Starting baby on solid food schedule
When, What, and How to Introduce Solid Foods | Nutrition
For more information about how to know if your baby is ready to starting eating foods, what first foods to offer, and what to expect, watch these videos from 1,000 Days.
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend children be introduced to foods other than breast milk or infant formula when they are about 6 months old. Introducing foods before 4 months old is not recommended. Every child is different. How do you know if your child is ready for foods other than breast milk or infant formula? You can look for these signs that your child is developmentally ready.
Your child:
- Sits up alone or with support.
- Is able to control head and neck.
- Opens the mouth when food is offered.
- Swallows food rather than pushes it back out onto the chin.
- Brings objects to the mouth.
- Tries to grasp small objects, such as toys or food.
- Transfers food from the front to the back of the tongue to swallow.
What Foods Should I Introduce to My Child First?
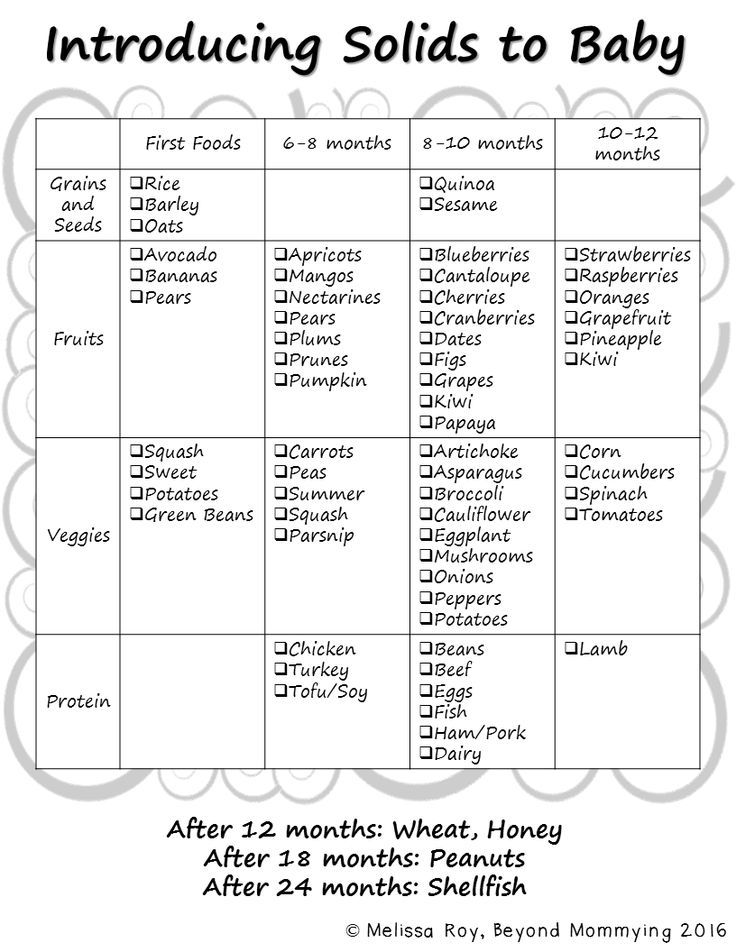
The American Academy of Pediatrics says that for most children, you do not need to give foods in a certain order. Your child can begin eating solid foods at about 6 months old. By the time he or she is 7 or 8 months old, your child can eat a variety of foods from different food groups. These foods include infant cereals, meat or other proteins, fruits, vegetables, grains, yogurts and cheeses, and more.
If your child is eating infant cereals, it is important to offer a variety of fortifiedalert icon infant cereals such as oat, barley, and multi-grain instead of only rice cereal. Only providing infant rice cereal is not recommended by the Food and Drug Administration because there is a risk for children to be exposed to arsenic. Visit the U.S. Food & Drug Administrationexternal icon to learn more.
How Should I Introduce My Child to Foods?
Your child needs certain vitamins and minerals to grow healthy and strong.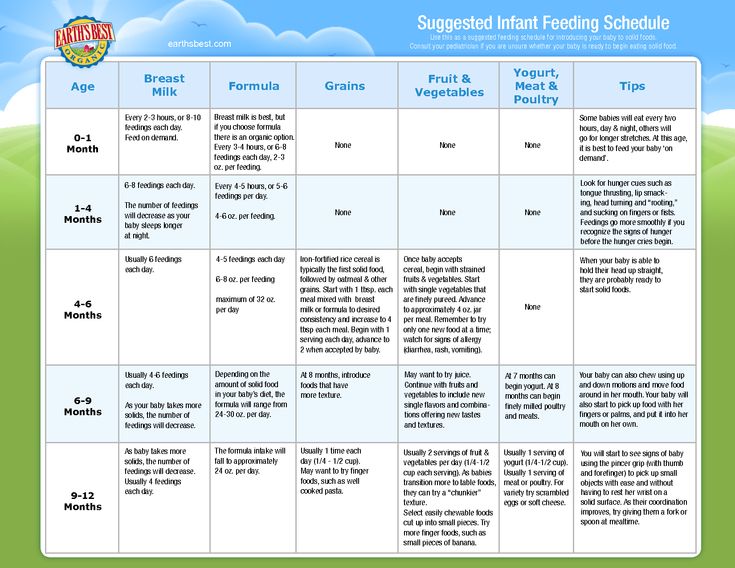
Now that your child is starting to eat food, be sure to choose foods that give your child all the vitamins and minerals they need.
Click here to learn more about some of these vitamins & minerals.
Let your child try one single-ingredient food at a time at first. This helps you see if your child has any problems with that food, such as food allergies. Wait 3 to 5 days between each new food. Before you know it, your child will be on his or her way to eating and enjoying lots of new foods.
Introduce potentially allergenic foods when other foods are introduced.
Potentially allergenic foods include cow’s milk products, eggs, fish, shellfish, tree nuts, peanuts, wheat, soy, and sesame. Drinking cow’s milk or fortified soy beverages is not recommended until your child is older than 12 months, but other cow’s milk products, such as yogurt, can be introduced before 12 months. If your child has severe eczema and/or egg allergy, talk with your child’s doctor or nurse about when and how to safely introduce foods with peanuts.
How Should I Prepare Food for My Child to Eat?
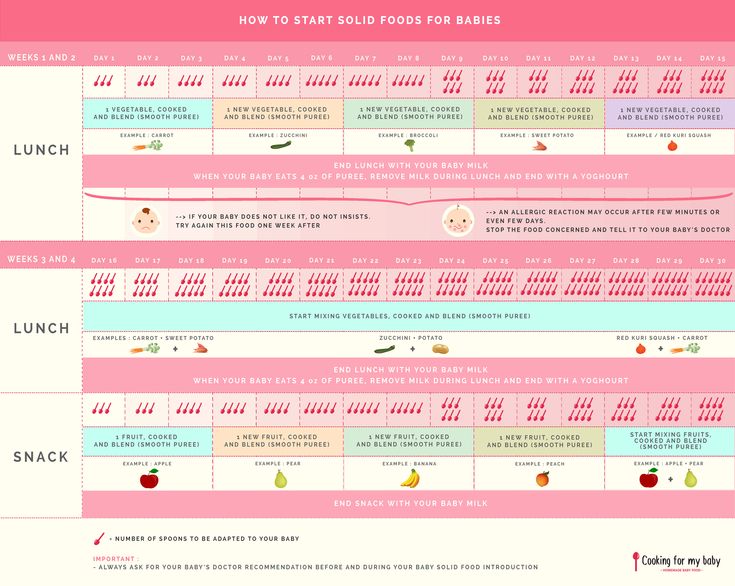
At first, it’s easier for your child to eat foods that are mashed, pureed, or strained and very smooth in texture. It can take time for your child to adjust to new food textures. Your child might cough, gag, or spit up. As your baby’s oral skills develop, thicker and lumpier foods can be introduced.
Some foods are potential choking hazards, so it is important to feed your child foods that are the right texture for his or her development. To help prevent choking, prepare foods that can be easily dissolved with saliva and do not require chewing. Feed small portions and encourage your baby to eat slowly. Always watch your child while he or she is eating.
Here are some tips for preparing foods:
- Mix cereals and mashed cooked grains with breast milk, formula, or water to make it smooth and easy for your baby to swallow.
- Mash or puree vegetables, fruits and other foods until they are smooth.

- Hard fruits and vegetables, like apples and carrots, usually need to be cooked so they can be easily mashed or pureed.
- Cook food until it is soft enough to easily mash with a fork.
- Remove all fat, skin, and bones from poultry, meat, and fish, before cooking.
- Remove seeds and hard pits from fruit, and then cut the fruit into small pieces.
- Cut soft food into small pieces or thin slices.
- Cut cylindrical foods like hot dogs, sausage and string cheese into short thin strips instead of round pieces that could get stuck in the airway.
- Cut small spherical foods like grapes, cherries, berries and tomatoes into small pieces.
- Cook and finely grind or mash whole-grain kernels of wheat, barley, rice, and other grains.
Learn more about potential choking hazards and how to prevent your child from choking.
Top of Page
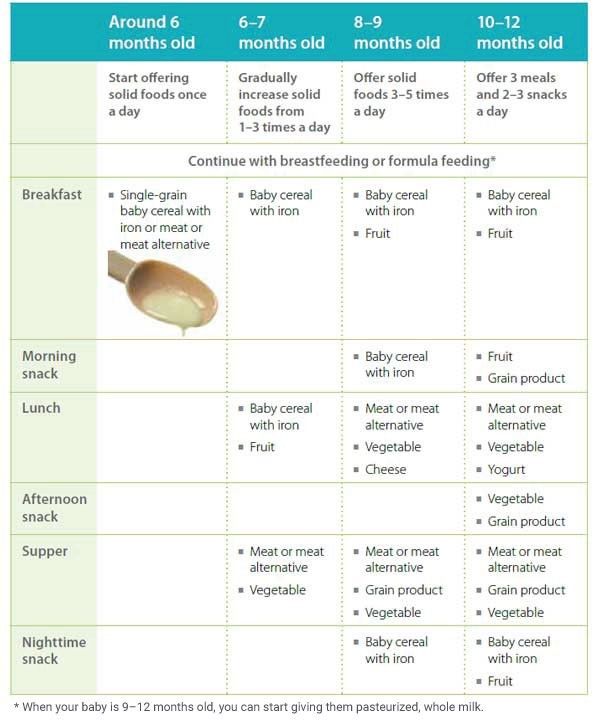
Sample Schedules for Starting Solids (6 to 12 Months)
Looking for sample schedules for starting solids? Ideas for how to introduce solids on a schedule. Including sample feeding schedule for 6 months old and beyond.
Including sample feeding schedule for 6 months old and beyond.
Ready to start solids with your babe? This is an exciting time!
Here’s everything you need to know about introducing solids safely including sample schedules for starting solids from 6 months to 12 months, plus recommended menu items.
Is Baby Ready for Solids?
The most important thing to consider as your baby approaches the 4-6 month mark, is whether they are showing signs of feeding readiness.
This includes things like:
- Baby is 6 months old (there is no benefit to starting solids before 4 months at the earliest)
- They are interested in food they see around them
- Baby is losing their tongue thrust reflex that keeps food out of their mouth
- They are sitting up on their own for at least 60 seconds at a time
If your baby is showing these signs, great! It’s time to start introducing some solids.
Note that baby should continue receiving breast milk and/or formula for at least the first year of life, as you begin the transition to solid foods.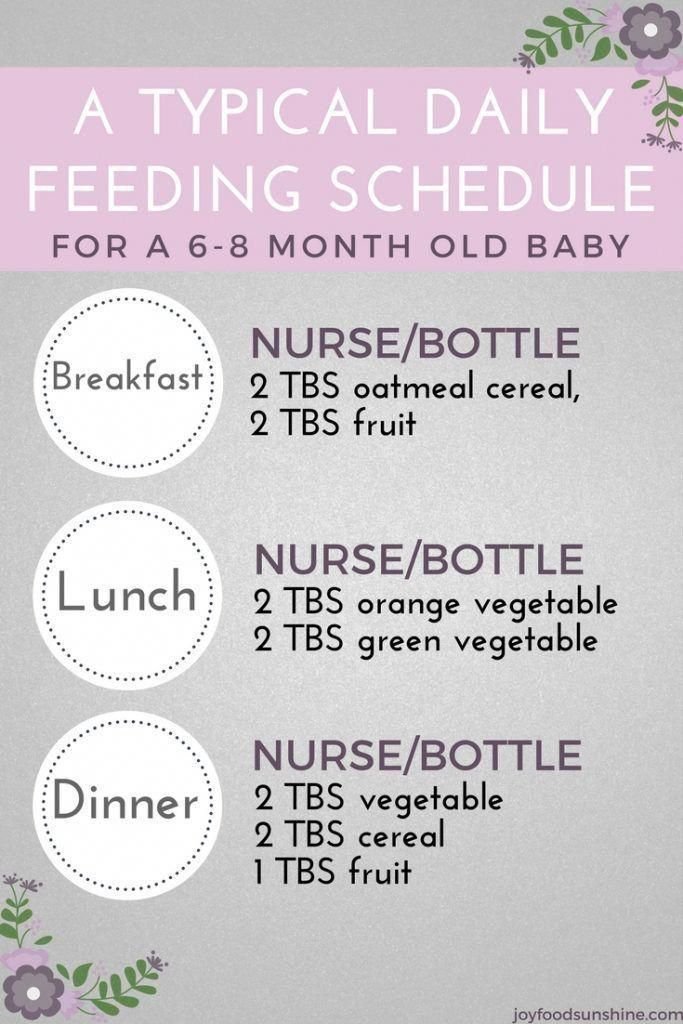
What Are the Benefits of Solids?
Eventually, your baby’s diet will be predominantly solid foods, but it takes some time to get there.
Solid foods expose your baby to a wide variety of textures, shapes, consistencies, and colors. They’re also important for nutrition, providing an array of vitamins, minerals, fiber, protein, fat, and energy.
Eating solids is also important for physical growth and development. As your baby matures, they become prepared to try new foods and get more of their nutrients from solids than breast milk/formula.
Plus, it’s fun to play with and try new foods!
However you decide to introduce solids – using a traditional spoon-feeding/puree approach or a baby-led weaning approach – your baby benefits from the nutrition and exposure.
Recommended Solid Foods for Babies
Below are some nutritious first foods that have worked well for us:
- Tofu
- Avocado
- Oatmeal
- Hummus
- Pancakes
- Soft fruits, like bananas, kiwi, mango
- Soft-cooked vegetables, like zucchini, sweet potato, and broccoli
- Beans, peas, lentils
- Toast, cut into strips
As you design your baby’s menu, these are some great nutrient-dense foods to incorporate that can also be prepared and served in an age-appropriate way.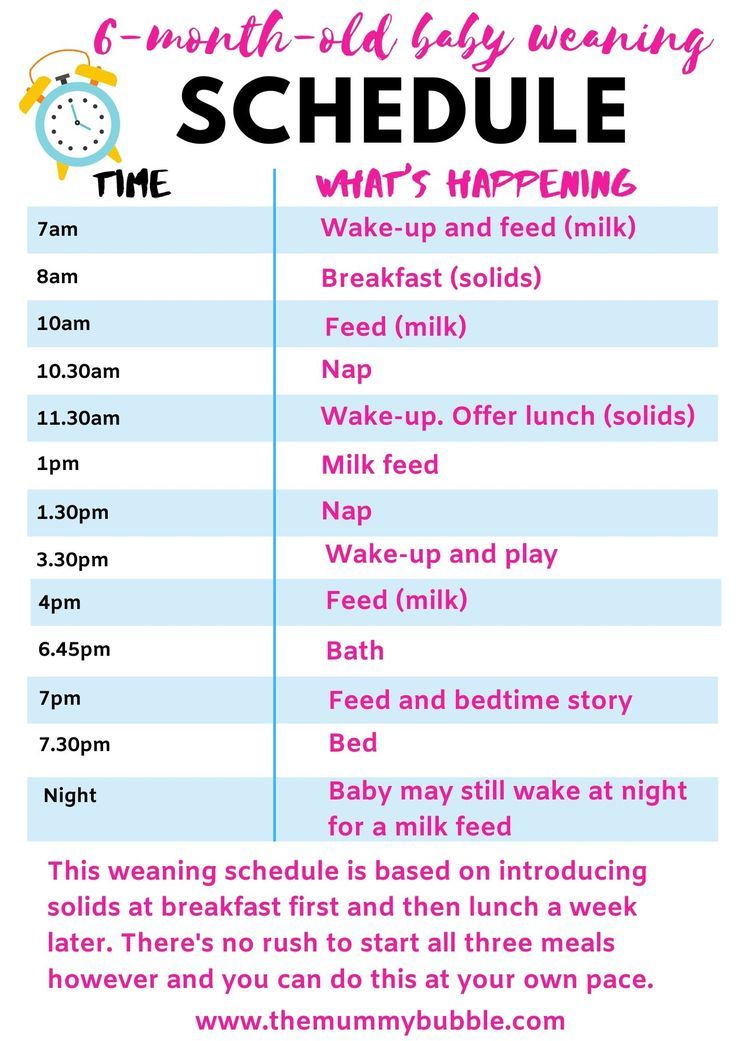
For a list of foods to avoid when starting solids, see this blog post.
Sample Schedules for Starting Solids
How you choose to design your baby’s solid feeding schedule depends on several things, including what your daily routine looks like.
We recommend beginning with 1 solid food meal per day for 6-month-old babes and increasing to 3 meals per day for 9-month-old babies.
Between these milestones, continue to slowly add new foods and increase how many meals/snacks you’re offering.
By 12 months old, your baby will be eating 3 meals and a few snacks per day of solid foods, using breast milk and/or milk/milk alternatives (e.g., fortified unsweetened soy or pea milk) as needed.
Keep in mind that it can take 10-15 times of offering a food before a baby even tries it, or decides whether they like it. If your baby doesn’t seem to be interested in a certain food, keep offering.
Below are a few example feeding schedules for offering solids to babes at least 6 months old.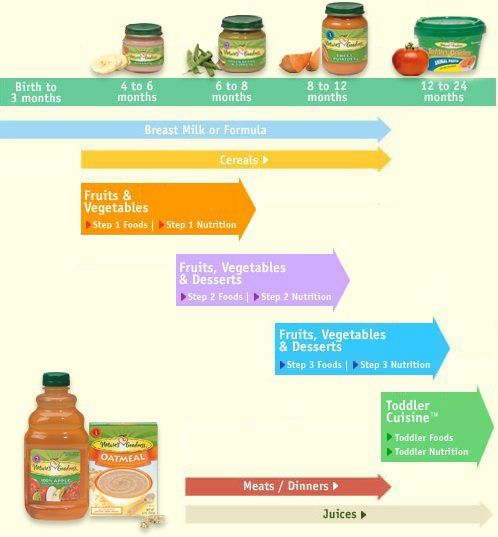
Feeding Schedule for 6 Months
- 7am: Breastfeed/bottle feed
- 8am: Breakfast – Iron-fortified baby oat cereal, peeled sliced peaches, avocado strips
- 11am: Breastfeed/bottle feed
- 2pm: Breastfeed/bottle feed
- 5pm: Breastfeed/bottle feed
- 7pm: Breastfeed/bottle feed
Note that you may continue to breastfeed/bottle feed babies this age during the night if they are still waking up.
Feeding Schedule for 9 Months
- 7am: Breastfeed/bottle feed
- 8am: Breakfast – Pancake strips, chopped raspberries and bananes
- 11am: Breastfeed/bottle feed
- 12pm: Lunch – Penne pasta with tomato sauce, green peas, melon slices with skin and seed removed
- 3pm: Breastfeed/bottle feed
- 5pm: Breastfeed/bottle feed
- 6pm: Dinner – Smashed black beans, tofu strips drizzled with thinned nut butter, sliced orange sections with outer membranes and pith removed
- 7pm: Breastfeed/bottle feed
Feeding Schedule for 12 Months
- 7am: Breast milk or milk/milk alternative
- 8am: Breakfast – Toast strips with mashed avocado, half of a banana (remove 2 inches of the skin, leaving the rest of the peel for easy handling)
- 10am: Mid-morning snack – chopped watermelon, diced grapes, hummus
- 12pm: Lunch – Quinoa-based veggie burger patty, steamed cauliflower and beet strips
- 3pm: Afternoon snack + breast milk or milk/milk alternative
- 6pm: Dinner – Lightly fried tempeh strips, kidney beans, roasted sweet potato cubes, steamed cucumber
- 7pm: Breast milk or milk/milk alternative
We hope these sample schedules for starting solids are helpful when your baby is ready for first foods. When you introduce solids on a schedule, this can help alleviate some of the stress of feeding while nourishing your baby well. Have fun with it!
When you introduce solids on a schedule, this can help alleviate some of the stress of feeding while nourishing your baby well. Have fun with it!
Chime In: If you’ve already done solids with your babe, what has your schedule looked like? Any other tips for new parents?
If you found this post helpful, we suggest you read these too:
- Spoon Feeding vs. Baby-Led Weaning
- Do Babies Really Need 11mg of Iron a Day?
- Plant-Based Baby-Led Weaning Grocery List
- How to Wean Baby to Plant-Based Milk
5 easy ways to transfer a child to an adult table: from mashed potatoes to pieces
How to transfer a child to an adult table, what are the rules for a healthy diet for a child after a year and how to teach a baby to chew: read about this and much more in our material.
Most often, by the age when grown-up babies have already learned to sit on their own, they show interest in the parent's table.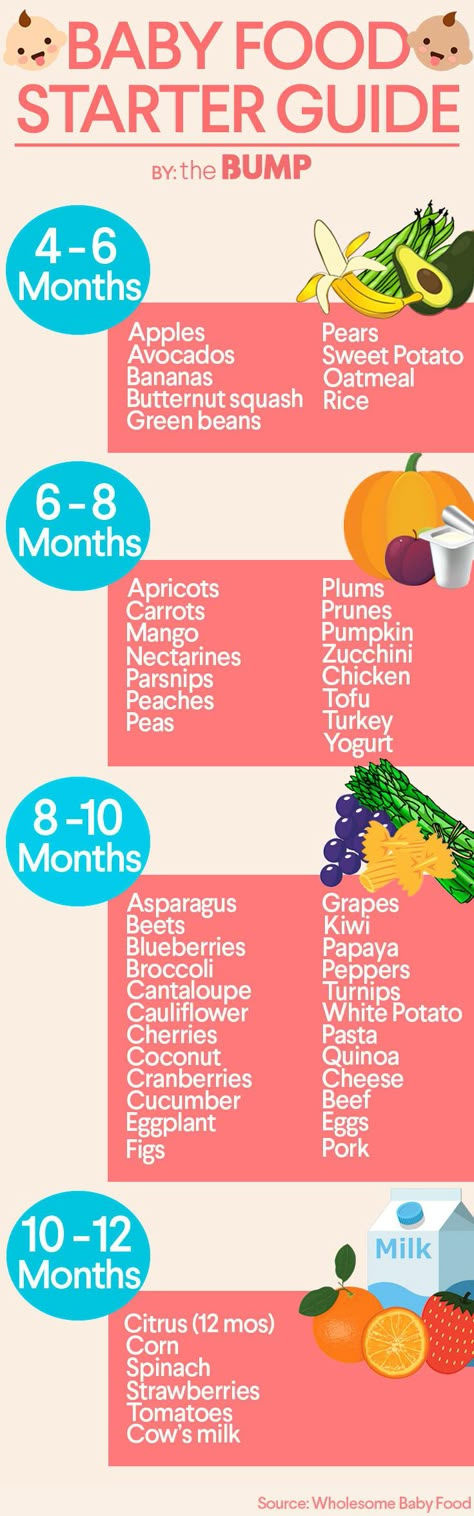 Sometimes, with great zeal, they strive to try everything that is on the plate of their parents or brothers and sisters. And if they managed to get a trophy in the form of adult food, they not only try it “by the tooth”, but they can also smear it on the table or throw it on the floor.
Sometimes, with great zeal, they strive to try everything that is on the plate of their parents or brothers and sisters. And if they managed to get a trophy in the form of adult food, they not only try it “by the tooth”, but they can also smear it on the table or throw it on the floor.
And now there comes a moment when every parent dreamily thinks that soon there will be no need to prepare a “special menu” for the youngest member of the family and everyone will finally eat the same thing. But when does this time come?
When is the right time?
Experts agree that there are no clear boundaries, because every baby develops at its own pace. Coordinating the work of all the muscles of the oral cavity and chewing hard pieces can be still difficult for babies. At the first stage of acquaintance with complementary foods, it is better to use homogenized purees, then - products with a puree-like consistency, and later - with pieces. Often at 8-9months, children try to gnaw everything that gets into their mouths, and they usually already have several teeth, and all this suggests that the structure of food can be complicated.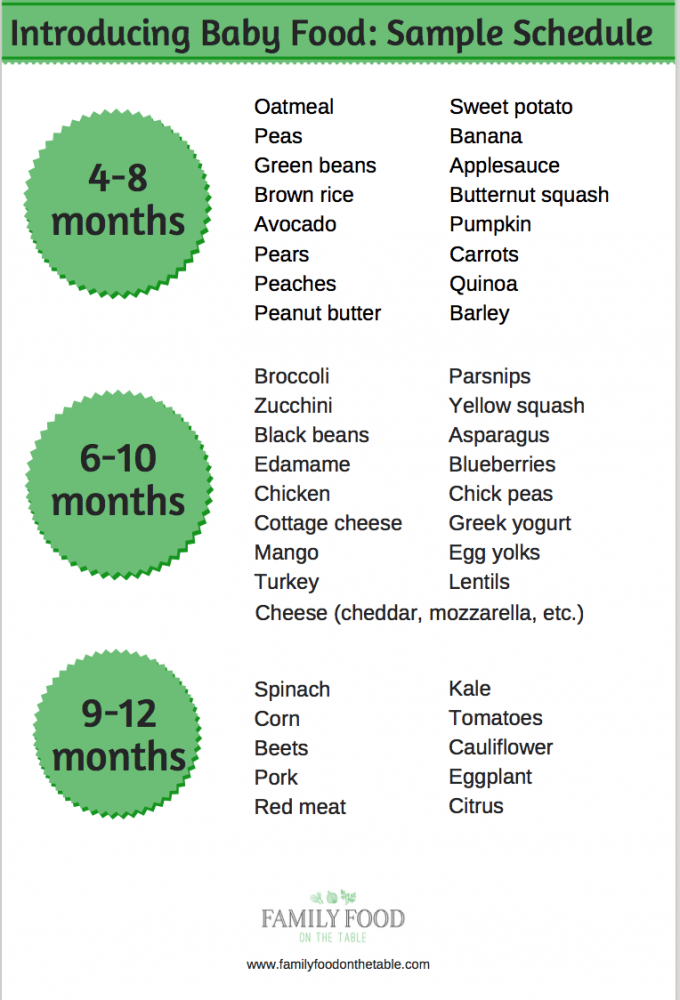 Let's see how.
Let's see how.
5 easy ways to transition your child to adult meals
1. Take it slow and encourage interest
Starting with mashed potatoes, slowly but steadily add thicker foods to your diet. At the age of 6 months (it all depends on the pace of development of your baby and his physiological characteristics, for example, on the number of teeth), you can safely treat children to special children's cookies.
It will also be useful to observe the food interest of the baby - to notice that he himself is drawn to some adult food.
Be sure to tell us about the taste, texture, color of the product.
Photo: shutterstock / Katrina Era2. Create a special atmosphere at the table
It is very important for kids to follow the routine - eat at the same time, do it in your own place and preferably with your children's appliances from your dishes, and, of course, in your chair. This disciplines, allows the gastrointestinal tract to work by the hour.
Baby chairs are ideal for feeding your baby. First of all, it is safe, but do not forget that the child must always be fastened. Show by your own example how to use cutlery, because kids repeat everything after adults.
Make family breakfasts, lunches or dinners (and conversations) a special time. Time at the table is the time of communication, let it be a good tradition and remain in the memory of the child.
3. Choose special products to transition to an adult table
During the transition to adult food, unfamiliar food may seem tasteless, the child may think that you are giving him something inedible. One of the best transition options would be a special combined puree, for example, the FrutoNyanya line with pieces of meat and vegetables, which will introduce the baby to a new consistency and help stimulate chewing skills due to the pieces of vegetables and crushed grains contained there. In addition, each jar of this line contains 12% of the physiological needs of the baby (aged 9months) in iron.
4. Cook meals that are suitable for the whole family
Cooking for the whole family is a great idea. The main rule: your diet should be suitable for the child, which means a minimum of salt and spices. Introduce baby vegetable "soups", boiled or steamed vegetables, lightly crushed with a blender or mashed with a fork, into the child's diet. You can give your child to try different foods with pieces. And if he doesn't like it, offer again in a couple of weeks. It is important here not to miss the moment, but also not to rush: if you start introducing thicker and solid foods into your baby’s diet too early, this can lead to eating disorders and other problems.
5. Avoid watching cartoons and using gadgets while eating
It is important to be patient and not distract your child with cartoons and gadgets. So he will be able to feel the taste of food and learn to enjoy the process of eating - both in the present and in the future.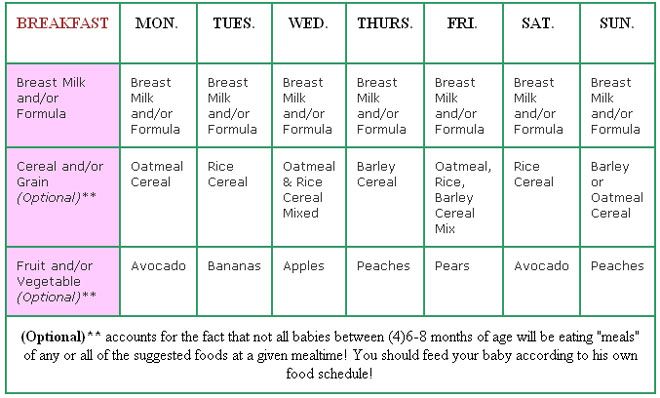 Of course, turning on the cartoon and quickly feeding the child is very convenient, but when the baby is fascinated by what is happening on the screen, his brain analyzes only the cartoon and does not think about the taste of food and satiety at all.
Of course, turning on the cartoon and quickly feeding the child is very convenient, but when the baby is fascinated by what is happening on the screen, his brain analyzes only the cartoon and does not think about the taste of food and satiety at all.
What happens if you miss the moment?
More and more mothers and fathers in parent groups on the Internet complain that their seemingly healthy child refuses to chew solid food. The reasons may be different - for example, "laziness" (kids do not want to chew, as at first this is not an easy process).
Delaying the introduction of more adult foods and foods with chunks too long can lead to a range of problems, from eating disorders to functional and even organic disorders. And, of course, the work of the gastrointestinal tract suffers.
The advice in the articles is advisory in nature and cannot replace a visit to your doctor.
Photo: shutterstock / BigLike Images
The BLW theory was introduced in 2010 in the book Baby-Led Weaning by Jill Rupley and Tracey Marquette.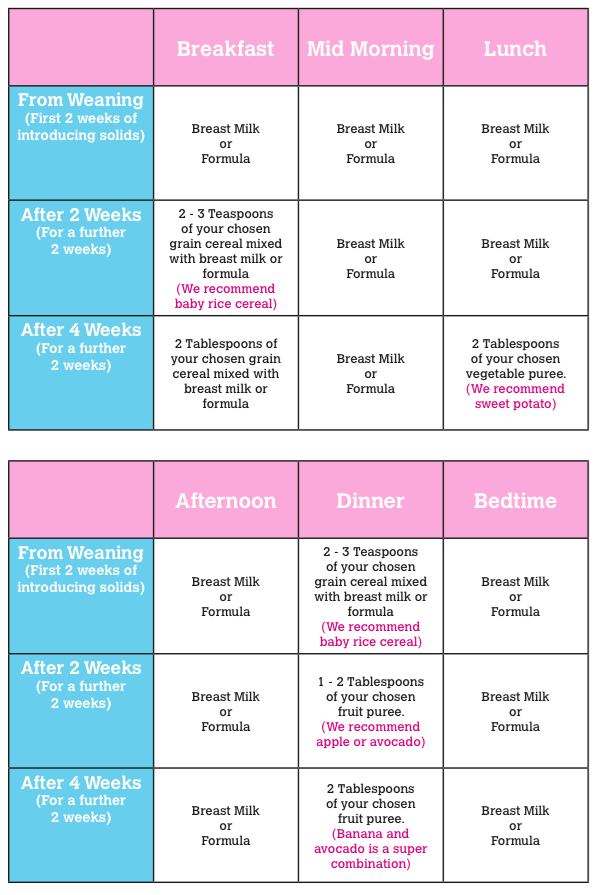 This approach to first foods is popular in the US, while there is not much information about it on the Russian-language Internet. In this article, we will talk about what are the features of BLW, what foods can be given to a child and what should not be, what precautions should be taken into account.
This approach to first foods is popular in the US, while there is not much information about it on the Russian-language Internet. In this article, we will talk about what are the features of BLW, what foods can be given to a child and what should not be, what precautions should be taken into account.
Baby-Led Weaning can be translated as “baby food of choice”. You can apply this method no earlier than six months of age, it is better - from eight months. According to BLW, from this age, the child can be given regular food (which one - we will discuss below), while continuing to breastfeed or feed formula milk.
Benefits of BLW
Compared to baby purees, BLW has a number of advantages, in particular:
- You don't have to spend time preparing baby purees.
- The child can be at the family table from the very beginning and eat the same food as the parents.
- This feeding method promotes the development of visual and fine motor skills.

- The child learns to chew, swallow and decides what and how much to eat - this is how the foundations of healthy eating behavior are laid.
Also read: From 1 year old and older - what and how to feed a small child
How to understand that a child can be given solid food
- There are several signs - how to understand that the child can already be given normal food:
- Child can sit up alone with little or no support.
- The child wants to chew something, even if he does not yet have teeth.
- He takes food with his thumb and forefinger instead of his palm.
- The child shows interest in food, grabs food from the table.
- It is advisable to consult a pediatrician before giving a normal meal to a child.
What foods can be given as first complementary foods
Of course, not all foods can be given as first complementary foods. Foods that are suitable for first foods according to BLW are:
- Steamed or baked vegetables (broccoli, carrots, pumpkin pulp, zucchini).
- Ripe fruits (apple, banana, avocado, mango, watermelon, peach, pear, plum).
- Protein food (natural cheese, egg yolk, meat, liver).
- Carbohydrates (gluten-free pasta, brown rice, millet, buckwheat, gluten-free bread).
Also read: 6 Months and Older - Which Dairy Foods to Give to Young Babies
BLW First Feeding Rules - Do's and Don'ts
- Make sure baby is ready to eat regular food .
- Continue breastfeeding or formula feeding until at least 10–12 months of age.
- Sit the child in a comfortable position - he should sit upright without leaning back.
- Cut food into large pieces so that it is easy for the child to take them.
- Start with soft foods: ripe fruits, steamed vegetables.
- Take your child to the family table.
- Get ready for a mess.
- Take your time and don't rush your baby - eating will take at least 10-15 minutes.
- Pay attention to signals - for example, if a child scatters food, he may have already eaten.
- Do not offer complementary foods if the child is tired or in a bad mood.
- Do not coax your child to eat another bite and do not offer too much food at a time.
- If your child doesn't want to eat regular food and likes baby purees more, don't be upset. Fortunately, there are many foods available for children today that can be spoon-fed, such as baby yogurt, cottage cheese spreads, and others.
See also: Baby food - 7 dairy products for young children
Precautions - things to consider
- Avoid foods that a child can choke on, such as nuts, grapes, cherries, grape tomatoes.
- If you want to give your child foods such as cherries and grapes, cut them in half and remove the pits.
- Hard foods that a child cannot chew should be boiled (eg carrots).
- Find out in advance how to give first aid if a child chokes.
- Be careful with foods that can cause allergies: foods containing gluten, peanuts and other nuts, egg whites, seafood and some types of fish, citrus fruits.
- Do not give your baby unhealthy food and fast food: chips, popcorn, foods containing sugar, sweets.
- Banned honey, sugar and chocolate. Salt - in very small quantities with the permission of a doctor.
- Never leave a child with food unattended.
Based on materials from parents.com, mamanatural.com, malyshi.livejournal.com
The information and recipes contained in this Blog may not meet the user's expectations, are presented for use without regard to the individual characteristics of the user's health and are used by the user at their own discretion and under personal responsibility.
Information, documents and related graphics and recipes taken from other sources and published on this site https://milkalliance.com.ua/ may contain technical errors and typographical errors.