What to feed a baby largemouth bass
What Do Baby Bass Eat?
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.
A Bass FishWhat do baby bass eat? Many bass fishermen have asked themselves this question, However, before we can answer that, we must first understand what bass is. There are numerous fish that are marketed as “bass” when they aren’t.
It’s crucial to grasp the distinctions between large and smallmouth bass if you want to catch them. These fish prefer different meals. Largemouth bass are like bigger animals, therefore it makes sense that they would eat them. Some basses, on the other hand, only eat crustaceans. Basses consume insects. Bass may also attack one another. A few species of bass will even consume everything.
The age of the bass is another element that has an influence on how basses should be fed. Baby bass must consume smaller animals, which makes sense. Adult bass frequently advances to more substantial meals, even if they don’t have to eat insects.
There are numerous species of bass across the United States, some of which we call bass. That’s a bit strange because certain species, such as the Peacock Bass, are more closely related to fish like tilapia than other fish. Other bass subspecies and scattered populations exist. They are not large enough numbers to be concerned about. If someone says they’re going bass fishing, they’ll almost certainly mean one of the species we’ll discuss in this article.
The species of fish varies from one to the next. Are there any similarities between smallmouth bass and striped bass? Of course! But they have distinct behaviors and diets that are determined by a variety of variables. This may be affected by such things as food availability, seasonality, and water temperatures.
What Do Baby Bass Eat?Baby bass will eat the vast majority of the time during the year. Season and weather, on the other hand, may have an impact on how often or energetically they eat. During the spawn, they won’t generally feed at all, but they may attack prey to protect their nests.
In the winter, on the other hand, they don’t require to feed as often. This is due to their metabolism slowing down so that they may save energy while there is less food around.
While they are spawning, the female bass will not be feeding very frequently; rather, she will typically feed aggressively both before and after the fertilization event, which is known as pre-spawning and post-spawning.
The pre-spawn is a wonderful time to fish since the bass will be moving to the shallow spawning areas and eating voraciously in preparation. The bass will continue to feed actively throughout the post-spawn period.
Bass feed more frequently at sunrise and sunset, particularly during the summer months, when the shallows may be too hot for bass in the middle of the day.
What Do Baby Bass Eat? (Largemouth)Crawfish CrawfishCrawfish, often known as crayfish or crawdads, may be found all around the world, with many different species of crawfish in the United States. They can survive in almost any body of water from lakes and ponds to rivers, streams, and marshes, making them a valuable source of food for bass in a range of habitats.
They can survive in almost any body of water from lakes and ponds to rivers, streams, and marshes, making them a valuable source of food for bass in a range of habitats.
Because crawfish like to hide in dark, quiet places, they may be found along the bottom of a lake or river. If you’re fishing near the floor in deep or shallow water, this can be a wonderful bait. They can also be an excellent choice for pre-spawn fishing since bass is seeking crawfish at this time of year.
Small Fish Small FishLargemouth bass will consume a range of smaller fish, such as shad, minnows, and bluegills. They’ll consume whatever small fish they can get their hands on at the time, depending on what’s accessible. Check to see whether any baitfish are accessible in the vicinity of the lake or river before going fishing.
Insects Insects Like Grasshoppers Are Eaten By Baby BassLargemouth baby bass can eat insects, which may occasionally be a food source for them. Larger insects are typically preferred by larger bass since they include bigger bugs and aquatic invertebrates like massive mayflies or even grasshoppers and crickets.
Larger insects are typically preferred by larger bass since they include bigger bugs and aquatic invertebrates like massive mayflies or even grasshoppers and crickets.
The season may have an impact on the effectiveness of insect lures; for example, it might be advisable to use insect lures in conjunction with when there are a lot of bugs flying about near water. This may occur during spring and summer in many locations.
Frogs FrogLargemouth baby bass appears to relish frogs, which makes frog lures a clever option, especially in the summer when frogs are more active. Bass, on the other hand, might consume frogs all year depending on your location.
The frog lures can be highly productive in locations with lotus pads or thick vegetation mats, which are habitats where frogs would typically be found. They may also be used just about anywhere near the banks.
What Do Baby Bass Eat? (Smallmouth)Minnows MinnowsSmallmouth baby bass, like other small basses, will eat anything that is available to them. Minnows might be a decent source of food, but they can also consume smaller fish such as shad and perch.
Minnows might be a decent source of food, but they can also consume smaller fish such as shad and perch.
Smallmouth may be found closer to the bottom if they’re eating smaller fish that smallmouth prefers. This might imply that when smallmouth feeds on these species in large lakes, they can be found farther down.
InsectsDuring insect season, smallmouth bass will frequently take advantage of the extra food, devouring wasps, beetles, cicadas, and other insects that come into or near the water. Because baby bass is frequently caught on fly fishing with insect bait, it’s common to find them biting anything that seems to be alive.
AmphibiansSmallmouth baby bass will eat frogs and lizards, depending on the region and time of year. When smallmouth bass is feeding closer to the surface, frog lures may be effective topwater baits.
What Do Baby Bass Eat in General?Young bass will eat insects, small aquatic invertebrates, and larger fish once they reach about 8 inches in length. When it comes to insect-eaters like bullhead catfish, young largemouth will consume crustaceans and little fish. In their early phases, smallmouth bass may prefer plankton.
When it comes to insect-eaters like bullhead catfish, young largemouth will consume crustaceans and little fish. In their early phases, smallmouth bass may prefer plankton.
The larger the baby basses are, the faster they will develop, which means that some of the younger basses may progress at a quicker rate than others. This can even cause bigger babies to consume smaller ones. Likewise, if adult bass has access to baby basses, they may eat them.
What Is The Difference Between Baby Smallmouth and Largemouth Bass? A Largemouth BassEveryone loves catching Smallmouth and Largemouth Bass, whether they’re professionals or novices. The Black Bass fishing industry is worth billions of dollars. Largemouth and smallmouth bass are among the most popular quarry species among tackle companies and tournament organizers. But, exactly, what distinguishes them? There are numerous brands and competitions dedicated to catching lunker Largemouth and super-sized Smallmouth. But, in reality, what distinguishes them?
But, in reality, what distinguishes them?
The most obvious distinction between Larger and Smallmouth Bass is the size of their mouths. Largemouth typically reach a maximum weight of around 10 pounds, although Large specimens might grow to be twice as heavy.
You may also determine the species by their color. Brown Bass is a popular name for Smallmouth, although Green Bass is more popular. In fact, while both fish may appear different colors depending on their age, location, and a variety of other factors, it’s not uncommon for them to vary. Don’t get nervous, there are three methods to tell the difference between a Smallmouth versus a Largemouth Bass.
Largemouth bass has larger mouths than small fish. Their upper jaw extends well past the eye, whereas Smallies’ jaws are typically in line with the eye. Their fins are the next things to look at. A gap separates the largemouth, while a small mouth doesn’t. Finally, even if the two fish are of identical color, Green Bass have dark horizontal lines while Brown Bass have vertical stripes.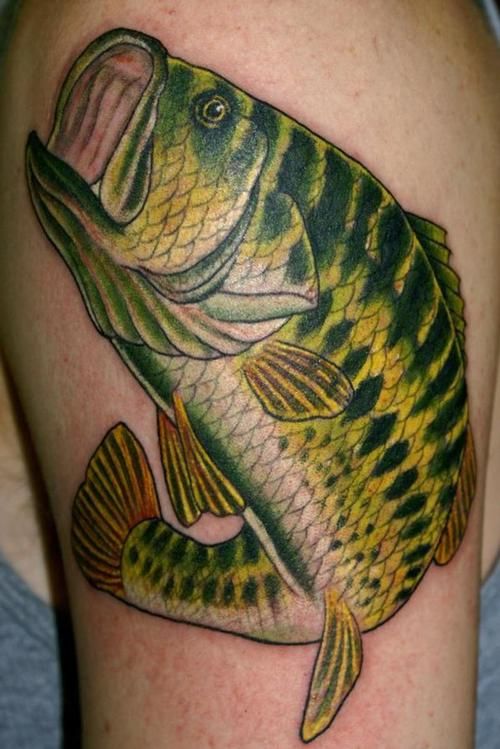
If you live in a state or municipality with public water restrictions, you’ll want to consult your state and local codes on whether it’s permissible to remove fish from the pool to keep them in a tank or release them into another location. Many regions have laws restricting this because introducing bass into a new ecosystem may do serious damage.
Aquarium
You must first choose the correct size aquarium to suit your native fish, such as bass, rather than exotic species. Choosing the right tank size will minimize the strain on your fish caused by a poor environment. It will also provide enough swimming area for your fish.
The tank must be big enough to fit your bass fish comfortably. A tank of 100 to 150 US gallons will be useful for your fish. Remember, this isn’t just a fish tank; it also includes add-ins like plants and buildings.
If your bass grows too large, you may need to move them to a larger tank so they are comfortable and healthy, especially if you wish to keep several basses in the same tank.
Always keep an eye on the amount of space your basses need to move about freely and seek refuge in mind. This will help to minimize the stress your bass may experience as a result of less-than-ideal living circumstances.
TemperatureAnother thing to think about is the temperature of your aquarium. Bass like a temperature of 60 to 65 degrees Fahrenheit, and your fish will be healthy and happy in this range.
You may use a chiller to keep the temperature in balance. You can also put a thermometer in the tank and check it on a regular basis to make sure the temperature stays where it should be. Your tank must maintain an appropriate range of temperatures.
The temperature can fluctuate, but it should be between 60 and 65 degrees Fahrenheit for your bass to be happy.
LightWhen it comes to the natural habitat of a bass, consider how important lighting is. The majority of bodies of water, such as ponds, rivers, and lakes, have enough light for around ten hours each day. Make use of appropriate lighting in your aquarium and program timers to keep the lights on the track.
Make use of appropriate lighting in your aquarium and program timers to keep the lights on the track.
The health advantages of sea bass and freshwater bass are numerous. One serving each is low in calories and high in selenium, protein, and essential omega-3 fatty acids, whether you consume bass caught from fresh or seawater.
Although they contain the same nutrients, different types of fish have varying amounts of some minerals, such as vitamin B12 and vitamin B6. Bass has one disadvantage: it contains mercury. You can still eat it, but pregnant women and children should limit their consumption.
Proteins & NutrientsProtein is just one of the numerous health advantages of sea bass and freshwater bass. Sea bass has 16 grams of protein in a 3-ounce serving, which is 40 percent of the daily value, according to the USDA.
The National Academies of Sciences advises that women consume 46 grams of protein each day, while men require 56 grams. For only 105 calories, you can enjoy a 3-ounce serving of sea bass and a 124-calorie portion of freshwater bass, which will give you all the protein you need.
For only 105 calories, you can enjoy a 3-ounce serving of sea bass and a 124-calorie portion of freshwater bass, which will give you all the protein you need.
Although the fat content of these two varieties is low, they are both excellent sources of two omega-3 fatty acids: Eicosapentaenoic acid, or EPA, and docosahexaenoic acid, or DHA. Omega-3 fatty acids help to lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels. According to the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, omega-3 fatty acids can aid in the prevention of heart disease and stroke.
In a 3-ounce serving, sea bass has 0.65 grams of combined EPA and DHA, whereas freshwater bass has 0.51 grams in the same amount, according to the USDA. According to Institute of Medicine recommendations, each serving may provide between 32 and 60 percent of your daily intake for men and women, depending on the type you consume and your gender.
Other NutrientsSelenium is another important nutrient provided by sea and freshwater bass. Selenium is required for the production of antioxidants and thyroid hormones in your body. According to the National Institutes of Health, seafood, such as bass, are an excellent dietary source of this mineral.
Selenium is required for the production of antioxidants and thyroid hormones in your body. According to the National Institutes of Health, seafood, such as bass, are an excellent dietary source of this mineral.
In terms of vitamin C, freshwater and sea bass nutrition differ. Sea bass is a good source of vitamin B6 and has three times as much as freshwater bass. Freshwater bass, on the other hand, has B12 which is 77% more than sea bass. This has been based on studies conducted by USDA.
Amazon and the Amazon logo are trademarks of Amazon.com, Inc, or its affiliates.
What Should You Feed Bass in a Fish Tank? (6 Great Options)
The purpose of this blog is to share general information and is written to the author's best knowledge. It is not intended to be used in place of veterinary advice. For health concerns, please seek proper veterinary care. In addition, as an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.
When most people think of pet fish, they probably think of koi ponds or exotic tropical fish in an aquarium. Bass and other gamefish don’t exactly spring to mind as attractive pets.
Bass and other gamefish don’t exactly spring to mind as attractive pets.
However, bass are becoming increasingly popular as aquarium pets. They are lively and it is entertaining to watch them swim back and forth in their aquarium.
Caring for bass is a little different from caring for tropical fish. They need a different living environment and have different feeding habits. Unfortunately, because bass are not very common pets, it can be difficult to find advice about what to feed them.
Here is everything that you need to know about maintaining a healthy diet and environment for your bass.
What Will Captive Bass Eat?
If there’s one thing that you can say about bass, it’s that this is not a fish that is a picky eater. Bass is known for its considerable appetite and diverse tastes.
Here are a few things that you can feed your captive bass. Most of these are either the same or similar to what a bass would eat in the wild.
1 – Worms
There is a reason fishermen use earthworms as bait—gamefish, including bass, love earthworms. Your bass will probably love these wriggly treats. Two types of worms that bass love in particular are nightcrawlers and bloodworms, but any worm will do.
Your bass will probably love these wriggly treats. Two types of worms that bass love in particular are nightcrawlers and bloodworms, but any worm will do.
You can dig them up in your garden if you’re lucky enough to have one, and you can even freeze dead earthworms to give your bass as a treat out-of-season (preferably in a different freezer from where you keep your food). Alternatively, you can get earthworms from a bait shop.
2 – Shrimp
Freshwater shrimp are a natural part of the food chain in the environments that bass tends to live in, so it is only natural that they will go for this treat in captivity. Although it can be a little expensive to keep feeding your bass shrimp on a daily basis, you can give it shrimp as an occasional treat.
You can buy fresh or frozen shrimp, preferably with the shell and head still attached, at the grocery store. If you really want to entertain your bass, get a live whiteshrimp or other kind of shrimp from the bait shop. Bass are attracted to movement so even those living a life of luxury in a fish tank like to hunt for their food every so often.
You can also try feeding your bass some other crustaceans, such as cockles. Hard shells are usually no match for the bass in the wild, so they will be just as ravenous in captivity.
3 – Insects
Bass don’t just eat animals that naturally live in the water, they are fans of insects and bugs as well. Two common types of bugs that bass like to eat are crickets and mealworms.
You can get insects at most bait shops. If there are no bait shops near you, many pet stores sell crickets because they are common meals for reptiles as well as fish. The only trouble is that you have to secure the cage if you are buying live crickets to avoid a great escape taking over your living room!
4 – Live Fish
In the wild, bass are the fearsome predators of the aquatic world. They will eat everything from large trout to baby birds that make the mistake of swimming in front of their path.
Captive bass in fish tanks don’t lose their voracious appetites and killer instinct. That is why occasionally feeding your bass live bait will keep it entertained and satisfied.
That is why occasionally feeding your bass live bait will keep it entertained and satisfied.
You can even raise bait for your bass in the same tank so that they have a constantly reproducing source of food. Just get males and females of whatever species you are supplying for your fish.
Common bait fish for bass include minnows and crayfish. These are also easy fish tank pets to keep (even easier since you know they’ll get eaten soon anyway).
Raising live fish for your bass does take extra effort, but it will keep the fish happy.
5 – Whitebait
This is another common bait that bass also love to snack on in captivity.
Whitebait is the name for any small fish that is not yet fully grown. It is usually no longer than two inches.
You can catch your own whitebait, although many municipalities have strict regulations around capturing and eating these fish because of their vital ecological niche. You can also get whitebait at most pet stores. A good rule of thumb is that if it’s good bait, then the bass will like to eat it.
6 – Pellets and Feed
Obviously in the wild, bass don’t eat dried fish food or pellets. However, they can eat this food in captivity.
Bass will eat anything, including flake food and fish pellets. You can buy special gamefish feed at bait stores, tackle shops, and hatcheries, or try feeding your bass regular fish food.
Some bass that were raised in the wild may have trouble adjusting to dried fish food and pellets. Try mixing more recognizable food into their diet and changing your feeding technique until the bass learns that food comes in all forms.
Can My Bass Eat Frozen Food?
Sourcing fresh fish, crustaceans, and bugs for your bass will take up time, clog up your storage spaces, and cost you a lot of money. You may be wondering if you can just order frozen shrimp or bloodworms in bulk and have a food supply on hand.
The good thing is that you can feed bass a variety of things, including frozen food. You can alternate between feeding your bass freshly caught animals, frozen food, live bait, and dried pellets.
Alternating your food sources will help your bass stay healthy and keep your wallet in good condition since fresh bait is far more expensive than frozen seafood or fish pellets.
How Much Does a Live Bass in a Fish Tank Eat?
How much your bass eats will depend on how large it is. For example, largemouth bass in captivity can be 15 to 25 inches long, depending on how long they live and how well they are fed.
Most bass eat about one third of their body weight per day. Some eat as much as two thirds of their own body weight in a day, particularly if they’re still young and growing.
That means that you will probably need several pounds of food for your bass each day. Before getting a bass for your fish tank, be ready to handle the expense and the hassle of going to the bait shop every few days to pick up more food.
Since bass have such voracious appetites every day, they also produce a lot of waste. Be ready to clean your fish tank’s filter every few days to keep your bass in a healthy environment.
What Is the Best Way to Feed a Captive Bass?
While bass in the wild are self-sufficient and hunt when they are hungry, bass in captivity thrive on a fixed routine. Feed your bass once a day and try to stick to a specific time.
When you feed your bass, you should have enough food to make up at least a third of its body weight on hand. Feed it for 15 to 20 minutes at a time and give it as much food as it can eat—the bass knows how much its body needs.
Sometimes, it takes the bass a bit to get used to new foods, particularly wild bass that are seeing fish flakes for the first time. If you’re noticing that your bass is not interested in its food, try switching its diet up and adding meals that are closer to what it would eat in the wild, such as worms and shrimp.
Another way to get your bass interested in food is to agitate the surface of the water. These natural hunters are trained to go after movement so mimicking the behavior of live fish, or feeding it live fish in the first place, will get a disinterested bass to remember that it is hungry.
When a Bass’s Appetite Becomes Too Much…
Bass are big fish and used to being the rulers of their ecosystem. This means that even when captive in a fish tank or pond, they will go after smaller species and hunt them.
Unless you are trying to create a hunting ground for your bass, don’t put it in with smaller fish such as crappies and koi. It will probably eat your other pets.
Feeding Bass in Fish Tanks
Bass have big appetites in the wild and in captivity. They can eat anywhere from a third to two thirds of their body weight per day.
Luckily, these fish aren’t picky eaters. They will eat everything from frozen bloodworms to fish flakes to live shrimp. Feed your bass a mix of dried food, frozen fish, and fresh bait to help it stay healthy. Feed it once a day at the same time to maintain a healthy feeding routine.
Perch Fishing Tips: How to Catch Perch
No other common freshwater sport fish surprises the angler more than perch. No other has the arsenal of tackle an angler needs to catch perch. No other instrument adapts to the environment and plays as easily as the bass.
No other instrument adapts to the environment and plays as easily as the bass.
Perch Fishing Tips
This large member of the spiny rays family may be due to these factors. Although perch can be eaten, it is not because of its habitat in water lilies, reeds, underwater stone piles, snags sticking up on the surface, and similar problem areas that anglers are frantically chasing them.
It's the excitement they seek from the bass that fuels the fever. The bass attacks the bait and imitates a circus performance as soon as it is hooked. For these reasons, it epitomizes the "sport" of sport fish.
Bass
Bass has a more spiny and larger rear dorsal fin than its anterior dorsal fin. Together, the dorsal fins run across most of the fish's back, unlike most other freshwater sport fish.
Generally, there are three types of freshwater bass: largemouth bass, smallmouth bass, and white bass, which are actually classified as "panfish" because of their smaller size and shape than their larger counterparts. For the sake of practicality, we will focus here on how to catch largemouths and smallmouths.
For the sake of practicality, we will focus here on how to catch largemouths and smallmouths.
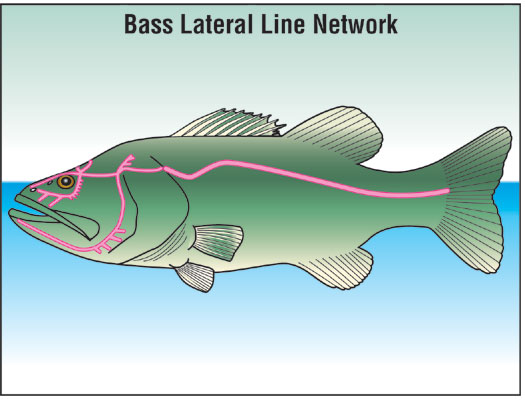
As their name suggests, smallmouths have smaller mouths than largemouths. However, the entrepreneurial spirit of the smallmouth still seems significant compared to other sport fish. Both types of bass are distinguished by their large weight. In addition to the mouth, they can be distinguished by their color and markings. The large mouth is usually greenish with a relatively thick, broken lateral line that resembles a heart rate reading on a monitor, if not a jagged or zigzag line of spots running from the gills to the tail.
The small mouth has a bronze body with vertical stripes. Since its mouth is smaller, its head and gills appear to be slightly smaller than those of a largemouth, and they lack a prominent lateral line.
Where do basses live?
The largemouth lives in ponds and lakes, including reservoirs or reservoirs behind dams, while the smallmouth extends its existence from the same reservoirs to streams and even large rivers.
Everyone needs their own hiding place where they can come up to feast on unsuspecting small fish and creatures. food.
From reptiles to small birds, minnows and juvenile fish, swimming insects, crustaceans such as crayfish and swimmers such as leeches, the perch's diet covers a wide area. The angler must figure out which of his favorite foods he is looking for during the day in order to find out where he lives at that particular moment.
Floating creatures, from leeches to frogs or salamanders, pull perches onto algae- and water lily-covered shallows of lakes. It is known that largemouths, especially in the shallow waters of lakes and ponds, even swallow baby ducks, mice or other rodents.
Largemouth Bass Fishing
Both smallmouth and largemouth bass will also hover around submerged stone mounds where not only minnows but also crustaceans, particularly crayfish, can congregate. Rocks or cliffs create a shadow directly below it, from which perch can fly out to devour minnows or other creatures as they pass on the edge of the shadow.
Water lily pads and similar weed cover provide shade in which bass can also hide while waiting for food. When the water gets too warm near the surface or too cold elsewhere, perch will gravitate towards their ideal temperature, between 80-82 degrees Fahrenheit, if they can find that kind of water.
Smallmouth's preferred range falls just a couple of degrees lower. Bass can live in cold water up to 40 degrees and in warm water up to 90, but they hibernate when the temperature drops below 39. As a rule, the colder the water, the less active the perch. However, it will continue to feed in water that drops to 40 degrees.
The best time to catch perch
You can fish for perch at almost any time of the day if it can find cover. Due to their ability to live in very warm water, the only negative aspect of midday and afternoon fishing is bright sun or high winds in lakes and ponds.
Perch will not want to be too visible to their prey or predator. At this time of the day, focus your offering on designs that hide and protect the bass. Morning brings a burst of activity of many small creatures. In this way, the perch will also become active with its feeding regimen.
Morning brings a burst of activity of many small creatures. In this way, the perch will also become active with its feeding regimen.
Best time to fish for perch
Immediately after sunrise, prey becomes more visible from afar, and the perch moves imperceptibly and voraciously along the line of a cliff, ledge, shallow water or other object.
When it comes to seasons, summer and autumn are the busiest days for perch. Oxygen levels decrease, daylight hours (i.e. feeding time) begin to shorten, water levels drop to their lowest level of the year, and water temperatures peak at this time. Their nutritional activity may decrease commensurately.
Spring and summer are the best times for perch fishing. Life seethes with increasing daylight hours, water temperatures only rise, not fall, and spring floods fill ponds, lakes and streams.
When is the best time to fish for perch in fresh water?
Most perch anglers use tackle to cast bait, whether it be a closed face reel or bait.
For reels, choose the one that is easiest and fastest to remove the bail when casting. Bass is casting, casting and casting. Some reels, especially spinning reels, come with a tape around the spool that allows you to reach the edge of the spool.
When casting perch, make sure your line on the spool does not end too far from the lip or cap of the spool. This can reduce casting distance, which is especially important when casting light balsa lures such as divers and swimming minnows.
If you are already used to spinning tackle, you can use it in most cases when fishing for perch, especially with small mouths.
Best Bait and Bait for Bass
Since, as mentioned, the list of baits for perch is not inferior to goat, the best baits and baits vary greatly.
As for live bait, salamanders, water dogs (of the salamander family), worms, minnows and other swimming creatures - even small crayfish - can be fruitful for perch.
You need to know which of these creatures thrive in your chosen lake, pond, or stream before hooking them. Bass lures probably have more variations and designs than any other type of lure.
Bass lures probably have more variations and designs than any other type of lure.
On the shelves you can find plastic worms and even worms that can be blown up to attract bigmouths.
You will find in the same abundance larvae (rubber cylindrical bodies with a fragile tail end) and jigs of countless colors in the body and skirt or scales. Many plastic baits have shiny fragments inside and outside of the body.
Best Bass Lures
Diving and floating lures are also available at tackle shops and retailers. These include balsa solids with a diving edge. Some of them are called wobblers. Again, they are made up of fairly buoyant bodies, but designed to simply dive, not float to the surface in perfect shape.
Lures with skirts or a brush around the shaft of the hook, which often points up to avoid snagging on the bottom, also come in a wide variety of sizes, shapes and colors.
Don't discount the old-fashioned perch spoon. Often a back skirt or even a comb will help push the bass closer to your proposal. Spoons are often equipped with weed guards to keep their hooks from snagging on bottom structure and weeds where they can be most effective.
Spoons are often equipped with weed guards to keep their hooks from snagging on bottom structure and weeds where they can be most effective.
Technique for Perch Fishing
Since perch is a bait that seduces, the action on said bait or lure is essential to success. Perch, like any other fish, responds best to natural baits.
If you want a worm or grub to go deeper, you can add a sliding pointy lead to the end of your main line just above the knot at the eye of the lure.
Most perch prey swim or splash in the water in waves. So, whether you're using fly or regular tackle, it's best to tug the rod tip occasionally, if not often, to mimic the nature of the bait that attracts bass.
Perch: what to feed, what to catch?
Komsomolskaya Pravda
Fishing Fishing: Winter fishing promising holes, in those where there were bites, or, in the opinion of the angler, of interest. Bait from animal organisms manages to keep the perch near the hole for a long time.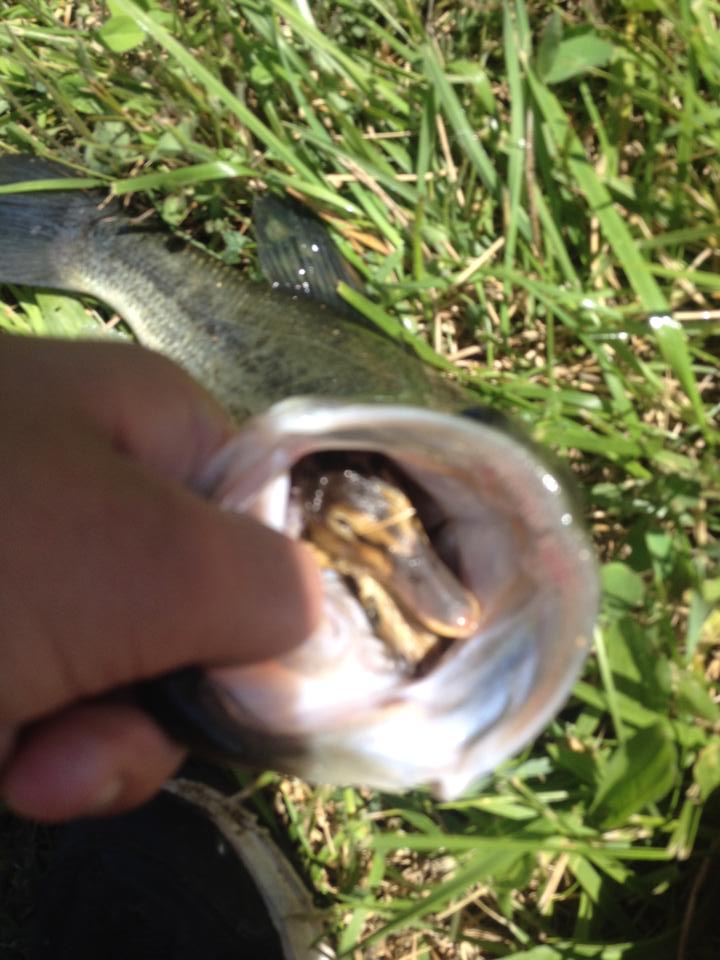
Usually fed small bloodworms . On the Don, it is practiced to add ground cake with husks of sunflower seeds into the hole . Settling to the bottom, such a suspension well attracts fry, and then a predator comes up. Chopped worms, minced meat from fresh or frozen fish, aquarium food are used.
At shallow depths and weak currents, bloodworms are mixed with sand or dry clay , moisten the composition and throw into the hole without using a feeder. At great depths and currents, a feeder is necessary; it can be opened in any horizon of water, at any height from the bottom.
Larva of burdock moth
Attachment is large and small bloodworms , larva of burdock moth, tail or half of a small worm, maggot and other insect larvae. There are different ways to put the bait on the hook. It is advisable to wear a large bloodworm in a half ring. When hunting for a large perch, they plant 5-6 pieces per head , and the last one is still a half ring. The larva of the burdock moth, or burdock, as anglers call it for short, is pierced through, stringing on small hooks with a short sting. A nozzle called a "sandwich" is very popular: first, a burdock is put on the hook, and then, in a half ring, a bloodworm.
The larva of the burdock moth, or burdock, as anglers call it for short, is pierced through, stringing on small hooks with a short sting. A nozzle called a "sandwich" is very popular: first, a burdock is put on the hook, and then, in a half ring, a bloodworm.
Various devices are used to speed up the hooking of bloodworms. One of them is a plastic tube with nipple gum rings put on it. Several pieces of bloodworms are placed in the tube and pulled together with a rubber ring. Or take a piece 3-3.5 cm of the old antenna from a radio receiver with a diameter 3-5 mm and on one side make 3-4 end cuts 1.5-2 cm long in it. The other end of the tube is placed on a small sharpened rod, through which it is convenient to put rubber rings from the nipple onto the tube. Having seized the bloodworm from a pile with a sawn part, they tighten it with a ring and attach the nozzle to the hook. Very comfortably. Bloodworms, burdock can be sprinkled with starch before fishing so that the larvae do not stick together.
Aleksey VASILTSOV, Rostov-on-Don
Age category of the site 18+
Online edition (website) registered by Roskomnadzor, certificate El No. FS77-80505 dated March 15, 2003 . EDITOR-IN-CHIEF - NOSOVA OLESIA VYACHESLAVOVNA.
I.O. chief editor of the site - Viktor Fedorovich Kansky
Messages and comments from site readers are posted without preliminary editing. The editors reserve the right to remove them from the site or edit them if the specified messages and comments are an abuse of freedom mass media or violation of other requirements of the law.
JSC "Publishing House "Komsomolskaya Pravda". TIN: 7714037217 PSRN: 1027739295781 127015, Moscow, Novodmitrovskaya d. 2B, Tel. +7 (495) 777-02-82.
Exclusive rights to materials posted on the website www.kp.ru, in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation for the Protection of the Results of Intellectual Activity belong to JSC Publishing House Komsomolskaya Pravda, and do not be used by others in any way form without the written permission of the copyright holder.