When should you stop feeding baby food
When to end purees and start soft table foods with your infant
Julia was delighted to begin solid foods with her 6-month-old son Brandon. Brandon was a champion eater and quickly learned to manage the iron-fortified rice cereal fed to him from a spoon. As Brandon grew, Julia began introducing pureed foods to provide a more balanced diet in addition to breast milk. By 8 months, Brandon grew impatient for his mother to spoon purees into his mouth. At 10 months, Brandon was communicating he was hungry even though he had eaten three bowls of puree an hour earlier. Julia was wondering why her son had such a veracious appetite and wasn’t content after eating
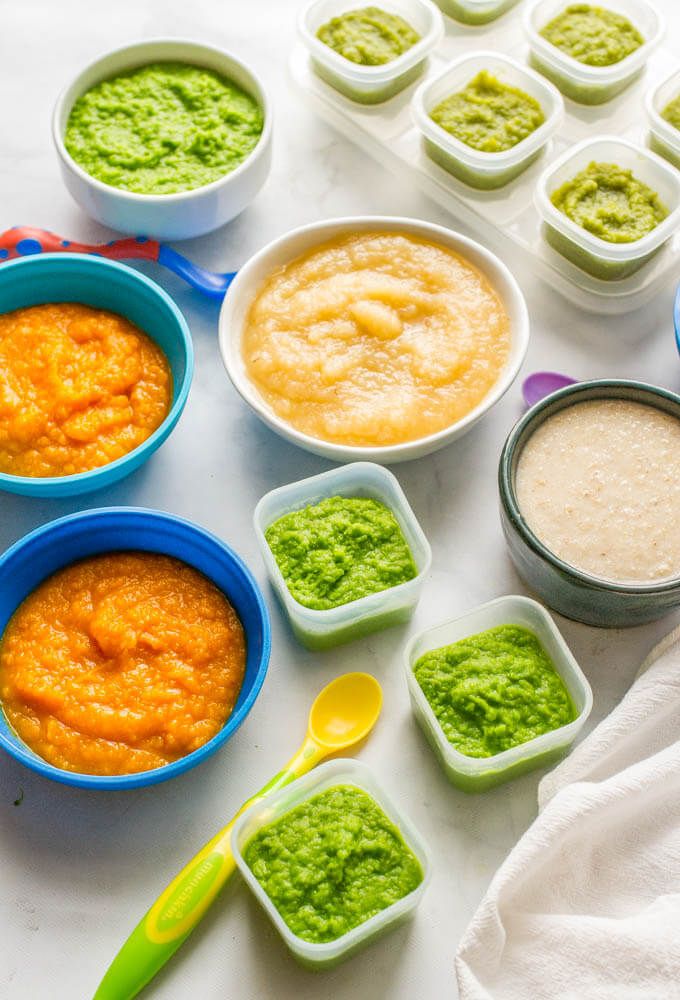
It is a pleasure to introduce infants to the new tastes of solid foods at 6 months of age. Watching their little tongues learn to move food from the front to the back of their mouths to swallow is mesmerizing. And as soon as they have mastered this skill, parents love to start introducing other foods in pureed form, such as fruits and vegetables. Later, protein sources such as meat, fish, or legumes are also added to the purees to provide a balanced diet in addition to breast milk or formula.
However well intentioned, some parents continue to provide purees rather than moving onto solid table foods because:
they fear that their baby won’t eat enough;
their baby will not be able to mash the soft foods with their gums;
their baby will choke on non-pureed foods; or
the parent enjoys spending time feeding their little one with a spoon.
Reasons such as these may lead parents to offer purees longer than is recommended.
Breastfeeding Bootcamp
Includes 16 lessons.
It doesn’t matter whether you are a new mom or if this is your second or third child: breastfeeding is not always easy. Each baby is unique, and your body is also…
View contents
Newborn Care
Includes 8 lessons.
The first three weeks of life are key to your baby’s development. What the newborn feels during this time constitutes their first experience of the world, and will…
View contents
Baby cereals and purees are only needed during the first months of learning to eat solid foods. Babies need to learn to control their tongues to move the food from the front of their mouths to the back of their mouths to swallow. Purees allow them the perfect consistency to master this skill. The next step is for them to accept food into their mouth and learn to chew the food with their gums before swallowing. This natural transition from swallowing a liquefied food (puree) to breaking down soft foods (chewing) helps prepare babies for feeding themselves independently.
Babies need to learn to control their tongues to move the food from the front of their mouths to the back of their mouths to swallow. Purees allow them the perfect consistency to master this skill. The next step is for them to accept food into their mouth and learn to chew the food with their gums before swallowing. This natural transition from swallowing a liquefied food (puree) to breaking down soft foods (chewing) helps prepare babies for feeding themselves independently.
When parents continue to offer purees rather than soft table foods, there are a few issues that can arise, including:
Babies take a passive role in eating because the parent is directly involved with spoon-feeding. This can interfere with the baby’s natural hunger and satiety responses;
It can be difficult for babies to accept foods with different types of textures because they are not used to feeling all the unique ways that solid foods feels in the mouth;
Babies can choke if they think they are supposed to swallow everything in their mouth without chewing. They need time and practice to learn to chew before swallowing; and
They need time and practice to learn to chew before swallowing; and
Purees pass through the stomach faster than solid foods because they are already partially broken down before being swallowed. This can lead to feelings of hunger and stress about when the next offering of food will occur.
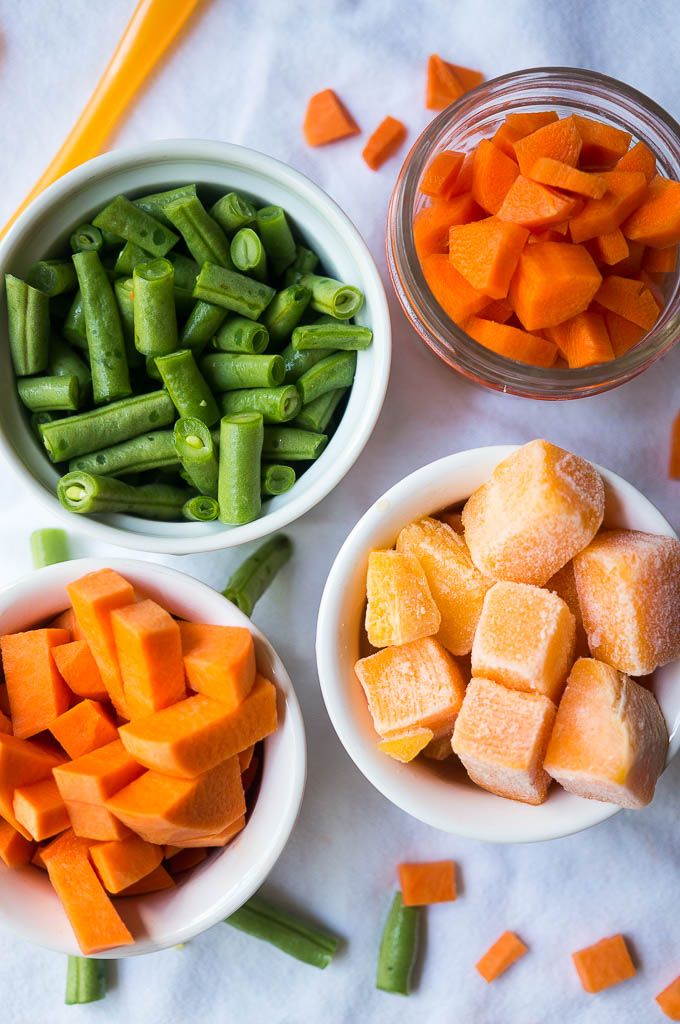
To help your baby avoid these and many other issues around feeding, it is recommended that purees are phased out and soft, solid foods are introduced as soon as your baby can move foods easily from the front of their mouth to the back to swallow. This usually happens for most infants by 6-8 months of age. After your baby has mastered this skill, you can start providing foods that the rest of your family is enjoying. You can offer well-cooked, mashed, or ground fruits and vegetables, mashed potatoes, sticky rice, or wheat-free dry cereals like Cheerios that have been broken in half in addition to breast milk or formula.
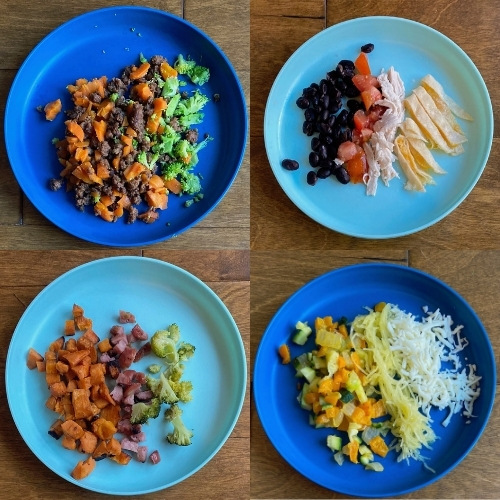
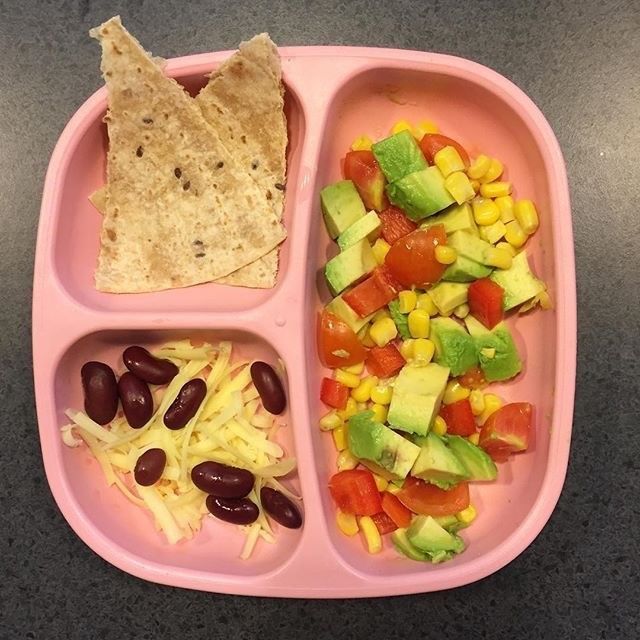
By 7-10 months, most infants are able to eat chopped cooked vegetables, canned or cooked fruits, cheese, mashed cooked dried beans, strips of toast, crackers and dry cereal, as well as breast milk or formula. And by 9-12 months, most babies can eat cut up soft cooked foods, cut up soft foods like bananas or peaches, tender chopped meats, dishes with noodles that are cut up, dry cereal, toast, crackers, eggs, and cheese, in addition to breast milk or formula. This progression is to prepare your baby to move onto being a toddler on their first birthday and be able to eat everything from the family table that is soft. Remember to avoid foods that can cause choking like whole grapes or sausage rounds. Meat should continue to be cut up into small pieces. Whole pasteurized milk can be given in place of breast milk or formula.
And by 9-12 months, most babies can eat cut up soft cooked foods, cut up soft foods like bananas or peaches, tender chopped meats, dishes with noodles that are cut up, dry cereal, toast, crackers, eggs, and cheese, in addition to breast milk or formula. This progression is to prepare your baby to move onto being a toddler on their first birthday and be able to eat everything from the family table that is soft. Remember to avoid foods that can cause choking like whole grapes or sausage rounds. Meat should continue to be cut up into small pieces. Whole pasteurized milk can be given in place of breast milk or formula.
How to Keep Your Teen From Becoming a J@ck@$$
Dr. Deanna Marie Mason PhD
This practical hands-on book explains how to help teens in the process of finding themselves as they grow into adulthood. It is a unique, special guide because it shares teens’ perspectives on what they need to become the people of their dreams…
View contents
Proactive Parenting: How to Raise Teenagers with Values
Dr.
 Deanna Marie Mason PhD
Deanna Marie Mason PhDCyberbullying, sexting, alcohol, drugs, unwanted pregnancies, bullying, academic disinterest, and eating disorders are just some of the worries parents face today. However, these situations or behaviors can be avoided if children are educated in values…
View contents
Allowing your baby to grow and adapt their eating habits during the first year of life, as their development permits, will set them up to learn to accept and enjoy a wide variety of foods that support a healthy diet. They will also learn to take more control over eating enough food to keep their bodies satisfied between meals and snacks. Encouraging your baby to transition from purees to solid foods is a wonderful way to support their growth and development.
Sources:
Satter, E. (2000). Child of mine: Feeding with love and good sense. Boulder, CO: Bull Publishing Company.
Swarzenberg, S. Georgieff, M. & Committee on Nutrition. (2018). Advocacy for improving nutrition in the first 1000 days to support childhood development and adult health. Pediatrics 141(2), doi: 10.1542/peds.2017-3716.
Pediatrics 141(2), doi: 10.1542/peds.2017-3716.
World Health Organization. (2003). Feeding and nutrition of infants and young children: Guidelines for the WHO European Region. Denmark: WHO Region Publications.
Share article
About the instructor
Proactive Parenting
Dr. Deanna Marie Mason PhD
More than 20 years of clinical experience helping families:
Bachelor's Degree in Registered Nursing, Master’s Degree in Pediatric Nurse Practitioner and PhD in Nursing. University professor, patient education specialist, pediatric researcher, published author and reviewer to first-line international scientific journals, continuous philanthropic activity related to health promotion and education, wife and mother of two children.
Solids, Finger Foods, and More
Written by Gina Shaw
In this Article
- Baby Milestone 1: When They Can Start Solids
- Baby Milestone 2: When They’re Ready to Move From Puree to Chunks
- Baby Milestone 3: When They Can Sit in a High Chair
- Baby Milestone 4: When They Can Manage Finger Foods
- Baby Milestone 5: When They Start Using Spoons
- Baby Milestone 6: When They Can Try Highly Allergenic Foods
- Baby Milestone 7: When They Can Drink Water
- Baby Milestone 8: When They Can Completely Feed Themselves
There are many milestones that need to be achieved when a baby is ready to start to eat solid foods. Here are some of the big ones.
Here are some of the big ones.
Baby Milestone 1: When They Can Start Solids
Most pediatricians, and the American Academy of Pediatrics, recommend introducing solid foods to babies when they are between ages 4 and 6 months. That’s when they start to lose the “tongue-thrust reflex” or extrusion reflex, which is important for sucking the breast or bottle when they are younger, but interferes with feeding. Babies at this point can also lift their heads up independently and hold their necks high.
If your baby is around this age, can sit up well with support, and shows interest in the foods they see you eating, it’s probably a good time to venture into feeding your baby solid food. If your baby is exclusively breastfed, it is recommended that you wait until they are 6 months to start solids.
Baby Milestone 2: When They’re Ready to Move From Puree to Chunks
“Chunking up” babies’ food is a process -- obviously, they shouldn’t go straight from rice cereal to raisin bran. But after the first few weeks of adjusting to eating rather than just drinking their food, your baby should be ready to handle a little more texture in solid foods.
But after the first few weeks of adjusting to eating rather than just drinking their food, your baby should be ready to handle a little more texture in solid foods.
Introduce new textures slowly. Good starters are mashed bananas or mashed avocados. You can also use the “staged” store-bought baby foods -- going from the smooth puree of stage 1 to the slightly thicker stage 2 and then the chunkier stage 3 by around 9 months of age. (Babies don’t necessarily have to have a lot of teeth to handle more texture in their foods -- they can often gum soft foods very well!)
Baby Milestone 3: When They Can Sit in a High Chair
When babies are ready to eat solid foods, they can sit upright with support and hold up their head and neck. They're capable of sitting in a high chair! That's a serious milestone, but you'll need to follow these safety rules: Always buckle a baby into their chair for safety, even if they are unable to get out with the tray in place. As they get older and become more active, they may be able to squirm out. It is a good habit to buckle a child as soon as you place them in their chair -- even if you think there's no chance they could fall out or climb out. You may get distracted for a moment, which happens really easily when we are trying to do a million things at once!
It is a good habit to buckle a child as soon as you place them in their chair -- even if you think there's no chance they could fall out or climb out. You may get distracted for a moment, which happens really easily when we are trying to do a million things at once!
Baby Milestone 4: When They Can Manage Finger Foods
Babies between ages 7 and 11 months usually tell you they’re ready to eat more grown-up foods by trying to grab them from you. Almost any food that is healthy and nutritious and has a soft texture makes a good finger food, if it’s cut small enough: diced pasta; small pieces of well-cooked vegetables such as carrots, peas, or zucchini; and pea-sized bites of chicken or soft meat. Small, unsweetened round cereals and cereal puffs are also a good choice. Avoid feeding your baby grapes, hot dogs (even cut up), nuts, and hard candy, as they are choking hazards.
At first babies “rake” food into their hand, but soon they develop the “pincer grasp” that allows them to pick up small objects between thumb and forefinger. At that point, your baby can become a pro at self-feeding, so encourage finger foods and let your baby explore!
At that point, your baby can become a pro at self-feeding, so encourage finger foods and let your baby explore!
Baby Milestone 5: When They Start Using Spoons
Almost as soon as babies adjust to being fed with a spoon, they'll want to hold and grab the spoon themselves and put it in their mouths. That doesn't mean they're graceful, of course.
Most babies don’t learn to use a spoon effectively until after their first birthday, but let a younger baby who’s interested give it a whirl for practice. Try giving them a soft-tipped spoon to hold while you feed them with another. They can get used to holding the spoon themselves and will also be distracted from grabbing yours.
When you think they are ready to actually navigate the spoon into their mouth, try thicker, stickier foods like yogurt, mashed potatoes, or cottage cheese. Another tip: Put some cream cheese on the spoon and then a few pieces of O-shaped cereal on top. The cream cheese won’t fly everywhere, and the baby can get the experience of actually getting the cereal into their mouth.
Expect a mess! Use a plastic or other waterproof bib, and put a mat under the high chair to make cleanup easier.
Baby Milestone 6: When They Can Try Highly Allergenic Foods
Some pediatricians still recommend waiting until children are at least age 1 before offering them certain foods that are considered highly allergenic, like eggs or fish. But current research doesn’t demonstrate any benefit to waiting past a certain age to introduce these foods, unless you have a significant family history of food allergies or other reasons to believe your baby may be predisposed to them.
There is no evidence that introducing highly allergenic foods to children under age 1 makes them any more likely to be allergic to them, and the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) now says it’s fine to give these foods before the baby's first birthday. Many pediatricians are still very cautious about shellfish and peanuts, however, because allergic reactions to these foods can be particularly dangerous.
Baby Milestone 7: When They Can Drink Water
Babies don't need water during their first 6 months of life. They get all the water they need from breast milk or baby formula. Babies under age 6 months should not be given any water at all, because it’s easy to fill up their tiny stomachs -- and they should be filling up on the nutrients they receive from the milk to grow. Once they start eating mostly solid foods, around age 9 months, they can start water with meals using a sippy cup.
If your older baby shows an interest in water that you’re drinking, there’s no harm in letting them have a few sips. Just don’t let it replace the nutritious breast milk or formula they should be getting.
Baby Milestone 8: When They Can Completely Feed Themselves
Mastering eating with utensils is a long process. Most babies do not become really skilled at it until they are well past their first birthday. Encourage your child to practice safely, and again, be prepared for a little mess. (How else will you get the “oatmeal in the hair” pictures that will embarrass them years later?)
(How else will you get the “oatmeal in the hair” pictures that will embarrass them years later?)
Breastfeeding after 1 month: what to expect
Do you know when breast milk production stabilizes? And how does the frequency and duration of feedings change as the baby grows? You will find answers to these questions in our recommendations for breastfeeding after the first month.
Share this information
Congratulations: You made it through the first month of breastfeeding. Your breast milk has reached full maturity 1 , its production stabilizes, and it leaks almost or not at all from the chest. Don't worry, it's not getting less milk, it's just that your breasts are better able to produce and store it now. 2 At the age of six weeks, your baby will begin to please you with his charming toothless smiles, and by two months you will already have 500-600 feedings behind you. With a favorable development of events, problems with latch on by this point will already be resolved, and you can simply enjoy the convenience and benefits of breastfeeding.
When does breastfeeding decrease?
"Normal" feeding frequency for babies aged one to six months varies considerably, with some needing four feedings a day, others asking to be breastfed 13 times a day. 3
“From the age of one month, the amount of milk a baby consumes per feed increases, so that he can go without food for longer,” explains Cathy Garbin, a recognized international expert on breastfeeding, “A baby’s stomach grows, so he eat more at one time. In addition, mature milk allows him to stay full longer.”
Feeding can last from 12 minutes to one hour -
the habits of babies vary so much! 3 But if the child is gaining weight and falls within this range, there is no cause for concern.
What is most surprising, no matter how often the baby eats, he consumes approximately the same amount of milk per day - both at one month and at six, when it is time to start complementary foods with solid food. 4
“However, sometimes the baby eats more and sometimes less, especially when he is unwell.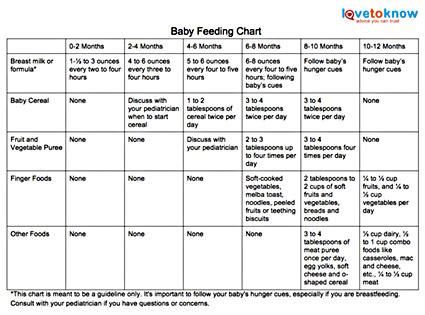 It’s better to just listen to his needs,” Katie explains.
It’s better to just listen to his needs,” Katie explains.
Is breast milk enough for the first six months?
Yes. Breast milk contains everything a baby needs for the first 90,023 six months of life—exclusively breastfed babies don't even need to drink more water! 5 Until about six months of age, a child's digestive system is simply not adapted to the digestion of solid food, and he will be able to drink cow's milk only after a year.
In addition, breastfeeding during this period prepares the child for further development. It strengthens the muscles of the mouth, develops the jaw and helps straighten the teeth 6.7 . All this will come in handy when the baby begins to eat and talk. And because what you eat and drink affects how your breast milk tastes, your baby discovers new tastes even before he starts eating solid foods. 8
In addition, when your baby is sick, your body produces breast milk that is
rich in antibodies that help fight infection. 9 In other words, milk continues to protect the baby for many months as he grows and becomes more active.
9 In other words, milk continues to protect the baby for many months as he grows and becomes more active.
Breastfeeding is also very comfortable once you get used to it. Claudia, a mother of two from the UK, notes: “No need to sterilize a mountain of bottles, prepare formula, carry it all with you, warm it up - in general, breastfeeding turned out to be very convenient, especially when my babies grew up and we began to leave the house more often. ".
At what age does a breastfed baby start sleeping through the night?
Waking up at night is normal for babies. Most babies between the ages of one and six months consume a fifth of their daily milk requirement at night, so nighttime feedings should not be neglected if you want your baby to get the required amount of calories. 3
"It really depends on what you mean by 'sleep through the night'," says Cathy. "And it's better than waking up every two hours anyway! I have met infants who, starting at six weeks old, fell asleep at 19:00 and woke up at 7:00, but most continue to wake up frequently at night after this age. All children are different."
All children are different."
In Wales, a study of more than 700 infants showed that almost 80% of children aged 6 to 12 months wake up at least once a night, and 25% of them wake up three times or more. And it did not depend on what type of feeding the child is on - breastfeeding or artificial. 10
And if nighttime awakenings are unavoidable anyway, breastfeeding is at least comfortable! Maina, a mother of two from Australia, agrees: “You can even take a nap while feeding in the middle of the night - both the body and the baby do their job on autopilot. No need to plan, measure, sterilize anything - ready-made food at the right temperature is right in your chest. I think it's ideal."
My child wakes up more often. Perhaps he is hungry?
Around four months of age, a baby's sleep patterns change as they develop deep and light sleep phases like an adult. Because of this, he may wake up more often at night. “At four months, sleep is more of a problem than feeding,” Cathy admits. “It can be exhausting, but try to adapt and be patient.”
“It can be exhausting, but try to adapt and be patient.”
Some call this " a four-month sleep regression ", but "progress" is more appropriate here. From the outside it may look like a step back, but in fact the child is approaching an important stage of development. He learns quickly, begins to become aware of the world around him, his perception is sharpened and, perhaps, there is anxiety about being separated from his mother. Crying when waking up and being able to eat milk cuddled up to mommy’s chest is a way for a baby to calm down. 11–13
Resist the urge to “supplement” your baby with formula or start solid foods early
in an attempt to improve his sleep. Breast milk contains
hormones that make you sleepy and help you both relax
. Research shows that breastfeeding mothers actually sleep longer at night than mothers of formula-fed or mixed-fed babies
. 14
How does teething affect breastfeeding?
Teething usually begins around four months of age. When a baby has gum pain, he becomes restless, throws his chest and cries. All this, of course, is unpleasant.
When a baby has gum pain, he becomes restless, throws his chest and cries. All this, of course, is unpleasant.
However, breastfeeding can be an excellent sedative.
Studies have shown that babies who are breastfed
during the vaccination period cry less and forget pain more quickly. 15 Breastfeeding during teething can have the same calming effect.
An unpleasant side effect may be the child's attempts to try out his new teeth on the mother's breast. “Sometimes children flirt and bite their mother’s nipples. This can be felt in advance by how the behavior of the child changes when feeding: before biting, he removes his tongue, explains Cathy, “Usually this is not a problem and only happens a couple of times. It is enough to stop feeding, affectionately say that biting is not good, and the baby will soon leave this fun.
How to continue feeding if you have to be separated from the baby?
It happens that during the first six months, when the baby is still fully breastfed, the mother needs to be away for several hours - or even longer if she has to go to work or go away on business for a couple of days.
But this does not mean that you should stop breastfeeding. You can still feed your baby healthy breast milk - just express it and have someone give it to your baby when you're away. Here's Katie's advice:
“Start expressing milk a couple of days in advance, in small batches, 40-60 ml at a time. So you will have the necessary supply for the time of your absence, but at the same time the amount of milk produced will remain the same.
If you have to return to work, check with your employer about your daily schedule. Many mothers breastfeed their babies in the morning, evening and night, and pump milk at lunchtime to relieve discomfort and create a reserve for the next day.
This usually turns out to be much easier than one might think, and today many companies are well placed to do this, notes Cathy. “Breast pumps make it easy to solve this problem.”
Natalie, mother from the USA, shares her experience: “I feed Dylan as soon as he wakes up, and sometimes again before leaving for work, in order to maintain milk production and not lose contact with the child. At work, I pump twice the next day (in my absence, he eats two bottles of breast milk), and after work I rush home for the evening feed. I don't pump on the weekends - we resume regular breastfeeding."
At work, I pump twice the next day (in my absence, he eats two bottles of breast milk), and after work I rush home for the evening feed. I don't pump on the weekends - we resume regular breastfeeding."
Can breastfeeding continue after the introduction of solid foods?
When your baby begins to show interest in food and can sit up on his own - usually around six months of age - it's time to start solid foods. However, it is not necessary to stop breastfeeding, Cathy explains: “A baby’s iron stores during pregnancy are depleted by six months, so he needs additional sources of this element.
Start complementary foods with solid foods, but remember that breast milk remains a more important source of calories and nutrients until the baby is eight to nine months old. By this time, he will be eating much more solid food, but he will still need to breastfeed four to five times a day. By 12 months, the frequency of feeding may be two to six times a day. All babies are different, and many of them at this age are still getting half their daily calorie intake from breast milk. ”
”
Don't forget that breast milk can be added to solid foods, such as cereals and purees, so that the baby can taste the familiar taste. If possible, use milk expressed just before feeding (not thawed) and add just before serving to keep bacteria and nutrients alive. 16
You may be pressured by others to stop breastfeeding when your baby is six months old, but the longer you breastfeed or pump milk, the better for you and your baby.
How long can I continue breastfeeding?
“The World Health Organization recommends breastfeeding along with solid foods until at least two years of age because it plays an important role in supporting immunity,” says Cathy. feels bad".
At eight months, the baby sometimes breastfeeds four times a day, but by one year old, the frequency of feedings can be reduced to two times a day. You yourself will understand which feeding regimen is more suitable for you and your baby. For example, Jane, a mother of two from the US, breastfed until the age of two: “I breastfed when I was at home - in the evenings and on weekends, when the children wanted to be close to me,” says Jane, “It helped a lot when they were sick .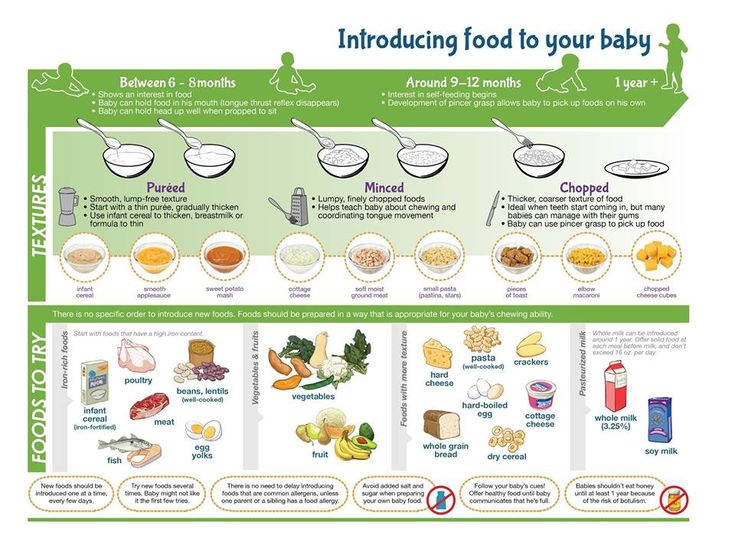 Breastfeeding has become my favorite form of comfort."
Breastfeeding has become my favorite form of comfort."
“When my son got a little older and bolder, he still often asked me to breastfeed him - as if to calm down and gain strength,” recalls Amy, a mother of two children from Canada, “When he happened to hit or skin his knee , breastfeeding was a wonderful way to comfort him.”
If your baby is over a year old and you are still breastfeeding, people around you will probably tell you that this way he will never wean. But if children are not pressured, they usually refuse to breastfeed themselves between the ages of two and four. 17
“I didn’t intend to breastfeed for so long, but as a result, I still breastfeed my four-year-old daughter and 22-month-old son,” says Suzanne, mother of two from the UK, “I breastfeed my youngest before and after work, and in I express milk on business trips. The eldest daughter likes to breastfeed a little before bed or when she is upset - this is a great way to make contact. When I get tired of it, I remind myself what great benefit and comfort it brings them. I now plan to pursue a baby-initiated end breastfeeding strategy — let them decide when to stop.”
When I get tired of it, I remind myself what great benefit and comfort it brings them. I now plan to pursue a baby-initiated end breastfeeding strategy — let them decide when to stop.”
For more information on what to expect and lots of tips and tricks, see our guide Breastfeeding Problems After the First Month.
Literature
1 Ballard O, Morrow AL. Human milk composition: nutrients and bioactive factors. Pediatr Clin North Am . 2013;60(1):49-74. - Ballard O., Morrow A.L., "Composition of breast milk: nutrients and biologically active factors." Pediatrician Clean North Am. 2013;60(1):49-74.
2 Kent JC et al. Principles for maintaining or increasing breast milk production. J 2012;41(1):114-21. - Kent J.S. et al., "Principles for Maintaining and Increasing Milk Production". J Obstet Ginecol and Neonatal Nurse. 2012;41(1):114-121.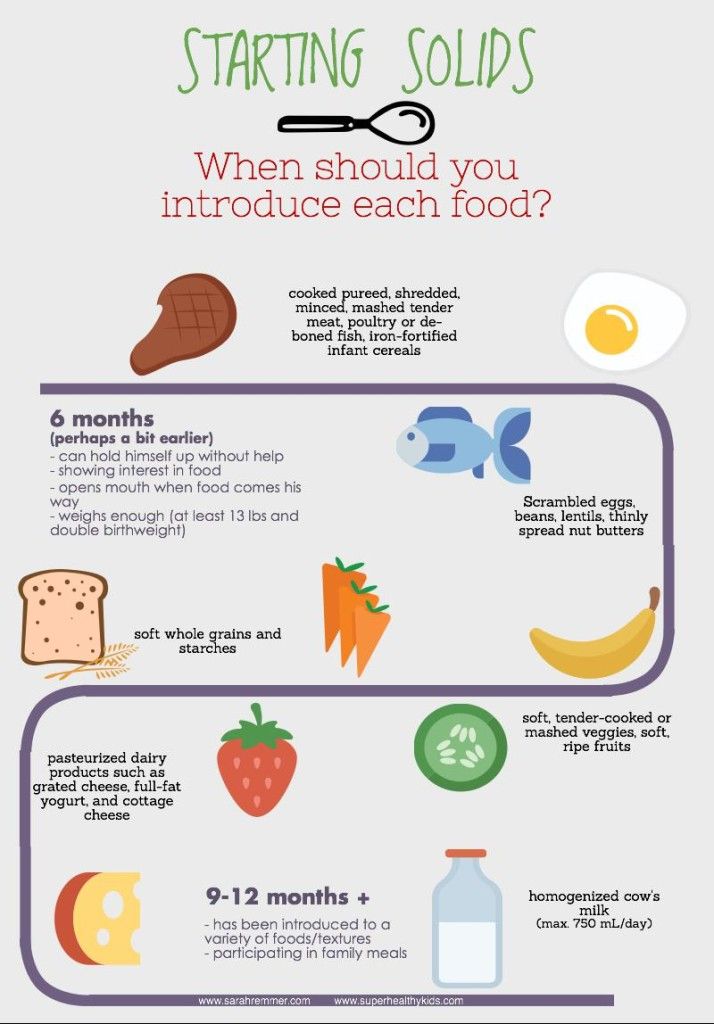
3 Kent JC Volume and frequency of breastfeedings and fat content of breast milk throughout the day. Pediatrics. 2006;117(3): e 387-395. - Kent J.S. et al., "Amount and frequency of breastfeeding and fat content of breast milk during the day." Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 2006;117(3):e387-95.
4 Kent JC et al. Longitudinal changes in breastfeeding patterns from 1 to 6 months of lactation. Breast Med . 2013;8(4):401-407. - Kent J.S. et al., Longitudinal changes in breastfeeding patterns from 1 to 6 months of lactation. Brest Med. 2013;8(4):401-407.
5 Almroth S, Bidinger PD. No need for water supplementation for exclusively breast-fed infants under hot and arid conditions. Trans R Soc 1990;84(4):602-604. - Elmroth S., Bidinger P.D. , "No need for supplementation of exclusively breastfed infants in hot, dry conditions." Trans R Sots Trop Med Hyg. 1990;84(4):602-604.
, "No need for supplementation of exclusively breastfed infants in hot, dry conditions." Trans R Sots Trop Med Hyg. 1990;84(4):602-604.
6 Victora CG et al . Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms, and lifelong effect. Lancet. 2016;387(10017):475-490. - Victor S.J. et al., "Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms and long-term effects". Lancet 2016;387(10017):475-490.
7 Peres KG et al. Effect of breastfeeding on malocclusions: a systematic review and meta - analysis. Acta Paediatr. 2015;104( S 467):54-61. - Perez K.G. et al., "The impact of breastfeeding on malocclusion: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Akta Pediatr. 2015;104(S467):54-61.
8 Mennella JA, Beauchamp GK. Maternal diet alters the sensory qualities of human milk and the nursling's behavior. Pediatrics. 1991;88(4):737-744. - Mennella, JA, Beauchamp, GK, "Maternal nutrition influences the organoleptic properties of breast milk and infant behavior." Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 1991;88(4):737-744.
Pediatrics. 1991;88(4):737-744. - Mennella, JA, Beauchamp, GK, "Maternal nutrition influences the organoleptic properties of breast milk and infant behavior." Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 1991;88(4):737-744.
9 Hassiotou F et al. Maternal and infant infections stimulate a rapid leukocyte response in breastmilk. Clin Transl immunology. 2013;2(4). - Hassiot F. et al., "Infectious diseases of the mother and child stimulate a rapid leukocyte reaction in breast milk." Clean Transl Immunology. 2013;2(4).
10 Brown A, Harries V. Infant sleep and night feeding patterns during later infancy: Association with breastfeeding frequency, daytime complementary food intake, and infant weight. Breast Med . 2015;10(5):246-252. - Brown A., Harris W., "Night feedings and infant sleep in the first year of life and their association with feeding frequency, daytime supplementation, and infant weight. " Brest Med (Breastfeeding Medicine). 2015;10(5):246-252.
" Brest Med (Breastfeeding Medicine). 2015;10(5):246-252.
11 Infant sleep information source. [Internet]. Normal Infant Sleep Development; December 2017 [cited 2018 Feb] - All about baby sleep. [Internet] "The development of normal sleep in a child", December 2017 [cited February 2018].
12 Baby sleep science. [Internet]. The-Four-Month-Sleep-Regression-What-is-it-and-What-can-be-Done-About-it. March 2014 [ cited 2018 Feb ] - The science of baby sleep. [Internet], "Four-month sleep regression: what it is and what to do about it." March 2014 [cited February 2018].
13 The Myth Of Baby Sleep Regressions – What’s Really Happening To Your Baby’s Sleep? [Internet]. Pinky Mckay ; December 2017 [ cited 2018 Feb ] - "The Myth of Baby Sleep Regression - What's Really Happening to Your Baby?" [Internet]. Pinky McKay, December 2017 [cited February 2018].
Pinky McKay, December 2017 [cited February 2018].
14 Kendall - Tackett K ET Al . The effect of feeding method on sleep duration, maternal well-being, and postpartum depression. Clinical Lactation . 2011;2(2):22-26. - Kendall-Tuckett K. et al., "Influence of feeding pattern on sleep duration, maternal well-being and the development of postpartum depression." Clinical Lactation. 2011;2(2):22-26.
15) Harrison D et al. Breastfeeding for procedural pain in infants beyond the neonatal period. Cochrane Database Syst Rev . 2014;10. — Harrison D. et al., "Breastfeeding for Relief of Medical Pain in the Neonatal Period." Cochrane Database of System Rev. 2014;10:CD11248
16 Czank C et al. Retention of the immunological proteins of pasteurized human milk in relation to pasteurizer design and practice. Pediatr Res . 2009;66(4):374. - Zhank S. et al., "Retention of immunological proteins in pasteurized milk depending on the technique and practice of pasteurization". Pediatrician Res. 2009;66(4):374.
17 Weaning from the breast. (2004). Paediatr Child Health, 9(4):249–253. - "Weaning from the breast" (2004). Pediatrician Child Health, 9(4):249–253.
How to stop breastfeeding | Philips Avent
search support iconSearch Keywords
Home ›› How to end breastfeeding comfortably for mom and baby
Home ›› How to end breastfeeding comfortably for mom and baby
↑ top how to stop
breast-feeding? Like all good things, breastfeeding eventually comes to an end.
Weaning is an important decision for both mother and baby, and the decision is entirely up to them. When the mother and baby are ready to start weaning, there are a few tips and techniques to help make the transition a positive one.
When the mother and baby are ready to start weaning, there are a few tips and techniques to help make the transition a positive one.
3 Philips Avent products to support you through your weaning period:
When should I start weaning my baby?
There is no definite and correct period for weaning a child. The mother-child relationship is different for everyone, and weaning is a purely personal decision for mother and baby, which they make when both are ready.
The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends exclusive breastfeeding for infants up to six months of age. Until a child reaches the age of one year, both solid food and breast milk must be present in his diet. If the baby is weaned before he is one year old, adapted infant formula can be fed instead of breast milk. If a baby is stopped breastfeeding at one year of age or older, infant formula milk products can be given instead. While the recommendations are, many mothers stop breastfeeding before their babies are 12 months old, and others breastfeed for up to two years or longer. The second option is called extended breastfeeding, and it's a completely healthy choice for mothers and babies who want to continue breastfeeding.
The second option is called extended breastfeeding, and it's a completely healthy choice for mothers and babies who want to continue breastfeeding.
Signs that a baby is ready to wean
Mothers often wonder how to stop breastfeeding, because babies rarely just stop suckling. Weaning a baby from the breast is usually a gradual process for both the mother and the baby.
There are several signs that will let you know that the baby is ready to start weaning:
- disinterest or fussiness during feeding;
- reducing the duration of feedings;
- baby is easily distracted while feeding;
- the child plays while suckling, eg pulling or biting the breast;
- baby suckles lightly but does not extract milk.
How do I wean a baby?
When mom and baby decide it's time to stop breastfeeding, there are a few things to keep in mind to make the transition smoother.
Here are our tips for weaning your baby when the time is right:
1. Wean gradually. When you decide to wean a baby, remember the main thing: do it gradually. This is necessary so that both mother and baby can adapt to physical and emotional changes. In addition, the gradual cessation of breastfeeding helps mothers avoid problems such as engorgement and general breast discomfort.
2. Express milk. To prevent breast engorgement when breastfeeding is stopped, the mother may need to express her milk, especially if the baby is less than a year old. One way to reduce and gradually stop breast milk production is to express less and less milk so that less milk is produced. Since pumping stimulates the flow of milk, it is important to use the pump for a shorter time than the duration of feeding the baby. Gradually, milk production will decrease and eventually stop completely.
Check out the Natural Motion Electronic Breast Pump, which combines nipple stimulation and pumping like a baby does for natural and gentle pumping.
3. Reduce the number of daily feedings by one every week. We recommend eliminating one of the daily feedings each week, such as feeding at noon or at another time, depending on which one the child likes the least. The latter, as a rule, exclude feeding before bedtime and immediately after waking up.
During the weaning period, the mother's breasts will continue to produce milk until she completely stops breastfeeding.
During this period, mums will love these soft bra pads to keep their clothes dry and clean all day long.
Check out this Natural bottle with an ultra-soft, breast-like nipple to help make the transition from breast to bottle easier.
4. Extra hugs may be needed. In addition to the physical changes that stopping breastfeeding brings, moms and babies will also experience emotional changes. During this period, you should hug the baby more often and express your love to him. Caress and other acts of love can help mother and baby retain the closeness and togetherness that breastfeeding has given them.
5. Introduce complementary foods at your baby's usual feeding times. Another way to help your baby adjust to change is to give him complementary foods at his usual feeding times. Babies who are a year old or older can substitute cow's milk for breast milk or offer other foods if the baby has already switched to solid foods.
We also recommend watching the webinar "How to End Breastfeeding Comfortably and Painlessly: Tips and Tricks".
Although weaning is the natural end to breastfeeding, a mother can make a huge difference in her baby's life at this stage. Along with a new sense of pride in a child who is growing and developing, it is quite natural for a mother to feel sadness. Breastfeeding creates a special bond between mother and baby. Therefore, breastfeeding mothers often find it difficult to say goodbye to breastfeeding.
If you have any questions, be sure to contact a specialist to get his opinion.
Philips Avent Articles & Tips
Baby+ App
Download the app and track your baby's development and growth with trackers and keep those special moments forever.











