Solid food for 1 month baby
Feeding Your 1- to 3-Month-Old (for Parents)
During your baby's first 3 months, breast milk or formula will provide all the nutrition needed. Doctors recommend waiting until your baby is about 6 months old to start solid foods. Some babies may be ready for solids sooner than 6 months, but wait until your baby is at least 4 months old.
What Changes Should I Expect?
As your infant grows, feeding will change. Babies will start drinking more milk during each feeding, so they won't need to feed as often and will sleep longer at night.
Your baby's appetite will increase during growth spurts. Continue to feed on demand and increase the number of feedings as needed.
Your infant also will become more alert as the weeks go by, cooing and smiling. So there will be more interaction between you and your baby during feedings.
The following are general guidelines, and your baby may be hungrier more or less often than this. That's why it's important to pay attention to your baby's signals of being hungry or full. A baby who is getting enough might slow down, stop, or turn away from the breast or bottle.
Breastfeeding: How Much and How Often?
As babies get older, they will start to breastfeed less often and sleep for longer periods at night. Your infant probably is eating enough if he or she:
- seems alert, content, and active
- is steadily gaining weight and growing
- feeds six to eight times per day
- is wetting and soiling diapers on a regular basis
Babies might not be eating enough if they:
- don't appear satisfied
- cry constantly
- are irritable, even after feeding
- are not making wet diapers
Call your doctor if you're concerned your baby isn't eating enough.
A few weeks after birth, breastfed babies tend to have fewer bowel movements (BMs, or poop) than they did before. At around 2 months of age, your baby may not poop after each feeding, or even every day. During growth spurts, you may notice that your little one wants to feed more often. This frequent nursing sends a signal to make more milk. Within a couple of days, supply and demand will get into balance.
This frequent nursing sends a signal to make more milk. Within a couple of days, supply and demand will get into balance.
Babies who get breast milk only should get vitamin D supplements within the first few days of life. Other supplements, water, juice, and solid foods aren't usually needed.
Formula Feeding: How Much and How Often?
Babies digest formula more slowly than breast milk, so if you're bottle-feeding, your baby may have fewer feedings than a breastfed infant.
As babies grow, they can eat more at each feeding and may go for longer stretches between feedings. You'll also notice that your baby is starting to sleep longer at night.
During the second month, infants may take about 4 or 5 ounces at each feeding. By the end of 3 months, your baby may need an additional ounce at each feeding.
It's easy to overfeed a baby when using a bottle because it easier to drink from a bottle than from a breast. Make sure that the hole on the bottle's nipple is the right size. The liquid should drip slowly from the hole and not pour out. Also, resist the urge to finish the bottle when your baby shows signs of being full.
The liquid should drip slowly from the hole and not pour out. Also, resist the urge to finish the bottle when your baby shows signs of being full.
Never prop a bottle. Propping a bottle might cause choking and it increases the chances of getting ear infections and tooth decay.
Should I Worry About Spitting Up?
It's normal for infants to "spit up" after eating or during burping. Spitting up a small amount — usually less than 1 ounce (30 ml) — shouldn't be a concern as long as it happens within an hour of feeding and doesn't bother your baby.
You can reduce spitting up in these early months by:
- feeding before your baby gets very hungry
- keeping your baby in a semi-upright position during the feeding and for an hour after
- burping your baby regularly
- avoiding overfeeding
- not jostling or playing vigorously with your baby right after a feeding
If your baby seems to be spitting up large amounts, is spitting up forcefully, is irritable during or after feedings, or seems to be losing weight or is not gaining weight as expected, call your doctor. And if your child has a fever or shows any signs of dehydration (such as not wetting diapers), call the doctor right away.
And if your child has a fever or shows any signs of dehydration (such as not wetting diapers), call the doctor right away.
Call your doctor if you have any questions or concerns about feeding your infant.
Reviewed by: Mary L. Gavin, MD
Date reviewed: November 2021
Movement, Coordination, and Your 1- to 3-Month-Old (for Parents)
Reviewed by: Mary L. Gavin, MD
en español Movimiento, coordinación y su bebé de 1 a 3 meses de edad
The reflexes babies had just after birth start to disappear now as they gain more control over their movements and start to interact with caregivers and world around them.
What Can My Baby Do?Newborns struggle to lift their heads. But as neck and upper body strength improve, they'll be able to lift their heads while on their bellies and eventually prop themselves up on their arms. Once there, they’ll hold their heads up and look around.
You also may notice your baby stretching and kicking the legs. This movement strengthens leg muscles, preparing your baby to roll over, which usually happens by 6 months of age. But be careful: Even very young babies can roll over on occasion, so it's important to never leave a baby unattended on a changing table, bed, or other high surface.
This movement strengthens leg muscles, preparing your baby to roll over, which usually happens by 6 months of age. But be careful: Even very young babies can roll over on occasion, so it's important to never leave a baby unattended on a changing table, bed, or other high surface.
Infants grasp reflexively from birth, but during the first 3 months of life they'll begin to open and shut their hands and start moving their hands to their mouths. Your baby may be able to hold a rattle or a toy that is placed in the hand — and drop it when no longer interested in it.
Vision also starts to improve as your little one develops the ability to follow a moving object with their eyes. Then watch as your baby tries to use their arms to swing at toys.
How Can I Encourage My Baby?Infants need to practice their skills. While babies should never sleep on their stomachs, give your child supervised tummy time during waking hours. This lets your little one practice lifting their head and strengthening the neck, arm, and shoulder muscles.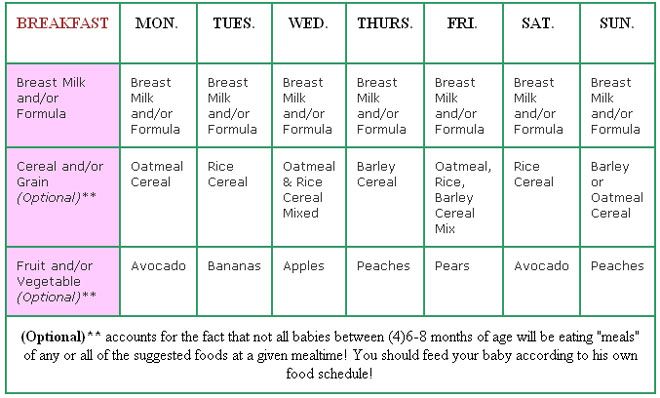
Your baby may get fussy and frustrated in this position, so keep the first tummy time sessions brief and gradually lengthen them. Always stay with your baby during tummy time.
Encourage hand–eye coordination by letting your baby reach for favorite toys while sitting on your lap or by placing them under an infant gym to bat at toys.
When Should I Call the Doctor?Normal child development tends to follow a certain pattern. The skills that babies develop early serve as building blocks for future skills. Still, the time it takes to develop these skills can vary widely among babies.
Let your doctor know if by your baby isn't doing the following:
By 2 months:
- hold their head up while lying on the tummy
- open their hands
By 4 months:
- grasp or hold objects put in their hands
- keep their head steady while being held
- lift the head and pushing up onto elbows/forearms during tummy time
Not reaching individual milestones doesn't always mean there is a problem.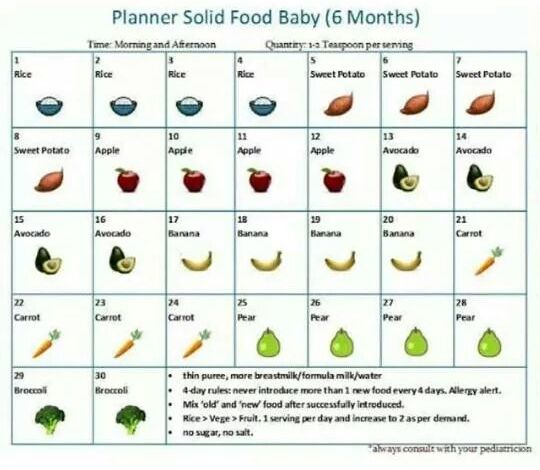 But talk to your doctor if you have questions or concerns about your baby's development.
But talk to your doctor if you have questions or concerns about your baby's development.
Reviewed by: Mary L. Gavin, MD
Date reviewed: May 2022
Introducing Solid Food: Why, When, What and How
Introducing Solid Food: Why Babies Need It
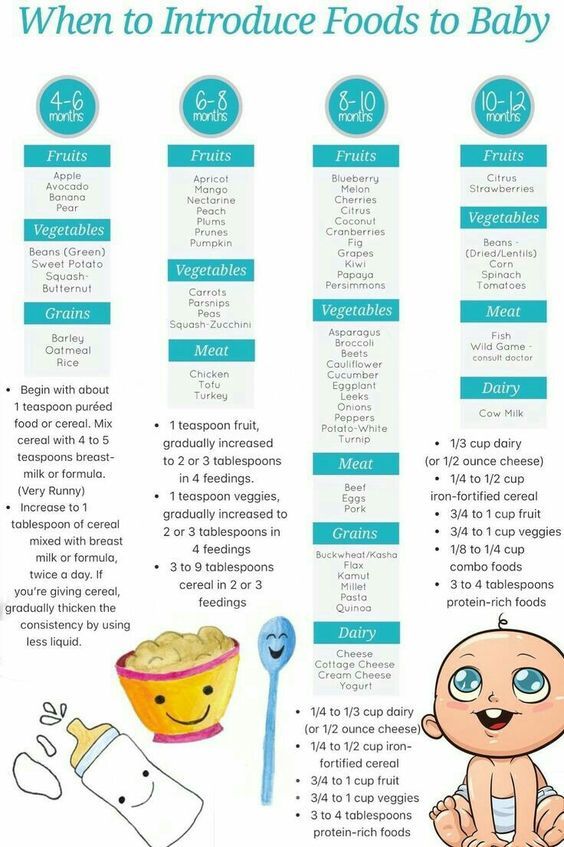
As babies grow older, the need for solid food arises, from which the body will receive enough iron and other nutrients necessary for growth and development.
During the first six months, the baby's body uses the iron stored in the womb. Some iron also comes from breast milk and/or formula. But as the baby grows, the reserves of this substance in the body decrease. And the iron that a child receives from breast milk or formula is already not enough at the age of about six months. nine0005
Through the introduction of solid foods, the child also learns to eat, gets to know new tastes and textures of different foods. At the same time, he develops teeth and jaws, and he also acquires skills that will later be needed for language development.
Signs it's time to introduce solid foods
You will know when it's time to introduce solid foods by how your baby develops and behaves.
Your child is ready for solid food if:
- holds head and neck well and can sit upright with support
- shows interest in food - for example, looking at the contents of your plate
- reaching for your food
- opens his mouth when you offer him food from a spoon.
Most children show these signs by about six months, but in general everyone is individual.
It is not recommended to introduce solid foods before four months of age.
If your baby is about seven months old and hasn't started solid foods yet, you can talk to a nurse or pediatrician. nine0005
The best time to offer solid food to your baby is when you and he are in a good mood for the first time.
He is also more likely to try new foods after breast milk or formula. The fact is that when a child is really hungry, he only wants milk or formula, because he knows that he will be satisfied. At the same time, there will still be room for other food in his tummy.
The fact is that when a child is really hungry, he only wants milk or formula, because he knows that he will be satisfied. At the same time, there will still be room for other food in his tummy.
Over time, you will learn to tell if your baby is hungry or full, wants to try something or is tired. nine0005
Your child is hungry, if:
- brightens up when he sees you cooking for him
- leans towards you while sitting in a highchair
- opens its mouth when you are about to feed it.
Your child no longer wants to eat if:
- turns away
- loses interest or gets distracted
- repels spoon
- purses his lips.
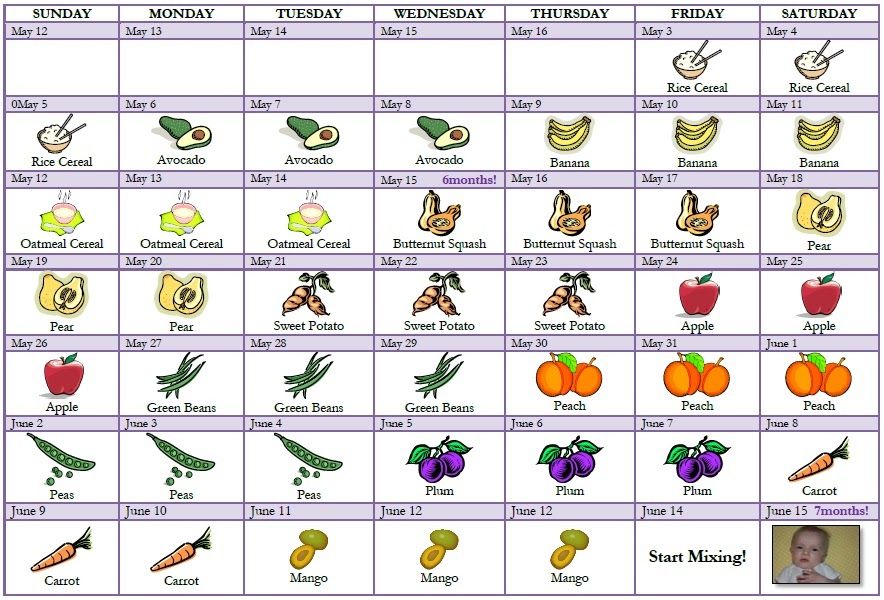
In what portions should the new food be introduced to the child? Start with 1-2 teaspoons and increase according to your baby's appetite. By 12 months, he should be eating about three small meals a day, plus breast milk or formula. nine0005
Consistency of solid food
The first solid food can be smooth, pureed or in soft pieces , depending on your baby's preference. Then the child can quickly move on to finely chopped, and then just to finely chopped foods.
Then the child can quickly move on to finely chopped, and then just to finely chopped foods.
The child needs food of various consistencies. This will help him learn to chew, and chewing, in turn, contributes to the development of speech. It also encourages the child to learn to eat on his own and will prevent eating problems as he develops. nine0005
By 12 months, the baby should already be eating the same as the rest of the family. You may have to cut some foods into smaller pieces, and boil the vegetables well.
Do not leave the child unattended while eating, make sure that he does not choke. Be especially careful with foods such as nuts and small-boned meats, as they are easy to choke on. If the child can already move around, try to seat him while eating. If you sit next to each other while the baby is eating, he will most likely sit more quietly. nine0005
Types of foods when introducing solid foods
The child will be happy to try any new food, so there is no need to prepare something “special” for him.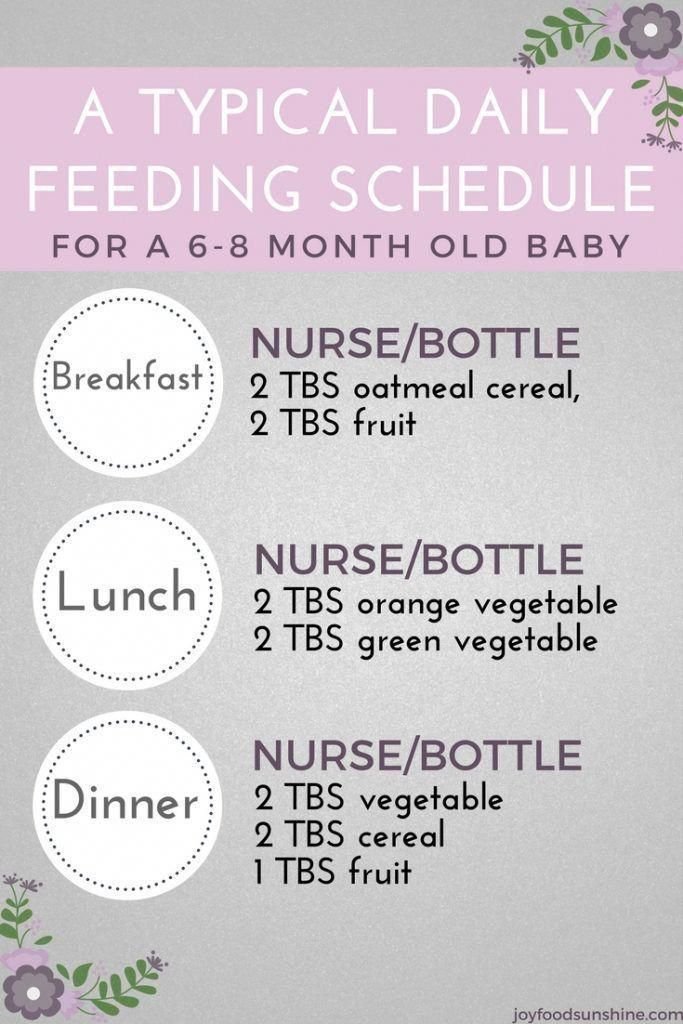
You can introduce solid foods in any order, as long as you include iron-rich foods and cook foods of the right consistency.
Foods rich in iron include:
- iron-fortified baby cereals
- minced meat, poultry and fish
- tofu and legumes, cooked
- mashed or boiled eggs (do not give raw or soft-boiled eggs).
Iron-rich foods can be supplemented with other healthy foods:
- vegetables such as boiled potatoes, carrots or green vegetables such as broccoli
- fruit - e.g. banana, apple, melon or avocado
- cereals - e.g. oats, bread, rice and pasta
- Dairy products such as yogurt and full fat cheese.
These products can be combined as there is no need to administer only one product at a time. By offering your child a variety of foods, you will allow him to try a variety of new tastes and get a lot of nutrients. nine0005
With our solid food introduction tips, you can get your child interested in new foods and make the eating process smoother and playful.
Breast milk and formula when introducing solid food
Continue breastfeeding or formula until at least 12 months while introducing solid food.
If you are unsure if your baby is getting the right amount of milk once solids are introduced, pay attention to his behavior. nine0005
For example, if a child has eaten a lot of solid food and is not getting enough or is not getting enough milk, the daily milk feeds may need to be made less frequent but longer. If the baby does not want to eat solid food, he may have had too much milk. This may be a signal that portions of milk should be reduced.
By about nine months of age, babies usually develop enough chewing and swallowing skills to eat solid foods before milk, not after. nine0005
Solid food does not replace breast milk or formula. If the transition to solid foods instead of milk and/or formula occurs too quickly, a child may miss an important milestone in their diet.
Water administration
At the age of six months, the child may be offered chilled boiled water in a cup during meals or at other times. This is to help your baby learn to drink from a cup, but at this age, he still doesn't need liquids other than breast milk or formula. When the child is one year old, he can be offered fresh tap water without boiling. nine0005
This is to help your baby learn to drink from a cup, but at this age, he still doesn't need liquids other than breast milk or formula. When the child is one year old, he can be offered fresh tap water without boiling. nine0005
Foods and drinks to avoid
Some foods should not be given to children under a certain age:
- honey under 12 months to avoid the risk of infant botulism
- raw eggs, soft-boiled eggs, and products containing raw eggs, such as homemade mayonnaise, up to 12 months - bacteria in raw eggs may be harmful to infants
- skim milk products up to two years
- Whole nuts and similar hard foods up to three years - due to risk of choking. nine0018
Also, up to a certain age, children should not be given certain drinks :
- pasteurized whole cow's milk as a main drink up to 12 months
- soy, goat and sheep milk up to two years (fortified soy products may be given up to two years)
- rice, oatmeal, almond or coconut milk up to two years of age, unless advised otherwise by a pediatrician or nurse
- Unpasteurized milk of all kinds, tea, coffee or sugar-sweetened beverages for all ages
- fruit juice - should be limited at any age (fruits contain the nutrients a child needs).

Salt and sugar should not be added to baby food. Infants and young children are not suitable for highly processed foods and packaged foods that are high in fat, sugar and/or salt. These include cakes, cookies, chips and fried foods.
Food allergy and introduction of solid foods
Early introduction of allergenic foods may reduce risk development of food allergy in a child.
All children, including children at high risk of allergies, should try allergenic foods from about six months of age . These foods include hard-boiled eggs, peanut butter, wheat (in wheat bread, cereals, and pasta), and cow's milk (but not as a staple drink).
It is recommended to consult a physician, health visitor, nutritionist, pediatrician, allergist or immunologist if:
- the child already has a food allergy
- you have a family history of food allergies and are concerned about introducing solid foods to your child
- you are worried about his reaction to the products.

Children with severe eczema and children of parents with food allergies are more likely to develop food allergies. But most children with food allergies do not have food allergy parents.
Solid food | Tervisliku toitumise informatsioon
From the age of 6 months, the baby should be supplemented with breast milk to provide with the necessary amount of energy and nutrients. As you grow older, you can gradually switch to regular food (cooking it without frying, and also without adding salt and sugar). Children over 1 year of age, in addition to regular food and complementary foods, can continue to drink breast milk, but by the age of two, the child should completely switch to a common table. Exposure of a child to grain-containing foods during breastfeeding may protect him from gluten intolerance in the future. When offering a child complementary foods or regular food, care should be taken, to have a varied diet . Both during breastfeeding and during the transition to regular food, the baby may experience gases or allergies .
For children over two years of age, the same nutritional guidelines apply as adults, but the recommended serving sizes are smaller.
Children under three years of age (actually, a person of any age) do not need salty or sweet snacks, carbonated drinks, deep fried and/or very sweet and salty foods! nine0028
By the sixth month of life, the infant's eating habits and digestive system are mature enough to offer more solid foods in addition to breast milk. Proteins, carbohydrates and fats contained in regular food are different from the easily digestible sugars, fats and proteins that enter the baby's body with breast milk. Therefore, a so-called certain familiarization period is needed so that the baby's digestive system has time to get used to a new type of food. If the baby is breastfed as often as before, then these feeds cover about 2/3 of the energy needed by an 8-month-old baby. The remaining approximately 200 kilocalories should come from the various macronutrients found in complementary food ingredients, i. e. proteins, fats and carbohydrates. Complementary foods are needed so that the child can slowly move to the common table, as well as to obtain the nutrients necessary for age. Complementary foods for babies are a completely unfamiliar thing. It differs significantly from breast milk and will take time to learn how to eat it. nine0005
e. proteins, fats and carbohydrates. Complementary foods are needed so that the child can slowly move to the common table, as well as to obtain the nutrients necessary for age. Complementary foods for babies are a completely unfamiliar thing. It differs significantly from breast milk and will take time to learn how to eat it. nine0005
Proper complementary foods are food that is hard enough to eat with a spoon, contains all the important foods (except sweets), is rich in nutrients and does not contain salt or sugar. Complementary foods should always be offered to the child from a spoon and never from a bottle, as in this case the child will never understand what to eat in an upright position using a spoon. In addition, bottle feeding contains too much water, so it may not provide enough energy and nutrients. As the child grows older, you can allow him to put pieces of food in his mouth with his fingers. Simultaneously with the gradual introduction of solid food into the baby's diet, his interest in breast milk gradually begins to fade. This is completely natural and as the first birthday approaches, you can start to slowly reduce the number of breastfeeds. All children are different, so their preferences and needs are also different, but it is important that the child's diet is varied and covers all the nutritional needs of a growing body for life and development. nine0005
This is completely natural and as the first birthday approaches, you can start to slowly reduce the number of breastfeeds. All children are different, so their preferences and needs are also different, but it is important that the child's diet is varied and covers all the nutritional needs of a growing body for life and development. nine0005
Complementary foods for babies by months:
0-6 months
6-8 months
9-11 months
substances can be markedly reduced.
World Health Organization recommendations for the introduction of complementary foods for children aged 6-23 months.
| Age (in months) | Frequency Frequency | The portion for 1 feeding | Consistency of food |
| 6 | 1 or 2 times a day 9000 quantity | Finely pounded or pureed | |
| 6-8 | 2-3 feedings per day 9 0239 to 1 DL | Trucified or pureed | |
|
| 3-4 feeding per day 1-2 Open 1-2 | Crowned or finely busy | |
| 12-2-23 | 3-4 feeding per day 1-2 snacks | 2-2. |