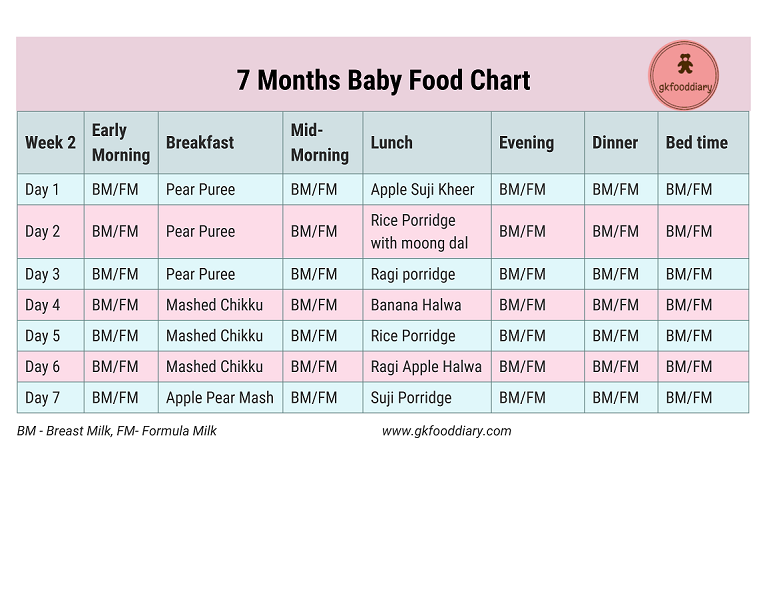
Starting food for 6 months baby
When, What, and How to Introduce Solid Foods | Nutrition
For more information about how to know if your baby is ready to starting eating foods, what first foods to offer, and what to expect, watch these videos from 1,000 Days.
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend children be introduced to foods other than breast milk or infant formula when they are about 6 months old. Introducing foods before 4 months old is not recommended. Every child is different. How do you know if your child is ready for foods other than breast milk or infant formula? You can look for these signs that your child is developmentally ready.
Your child:
- Sits up alone or with support.
- Is able to control head and neck.
- Opens the mouth when food is offered.
- Swallows food rather than pushes it back out onto the chin.
- Brings objects to the mouth.
- Tries to grasp small objects, such as toys or food.
- Transfers food from the front to the back of the tongue to swallow.
What Foods Should I Introduce to My Child First?
The American Academy of Pediatrics says that for most children, you do not need to give foods in a certain order. Your child can begin eating solid foods at about 6 months old. By the time he or she is 7 or 8 months old, your child can eat a variety of foods from different food groups. These foods include infant cereals, meat or other proteins, fruits, vegetables, grains, yogurts and cheeses, and more.
If your child is eating infant cereals, it is important to offer a variety of fortifiedalert icon infant cereals such as oat, barley, and multi-grain instead of only rice cereal. Only providing infant rice cereal is not recommended by the Food and Drug Administration because there is a risk for children to be exposed to arsenic. Visit the U.S. Food & Drug Administrationexternal icon to learn more.
How Should I Introduce My Child to Foods?
Your child needs certain vitamins and minerals to grow healthy and strong.
Now that your child is starting to eat food, be sure to choose foods that give your child all the vitamins and minerals they need.
Click here to learn more about some of these vitamins & minerals.
Let your child try one single-ingredient food at a time at first. This helps you see if your child has any problems with that food, such as food allergies. Wait 3 to 5 days between each new food. Before you know it, your child will be on his or her way to eating and enjoying lots of new foods.
Introduce potentially allergenic foods when other foods are introduced.
Potentially allergenic foods include cow’s milk products, eggs, fish, shellfish, tree nuts, peanuts, wheat, soy, and sesame. Drinking cow’s milk or fortified soy beverages is not recommended until your child is older than 12 months, but other cow’s milk products, such as yogurt, can be introduced before 12 months. If your child has severe eczema and/or egg allergy, talk with your child’s doctor or nurse about when and how to safely introduce foods with peanuts.
How Should I Prepare Food for My Child to Eat?
At first, it’s easier for your child to eat foods that are mashed, pureed, or strained and very smooth in texture. It can take time for your child to adjust to new food textures. Your child might cough, gag, or spit up. As your baby’s oral skills develop, thicker and lumpier foods can be introduced.
Some foods are potential choking hazards, so it is important to feed your child foods that are the right texture for his or her development. To help prevent choking, prepare foods that can be easily dissolved with saliva and do not require chewing. Feed small portions and encourage your baby to eat slowly. Always watch your child while he or she is eating.
Here are some tips for preparing foods:
- Mix cereals and mashed cooked grains with breast milk, formula, or water to make it smooth and easy for your baby to swallow.
- Mash or puree vegetables, fruits and other foods until they are smooth.

- Hard fruits and vegetables, like apples and carrots, usually need to be cooked so they can be easily mashed or pureed.
- Cook food until it is soft enough to easily mash with a fork.
- Remove all fat, skin, and bones from poultry, meat, and fish, before cooking.
- Remove seeds and hard pits from fruit, and then cut the fruit into small pieces.
- Cut soft food into small pieces or thin slices.
- Cut cylindrical foods like hot dogs, sausage and string cheese into short thin strips instead of round pieces that could get stuck in the airway.
- Cut small spherical foods like grapes, cherries, berries and tomatoes into small pieces.
- Cook and finely grind or mash whole-grain kernels of wheat, barley, rice, and other grains.
Learn more about potential choking hazards and how to prevent your child from choking.
Top of Page
Baby's first foods: How to introduce solids to your baby
Babies are typically ready to start solids between 4 and 6 months, as long as they're showing signs of readiness, such as being able to sit upright with good head control. Talk to your baby's doctor about which foods to introduce first, particularly if you're concerned about a risk for an allergy. In general, infant cereal and pureed, one-ingredient veggies, fruits, and meats are great first foods. Try spoon-feeding or baby-led weaning, and keep up the breast milk or formula until your baby's first birthday.
Talk to your baby's doctor about which foods to introduce first, particularly if you're concerned about a risk for an allergy. In general, infant cereal and pureed, one-ingredient veggies, fruits, and meats are great first foods. Try spoon-feeding or baby-led weaning, and keep up the breast milk or formula until your baby's first birthday.
When do babies start eating baby food?
It depends. As long as your baby shows signs of readiness, your pediatrician will probably give you the go-ahead to start baby food (also called solid food or solids) any time between 4 and 6 months.
Until then, breast milk or formula provides all the calories and nourishment your baby needs. Infants don't yet have the physical skills to swallow solid foods safely, and their digestive system isn't ready for solids until they're at least 4 months old.
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) and World Health Organization (WHO) recommend breastfeeding exclusively for the first six months of your baby's life and introducing solids at 6 months old. The AAP advises breastfeeding until age 1 – and longer if you and your baby want to.
The AAP advises breastfeeding until age 1 – and longer if you and your baby want to.
Signs your baby is ready for solids
Your baby will give you clear signs when they're ready. Look for:
- Head control. Your baby needs to be able to keep their head in a steady, upright position.
- Sitting well when supported. Your baby needs to be able to sit upright in a baby seat or highchair to swallow well.
- Losing the "extrusion reflex." Your baby's mouth and tongue develop in sync with their digestive system. To start solids, they should be able to move food to the back of their mouth and swallow it, instead of using their tongue to push food out of their mouth.
- Curiosity about food. Your baby may start showing interest in what you're eating, reaching for your food or even opening their mouth if you offer them a spoonful.
Starting solids by 6 months old is important for your baby's oral motor development (the use of their lips, tongue, jaw, teeth, and hard and soft palates). Also, solid foods can provide specific nutrients your baby needs, such as iron and zinc. (These are especially important if your baby has been exclusively breastfed.)
Also, solid foods can provide specific nutrients your baby needs, such as iron and zinc. (These are especially important if your baby has been exclusively breastfed.)
What are the best first baby foods?
Start your baby with any pureed, single-ingredient food. Although it used to be standard for parents to give rice cereal as a first food, that's not necessary. In fact, pediatricians often don't recommend baby rice cereal since it can contain inorganic arsenic, and it's not as nutritious as some other first foods.
Good first baby foods include
- pureed squash
- applesauce
- mashed bananas
- mashed avocado
- pureed peaches
- pureed pears
- pureed meats
- whole-grain, iron-enriched baby cereal such as oatmeal
Advertisement | page continues below
If your baby is breastfed, the AAP suggests meat as a first food because the iron in beef, chicken, and turkey helps to replace iron stores, which start to diminish at about 6 months of age.
How to introduce solids to your baby
The traditional way to start solids is by spoon-feeding your baby cereal or purees, but some parents use a different method called baby-led weaning. Using this method, you put chunks of soft, developmentally appropriate food on the highchair tray or table and let your baby grab the food and feed themself.
Here's how to start spoon-feeding your baby:
For your first few feedings, start with just 1 or 2 teaspoons of pureed solid food or baby cereal about an hour after nursing or bottle-feeding (so your baby isn't too hungry or full).
Use a soft-tipped plastic spoon to feed your baby to avoid injuring their gums. Put a small amount of food on the tip of the spoon and offer it to them. If your baby doesn't seem very interested, just let them smell the food for now and try again another time.
If you're feeding your baby ready-to-eat jars or pouches of baby food, put some into a small dish and feed them from that. (If you dip the feeding spoon into the jar, it's not a good idea to save the leftovers because bacteria from your baby's mouth will now be in the jar. ) Store leftovers in the fridge and throw away any opened baby food jars or pouches within a day or two of opening them.
) Store leftovers in the fridge and throw away any opened baby food jars or pouches within a day or two of opening them.
If you decide to start with cereal, give your baby 1 to 2 teaspoons of diluted infant cereal. Add breast milk or formula to a tiny pinch of cereal. It will be very runny at first, but as your baby starts to eat more solid foods, you can gradually thicken the consistency by using less liquid.
Begin with one daily feeding in the morning whenever your baby isn't too tired, hungry, or cranky. Your baby may not eat much at first, but give them time to get used to the experience. Don't be surprised if your baby is confused or rejects solid food at first. Some babies need practice keeping food in their mouths and swallowing.
Eventually you can start giving your baby more solid food until they're having a few tablespoons a day, over two feedings. In general, your baby could start with pureed or semi-liquid food, then move on to strained or mashed food, and finally graduate to small pieces of finger foods.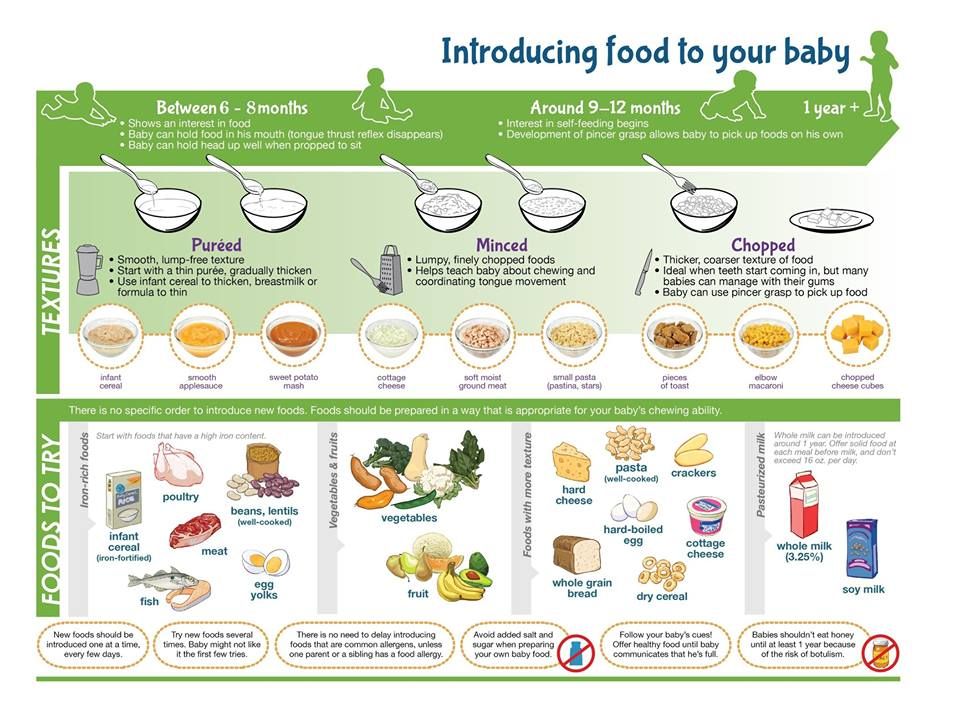
Signs that your baby is full
Your baby's appetite will vary from one feeding to the next, so a strict accounting of how much they've eaten isn't a reliable way to tell when they've had enough. Look for these signs that your baby's probably done:
- They lean back in their chair
- They turn their head away from food
- They start playing with the spoon
- They refuse to open up for the next bite (Sometimes a baby will keep their mouth closed because they haven't finished the first mouthful, so give them time to swallow.)
Food allergies and introducing solids
Experts recommend that you introduce one food at a time to your baby, and wait 3 to 5 days before introducing another food, so you can watch for any allergic reactions. It's also a good idea to write down the foods your baby samples. If they have an adverse reaction, a food log will make it easier to pinpoint the cause.
You don't have to hold off on giving allergenic foods such as eggs, peanut butter, or soy.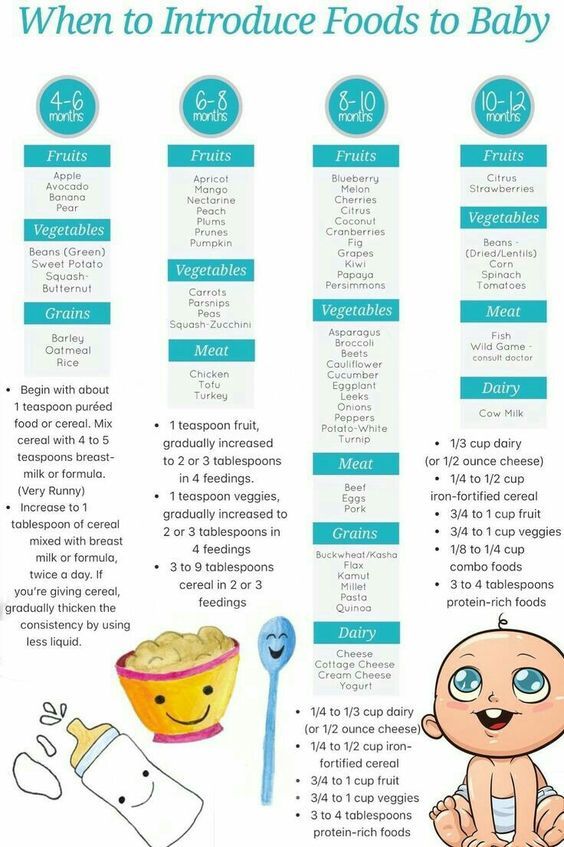 There's no evidence that waiting to introduce certain foods will help your baby avoid allergies. In fact, there's evidence that the opposite is true.
There's no evidence that waiting to introduce certain foods will help your baby avoid allergies. In fact, there's evidence that the opposite is true.
According to the American Academy of Allergy Asthma and Immunology (AAAAI), incorporating commonly allergenic foods into your baby's diet starting at around 4 to 6 months (and continuing through childhood) may actually help prevent the development of food allergies.
Start with traditional first foods, such as iron-fortified infant cereal, pureed veggies, fruits, and meats. Once you've tried a few of these foods and your baby seems to be tolerating them well, you can introduce more commonly allergenic foods, such as soy, eggs, wheat, fish, and peanut products.
Food manufacturers have products on the market designed to help you incorporate commonly allergenic foods into your child's diet. These stir-in powders and finger foods may contain one commonly allergenic protein or a blend of several.
Special precautions need to be taken with certain babies. If your child falls into any of the following categories, consult with your baby's doctor or an allergist to create a customized feeding plan before adding solids to your baby's diet:
If your child falls into any of the following categories, consult with your baby's doctor or an allergist to create a customized feeding plan before adding solids to your baby's diet:
- Your baby has a sibling with a peanut allergy.
- Your baby has moderate to severe eczema despite following a doctor's treatment plan.
- Your baby previously had an immediate allergic reaction to a new food or has been diagnosed with a food allergy.
If your baby is allergic to a new food, you'll see signs of a reaction within a few minutes or hours. Most children with food allergies have mild reactions. If you notice a few hives, a new rash, or diarrhea, call your baby's doctor for advice.
If you notice wheezing, difficulty breathing, vomiting, facial swelling (including the tongue and lips), or more than two body systems affected (such as hives and vomiting), your baby may be having a life-threatening reaction called anaphylaxis. Call 911 or your local emergency number immediately.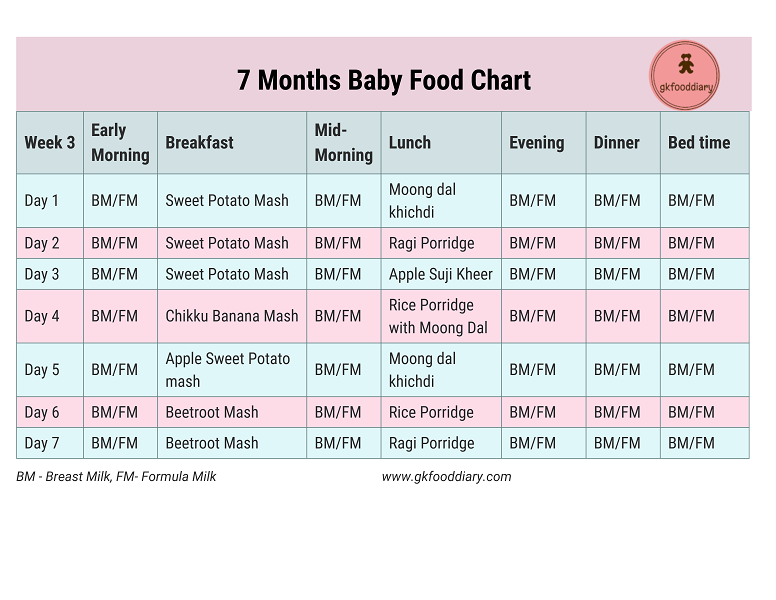
Baby food feeding tips
- Offer fruits or vegetables in any order. Some parents may tell you to start with vegetables instead of fruits so your infant won't develop a taste for sweets. But babies are born with a preference for sweets, so you don't have to worry about introducing sweet or savory foods in any particular order.
- Feed cereal with a spoon only. Unless your baby's doctor asks you to, don't add cereal to a bottle – your baby could choke or end up gaining too much weight.
- Encourage adventurous eating. You don't have to stick with bland and boring. See how to make your own baby food and use spices and seasonings to create delicious baby food flavors.
- Give new foods time. If your baby turns away from a particular food, don't push. Try again in a few days.
- Check for added sugars and too much salt. Check the Nutrition Facts label on canned, frozen, or packaged foods for "Added Sugars.
 " If there's 1 gram or more listed, give your baby something else. Also look at sodium amounts. Babies shouldn't have no more than 1,200 mg of sodium per day.
" If there's 1 gram or more listed, give your baby something else. Also look at sodium amounts. Babies shouldn't have no more than 1,200 mg of sodium per day. - Avoid unsafe foods. Don't give your baby foods that could cause choking, such as whole grapes or popcorn. Babies under 1 can't have honey, cow's milk, or soy milk. Also, unpasteurized juices and undercooked fish, meat, eggs, or poultry could be a source of bacteria.
- Watch for constipation. Your baby's poop sometimes changes when their diet does. Although it's usually temporary, your baby may have constipation after you introduce solids. If you notice that your baby is having less frequent bowel movements, or that their stools have become hard or dry and seem difficult to pass, let their doctor know. Some doctors recommend adding high-fiber fruits such as pears, prunes, and peaches to a baby's diet, or giving a few ounces of prune, apple, or pear juice every day until bowel movements are back to normal.

Also, don't be surprised if your baby's poop changes color and odor when you add solids to their diet. If your baby has been exclusively breastfed up to this point, you'll probably notice a strong odor to their formerly mild-smelling stools as soon as they start eating even tiny amounts of solids. This is normal.
If your baby shies away from new foods, here are a few things you can try:
- Test a range of textures. If your baby doesn't like pear puree, try giving them pieces of very ripe pear instead.
- In a similar vein, try different cooking methods. If your baby doesn't like steamed veggies, try giving them roasted vegetables.
- Serve food at different temperatures. Some babies prefer broccoli cold rather than warm, for example.
- Combine the new food with a familiar favorite. If your baby rejects a new food on its own, mix it in with something you know they like.
- Add a dipping sauce! Try shredded chicken with applesauce, yogurt with baked apple slices, or hummus with well-cooked pieces of carrot.
- Above all, be patient. Sometimes it takes a while for a baby to get used to new flavors and textures, so keep trying and eventually they'll accept the new food.
How many times a day should my baby eat solids?
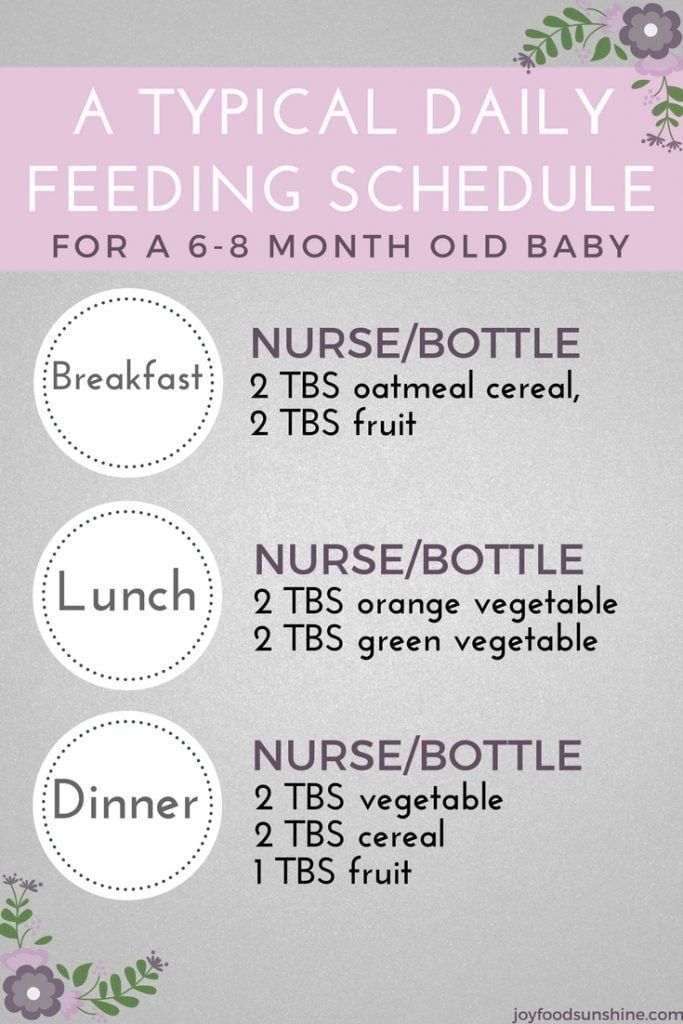
At first your baby will eat solid food just once a day. By around 6 to 7 months, two meals a day is the norm. Starting around 8 to 9 months, they may be eating solid food three times a day plus a snack. A typical day's diet at 8 months might include a combination of:
- Breast milk or iron-fortified formula
- Iron-fortified cereal
- Vegetables
- Fruit
- Small amounts of protein, such as eggs, cheese, yogurt, poultry, lentils, tofu, and meat
- High-allergy foods, if appropriate
See our age-by-age baby feeding guide for more detail on how much to feed your baby and when.
How much breast milk or formula does my baby need after we introduce solids?
Even after your baby starts solids, breast milk or formula will provide the majority of their calories and nutrition until they're 9 months to 1 year old.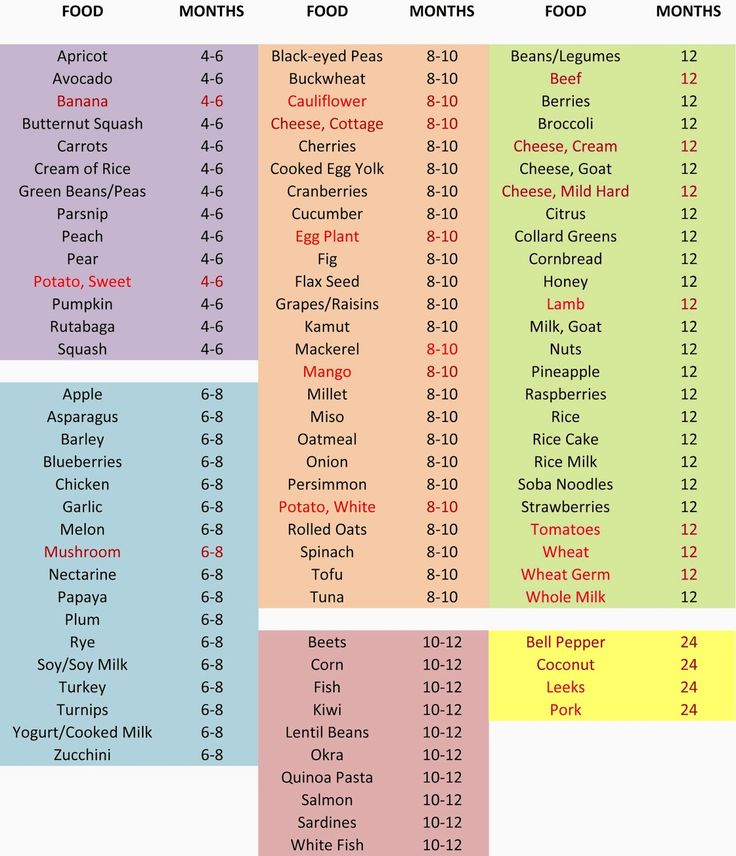 Breast milk and formula contain important vitamins, iron, and protein in a form that's easy to digest.
Breast milk and formula contain important vitamins, iron, and protein in a form that's easy to digest.
You may notice that as your baby starts to eat more solid foods (around 9 months old), they'll gradually decrease their intake of formula or breast milk. This is normal. Over time, your baby will take fewer bottles with more ounces in each.
Here's how much breast milk or formula babies need after starting solids:
- 4 to 6 months old: 4 to 6 feedings a day (breastfeeding, or bottles with 4 to 6 ounces)
- 6 to 8 months old: 3 to 5 feedings a day (breastfeeding, or bottles with 6 to 8 ounces)
- 8 to 12 months old: 3 to 4 feedings a day (breastfeeding, or bottles with 7 to 8 ounces)
What equipment do I need to introduce solids?
It's helpful to have:
- A highchair
- Baby bowls and plates
- Baby spoons
- Bibs
- A splat mat on the floor
You may also want to introduce your baby to a sippy cup soon after you start solids.
If you're making your own baby food, you'll need:
- A tool to puree the food, like a blender, food processor, or baby food maker
Storage containers for refrigerating and freezing extra portions (Some parents use ice cube trays – or similar devices made just for baby food – to store and freeze individual portions.)
Diet for a child from 6 months to a year
From 6 to 12 months, your baby develops at an incredible pace. It is during this period that his body needs a sufficient amount of nutrients and trace elements. The right diet will help provide your little one with the necessary nutrients and energize them to explore the world around them and gain new skills! In order to properly build a diet from 6 months old, we have prepared approximate menus for a child, broken down by months, and the feeding table itself from 4 months old can be downloaded here.
Menu at 6 months
Menu at 7 months
Menu at 8 months
Menu at 9 months
Menu at 10 months
Menu at 11 months
Menu at 12 months
Menu at 6 months
At 6 months, the baby's diet contains monocomponent vegetable purees (broccoli, zucchini, cauliflower), 1-2 types of porridge, monocomponent meat puree and children's cottage cheese.
| 6.00 | Breast milk, 200 gr (until saturation) |
| 09:00-09:30 | Dairy-free porridge 10-150 gr (depending on the introduction of complementary foods) + breast milk at the request of the child |
| 13:00-13:30 | Vegetable puree 10-150 gr, meat puree, e.g. Hamé Turkey, 10-30 gr (depending on complementary foods) + breast milk at the request of the child |
| 18:00-18:30 | Cottage cheese 10-40 gr, fruit puree 10-40 gr (depending on the introduction of complementary foods) + breast milk (until saturation) |
| 21:00-21:30 | Breast milk, 200 gr (until saturation) |
| 00:00 | Breast milk, 200 gr (until saturation) |
Vegetable oil can be added to vegetables and porridge.
Menu at 7 months
By 7 months, the volume of complementary foods increases, new types of meat, vegetables and fruits are introduced. Also in the diet of the child appears yolk.
| 6.00 | Breast milk, 200 gr (until saturation) |
| 09:00-09:30 | Dairy-free porridge 150 gr + breast milk at the request of the child |
| 13:00-14:00 | Vegetable puree 150-170 gr, meat puree, e.g. Hamé Veal, 30 gr, 1/4 egg yolk + breast milk at the request of the child |
| 18:00-18:30 | Fruit and cottage cheese puree 80 gr + breast milk (until saturation) |
| 21:00-21:30 | Breast milk, 200 gr (until saturation) |
| 00:00 | Breast milk, 200 gr (until saturation) |
You can add butter or vegetable oil to vegetables and porridge.
Menu at 8 months
From 8 months you can introduce baby purees with fish and meat purees with the addition of offal. You can also start offering fruit in a nibbler so your little one can scratch their teeth and try new flavors.
| 6.00 | Breast milk, 200 gr (until saturation) |
| 09:00-09:30 | Dairy/dairy-free porridge 150 gr, fruit puree 40 gr + breast milk at the request of the child |
| 13:00-14:00 | Vegetable puree 150 gr, meat puree, e.g. Hamé Beef with tongue, 50 gr, 1/2 egg yolk + breast milk on request |
| 18:00-18:30 | Fruit and cottage cheese puree 80 gr + breast milk (until saturation) |
| 21:00-21:30 | Porridge with butter 60 gr + breast milk (until full) |
| 23:30-00:00 | Breast milk, 200 gr (until saturation) |
A more satisfying dinner with the addition of porridge contributes to sound sleep without frequent awakenings for feeding.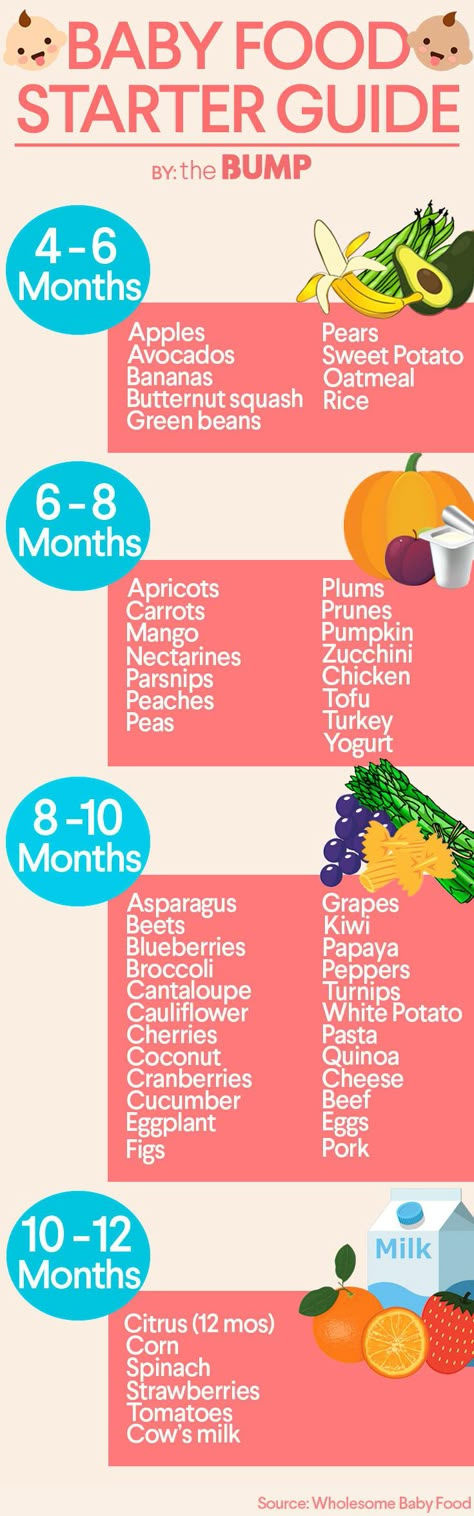
Menu at 9months
The daily menu is filled with new types of products from all categories: fish purees, sour-milk products and cereals.
| 6.00 | Breast milk, 200 gr (until saturation) |
| 09:00-09:30 | Milk/dairy-free porridge 150 gr, fruit puree 40 gr + breast milk at the request of the child |
| 13:00-14:00 | Vegetable puree 150 gr, fish or meat puree, e.g. Hamé Chicken, 60 gr, 1/2 egg yolk + breast milk as desired by the child |
| 18:00-18:30 | Fruit and cottage cheese puree 100 gr + breast milk (until saturation) |
| 21:00-21:30 | Porridge with butter 60 gr + breast milk (until full) |
| 23:30-00:00 | Breast milk, 200 gr (until saturation) |
At 9 months, you can enter baby cookies and up to 10 grams of bread.
Menu at 10 months
At this age, the baby’s menu can be slightly diversified with some dishes from the general table: weak broths, cottage cheese puddings or casseroles, vegetables and fruits, grated on a fine grater.
| 6.00 | Breast milk, 200 gr (until saturation) |
| 09:00-09:30 | Milk/dairy-free porridge 150 gr, fruit puree 60 gr + breast milk at the request of the child |
| 13:00-14:00 | Vegetable puree 150 gr, fish or meat puree, e.g. Hamé Beef with heart, 70 gr, 1/2 egg yolk + breast milk as desired by the child |
| 18:00-18:30 | Cottage cheese 50 gr, fruit puree 80 gr + breast milk (until full) |
| 21:00-21:30 | Porridge with butter 60 gr + breast milk (until full) |
| 23:30-00:00 | Breast milk, 200 gr (until saturation) |
During the day, you can offer children's cookies and up to 10 grams of bread.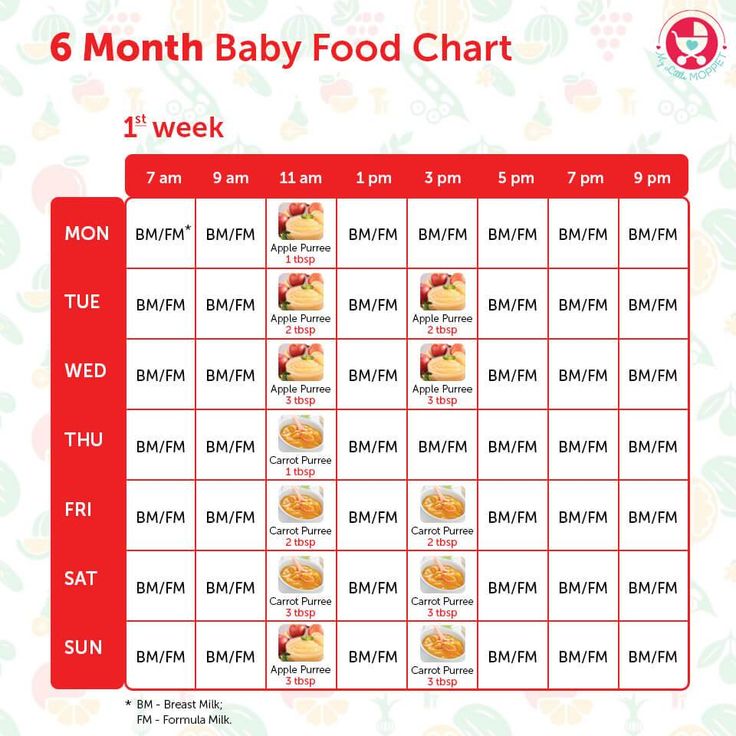
Menu at 11 months
At this age, the baby makes the first attempts to eat on its own. Parents can help by offering chopped soft fruits and vegetables. Steamed meat dishes are also suitable: meatballs, meatballs, fish fillet or finely chopped boiled chicken.
| 6.00 | Breast milk, 200 gr (until saturation) |
| 09:00-09:30 | Milk/dairy-free porridge 150 gr, fruit puree 60 gr + breast milk at the request of the child |
13:00-14:00 | Vegetable puree 150 gr, fish or meat puree, e.g. Hamé Beef with liver, 80 gr, 1/2 egg yolk + breast milk on request |
| 18:00-18:30 | Fruit and cottage cheese puree 100 gr + breast milk (until saturation) |
| 21:00-21:30 | Porridge with butter 60 gr + breast milk (until full) |
| 23:30-00:00 | Breast milk, 200 gr (until saturation) |
During the day, you can offer children's cookies and up to 10 grams of bread.
Menu at 12 months
At this age, parents begin to introduce the baby to a common table adapted to his needs, gradually expanding the diet with new tastes and textures of products. You can offer your child baby vermicelli, greens, forest and garden berries. Meat puree can be coarsely ground, your baby will gobble up meatballs and cutlets with great pleasure.
6.00 | Breast milk, 200 gr (until saturation) |
| 09:00-09:30 | Milk/dairy-free porridge 150 gr, fruit puree 80 gr + breast milk at the request of the child |
| 13:00-14:00 | Vegetable puree 150 gr, fish or meat puree, e.g. Hamé Beef with chicken and beef 80 gr, 1/2 egg yolk + breast milk as desired by the child |
| 18:00-18:30 | Fruit and cottage cheese puree 100 gr + breast milk (until saturation) |
| 21:00-21:30 | Porridge with butter 60 gr + breast milk (until full) |
| 23:30-00:00 | Breast milk, 200 gr (until saturation) |
At this age, baby food can be slightly salted or sweetened.
diet for a 6-month-old baby with breast and artificial feeding, sample menu for a week in the table, diet for day
Published: 02/10/2021
Reading time: 4 min.
Number of reads: 226457
Author of the article: Ponomareva Yulia Vladimirovna
Pediatrician, Candidate of Medical Sciences, allergist-immunologist
Changes in a child in the first year of life are very rapid, and each month is not like another. The 6-month milestone is very important, it is largely evaluative and transitional. By this age, most babies have doubled their birth weight, are about 15 cm tall, and some babies have already erupted their teeth. The age of 6 months is also transitional in terms of nutrition. Breast milk or an adapted formula is still the basis of the diet, but with the beginning of the second half of life, all children, without exception, should begin to receive complementary foods. Despite the general graph of growth and weight gain and indicators of psychomotor development, the status and diet of children at 6 months can be very different.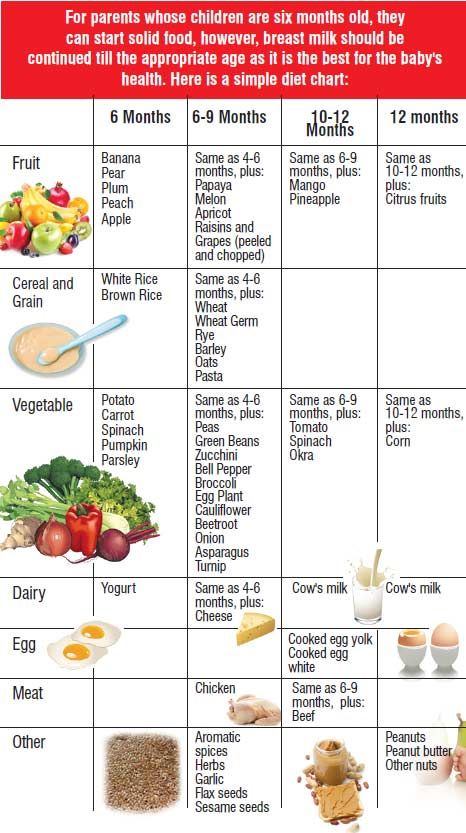
Content: Hide
- The first feeding of 6 months
- The start of complementary foods at 4-5 months
- The second half of life
- Mamit menu for a week for a child at 6 months
The first feeding of 6 months
9000 9000 9000 9000 If the baby is healthy and breastfed, and his mother eats a full and varied diet, exclusive breastfeeding is possible until this age. Cereal complementary foods in this case are preferable to start. This is due to the high energy and nutritional value of cereals, the ability to significantly enrich the baby's diet with a delayed start of the introduction of complementary foods.
However, the rate of expansion of the child's diet in this situation will be accelerated. Before the 8th month of life, it is necessary to introduce all basic food groups into the baby’s menu, since in the second half of the year the need for additional intake of nutrients and micronutrients is very high. Another reason explaining the importance of the rapid introduction of complementary foods is the formation of immunity of the immune cells of the intestine to ordinary food. If a child is introduced to these foods at the age of 4-8 months, the risk of developing food allergies has been proven to be reduced.
Another reason explaining the importance of the rapid introduction of complementary foods is the formation of immunity of the immune cells of the intestine to ordinary food. If a child is introduced to these foods at the age of 4-8 months, the risk of developing food allergies has been proven to be reduced.
Complementary feeding starts at 4-5 months
In modern life, the nutrition of a nursing mother, unfortunately, is not always complete. Therefore, for most breastfed babies, complementary foods already need to be introduced from 5 months in order to prevent deficient conditions.
If a child is bottle-fed, then by the 4th month of life, the baby will not have enough adapted formula alone, and in this group of children, the timing of the introduction of complementary foods usually shifts a month earlier than in breast-fed babies. Accordingly, by 6 months, children will have vegetable puree and gluten-free porridge (buckwheat, corn and rice) in their diet. In the first half of life, monocomponent meals are used (that is, from one type of grain and vegetables), prepared on the basis of water, breast milk or an adapted mixture.
Fruit puree and juice can be another possible complementary food for children under 6 months of age without allergy symptoms. In a child with a risk of developing or manifesting allergies, the timing of the introduction of fruit complementary foods is shifted to the 8th month.
Second six months of life
Children over 6 months of age can supplement their diet with cereals containing gluten. First of all, these are oatmeal and wheat porridge, and then multi-cereal dishes with the addition of other cereals (millet, barley, rye). If the child does not have any manifestations of allergies, milk porridge can be included in the menu at this age. Bebi Premium industrial baby food products include specially prepared milk that is safe to use in healthy babies in the first year of life.
From the age of 6 months, the baby's diet is expanded with such important products as meat and cottage cheese. These products are a source of high-quality protein, fats, and are also rich in minerals such as iron, calcium, and phosphorus.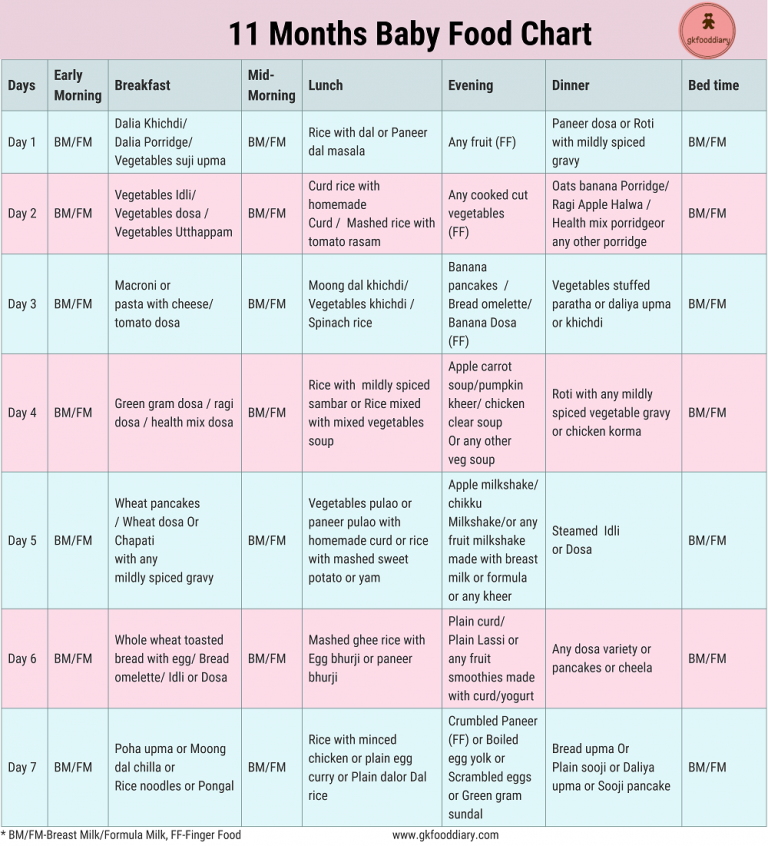 Pediatricians and nutritionists recommend introducing meat and cottage cheese as part of combined dishes based on a fruit and vegetable and / or grain component in a ratio of 1 (cottage cheese / meat): 4–5 (fruits / vegetables / cereals).
Pediatricians and nutritionists recommend introducing meat and cottage cheese as part of combined dishes based on a fruit and vegetable and / or grain component in a ratio of 1 (cottage cheese / meat): 4–5 (fruits / vegetables / cereals).
To enrich the diet with polyunsaturated fatty acids in the second half of the year, the menu includes vegetable oil in the amount of 3–5 grams per day, which can be added to the complementary food dish. The volume of each feeding is approximately 150-170 ml, and the child can already stand up to 3.5 hours between meals.
In the table below, we offer a menu of 6 months for a week for a child who started receiving complementary foods at the age of 4-5 months, and by the time the second half of life begins, dairy-free gluten-free cereals, vegetable and fruit purees have already been introduced into his diet.
1st day
| Meeting | Menus | ml/g |
| Early morning | Breast milk/mixture | 150 |
Lunch (12.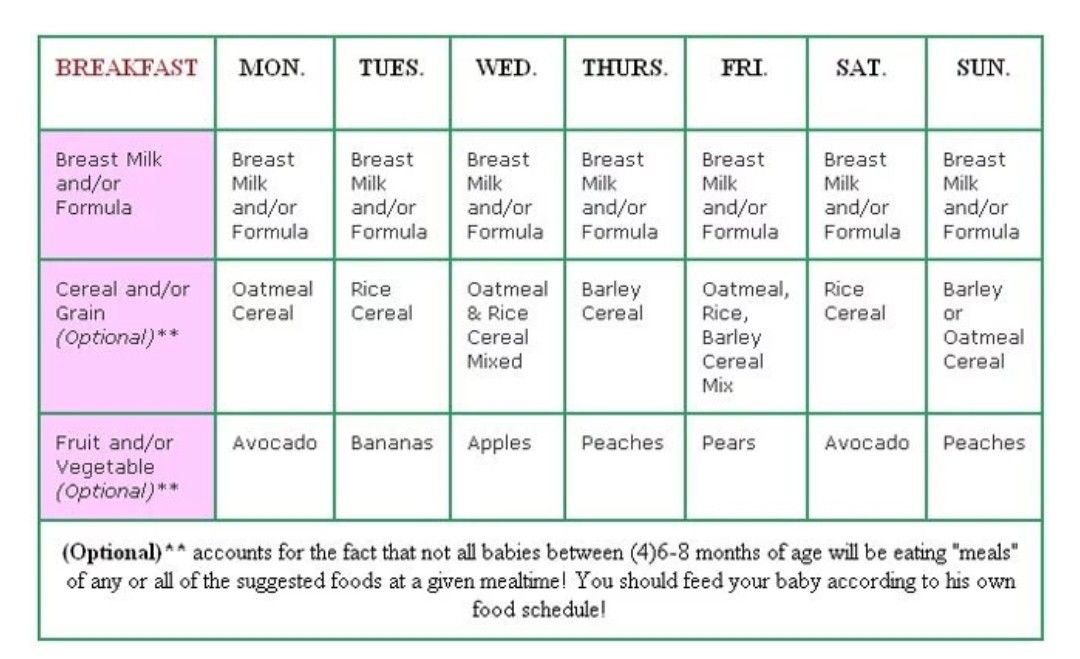 |