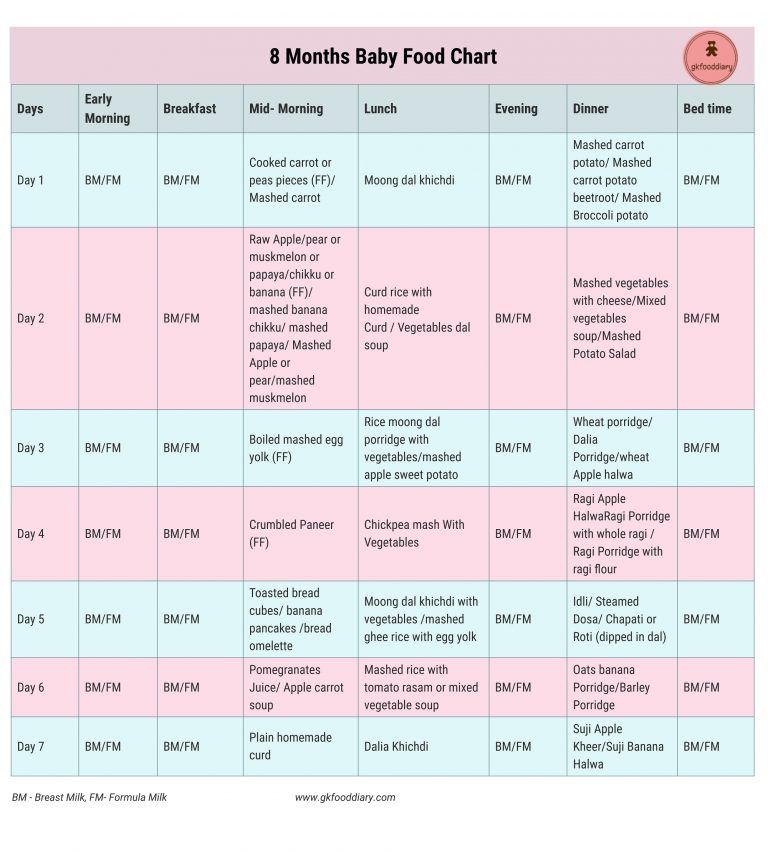
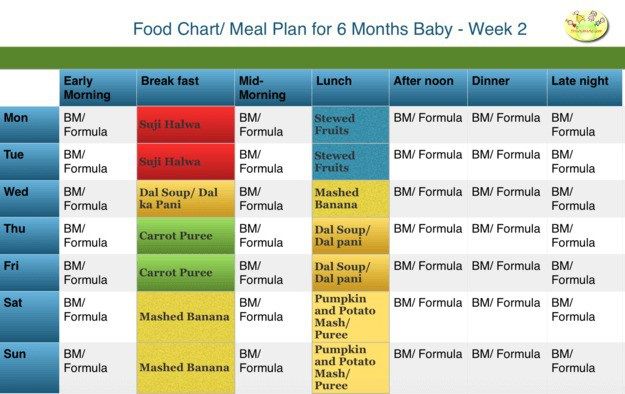
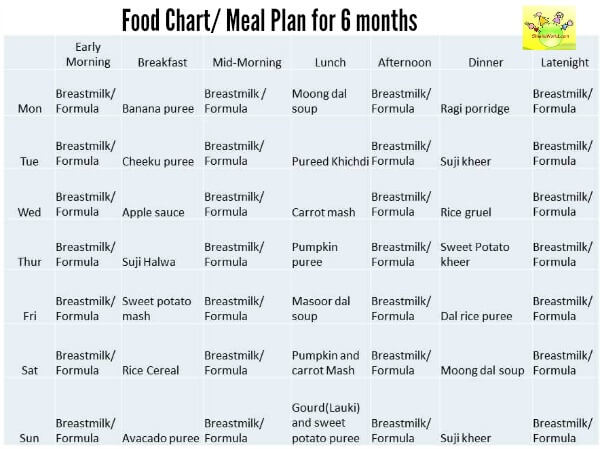
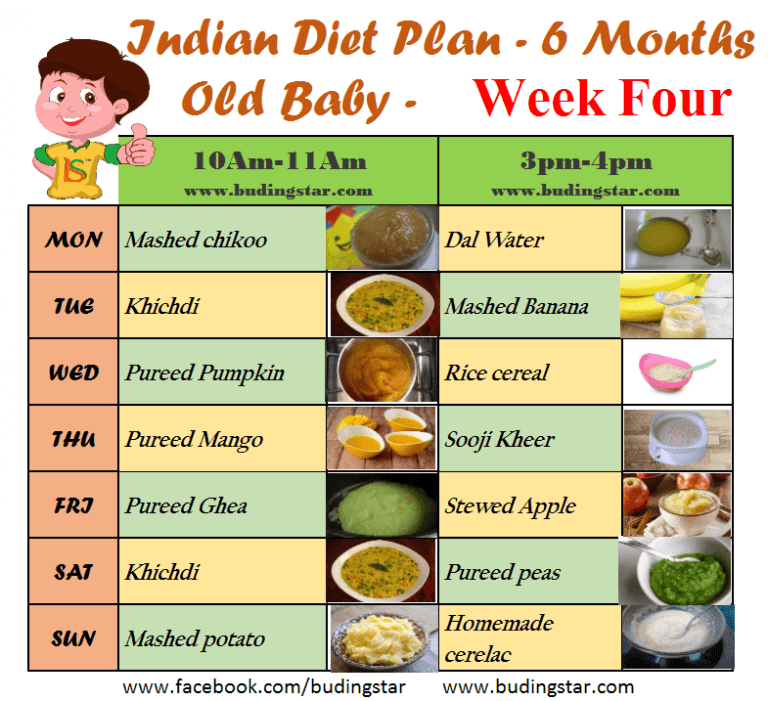
2 years baby food chart india
Indian Diet Plan for Toddlers (1 to 3 years)
The best indicator that your toddler is getting adequate nourishment is her regular weight gain, growth, general appearance and contentment.
Thinking of which foods are healthier for your baby will be much easier for you by now, as you will be an expert on which foods your child is best able to cope with. All the foods groups, viz. cereals, pulses, fruits, vegetables and milk are equally important and are extremely healthy for your child.
An adequate amount of these food groups will ensure a healthy growing child. Very few of us really know the intake required by our little toddlers. The daily food guide that follows will help you to know the right amount of food for your child.
1. Cereals and their flours : Whole wheat, unpolished rice, jowar, bajra, ragi (nachni), bulgur wheat (dalia), buckwheat are some healthy cereals which should be included in your toddlers diet. Include at least 5 to 6 servings per day. Use them to make Mini Bajra Oats Uttapa and Multigrain Palak Paneer Roti for Toddlers and Kids.
2. Pulses and Dals: Whole Moong, chawli beans, rajma, chick peas (kabuli chana) etc. Sprout them to make them easily digestible for kids and also to get enhanced nutritional benefits. Also include moong dal, toovar (arhar) dal, masoor dal, chana dal, urad dal etc. Their flours like moong dal flour, chana dal flour (besan) etc. also form a part of this food group. Include at least 1 to 2 servings per day. Make their food interesting by serving them Moong Sprouts Dosa and Rajma Salad for Toddlers. Form a habit of family dinner and boost them to eat on their own.
3. Vegetables: These include greens like spinach (palak), fenugreek (methi), lettuce, radish leaves, coriander, cow pea (chawli) leaves, colocasia, cabbage etc.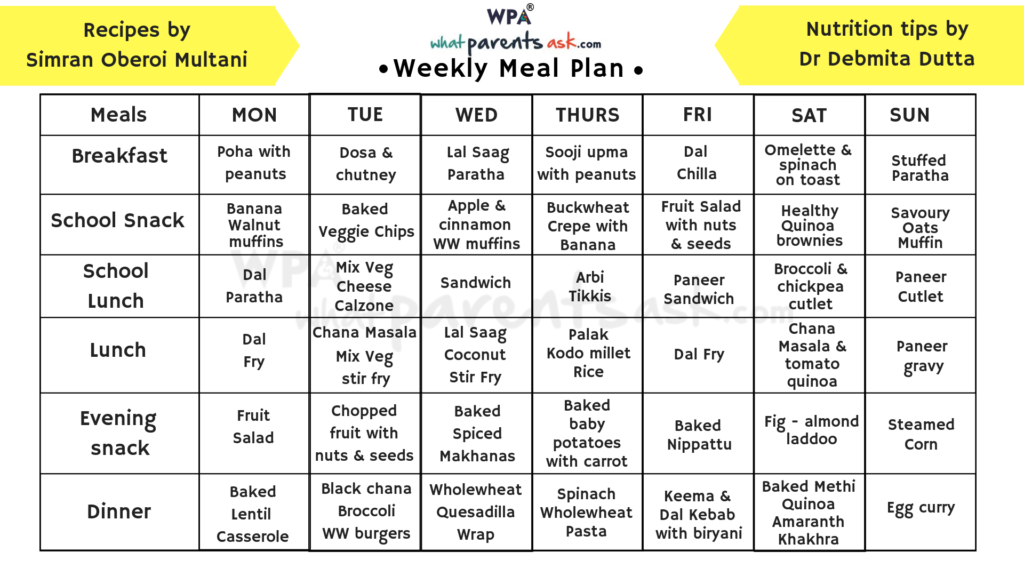 Use them to make a small meal like Dal and Vegetable Soup. Other veggies like carrot, beetroot, cucumber, brinjal, French beans, cluster beans (gavarfali), cauliflower florets etc. also form a part of this group. Include at least 2 to 3 servings per day.
Use them to make a small meal like Dal and Vegetable Soup. Other veggies like carrot, beetroot, cucumber, brinjal, French beans, cluster beans (gavarfali), cauliflower florets etc. also form a part of this group. Include at least 2 to 3 servings per day.
4. Fruits: Pineapple, sweet lime, orange, guava, watermelon, mango, apple etc… so many colourful fruits are available. Use a new fruit daily. Include at least 2 fruits a day. If your child doesn’t like whole fruits, serve them in the form of Chana Salad for Kids and Toddlers.
5. Nuts and Oilseeds: Almonds, cashewnuts, walnuts, sesame seeds (til), peanuts, dates, figs, apricots etc. Include a few of them for sure. They are a good source of protein and omega-3 fatty acids. Try Til Chikki. Make small pieces and let them nibble on it. Be careful that it doesn’t choke.
6. Dairy Products: These include milk, curd, paneer and cheese. Most kids grown up drinking at least 2 glasses of milk per day. Teach them to include curd in their diet. It is probiotic and good for their digestive system. Serve them chaas in an attractive glass. Use paneer to make Paneer Vegetable Paratha for Kids. Include at least 2 servings per day.
Most kids grown up drinking at least 2 glasses of milk per day. Teach them to include curd in their diet. It is probiotic and good for their digestive system. Serve them chaas in an attractive glass. Use paneer to make Paneer Vegetable Paratha for Kids. Include at least 2 servings per day.
7. Fats and Sugar: These are ghee, oil, butter, sugar and jiggery. Although there is no specific recommendation for this group, approximately 2 tablespoons of fat and sugar can be consumed as per your paediatricians advice. Prefer jaggery over sugar in the form of Jowar Golpapdi for Kids.
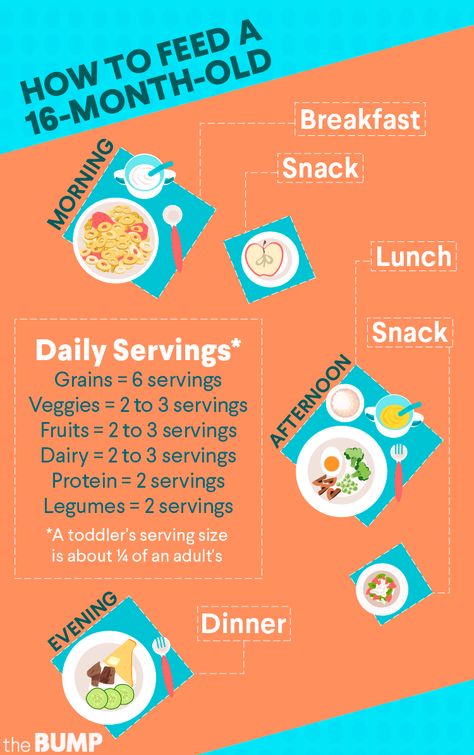
Daily Food Guide for Toddlers
| FOOD GROUPS | Number of servings per day | What makes 1 serving | Suggested Recipes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cereals and their flours Whole wheat, unpolished rice, jowar, bajra, ragi (nachni), bulgur wheat (dalia) | 5 to 6 servings | 2 phulkas (30 gm)* or 1 chapati (25 gm)* or 1/2 cup cooked cereals or whole wheat pasta (60 to 80gm)* | Mini Bajra and Oats Uttapa, Multigrain Palak Paneer Roti |
| PULSES Whole Moong, lobhia beans, rajma, chick peas (kabuli chana),etc. 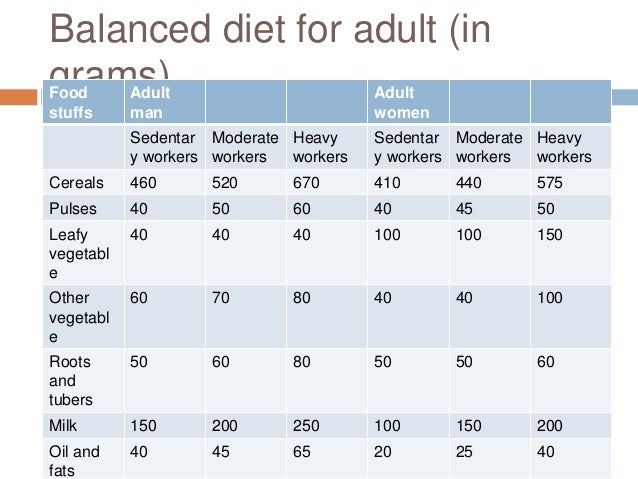 Sprouts Moong, rajma, matki etc. Dal Moong dal, toovar (arhar) dal, masoor dal, chana dal, urad dal etc. Flours Moong dal flour, chana dal flour (besan) etc. | 1 to 2 servings | 1/ 4 cup raw whole pulses (35 to 40 gm) or 1/2 cup cooked whole pulses (70 to 80 gm) * or 1/2 cup of raw or cooked dals (70 to 80 gm) * or 1/2 cup of flours (40 to 60 gm) * | Rajma Salad, Moong Sprouts Dosa, Sprouts Khichdi, Mini Mixed Moong Dal Chila |
| VEGETABLES Carrot, beetroot, cucumber, brinjal, French beans, cluster beans (gavarfali), cauliflower florets etc. Leafy Vegetables Spinach (palak), fenugreek (methi), lettuce, radish leaves, coriander, cow pea (chawli) leaves, colocasia, cabbage etc. | 2 to 3 servings | 1/2 cup raw vegetables (50 to 70 gm)* or 1/2 cup cooked vegetables (50 to 70 gm)* or 1 cup raw leafy vegetables (15 gm of vegetables like mint, coriander, fenugreek and 40 to 60 gm of other leafy vegetables ) * or 1/2 cup cooked leafy vegetables (15 gm of vegetables like mint, coriander, fenugreek and 40 to 60 gm of other leafy vegetables ) * | Paneer and Vegetable Paratha, Beetroot and Carrot Raita, Dal and Vegetable Soup, Cheesy Corn and Vegetable Cutlets |
| FRUITS Pineapple, sweet lime, orange, guava, watermelon, mango, apple etc.  Dried fruits Almonds, cashewnuts, walnuts, sesame seeds (til), peanuts, dates, figs, apricots etc. | 2 servings | 1/2 cup chopped fruits (50 to 60 gm) * or 1 big piece of fruit e.g. melon wedge (100 to 130gm) * or 1/4 cup dried fruits. (20 to 30gm) * | Fruity Chana Salad |
| DAIRY PRODUCTS Milk, curd, paneer | 2 servings | 1 cup milk (200 ml) * or 1 cup curds (200 ml) * or 1/4 cup chopped paneer (35gm) * or 1/4 cup grated cheese (35gm) * | Multigrain Palak Paneer Roti, Paneer and Vegetable Paratha, Chickoo Milkshake |
| FATS AND SUGAR Ghee, oil, butter, sugar and jaggery | ** | Although there is no specific recommendation for this group, approximately 2 tablespoons of fat and Sugar can be consumed as per your paediatricians advice. | ---- |
* The weights of all the foods mentioned in the above table are approximate values.
** Fats should be consumed in moderation as some foods like walnuts, sesame seeds and even cereals contain invisible fats which are also a part of our diet. Excessive fat can disturb the absorption of important nutrients like calcium in your little one's body, apart from increasing the risk of obesity later in life.
Other related articles on this :
Major Nutrients needs for Infants and Toddlers
Recommended Daily Allowance for Infants and Toddlers
Guide to Weaning
Best food for feeding Mothers to get more milk
When and how much to feed your Baby
Components of Breast Milk
Recipes for Baby (10 to 12 Months)
We would love to hear from you if you liked the article. Please post your comments. Thanks!
https://www.tarladalal.com/Moong-Sprouts-Dosa-for-Kids-3100r
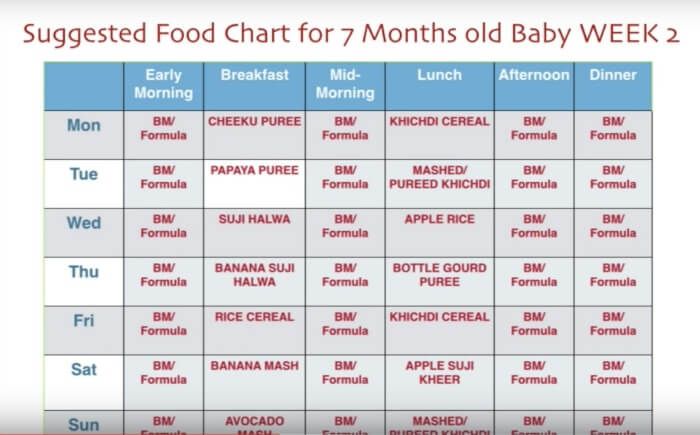
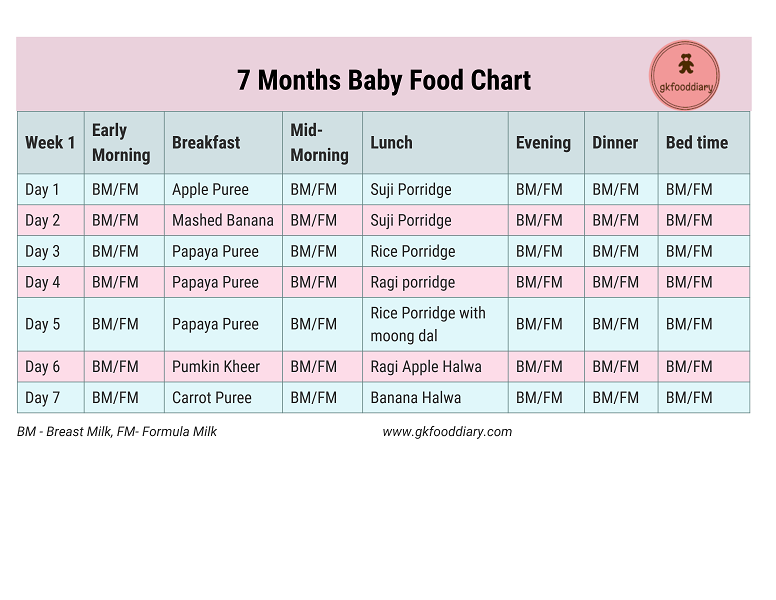
indian diet plan for toddlers (1 to 3 years)
Healthy Foods for 2 Year Old Child Along with Recipes
Food habits change rapidly as your infant grows. Within the first two years, your baby will have begun teething, moved on to solid foods, and more or less integrated with family mealtimes. Here is a food chart, as well as some recipes on how to integrate healthy eating habits in your child and include good, wholesome and nutritious food in his diet.
Within the first two years, your baby will have begun teething, moved on to solid foods, and more or less integrated with family mealtimes. Here is a food chart, as well as some recipes on how to integrate healthy eating habits in your child and include good, wholesome and nutritious food in his diet.
How Does Your Toddler’s Meal Time Change?
Your child will have begun eating solid foods as he starts teething. Kids this age are impatient and even fussy around mealtimes. At one and a half years (18 months), toddlers usually manage to handle a spoon to feed themselves. By 24 months, your child will have joined the grown-ups table as a regular!
Some Useful Steps to Form Good Eating Habits in Your Child
A toddler’s eating habits and tastes are only being established as he first starts eating solid foods. This is the time when parents should strive to build a healthy eating habit.
- Delay your child’s introduction to fast food and sweetened aerated drinks, and help build a preference for fresh, wholesome food.

- Stick to strict meal timings. Establishing a routine will lead to your child developing a fixed mealtime by getting hungry at the right time.
- Do not feed your child heavy snacks or lots of liquid rights before mealtime.
- Each meal should last for 20 minutes and no longer.
Food for a 2-Year-Old Baby
While a balanced diet is essential for us, children need a boost of nourishment that helps them grow.
1. Dairy Products
Milk, yoghurt, and paneer are all rich in calcium. Calcium helps build strong bones. In case your child is lactose intolerant, he may need to take calcium from other sources like nuts and pulses to make up for a gap in the calcium intake.
2. Chicken
Chicken and other non-vegetarian foods contain good quantities of easily absorbable iron and protein. Iron helps power haemoglobin in the blood and prevents anaemia. Iron found in vegetarian food is harder for the body to absorb and, hence, your child will need to consume at least twice as much of it to get the required amount.
3. Fish
Fish is a good source of Essential Fatty Acids (EFAs). EFAs help builds immunity and strengthens the cardiovascular system. Vegetarians will need proper substitution of EFA sources, as it is not produced in the body and can only be gained externally.
4. Healthy Oils
Flaxseeds, walnuts, soybeans, and other nuts and their oil contain reasonable amounts of EFAs and minerals.
5. Carrots
Carrots are famous as a rich source of Vitamin A. Spinach, kale, and other vegetables also contain high levels of Vitamin A. It is essential to include foods rich in different vitamins in your child’s diet. Vitamin A helps in boosting eyesight and immunity.
6. Citrus Fruits
Lemons and oranges are renowned for their Vitamin C content. Deficiency of Vitamin C can lead to serious diseases like scurvy. Vitamin C helps in strengthening gums and blood vessels and recovering from bruises. Guavas, mangos, bananas, tomatoes, and spinach also contain Vitamin C.
7. Sunshine
Although this isn’t technically a food, it is something the body absorbs. Hence, it is included in this list, considering the integral role it plays in growth. The element we gain from sunshine is Vitamin D. Vitamin D is essential for a child to achieve his maximum growth potential. Foods that contain Vitamin D are fish and dairy products.
8. Bananas
Magnesium and potassium, are essential elements for cardiac health, and muscle condition, and are found in bananas. Incorporate this beneficial fruit into cereals and other foods to make it a staple.
Food Chart/Schedule for 2-Year-Old Baby
| Breakfast | Mid Morning | Lunch | Afternoon | Dinner | |
| Sunday | Poha/Upma with vegetables/ sprouts/ peanuts and milk/ curd | Cup of milk and fruits | Curry made with any pulses or rice and dahi | Paneer cutlet with milk | Aloo matar with missi roti |
| Monday | Dosa or Moong dal cheela with added vegetables and curd | Seasonal Fruits | Mixed vegetables curry with chapatti | Fruit milkshake | Chapatti with fried soya chunks |
| Tuesday | Egg roll in roti or egg rice | Vegetable soup / fruits | Veg biryani with cucumber sticks | Boiled corn or boiled peanuts + fruit | Vegetable khichdi with curd
|
| Wednesday | Idli and sambar | Almonds/ raisins | Aloo paratha with dahi | Fruits | Boiled chicken with rice |
| Thursday | Ragi porridge with chopped nuts | Fruit | Chana dal khichdi with curd
| Upma with curd/ milk
| Vegetable soup with 2 cutlets (veg or non-veg) |
| Friday | Oats cooked in milk | Fruit smoothie or custard | Chole curry with chapattis | Oats khichdi | Sambar with rice |
| Saturday | Vegetable paratha | Fruits and nuts | Paneer pulao | Omlette or cheese-chapati roll | Vegetable pulao with dahi |
Homemade Food Recipes for 2-Year-Old Baby
Here are some select recipes from the food chart that may not be too familiar to you.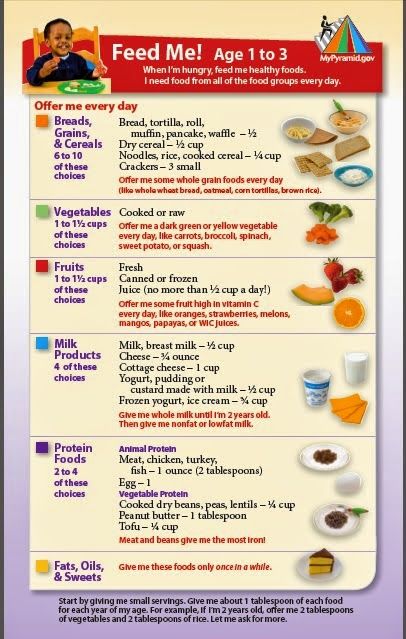
1.
Moong Dal CheelaA power-packed start to your day!
Ingredients:
- 1 cup moong dal
- ¼ teaspoon turmeric
- ¼ teaspoon red chilli powder
- ½ teaspoon roasted cumin
- Salt to taste
- ¼ cup chopped onions
- 1 teaspoon grated ginger
- Finely chopped green chillis
- A pinch of hing (asafoetida)
- Butter
How to Prepare:
- Soak the moong dal in water overnight.
- Drain the water and grind with adequate water to form a thick paste – similar to dosa batter.
- Add spices to the batter and mix well.
- Add the seasoning and a pinch of hing, and mix again.
- Allow the batter to rest for 15-20 minutes.
- Heat butter in a non-stick pan and spread the batter like you would a dosa.
2. Coconut
ChutneyA traditional accompaniment to dosas and idlis!
Ingredients:
- ½ cup fresh grated coconut
- 2 tablespoons fried yellow gram
- ½ teaspoon cumin
- 2 green chillis
- 1 garlic clove
- ¼ teaspoon mustard
- 1 dried red chilli
- ¾ teaspoon urad dal
- Hing
- Curry leaves
How to Prepare:
- Blend all the ingredients, except the seasoning, together.
- Add water and salt (to taste) while blending.
- In a few drops of oil heated in a pan, saute the seasonings.
- Add the blended chutney to the seasoning and turn off the heat. Serve with idli or dosa.
3.
Chana Dal KhichdiA simple recipe that uses very little seasoning and embraces the natural flavour of chana.
Ingredients:
- 1/2 teaspoon of red chilli powder
- 1 pinch of asafoetida
- ½ cup of rice
- ½ cup chana dal
- Oil
- Water
- Salt
How to Prepare:
- Soak the rice for 30 minutes prior to preparation.
- The chana dal should be soaked for 4-5 hours, prior to preparation. (If time does not permit, you may soak it in hot water for about 30 minutes)
- Heat 1 tablespoon oil in a pressure cooker and add the seasoning.
- Add the rinsed chana dal with salt to taste and stir.

- Add 1 cup of water and cook under pressure for 6 minutes or 2 whistles.
- After it has cooled down, add the rice and cook for 1 or 2 whistles.
4.
Paneer CutletPaneer provides a boost of protein and calcium to the common vegetable cutlet and gives a uniquely soft texture to the cutlet too.
Ingredients:
- 2 pinches of turmeric powder
- ¼ teaspoon red chilli powder
- ½ teaspoon coriander powder
- ½ teaspoon cumin powder
- ¼ teaspoon garam masala
- 200gms paneer
- 150gms potato
- 100gms carrot
- 1/3 cups peas
- Paste: 1 green chilli
- 2 cloves of garlic
- 1-inch slice of ginger
- 3 tablespoons rice flour
- 3 tablespoons rava
- 3 tablespoons oil
How to Prepare:
- Cut the green chilli, garlic and ginger, and grind to a paste.
- Peel and cut the vegetables and cook for up to 4 whistles in a pressure cooker, with 2 cups of water.
- Drain the water when cooled and transfer the cooked vegetables to a mixing bowl.
- Mash the vegetables, add the paste and seasoning, and mix well.
- Add the paneer (Paneer should be crumbled or grated).
- Add 3 tablespoons of rice flour and salt to taste, and mix again.
- Take small portions of the mixture and shape into patties.
- Coat with rava and fry in a shallow pan until both sides are golden brown. Serve with ketchup or chutney.
5. Soya Chunks Fry
A healthy and tasty dish that is simple to make. It goes great with both chapattis and rice!
Ingredients:
- 1/2 cup soya chunks
- 2 onions, shredded
- 2 green chillis, slit
- 1 big piece of ginger cut into thin strips
- 4 garlic cloves, sliced
- 1/2 Tsp garam masala
- 1/2 Tsp chaat masala
- ½ tsp red chilli powder
- 2 tomato, finely chopped
- Coriander leaves
- 2 tablespoons oil
How to Prepare:
- Immerse the soya in hot water for about 20 minutes.
- In a pan, saute the onions in oil.
- Once the onions are golden-brown, add the garlic and ginger.
- Add the green chillis and then the tomatoes.
- As the mixture cooks, add the seasoning and mix well. Turn off the flame.
- Now, drain the soya chunks (You may need to squeeze them with the help of a sieve to drain them well).
- Add the soya chunks to the mixture and begin cooking again.
- Add salt to taste and mix the contents of the pan thoroughly so that the soya chunks are well coated with the masala (You can also add a bit of lemon juice to this, for a hint of tanginess).
- Cook in a pan till the soya chunks are browned.
- Turn off the flame and garnish with plenty of finely chopped coriander leaves. Serve warm.
Feeding Tips
- While providing healthy food for 2-year-old baby do not fixate on the amounts eaten. This will change from child to child and between different days and mealtimes.

- A 2-year-old toddler’s food requirement does not have to include artificial supplements.
- Indian baby food recipes for a 2-year-old can be spicy. If your child is fussy about this, you can experiment with reducing the amount of seasoning, especially red chilli powder.
- Give your child notice before every mealtime. This gets him thinking about food and builds up an appetite.
- Have the food ready and plated for mealtime when your child arrives.
- Do not punish or reward your child’s eating habits, as it can create a problematic attitude towards food and harm your child’s relationship with food.
- Don’t allow your toddler to watch T.V. during mealtime, as he needs to focus on the food. Talk to him instead and include him in conversations with all the family members.
Disclaimer:
- Look out for allergies. Your child could be allergic to certain nuts, grains or dairy products. Make sure you avoid these food items and consult your doctor about the allergies.

- When introducing your toddler to new foods, you should ensure that you introduce new food one at a time as this will make it easier for you to check for allergies and help you understand your child’s preferences.
- If your child is suffering from diarrhoea, don’t stop feeding him. Consult a doctor and feed him foods that are nutritious and can control the diarrhoea.
- Don’t force-feed your toddler. Toddlers can be fussy with food, be patient and know when he has eaten enough.
Eating nutritious food that is fresh and doesn’t contain preservatives is seen by many as something that takes too much effort, but with the right motivation, it can be a habit and not a chore! Include different fresh fruits in your child’s diets, so his tastes vary and he is less likely to become fussy over time.
Previous Year: 1 Year Old Baby Food Chart
Nutrition of a child in the 2nd year of life: regimen, diet, menu, necessary products | Mamovediya
The child in this period of life grows intensively and therefore must receive nutrition that quantitatively and qualitatively satisfies the needs of his body.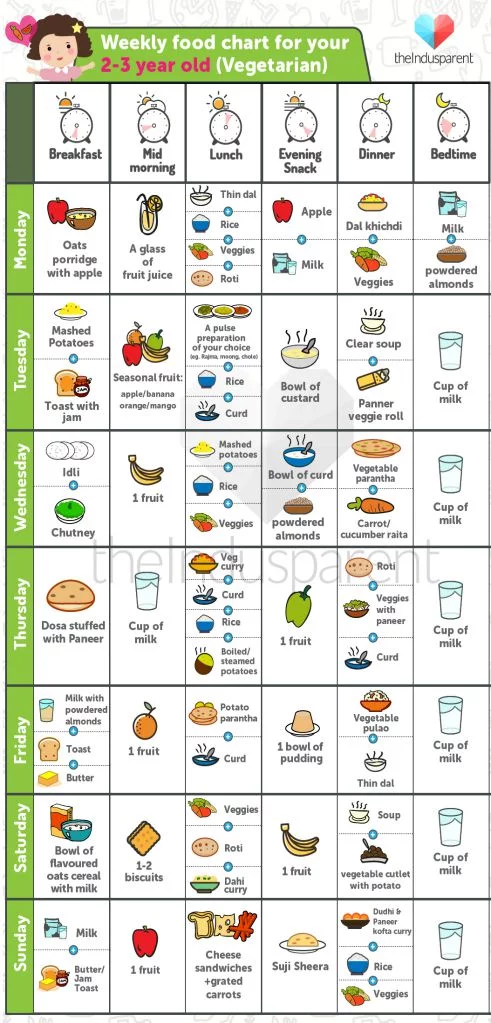
Nutrition should be rational: balanced and consistent with the daily routine. Balance - the inclusion of all the necessary nutrients (proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, trace elements) in the appropriate proportions that the child's body can absorb.
Nutrition is considered rational if it meets the age needs of the child and is carried out according to the daily routine.
In addition, the so-called rational nutrition includes the culinary processing of food used for a given age, and the correct methodological methods of parents in the process of feeding a child.
The environment surrounding the baby during the meal, the appearance of the dishes served should excite the child's appetite.
Child's appetite is a state of organic need for food, expressed in the child's desire to eat. At the same time, an adequate positive attitude of the child to food is noted.
A good appetite, as a rule, depends not only on how well the menu is compiled, but also on the correct organization of the feeding process. To form and maintain a good appetite, parents must clearly know: what, when and how to feed the child.
To form and maintain a good appetite, parents must clearly know: what, when and how to feed the child.
How nice it is to feed a child who has a good appetite. It brings pleasure to adults and great benefits for the baby. However, very often it is necessary to observe cases of violation of normal appetite from small deviations (decrease in appetite, refusal of certain dishes) up to its complete absence (anorexia - as it is called in medical practice).
A child with a decrease or lack of appetite at the mere sight of writing or a reminder of food expresses protest, turns away, defends himself, tightly closes his lips and teeth. It looks like an unnatural negative reaction of the baby to food. Why does a child lose his appetite? Who is to blame for this? The reasons often lie in the wrong method of feeding (strong pressure on the child's tongue with a spoon, the child's lack of interest in food), in the negative sensations associated with eating (too hot food, poor taste), improper organization of the situation during feeding (distraction with a book, toy, punishment), etc.
Many parents, seeing a decrease in appetite, try to force-feed their child, but this further reinforces the child's negative attitude towards food and everything connected with it. This is strictly prohibited.
If a child suddenly lost his appetite, first of all think about whether you could have made mistakes in the process of upbringing and feeding, in especially persistent cases, you should consult a pediatrician.
During feeding, do not forget to introduce the child to the names of dishes (soup, cutlet, compote, etc.) and the properties of objects (food is tasty, sweet, sour, salty, hot, cold, a large spoon, a small one, etc.) .). In this way, the child will form the first ideas, concepts.
Eating processes should be organized in such a way that the child has a desire to eat. Before eating, you should arrange a calm pause after a long walk or noisy and active games.
You should not give your child new interesting toys shortly before feeding, and quickly take them away before eating. By doing this, you will cause a strong emotional reaction that will slow down food arousal and reduce appetite.
By doing this, you will cause a strong emotional reaction that will slow down food arousal and reduce appetite.
While eating with a child, one should only talk about what is connected with this process, concentrating his attention on food, developing the child's active participation in eating.
A child's appetite is increased not only by deliciously cooked food, but also by its beautiful design, attractive dishes specially painted for children. Children should only be seated at the table when food has already been served. You should not put all the dishes on the table at once, the child is distracted from the first dish, reaches for the third or second, as a result, the sequence of eating is disturbed. Remember that many violations in the health of the baby are associated with errors in his diet.
By the age of 1 year 3 months, the baby can already eat solid food with a spoon, and at 1 year 6 months he can eat any food - thick and liquid. Try to develop these independent skills and abilities, which are very important for later life, in your son or daughter. How joyful it is to look at a baby who skillfully takes food from a plate with a spoon, without mistake brings it to his mouth and actively removes it with his lips. Something, of course, still pours from the spoon past and remains on the lips or chin of the child, but these errors in eating will soon pass, and the baby will learn to carefully eat the entire portion. Remember that a large amount of food contributes to a decrease in appetite, and an insufficient one does not cause a feeling of fullness.
Try to develop these independent skills and abilities, which are very important for later life, in your son or daughter. How joyful it is to look at a baby who skillfully takes food from a plate with a spoon, without mistake brings it to his mouth and actively removes it with his lips. Something, of course, still pours from the spoon past and remains on the lips or chin of the child, but these errors in eating will soon pass, and the baby will learn to carefully eat the entire portion. Remember that a large amount of food contributes to a decrease in appetite, and an insufficient one does not cause a feeling of fullness.
A child of this age should be able to chew food. Make sure that he does not keep the pieces in his mouth for a long time, but swallows them in time.
A child of the 2nd year of life is fed 4 times a day with an interval of 3.5-4.5 hours. However, in the first half of the year, the baby can receive another fifth feeding - kefir or milk at 23-24 hours if he wakes up at night or at 6 o'clock in the morning.
Establishing rational nutrition is painstaking and very responsible work, but if you do it systematically, without giving "indulgence" to yourself and your child, then your reward will be good health and good physical development of the baby.
When compiling the menu, it is necessary to correctly distribute how much and what kind of food the child will receive during the day. Feed your baby 4-5 times a day. In the morning it is better to cook dairy dishes, lunch should always consist of soup, meat in the form of mashed potatoes or meatballs with a vegetable side dish, compote or jelly, fruits, kefir are given in the afternoon, a vegetable dish is prepared for dinner.
The one-time amount of food consumed in children of the 2nd year of life is different - up to 1.5 years, somewhat less than in the second half of the year.
Under no circumstances should children of this age be given food from the common table. This is very harmful. Malnutrition of a child older than a year will undoubtedly affect his health in the future. Injury by coarse food to the still unprotected mucous membrane of the child's stomach, the stressed state of the organs of the gastrointestinal tract lead to the formation of early gastritis, enteritis, cholecystitis and other diseases.
Malnutrition of a child older than a year will undoubtedly affect his health in the future. Injury by coarse food to the still unprotected mucous membrane of the child's stomach, the stressed state of the organs of the gastrointestinal tract lead to the formation of early gastritis, enteritis, cholecystitis and other diseases.
The menu can be diversified by replacing meat with cottage cheese, fish, eggs, introducing a variety of vegetable or cereal dishes, changing the culinary processing of food (mashed potatoes, cutlets, jelly, compote, etc.), improving its taste, adding greens (dill, parsley, celery, etc.).
If a dairy dish is served for breakfast, then in the afternoon you should feed the baby with vegetables and vice versa; if vegetable soup is prepared for lunch, then the second dish should be cereal, etc. To maintain appetite, make sure that meals are not repeated during the day.
This set of products does not have to be used every day, and it is practically difficult, for example, to measure 3 g of cheese for a child. It is important that during the week the proposed list of products be used in baby food. Therefore, cheese can be used once a week and immediately in the amount of 20 g (3 x 7, say, give the baby vermicelli with grated cheese for breakfast.
It is important that during the week the proposed list of products be used in baby food. Therefore, cheese can be used once a week and immediately in the amount of 20 g (3 x 7, say, give the baby vermicelli with grated cheese for breakfast.
A few words about food products intended for baby food, or rather, their brief description.
Milk and dairy products. Natural milk can be given to a child only after boiling. One-day kefir and cottage cheese are very useful. Milk should be boiled in a heavy-bottomed saucepan with the lid closed. When preparing dishes from milk (porridge, mashed potatoes), raw milk is added and allowed to boil once with ready-made cereals or vegetables. Milk must not be boiled twice. It should be remembered that excessive milk reduces the child's appetite, so milk should not be given to quench thirst instead of water.
Oils. In the diet of children of the 2nd year of life, both butter and vegetable oil can be used, and the amount of vegetable oil should not exceed 10-15% of the total amount of oil consumed per day (i. e., not more than 2 g per day) . Vegetable oil should be stored in a sealed container, protected from light and air. It cannot be boiled, so it is better to lay it in the finished dish. In the diet of children, it is not recommended to use refractory fats - beef, pork, cooking oil, and margarine.
e., not more than 2 g per day) . Vegetable oil should be stored in a sealed container, protected from light and air. It cannot be boiled, so it is better to lay it in the finished dish. In the diet of children, it is not recommended to use refractory fats - beef, pork, cooking oil, and margarine.
Meat and meat products. Lean beef, rabbit meat, chickens are useful for children You can use offal - liver, tongue, heart, brains, chicken giblets. Meat should not be soaked in water, as this transfers some of the nutrients into the water. The liver should be fried under the lid and given to the child in a puréed semi-liquid form. For children under 1.5 years old, meat, like other food, should be cooked pureed. This is due to the absence of chewing teeth in a child at this age, the underdevelopment of chewing muscles and the insufficient activity of digestive juices.
Fish and fish products. Children can only be given low-fat varieties of fish - hake, cod, sea bass, pike perch. Fish is equivalent to meat in its nutritional properties, but, in addition, it contains trace elements important for the growth and development of the child (iodine, phosphorus, copper, etc.). Keto or sturgeon caviar should be treated with caution, as it can cause unwanted allergic reactions in children.
Fish is equivalent to meat in its nutritional properties, but, in addition, it contains trace elements important for the growth and development of the child (iodine, phosphorus, copper, etc.). Keto or sturgeon caviar should be treated with caution, as it can cause unwanted allergic reactions in children.
Eggs. It is recommended to give children only chicken eggs and be sure to boil them. Raw eggs should not be served, as they can be contaminated with pathogens due to the porosity of the shell, and raw protein is poorly digested in the stomach, and raw yolk can cause allergies. Duck, goose, and eggs of other birds are prohibited from being included in the children's menu.
Bread and bakery products. It is useful for children to give both rye and wheat bread. You can give bagels, bagels, crackers, by the way, children love them very much.
Cereals and pasta. The most valuable in terms of mineral composition are bean, buckwheat, oat and millet groats. But you can use their other types - semolina, peas, as well as pasta. The groats are boiled in water (oatmeal and buckwheat - for l '/g h, millet - 1 hour, semolina - 20 minutes), then unboiled milk is added, and after removing the porridge from the heat - butter and sugar to taste.
But you can use their other types - semolina, peas, as well as pasta. The groats are boiled in water (oatmeal and buckwheat - for l '/g h, millet - 1 hour, semolina - 20 minutes), then unboiled milk is added, and after removing the porridge from the heat - butter and sugar to taste.
Sugar and confectionery . In children's food - in tea, milk, cereals, compotes, kissels - you can add sugar, but in moderation. Remember that excess sugar is harmful to a child, as it can contribute to obesity or diabetes. Other sweets are recommended marmalade, jams, marshmallows, marshmallows, cookies, especially oatmeal, waffles. Do not give children cakes with rich creams, chocolates and chocolates, as well as lollipops, especially rounded ones.
Vegetables, fruits, berries, herbs. All these products are very useful for young children, because, in addition to vitamins, they contain fiber, organic acids, pectin, tannins and volatile substances, as well as minerals and trace elements. Raw vegetables can also be used in children's nutrition. At the same time, they must be thoroughly washed, poured over with boiling water, and then grated on a fine grater. Fruits and berries are best given fresh to a child, and raw juice should be added to a boiled fruit and berry dish. In the nutrition of children, you can use canned vegetables and fruits specially prepared for baby food, as well as compotes, juices, freshly frozen and dried vegetables and fruits. Boil vegetables and fruits in a saucepan with a lid to preserve as many vitamins as possible.
Raw vegetables can also be used in children's nutrition. At the same time, they must be thoroughly washed, poured over with boiling water, and then grated on a fine grater. Fruits and berries are best given fresh to a child, and raw juice should be added to a boiled fruit and berry dish. In the nutrition of children, you can use canned vegetables and fruits specially prepared for baby food, as well as compotes, juices, freshly frozen and dried vegetables and fruits. Boil vegetables and fruits in a saucepan with a lid to preserve as many vitamins as possible.
From 1 year to 1 year 3 months
You can be told about the methods of preparing various children's meals by a district nurse or a nurse in a healthy child's office in a children's polyclinic.
The menu for a baby at this age can be compiled as follows:
Breakfast
- Porridge (vegetable puree) -150.0
- Tea with milk (milk) -100.0
- Bread with butter Lunch
- Soup (vegetable, meat) —100.
 0
0 - Meat puree (patty) — 40.0
- Side dish (vegetable puree, vermicelli) — 50.0
- Compote (fruit juice) —100.0
- Cottage cheese - 30.0
- kefir (milk) with a bun of –150.0
- Fruits - 50.0
- Puree vegetable (porridge) –150.0
- milk -150.0
Second supper
- Kefir (milk) -150.0
Recall that the second dinner is provided for those children who wake up at 23-24 hours
From 1 year 3 months to 1 year 6 months vegetables, finely chopped in the form of a salad, seasoned with vegetable oil. This is a very healthy dish, because, in addition to the vitamins it contains, it makes the baby chew food thoroughly, which means it stimulates the development of the child's chewing apparatus.
The following foodstuffs can be included in the sample menu:
Breakfast
Porridge (vegetable puree) -150.
 0
0 Tea with milk (milk) -150.0
Bread with butter
3
Lunch
- Vegetable salad - 10.0
- Soup -150.0
- Cutlet (meat, fish, liver) - 50.0
- Garnish (cereal, vegetable) - 80.0
- Compote -100.0
- Snack
- Cottage cheese — 50.0
- Fruits –100.0
- Tea with cookie --150.0
Dinner
- Vegetable puree (porridge) –150.0
- kefir (milk) –150.0
of 1 year from 1 year old from 1 year from 1 year 6 months to 1 year 9 months
Do you consider a child's taste? Children very early begin to distinguish tasty food from tasteless, they have favorite and unloved dishes. Try not to include foods that are vital for the development of the child's body.
Sample menu for a child of this age.
breakfast
- Gate carrot - 30.0
- Dairy porridge --150.0
- Tea with milk –150.
 0
0 - Bread with oil
- Soup (vegetable, meat) —100.
- Salad from vegetables - 40 ,0
- Soup (shchi, borscht) -100.0
- Meat puree (patty) - 60.0
- Garnish (vegetable, cereal) -100.0
- Fruit juice -100.0
- kefir with a bun --200.0
- Fruits –100.0
Dinner
- Puree vegetable (porridge) —200.0
- Milk (kefir) –150.0 9000 9000 9000 From 1 year 9 months to two years
- In the intervals between feedings, the child can be given a drink (no more than 100 g) of water.
Children's food in this age period can be liquid, semi-liquid, steamed, and also in the form of pieces (for the development of the child's chewing apparatus). The kid should equally willingly eat any food, no matter in which of the listed types it is served. We recommend the following menu:
We remind you that in order to prevent allergies, it is better to exclude chocolate from the child's diet, limit the consumption of foods that are high in carbohydrates, such as condensed milk, honey, sweets, and confectionery.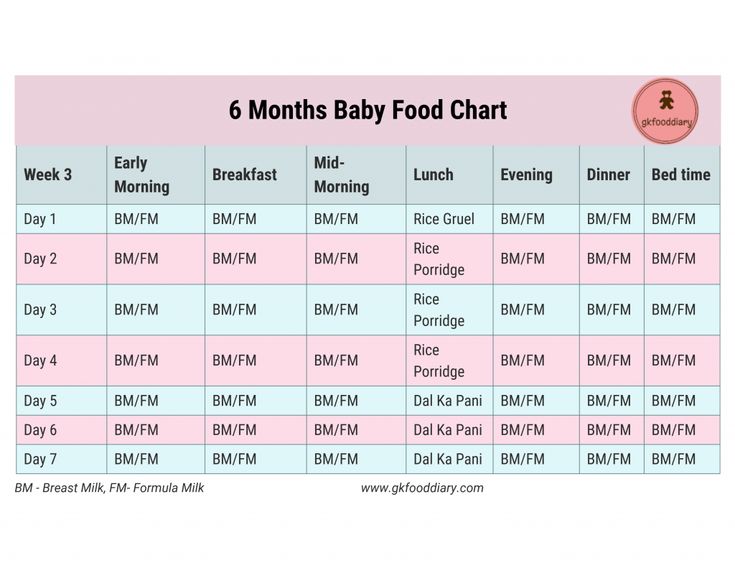
The child's food should be varied, full of vitamins. In addition to the well-known sources of vitamins, you can also use such as mountain ash, wild rose, various vegetable mixtures (turnip, rutabaga, lettuce) and greens (dill, parsley, celery), which not only enrich the nutritious diet, but also decorate dishes, which attracts children and stimulates their good appetite.
It is desirable that parents feed the child at the same time and try to form the right attitude to food in the baby from an early age and teach the culture of behavior at the table.
Education in India is third after China and the USA
Education in India, where such sharp contrasts between wealth and poverty, seems to lose all interest for an immigrant. However, the practice of studying in this exotic country shows very different results. A large enrollment flow rushes towards India every year. The goal of each potential student is a good education for little money, in the long term - life abroad.
The history of Indian education and basic principles
The history of the development of the education system in India is a long period of time, the beginning of which, according to various estimates, falls on the 5th century BC. Even then, educational institutions endowed with the properties of a higher school were created in Ancient Taxila.
The ancient city of Taxila was considered the center of higher education in India . It was there, along with Hindu temples and Buddhist monasteries, that secular institutions first began to be created. These institutions attracted foreigners with training in Indian medicine. However, in addition to the study of living matter, Indian education opened the way to knowledge of logic, grammar, and Buddhist literature.
Education in India began to emerge in the 5th century BC
The ancient educational system of India supported the principle of dividing society into castes. Depending on belonging to a particular caste, she gave people the necessary knowledge. The modern world has changed somewhat. Indian education in its current form allows you to learn any skill, regardless of the caste of a person.
The modern world has changed somewhat. Indian education in its current form allows you to learn any skill, regardless of the caste of a person.
The country adheres to the main principle of educating its citizens - "10 + 2 + 3" . This model provides for 10 years of schooling, 2 years of college, plus 3 more years of study is allocated to the first stage of higher education.
Ten years of school includes 5 years of elementary education, 3 years of high school education and 2 years of vocational training.
Features of Indian education
Pre-school education
Education of Indian children before entering school goes through the system of nurseries and kindergartens. The nursery accepts babies aged 6 months and older. At this stage, the educational process can continue until the age of three. From three to five (six) years old, kids are educated in kindergartens, which are usually the first element of primary school.
Indian educational system from beginning to end
There are public and private preschools in India . Moreover, there are almost 2 times more private kindergartens. The services of municipal children's institutions are usually free of charge, except for small fees for household needs from the administration and donations from parents. However, the quality of education here is lower than in private institutions where parents pay for the service.
Moreover, there are almost 2 times more private kindergartens. The services of municipal children's institutions are usually free of charge, except for small fees for household needs from the administration and donations from parents. However, the quality of education here is lower than in private institutions where parents pay for the service.
... My son went to kindergarten in India, and now he goes to Moscow. My personal opinion is that in an Indian kindergarten, a child is given almost free of charge something for which in Moscow you need to lay out a lot of money. For in the state kindergartens in Moscow, children are not taught, but supported. Moreover, constant fees from the parent committee is not clear for what. At the first opportunity, while in India, I will try to send my son to a local traditional kindergarten. The only problem was food, in Moscow they feed, in India they don’t ...
Nadezda Lisina
Private.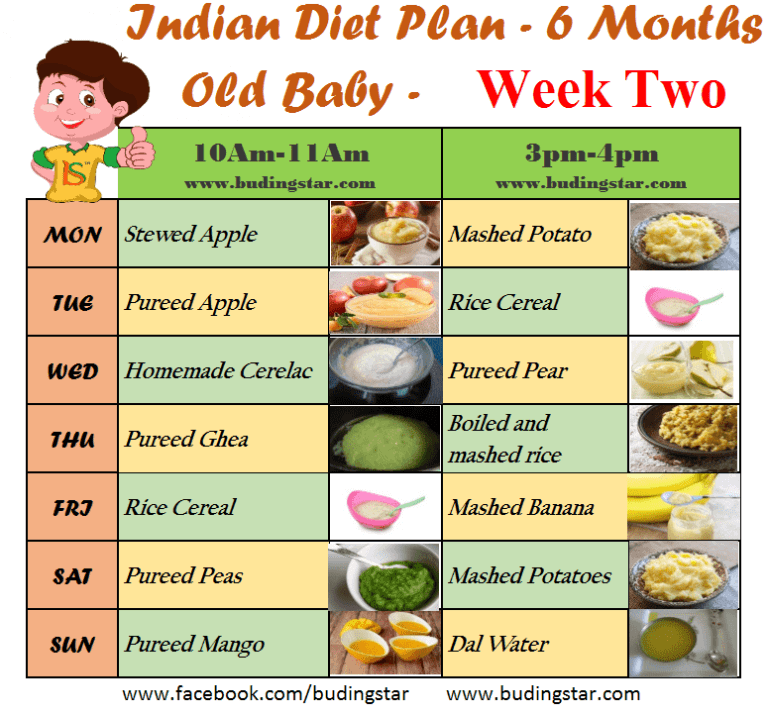 But only children from the poorest families go to state kindergartens. Ours costs just over $10 a month. Many people can afford this…
But only children from the poorest families go to state kindergartens. Ours costs just over $10 a month. Many people can afford this…
ttshka
0376 Schooling in India Compulsory schooling is required for children between the ages of 5 and 14. The school year in Indian schools begins in late March - early April. Studying in schools is divided into two semesters: April-September, October-March. The longest school holidays are in May-June, when heat (45-55º C) covers many parts of India. School education is compulsory in India Compulsory education is a public policy priority in India . Approximately 80% of primary schools are state-owned or supported by the authorities. Education is free. Parents of students pay only small amounts for school needs. All tuition costs are covered by the state. Indian schools are divided into types: Public and non-government schools are operated and funded locally by state governments and local national boards. As a general rule, parents of public school students pay the tuition fee for their children once, at the time of admission. Most public schools in India are affiliated with the CBSE (Central Board of Secondary Education) and ICSE (International Center for Secondary Education) organizations. Public schools are funded and run exclusively by the national government. This type of institution is characterized by the lowest cost of education services. Maintenance funds are provided by the state and CBSE affiliates operating in the area where the school is located. In public schools, all teachers are male. Students are required to wear school uniform . Moreover, each school provides students with uniforms of an individual style. Many private schools in India require uniforms to be worn State-supported private schools are not owned by the government, but operate under rules set by the Indian authorities. Boarding schools are an educational structure that provides not only conditions for studying, but also for living. The services of boarding schools are paid - from $2,300 to $6,000 per year. Special schools in India are for children in need of special care with developmental disabilities. Children receive standard or vocational education in special schools, acquire the skills necessary for a fulfilling life. ... Every Indian school has its own school uniform, which includes not only shirts, skirts, jackets and trousers, but even socks, ties and boots. The smallest ones must wear badges with their name and address ... Anna Aleksandrova http://pedsovet.su/publ/172–1-0–5156
 Tuition here varies depending on the level of service and prestige . Therefore, rates can range from $15 for a month of training to $15 for one day of lessons.
Tuition here varies depending on the level of service and prestige . Therefore, rates can range from $15 for a month of training to $15 for one day of lessons.
Video about the school from the lips of an Indian student
Secondary school in India senior high school course, Indians usually complete in 6 years (12–18). The last two years are considered high-level secondary education with a vocational focus.
Already from the age of 15, everyone is given the opportunity to take exams approved by the directives UGC, NCERT, CBSE .
UGC (University Grants Commission) is a university grants commission in Sri Lanka. He is engaged, among other things, in regulating the admission of applicants to universities. NCERT (National Council Of Educational Research) is the national council of educational research. CBSE (Central Board of Secondary Education) is the central board of secondary education that approves examination processes in schools.
The standard examination process is for students aged 17-18 (completion of high school). Successful completion of the examination procedure is the receipt of a certificate of completed secondary education. The document is necessary for everyone who plans to improve knowledge through the higher school of India.
The document is necessary for everyone who plans to improve knowledge through the higher school of India.
International Schools
In January 2015, there were over 400 International Schools (ISCs) in India. International schools provide complete secondary education, usually in English. In addition to school knowledge, ISC students acquire vocational skills.
Many of the international schools are positioned as public . Teaching in such institutions is modeled on British public schools. These are expensive and prestigious educational institutions, among which are, for example, Delhi Public Schools or Frank Anthony Public Schools.
Indian college education
The number of Indian colleges in 2011 exceeded 33,000 institutions. Of this number, 1800 had the status of women's educational institutions. In fact, this type of educational sites belongs to the country's higher education system. On the basis of colleges, numerous courses are organized, covering the humanities and natural sciences, as well as courses in foreign languages, in particular English.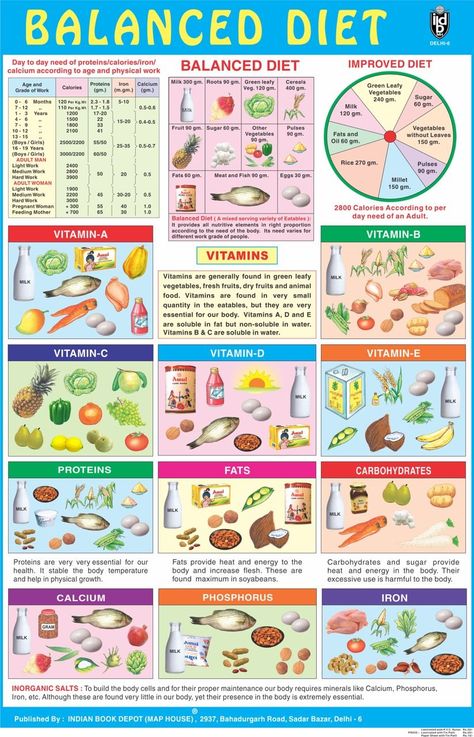 Many colleges are owned by Indian universities. In fact, all of them are the initial stage of university education.
Many colleges are owned by Indian universities. In fact, all of them are the initial stage of university education.
Colleges, as a rule, represent the initial stage of university education
The priority direction of study in colleges is technical and technological specialties. Medical education and business management are also popular. Technical colleges in India are often referred to as institutes. The list of the best institutes contains more than 500 positions. Here are just the first 5 of the list:
- Indian Institute of Technology in Bombay.
- Indian Institute of Technology at Madras.
- Kanpur Institute of Technology.
- Tiruchirappalli National Institute of Technology.
- Punjab Institute of Engineering and Technology.
India's university education system
India's higher education system is second only to China and the US in terms of scale . The peak of development of Indian higher education fell on the period 2000-2011. At the end of 2011, more than 40 international universities, about 300 state universities, 90 private. Another 130 educational institutions were at the stage of transition to the university rank. The following Indian institutions of higher education are distinguished by a high level of education, recognized at the global world level:
At the end of 2011, more than 40 international universities, about 300 state universities, 90 private. Another 130 educational institutions were at the stage of transition to the university rank. The following Indian institutions of higher education are distinguished by a high level of education, recognized at the global world level:
- National Institute of Technology.
- Indian Institute of Information Technology.
- Indian Institute of Management.
- International Institute of Information Technology.
- University of Mumbai.
- Jawaharlal Nehru University.
- Indira Gandhi National Open University.
Students are usually admitted without exams . The academic year for universities in India starts in August and ends in April. Traditionally, Indian universities taught on the principle of a single semester, covering a period of 10 to 12 months. At the end of each year, students take exams.
Now there is a reform taking into account European principles.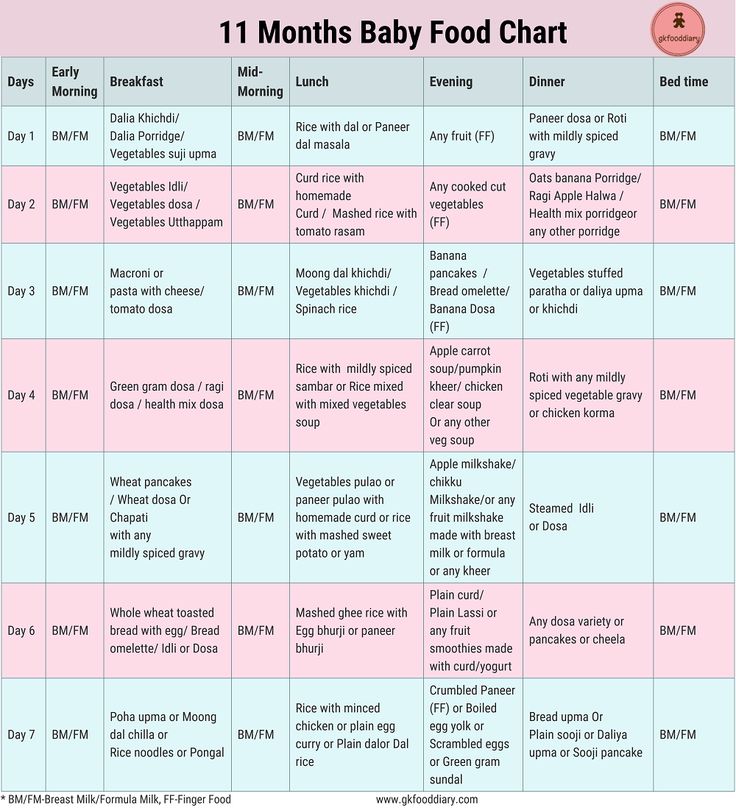 Many higher education institutions have already switched to a scheme of two semesters lasting 5-6 months each. Exams are taken at the end of each semester. English is the main language of instruction for the vast majority of universities. Students are offered a wide range of educational programs. For example, from the following set:
Many higher education institutions have already switched to a scheme of two semesters lasting 5-6 months each. Exams are taken at the end of each semester. English is the main language of instruction for the vast majority of universities. Students are offered a wide range of educational programs. For example, from the following set:
- India - The IT Superpower,
- Sample IT Curricula,
- English Training,
- Internship Programs.
…I was applying for a master's degree at Bangalore University. Requires a translation of a Russian diploma (degree certificate) into English (you can do it without a notary and an apostille. We did it in India). At the same time, they are interested in the final score as a percentage. We used to not put interest in diplomas. The result was not even indicated by numbers, but by the words: “good”, “excellent”, “satisfactory” ...
DHIMANIKA
http://www. indostan.ru/forum/2_7057_4.html#MSG363097
indostan.ru/forum/2_7057_4.html#MSG363097
Videos about the Buddhist University
Some popular educational educational institutions of the India
Training (NIOS) is an institution set up by the Ministry of Human Resources Development in the Government of India . Formerly called the National Open School, it was intended to provide education in remote areas of the country. Administers examinations of open schools in rural areas.
Rajkumar College is one of the oldest colleges in India providing students with K-12 (12-year vocational education) . Located in the center of Rajkot city. The institution was built back in 1868 by a certain Colonel Keating. However, today it has the most modern facilities and a comfortable student hostel.
Indira Gandhi National Open University is an institution of higher learning administered by the Government of India . One of the largest universities, where, in addition to standard types of education, distance learning is offered. In total, the university provides higher education to more than 4 million students.
In total, the university provides higher education to more than 4 million students.
The Calcutta Institute of Engineering is actually the world's largest multidisciplinary engineering professional community . The institute was founded in 1920. And in 1935, the institution was registered by Royal Charter. Students from different countries receive here high-quality higher education in the field of mechanical engineering and other technical areas.
The Indian Institute of Architects is another unique institution established in 1917 . The Institute provides professional education in four areas of architectural art. On the basis of the institute, there are numerous courses that teach the basics of urban planning, infrastructure development and other subtleties of the construction sector.
Photo gallery of popular educational institutions in India
- Calcutta Institute of Engineering is a full member of the Royal Charter0588
- Administrative Corps of the National Open University of Indira Gandhi is always ready to accept students
- College Razhkumar for many years of their activities have been prepared by many specialists in the RECOMINAL REDICAL REDICAL
-
- ERE
- The Indian Institute of Architects prepares high-class specialists for a unique field of activity
Video: Indian education in Delhi
Tuition fees in India
Free education in India for Russians, Ukrainians, Kazakhs is possible, but only within the framework of the Indian economic program ITEC. Advanced training and internships are the main areas of short-term (2-3 months) education provided by the ITEC program. Everything else is paid at established international rates.
Since 2008 spending on educational services in India has multiplied . Secondary education and vocational education is costing the Indian government more and more each year. The Ministry of Statistics recently published information on this matter.
Expenditure on Indian education has increased by 175% in a few years
Nevertheless, the cost of Indian higher education remains low for local residents . Indians pay about $300–350 per semester to study at a university for a bachelor's degree. International students pay more, up to $6,000 per academic year.
International students pay more, up to $6,000 per academic year.
…When a representative of the Indian consulate in St. Petersburg came to our faculty with a lecture, he strongly recommended the ITEC program. This, of course, cannot be called either a magistracy or a graduate school, but it is free, provided that you are selected ... =6673234#t6673234
…Studied for a year at Hyderabad Central University for an MA in Anthropology through ICCR. Education and accommodation are free, they pay a scholarship. Applications must be submitted in January. From good universities: IFLU in Haida, in Pune, Delhi University and J. Nehru University are also in Delhi. Looks good in Pondicherry, and the city is great…
zaryaa
http://ru-india.livejournal.com/824658.html?thread=6672978#t6672978
What are the admission requirements for foreigners?
The step-by-step process is as follows:
- make a request to the educational institution through any modern means of communication,
- select the faculty of interest,
- apply for admission (by regular mail, online, in another way),
- if approved fill in a temporary application, pay an entrance fee of €1000 + €100 service fee,
- receive a certificate confirming the fact of admission,
- apply for a student visa at the Indian Embassy by presenting a certificate of admission,
- complete a permanent student application form and send along with a package of documents.

A package of documents for the student's application form (translated into English):
- certificate or diploma,
- list of subjects of the qualification exam certified by the administration of the former educational institution,
- certified copy of the passport,
- student visa (original),
- medical certificate, including HIV test results,
- certificate of English proficiency (if required by the university) ,
- medical insurance premium for the first year of study in the amount of €45.
Scholarships and grants for Russians and not only
Each new academic year, the Government of India approves a package of scholarships and grants for international students. Usually, all available scholarship offers are sent to different countries of the world through diplomatic missions. Therefore, all information on state Indian scholarships and grants can be obtained from the embassy or consulate of India.
Russian, Ukrainian, Kazakh students are interested in scholarships and grants, which are provided according to the following schemes:
- General Cultural Scholarship Scheme (GCSS) - General Cultural Scholarship Scheme.
- Indian Council for Cultural Relations (ICCR) is a scheme of the Indian Council for Cultural Relations.
- Commonwealth Fellowship Plan - Commonwealth Fellowship Plan (Postgraduate only).
Student Housing and Living Costs
The level of expenses for accommodation, meals, entertainment, etc. directly depends on the location of the student. If you study in cities such as Delhi or Mumbai, you should be prepared for the fact that the standard of living in these cities is comparable to major cities in Europe, Australia, and the USA. In general, the cost of living in India is significantly lower than in other countries of the world.
The usual student housing options are campus or private housing .
The device on student campuses is free only for local citizens. Foreigners have the opportunity to live in dormitories for students, but for a fee - from $60 to $100 per month. Renting an apartment is about $150-200 (two-room apartment in Mumbai). On average, $100–150 is spent on food and other needs per month.
Visa requirements
Immigrant student must have:
- original passport and photocopies of important pages ),
- one photo 2x2 cm, color, on a white background (full face, without glasses),
- letter from the administration of the educational institution where the student entered (indicating the details of training),
- a photocopy of an identity card issued in the student's country of residence,
- a bank statement showing sufficient funds to study and live in India.
All student visa fees must also be paid. If accompanying persons are sent to the country with the applicant, they also need to issue an entry permit and a residence permit.

Work while studying, job prospects
There are practically no opportunities for foreign students in India to work while studying . The administration of universities treats work while studying, to put it mildly, unfriendly. But after graduation, graduates have good job prospects. High-tech graduates can always count on profitable contracts. Such specialists are in great demand by foreign companies. Engineers and architects, financiers and technologists are also valued.
… You can't work. The scholarship is tiny, I agree, therefore, the help of parents is needed in any way. You can live in a student hostel or rent an apartment, which is more expensive, but better. Learning is interesting, which covers all the disadvantages ...
The level of comfort of living and the quality of food are not always satisfactory There are prospects for getting a good job after graduation Employment opportunities after graduation strongly depend on the specialty Climate conditions allow for a few expenses for clothes 0 0 the summer months are very hot, which is unusual for Europeans Studying in India, as student examples show, allows you to successfully achieve your goals.