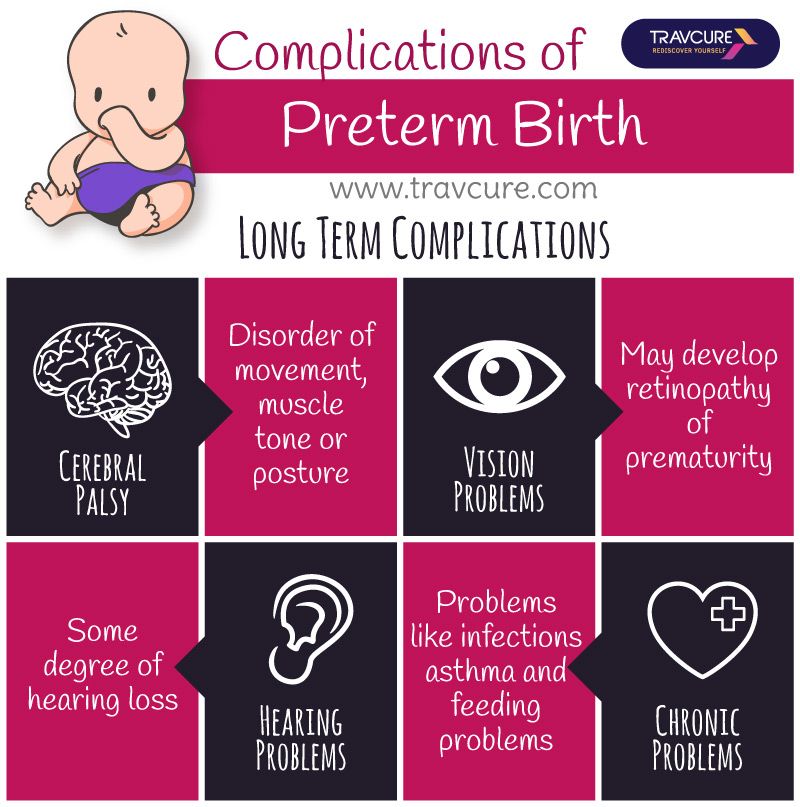
What to do when baby chokes while feeding
First aid for a baby who is choking
Common questions about first aid for a baby who is choking
What can a baby choke on?
How hard should the back blows be?
Why do I have to hold a baby with its head lower than its bottom?
Why do I have to support the head?
Can I do abdominal thrusts (Heimlich manoeuvre) on a baby?
Should I try to pull the object out with my fingers?
What should I do if a baby becomes unresponsive and stops breathing?
If a baby is choking, should I hold them upside down by their feet?
How do I help a child who is choking?
How do I help an adult who is choking?
What can a baby choke on?
Newborn babies can choke on things like curdled milk, mucus or vomit. As they get older, they move on to solids and explore by putting things into their mouth. This means food or small toys can easily get stuck in their throat, stopping them from breathing.
Back to questions
How hard should the back blows be?
You should change the force of the back blows depending on the size of the baby: be gentler with a smaller baby than with a larger baby. The force you use to deliver the back blows should also be relative to your own strength. The back blows need to be hard enough to cause a vibration in the airway and dislodge the blockage.
Back to questions
Why do I have to hold a baby with its head lower than its bottom?
Babies commonly choke on liquid (mucus or curdled milk), so keeping their head lower than their bottom helps the liquid to drain out – gravity will help.
Back to questions
Why do I have to support the head?
Supporting the head will help to keep the baby’s airway open, helping to dislodge the blockage from the airway.
Back to questions
Can I do abdominal thrusts (Heimlich manoeuvre) on a baby?
No, don’t squeeze a baby’s tummy.
Abdominal thrusts are used to help choking children and adults only. Using abdominal thrusts on a baby could damage their internal organs, which are fragile and still developing.
If back blows do not dislodge the blockage, you should use chest thrusts instead.
Back to questions
Should I try to pull the object out with my fingers?
Do not put your fingers into their mouth if you cannot see an object. You risk pushing any blockage further down or damaging the back of the throat, which could swell and cause further harm.
However, if you can clearly see an object in a baby's mouth and you are able to pluck it out safely with your fingertips, you could do so.
Back to questions
What should I do if a baby becomes unresponsive and stops breathing?
Find out how to help a baby who is unresponsive and not breathing.
Back to questions
If a baby is choking, should I hold them upside down by their feet?
No. This is not effective. You may cause further injury if you happen to drop them. The action of tipping them upside down may also move the blockage further down their throat.
This is not effective. You may cause further injury if you happen to drop them. The action of tipping them upside down may also move the blockage further down their throat.
Back to questions
How do I help a child who is choking?
Find out how to help a child who is choking.
Back to questions
How do I help an adult who is choking?
Find out how to help an adult who is choking.
Back to questions
Email us if you have any other questions about first aid for a baby who is choking.
Help! My Baby Is Choking on Milk!
Many parents look forward to feeding time with their baby. It’s a chance to bond and also gives you a few minutes of peace and quiet.
But for some, bottle feeding or breastfeeding can lead to gagging or choking sounds, which are alarming if you’re a new parent. Fortunately, there are things you can do to help prevent your baby from choking on milk or formula.
If your baby seems to gag a lot while eating, don’t panic. “Choking and gagging during feeding is common in young infants,” says Robert Hamilton, MD, FAAP, a pediatrician at Providence Saint John’s Health Center in Santa Monica.
“Choking and gagging during feeding is common in young infants,” says Robert Hamilton, MD, FAAP, a pediatrician at Providence Saint John’s Health Center in Santa Monica.
Hamilton says babies are born with an exaggerated but protective “hyper-gag reflex,” which can cause gagging while feeding. Plus, babies gag easily due to their own neurologic immaturity.
“Babies are growing and learning new ways to use their body (and mouths) every day,” says Amanda Gorman, CPNP and founder of Nest Collaborative, a collection of International Board Certified Lactation Consultants.
“Often, just stopping the feed and positioning the baby upright with good head and neck support will give them a few seconds to manage the problem.”
Gina Posner, MD, a pediatrician at MemorialCare Orange Coast Medical Center, says if your baby begins to choke, let them stop feeding for a little bit and pat their back. “Typically, if they’re choking on liquids, it will resolve quickly,” she says.
The most common reason a baby chokes during breastfeeding is that milk is coming out faster than your baby can swallow.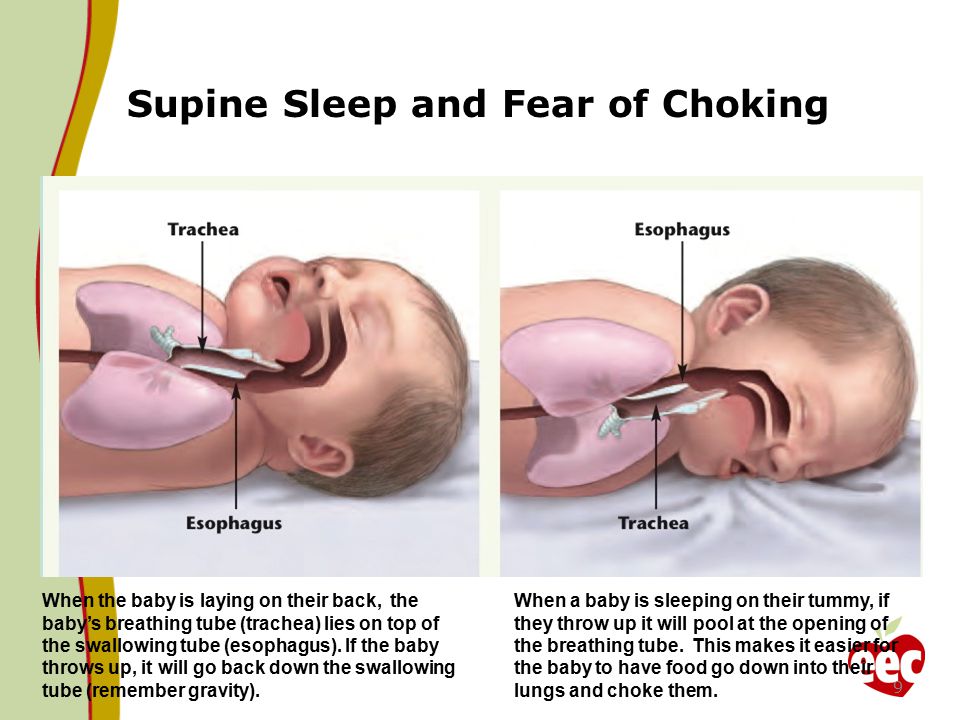 Usually, this happens when mom has an oversupply of milk.
Usually, this happens when mom has an oversupply of milk.
According to the La Leche League International (LLLI), common signs of oversupply include restlessness at the breast, coughing, choking, or gulping milk, especially at let down, and biting on the nipple to stop the flow of milk, among others.
You might also have an overactive let down, which causes a forceful flow of milk into your baby’s mouth. When your breasts are stimulated by your baby suckling, oxytocin causes the let-down reflex that releases the milk.
If you have an overactive or forceful let down, this release happens too fast for your baby to respond appropriately, causing them to gulp or choke while breastfeeding.
How do I prevent my baby from choking on milk when breastfeeding?
One of the first things you can do to help prevent your baby from choking while eating is to change the feeding position.
“For breastfeeding mothers who appear to have overactive let down, we typically recommend they nurse in a laid-back position, which reverses gravity’s effect and allows baby to have more control,” says Gorman.
Posner recommends pulling your baby off the breast every once in a while to help them catch their breath and slow down. You can also take your baby off the breast for 20 to 30 seconds when your milk first lets down.
In addition to a laid-back position, the LLL recommends lying on your side so your baby can allow milk to dribble out of his mouth when it flows too quickly.
Furthermore, expressing milk for 1 to 2 minutes before bringing your baby to your breast can help. Doing so allows the forceful let down to happen before baby latches. That said, be careful with this technique, as pumping for too long will tell your body to make more milk and worsen the problem.
When your baby gags when drinking from a bottle, it’s often due to the positioning. Lying your baby on their back while bottle feeding will lead to a faster milk flow, making it harder for your baby to control the rate of feeding.
“Tilting the bottom of the bottle higher than the nipple increases the rate of milk flow, as will a nipple with too large of a hole for the infant’s age,” Gorman advises. Tilting the bottle too high can lead to involuntary increases in intake and contribute to problems like reflux.
Tilting the bottle too high can lead to involuntary increases in intake and contribute to problems like reflux.
Instead, when bottle-feeding an infant, try using a technique called paced bottle-feeding. “By keeping the bottle parallel to the ground, the baby remains in control of the milk flow, as they are at the breast,” Gorman says.
This technique allows your baby to actively pull milk out of the bottle using their sucking skills and lets them easily take a break when needed. Otherwise, gravity is in control.
For babies who are bottle-fed by multiple caregivers, Gorman says all of the people who administer feeds should be educated on paced bottle-feeding.
Finally, you should never prop the bottle up to feed your baby and walk away. Since they can’t control the flow of the milk, it will keep coming even if your baby is not ready to swallow.
“The mechanism of swallowing is complicated and requires several muscle groups working together in concert and in the right time sequence,” Hamilton says. Fortunately, gagging usually diminishes as children get older and become better at swallowing.
Fortunately, gagging usually diminishes as children get older and become better at swallowing.
Still, if you’re a new parent or caregiver, it’s smart to take infant cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). While rare, a choking episode that caused your baby to turn blue or lose consciousness would be an emergency.
If you’re having problems related to breastfeeding, contact a LLL leader or International Board Certified Lactation Consultant (IBCLC). They can help you with your baby’s latch, positioning, oversupply issues, and forceful let-down problems.
If you’re having problems related to bottle feeding, contact your child’s pediatrician. They can help you with bottle and nipple selection, as well as feeding positions that prevent choking on milk or formula.
If your baby continues to choke even after slowing down the rate of feeding, you should contact your pediatrician to rule out any anatomical reasons why swallowing may be challenging.
When you hear your baby gagging or choking during feeding, don’t panic. Take baby off the nipple and prop them up to help them clear their airway.
Take baby off the nipple and prop them up to help them clear their airway.
Often it will take a little time for your baby to learn suckle with ease. In the meantime, try keeping your baby upright during feedings and make the flow of milk slower, if possible. Soon enough, feeding time will be a sweet snuggle session!
The child chokes when feeding: what to do?
Nikulina Anastasia Anatolyevna
pediatrician
A newborn chokes when feeding for various reasons. Some of them the mother can eliminate, while others depend on the health of the baby. The pediatrician Anastasia Anatolyevna Nikulina will explain the causes and solutions to this problem.
— Anastasia Anatolyevna, at what age do children most often choke while feeding? nine0010
— In the first weeks of life, when the swallowing reflex is still very weak, it is difficult to dose milk supply from the breast. From the bottle, the flow of formula is controlled by the opening in the nipple and the tilt. If the hole in the nipple is not age appropriate, it is tight, then the newborn swallows air. Excess air with the mixture will enter the intestines, causing discomfort to the baby.
If the hole in the nipple is not age appropriate, it is tight, then the newborn swallows air. Excess air with the mixture will enter the intestines, causing discomfort to the baby.
Why does the baby choke while breastfeeding or bottle feeding
- Baby position or bottle angle not optimal. in the optimal position. In the right position, the hand of the woman who holds the child lies on the support. Hold the baby by the back and shoulders, directing the head to the chest. You can’t press hard on the head - the baby will recline it back reflexively. nine0019
- Anatomical features of the mother's breast, in which a woman produces enough breast milk, but it is difficult for a child to suck it out, to eat. Before feeding, the mother needs to express some of the milk or massage the breast: it will become soft, and it will be easier for the baby to suck.
- Large nipples are difficult for a baby to grab - to solve the problem, there are special nipple covers through which newborns are fed.
 You can feed your baby with expressed milk through a bottle and a nipple that is correctly selected for age. nine0019
You can feed your baby with expressed milk through a bottle and a nipple that is correctly selected for age. nine0019 - Hyperlactation. Pressurized breast milk squirts into the baby's mouth. Before feeding, some of the foremilk is expressed, and the following, more fatty, does not form a strong flow. Breaks in the sucking process also help.
- Frequent breastfeeding. The absence of long breaks between attachments to the breast prevents children from hunger and, with it, the rush to feed.
- Incorrect bottle delivery method. The neck of the bottle must be completely filled with milk: this way there will be no air in the milk. The nipple is selected taking into account the age of the baby. nine0019
- Disease. Nasal obstruction or cough interferes with feeding. Relief of the symptoms of the disease will improve nutrition. For some children, problems can be caused by improper swallowing or reflux.
- To understand why the baby is having difficulty swallowing, you need to gradually eliminate each of the possible causes.
 Even the environment matters. During feeding hours, it is desirable for a woman to be alone with the child, nothing should distract him from the process. If the mother finds it difficult to identify the cause, a pediatrician will help her. nine0019
Even the environment matters. During feeding hours, it is desirable for a woman to be alone with the child, nothing should distract him from the process. If the mother finds it difficult to identify the cause, a pediatrician will help her. nine0019
— What should I do if my child chokes on milk or formula?
- Spontaneous cough is the main symptom that appears when the act of sucking and swallowing is disturbed. The baby is crying and refuses to eat.
First aid for choking children
If you can’t cough up excess milk on your own or the baby chokes on saliva and starts to choke, you need to do the following, dosing the force of your actions:
- Place the baby on one hand with the belly down, with your free hand apply pressure on the area above the navel (on the area of the baby's stomach), supporting the chin.
- Tilt the child slightly forward, lightly pat on the back. This will increase the cough and help restore breathing.

- Can I continue feeding after the baby clears his throat, or should I take a break?
- Feeding can be continued after the baby clears his throat. It is advisable to vilify it with a column for two to three minutes, so that excess air comes out, and then resume feeding. nine0003
- Does increasing the interval between feedings help with the problem?
- On the contrary, the prevention of flooding will be frequent feeding. With numerous attachments, less milk accumulates in the woman’s breast, it becomes easier for the mother to feed.
If the child is choking, feeding should be interrupted. The baby will cough, rest and continue to suck. If the situation recurs frequently, be sure to consult your pediatrician. Your doctor can help you find the best breastfeeding or formula-feeding method for you. nine0003
* Breast milk is the best food for babies. WHO recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months of a child's life and continued breastfeeding after complementary foods are introduced until the age of 2 years. Before introducing new products into the baby's diet, you should consult with a specialist. The material is for informational purposes and cannot replace the advice of a healthcare professional. For feeding children from birth. The product is certified.
Before introducing new products into the baby's diet, you should consult with a specialist. The material is for informational purposes and cannot replace the advice of a healthcare professional. For feeding children from birth. The product is certified.
#Tips for Mom #regurgitation 7-12 #regurgitation 12 plus
See also
How to properly rock a baby to sleep
#Advice for Mom
nine0002 Kizino Polina Alexandrovnapediatrician, perinatal psychologist
Calendar of doctor visits during the first year of a child's life
#Advice for Mom
Kizino Polina Alexandrovna
pediatrician, perinatal psychologist
Neurologist for a child under one year old: first examination
#Tips for Mom #Baby development
Yakovenko Margarita Pavlovna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Pediatrician, Pediatric Neurologist, Medical Advisor MAMAKO ®
Principles of successful lactation: checklist for mom
#Tips for Mom #breastfeeding
Yakovenko Margarita Pavlovna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Pediatrician, Pediatric Neurologist, Medical Advisor MAMAKO ®
How to tell if a baby has a food allergy
#allergy #Tips for mom #breast-feeding #baby formula #lure
Kiseleva Elena Sergeevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Scientific Advisor MAMAKO ®
nine0002 Goat milk in children's nutrition: for or against#Food #Tips for mom #Baby digestion #breastfeeding
Javier Diaz Castro
professor, lecturer
First tests and vaccinations: how to prepare yourself and your child
#Advice for Mom
nine0002 Kizino Polina Alexandrovnapediatrician, perinatal psychologist
Omicron in children: how dangerous it is and how babies get sick up to a year
#Advice for Mom
Kiseleva Elena Sergeevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Scientific Advisor MAMAKO ®
Why DHA, ARA and lutein are added to infant formula
#baby formulas #Baby development
Yakovenko Margarita Pavlovna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Pediatrician, Pediatric Neurologist, Medical Advisor MAMAKO ®
Digestion in newborns and infants and its features
#Baby Digestion #breast-feeding #baby formula #Lure #Tips for mom #Baby development
Kiseleva Elena Sergeevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Scientific Advisor MAMAKO ®
See all
View all
Goat's milk in children's nutrition: for or against
# Lure # Tips for Mom # Baby's digestion # breastfeeding
Javier Diaz Castro
professor, lecturer
Digestion in newborns and infants and its features
# Baby digestion # breast-feeding # infant formula # Lure # Tips for Mom # Baby development
Kiseleva Elena Sergeevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Scientific Advisor MAMAKO ®
Neurologist for a child under one year old: first examination
# Tips for mom # Baby development
Yakovenko Margarita Pavlovna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Pediatrician, Pediatric Neurologist, Medical Advisor MAMAKO ®
Calendar of doctor visits during the first year of a child's life
nine0002 # Tips for momKizino Polina Alexandrovna
pediatrician, perinatal psychologist
Principles of successful lactation: checklist for mom
# Tips for mom # breastfeeding
Yakovenko Margarita Pavlovna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Pediatrician, Pediatric Neurologist, Medical Advisor MAMAKO ®
How to properly rock a baby to sleep
# Tips for mom
Kizino Polina Alexandrovna
pediatrician, perinatal psychologist
Why DHA, ARA and lutein are added to infant formula
# infant formula # Baby development
Yakovenko Margarita Pavlovna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Pediatrician, Pediatric Neurologist, Medical Advisor MAMAKO ®
Omicron in children: how dangerous it is and how babies get sick up to a year
# Tips for mom
Kiseleva Elena Sergeevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Scientific Advisor MAMAKO ®
See all
nine0002 First tests and vaccinations: how to prepare yourself and your child# Tips for mom
Kizino Polina Alexandrovna
pediatrician, perinatal psychologist
How to tell if a baby has a food allergy
# allergy # Tips for Mom # breast-feeding # infant formula # lure
Kiseleva Elena Sergeevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Scientific Advisor MAMAKO ®
See all
View all
View all
What to do if a child chokes
It is impossible to control 100% of all the actions of the baby, therefore, cases when children get something into the respiratory tract or they choke on something often occur. Most often, parents do not need to take any action, because. the child's body is able to independently get rid of a foreign object with the help of a cough. A sign that the airway is not blocked is that the child may cry and/or call for help. Then you just calm the baby and keep the situation under control. nine0003
Most often, parents do not need to take any action, because. the child's body is able to independently get rid of a foreign object with the help of a cough. A sign that the airway is not blocked is that the child may cry and/or call for help. Then you just calm the baby and keep the situation under control. nine0003
Signs that intervention is needed?
- eyes wide open in panic
- he cannot utter words, cry and scream, or does it quietly and wheezing
- there is increased salivation
- baby opens mouth wide
- skin turns red and then turns blue
- older children may hold their throats
- loss of consciousness
The first thing to do is to call an ambulance. It is advisable to have someone else do this so that you can immediately begin to provide first aid.
First aid for children under one year old
As a rule, infants choke while eating or drinking due to incorrect posture.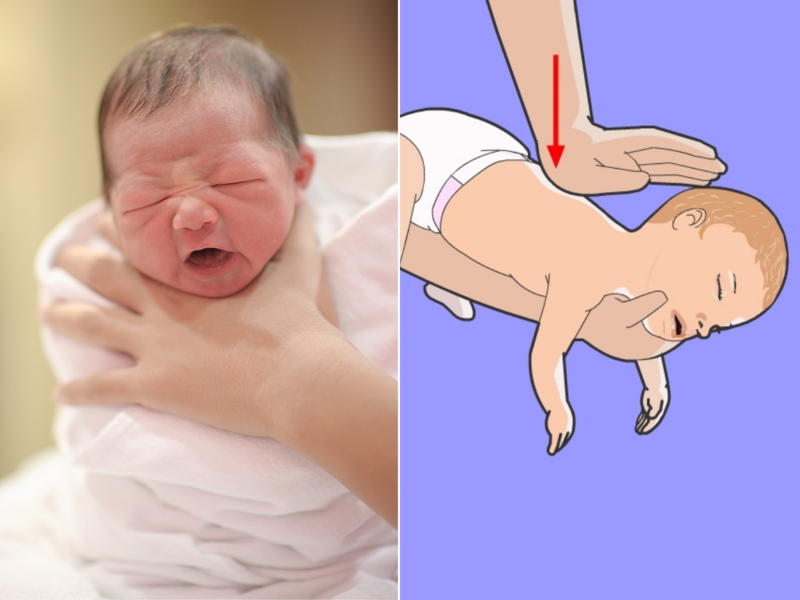
Your possible actions:
1. Raise the baby's hands up. Despite its unusualness and simplicity, this method helps to normalize the breathing process by expanding the airways. nine0003
2. Put the child on your hand with your stomach down and make five pats between the shoulder blades with the edge of your palm.
3. In the case when the baby choked on a small object, it is necessary by the child's legs so that the head is down and also pat between the shoulder blades
4. Tilt the body of the child down, press on the root of the tongue, thereby causing vomiting.
5. If the baby choked on the liquid and began to cough, choke with a cough, breathe noisily, and also in case of a solid object getting stuck, it is necessary to turn it with its back to you, hug your hand while pressing it on the stomach area, tilt the child forward and pat on the back, as described in the first paragraph. nine0003
If there are no signs of improvement, lay him on his back so that his head is lower than his torso. Place your middle and index fingers under your baby's breastbone. Do five pressures to a depth of 1-2 cm, making sure that after each of them the baby's sternum straightens without removing the fingers. You should alternate pressure and pats on the back until the doctors arrive. After each pop, check to see if the airway blockage has been cleared.
Place your middle and index fingers under your baby's breastbone. Do five pressures to a depth of 1-2 cm, making sure that after each of them the baby's sternum straightens without removing the fingers. You should alternate pressure and pats on the back until the doctors arrive. After each pop, check to see if the airway blockage has been cleared.
Attention! All pressing and patting should be gentle but sharp! nine0003
You can find on the Internet a recommendation to check the child's larynx with your finger and, if possible, remove the stuck object. Such advice is useful if the foreign object is something soft, such as cotton wool. In other cases, there is a great risk of aggravating the situation by accidentally moving the subject even further.
First aid for a child over one year old
Remain calm so as not to aggravate the child's panic. nine0003
You can use the above methods for older children as well. 5 point will differ by the posture of the child. See picture below:
See picture below:
Also for children aged from a year (in no case for children younger!) The Helmich method is effective. The sequence of your actions will be as follows:
- stand behind the baby, you can kneel if his height is still small
- clench the hand of one hand into a fist and place the thumb inside between the ribs and the navel of the child
- clasp the fist with the palm of the other hand
- spread your elbows to the sides and press on the child's stomach from the bottom up
- continue until the foreign object is out of the respiratory tract
If the child's breathing has stopped
If the child's breathing stops during removal of the foreign body and does not resume after removal, this may be the result of a spasm in the throat due to stress. Breathing resumption method:
- lay the child on its side on a flat hard surface
- tilt head back a little
- lift chin
If the attempt was unsuccessful, it is urgent to start performing artificial respiration and chest compressions.