When to feed baby solids after breastfeeding
Breastfeeding FAQs: Solids and Supplementing (for Parents)
Breastfeeding is a natural thing to do, but it still comes with its fair share of questions. Here's what you need to know about about introducing formula, solids, and more.
Is it OK to Give My Baby Breast Milk and Formula?
Breast milk is the best nutritional choice for babies. But in some cases, breastfeeding (or exclusive breastfeeding) isn’t possible or an option. What’s best for your baby's health and happiness is, in large part, whatever works for your family. So if you need to supplement, your baby will be fine and healthy, especially if it means less stress for you.
Babies who need supplementation may do well with a supplemental nursing system. This is when moms place a small tube by their nipple that delivers pumped milk or formula while a baby is breastfeeding.
Babies also can get pumped milk or formula by bottle. But it’s a good idea to wait until your baby has gotten used to and is good at breastfeeding. Lactation professionals recommend waiting until a baby is about 3-4 weeks old before offering artificial nipples of any kind (including pacifiers).
If I Give My Baby Formula, How Do I Start?
If you're using formula because you're not producing the amount of milk your baby needs, nurse first. Then, give any pumped milk you have and make up the difference with formula as needed.
If you're stopping a breastfeeding session or are weaning from breastfeeding altogether, begin to replace breastfeeding with bottle feeds. As you do this, pump to reduce uncomfortable engorgement. Engorgement is when your breasts overfill with milk and other fluids and get painful, swollen, warm, or hard. This can lead to problems with plugged ducts (when the ducts won’t drain well or at all) or a breast condition called mastitis.
When you reduce the number of nursing sessions, your milk supply will decrease. Your body will adapt to produce just enough milk to fit your new feeding schedule.
How Might a Diet With Formula Affect My Baby?
Starting your breastfed baby on formula can cause some change in the frequency, color, and consistency of your baby’s poop. Be sure to talk your doctor, though, if your baby has trouble pooping.
If your baby refuses formula alone, you can try mixing some of your pumped breast milk with it to help the baby get used to the new taste.
Is it OK for Me to Give My Baby the First Bottle?
If possible, have someone else give the first bottle. This is because babies can smell their mothers and they're used to receiving breast milk from mom, not a bottle. So try to have someone else — like a caregiver or partner — give the first bottle.
Also consider being out of the house or out of sight when your baby takes that first bottle, since your little one will wonder why you're not doing the feeding as usual. Depending on how your baby takes to the bottle, you might need to keep doing this until your baby gets used to bottle feeding.
If your baby has a hard time adjusting to this new form of feeding, be patient and keep trying. Talk to your doctor if you have questions.
Does My Breastfed Baby Need Supplements?
Breast milk contains many vitamins and minerals. But it’s a good idea to give a daily supplement for some nutrients that may be lacking. It all depends on your baby’s age.
Here are some guidelines:
- Vitamin D. Breastfed babies need to take a daily vitamin D supplement. Vitamin D is added to infant formulas. Vitamin D is made by the body when the skin is exposed to sunlight, but it is not safe for infants under 6 months to be in direct sunlight. (After 6 months, use sunscreen when in the sun to protect your baby’s sensitive skin).
- Iron. Iron is a mineral found in breastmilk during the first 4 months of life. After that, babies need an iron supplement until they begin eating enough iron-rich foods (such as cereals or meats) when they’re around 6 months old.
 If your baby gets a mix of breast milk and iron-fortified formula, talk to your doctor about whether your little one needs a supplement. After they start on solids, some babies still need iron supplements if they don’t eat enough iron-rich foods. You doctor can tell you if your baby is getting enough iron.
If your baby gets a mix of breast milk and iron-fortified formula, talk to your doctor about whether your little one needs a supplement. After they start on solids, some babies still need iron supplements if they don’t eat enough iron-rich foods. You doctor can tell you if your baby is getting enough iron. - Fluoride. Babies younger than 6 months do not need a fluoride supplement. After your baby is 6 months old, you can start supplementing with fluoride if your water supply lacks fluoride. Well water, bottled water, tap water in some communities, and ready-to-feed formulas do not have fluoride.
It’s important to find out if your water supply has fluoride in it. You can ask your doctor, dentist, or local water utility agency if the water in your community is fluoridated. Giving a child too much fluoride can cause white marks on the teeth, so there is no need to give a fluoride supplement if your child gets enough fluoride from water.
When Should I Introduce Solid Foods?
The best time to introduce solid foods is when your baby has the skills needed to eat, usually between 4 and 6 months of age.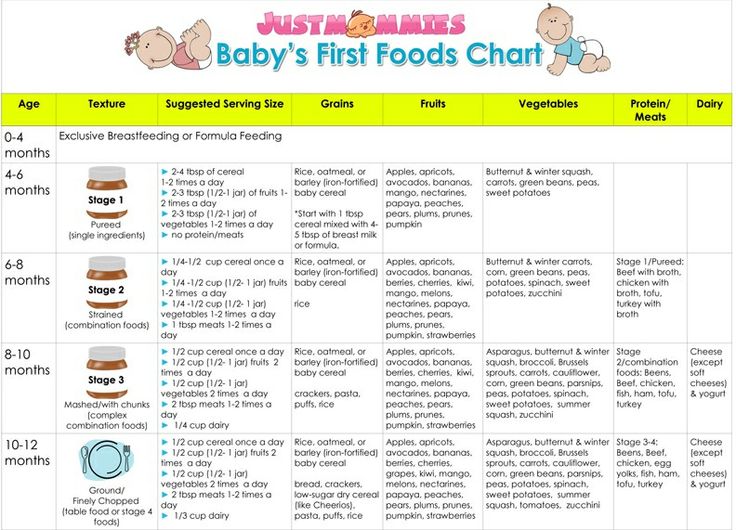 This is when your baby:
This is when your baby:
- has good head and neck control
- can sit up
- has lost the tongue-thrust reflex (which causes babies to push food out of the mouth)
- has the motor skills needed to transfer food to the back of the mouth to swallow
- shows an interest in food (by watching others eat, reaching for food, or opening the mouth as food approaches)
By this age, babies usually weigh twice their birth weight, or close to it.
Wait until your baby is at least 4 months old and shows these signs of readiness before starting solids. Many babies exclusively breastfeed until 6 months of age, which is perfectly healthy.
Babies who start solid foods before 4 months are at a higher risk for obesity and other problems later on. They also aren't coordinated enough to safely swallow solid foods and may choke on the food or inhale it into their lungs.
How Should I Start Solids?
When the time is right, start with a single-grain, iron-fortified baby cereal. Rice cereal has traditionally been the first food for babies, but you can start with any you prefer. Start with 1 or 2 tablespoons of cereal mixed with breast milk, formula, or water. Never add cereal to a baby's bottle unless your doctor recommends it.
Rice cereal has traditionally been the first food for babies, but you can start with any you prefer. Start with 1 or 2 tablespoons of cereal mixed with breast milk, formula, or water. Never add cereal to a baby's bottle unless your doctor recommends it.
Another good first option is an iron-rich puréed meat. Feed your baby with a small baby spoon.
At this stage, solids should be fed after a nursing session, not before. That way, your baby fills up on breast milk, which should be your baby's main source of nutrition until age 1.
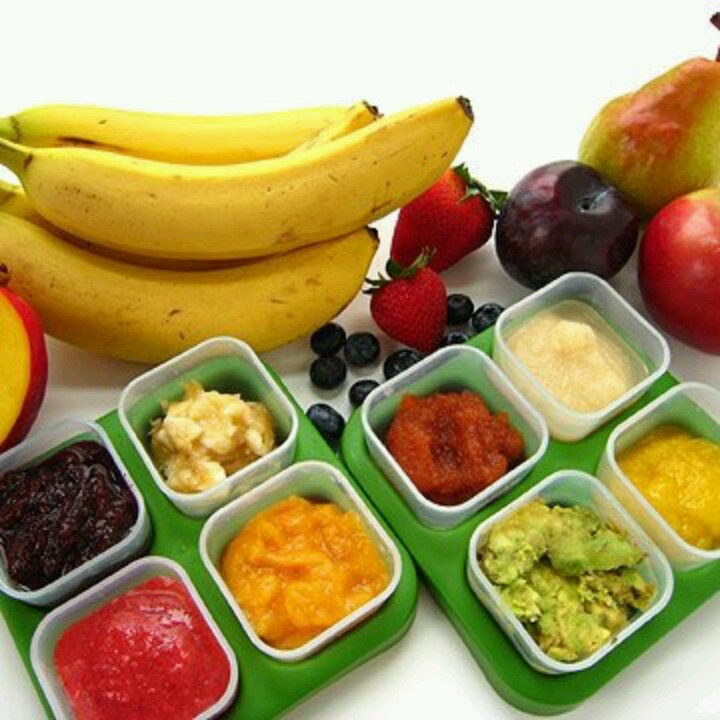
When your baby gets the hang of eating the first food, introduce others, such as puréed fruits, vegetables, beans, lentils, or yogurt. Wait a few days between introducing new foods to make sure your baby doesn't have an allergic reaction.
Experts recommend introducing common food allergens to babies when they're 4–6 months old. This includes babies with a family history of food allergies. In the past, they thought that babies should not get such foods (like eggs, peanuts, and fish) until after the first birthday. But recent studies suggest that waiting that long could make a baby more likely to develop food allergies.
But recent studies suggest that waiting that long could make a baby more likely to develop food allergies.
Offer these foods to your baby as soon as your little one starts eating solids. Make sure they're served in forms that your baby can easily swallow. You can try a small amount of peanut butter mixed into fruit purée or yogurt, for example, or soft scrambled eggs.
When Can I Give My Baby Water?
In their first few months, babies usually don't need extra water. Breast milk and formula supply all the fluids that your baby needs. On very hot days, most babies do well with extra feedings.
When your baby starts eating solid foods, you can offer a few ounces of water between feedings, but don't force it.
What About Juice?
Fruit juices are not recommended for babies. Juice offers no health benefits, even to older children. Juice can fill them up (leaving little room for more nutritious foods), promote obesity, cause diarrhea, and even put a baby at risk for cavities when teeth start coming in.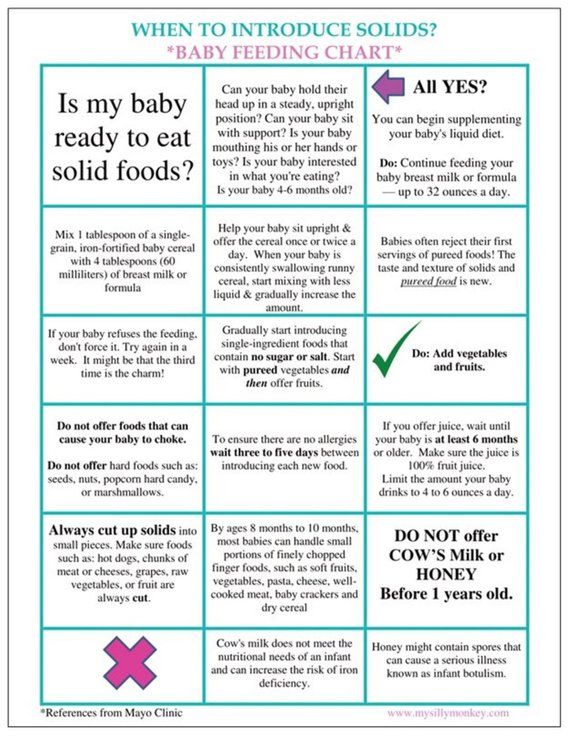
Starting Solid Food - La Leche League GB
Human milk is the perfect first food
Introducing your baby to other foods is a big milestone, and can be fun too. The simplest approach is to continue your usual breastfeeding pattern and let your baby join you at family mealtimes. Your baby will be able to learn about new foods gradually and in their own time.
Signs of readiness for complementary foods
Babies begin eating solid foods according to their own unique timetables, just as they will walk and talk when they are ready. Readiness to try new foods is just another developmental step and it isn’t necessary to do anything special.
Babies show signs of readiness for complementary foods (to complement their milk intake) around the middle of the first year.
Although previous research suggested that signs of readiness for starting solids were related to developmental changes which happen at around 4 months, recent research indicates the following signs of readiness:1
Fact: Ability to sit up well when supported
Once your baby can sit up well when supported (for at least a few minutes) let them join you at family mealtimes and allow them to pick up food.
Fact: Loss of the tongue thrust reflex
Babies who have not yet lost their tongue thrust reflex will push food out of their mouth with their tongue. The tongue thrust reflex is a sign that they are not developmentally ready for solid food.
Fact: Ability to pick up food, put it in their mouth and chew
A baby who is able to reach out and grab a piece of food, then bring it to their mouth and chew it is generally ready for solids. Research indicates that the ideal time to start solid food in terms of oral-motor developmental readiness is between six and eight months. As with other developmental stages, babies learn to chew when they are ready, not because solid food has been introduced by six months.
Myth: Breastfeeding more often
Your baby may ask to breastfeed more, yet still not be ready for solid food. They may just be unwell, having a growth spurt, teething, or reacting to stress. Offering your baby both breasts during each feed may be all that is needed.
Myth: Waking at night
Waking at night is normal and common behaviour and is not a sign that a baby is ready to start other foods even if they have previously slept for longer periods.
Myth: Watching you eat
Babies are interested in and want to copy what they see around them, so watching others eat does not necessarily mean they are ready to start eating solid foods.
Why follow your baby’s cues?
Human milk is the most important food in your baby’s diet during their first year, providing them with most of the calories and fluids they need, as well as a wide range of nutrients. Allowing solids to replace breastmilk too quickly may lead to undernutrition, imbalance of nutrients, or poor weight gain. Breastfeeding continues to be a valuable source of nutrition and calories if your baby is unwell or teething, and doesn’t want to eat solid food.
Breastfeeding provides your baby with antibodies, other immune factors, stem cells, and many other components unique to breastmilk. Breastfeeding alongside introducing solids helps to prevent harmful bacteria, such as E.coli, growing in your baby’s gut. Replacing your milk with solid food too early reduces the level of protection they receive.
Breastfeeding alongside introducing solids helps to prevent harmful bacteria, such as E.coli, growing in your baby’s gut. Replacing your milk with solid food too early reduces the level of protection they receive.
Developmental readiness inside and out
Your baby’s digestive system gradually matures during the first six months. Introducing solids when your baby is developmentally ready means they will be able to eat and digest these new foods.
Preterm babies, babies with special needs or developmental delay may not be ready for solids until later than six months. Following their readiness signs will help you know when to offer solids. Speak to your baby’s healthcare team regarding their individual nutritional needs.
Carry on breastfeeding
Starting solid food is a new experience for your baby and is about taste, texture and learning new skills, not about replacing your milk. Babies are more likely to try something new if they aren’t too hungry – they may refuse solids when they really want to breastfeed. Remember that your baby isn’t likely to eat very much to start with.
Remember that your baby isn’t likely to eat very much to start with.
You may feel pressured into limiting breastfeeds so that your baby will take more solid food, but this can have the opposite effect. If your baby is happy and content after a breastfeed they may be more open to the idea of trying some new foods.
Breastmilk gradually and gently introduces babies to the foods their mother eats because traces of those appear in her milk. This provides a variety of flavour experiences in a natural way, helping prepare the baby for the foods they will eat at the family table. Babies will want to eat whatever food is on the table, so this is a good opportunity to review the whole family’s diet.
First tastes
Baby–led weaning
The principle behind baby-led weaning is that babies will instinctively start to feed themselves when they are developmentally ready, given the opportunity. The skills to feed themselves and readiness of their body to process food occur naturally and do not need to be taught.
Babies who are in control of feeding themselves (in contrast with spoon feeding) will only be able to pick up food, put it in their mouth and chew it when they are developmentally ready. This approach also lets babies determine which foods and how much they want to eat: they will naturally progress at their own pace and reduce breastfeeds when they are ready.
Allowing babies to join in with family mealtimes will expose them to a wide variety of different foods, enable them to copy how other children and adults eat, and help make eating a pleasant experience, encouraging a positive lifelong relationship with food. A baby who is allowed free choice of good, nutritious foods tends to balance their own diet.
For more information on baby-led weaning, see book Baby-led Weaning: The Essential Guide (2019).
How to present food – shapes and sizes
Babies love to use their hands, so offer foods that they can easily hold and put into their mouth. Until they have developed a pincer grip, babies can’t pick up small pieces of food. Offer sticks or pieces of food the shape/size of an adult’s finger. Most 6-month-old babies will be able to pick up the piece, hold it in their fist and gnaw the end sticking out of their fist.
Offer sticks or pieces of food the shape/size of an adult’s finger. Most 6-month-old babies will be able to pick up the piece, hold it in their fist and gnaw the end sticking out of their fist.
Softer foods can be spread on unsalted oat cakes, rice cakes or crackers, or dipped into with a suitable piece of food so your baby can manage by themselves. For tastes of soup, yoghurt or porridge, offer your baby a spoon with a small amount of food on, or let them dip their fingers in and lick off the food.
Different tastes and textures
It is important to offer your baby a wide variety of different foods as this will expose them to a range of tastes and textures. The ability to explore the different taste, texture,colour and smell of food may help babies to have a healthier relationship with food.
Aim to offer tastes of a wide variety of foods in as close to their natural state as possible. Given access to a range of food groups, your baby will show you what they need.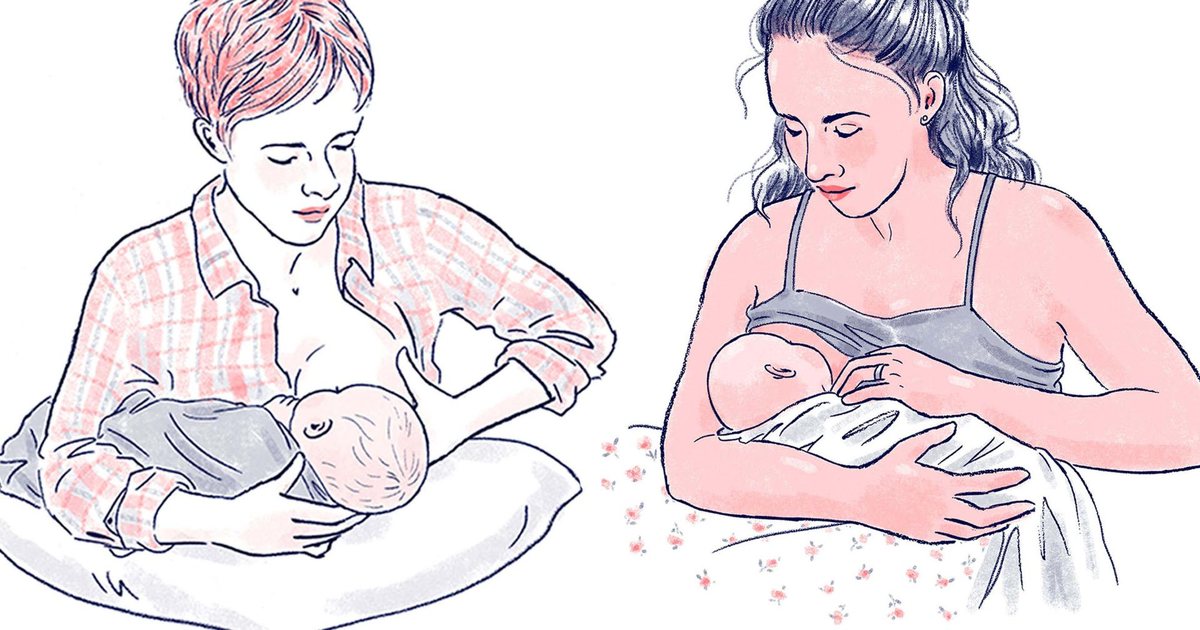 If they don’t want a certain food, try something else, but do offer it again.
If they don’t want a certain food, try something else, but do offer it again.
You don’t need to purée foods or even mash them. Puréeing often requires liquid to be added, diluting the nutritional content. Solid (un-mashed) food aids development of chewing skills, which babies don’t get from sucking puréed food. Early exposure to different textures can also prevent a baby refusing to eat lumpy food later on.
Gagging and choking
Gagging happens when food triggers a baby’s gag reflex and the food is pushed forwards to prevent it from blocking the airway. A baby gagging will usually be calm and breathing normally. Gagging is a natural protective mechanism to prevent choking and usually doesn’t need any intervention.
Choking happens when a baby’s airway is (fully or partially) blocked and they can’t breathe. A baby choking will be coughing or silent (unable to make any noise), not breathing, and their face or lips may change colour. Choking is an emergency and they may need first aid to clear the blockage.
Choking is an emergency and they may need first aid to clear the blockage.
Babies are less likely to choke on food if they are sitting upright and feeding themself. Research shows baby-led weaning is not associated with an increased risk of choking.2
Certain foods are a choking risk for children under three years of age and should be avoided, including whole grapes, whole cherry tomatoes, popcorn, large amounts of peanut butter and any food that could break off in large chunks, such as raw carrot, hard apple or celery sticks. Nuts are a choking risk up to five years of age.
At first, you may want to check your baby’s mouth for unswallowed food after a meal, including their cheeks and palate. Never leave your baby alone with food or when they are eating.
Plan for a little mess!
Solid foods are another part of the world your baby is exploring and they will do this as much by touch and smell as by taste. This can be messy, but is an important learning experience for them. To make cleaning up easier, roll up their sleeves, use a bib or apron and put a clean plastic cloth on the floor so you can safely re-offer dropped foods.
To make cleaning up easier, roll up their sleeves, use a bib or apron and put a clean plastic cloth on the floor so you can safely re-offer dropped foods.
Natural appetite control
It is normal for your baby’s appetite to go up and down over the course of days, weeks and months. Don’t worry. Just offer more of any food they ask for and stop when they don’t want any more. There is no need to ‘top them up’ with a spoon if they haven’t eaten much at a meal. Allowing a baby to feed themselves and take their time over a meal helps them to tune in to their feelings of fullness and to stop eating, which is important throughout their life.
If your baby refuses food, they are not rejecting you or your efforts. They may simply not be hungry. If they are ill or teething, unrestricted breastfeeding will ensure they receive good nutrition and will comfort them until they feel well and interested again.
Allergy & Food Intolerance
Common allergens
The most common allergens (in order of incidence) are:
- Milk and other dairy products such as butter, yoghurt, cheese, whey, casein, caseinate, lactose
- Egg
- Peanut and tree nuts (almonds, hazelnuts, walnuts, cashews, etc.
 )
) - Soy
- Wheat
- Fish and Shellfish: crustaceans (e.g. crab, lobster, crayfish, shrimp, prawn), molluscs (e.g. mussels, oysters, squid)
- Sesame seeds (in tahini and hummus)
- Lupin/lentils (including chickpeas which are in hummus)
- Fenugreek (closely related to peanuts)
- Celery and celeriac
- Mustard
Introducing peanut and egg
Peanut and hen’s egg are common allergens for babies. Current guidance recommends that foods containing peanut or hen’s egg need not be differentiated from other solid foods and can be introduced from around 6 months along with other foods.
The deliberate exclusion of peanut or hen’s egg beyond 6 to 12 months of age may increase the risk of allergy to the same foods. Once introduced, and where tolerated, these foods should continue to be part of your child’s usual diet. If initial exposure is not continued as part of your child’s usual diet, then this may increase the risk of sensitisation and subsequent food allergy. 3
3
Eczema
If your baby has eczema, suspected food allergy, or a family history of food allergy you may wish to seek medical advice before introducing allergenic foods. If eczema is well-controlled (i.e. mild or cleared), it is easier to assess your baby’s tolerance to new foods.
Offer allergenic foods in very small amounts and watch carefully for any symptoms of an allergic reaction. If eczema becomes difficult to manage after food introduction, stop the allergen and seek medical advice.
Allergic reactions and symptoms to watch for
In very rare cases allergy can cause a severe life-threatening reaction called anaphylactic shock. If your baby has a severe and immediate allergic reaction, which may include swelling of the lips, tongue, eyes or face, seek emergency medical care.
Food sensitivity reactions can include eczema, nettle rash (urticaria), a sore bottom, wheezing, asthma, colic, vomiting, constipation and diarrhoea. If a food causes a mild reaction, talk to your health visitor or doctor about whether you should continue to give it. For further information, see Allergies & Food Intolerances.
If a food causes a mild reaction, talk to your health visitor or doctor about whether you should continue to give it. For further information, see Allergies & Food Intolerances.
Nutrition Requirements
Vitamins and minerals
The UK Department of Health recommend that all babies be given supplements including vitamins A, C and D from 6 months, and a vitamin D supplement from birth for breastfed babies and those receiving less than 500ml of formula per day.4
Iron
A healthy full-term baby has sufficient iron stores at birth, and delayed cord clamping helps to increase a baby’s iron levels. Iron is present in human milk and bioavailable to the baby, which is sufficient for the first 6 months of a baby’s life. Introduce iron rich foods from six months such as meat, poultry, fish, egg, pulses/legumes (e.g. chickpeas and lentils) and fortified cereals.
Vitamin D
This is produced when our bodies are exposed to sufficient sunlight. Wearing clothes and suncream to protect against skin cancer limits how much vitamin D we can produce. Vitamin D supplements are particularly important for babies who have limited exposure to sunlight and for babies with darker skin colour living in the UK. Breastmilk doesn’t contain high levels of vitamin D as, in the past, babies would absorb most of their vitamin D from exposure to sunlight.
Wearing clothes and suncream to protect against skin cancer limits how much vitamin D we can produce. Vitamin D supplements are particularly important for babies who have limited exposure to sunlight and for babies with darker skin colour living in the UK. Breastmilk doesn’t contain high levels of vitamin D as, in the past, babies would absorb most of their vitamin D from exposure to sunlight.
Vitamin B12
This is found in animal protein. Your baby may need vitamin B12 supplements if you eat a strict vegetarian or vegan diet.5
Nutritional needs of preterm babies
A premature baby does not have a good iron store at birth. If your baby was born before 34 weeks, they may already be receiving iron, zinc and vitamin supplements. Your preterm baby’s healthcare team will be able to give more specific guidance regarding their individual nutritional needs.
Good First Foods
Offering your baby a wide variety of foods in as close to their natural state as possible will ensure they receive a range of nutrients. Highly processed, low-fat or ready-prepared adult foods are not suitable for babies. You don’t need to buy ready-prepared baby food. These foods are expensive, often come in over-large portions and may contain added ingredients your baby doesn’t need. If you choose to buy convenience foods, check labels carefully.
Highly processed, low-fat or ready-prepared adult foods are not suitable for babies. You don’t need to buy ready-prepared baby food. These foods are expensive, often come in over-large portions and may contain added ingredients your baby doesn’t need. If you choose to buy convenience foods, check labels carefully.
To preserve nutrients as much as possible, bake, steam or cook foods in water. Take out a small portion for your baby before adding any salt or sugar to the rest. Allow it to cool to a suitable temperature. Offering finger foods avoids the need to add extras your baby may not be ready for, such as milk or butter.
Note: Some foods can trigger allergic reactions in some babies. See further down this article for more information.
| Food | Serving Suggestion | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Vegetables (e.g. carrot, pea, sweet potato, potato) | Cook lightly to soften if needed. Give sticks or adult finger-sized pieces.  | Remove skin if needed. Avoid small chunks of raw hard vegetables, such as carrots, which could cause choking. |
| Fruit (e.g. apple, banana, avocado) | Give your baby a whole fruit or large piece to hold. | Remove skin and stones if needed. Small chunks can cause choking |
| Poultry (e.g. chicken) Meat | Give large pieces of lean cooked meat, moisten with meat juices. | Make sure to remove any bones and gristle. |
| Fish | Poach in a little water (no salt) or oven bake. | Check carefully for bones. Fish can be allergenic so introduce it with caution. Don’t introduce shellfish, smoked fish or pickled fish until your baby is over 12 months. |
| Rice cakes Oat cakes Crackers | Spread soft foods on, or use them for dipping. | Plain, unsalted rice cakes, oat cakes and crackers are useful alternatives to rusks. |
| Beans Lentils | Cooked beans and lentils can be mashed to make a spread or dip.  | Cook all beans and lentils thoroughly. |
| Dried fruit | Cut up larger fruits such as apricots. Apricots and prunes can be cooked in a small amount of water to make a nutritious spread. | Although rich in nutrients, dried fruit can stick to teeth and if given frequently can cause tooth decay even if you clean your baby’s teeth regularly. |
| Wholegrain cereals such as oats, corn (maize) and wheat | Can be cooked with water, without salt, sugar or sweetener. Choose unsweetened breakfast cereals. | Most cereals contain a protein called gluten, a potential sensitizer, so avoid mixed-grain cereals until you know your baby can tolerate each one individually. |
| Bread Pasta Rice | Bread and pasta are easy finger foods. Serve pasta plain, with butter or grated cheese. | Avoid pasta made with eggs until you know your baby can tolerate egg. |
| Cottage cheese, yoghurt, fromage frais, butter, unprocessed cheese | Your baby can use a spoon or their fingers.  Useful with cooked vegetables. Grate cheese or serve slices. Useful with cooked vegetables. Grate cheese or serve slices. | Use unsalted butter. |
| Eggs | Can be served scrambled, boiled, poached, in an omelette, etc. | If lion-stamped, egg can be served raw. Otherwise, cook until both white and yolk are solid. |
| Nuts and seeds (e.g. peanut butter, tahini) | Should be spread thinly. Only use smooth varieties. | Never give whole nuts or seeds until 5 years of age. Crunchy nut butter varieties can cause choking. |
Foods to avoid
Salt can overload a baby’s system and too much can cause kidney failure. Highly salted foods may foster a taste for salty foods. Avoid and minimize the use of processed foods, packet mixes, crisps, savoury snacks, gravy and condiments such as ketchup, yeast extract, mustard and brown sauce. When buying convenience foods look for low salt versions, including tinned beans and vegetables canned only in water.
White sugar contains virtually no nutrients and is a major factor in tooth decay. When checking food labels watch for other names for sugars – such as glucose, dextrose, sucrose, corn syrup and fructose. Molasses, maple syrup and honey are also almost pure sugar and can displace healthy nutritious foods. Many processed foods which are advertised for babies have high sugar content and should be avoided, including teething biscuits and baby rusks.
Honey may contain botulism spores and should not be given to babies younger than one year.
Teething biscuits are often high in sugar. Your baby can teethe using anything hard and safe to chew on, including unsalted rice cakes or crusty bread.
Artificial sweeteners are present in many processed foods and drinks aimed at babies and children, including juice drinks, ready meals and jars, and snack foods. Children who eat food with artificial sweeteners may be more likely to develop a ‘sweet tooth’ and a preference for sweet food in later life.
Children who eat food with artificial sweeteners may be more likely to develop a ‘sweet tooth’ and a preference for sweet food in later life.
Artificial flavourings and food colouring are unnecessary chemicals.
Foods high in saturated fats. While babies need fats in their diet, foods containing unnecessary saturated fats, such as fried foods, should be offered only in moderation.
Very hot spicy food. Many babies like spicy food, but very hot spices, especially chillies, may be unpleasant for a baby.
Shark, swordfish and marlin all contain high levels of mercury.
Drinks
Water, human milk and formula are the only recommended drinks until 1 year old.
At mealtimes offer some plain tap water in a baby-sized (shot glass size) cup. You don’t need to use bottles or spouted cups but, if you do, a free flow cup is better than one with a non-spill valve on which a baby needs to bite to get the drink to flow.
Avoid juices, sugary drinks and those with artificial sweeteners. Even unsweetened juices contain natural fruit sugars and acids that can damage teeth. They can leave no room for nutritious foods and it can be hard to limit them once you start them.
Avoid giving bottled water, which may have high mineral levels, and drinks that contain caffeine. This includes fizzy and other soft drinks, tea and coffee.
Can I offer cow’s milk as a drink?
Cow’s milk is not suitable as a drink until after 12 months. Instead offer water, human milk or formula. However, you can use cow’s milk when cooking for your baby, for example in porridge and sauces. Other dairy products can be offered to your baby as a food e.g. cheese, yogurt, cream.
After 1 year of age, cow’s milk can be given as a drink. Follow-on and toddler formulas are not necessary.
Further Reading
The Womanly Art of Breastfeeding. LLLI. London: Pinter & Martin, 2010.
My Child Won’t Eat. González, C. MD. London: Pinter & Martin, 2020.
Baby-Led Weaning The Essential Guide. Rapley, G. & Murkett, T. Experiment, 2019.
Why Starting Solids Matters. Brown, A. Pinter & Martin, 2017.
Starting Solids DVD. LLLGB, 2007.
How Weaning Happens. Bengson, D. Schaumburg, IL: LLLI, 1999.
LLLGB articles (and Leaflets & Information Sheets available from our LLLGB Shop)
Allergy and Food Intolerance
Amazing Milk
Thinking of Weaning?
Still Nursing
Toddlers and Food
Online Information
First Steps Nutrition Trust firststepsnutrition.org/ eating-well-infants-new-mums
NHS: Your baby’s first solid foods
Start 4 life nhs.uk/start4life/weaning/safe-weaning
Unicef unicef.org/nutrition
GP Infant Feeding Network gpifn.org.uk/introducing-solids/
References
1Why Starting Solids Matters. Brown, A. Pinter & Martin, 2017.
2LLLGB: Baby-led weaning and choking
3Scientific Advisory Committee on Nutrition. Feeding in the First Year of Life, July 2018:
4NHS: Vitamins for Children
5NHS: Vegetarian and vegan diets Q&A
How to introduce complementary foods while breastfeeding: Monthly chart
Reviewer Kovtun Tatiana Anatolievna November 24, 2021
Login or register to save articles and products to your favorites
Before every parent one day the question arises - how to introduce complementary foods for months and do it right?
When to start complementary foods
The question of the timing of the introduction of complementary foods is still debatable. Over the past decades, doctors have agreed that the introduction of complementary foods with any type of feeding should be started at 4-6 months. However, the principle of an individual approach to each child remains unshakable in the organization of complementary foods. There are quite a few factors that affect the age of the first complementary foods. Therefore, before giving your baby new products, you should consult a pediatrician [1, 2] .
Over the past decades, doctors have agreed that the introduction of complementary foods with any type of feeding should be started at 4-6 months. However, the principle of an individual approach to each child remains unshakable in the organization of complementary foods. There are quite a few factors that affect the age of the first complementary foods. Therefore, before giving your baby new products, you should consult a pediatrician [1, 2] .
The order of introduction of products is also determined individually. So, for example, porridge is recommended to be administered first with a lack of body weight. If the baby's weight is normal or in excess, it is better to start with vegetable puree. However, these recommendations should be based only on the opinion of the pediatrician.
Which products should be preferred: ready-made or homemade
Experts answer this question as follows: let's say any option, depending on the individual conditions, developmental characteristics and health status of the baby, the capabilities and desires of the family. However, the decision must also be made after consultation with your pediatrician. Industrial products have a number of advantages. Firstly, for their preparation only safe raw materials are used, which pass all the necessary checks and quality control. In addition, for the manufacture of baby food, technologies are used that meet all hygienic standards. Secondly, when developing their composition, the required level of grinding is taken into account. Thirdly, specialists who are responsible for safety are involved in the manufacture of complementary foods.
However, the decision must also be made after consultation with your pediatrician. Industrial products have a number of advantages. Firstly, for their preparation only safe raw materials are used, which pass all the necessary checks and quality control. In addition, for the manufacture of baby food, technologies are used that meet all hygienic standards. Secondly, when developing their composition, the required level of grinding is taken into account. Thirdly, specialists who are responsible for safety are involved in the manufacture of complementary foods.
Where to start complementary foods
Dairy-free cereals
For the first acquaintance with grain products, rice or buckwheat baby porridge is suitable. It is better to give preference to cereals of industrial production. Despite the great desire of parents to cook porridge on their own, it must be understood that during cooking, cereals can lose a number of important nutrients. Instant cereals, that is, soluble, are distinguished by the fact that during their production the substances necessary for a small organism are preserved. In addition, the required degree of grinding is taken into account and observed at the baby food production plant.
In addition, the required degree of grinding is taken into account and observed at the baby food production plant.
Vegetables
It is better to start complementary foods with one-component puree of broccoli, cauliflower or courgettes [1] . All these products should be introduced in turn, observing the reaction. If the baby has taken well one type of vegetable, you can offer another, gradually expanding the diet. Experts recommend starting a child's training in vegetables with industrial baby purees. This approach guarantees the safety of the first complementary foods, because their production undergoes a multi-stage test. The FrutoNyanya baby puree contains only natural vegetables, without the addition of starch, salt or preservatives.
Breastfeeding complementary feeding chart by month
These recommendations are generalized and do not take into account the individual characteristics of each child, so the exact scheme and timing of the introduction of complementary foods should be checked with your pediatrician.
| Product names (g, ml) | 4–5 months | 6 months | 7 months | 8 months | 9-12 months |
| vegetable puree | 10 - 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 |
| Porridge | 10 - 150 | 150 | 150 | 180 | 200 |
| Meat puree of industrial production*/boiled meat | - | 5–30/ 3–15 | 40–50/ 20–30 | 60–70/ 30–35 | 80–100/ 40–50 |
| Fruit puree** | 5 - 50 | 60 | 70 | 80 | 90-100 |
| Cottage cheese (not earlier than 5.5 months)*** | - | - | - | 10-40 | 50 |
| Yolk (pcs.) | - | - | ¼ | ½ | ½ |
| Fish puree | - | - | - | 5-30 | 30-60 |
| Fruit juice | - | - | - | 5-60 | 80-100 |
| Kefir and other non-adapted dairy drinks for children | - | - | - | 200 | 200 |
| Baby biscuits | - | 3 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Wheat bread, crackers | - | - | - | 5 | 10 |
| Vegetable oil**** | 1-3 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 6 |
| Butter***** | 1-3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| * without vegetable raw materials added ** not for first foods *** according to indications from 6 months ****added to vegetable puree | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
General rules for the introduction of complementary foods
- Complementary feeding schedule - the age of introduction, the type and amount of products - should be determined by the pediatrician.
 Only a doctor can develop an individual scheme for the first feeding for a baby by months, because he knows about the features of the growth and development of the baby.
Only a doctor can develop an individual scheme for the first feeding for a baby by months, because he knows about the features of the growth and development of the baby. - Complementary foods should be introduced gradually, ½ tsp in the first half of the day, before the main feeding for 5–7 days, increasing the volume in accordance with the age norm. After mastering one type of complementary foods, you can proceed to the next.
- The first complementary foods should be puree-like consistency. Gradually, the dishes should become thicker, and by 8-10 months, pieces may appear in them.
- It is better to introduce new products in the morning, so it is easier to follow the reaction of the baby during the day. After the first “tasting”, you need to carefully monitor the condition of the skin, stool and evaluate the general behavior of the child. If everything is in order, then the body has accepted a new product and you can continue to adapt to it. It is recommended to keep a food diary.

- You need to offer the child complementary foods from a spoon, after checking the temperature of the food - it should correspond to body temperature. During the trial of new products, the baby should be seated in high chair (if the baby is already sitting well). It provides an anatomically correct posture for eating.
- If the child is breastfed, after each feeding during the introduction of complementary foods, it is recommended to apply it to the breast. This will help maintain lactation.
List of sources
1. The program for optimizing the feeding of children in the first year of life in the Russian Federation: guidelines / FGAU "NMIC of Children's Health" of the Ministry of Health of Russia. — M.: b. i., 2019. - 112 p.
2. Borovik T. E., Skvortsova V. A., Netrebenko O. K. Complementary foods in infant nutrition // Pediatrics. Journal them. G. N. Speransky. 2008. No. 4.
Reviewer Kovtun Tatiana Anatolievna
Scientific adviser of PROGRESS JSC, candidate of medical sciences
All expert articles
404
page not found :(
The address was typed incorrectly, or such page
no longer exists on the site.
To main
See also
Child nutritionHow much calcium does a child need?
Calcium deficiency in children is often associated with an increased risk of fractures later in life and stunted growth. However, in reality, the negative consequences of its lack in the body are much greater.
5 important questions new parents ask about food allergies in newborns
Alas, the reality is that among patients with food allergies, doctors even meet children who are not even a month old
First foodHow to introduce fruits into complementary foods
Mother's milk for a baby is ideal nutrition, especially in the 1st year of life.











