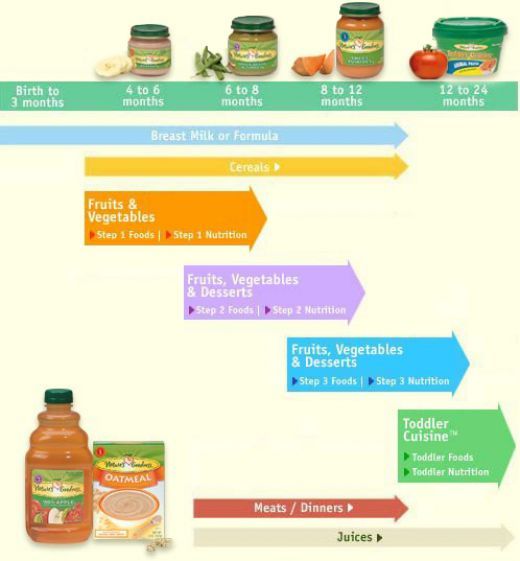
What foods to start baby on first
Dos and Don'ts for Baby's First Foods
Wavebreak Media/Thinkstock
Breastfeeding has been shown to improve infant, child and maternal health outcomes and help control healthcare costs, but how long should breastfeeding last and when should parents introduce solid foods?
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommend exclusive breastfeeding, meaning the infant receives only breast milk, during the first six months of life for optimal nutrition and health benefits.
Once solid foods are introduced, health professionals recommend continuing breastfeeding through 12 months of age and, after that, as desired by mother and baby. Introducing your baby to solid foods is an exciting milestone. When you start introducing children to the world of solid foods, you are helping them shape their relationship with food and establish a healthy eating style. The timing for introducing solid foods will depend on the infant, but it is not recommended before the age of four months or after the age of six months.
Not sure how to get your baby started on solid foods? Consider these helpful tips.
Is Your Baby Ready to Transition?
Each child's readiness for solid food depends on their own rate of development. Signs a baby may be ready to start solid foods include sitting up with minimal support, demonstrating good head control, bringing objects to the mouth or grasping at small objects. Check with your pediatrician before starting solid foods.
Getting Started With Solids
Solid foods may be introduced in any order. However, puréed meats, poultry, beans and iron-fortified cereals are recommended as first foods, especially if your baby has been primarily breastfed, since they provide key nutrients. Only one new single-ingredient food should be introduced at a time.
Softer textures are very important when first introducing foods. Infants usually start with pureed or mashed foods around six months. As infants develop chewing and motor skills, they are able to handle items like soft pieces of fruit and finger foods. As the child ages, a variety of healthful foods is encouraged.
As the child ages, a variety of healthful foods is encouraged.
Weaning From Breastfeeding
When deciding if you should wean your baby to a bottle or a cup, consider their developmental readiness. Between 7 and 8 months, most infants will drink small amounts of liquid from a cup or a glass when someone else holds it. Older babies and toddlers often have the coordination to drink fluids from a cup by themselves.
If your baby is under 12 months of age and you are not continuing to breastfeed, wean from breast milk to iron-fortified infant formula. If your baby is 12 months or older, whole cow’s milk is appropriate.
Food Safety Do’s and Don’ts
Food safety concerns for infants and toddlers include food allergies, choking and risks for foodborne illness. Keep the following safety tips in mind:
Do talk with your pediatrician about the risk of food allergies. Introducing one new food at a time, every several days, allows time to monitor for allergic reactions. Current evidence does not indicate needing to wait beyond 4 to 6 months before introducing potential allergy-causing foods such as eggs, dairy, soy, peanuts and fish. In fact, introducing peanut-containing foods as early as 4 to 6 months of age may help prevent a peanut allergy. The Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommends introducing potentially allergenic foods when other complementary foods are introduced to an infant’s diet. Parents with concerns about food allergies should discuss how to include these foods with their pediatrician.
Current evidence does not indicate needing to wait beyond 4 to 6 months before introducing potential allergy-causing foods such as eggs, dairy, soy, peanuts and fish. In fact, introducing peanut-containing foods as early as 4 to 6 months of age may help prevent a peanut allergy. The Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommends introducing potentially allergenic foods when other complementary foods are introduced to an infant’s diet. Parents with concerns about food allergies should discuss how to include these foods with their pediatrician.
Don’t feed your baby solid foods from a bottle. It can be a choking hazard and despite a popular misconception, putting cereal in a baby's bottle won't help with sleeping through the night. Other foods that are considered to be choking hazards are listed below.
Do supervise your child while eating. Infants should be able to sit upright and face forward when you first introduce solid foods. This makes swallowing easier and choking less likely.
Don’t feed directly from the jar of food but instead spoon some food into a separate dish first. Feeding directly from the jar may introduce bacteria from your baby's mouth to the spoon and back into the food, creating a food safety issue.
Don’t feed honey to children under 12 months of age due to the risk of foodborne illness.
Examples of appropriate solid foods listed by age:
6 months:
- Well-cooked and pureed meat, poultry or beans
- Ground, cooked, single-grain cereal or infant cereal with breast milk or formula
- Cooked and pureed vegetables
- Mashed banana or avocado
9 months:
- Well-cooked, minced or finely chopped meat, poultry or beans
- A variety of cooked vegetables cut into small, ½ inch pieces, such as squash and green beans
- Sliced and quartered bananas or small pieces of other soft fruits
12 months:
- Soft, shredded meat, poultry or fish
- Small pieces of cooked vegetables
- Small pieces of soft, easy to chew fruits
- Mixed food dishes the family is eating in appropriately sized pieces
Not recommended for those under 4 years of age due to the risk of choking:
- Popcorn and whole kernel corn
- Nuts and seeds
- Large chunks of meat, poultry and cheese
- Candy, gum drops and jelly beans
- Hard, raw fruits or vegetables such as apples, celery and carrots
- Whole grapes and cherry tomatoes, unless cut into quarters
- Hot dogs, unless cut into strips and age appropriate, bite-size pieces
- Sticky foods, such as peanut butter, which can get stuck in the back of the mouth – peanut butter is okay if spread thinly on bread
For toddlers and preschoolers, chop grapes, meat, poultry, hot dogs and raw vegetables and fruits into small pieces (about ½ inch or smaller).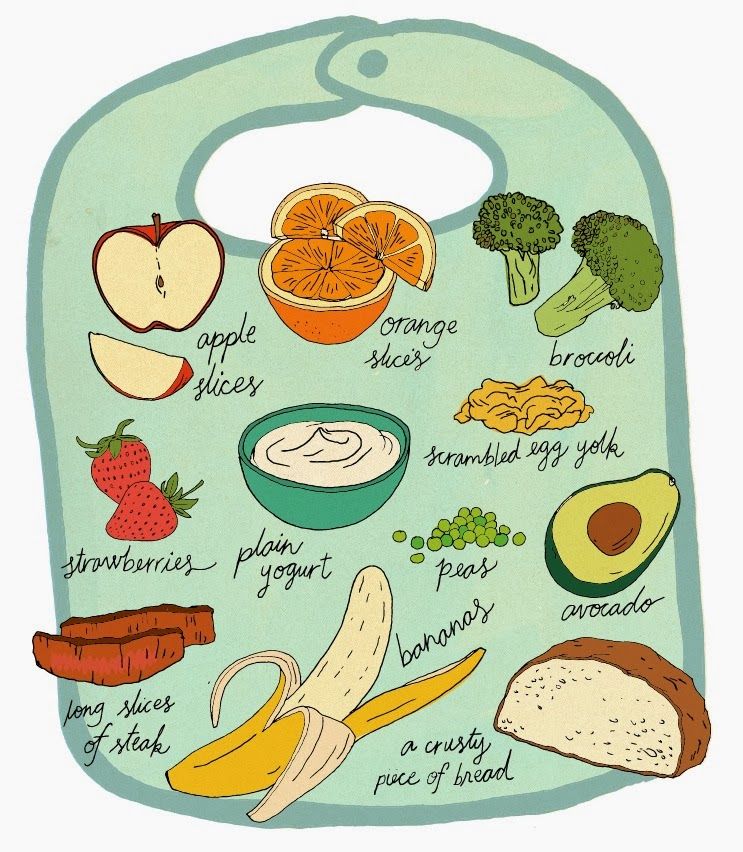
Nurturing Healthy Relationships with Food
Establishing a positive feeding relationship during infancy can have lifetime benefits. Keep in mind that children are responsible for how much and whether they eat so always wait for your baby to pay attention to each spoonful before you feed them. Don't be afraid to let your baby touch the food in the dish and on the spoon. You wouldn't want to eat something if you didn't know anything about it, would you? In addition, know the cues that your baby is done eating. A common cue babies are full is head turning.
Whatever happens, don't get discouraged and enjoy the experience. With a little patience and creativity, you can make your baby's first solid food eating experience fun for everyone involved!
When, What, and How to Introduce Solid Foods | Nutrition
For more information about how to know if your baby is ready to starting eating foods, what first foods to offer, and what to expect, watch these videos from 1,000 Days.
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend children be introduced to foods other than breast milk or infant formula when they are about 6 months old. Introducing foods before 4 months old is not recommended. Every child is different. How do you know if your child is ready for foods other than breast milk or infant formula? You can look for these signs that your child is developmentally ready.
Your child:
- Sits up alone or with support.
- Is able to control head and neck.
- Opens the mouth when food is offered.
- Swallows food rather than pushes it back out onto the chin.
- Brings objects to the mouth.
- Tries to grasp small objects, such as toys or food.
- Transfers food from the front to the back of the tongue to swallow.
What Foods Should I Introduce to My Child First?
The American Academy of Pediatrics says that for most children, you do not need to give foods in a certain order. Your child can begin eating solid foods at about 6 months old. By the time he or she is 7 or 8 months old, your child can eat a variety of foods from different food groups. These foods include infant cereals, meat or other proteins, fruits, vegetables, grains, yogurts and cheeses, and more.
Your child can begin eating solid foods at about 6 months old. By the time he or she is 7 or 8 months old, your child can eat a variety of foods from different food groups. These foods include infant cereals, meat or other proteins, fruits, vegetables, grains, yogurts and cheeses, and more.
If your child is eating infant cereals, it is important to offer a variety of fortifiedalert icon infant cereals such as oat, barley, and multi-grain instead of only rice cereal. Only providing infant rice cereal is not recommended by the Food and Drug Administration because there is a risk for children to be exposed to arsenic. Visit the U.S. Food & Drug Administrationexternal icon to learn more.
How Should I Introduce My Child to Foods?
Your child needs certain vitamins and minerals to grow healthy and strong.
Now that your child is starting to eat food, be sure to choose foods that give your child all the vitamins and minerals they need.
Click here to learn more about some of these vitamins & minerals.
Let your child try one single-ingredient food at a time at first. This helps you see if your child has any problems with that food, such as food allergies. Wait 3 to 5 days between each new food. Before you know it, your child will be on his or her way to eating and enjoying lots of new foods.
Introduce potentially allergenic foods when other foods are introduced.
Potentially allergenic foods include cow’s milk products, eggs, fish, shellfish, tree nuts, peanuts, wheat, soy, and sesame. Drinking cow’s milk or fortified soy beverages is not recommended until your child is older than 12 months, but other cow’s milk products, such as yogurt, can be introduced before 12 months. If your child has severe eczema and/or egg allergy, talk with your child’s doctor or nurse about when and how to safely introduce foods with peanuts.
How Should I Prepare Food for My Child to Eat?
At first, it’s easier for your child to eat foods that are mashed, pureed, or strained and very smooth in texture. It can take time for your child to adjust to new food textures. Your child might cough, gag, or spit up. As your baby’s oral skills develop, thicker and lumpier foods can be introduced.
It can take time for your child to adjust to new food textures. Your child might cough, gag, or spit up. As your baby’s oral skills develop, thicker and lumpier foods can be introduced.
Some foods are potential choking hazards, so it is important to feed your child foods that are the right texture for his or her development. To help prevent choking, prepare foods that can be easily dissolved with saliva and do not require chewing. Feed small portions and encourage your baby to eat slowly. Always watch your child while he or she is eating.
Here are some tips for preparing foods:
- Mix cereals and mashed cooked grains with breast milk, formula, or water to make it smooth and easy for your baby to swallow.
- Mash or puree vegetables, fruits and other foods until they are smooth.
- Hard fruits and vegetables, like apples and carrots, usually need to be cooked so they can be easily mashed or pureed.
- Cook food until it is soft enough to easily mash with a fork.

- Remove all fat, skin, and bones from poultry, meat, and fish, before cooking.
- Remove seeds and hard pits from fruit, and then cut the fruit into small pieces.
- Cut soft food into small pieces or thin slices.
- Cut cylindrical foods like hot dogs, sausage and string cheese into short thin strips instead of round pieces that could get stuck in the airway.
- Cut small spherical foods like grapes, cherries, berries and tomatoes into small pieces.
- Cook and finely grind or mash whole-grain kernels of wheat, barley, rice, and other grains.
Learn more about potential choking hazards and how to prevent your child from choking.
Top of Page
What foods can be given to a baby at 4 months
Reviewer Kovtun Tatiana Anatolievna
831 views
September 06, 2022
Login or register to save articles and products to your favorites
Most often, the need for complementary foods at four months arises according to individual indications. How to properly introduce the baby to adult food and what to offer him?
How to properly introduce the baby to adult food and what to offer him?
Breast milk or infant formula recommended by a specialist remains a key and indispensable product for a baby up to a year of life, and it is better, according to the recommendations of the World Health Organization, to keep it up to two years. But in some cases, a specialist may recommend the first purees at the age of more than four months of age.
The decision on early complementary feeding should be made by parents together with the specialist who is watching the child. He will tell you what to pay attention to and what products to offer the baby in the first place.
If your baby needs complementary foods at four months, don't worry that it's too early. At this time, the gastrointestinal tract of some children is already becoming quite mature. In a baby, the permeability of the mucous membrane of the small intestine decreases and a number of digestive enzymes mature. The child can already swallow semi-liquid food.
What can a baby eat at 4 months
For the first feeding of the baby, choose either dairy-free baby porridge or baby vegetable puree.
Then add meat puree (over 6 months old), fruit puree and juices, baby dairy products (over 8 months old), fish puree (over 8 months old), egg yolk, as well as vegetable and butter.
Usually, a specialist, based on the condition of the child, determines in what order to offer products, and builds a nutrition scheme.
In the fifth month of life, the diet of crumbs may include porridge and vegetable purees. This recommendation does not take into account the individual characteristics of the baby and must be agreed with a specialist. Only he will tell you exactly what you can feed a baby at 4 months.
Complementary feeding rules at four months of age
You need to offer the dish with ½ teaspoon in the morning. So parents can track the reaction of the crumbs to a new product during the day. At the same time, you need to introduce the baby to only one product and gradually increase its volume over several days. As soon as the child tastes it, you can offer something else.
At the same time, you need to introduce the baby to only one product and gradually increase its volume over several days. As soon as the child tastes it, you can offer something else.
Simultaneously with the introduction of complementary foods, you need to acquaint the baby with the basic rules of etiquette. Meals should be arranged only at the table in a special chair, so that the child immediately gets used to the rules in the house.
Sample menu for a 4 month old baby
When the baby gets acquainted with the basic products for the first feeding, you can build the first menu. In the morning after the main feeding, he can be offered a new product. The diet of a 4-month-old baby should be agreed with a specialist.
Buy ready-made puree or make your own
Many parents enjoy cooking for their children, and some prefer ready-made mashed potatoes. In the first case, you need to spend more time: for example, select vegetables, wash them and steam them. In addition to this, it should be remembered that cooking at home is not safe, since it is rarely possible to check the raw materials for the content of nitrates, toxins and other hazardous substances at home.
In addition to this, it should be remembered that cooking at home is not safe, since it is rarely possible to check the raw materials for the content of nitrates, toxins and other hazardous substances at home.
In addition, at home it is difficult to follow the technological process of preparation and track the optimal degree of grinding of the product. Therefore, experts recommend the use of industrial products in the nutrition of young children.
This option is optimal for those who are afraid of making mistakes at the stages of choosing ingredients or cooking. Puree "FrutoNyanya" undergoes strict control of the recipe and the preparation process, which makes it possible to exclude the ingress of any pathogenic bacteria into the product.
You can not refuse breast or artificial feeding if the baby has already begun to get acquainted with adult products. This will help him develop organically and gain weight well.
Reviewer Kovtun Tatiana Anatolievna
Scientific adviser of PROGRESS JSC, Ph. D.0005
D.0005
Complementary feeding
How to introduce complementary foods correctly is one of the most pressing issues that concern parents.
In the first months of life, the main food for the baby is breast milk or an adapted milk formula, however, as the child grows and develops, this becomes insufficient and it is necessary to think about the introduction of complementary foods.
Your baby is over 4 months old. He has noticeably grown up, become more active, is interested in objects that fall into his field of vision, carefully examines them and reaches for them. The child's emotional reactions have become much richer: he smiles happily at all people, makes various sounds. Perhaps you notice that the child looks into your plate with interest, closely monitors what and how you eat, does this mean that it is time to introduce complementary foods? And where is the best place to start? Let's figure it out!
When should complementary foods be started?
According to the Program for optimizing the feeding of infants in the first year of life in the Russian Federation (2019), the recommended age for the introduction of complementary foods is in the range from 4 to 6 months.
The following points will help determine the readiness of the baby for the introduction of complementary foods:
1. Food interest - you can check its presence as follows: during your meal, give the baby an empty spoon or fork, and if he plays with it, licks it, then there is no food interest yet; but if the child is dissatisfied with the fact that the spoon is empty, food interest has probably appeared. “But how does a child understand that there should be food in a spoon?” Parents often ask. The answer is quite simple: take your baby to the table with you so that he can see how you eat!
2. The child can sit alone or with support. It is unacceptable to feed the child lying down, because he may choke.
3. Extinction of the “pushing out” reflex - when the baby pushes out of the mouth both the offered food and the pacifier, etc.
Why is it not recommended to introduce complementary foods before 4 and after 6 months of life?
Before 4 months of life, the baby is not yet ready to digest food other than breast milk or infant formula. By this age, a number of digestive enzymes mature, a sufficient level of local immunity is formed, which reduces the risk of developing allergic reactions, the child acquires the ability to swallow semi-liquid and thicker food, which is due to the extinction of the “spoon ejection reflex”. The introduction of complementary foods after 6 months can cause a pronounced deficiency of micronutrients (iron, zinc, etc.) and lead to a delay in the formation of chewing skills for thick foods. Too late the introduction of a variety of products increases the risk of allergic reactions. Remember that the timing of the introduction of complementary foods is set individually, taking into account the readiness of the child to accept new foods.
By this age, a number of digestive enzymes mature, a sufficient level of local immunity is formed, which reduces the risk of developing allergic reactions, the child acquires the ability to swallow semi-liquid and thicker food, which is due to the extinction of the “spoon ejection reflex”. The introduction of complementary foods after 6 months can cause a pronounced deficiency of micronutrients (iron, zinc, etc.) and lead to a delay in the formation of chewing skills for thick foods. Too late the introduction of a variety of products increases the risk of allergic reactions. Remember that the timing of the introduction of complementary foods is set individually, taking into account the readiness of the child to accept new foods.
Basic principles for the introduction of complementary foods:
1. introduce a new product in the first half of the day to track possible reactions to it;
2. cereals, vegetable / fruit / meat purees should be introduced, starting with monocomponent ones, gradually adding other products of this group;
3. start giving a new product with 1/2 teaspoon, gradually increasing the volume to the age norm within a week;
4. It is not recommended to introduce new products during acute infectious diseases or at some special moments (moving to another apartment, leaving the city, on vacation, illness of parents, etc.).
What is the best way to start complementary foods?
The first complementary food can be anything. Often parents worry that if the child first tries the fruit, then because of its sweet taste, he will refuse other foods. We hasten to reassure you: breast milk is also sweet, so babies may like sweet fruits / berries more, but this does not mean at all that he will refuse vegetables or cereal. Traditionally, they begin to introduce complementary foods in the form of mashed potatoes, but if the child shows interest in “pieces”, then, observing the safety rules, you can give them. Also, along with the introduction of complementary foods, you can offer the child water.
With the start of the introduction of complementary foods, the child is gradually transferred to a 5-time feeding regimen. If the baby shows that he is full and no longer wants to eat (for example, leaning back or turning away from food), then you should not continue to force him to feed, because this can lead to eating disorders in the future. Also, do not force the child to eat as much as possible before bedtime in the hope that he will not wake up for nightly feedings.
Traditionally, in our country, complementary foods begin with vegetables or cereals.
Vegetables: zucchini, broccoli, cauliflower, pumpkin, etc. If the child did not like the dish, for example, broccoli, do not give up on your plan and continue to offer this vegetable in small quantities daily, you can even not once, but 2-3 times, and after a while (7-14 days) the baby will get used to the new taste. This diversifies his diet, will help form the right taste habits in the child.
As for cereals, it is worth starting with dairy-free gluten-free ones - buckwheat, corn, rice. You can use commercial baby food porridge, which is enriched primarily with iron. In addition, such porridge is already ready to eat, you just need to dilute it with water, which will save you a lot of time.
You can use commercial baby food porridge, which is enriched primarily with iron. In addition, such porridge is already ready to eat, you just need to dilute it with water, which will save you a lot of time.
It is also recommended to add oil to food, for example, vegetable puree to vegetable puree, and butter to porridge.
Of meat products, lean meats, such as mashed turkey or rabbit, are most preferred to start complementary foods. Meat puree contains iron, which is easily absorbed, and adding meat to vegetables improves the absorption of this micronutrient from them. Subsequently, the daily use of children's enriched porridge and mashed meat allows you to meet the needs of babies for iron, zinc and other micronutrients.
When introducing fruit purees (apple, pear, peach, prunes, etc.) into your baby's diet, you should pay special attention to the composition of the product - it is important that it does not contain added sugar.
Fish is a source of easily digestible protein and contains a large amount of polyunsaturated fatty acids, including the omega-3 class, as well as vitamins B2, B12, and minerals. Preference should be given to oceanic fish, preferably white (cod, hake, pollock, sea bass, etc.), salmon can be recommended from red, and pike perch from river.
Preference should be given to oceanic fish, preferably white (cod, hake, pollock, sea bass, etc.), salmon can be recommended from red, and pike perch from river.
Fermented milk products are prepared using a special starter culture that breaks down milk protein, so that the baby can get an indispensable set of amino acids in a well-available form. Some foods have added prebiotics, certain vitamins and minerals. Their regular use favorably affects the functioning of the intestines, increases appetite and the absorption of micronutrients.
Recommendations and timing of the introduction of complementary foods for children at risk of developing food allergies and suffering from food allergies are the same as for healthy children. Delayed introduction of highly allergenic foods has previously been recommended to prevent the development of allergic diseases in children at risk. There is now evidence that this practice may lead to an increase rather than a decrease in the incidence of food allergies. The most common highly allergenic foods include cow's milk, chicken eggs, soybeans, wheat, peanuts, tree nuts, shellfish and fish. If a child has a high risk of developing allergies or an existing allergic disease, it is recommended to consult a pediatrician, an allergist-immunologist before introducing highly allergenic products.
The most common highly allergenic foods include cow's milk, chicken eggs, soybeans, wheat, peanuts, tree nuts, shellfish and fish. If a child has a high risk of developing allergies or an existing allergic disease, it is recommended to consult a pediatrician, an allergist-immunologist before introducing highly allergenic products.
By the age of 8 months, when all the main food groups have already been introduced and your baby is improving his skills to eat on his own, special attention should be paid to the diversity of the composition of dishes and the change in food consistency - from puree to finely and coarsely ground. Soft foods cut into small pieces (fruits, vegetables, meat, etc.) are perfect for a little gourmet, which diversifies his diet and will contribute to the formation of chewing skills.
By 9-12 months, most babies have the dexterity to drink from a cup (holding with both hands) and to eat foods prepared for other family members. This behavior needs to be encouraged, but combined with regular feeding to meet energy and nutrient requirements.
It is advisable to use industrial products that are designed specifically for young children after a year.
What should not be given to the baby?
It is not recommended to add salt or sugar to food to enhance the taste.
Drinks that should be avoided include fruit juices, whole cow and goat milk (whole milk is not recommended for children under one year old, and even longer, due to a high risk of developing iron deficiency and increased kidney stress), sweet fruit drinks, compotes and carbonated drinks.
Also, some foods should be excluded from the diet of infants: solid round foods (for example, nuts, grapes, raw carrots, raisins, peas, etc.), due to the fact that the child can choke on them.
It is not recommended to eat products with added sugar, for example, confectionery (marshmallow, marshmallow, marmalade, jam, jam, cookies, waffles, etc.), etc.
You should not give your child the meat of large predatory fish (shark, bigeye tuna, king mackerel, swordfish): these types of fish accumulate more harmful substances than others.
It is forbidden to give honey to children under one year old due to the fact that it may contain spores of Clostridium botulinum bacteria, which in the still immature digestive system of babies are able to multiply, produce toxins directly inside the intestines and, thus, cause infant botulism, which can be fatal. outcome.
Do not give babies raw meat, fish, eggs, caviar, salted fish, soft pickled cheeses because of the risk of intestinal infections.
If you follow all these simple rules, your baby will grow up healthy and happy!
Diets for different ages
References:
1. Methodological recommendations. The program for optimizing the feeding of children in the first year of life in the Russian Federation. [Internet]. - M.: Union of Pediatricians of Russia, 2019. [Methodicheskie rekomendaczii. Programma optimizaczii vskarmlivaniya detej pervogo goda zhizni v Rossijskoj Federaczii. [Internet]. – Moscow: Soyuz pediatrov Rossii, 2019.