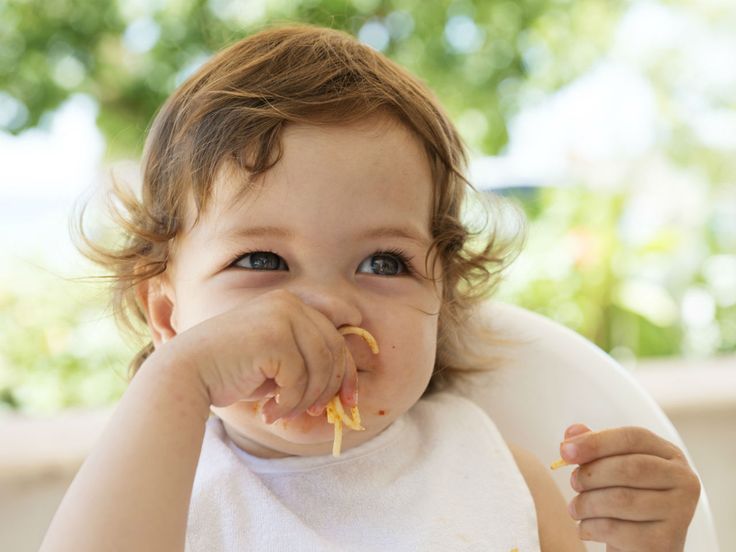
When baby feed self
7 Tips for Teaching Your Baby to Self-Feed
Now that your baby has been introduced to solids and is experiencing different foods and flavors, you may be ready to help your little one begin to self-feed. But when is the right time to encourage this new skill? What are the signs of readiness that we should look for? And what are the best foods to begin with when teaching baby to self-feed? We are answering all of your questions and sharing our tips on making this milestone easier for you and your child.
When will my baby be able to self-feed?
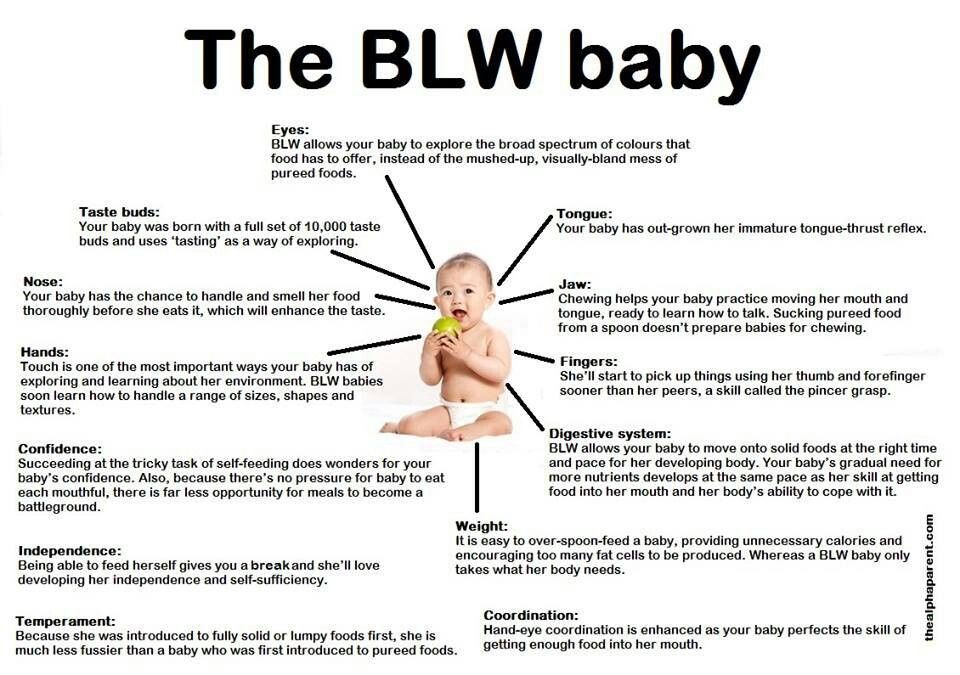
Usually, by about nine to 12 months of age, you may notice your baby showing an interest in self-feeding. They have become more experienced with eating solids at this age and are feeling the different textures of foods between their fingers. Hopefully, they are also making attempts at bringing some of that food to their mouth to lick and taste. This usually looks like them grasping for their food with their whole hand in a raking-like motion and then trying to shove what they have in their hand all into their mouth. You may even notice your baby trying to grab the food with their thumb and forefinger, which is an important fine motor skill called the pincer grasp. These are all good signs and are great indications that your baby is ready to begin self-feeding.
What are the signs that my baby is ready to self-feed?
There are a few readiness signs to look for that will indicate it’s the right time to begin teaching your baby to self-feed:
- Grabbing the spoon while you are holding it during mealtime.
- Reaching for their food on their plate, bowl, or tray.
- Reaching for your food or plate.
- Practicing the pincer grasp — bringing food and other items to their mouth during mealtime or playtime.
- Pushing your hand away when you try to feed them.
It’s important to pay attention to these readiness signs and not just rely on your child’s age. If a baby is 9 or 10 months old but does not show these readiness signs, parents should wait until they do. But once your baby does show these self-feeding readiness signs, it’s important to provide many opportunities for them to practice this skill. Allow them to try and try again. That’s how they will learn and master this skill!
But once your baby does show these self-feeding readiness signs, it’s important to provide many opportunities for them to practice this skill. Allow them to try and try again. That’s how they will learn and master this skill!
What are the best foods to start with self-feeding?
The best foods to give your baby to practice self-feeding are easy for them to grab, hold, pick up, and bring to their mouth. Here are some recommendations to try:
- Stonyfield Organic YoBaby Yogurt Pouches
- Soft cooked carrots, sweet potatoes, butternut squash, or peas
- Small pieces of soft, ripe bananas, avocados, kiwi, or peaches
- Soft-cooked apples or pears
- Soft-cooked whole grain pasta
- Diced pieces of cooked chicken, turkey, or fish
- Cubes or strings of cheese
YoBaby® yogurt pouches are a great option for multiple reasons. First, they are easy for your little one to pick up and bring to their mouth. Second, they nourish little tummies with real fruit, live and active cultures, vitamin D, calcium, protein, and prebiotics! Third, the consistency is creamy and delicious — easy for baby to eat and swallow. And four, it combines whole milk yogurt and oats for a quick meal for baby!
And four, it combines whole milk yogurt and oats for a quick meal for baby!
All foods should be soft, easy to mash, and big enough for your baby to pick up but small enough to prevent them from choking.
What are the foods to avoid when my baby is beginning to self-feed?
Foods that should be avoided when beginning to teach your baby to self-feed are foods that pose a potential risk of choking.
- Nuts
- Popcorn
- Raw carrots
- Whole grapes
- Raisins
- Hot dogs
- Portions of food that are too large
Your baby doesn’t have all of his teeth, so all foods should be soft. Once your baby’s 2-year molars come in, your child will be able to chew harder food properly. If you want to test to see which foods are safe and soft enough for your baby to eat, take a piece of their food and try to mash it between your fingers. If you cannot easily mash it, it’s probably too hard for your baby to chew.
How do I teach my baby to self-feed?
Now that you know your baby is ready to start self-feeding and you know which foods are best to start with, how do you begin? Here are some helpful tips.
The more opportunities you give them to practice, the quicker they will learn and master self-feeding. Give them opportunities to try self-feeding with their hands and with utensils.
2. Begin with encouraging hand feeding.Before introducing feeding utensils to your baby, encourage her first to use her hands to move the food toward her mouth. A good way to start is to place a yogurt pouch or a few pieces of food on your baby’s highchair tray. Encourage her to reach for it, feel it, and play with it with her pincer grasp. It may look as if she isn’t doing much and not eating, but that’s actually how she starts to learn.
3. Also, introduce and encourage baby to use utensils.It’s never too early to introduce utensils to your baby! It’s good for them to get used to utensils during mealtime. In the beginning, I recommend having two spoons–one for you to help feed baby a few bites and one for them to hold and practice using. He may even try to imitate your motions by dipping his spoon into the food and maybe attempting to bring it to his mouth.
He may even try to imitate your motions by dipping his spoon into the food and maybe attempting to bring it to his mouth.
Another thing you can try is pre-loading his spoon with food and handing it to him. This can help him practice balancing the food on the spoon as he brings it to his mouth. With this, I recommend using thicker foods like yogurt and oatmeal. They are good practice foods since they stick more easily to the spoon. Overall, be sure to allow plenty of practice opportunities with both utensils.
4. Stay close to your baby during meals.As your baby practices self-feeding, it’s important that you stay close and monitor her. We don’t want any food getting stuck in her nose or anywhere else, and you want to ensure that she is tolerating all of the new textures and flavors. By staying close, you will also monitor how much or little she is putting in her mouth and eating. These are all reasons why remaining by her side is necessary. She’s learning something new, and she needs your help and guidance!
5. Be prepared and expect a big mess.
Be prepared and expect a big mess.When babies are allowed to touch and explore new foods and feeding themselves, things get messy. And that’s okay! Don’t stress about it, and expect the mess. Have your baby wear a baby apron, put a towel on the floor if you’re worried about food falling, or undress your baby down to her diaper! Also, have baby wipes and power towels close by. You may even have to give your baby a bath after mealtime. Again, this is normal. A messy meal is still a success because that means your baby was trying to self-feed. Soon enough, she’ll get better at handling the different foods and make less of a mess. This is all a part of the process.
6. Eat together as a family.One of the best ways to teach your baby to self-feed is to have them watch the family eat. Babies are learning new things all the time, and they learn from modeled behaviors. By watching how their parents and siblings use their utensils and eat their food, babies want to mimic the same behaviors. They gain confidence watching you and believe that they can do it too! If you are feeding your baby at a different time than the rest of the family, they are missing out trying to mimic your movements with utensils and foods and observing other appropriate mealtime behaviors.
They gain confidence watching you and believe that they can do it too! If you are feeding your baby at a different time than the rest of the family, they are missing out trying to mimic your movements with utensils and foods and observing other appropriate mealtime behaviors.
It takes time to learn how to self-feed, so be patient with your little one. Don’t try to rush the process or mealtimes. Your baby should set the pace because they understand their hunger and fullness cues. This is why it’s good to allow plenty of time for their meals. With lots of practice and patience, your baby will be self-feeding in no time!
What if my baby starts gagging or choking?
When teaching your baby to self-feed, expect some gagging to occur. Gagging is a natural occurrence and is the body’s natural defense against choking. This happens when babies have too much food in their mouth and are presented with new textures and flavors. As long as they aren’t gagging too much during mealtime or causing them distress, gagging is common. However, if they are frequently gagging when trying to self-feed, this can cause them to have negative associations with eating or eating aversions. If this happens, avoid giving those foods or preparing those negative associations at the next mealtime.
As long as they aren’t gagging too much during mealtime or causing them distress, gagging is common. However, if they are frequently gagging when trying to self-feed, this can cause them to have negative associations with eating or eating aversions. If this happens, avoid giving those foods or preparing those negative associations at the next mealtime.
Choking, however, is different and much more serious than gagging. Choking is when a piece of food gets lodged in the airway. Your baby may first begin coughing, then become silent. He will show difficulty breathing and will not be able to cry or make sounds due to the food obstructing his airway. This is a serious and life-threatening matter. This is why the types of food, foods’ sizes, and the consistency of foods are important when teaching your baby to self-feed.
Final Thoughts
This is an exciting time in your baby’s development. Remember, self-feeding is a learning process and takes time. If you see that your baby isn’t able to self-feed enough foods to fill them up during mealtime, which is common in the beginning, alternate feeding them purees and finger foods to fill them. I also suggest offering them a YoBaby yogurt pouch to fill them and allow them to continue practicing self-feeding! In the meantime, take lots of pictures of this fun and messy milestone and enjoy the process!
I also suggest offering them a YoBaby yogurt pouch to fill them and allow them to continue practicing self-feeding! In the meantime, take lots of pictures of this fun and messy milestone and enjoy the process!
Note that the views and opinions expressed in this post are solely that of Baby Chick and do not necessarily reflect the opinions and views of Stonyfield. The content provided and in any linked materials are not intended and should not be construed as medical advice. If you have any questions about health or nutrition, we always think it’s best to consult with your doctor or healthcare practitioner.
Teaching Your Baby to Self-Feed
Read time: 5 minutes
What should I know about teaching my baby to feed themself?Signs your baby is ready to self-feed
Ideas for first finger foods
Tips for introducing spoons and cups to your baby
As your baby becomes more experienced with eating, you may notice them becoming more interested in feeding themself. This transition to self-feeding usually starts between 7 and 9 months.1,2,3
This transition to self-feeding usually starts between 7 and 9 months.1,2,3
Grabbing the spoon while you are holding it
Reaching for food from their (or your!) plate
Even grabbing other objects, like toys, and bringing them to their mouth4,5
Once your baby starts showing an interest in feeding themself, it’s important to provide many opportunities for them to practice this skill. The key to mastering self-feeding is to let your baby try and try again.
Don’t wait until your baby’s teeth emerge to start finger foods! Babies do not actually need teeth in order to enjoy foods beyond purees. In fact, the teeth we use to chew are the molars, and those teeth generally don’t come in until well after baby’s first birthday.15
In fact, the teeth we use to chew are the molars, and those teeth generally don’t come in until well after baby’s first birthday.15
Babies’ gums are incredibly strong – if your little one has ever gnawed on your finger when teething, you know! And as long as the foods you present to your baby are size and texture appropriate, they can chew perfectly well without a full mouth of teeth.14
Ideally, the food you provide your little one should be soft and pea-sized to prevent choking. Make sure the food is ‘smushable’ between your fingers so that it’s soft enough to be gummed by your baby.
How to start teaching your baby to self-feed with finger foodsA good way to start is placing a few small pieces of food on your baby’s highchair tray. Let your baby feel it. It may seem as if baby is just playing with the food, but touching and playing is a step in their learning process.2,5
Initially, your baby may grab for the food with a raking motion, using the entire fist to move the food toward their mouth. Grabbing the food in this way is called the palmer grasp, which is when baby’s fingers close over an object (such as your finger) in the palm of their hand.16
Grabbing the food in this way is called the palmer grasp, which is when baby’s fingers close over an object (such as your finger) in the palm of their hand.16
Around 9 months, your little one will develop the fine motor skill of grasping food with their thumb and forefinger, called the pincer grasp.5
Read more: Introducing Solids: First Foods and Advancing Textures
When to practice self-feedingYou can go about practicing self-feeding in many ways. First, try setting aside time at the beginning of the meal for practice. Since baby is hungrier at the start, this may help in motivating your little one to bring the food to their mouth themself.
Another way to try is to simply leave several pieces of food on baby’s tray to play and practice with while you alternate with spoon feeding. Allow your little one to try and put food in their mouth, then practice chewing and swallowing. Be sure that baby’s mouth is clear of food before offering anything from the spoon.
If your baby gets frustrated, allow them to finish the meal and eat how they normally would (such as with spoon feeding). Just remember to keep trying at other meals throughout the day (and every day).
Read more: Meal Plan for 6 to 9 Month Old Baby
First finger foodsThe foods you give your baby to practice self-feeding should be soft, easily ‘smushed’ between your fingers, and cut into small pea-sized pieces.
Here are some ideas for first finger foods:
Small pieces of ripe, soft bananas, avocados, peaches, mango, kiwi
Soft cooked sweet potatoes, carrots, butternut squash, turnips
Grated or soft cooked (skinless) apples and pears
Soft cooked whole grain pasta
Scrambled eggs
Cubes, strings, shredded, or small pea-sized pieces of cheese
Cooked shreds, small diced pieces, or ground cooked chicken, fish, or turkey
Berries cut into quarters
Beans cut into halves or quarters
In addition to the above ideas, your baby can eat bits of what you eat (without added salt or sugar) including different fruits, veggies, grains, meat, beans, spices and seasonings as long as the foods are small and soft enough to reduce choking risk.
Foods that pose a risk of choking should be avoided. Examples include nuts, whole grapes, hot dogs, raw carrots, raisins, popcorn, and portions of food that are too large.14 Also note that honey should not be given to infants before the age of 1 year.
Read more: Preventing Choking in Infants and Toddlers
Time to practice with spoons and cupsLearning how to use spoons and cups not only involves demonstrating how to use each one, but also allowing your baby lots of practice both with your help and without. Let your little one get messy as they step into their independence with eating and drinking!
Teaching your baby to use a spoonAfter your baby masters self-feeding with their hands, the next step is offering utensils. Most children become good at using spoons and forks to self-feed between 15 to 18 months, but that doesn’t mean you need to wait until then to start exposing them to utensils. 1,6,7
1,6,7
Just as your baby needed a lot of practice eating with their hands, they will also need many opportunities to attempt eating with utensils. A good way to begin encouraging this transition is to give them their own baby or toddler-friendly spoon or fork.
Teaching your baby to use a cupLearning to drink from a cup can also begin around this time.4,7 Use an open, sippy, or straw cup and allow your little one to practice with a small amount of water. Since formula and/or breastmilk will still provide a large amount of nutrition and all of the hydration for your little one at this age, only about 4 to 8 ounces of water total spread through the day are recommended.8
Letting your baby drink water from a cup on their own will not only build their fine motor skills (which may include lots of spills!), but will also help them form the important habit of drinking water.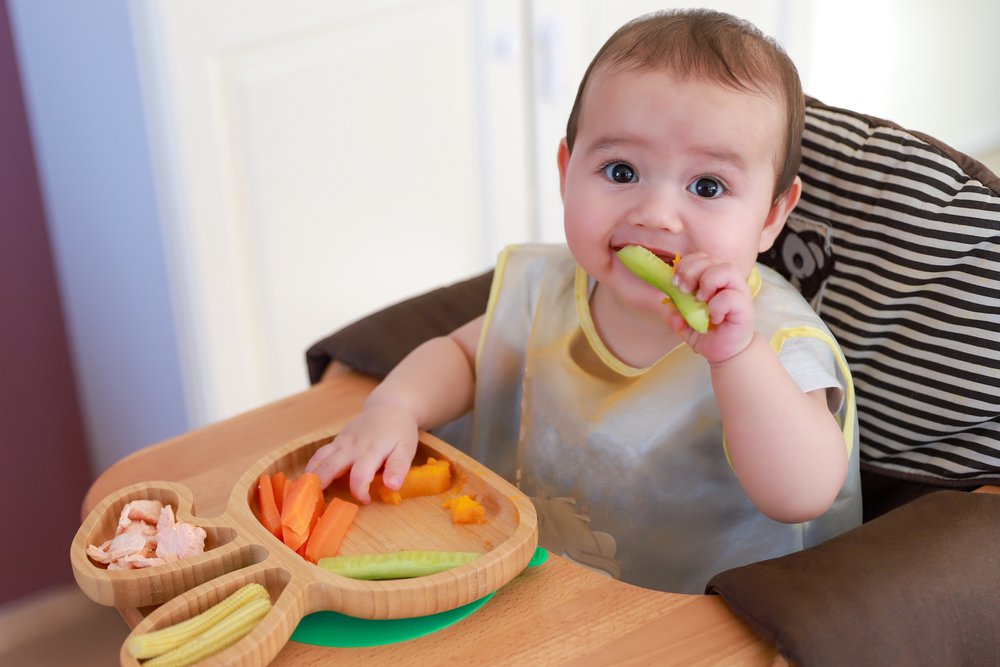 8
8
Which should you use: cups? Sippy cups? Straw cups? Learn more here: Transitioning to Cups for Babies and Toddlers
Which foods to use when practicing using a spoonThicker foods like oatmeal, mashed sweet potatoes, or yogurt blended with fruit are good practice foods since they will more easily stick to the utensil. It will be messy for a while but just remember that practice makes progress.
Once your baby has gotten the hang of dipping the utensil into the food and bringing it to their mouth, consider giving baby their own small bowl. There are some bowls with suction cups on the bottom and some that are attached to a mat – these may help prevent too many spills.
Let your baby to feed themself from their bowl while still feeding them from yours. Soon enough they’ll be eating a full meal without your help!
Remember, it is a learning process; it will take quite a while before your little one is neatly and skillfully feeding themself. In the meantime, have fun and be prepared to get messy!
In the meantime, have fun and be prepared to get messy!
It’s important to monitor your baby as they begin to eat more independently. Your baby is not only getting used to a new way of eating, but new textures too. Remaining by your baby during meals will allow you to monitor their tolerance for new textures and the amounts they are putting into their mouth.9
Know the difference between gagging and chokingGagging is the body’s natural defense against choking and is very common when babies start eating solid foods.10,11 Gagging may occur if the baby has too much food in their mouth or if the food moves towards the back of the mouth before they have chewed it sufficiently. While your baby may look scared and be making gagging noises, baby’s airway is not blocked. The gag reflex helps baby move the food back toward the front of the mouth so they may chew it more before swallowing.
The gag reflex helps baby move the food back toward the front of the mouth so they may chew it more before swallowing.
Choking is when a piece of food becomes lodged in the airways causing baby to stop breathing.12 Your baby will be silent and perhaps flailing their arms. Choking is life threatening and requires immediate attention.
Learn more: Preventing Choking in Infants and Toddlers
Expect and embrace the messTeaching your baby to feed themself will be messy. Invest in a few good bibs or apron type smocks that can better catch the food. Consider placing an old towel underneath the highchair if you are concerned with food falling on the floor. Keep a damp washcloth or paper towel by your side to help with spills.
Enjoy family mealsBabies learn from you! If your baby is eating meals with the rest of the family, they will observe how everyone else is using their utensils to feed themselves, eating healthy foods, as well as other appropriate mealtime behaviors. 4,13
4,13
Read more: Family Meals: Developing Healthy Eating Patterns
Be patientLearning to self-feed takes time. Allow plenty of time for meals and never rush your baby to finish. Your little one is eating at the pace they are most comfortable with, allowing them to boost their learning.
Let's Chat!We know parenting often means sleepless nights, stressful days, and countless questions and confusion, and we want to support you in your feeding journey and beyond.
Our Happy Baby Experts are a team of lactation consultants and registered dietitian nutritionists certified in infant and maternal nutrition – and they’re all moms, too, which means they’ve been there and seen that. They’re here to help on our free, live chat platform Monday - Friday 8am-6pm (ET). Chat Now!
Read more about the experts that help write our content!
For more on this topic, check out the following articles:Introducing Solids: Signs of Readiness
Learning to Love Healthy Foods
Understanding your Baby’s Hunger and Fullness Cues: Responsive Feeding
Introducing Solids: Baby Led Weaning
Feeding Tips for Healthy Weight Gain in Infants and Toddlers
Nutrient Needs and Feeding Tips for 6 to 12 Month Olds
Sources
Pediatrician "SM-Doctor" about the age until which a child should be breastfed
Some new mothers try to do this as early as possible. Others continue to put the baby to the breast at 4 and 5 years. Play their role and "national" features. For example, in the UK, only a third of babies in their six months still receive mother's milk, while the rest are transferred to formula. And in the UAE, the law prescribes to breastfeed children up to two years, otherwise you can get severe punishment.
Others continue to put the baby to the breast at 4 and 5 years. Play their role and "national" features. For example, in the UK, only a third of babies in their six months still receive mother's milk, while the rest are transferred to formula. And in the UAE, the law prescribes to breastfeed children up to two years, otherwise you can get severe punishment.
In fact, it is on the figure “two years” that most doctors around the world agree. It is believed that after this age, mother's milk no longer brings additional health benefits. Is it so? we deal with experts.
Tatyana Kuznetsova
TATYANA KUZNETSOVA
pediatrician, nephrologist, breastfeeding consultant at the SM-Doctor clinic.
On the recommendation of the World Health Organization and the UN Children's Fund, it is desirable to maintain breastfeeding up to 2 years, longer - at the mutual desire of the mother and child. Domestic pediatricians, based on practical experience and scientific research, voice the figure up to 1. 5 years.
5 years.
It is now not uncommon to see mothers who breastfeed their children after two years of age. Such prolonged breastfeeding is commonly referred to as long-term feeding.
In any case, after 2.5 years, the child goes through the process of natural extinction of the sucking reflex, there is a gradual self-weaning and, thus, the smooth completion of breastfeeding.
Regardless of the recommendations, the choice always remains with the mother. And the duration of breastfeeding will depend, first of all, on the readiness of both the mother and the child to stop this process.
What are the health risks of early weaning?
Breast milk substitutes do not contain anti-infectious factors, so an artificially fed baby is more likely to get intestinal infections and respiratory diseases. These include frequent acute respiratory viral infections, otitis media, bronchitis, pneumonia, intestinal infections (usually of a viral nature) with prolonged diarrhea, fungal intestinal diseases, as well as a formidable life-threatening condition - necrotizing enterocolitis of newborns.
Quite often, infants on mixtures develop intolerance to animal milk proteins (bovine, goat) with the development of allergic reactions, in particular, food allergies in the form of atopic dermatitis. Unfortunately, in the future such children are at risk for the development of allergic bronchitis, bronchial asthma.
Formula feeding increases the risk of developing diabetes mellitus, as well as obesity associated with excessive formula intake that exceeds the needs of the child. Perhaps the development of seizures due to excess content in mixtures of sodium, calcium, phosphorus.
Infants receiving formula may have reduced intellectual development due to a lack of amino acids, omega-fatty acids, which are necessary for the growing brain of a child.
In addition, according to some studies, not breastfeeding increases the risk of sudden infant death syndrome.
And what are the disadvantages of late weaning?
Not only abroad, but also in Russia, there are many studies that have proven the benefits of mother's milk at any time of feeding. After a year, breast milk changes its composition, but not for the worse.
After a year, breast milk changes its composition, but not for the worse.
The main reason for these changes is that milk is no longer the main food for the baby, and other functions come to the fore.
The older the child becomes, the greater the concentration of immunoglobulins in milk increases, which protect the child from infectious diseases. Breast milk contains leukocytes and a number of anti-infectious factors, as well as antibodies against infectious agents previously transferred by the mother.
How does breastfeeding affect the child's psyche?
Today it is becoming very fashionable to instill early independence in children, and premature weaning is seen by some parents as a means to make the child more independent.
However, psychologists who are closely involved in the study of child development warn that premature weaning can, on the contrary, provoke a delay in emotional development and increase dependence on parents.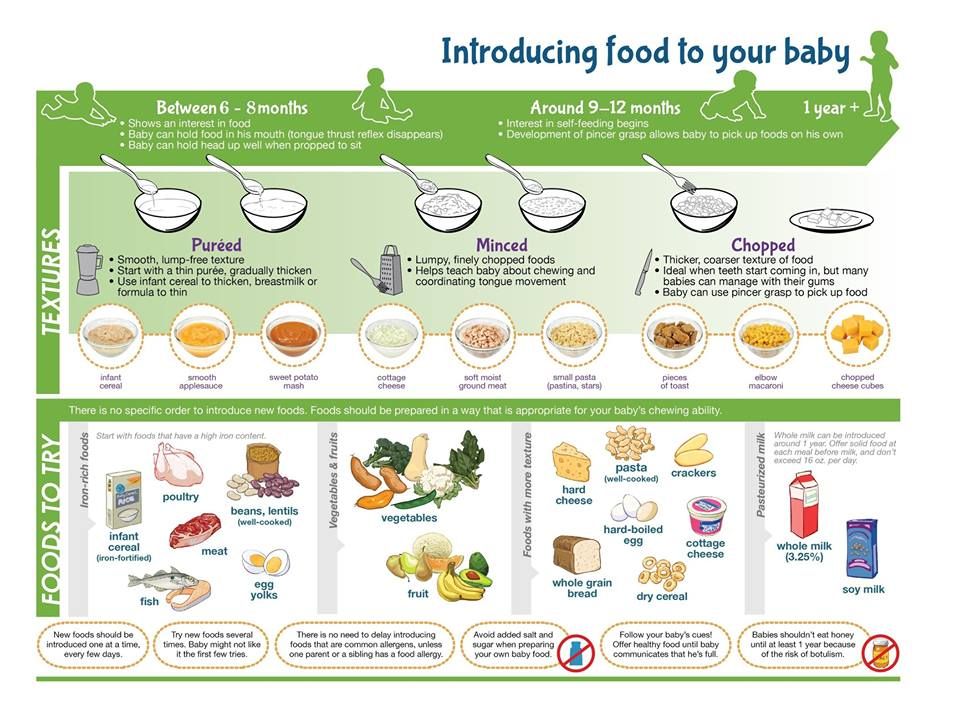 Imposed independence turns into psychological isolation and abandonment. It is much better to give the child the opportunity to become independent when he is ready for it.
Imposed independence turns into psychological isolation and abandonment. It is much better to give the child the opportunity to become independent when he is ready for it.
This is well illustrated by the results of foreign studies: for example, one of them showed that the greatest achievements in school were in children who were fed longer. And in the course of another, they found that the longer a child breastfeeds, the better social adaptation goes later, at the age of six to eight. Both mothers and teachers acknowledged that babies who were breastfed for a long time were much less likely to develop problem behaviors.
Yes, and Russian doctors, who undertook to study the effect of breastfeeding on the neuropsychic development of children, found that babies who ate their mother's milk for a long time show much better results both at two years, in tests of speech development, and at three years , in tests of the correct performance of skills.
Many long-term breastfeeding mothers successfully combine feeding with work, and also take their children to kindergartens. Applications remain only at bedtime and at night. The rest of the time, the baby usually does not need to breastfeed. Ideally, the child should stop asking for breasts during the day, and then at bedtime and at night. As a rule, this happens about 2.5 - 3 years.
Applications remain only at bedtime and at night. The rest of the time, the baby usually does not need to breastfeed. Ideally, the child should stop asking for breasts during the day, and then at bedtime and at night. As a rule, this happens about 2.5 - 3 years.
But if the child continues to breastfeed after 3.5 years, this may indicate some psychological problems of the baby or mother, in this case it is advisable to contact a psychologist, but not an ordinary one, but a friendly one for long-term feeding.
What if I can't breastfeed?
Sergey Butriy
SERGEY BUTRIY
Pediatrician, author of books on child health
A well-known doctor spoke about this in a podcast for Cuprum.
- One of the most "explosive" topics in the pediatrician's office after vaccinations is breastfeeding. Now it's fashionable to be for GW. Of course, formula is not quite the same as breast milk. There is only one "but".
Mothers who failed to breastfeed for health reasons experience a huge sense of guilt. They are pressed by society, other mothers, breastfeeding consultants. Many become depressed because of this, trying to feed through physical pain. But not so perishing GV and it is important. "Die but feed" is not our method. And there are many such mothers, they come to the doctor and cry. It hurts them even to think that they will not give something to the child.
Breastfeeding is great, but it's not the only way. Artificial feeding is not shameful. You can raise a healthy child and mixtures. The main thing is that mom is calm.
Published on the parents.ru portal
How to teach a child to eat with a spoon and at what age is it better to start
Usually parents feed their children with a spoon not out of tenderness, but for practical reasons: it’s faster and cleaner. Pediatrician Olga Kulakova explains at what age a child can handle eating with a spoon and fork and whether this process can be somehow accelerated.
Question. My daughter is already 1.5 years old, but she just can't eat with a spoon on her own. By what age should a child learn to use cutlery? And are there ways to teach him?
Answer. The first acquaintance of a child with a spoon begins in the first year of life and coincides in time with the beginning of the introduction of complementary foods. At 6–7 months, the baby may begin to show interest in the spoon as an object. This is an excuse to buy another baby spoon and put it next to the plate. Let the child turn it in his hands, examine it and try to use it for its intended purpose.
At around 9 months of age, your baby can start picking up a spoon on their own. But this does not mean that he will be able to scoop up food and bring it to his mouth. Rather, it is about the fact that the child is trying to copy the movements of adults.
A child usually masters a full-fledged spoon by about one and a half years. But here it is important to remember that everything is very individual. Someone already a year old is excellent at using a spoon, and someone is still fed by their parents even at two years old. And it’s not worth worrying that the child is over a year old, and he is still just learning and he doesn’t succeed.
Someone already a year old is excellent at using a spoon, and someone is still fed by their parents even at two years old. And it’s not worth worrying that the child is over a year old, and he is still just learning and he doesn’t succeed.
Under no circumstances should children be forced to learn this science. Aggressive training can cause a backlash: the child will no longer want to pick up cutlery.
How to teach a child to use a spoon:
- Have him sit at a common table, let him watch how family members eat.
- Do not force feed your baby. Let him eat with his hands. He will not be able to eat porridge and soup like that - he will have to try to master the spoon.
- Play role-playing games with him more often, in which the child feeds his toys from a spoon.
At this age, the child actively copies the behavior of his loved ones, and it is important that he sees how the whole family eats with cutlery.
Children learn to use a fork by about three years of age: at this age they already understand that a fork is a sharp object and can be hurt.
Pay attention to how the child grasps cutlery:
- At 1–2 years old, he holds a spoon in his fist in the middle of the handle.
- By two years - closer to the wide back.
- From the age of three, he can begin to hold the spoon with three fingers: thumb, index and middle.
Sooner or later the child will pick up the spoon and fork on his own as it should be
Children are given long time intervals to acquire certain developmental skills. For example, some children can learn to walk at 9 months, and others by one and a half years, and both will be the norm. The same story with cutlery: one child may become interested in them at 7-8 months, the other at 9months or after a year. All of these are variations of the norm.
However, by the age of two, a child should normally pick up a spoon and try to eat on his own. This does not mean that he will eat all the soup in the bowl, but at least a few spoons he should be able to bring to his mouth.