculating).
- Observe breaks between feedings. During the day they should be 3.5 hours, at night - 6. Try not to break the schedule.
- Give your child water. Supplementation with water is a necessity for artificial feeding. Water should be given somewhere in the middle of the interval between feedings or 10-15 minutes after it. Avoid supplementation before meals.
Major mistakes in artificial feeding
Overfeeding. The desire to feed the child is understandable, but in the case of mixtures, feeding must be approached strictly. On artificial feeding, the child is normally gaining weight very well. Excess body weight is an additional burden on the body and health problems. Even an adult can find it difficult to cope with problems from being overweight. What to say about the tiny weak body of a newborn? Follow the diet and control the daily milk intake. Fortunately, you can always see how much the child ate.
Excess body weight is an additional burden on the body and health problems. Even an adult can find it difficult to cope with problems from being overweight. What to say about the tiny weak body of a newborn? Follow the diet and control the daily milk intake. Fortunately, you can always see how much the child ate.
Unreasonable mixture change. If the child eats the current mixture well, then it is not necessary to change it. The baby will have to go through a difficult period of adaptation again, and it’s not a fact that his body will accept new food just as well.
Use of old mix. The child's food must be fresh. If the child has not finished eating, then literally after half an hour the milk can only be poured out. Milk mixtures are an excellent environment for the life of pathogenic bacteria.
Pet milk feeding. Do you think this is a more natural option than artificial mixtures? This is an erroneous opinion. For a child under one year old, cow or goat milk, even boiled, is strictly prohibited.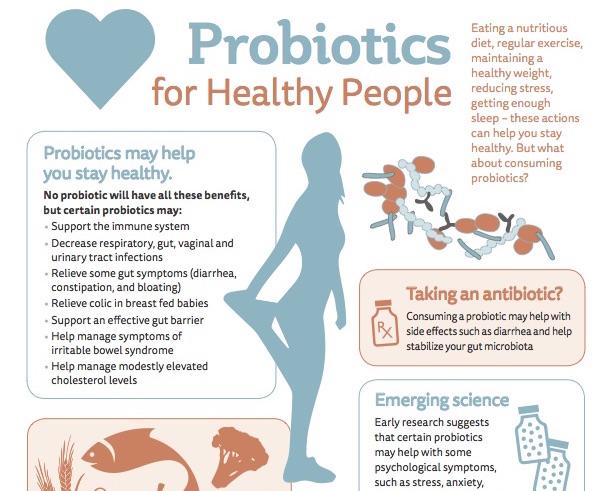 The composition of such milk is very different from that of women, which can lead to the development of allergies, diseases, problems with the skeletal system in the baby.
The composition of such milk is very different from that of women, which can lead to the development of allergies, diseases, problems with the skeletal system in the baby.
If you have any doubts about your baby's nutrition, please consult neonatologists and paediatricians. Do not rush to make decisions without expert advice. After all, nothing is more important than your baby's health.
#Nutrition for children up to a year
feeding rules, types of mixtures, tips for nursing mothers
If breastfeeding is impossible, do not be upset: modern technologies make it possible to achieve maximum compliance of artificial feeding with all healthy nutrition standards. We talk about the basic rules of artificial feeding and common mistakes.
Website editor
Tags:
Health
weight loss
Children
Nutrition
VOICE recommends
The health of a newborn is directly dependent on his nutrition.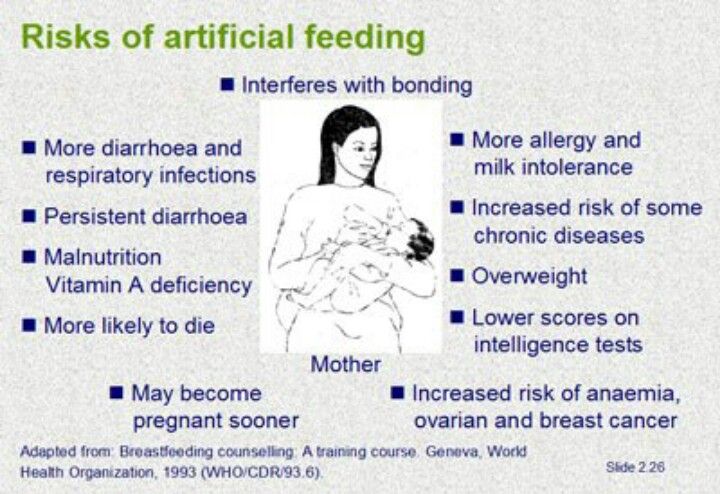
⚡️⚡️⚡️ TO STAY CONNECTED NO matter what, LOOK FOR US IN Yandex.Zen, VK, Telegram, Odnoklassniki.
If you can breastfeed, great, this is the best food for your baby. But if for some reason natural feeding is not possible, this is not a reason to panic: there are now many healthy mixtures that can replace mother's milk. Study our rules for artificial feeding, and everything will work out!
When to switch to artificial feeding
- Inability to breastfeed for medical reasons. With some diseases, as well as when taking a number of medications, breastfeeding is prohibited, since milk can be dangerous for the baby due to the content of toxic substances. Sometimes the reason to stop breastfeeding may be the child's disease (for example, cleft lip or severe malformations).
- Cessation of lactation. If there is not enough milk or it has disappeared completely, there is nothing to do, you need to supplement the baby with mixtures.
 As a rule, mixed and artificial feeding solve the problem.
As a rule, mixed and artificial feeding solve the problem. - Inability to feed regularly. For example, you can go to work or end up in a hospital, and this is not a reason to starve a child, but a reason to switch to mixed or artificial feeding: the rules for feeding and portion sizes change somewhat.
- Inadequate nutritious milk from the mother. Sometimes the problem is solved by changing your diet, but if the milk remains watery and the baby is screaming with hunger, then it's time to supplement him with mixtures, and later switch to them completely.
- The wish of the child's mother. No matter how pediatricians talk about the benefits of breastfeeding, sometimes women who have every opportunity to breastfeed still prefer to give their baby a bottle. Well, that's your right. Just learn first the rules of artificial feeding of infants!
ADVERTISING - CONTINUED BELOW
Rules for artificial feeding of a child
1.
 How to choose a formula?
How to choose a formula? It is best to ask a pediatrician for recommendations, but in principle, if the baby is not lactose intolerant, any mixture approved by the Union of Pediatricians of Russia will do. It is great if the mixture contains Omega 3 and Omega 6 fatty acids, they contribute to the harmonious development of the nervous system.
For example, Nutricia's "Baby" formula meets all the standards and rules of artificial feeding, is produced according to European technologies with the strictest quality control and is recommended as an alternative to breast milk, even for newborns. Nutricia regularly evaluates the quality and demand for its products among consumers and doctors, analyzing the results of independent surveys of pediatricians and mothers with children up to 24 months of age.Iodine, selenium, zinc, iron with enough vitamin C (for better absorption), choline, taurine, L-carnitine are modern ingredients, the amount of which is specially selected in formulas to meet the needs of children.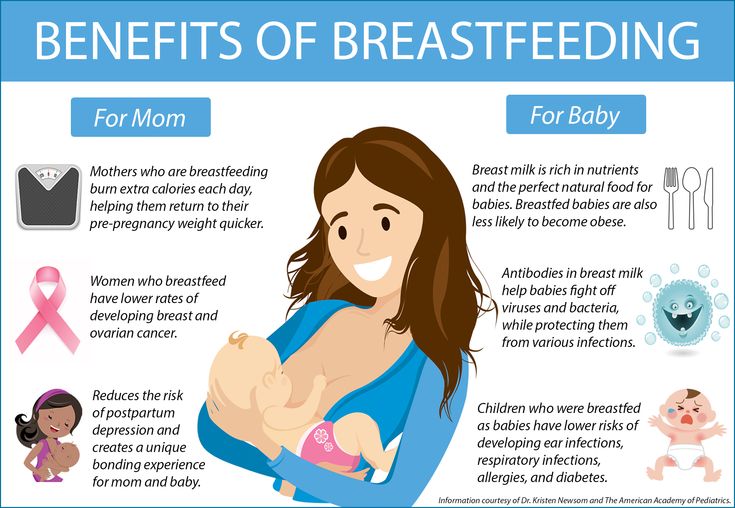 The quality is monitored by the Dutch research center Numico, the milk base for formulas is made in the most environmentally friendly country - Ireland, and production is open in Russia, at a plant in Istra, which received the international ISO 22000 certificate - maximum food safety control who in.
The quality is monitored by the Dutch research center Numico, the milk base for formulas is made in the most environmentally friendly country - Ireland, and production is open in Russia, at a plant in Istra, which received the international ISO 22000 certificate - maximum food safety control who in.
Bibikol New Zealand brand mixture is produced on the basis of wholesome goat milk. The range of the brand includes mixtures for the smallest and older children, and the quality of the products is confirmed by Russian pediatricians. As a rule, formula feeding does not cause serious side effects even during the adaptation period.
The Dutch brand Kabrita also makes milk formulas based on goat's milk, which is easier to digest than traditional cow's milk. The brand's products contain vitamins, microelements and other functional ingredients necessary for the development of the child.
The mixtures of another Dutch brand, Friso, are considered among the best due to their high quality. The brand offers mixtures for both newborns and older children. Subject to the rules for artificial feeding, this is an excellent choice for babies of different ages.
The brand offers mixtures for both newborns and older children. Subject to the rules for artificial feeding, this is an excellent choice for babies of different ages.
2. How do I know if formula is right for my baby?
If possible, the transition to artificial feeding should be done according to the rules, gradually replacing breast milk with formula. Pediatricians believe that adaptation to a new diet in babies under the age of one year takes from 3 to 7 days. During this period, stool changes, gas formation are possible, and this should not be frightened. As a rule, after a week, the baby stops worrying about the tummy and gets used to the new mixture. If this does not happen, it is worth choosing another food for him. For example, instead of the usual milk mixture, offer a fermented milk analogue. Major brands, like Nutricia's Malyutka, always have both options in their product line.
Formula milk can be used from birth
To improve digestion, a pediatrician can recommend fermented milk formula for formula feeding
3.
Feeding bottles are available in plastic and glass, and each has its own advantages, there are no strict rules for artificial feeding in this regard. Plastic ones are safer because they don't break. They are lighter, so it is convenient to take them with you for a walk. Glass is good because it can be sterilized many times, while plastic can deteriorate. Which bottle to choose for a newborn depends on the age of the baby. For the smallest, glassware is better, since sterility is in the first place. For older babies outside the home, it is better to use plastic bottles, but for home feeding, still leave glass bottles.
4. How to properly store baby food?
Prolonged exposure to abnormal temperatures, both low and high, can change the organoleptic properties of the product, affect its solubility, and cause swelling of the foil bag or the protective membrane of the can. In case of repeated heating and cooling of the mixture, especially in winter, further use of the product may cause a painful reaction in the child. Therefore, it is very important to observe temperature control from 0ºС to +25ºС. Formula feeding regulations do not recommend storing product near heat sources such as stoves, electric kitchen appliances, radiators, or on windowsills.
5. How long can I keep formula formula?
Less than an hour. If the baby has not finished eating, and you intend to finish feeding him in 15-20 minutes, you can not prepare a new mixture. But if the baby has eaten enough, and the feeding regimen for artificial feeding provides for the next feeding only after 2.5 - 4 hours, then the leftovers should be poured out, and a new portion should be prepared for the next time.
6. Does my child need probiotic formula?
GOS/FOS prebiotics are natural dietary fibers similar in composition to breast milk prebiotics, they are added as high-quality mixtures to improve digestion. The child quickly and painlessly gets used to such a mixture, absorbs it well and encounters stool disorders less often. Rules for artificial feeding of newborns and older children recommend giving preference to such mixtures, although this is not a strict requirement.
7. How do you know if your baby is eating enough?
You can use the Shkarin formula: The volume of the mixture per day = 800 ml + 50 x (M-2), where M is the number of months of the child's life. But this method is only suitable for babies older than 2 months. For newborns, everything is very individual, since babies are born with different weights and heights, so if you are afraid that the baby is malnourished or overeating, consult a doctor before feeding the baby formula again.
8. Should I change my formula?
If there is no reason to doubt the quality of the mixture and its tolerance by the baby, you should not change your child's usual diet just because the new mixture seems more useful, modern, etc. to you. Replacing the mixture can be a real stress for the child's body. And there is no guarantee that a new diet will not cause any signs of intolerance. Replacing the mixture is justified when passing the next age limit, and even in this case, the rules for artificial feeding recommend remaining faithful to one manufacturer.
9. What is the correct way to mix?
According to the rules of artificial feeding, most mixtures are prepared as follows: cool boiled water to a temperature of 50-60 ° C (a higher temperature cannot be used, live bifidobacteria die and some vitamins are destroyed). Pour it into a bottle, add the exact amount of the dry mixture there. Close the bottle, mix the mixture thoroughly, shaking the contents of the bottle. Look at the light so that there are no lumps, the milk should turn out homogeneous. To check the temperature of the food - put a few drops on your wrist or elbow crease (the most sensitive place). The mixture should be slightly warmer than body temperature—i.e. practically not felt.
10. Technique and rules of artificial feeding
How to formula feed correctly? In order to make it comfortable not only for the baby, who should be in a semi-vertical position, but also for the mother during feeding, you can use additional pillows by placing them under the back. The position of the mother's legs can be different: you can put your foot on the foot, you can put a low bench under your feet, you can feed the baby in the prone position, while gently holding the baby. To reduce air swallowing, tilt the bottle so that the milk fills the nipple and the air rises to the bottom of the bottle. Hold your baby upright for a few minutes after feeding to reduce the chance of spitting up.
Mistakes in formula feeding
- Blame yourself for being an "artificial" baby. Yes, mother's milk is considered the best food for babies, but if for some reason you cannot provide a child with them, this is not a reason to declare yourself a bad mother.