2 week old baby wants to feed constantly
My Baby Wants to Breastfeed All the Time! Is This Normal?
Frequent Feeds Are Very Common!
In the first few days after birth, it is very common for newborns to feed constantly, probably around 12 or more times per 24 hours. Newborn babies drink very small amounts frequently in the first 1-2 days.
Most newborn babies only drink about a teaspoon (5-7ml) of colostrum at each feed on day one. This is just perfect as their tummy is about the size of a cherry and holds about 7mls at each feed on day one! Perfectly designed!
By day two you start to make a little bit more colostrum at each feed and this gradual increase in milk each day stretches bub’s tummy allowing them to drink more.
Colostrum is a sugary delicious drink but it is not jam-packed with fat at this stage, which means baby needs to keep feeding very often to stay full up.
Remember, every time your baby feeds it helps your breasts build your milk supply in the first month. As your milk increases in volume, from around day 3 onwards, you will notice your baby starts to have longer sleep periods of around 1. 5 – 3 hours mostly.
During the first month, newborn babies need to feed on average 8 – 12 times every 24 hours to ensure they are getting enough milk and that you stimulate the breasts enough to keep building your milk supply. One you have established a good milk supply in the first month you may find that your baby changes their feeding pattern again. Many mums report this happens around 6-8 weeks after birth.
After this first month, research has shown us that babies will breastfeed anywhere from 4-13 times every 24 hours, but most babies still feed on average 10-11 feeds every day.
Each mum and baby’s breastfeeding pattern is different and this is perfectly normal. It is just down to the levels of fat in your milk (and fat levels change throughout the day) and the amount of milk your breast can hold at each feed, as well as how your baby is feeling.
Babies Find Breastfeeding Relaxing
Most babies find breastfeeding very comforting and, just like if we feel upset a hug can do wonders. Likewise, a short extra breastfeed does the same for calming our babies!
Likewise, a short extra breastfeed does the same for calming our babies!
Do not compare yourself with another mum and baby’s feeding pattern. It will most likely be completely different from yours. Trying to “force” your baby into strict routines often brings with it tears and stress for mum and bub!
There are, of course, some mums who say that a routine was the best thing for their baby. But these babies are probably the very small percentage of babies who naturally feed every 4-5 hours and would’ve gotten themselves into a strict schedule anyway!
For most babies, a strict routine does not work! Try and go with the flow, listen to your baby’s cues for when they would like a feed and feed them. Just like us, they will not stick to the same “routine” every day.
I bet you didn’t have the same things to eat, in the same quantity, at the same time, with the same glasses of water, cups of tea or snacks as you have today! So why do we think this is normal for our babies?!
Cluster Feeds Continue After the First Few Days
Most mums report that their baby feeds frequently and is unsettled more so during the evening hours, most commonly between 6 – 10pm. Mums often say that their baby wants to be held constantly and feed “all the time” and that baby cries when put down in their cot.
Mums often say that their baby wants to be held constantly and feed “all the time” and that baby cries when put down in their cot.
This is a very normal and common behaviour for babies who are otherwise content during other parts of the day, feeding and gaining weight well and are generally healthy.
Babies do have these periods of cluster feeding, often most present between 2 and 9 weeks of age, but of course some babies will have these periods for several more weeks and still be totally healthy.
Researchers think it is a developmental stage that all babies naturally need to go through. There are a huge number of processes going on in a baby’s brain in the first year. Babies can easily get overwhelmed or dysregulated in the first few months in particular.
Babies who are overtired or overwhelmed, find it hard to calm down by themselves in the first few months of life and need someone to help them. And what better way to be calmed than having a breastfeed, which of course is not just food, but also a pain reliever and a happy hormone giver!
Also, being held and rocked allows baby to feel safe and warm, like being back in the womb. So, it makes sense that they need to be held and fed so much in the evenings after a big day in the big wide world!
So, it makes sense that they need to be held and fed so much in the evenings after a big day in the big wide world!
Normal Can Still Be Tiring!
Even though this is normal, it doesn’t stop it being exhausting. So, it’s important to note how you are feeling and coping.
Some of us have another person around to help us out, whilst other new mums have to manage alone during the cluster feeds. Regardless of your situation, it is important to realise that cluster feeding is normal.
If you are responding to your baby by holding them and feeding them, yet they are still crying in-between feeds you are not causing harm to your baby, you are still showing them love and they will calm when they are able to.
The other thing to remind yourself is that this is temporary. It is important to not place any demands on yourself during these times. Try preparing dinner at times in the day when baby is sleeping well and just re heat and eat when you can during the cluster breastfeeds!
If you have support, share the holding and rocking of baby with another person to give you a break. If you do not have supports around at that time, listen to your instincts; if you are starting to feel like it is all too much and you feel worried that you are not coping, place your baby safely in their bassinet and walk away to calm down for a few minutes, before coming back to hold baby again.
If you do not have supports around at that time, listen to your instincts; if you are starting to feel like it is all too much and you feel worried that you are not coping, place your baby safely in their bassinet and walk away to calm down for a few minutes, before coming back to hold baby again.
You could also try knocking on the door of your neighbour, who you know and trust, and asking them to hold your baby for 15 mins or so to give you a break.
Most people will understand and, if they have children, they will have gone through the same themselves. Doing this will not harm your baby, but, will give you time to relax a little and recharge.
If you are finding that you are not coping during other parts of the day then it is important to talk with your GP or contact PANDA http://www.panda.org.au/ for some extra help and support.
If you are concerned that your baby’s crying seems abnormal and you are worried if your baby may be unwell. Please get first line advice from these helplines (below). They will be able to give you support and further guidance:
They will be able to give you support and further guidance:
Health Direct helpline (covers all of Australia) 1800 882 436
Maternal and Child Health Nurse 24-hour helpline on 13 22 29 (if you are in the state of Victoria)
Other Things Which Can Help to Relax Babies During Cluster Feeding Times
Skin to skin contact
Having a bath with your baby – only do this if you have another person to help you and baby in and out of the bath and keep you both safe.
“Rocking your pelvis like Elvis” – Whilst holding your baby, try some rocking and swaying moves whilst holding baby either upright, over your arm like superman or in a cradle hold. Each baby will be different in the positions they prefer. You Maternal and Child Health nurse can show you positions for holding and calming babies.
Carrying your baby in a sling. This keeps baby nice and close and creates a womb like environment.
As you rock your baby make a loud “shuuusssshhhh” noise. This is actually calming for babies as it mimics the sounds of being inside the womb.
This is actually calming for babies as it mimics the sounds of being inside the womb.
Try taking 5 deep breaths with your eyes closed before breastfeeding baby to ensure you are relaxed and not tense.
Make sure you get extra sleep in the day time, even if you don’t feel like it make sure you lay down in a darkened, quiet room to rest your body and brain. Over the next few days you’ll soon be drifting off to la la land easily.
Lastly, remember that you cannot spoil a baby by holding them too much. All the information about spoiling babies came out of textbooks written in the early 1900’s!
We have known for years and years that holding and listening to your baby’s needs is the best thing to do, yet we still hear this very bad advice! So listen to your gut instinct and cuddle, love and feed your baby as they need it. This phase will pass and get easier over the next few weeks.
For more information head over to our Medela Australia Facebook page.
Do you ever feel like your baby wants to feed all the time, especially at certain times during the day? Let’s have a chat and support each other!
How to Handle a Newborn Constantly Feeding
A newborn constantly feeding can exhaust any parent. Here’s how to handle the cluster feeding, especially when you’re breastfeeding.
Here’s how to handle the cluster feeding, especially when you’re breastfeeding.
I just about had it.
The sore nipples from a bad latch, the cluster-feeding sessions, the leaking—I was over it. I felt glued to my baby and shot dagger eyes at anyone who suggested feeding him the second he’d fuss. I was ready to give up.
And that was just five days in with breastfeeding.
But beyond the physical pain, breastfeeding for many moms is especially hard when your newborn is constantly feeding. Your baby wants to nurse all the time, hungry and unsatisfied despite the frequent nursing.
For instance, within a two-hour time frame, she’s already nursed a whopping four times.
As a first-time mom, you’re curious whether this is normal. If other babies also want to eat within minutes of having been just fed. You wonder whether it’s even possible to overfeed a newborn or if yours is eating too much—especially since she’s constantly wanting to be fed.
How to handle your newborn constantly feeding
Rest assured friend, you’re not alone. And more importantly, your newborn constantly feeding is normal and common.
Known as newborn cluster feeding, frequent feeding is her way of getting your body to produce enough milk, especially during a growth spurt. Think of it as nature’s way of increasing your breast milk supply. After all, the more demand for milk, the more your body will produce.
Plus, she likes to be near you not just for food but for comfort. You smell good, you’re the perfect temperature for her body, sucking is soothing—it’s no wonder she simply wants to be snuggled and fed.
That said, I don’t blame you if you feel exhaustion and even—let’s be honest here—resentment of being the only one able to feed her. I totally understand that feeling of being tied down, and the lack of freedom that a newborn constantly feeding can bring.
So, here are a few practical ways of coping with cluster feedings, both to see if she can gradually wean from them, as well as how to cope in the meantime.
1. Make sure your newborn is emptying the breast
Did you know that breast milk comes in stages? During the first few minutes, your newborn is drinking the fore milk (or the lighter part of the milk). Afterward, she drinks the hind milk (the fattier, more filling part).
If she’s only nursing a few minutes on each side, she might not be getting the hind milk, and ends up hungrier sooner than later.
Instead, make sure she’s emptying the entire breast so she gets both kinds of breast milk from each side. This will help fill her up so she’s able to go longer between feeds.
A simple way to make sure she empties the breast? Don’t let her sleep on the job. Feed her after she wakes up, not before she’s about to sleep, so that she doesn’t doze off during feeding.
Besides making sure she’s emptying the breast completely, offer her both of them as well. That way, not only is she getting both kinds of breast milk, but she’s also getting double the serving.
Free resource: Do you struggle with getting her to sleep? Her awake time just might be affecting how well she sleeps or not. Join my newsletter and get One Mistake You’re Making with Your Baby’s Awake Time—at no cost to you.
Don’t make the same mistakes I did—help her fall asleep with this one simple trick! As one parent said:
“I LOVE your content and want you to know you’re helping so many of us.” -Jordin Edwards
2. Burp between switching sides
Do you find that your baby fusses during feedings, cutting them short? She could be uncomfortable from taking in gas while she eats.
One simple way to eliminate gas is to burp her between switching sides. Simply hold her upright and allow any gas to escape, as well as the food to digest down. Not only are you helping her release gas, you’re also holding her upright, which can prevent spitting up food.
Get more tips on how to burp a baby that is hard to burp.
3. Watch for excessive spit-up
Your newborn could also be extra hungry if she’s not actually taking in the food she had just eaten. In other words, she’s spitting the food right back up.
Like we talked about, holding her upright (especially after a feeding) can help avoid excess spit-up. Make sure you’re also holding her at an angle when you breastfeed to prevent her from feeding flat on her back.
If all else fails, talk with her pediatrician to further discuss health issues or even medicines that can help her stop spitting up so much.
4. Pay attention to weight gain and wet diapers
Your doctor or lactation consultant will know your baby is just fine by making sure she’s gaining the weight she’s supposed to. If you feel like she’s still not feeling satisfied despite frequent feedings, have your doctor check whether her weight gain.
You’ll also want to pay attention to how many wet diapers she goes through. While weight gain is a better gauge of how well your baby is feeding, seeing enough wet diapers can also reassure you that she is, in fact, taking in the milk.
5. Feed on demand
The newborn stage, particularly the early days and weeks, is not the time for a strict feeding schedule. This is when your baby can take a five-hour nap, only to take a 20-minute one next. And the same is true for when and how long she sleeps as well.
While she might cry because of a soiled diaper or uncomfortable pajamas, more often than not, your baby’s hunger is the likely cause. Breast milk digests easily, which means she can be hungrier earlier than formula-fed infants.
And don’t worry that you’re setting her up with “bad habits” by feeding her when she’s hungry. Feeding on demand doesn’t mean she’ll always expect to eat frequently. Instead, she’ll eventually develop her own routine and flow, especially the larger her stomach gets (and the more food she can take).
For now, feed her when she’s hungry, knowing that this is a temporary and important stage in her growth. She knows what her body needs, and this is her way of letting you know she needs to eat.
Learn how to handle a baby feeding every hour and not sleeping.
6. Find a comfortable feeding position
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links, which means I will earn a commission—at no extra cost to you—if you make a purchase.
Perhaps the simplest way to handle your newborn constantly feeding is to make it as comfortable as possible. Sometimes we feel “stuck” in our positions, unable to move around like the rest of the family, making us even more frustrated.
But you can make the most of it by having a comfortable feeding station. Start by using a good nursing pillow and back support. Keep often-used items within arm’s reach, from tissue paper to snacks. Use it as an opportunity to watch a movie, listen to a podcast, or read a book.
And consider creating several feeding stations throughout the house. That way, you won’t feel alone and isolated in, say, your bedroom, while everyone else is enjoying dinner on the other side of the house.
Conclusion
That first month with my newborn was rough. I must have looked online to read the benefits of breastfeeding every single day just to keep going.
But despite the first few days or weeks, breastfeeding does get easier and will happen in longer stretches. Your baby will feel less fragile and can nurse without a pillow. Your nipples will adjust and you won’t need ointment for long. And most importantly, she won’t cluster feed as frequently as she does now.
Still, in the meantime, you can make this stage as easy and smooth as possible. Make sure she’s emptying each breast so she’s getting both kinds of breast milk (as well as emptying both breasts). Burp between switching sides so she doesn’t fuss because of gas and digestive issues.
Watch for excessive spit-up so you know she’s keeping her food in. Pay attention to how many wet diapers she goes through, and confirm with the pediatrician that she’s gaining enough weight. Feed when your baby’s hungry, not from a set schedule.
And finally, find a comfortable feeding station (or a few) so that you’re at least as happy and content as possible.
Don’t worry, mama—she won’t always feed this frequently. Especially if, like me, you’re just five days in and ready to throw in the towel.
Get more tips:
- 5 Tips to Stop the Pain After Breastfeeding
- Burping a Newborn After Breastfeeding: Necessary or Not?
- 6 Ways Dads Can Support Breastfeeding Moms
- 12 Breastfeeding Secrets Every Mom Should Know
- How to Burp a Sleeping Baby
Don’t forget: Join my newsletter and get One Mistake You’re Making with Your Baby’s Awake Time below:
The child asks for food every hour: feed according to the regimen or on demand?
Kizino Polina Aleksandrovna
pediatrician, perinatal psychologist
What should and should not be done if a newborn baby asks for food every hour? Polina Kizino, a pediatrician and leading expert of the Smart Mama online school, gives advice on breast milk and formula feeding, as well as on cluster feeding of an infant, which will help even experienced mothers.
— Polina Alexandrovna, why does the child ask for food every hour?
— A child needs frequent feedings at certain periods of his life and development. Here, the main problem is that often mothers do not distinguish between the child's need for food and his anxiety for other reasons. For them, a fussy baby is always hungry and needs to be fed. But acting by mistake, you can go beyond the norm.
— Is it worth keeping a baby's diet at all and how to avoid overeating?
— When breastfeeding, a baby can suck out different amounts of milk in different feedings and get hungry a little earlier or a little later, so a nursing mother needs to trust the baby more and follow his needs. The mixture stays in the baby's stomach a little longer than breast milk, and to avoid overfeeding, clear intervals between bottles are introduced. Mixed feeding will be a cross between breastfeeding and artificial feeding.
Overeating in a small child is rare. In extreme cases, if so much is eaten that the stomach does not hold food, the baby will spit up an extra amount of milk or formula.
In extreme cases, if so much is eaten that the stomach does not hold food, the baby will spit up an extra amount of milk or formula.
Read also
- How much and how often to feed the baby day and night, and whether to set feeding hours.
How often to feed a newborn
— Why is the baby constantly hungry? And what if he often asks for food at night?
— With night feedings, you need to be careful and careful. When a baby asks for food and is fed every hour, this is called cluster feeding. It is acceptable for one or two days, but if this happens for a long time, it is not normal.
The problem is that frequent "snacking" may be a constant violation of the regime, due to the fact that the baby does not receive enough attention from his mother. He may be full, but he needs to make contact with his mother, kiss her breast and thus relieve his anxiety. Therefore, you need to analyze the situation and try to understand why night feedings occur.
- Is it rational to reduce the amount of milk depending on the intervals between feedings?
— In the first month, you should not increase the intervals: on the contrary, you should try to stimulate lactation so that by the month it becomes mature. When a baby eats every three hours, and the mother suddenly takes a break, for example, at nine o'clock, this can affect the amount of milk later.
The baby is definitely growing. And if he received breasts at intervals of three hours quite regularly, then with the introduction of complementary foods, one feeding goes away, and the break becomes longer. With a systematic and gradual reduction in feeding, milk production adjusts to the rhythm of the baby's nutrition. The alternation of large intervals and frequent applications can negatively affect lactation. The body gets used to the lack of stimulation, and then it will be more difficult to increase the amount of milk in multiple feedings. Therefore, it is better to go to reduce breastfeeding gradually.
— Is feeding according to the schedule always a good thing?
- Feeding at the same time can be both a plus and a minus. Mom is calm, trying to adapt to the children's routine and understands what awaits her in the near future. The baby also adjusts to a certain routine, which gradually prepares him for complementary foods on schedule.
The disadvantages begin when the mother artificially tries to adhere to the regime, not relying on the needs of her baby and not “feeling” him. Even under a regime, allowance must be made for new circumstances. And if a child has a need for food, he does not need to refuse, especially a very small one who still does not know how to wait for physiological reasons.
— How to determine how much to give during one feeding?
- When breastfeeding, it makes no sense to calculate the volume, and it is difficult to measure it. On artificial feeding, the calculation is based on the age and weight of the baby. Usually, the amount of food per day is calculated: it is divided by the number of feedings at the moment. For example, if a child eats every three hours, then the volume is divided by eight or seven, and for older babies - by fewer feedings. Each age has its own formulas and calculations.
Usually, the amount of food per day is calculated: it is divided by the number of feedings at the moment. For example, if a child eats every three hours, then the volume is divided by eight or seven, and for older babies - by fewer feedings. Each age has its own formulas and calculations.
Approximate amount of infant formula by age and frequency of feedings
— How can you tell if a baby is gaining weight?
- We discussed earlier that at each age there are average norms (range) of weight gain. But gains above the norm does not mean the threat of obesity. Physiological features, height-weight proportions of the baby are taken into account. Even if the weight gain prevails over the increase in height, it is still not necessary to restrict the child in nutrition. It is important to meet his nutritional needs and not replace the milk/formula with water or dilute the formula with more water to reduce its calorie content. When nutrition is adequate, and the correct feeding regimen and eating behavior has developed in the family, as the child grows and masters new skills, the child will begin to expend more energy, and the reserves accumulated in previous months will quickly be used up.
— When is it time for an overweight baby to see a doctor?
— Babies under one year old are seen by a pediatrician every month. At the appointment, the doctor can look at more pronounced weight gain and discuss whether the child is active enough for his age or needs stimulation. After all, it happens that babies are ready to crawl and roll over, and parents leave them to sit in a deck chair without the possibility of moving, or children spend a lot of time in a stroller, where they are also unable to realize their motor needs.
Don't forget about endocrine diseases that lead to obesity, although they occur very rarely. If necessary, the pediatrician will prescribe a consultation with an endocrinologist.
— What advice does the World Health Organization give about feeding children?
- WHO says baby should be breastfed on demand. Wants to eat every 40-60 minutes - you need to feed and not wait until he stops asking for a breast or the time between feedings is maintained.
However, a child's anxiety does not always indicate that he is hungry. Breastfeeding is not only about nutrition, but also about interaction. Sometimes breastfeeding becomes a satisfaction of the need not so much for food as for communication. If the child lacks attention, affection, care, then he can ask for a breast much more often, because at the time of feeding he has the opportunity to closely contact his mother.
— What are cluster feedings and why do they occur?
— Cluster feedings have been talked about relatively recently. These are situations when the baby is applied to the breast very often for some time, literally "hanging on the chest" to be with his mother.
Peculiarities of cluster feeding:
- are often observed in babies of the first month of life;
- may appear in two to three months or recur sooner;
- often coincide with growth spurts, when the baby's excitability increases, he learns new skills, receives a lot of information from the outside;
- usually last one or two days, and if it drags on, then it is necessary to analyze the sleep and wakefulness regimen, the presence of overvoltage, the adequacy of the child's nutrition and, if necessary, take measures;
- are not related to the mother's diet - however, in such a rather difficult period, it is desirable that the mother does not have aggravating factors in the form of a strict diet, which will negatively affect her well-being and mood.

A small child depends on his mother. When his level of anxiety rises due to certain changes in the body, he wants his mother to be around as often and as long as possible. Being on his chest for a long time, he calms down. This condition is normal for a child, and there is no need to wait for him to stop asking for breasts or asking for pens. You need to come to terms with the fact that there are such periods in the life of a baby, and organize your life in such a way that frequent cluster feedings do not interfere (slings and other carriers help).
Cluster feedings occur less often on artificial feeding, because the baby does not associate food with mother as closely as with natural feeding. Mom has other ways of interacting with her baby that compensate for communication during feeding. Feeding on such days usually takes place, but the baby spends more time in her arms, and the mother is more actively involved in his life and pays more attention to him.
It is impossible and unnecessary to feed the child chaotically all the time. When breastfeeding, it is important to take into account the needs of the baby and try to choose something between a regimen and its complete absence. Artificial feeding is easier - the ideal regimen depends on the frequency of feeding in accordance with the age and weight of the baby. When a child begins to ask for food every hour, the first thing to decide is whether he is hungry or has some other need. There are times when a baby needs a mother and he needs more communication, a change in position, a feeding place. This is the norm, not a disease that needs to be treated. Mom needs to carefully observe her baby, learn to feel his needs, and everything will be in order.
When breastfeeding, it is important to take into account the needs of the baby and try to choose something between a regimen and its complete absence. Artificial feeding is easier - the ideal regimen depends on the frequency of feeding in accordance with the age and weight of the baby. When a child begins to ask for food every hour, the first thing to decide is whether he is hungry or has some other need. There are times when a baby needs a mother and he needs more communication, a change in position, a feeding place. This is the norm, not a disease that needs to be treated. Mom needs to carefully observe her baby, learn to feel his needs, and everything will be in order.
*The ideal food for a baby is mother's milk. WHO recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months. MAMAKO ® supports this recommendation. Before introducing new foods into your baby's diet, consult with a specialist.
* Breast milk is the best food for babies. WHO recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months of a child's life and continued breastfeeding after complementary foods are introduced until the age of 2 years. Before introducing new products into the baby's diet, you should consult with a specialist. The material is for informational purposes and cannot replace the advice of a healthcare professional. For feeding children from birth. The product is certified.
Before introducing new products into the baby's diet, you should consult with a specialist. The material is for informational purposes and cannot replace the advice of a healthcare professional. For feeding children from birth. The product is certified.
#advice for mom #breastfeeding
See also
Formula-fed regimen
#Advice for Mom
Kizino Polina Alexandrovna
pediatrician, perinatal psychologist
Baby's diet and menu at one year old
#Food #transfer to common table
Shalunova Anastasia Ivanovna
member of the Russian Union of Nutritionists, Nutritionists and Food Industry Specialists
Night feedings of a bottle-fed baby
#Advice for Mom
Kizino Polina Alexandrovna
pediatrician, perinatal psychologist
See all
View all
Night feedings of a bottle-fed baby
# Tips for mom
Kizino Polina Alexandrovna
pediatrician, perinatal psychologist
Formula-fed regimen
# Tips for mom
Kizino Polina Aleksandrovna
pediatrician, perinatal psychologist
See all
View all
View all
Diet and menu for a one year old baby
# Lure # transfer to the general table
Shalunova Anastasia Ivanovna
member of the Russian Union of Nutritionists, Nutritionists and Food Industry Specialists
See all
Top
Breastfeeding in the first month: what to expect
Not sure how to establish lactation and increase milk production? If you need help, support, or just want to know what to expect, read our first month breastfeeding advice
Share this information
The first weeks of breastfeeding are a very stressful period. If at times you feel like you can't handle it, know that you are not alone. Feeding your baby all day long is completely natural and helps produce breast milk, but can be quite tiring at times. Be patient, think about yourself and remember: after the first month, when milk production stabilizes, it will become easier.
If at times you feel like you can't handle it, know that you are not alone. Feeding your baby all day long is completely natural and helps produce breast milk, but can be quite tiring at times. Be patient, think about yourself and remember: after the first month, when milk production stabilizes, it will become easier.
How often should a baby be breastfed?
Babies are born with a small stomach that grows rapidly with increasing milk production: in the first week it is no larger than an apricot, and after two weeks it is already the size of a large chicken egg. 1.2 Let the child eat as much as he wants and when he wants. This will help him quickly regain the weight lost after birth and grow and develop further.
“Be prepared to feed every two to three hours throughout the day. At night, the intervals between feedings can be longer: three to four or even five hours, says Cathy Garbin, a recognized international expert on breastfeeding. Some eat quickly and are satiated in 15 minutes, while others take an entire hour to feed. Do not compare your breastfeeding regimen with that of other mothers - it is very likely that there will be nothing in common between them.
Do not compare your breastfeeding regimen with that of other mothers - it is very likely that there will be nothing in common between them.
At each feed, give your baby a full meal from one breast and then offer a second one, but don't worry if the baby doesn't take it. When the baby is full, he lets go of his chest and at the same time looks relaxed and satisfied - so much so that he can immediately fall asleep. The next time you feed, start on the other breast. You can monitor the order of the mammary glands during feeding using a special application.
Why does the child always ask for a breast?
The first month is usually the hardest time to breastfeed. But do not think that because the baby is constantly hungry and asks for a breast almost every 45 minutes, then you do not have enough milk.
In the first month, the baby needs to eat frequently to start and stimulate the mother's milk production. It lays the foundation for a stable milk supply in the future. 3
3
In addition, we must not forget that the child needs almost constant contact with the mother. The bright light and noise of the surrounding world at first frighten the baby, and only by clinging to his mother, he can calm down.
Sarah, mother of three from the UK, confirms: “Crying is not always a sign of hunger. Sometimes my kids just wanted me to be around and begged for breasts to calm them down. Use a sling. Place the cradle next to the bed. Don't look at the clock. Take advantage of every opportunity to relax. Forget about cleaning. Let those around you take care of you. And not three days, but six weeks at least! Hug your baby, enjoy the comfort - and trust your body."
Do I need to feed my baby on a schedule?
Your baby is still too young for a strict daily routine, so
forget about breastfeeding schedules and focus on his needs.
“Volumes have been written about how to feed a baby on a schedule, but babies don't read or understand books,” Cathy says. - All children are different. Some people can eat on a schedule, but most can't. Most often, over time, the child develops his own schedule.
- All children are different. Some people can eat on a schedule, but most can't. Most often, over time, the child develops his own schedule.
Some mothers report that their babies are fine with scheduled feedings, but they are probably just the few babies who would eat every four hours anyway. Adults rarely eat and drink the same foods at the same time of day - so why do we expect this from toddlers?
Offer your baby the breast at the first sign of hunger. Crying is already the last stage, so be attentive to early signs: the baby licks his lips, opens his mouth, sucks his fist, turns his head with his mouth open - looking for the breast. 4
What is a “milk flush”?
At the beginning of each feed, a hungry baby actively sucks on the nipple,
thereby stimulating the milk flow reflex - the movement of milk through the milk ducts. 5
“Nipple stimulation triggers the release of the hormone oxytocin,” explains Cathy. “Oxytocin is distributed throughout the body and causes the muscles around the milk glands to contract and the milk ducts to dilate. This stimulates the flow of milk.
This stimulates the flow of milk.
If the flushing reflex fails, milk will not come out. This is a hormonal response, and under stress it may not work at all or work poorly. Therefore, it is so important that you feel comfortable and calm when feeding.
“Studies show that each mother has a different rhythm of hot flashes during one feed,” Kathy continues, “Oxytocin is a short-acting hormone, it breaks down in just 30-40 seconds after formation. Milk begins to flow, the baby eats, the effect of oxytocin ends, but then a new rush of milk occurs, the baby continues to suckle the breast, and this process is repeated cyclically. That is why, during feeding, the child periodically stops and rests - this is how nature intended.
The flow of milk may be accompanied by a strong sensation of movement or tingling in the chest, although 21% of mothers, according to surveys, do not feel anything at all. 5 Cathy explains: “Many women only feel the first rush of milk. If you do not feel hot flashes, do not worry: since the child eats normally, most likely, you simply do not understand that they are.
If you do not feel hot flashes, do not worry: since the child eats normally, most likely, you simply do not understand that they are.
How do you know if a baby is getting enough milk?
Since it is impossible to track how much milk a baby eats while breastfeeding, mothers sometimes worry that the baby is malnourished. Trust your child and your body.
After a rush of milk, the baby usually begins to suckle more slowly. Some mothers clearly hear how the baby swallows, others do not notice it. But one way or another, the child himself will show when he is full - just watch carefully. Many babies make two or three approaches to the breast at one feeding. 6
“When a child has had enough, it is noticeable almost immediately: a kind of “milk intoxication” sets in. The baby is relaxed and makes it clear with his whole body that he is completely full, says Katie, “Diapers are another great way to assess whether the baby is getting enough milk. During this period, a breastfed baby should have at least five wet diapers a day and at least two portions of soft yellow stool, and often more. ”
”
From one month until weaning at six months of age, a baby's stool (if exclusively breastfed) should look the same every day: yellow, grainy, loose, and watery.
When is the child's birth weight restored?
Most newborns lose weight in the first few days of life. This is normal and should not be cause for concern. As a rule, weight is reduced by 5-7%, although some may lose up to 10%. One way or another, by 10–14 days, almost all newborns regain their birth weight. In the first three to four months, the minimum expected weight gain is an average of 150 grams per week. But one week the child may gain weight faster, and the next slower, so it is necessary that the attending physician monitor the health and growth of the baby constantly. 7.8
At the slightest doubt or signs of dehydration, such as
dark urine, no stool for more than 24 hours, retraction of the fontanel (soft spot on the head), yellowing of the skin, drowsiness, lethargy, lack of appetite (ability to four to six hours without feeding), you should immediately consult a doctor. 7
7
What is "cluster feeding"?
When a baby asks for a breast very often for several hours, this is called cluster feeding. 6 The peak often occurs in the evening between 18:00 and 22:00, exactly when many babies are especially restless and need close contact with their mother. Most often, mothers complain about this in the period from two to nine weeks after childbirth. This is perfectly normal and common behavior as long as the baby is otherwise healthy, eating well, gaining weight normally, and appears content throughout the day. 9
Cluster feeding can be caused by a sudden jump in the development of the body - during this period the baby especially needs love, comfort and a sense of security. The growing brain of a child is so excited that it can be difficult for him to turn off, or it just scares the baby. 9 If a child is overworked, it is often difficult for him or her to calm down on his own and adult assistance is needed.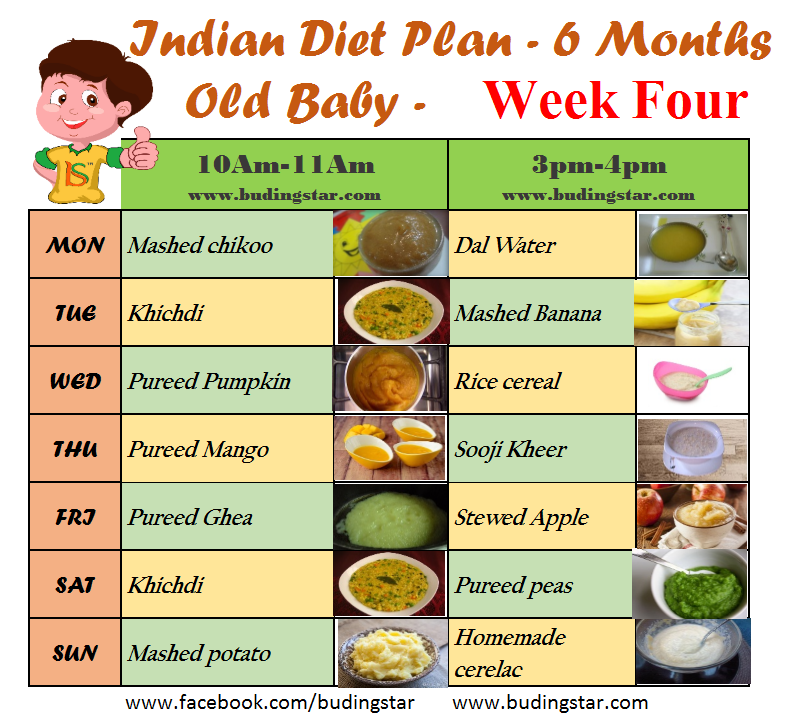 And breastfeeding is the best way to calm the baby, because breast milk is not only food, but also pain reliever and a source of happiness hormones. 10
And breastfeeding is the best way to calm the baby, because breast milk is not only food, but also pain reliever and a source of happiness hormones. 10
“Nobody told me about cluster feeding, so for the first 10 days I just went crazy with anxiety - I was sure that my milk was not enough for the baby,” recalls Camilla, a mother from Australia, “It was a very difficult period . I was advised to pump and supplement until I finally contacted the Australian Breastfeeding Association. There they explained to me what was happening: it turned out that it was not about milk at all.
Remember, this is temporary. Try to prepare dinner for yourself in the afternoon, when the baby is fast asleep, so that in the evening, when he begins to often breastfeed, you have the opportunity to quickly warm up the food and have a snack. If you are not alone, arrange to carry and rock the baby in turns so that you have the opportunity to rest. If you have no one to turn to for help and you feel that your strength is leaving you, put the baby in the crib and rest for a few minutes, and then pick it up again.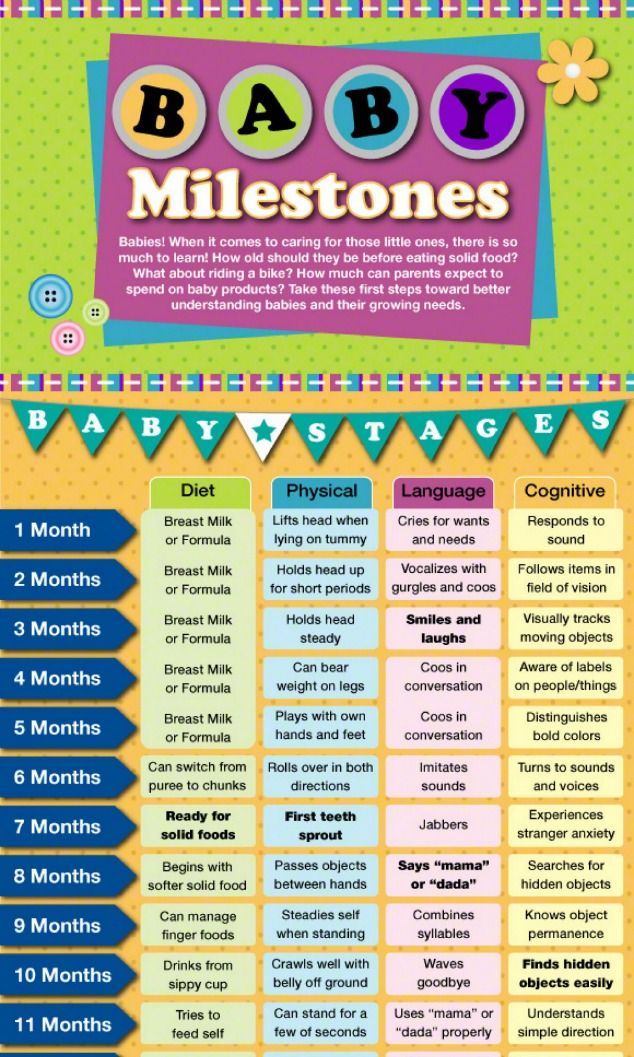
Ask your partner, family and friends to help you with household chores, cooking and caring for older children if you have any. If possible, hire an au pair. Get as much rest as possible, eat well and drink plenty of water.
“My daughter slept a lot during the day, but from 23:00 to 5:00 the cluster feeding period began, which was very tiring,” recalls Jenal, a mother from the USA, “My husband tried his best to make life easier for me - washed, cleaned, cooked, changed diapers, let me sleep at every opportunity and never tired of assuring me that we were doing well.
If you are concerned about the frequency of breastfeeding, it is worth contacting a specialist. “Check with a lactation consultant or doctor to see if this is indicative of any problems,” recommends Cathy. “Resist the temptation to supplement your baby with formula (unless recommended by your doctor) until you find the cause. It may not be a matter of limited milk production at all - it may be that the child is inefficiently sucking it.
When will breastfeeding become easier?
This early stage is very special and does not last long. Although sometimes it seems that there will be no end to it, rest assured: it will get easier soon! By the end of the first month, breast milk production will stabilize, and the baby will become stronger and learn to suckle better. 2.3 Any problems with latch on will most likely be resolved by this time, and the body will be able to produce milk more efficiently, so inflammation and leakage of milk will begin to subside.
“The first four to six weeks are the hardest, but then things start to get better,” Cathy assures. It just needs to be experienced!”
The longer breastfeeding continues, the more benefits it brings, from saving on formula and improving sleep quality 11-13 to boosting your baby's immune system 14 and reducing your risk of developing certain types of cancer. 15
“When you feel like you're pushing yourself, try to go from feed to feed and day to day,” advises Hannah, a UK mom. “I was sure I wouldn’t make it to eight weeks. And now I have been breastfeeding for almost 17 weeks, and I dare say it is very easy.”
“I was sure I wouldn’t make it to eight weeks. And now I have been breastfeeding for almost 17 weeks, and I dare say it is very easy.”
Read the resource Breastfeeding beyond the first month: what to expect
Literature
1 Naveed M et al. An autopsy study of relationship between perinatal stomach capacity and birth weight. Indian J Gastroenterol .1992;11(4):156-158. - Navid M. et al., Association between prenatal gastric volume and birth weight. Autopsy Indian J Gastroenterol. 1992;11(4):156-158.
2 Neville MC et al. Studies in human lactation: milk volumes in lactating women during the onset of lactation and full lactation . Am J Clinl Nutr . 1988;48(6):1375-1386. at the beginning and at the peak of lactation." Am F Clean Nutr. 1988;48(6):1375-1386.
3 Kent JC et al. Principles for maintaining or increasing breast milk production. J Obstet , Gynecol , & Neonatal Nurs . 2012;41(1):114-121. - Kent J.S. et al., "Principles for Maintaining and Increasing Milk Production". J Obstet Ginecol Neoneutal Nurs. 2012;41(1):114-121.
Principles for maintaining or increasing breast milk production. J Obstet , Gynecol , & Neonatal Nurs . 2012;41(1):114-121. - Kent J.S. et al., "Principles for Maintaining and Increasing Milk Production". J Obstet Ginecol Neoneutal Nurs. 2012;41(1):114-121.
4 Australian Breastfeeding Feeding cues ; 2017 Sep [ cited 2018 Feb ]. - Australian Breastfeeding Association [Internet], Feed Ready Signals; September 2017 [cited February 2018]
5 Kent JC et al. Response of breasts to different stimulation patterns of an electric breast pump. J Human Lact . 2003;19(2):179-186. - Kent J.S. et al., Breast Response to Different Types of Electric Breast Pump Stimulation. J Human Lact (Journal of the International Association of Lactation Consultants). 2003;19(2):179-186.
J Human Lact (Journal of the International Association of Lactation Consultants). 2003;19(2):179-186.
6) Kent JC et al . Volume and frequency of breastfeedings and fat content of breast milk throughout the day. Pediatrics. 2006;117(3): e 387-395. - Kent J.S. et al., "Amount and frequency of breastfeeding and fat content of breast milk during the day." Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 2006;117(3):e387-95.
7 Lawrence RA, Lawrence RM. Breastfeeding: A guide for the medical profession. 7th ed. Maryland Heights MO, USA: Elsevier Mosby; 2010. 1128 p . - Lawrence R.A., Lawrence R.M., "Breastfeeding: A guide for healthcare professionals." Seventh edition. Publisher Maryland Heights , Missouri, USA: Elsevier Mosby; 2010. P. 1128.
8 World Health Organization. [Internet]. Child growth standards; 2018 [cited 2018 Feb] - World Health Organization. [Internet]. Child Growth Standards 2018 [cited February 2018].
[Internet]. Child growth standards; 2018 [cited 2018 Feb] - World Health Organization. [Internet]. Child Growth Standards 2018 [cited February 2018].
9 Australian Breastfeeding Association . [ Internet ]. Cluster feeding and fussing babies ; Dec 2017 [ cited 2018 Feb ] - Australian Breastfeeding Association [Internet], Cluster Feeding and Screaming Babies; December 2017 [cited February 2018].
10 Moberg KU, Prime DK. Oxytocin effects in mothers and infants during breastfeeding. Infant . 2013;9(6):201-206.- Moberg K, Prime DK, "Oxytocin effects on mother and child during breastfeeding". Infant. 2013;9(6):201-206.
11 U.S. Department of Health & Human Services [Internet]. Surgeon General Breastfeeding factsheet; 2011 Jan 20 [cited 2017 Feb] - Department of Health and Human Services [Internet], "Breastfeeding Facts from the Chief Medical Officer", Jan 20, 2011 [cited Feb 2017]
12 Kendall-Tackett K et al. The effect of feeding method on sleep duration, maternal well-being, and postpartum depression. clinical lactation. 2011;1;2(2):22-26. - Kendall-Tuckett, K. et al., "Influence of feeding pattern on sleep duration, maternal well-being and the development of postpartum depression." Clinical Lactation. 2011;2(2):22-26.
The effect of feeding method on sleep duration, maternal well-being, and postpartum depression. clinical lactation. 2011;1;2(2):22-26. - Kendall-Tuckett, K. et al., "Influence of feeding pattern on sleep duration, maternal well-being and the development of postpartum depression." Clinical Lactation. 2011;2(2):22-26.
13 Brown A, Harries V. Infant sleep and night feeding patterns during later infancy: Association with breastfeeding frequency, daytime complementary food intake, and infant weight. Breast Med . 2015;10(5):246-252. - Brown A., Harris W., "Night feedings and infant sleep in the first year of life and their association with feeding frequency, daytime supplementation, and infant weight." Brest Med (Breastfeeding Medicine). 2015;10(5):246-252.
14 Hassiotou F et al. Maternal and infant infections stimulate a rapid leukocyte response in breastmilk.










