3 week old baby feeding every 4 hours
Do's & Dont's (Plus How To Do It Right)
What's in this post...
Are you busy with a cluster feeding newborn? This will help you know what to do so you’re not up all night feeding a baby every hour.
Newborns are perfectly snuggly and sweet and warm and wonderful. It’s like you are focused on being so heavily pregnant and making it to birth and then… in an instant you have a tiny person that is so perfect.
And dependent on you.
But it can be hard to survive.
If they won’t sleep well, don’t seem to be eating well, and are irritable due to gas pain, overtiredness, or even baby teething… then you can feel like you’re slowly starting to lose your mind from lack of sleep and complete world upheaval.
A common phenomenon with little ones… cluster feeding.
What is it?
Cluster feeding (n): A breastfeeding pattern when baby groups several feeding sessions in a short window of time. It can happen for a number of reasons (some purposeful, some not), which we’ll dive into below.
Some other names for this are topping up or tanking up (giving baby a bit more to make sure they aren’t hungry when they go to bed) or even split feeding.
Split feeding is used when you sort of divide up a feed into two so that baby gets what they need immediately, then some more again before going off into dreamland.
How babies cluster feed – 4 likely scenarios:
- Baby cluster feeds at night, but not during the day.
- Baby cluster feeds both day and night.
- Or baby snacks all day but never takes full long feeds.
- Baby cluster feeds sometime in the late afternoon/early evening period (5 pm to 11 pm) on purpose.
Rules of thumb while cluster feeding your newborn
Cluster feeding can really feel difficult or confusing, but I want to assure you that these newborns days are intense yet they will pass.
And the habits you start now can create a strong foundation then fade out naturally into a mutually beneficial routine.
Remember, during this time you may find your baby log comes in handy to refer back to. You certainly don’t need to keep track of anything, but organized mamas often feel comforted by this. Knowing that baby is getting enough milk and sleep throughout the day.
Reasons cluster feeding works
So first of all, you’ll end up cluster feeding at some point in the day with your newborn.
Their tummies are tiny and they need to fill them up at regular intervals.
This is actually a good thing and you can use this feeding rhythm to your benefit in a way that means baby gets more sleep and you do too.
Read: End Baby’s Witching Hour — In 4 Simple Steps
If you are reading this, exhausted from excessive breastfeeding (which according to research is a common reason many mothers abandon breastfeeding altogether) then please know you don’t have to feed every hour around the clock to successfully breastfeed.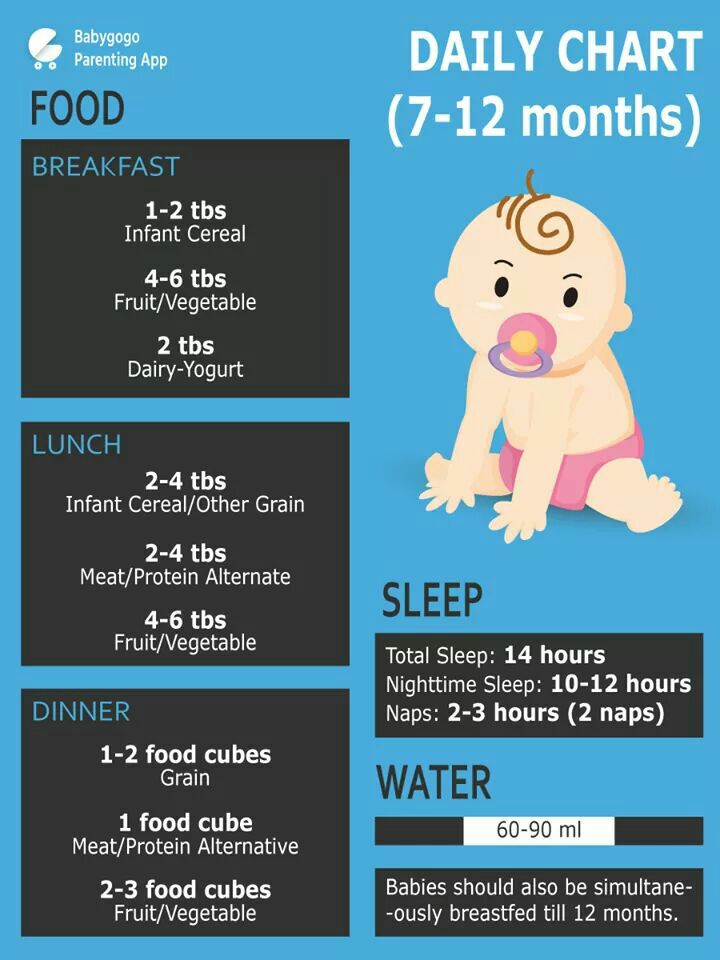
As a certified infant and child sleep consultant and mother of 5, I can attest to this.
Reasons Tanking Up Is Beneficial And Why Babies Do It:
- Your baby gets lots of nourishment in a shorter period of time which is beneficial during the late afternoon/early evening hours when, depending on your personal stress levels, milk quality may be lower.
- Baby can sleep longer stretches after cluster feeding periods.
- Mom can sleep longer stretches because baby is sleeping longer stretches.
- Milk supply can be kept up with regular feeding.
- Cluster feeds help babies get through growth spurts by maintaining adequate milk supply.
- Your baby is less likely to wake up early from a nap or night sleep due to hunger.
Read: Dreamfeed: The Why, The How, & When To Stop
Watch my video on an important cluster feeding issue.
Hourly feedings at night: day night confusion?
If your baby cluster feeds at night, but not during the day then sweet baby probably has some day night confusion going on.
The goal is to make those cluster feeds during daytime hours so they’re sleeping longer stretches at night.
If baby wants to nap for 4 hours during the day… well… don’t let him!
Follow my newborn sample routine or my week by week newborn schedule and do what works for you, but know that if you let baby sleep long stretches during the day he will be up more frequently at night.
Lots of lengthy daytime naps lowers baby’s sleep need. A baby only needs so much deep sleep in a 24 hour period and if he’s getting it during the day… he won’t at night.
Read: What To Do When Baby Is Feeding Every Hour (& Not Sleeping!)
Newborn Settling Guide
Tried-and-true *hands on* newborn settling strategies that even the most fussy (or wide-awake-sleep-refusing) newborns cannot resist!
Learn More
The way forward?
Purposefully cluster feed your newborn in late afternoon and early evening and make sure baby is taking full feeds.
This means at least 10 minutes per breast if you’re nursing, often times twice that.
Read: Cocooning a Newborn & 7 Reasons Why it Can Be Good For The Family
PRO TIP
You can tell when baby is no longer actively nursing but just remaining latched on in a few ways.
First, look at the muscles on baby’s cheek. If they are nursing it will be moving up and down. Next, discern whether baby is swallowing or not.
Then, look at baby’s chin, is it moving as it does during active sucking (aka nursing).
If none of these are happening baby is likely asleep and engaging in non-nutritive sucking.
Read: How To Fix Day/Night Confusion In 3 Nights Or Less
Cluster Feeding CHECKLIST
Use our checklist to use cluster feeding to your advantage without feeding every hour all day every day!
How to stop cluster feeding at night (if you’re ready)
Whew.
Ain’t no mama want to be up every hour at night. The good news is you don’t have to be.
Even if you are feeding every hour through the night, you can shift that and begin getting longer stretches at night.
What’s the only way to stop cluster feeding at night?
Make sure baby is getting as much milk as they can throughout the day.
Don’t let baby snack while nursing. 10 minute feeds throughout the day mean baby will be up all night because baby is hungry and needs milk.
When you start giving baby full feeds throughout the day (this will mean you’ll have to do jump through some hoops to keep baby up) and baby settles into a predictable routine then they’ll sleep longer stretches at night.
Read These While You’re At It
Purposefully cluster feed in the late afternoon period when the milk supply is at its lowest quality (4 pm onwards) so that baby’s tummy is as full as it can be.
This will promote deeper sleep.Eventually, even if baby wakes frequently at night for feeds, if you are not giving long full feeds throughout the night baby will get it.
It’s super hard when your newborn is cluster feeding all night, but you will get there and it will get easier!
Read These While You’re At It
Are you feeding your newborn both day and night?
If you have a cluster feeding newborn both day and night there are only a few likely alternatives.
- Milk supply is low and baby is starving.
- Baby is going through a growth spurt and is starving.
- Baby is only “snacking” and not taking full feeds or getting to the hindmilk rich in nutrients because he just takes a bit then stops.
The best way to help baby stop cluster feeding day and night is to determine which issue you’re having.
If it’s milk supply then continue feeding until your supply is up or supplement with formula (see a lactation expert).
Alternatively, if baby is going through a growth spurt then there’s nothing to do but wait it out and feed baby as much as possible to keep them full and get your supply up to meet the demand.
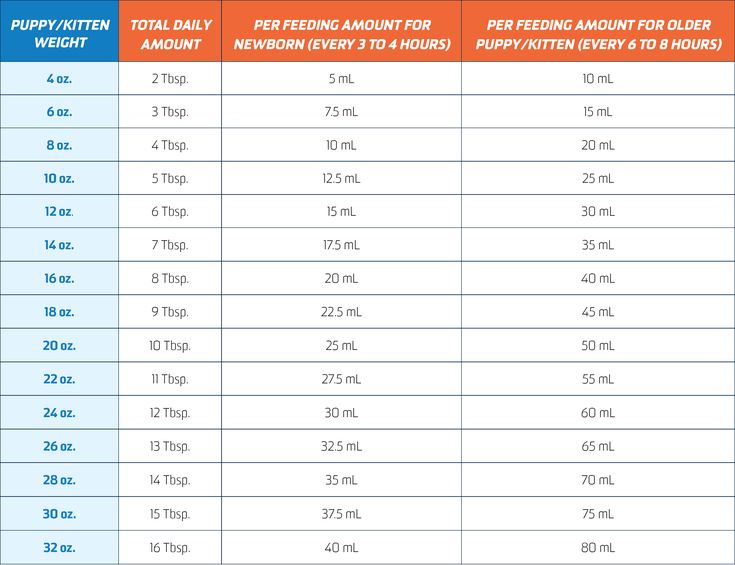
Newborn Feeding Chart
Use this simple printable chart to track your feeds to make sure baby is fed, your supply is up, and everyone is well.
What to do if baby only “snacks”
- Keep baby awake during feeds by taking off their clothes except diaper.
 You can also rub their feet, cheeks, or hands with a baby wipe or keep trying to stimulate them to stay awake long enough to feed. You can put them on a soft blanket or tummy time mat and let them kick in their diaper until they’ve woken up, then continue feeding.
You can also rub their feet, cheeks, or hands with a baby wipe or keep trying to stimulate them to stay awake long enough to feed. You can put them on a soft blanket or tummy time mat and let them kick in their diaper until they’ve woken up, then continue feeding. - Try not to put baby down to sleep if they fall asleep while nursing unless they just won’t wake up. Keep trying to feed baby even if it takes a bit of time so they’ll get as much as they can.
- Differentiate between active nursing and non-nutritive sucking, and let baby do one but maybe not the other.
- Give the baby a pacifier (the pacifier I recommend that stays in baby’s mouth) if they wake and want to nurse right after having nursed a short time ago. They might just need to satisfy the sucking urge and this will help. Also, the next time they feed after this will mean they’ll take more milk and keep your supply up. “Snacking” can contribute to a lower milk supply because baby is never emptying a breast and getting the rich milk.

Eventually by doing those things baby will stop snacking and start taking fuller feeds which will naturally result in longer times between feeds.
Read: The Ultimate Newborn Sleep Schedule: Week By Week For The Postpartum Period
Cluster feeding in the early evening
The prime time to have newborn cluster feeding sessions is the late afternoon early evening.
As I previously said, the milk supply can be lower in quantity and quality at this time due to the stresses of the day.
Because of this, feeding baby every 2 hours for a few hours will help keep your supply up, will keep the little one happy, and will set them up to sleep longer stretches at night.
Your evening routine might look something like this.
4:30 p.m. Nurse and nap
6:30 p.m. Nurse and catnap (or skip nap)
8:30 p.m. Nurse and bed
10:30 p.m. Dreamfeed
By purposefully cluster feeding in the right time you’ll help everyone sleep more at night while keeping your precious one topped up on milk.
Summary
- Feed every 1.5 to 2 hours during the early evening.
- Give baby plenty of milk before their bedtime so they are satisfied and sleep longer.
- Cluster feed during the DAY so you don’t find yourself having to cluster feed at NIGHT.
- Drop the cluster feeds when baby is no longer interested in one of the feeds.
Remember, feeding at frequent intervals in the late afternoon early evening will not solve actual sleep problems, but it will help your little one have a full tummy.
Sleep issues might subside if they were hunger related.
Cluster Feeding CHECKLIST
Use our checklist to use cluster feeding to your advantage without feeding every hour all day every day!
Rhythms, Routines, & Schedules Pack
Easy to implement routines, rhythms and schedules from birth through school-aged kids to help you streamline day-to-day life with kids, including a step-by-step guide for getting started.
Learn More
Need sample routines for babies 6 weeks and older?
By now, you know how to handle the early days, but what after? Here is the good news: you’ve set your baby up for a foundation of success.
Now all you need to do is continue to find routines that work for you and your baby as they grow up and begin getting bigger and bigger.
Sob.
After having 5 babies with 5 different personalities, I know a thing or two about finding a good schedule.
This is why I’ve created a book of sample routines and schedules for babies ages 6 weeks up to 5 years.
The book includes information on how long to let baby stay awake, how much play time is good for each age, what to do with baby when baby is awake but not quite mobile, and even how to manage toddler and baby joint routines.
Chapters covered in Rhythms, Routines & Schedules include:Section One: Sample Schedules
- 6 Weeks to 3 Months Old
- 3-6 Months Old
- 7-9 Months Old
- 9-12 Months Old
- 12-18 Months Old
- 2-3 Years Old
- 4-5 Years Old
Section Two: Tips and Tricks
- Tips for Managing the Day With Multiple Children
- Daily Rhythms for an Only Child Ages 1-4 Years Old
- Daily Rhythms for Multiple Small Children Ages 0-5
- Sample Bedtime, Mealtime, and Playtime Routines
- Tips for Keeping Kids Busy Throughout the Day
For more sample routines, mom tested and approved schedules for babies ages 6 weeks and up, check out Rhythms, Routines & Schedules right now.
Cluster Feeding FAQ
How long does cluster feeding last?
Cluster feeding typically will happen until around 4 or 5 months of age. Once baby is around 5 months (see the 5 month old schedule here) and they are eating solids, there isn’t as much of a need for cluster feeding.
Does cluster feeding increase milk supply?
If your supply is low and baby is frequently feeding, this will increase your supply. Milk supply and quality is typically lower in the late afternoon early evening and cluster feeding can help fill baby.
Can you overfeed a breastfed baby?
Babies need to eat when they are hungry. Too much “snacking” can mean that baby is getting a lot of the foremilk which is less nutrient dense and will contribute to more feeding. Solution? Full feeds with hindmilk for baby.
Is cluster feeding all day normal?
Yes and no. Babies can tend to feed every hour all day long if they aren’t getting enough milk or they are snacking. If baby is feeding every hour all day long they’re not actually getting much food, they are using your breast as a snack bar. If you’re okay with this, then you’re good to go. And if not, focus on full feeds.
If you’re okay with this, then you’re good to go. And if not, focus on full feeds.
Is it normal for a newborn to breastfeed every half hour?
If babies take full feeds (nursing for 30 to 45 minutes typically) they won’t need food every half hour or even every two hours. If they snack they will feed more frequently.
Sources:
- Fatigue associated with breastfeeding is a major cause in why women stop
- Excessive night waking is associated with increased maternal depression
- Breast milk composition (specifically nucleotides) helps varies by time expressed, late evening feeding linked to more melatonin production in babies
Family Routines Reboot
Take our 3 day challenge to create life-giving family, child, and self-care routines.
Learn More
::
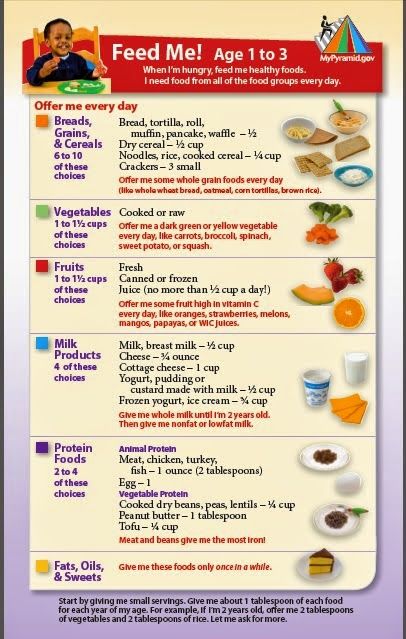
Formula Feeding FAQs: How Much and How Often (for Parents)
Whether you plan to formula feed your baby from the start, want to supplement your breast milk with formula, or are switching from breast milk to formula, you probably have questions.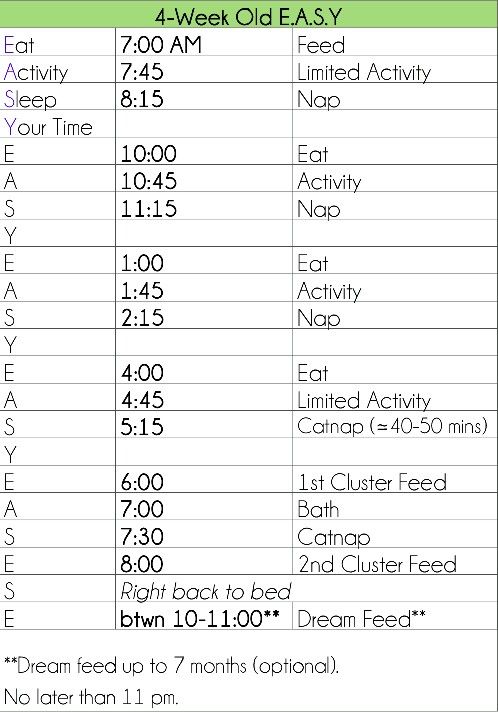
Here are answers to some common questions about formula feeding.
How Often Should I Feed My Baby Formula?
Newborns and young babies should be fed whenever they seem hungry. This is called on-demand feeding.
After the first few days of life, most healthy formula-fed newborns feed about every 2–3 hours. As they get bigger and their tummies can hold more milk, they usually eat about every 3–4 hours. As babies get older, they’ll settle into a more predictable feeding routine and go longer stretches at night without needing a bottle.
Talk to your doctor if you have concerns about feeding your baby, especially if your baby is very small, is not gaining weight, or was born early (prematurely).
How Can I Tell When My Baby Is Hungry?
Signs that babies are hungry include:
- moving their heads from side to side
- opening their mouths
- sticking out their tongues
- placing their hands, fingers, and fists to their mouths
- puckering their lips as if to suck
- nuzzling again their mothers' breasts
- showing the rooting reflex (when a baby moves its mouth in the direction of something that's stroking or touching its cheek)
Babies should be fed before they get upset and cry. Crying is a late sign of hunger. But every time your baby cries is not because of hunger. Sometimes babies just need to be cuddled or changed. Or they could be sick, tired, too hot or too cold, in pain, or have colic.
Crying is a late sign of hunger. But every time your baby cries is not because of hunger. Sometimes babies just need to be cuddled or changed. Or they could be sick, tired, too hot or too cold, in pain, or have colic.
How Much Formula Should I Feed My Baby?
In the first few weeks, give 2- to 3-ounce (60- to 90-milliliter) bottles to your newborn. Give more or less depending on your baby’s hunger cues.
Here's a general look at how much your baby may be eating at different ages:
- On average, a newborn drinks about 1.5–3 ounces (45–90 milliliters) every 2–3 hours. This amount increases as your baby grows and can take more at each feeding.
- At about 2 months, your baby may drink about 4–5 ounces (120–150 milliliters) every 3–4 hours.
- At 4 months, your baby may drink about 4–6 ounces (120-180 milliliters) at each feeding, depending on how often they eat.
- By 6 months, your baby may drink 6–8 ounces (180–230 milliliters) about 4–5 times a day.

Watch for signs that your baby is hungry or full. Respond to these cues and let your baby stop when full. A baby who is full may suck with less enthusiasm, stop, or turn away from the bottle.
Why Does My Baby Seem Hungrier Than Usual?
As babies grow, they begin to eat more at each feeding and can go longer between feedings. Still, there may be times when your little one seems hungrier than usual.
Your baby may be going through a period of rapid growth (called a growth spurt). These can happen at any time, but in the early months are common at around:
- 7–14 days old
- between 3–6 weeks
- 4 months
- 6 months
During these times and whenever your baby seems especially hungry, follow their hunger cues and continue to feed on demand, increasing the amount of formula you give as needed.
Is My Baby Eating Enough?
At times, you may wonder whether your baby is getting enough nutrients for healthy growth and development.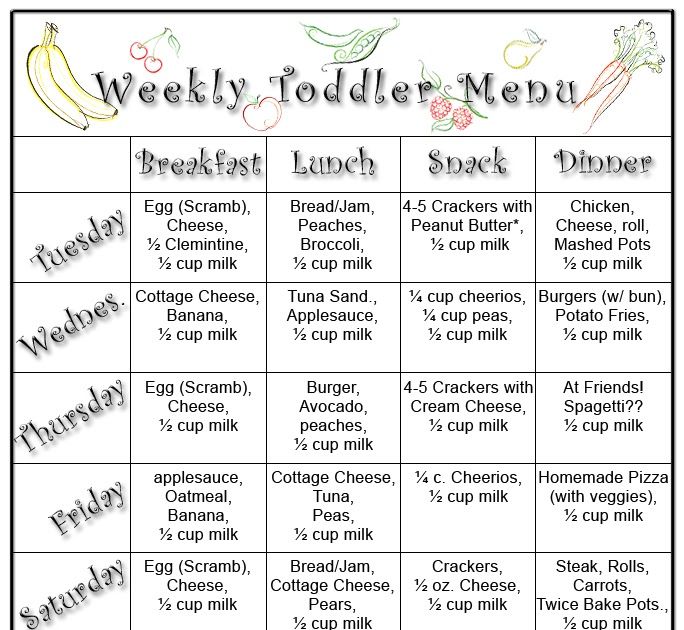 Babies who get enough to eat seem satisfied after eating and are regularly peeing and pooping.
Babies who get enough to eat seem satisfied after eating and are regularly peeing and pooping.
At your baby’s checkups, the doctor will review your baby’s growth chart, track your little one’s development, and answer any questions. Talk to your doctor if you have any concerns about your baby’s feeding and nutrition.
Reviewed by: Mary L. Gavin, MD
Date reviewed: November 2021
Breastfeeding on demand
You can often hear from a nursing mother: "I feed on demand, my baby requires a breast every 3.5 hours." Or: “I have always fed on demand. In a year, we already had 1 feeding in the evening, and my child calmly refused to breastfeed. Before talking about the demand of the child, it is necessary to find out what modern women mean when they say - "I breastfeed."
Modern mothers consider breastfeeding necessary for feeding their baby. Just for feeding. Breast milk is food, the mother supplies the baby with the nutrients necessary for growth and development. When a baby suckles at the breast, he eats. Breastfeeding makes sense only as a process of supplying proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and microelements.
When a baby suckles at the breast, he eats. Breastfeeding makes sense only as a process of supplying proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and microelements.
During suckling, the baby receives the nutrients it needs with mother's milk. This is the absolute truth. There is another unconditional truth, which is not given any importance in modern society, it is not taken into account and is not considered. Breastfeeding for a child is communication with the mother. We need to figure out how the child understands feeding on demand? Can he understand anything at all? Is there any difference for him how he is fed, for 15-20 minutes after 3.5 hours or in some other way?
What is on-demand feeding
On-demand feeding of a newborn baby means putting it to the breast for every squeak or search. Squeak and search movements in newborns, even as early as the second or third day of life, begin to appear much more often than after 3.5 or 2.5 hours. The need for attachments increases rapidly, and by the 10-12th day of life, the need to attach to a child may occur 15-16 or more times a day. Applications vary in duration. The baby can fall asleep and sleep while sucking for, for example, 1.5-2 hours. Can release the breast after 1-2 minutes. And then ask her again. Why does a child need such frequent contact with his mother's breast?
Applications vary in duration. The baby can fall asleep and sleep while sucking for, for example, 1.5-2 hours. Can release the breast after 1-2 minutes. And then ask her again. Why does a child need such frequent contact with his mother's breast?
That's why. Being in the mother's belly, in a calm, familiar environment, listening to the noises of the mother's body, being in a warm, cramped, confined space, the baby sucked his fist, fingers, loops of the umbilical cord, swallowed amniotic fluid. Learned to suck and swallow. After birth, experiencing discomfort for any, the most insignificant reason, the baby tries to get rid of it. You can get rid of discomfort by getting into the usual conditions of a comfortable stay. The only place where the baby after birth can feel the sensations familiar to him is in the arms of the mother. The only familiar action is sucking. The only familiar taste and smell is the taste and smell of milk and lube in the areola. Milk and lubricant have an odor and taste similar to the taste and smell of amniotic fluid. Therefore, experiencing discomfort, the baby squeaks, or begins to look for an object to suck with his mouth. Ideally, it is immediately applied to the chest. The baby becomes warm, cramped, he hears the beating of his mother's heart, breathing, grumbling in the intestines, he sucks and feels the familiar taste and smell. If such an action happens constantly, the baby gains confidence, no matter what happens, he will solve all his problems with his mother. The place of comfort is now under the breast, and you can suck on the breast.
Therefore, experiencing discomfort, the baby squeaks, or begins to look for an object to suck with his mouth. Ideally, it is immediately applied to the chest. The baby becomes warm, cramped, he hears the beating of his mother's heart, breathing, grumbling in the intestines, he sucks and feels the familiar taste and smell. If such an action happens constantly, the baby gains confidence, no matter what happens, he will solve all his problems with his mother. The place of comfort is now under the breast, and you can suck on the breast.
This whole process is biologically justified. A newborn child does not feel the feeling of hunger, this feeling is not formed in him. It will begin to form at about two months of age. How to feed a creature that does not experience hunger ?! How to encourage him to take some action to get food? This can be done only at the expense of some other incentives. This stimulus for the newborn is constant bodily discomfort, thanks to which he wants to suckle all the time! The most intense, frequent and prolonged sucking in infants is observed in the first two or three months of life. It is in these first months that the main weight gain of the baby occurs.
It is in these first months that the main weight gain of the baby occurs.
Feeding in the first month
Baby falls asleep with breast in mouth, sleeps sucking for a while. Falling asleep deeply, lets go of the chest. After sleeping for a while, he wakes up, and is applied on waking. After sleep, he can stay awake for some time, for example, an hour and a half. During wakefulness, he may feel discomfort 2-3 times, for example, from a completely natural desire to pee, and having called his mother for help, having kissed for a couple of minutes, he will do his deeds. Then he will want to sleep, feel discomfort and, kissing his chest, will again fall asleep sucking. After some time, he will wake up and attach again. Then again a little "walk". And after some time, he will fall asleep at the chest again.
The daytime naps of a one-month-old infant feeding on demand vary in duration and number. There can be 4-6 dreams during the day, and they can last from 5-15 minutes to 2-2. 5 sometimes 3 hours. "Around" each dream, the baby is applied to the chest, and applied between dreams several times. At night, the child falls asleep at the breast. Usually in the early morning hours, he begins to fuss and apply. In the morning, he almost never fully wakes up. The baby sleeps, from time to time, sucking on his mother's breast. Waking up in the morning, the baby is again applied to the chest. If you count all the attachments that have happened in a baby of one month of age, then approximately 16-20 attachments are obtained. This is how a newborn human cub behaves if it is given the opportunity to behave in accordance with physiological and psychological needs, which, by the way, are genetically determined. The child of the first months of life does not separate his personality from the personality of the mother and from her breast. Mom and her breasts, and everything connected with them, are the universe of the baby and himself.
5 sometimes 3 hours. "Around" each dream, the baby is applied to the chest, and applied between dreams several times. At night, the child falls asleep at the breast. Usually in the early morning hours, he begins to fuss and apply. In the morning, he almost never fully wakes up. The baby sleeps, from time to time, sucking on his mother's breast. Waking up in the morning, the baby is again applied to the chest. If you count all the attachments that have happened in a baby of one month of age, then approximately 16-20 attachments are obtained. This is how a newborn human cub behaves if it is given the opportunity to behave in accordance with physiological and psychological needs, which, by the way, are genetically determined. The child of the first months of life does not separate his personality from the personality of the mother and from her breast. Mom and her breasts, and everything connected with them, are the universe of the baby and himself.
In most cases, a modern woman, being afraid to “accustom a child to hands”, strives to limit his requests for sucking. A pacifier and a bottle of tea or water come to her aid in this matter. They, too, can be sucked ... The need for sucking seems to be satisfied. But only the need for communication with the mother during suckling is not satisfied, the peculiar chain of mutual assistance and cooperation between mother and baby is destroyed, the formation of maternal affection and concentration is disrupted. Is the difference in the two actions noticeable to the reader: the baby cried, the mother took him, put him to her chest and started rocking him, or gave him a pacifier and started rocking the stroller, even with the words “Why are you crying, my sun?”
A pacifier and a bottle of tea or water come to her aid in this matter. They, too, can be sucked ... The need for sucking seems to be satisfied. But only the need for communication with the mother during suckling is not satisfied, the peculiar chain of mutual assistance and cooperation between mother and baby is destroyed, the formation of maternal affection and concentration is disrupted. Is the difference in the two actions noticeable to the reader: the baby cried, the mother took him, put him to her chest and started rocking him, or gave him a pacifier and started rocking the stroller, even with the words “Why are you crying, my sun?”
The modern woman who gives a pacifier and pumps a stroller is not a bad person deliberately harming an infant. She is simply in captivity of prejudices regarding the relationship between mother and baby. She does not know how to behave correctly, does not know what to do in accordance with the natural needs of the child. If you tell her what the child really needs, she will exclaim in horror: “What is it, don’t let him get away with?!” Indeed, the child of the first months of life must not be let off the hook. For a woman who does not know how to comfortably carry a baby, and who does not know how to feed him in various positions (sitting, lying, standing and even moving), this can be very difficult. Especially if she is not sure of the correctness of her actions.
For a woman who does not know how to comfortably carry a baby, and who does not know how to feed him in various positions (sitting, lying, standing and even moving), this can be very difficult. Especially if she is not sure of the correctness of her actions.
An action that should become automatic for the mother of a newborn: when the baby cries or shows other signs of anxiety, put the baby to the breast.
What's next?
The baby is growing. A fairly stable rhythm of daytime sleep begins to form in him, and a 3-4-month-old baby behaves quite differently from a newborn. Feeding on demand at this age looks something like this...
- At three months, the baby has 10-12 feeds during the day and 2-4 at night. There are frequent applications for a short time, but their number is reduced. There may be a long night break in feedings, about 5 hours, but this is very rare. Much more often the night break is 2.5-3.5 hours. By this age, the baby's body is noticeably rounded.
- At four months, the baby begins to breastfeed noticeably less frequently. The main feedings are associated with sleep: the baby suckles before bedtime, during awakening and during sleep, both daytime and nighttime. In this regard, he has a fairly accurate feeding regimen. And many babies stop breastfeeding when they wake up after daytime sleep, sometimes as early as 2.5-3 months.
- At five months, the baby has 8-10 daytime feedings and 2-3 nighttime, attachments as well as in the fourth month of life, are organized around dreams - the baby eats when going to bed and some babies suck during awakening.
- At six months, the feeding regimen changes. The most active sucking shifts to the last 2-3 hours before waking up from a night's sleep. The period of daytime wakefulness can be divided into two periods: in the morning, when the baby sucked during the night is rarely applied to the breast, and in the evening, when attachments become very frequent. In total, there can be 7-10 day applications and 3-4 night applications.
 At this age, the baby begins a period of acquaintance with new food - pedagogical complementary foods. Sometimes there are attachments associated with the introduction of complementary foods, the baby “washes down” samples of new food with mother's milk. But many children do not want to drink complementary foods. When complementary foods are introduced to an on-demand baby, it is never meant to replace feedings with complementary foods. This is practically impossible, because the main feedings of the baby are associated with sleep, and mother's breakfasts, lunches and dinners, during which the baby gets acquainted with new food, are located between the baby's dreams, during his wakefulness.
At this age, the baby begins a period of acquaintance with new food - pedagogical complementary foods. Sometimes there are attachments associated with the introduction of complementary foods, the baby “washes down” samples of new food with mother's milk. But many children do not want to drink complementary foods. When complementary foods are introduced to an on-demand baby, it is never meant to replace feedings with complementary foods. This is practically impossible, because the main feedings of the baby are associated with sleep, and mother's breakfasts, lunches and dinners, during which the baby gets acquainted with new food, are located between the baby's dreams, during his wakefulness. - At seven months, the frequency of application is about the same.
- At eight months, the feeding regimen changes. Since the baby shows high motor activity and is very busy exploring the surrounding space, in the daytime he forgets to breastfeed. In this regard, the number of daily feedings can be reduced to 6-8 times.
 The baby compensates for the reduction in daytime feedings by increasing the frequency and duration of nighttime feedings up to 6 times.
The baby compensates for the reduction in daytime feedings by increasing the frequency and duration of nighttime feedings up to 6 times. - In the second half of the year, babies who stopped breastfeeding when waking up after daytime naps recall this habit again. The baby’s daytime sleep in the second half of life, as well as in the region of a year and older, looks something like this: the baby falls asleep sucking, sleeps quietly for a while, for example 1-1.5 hours, then starts tossing and turning, fiddling, worrying, at this moment the mother lies down next to , gives him a breast and the baby can fill up 10-15-30 minutes sucking. Mom may well use this time for her own rest - lie down, read, while the baby sleeps while sucking. I know my mother, a lover of embroidery, who used this time specifically for embroidery ...
- Breastfeeding becomes more frequent at nine to ten months. In the daytime, this is 4-6 full feedings and about the same number of attachments for various reasons.
 The baby has new reasons for attachment. If, during active actions to master the world, the baby fills a bump or gets scared, he calms down with his mother's breast. There may be situations when you can comfort the baby by sitting next to him and hugging him. At night, 4-6 feedings remain, the baby begins to suckle more actively in the morning between 3 and 8 hours.
The baby has new reasons for attachment. If, during active actions to master the world, the baby fills a bump or gets scared, he calms down with his mother's breast. There may be situations when you can comfort the baby by sitting next to him and hugging him. At night, 4-6 feedings remain, the baby begins to suckle more actively in the morning between 3 and 8 hours. - At eleven months, a baby can already have 2-3 complete complementary foods. Initiation to adult food in the mind of a child is not associated with breastfeeding: attachment to the mother's breast is something other than the desire to get enough of the product they like. As a rule, after the baby has eaten, he feels the need to attach himself to the breast. The number of daily feedings remains the same in the child, but the number of short-term attachments increases. There are active mid-morning feedings between 4 and 8 o'clock in the morning.
- At ten or twelve months, the baby, if he is already walking, can sometimes breastfeed every time he comes to his mother, i.
 e. about every 15-30 minutes. Attachments around dreams and night sucking persist. Therefore, if a mother says that a child suckles once or twice a day, this means that there is no feeding at the request of the child. There are restrictions imposed by the mother, with which the baby has come to terms. He treats breast sucking like food, sucks on a pacifier or a finger to fall asleep or soothe, or falls asleep just like that, without calming down.
e. about every 15-30 minutes. Attachments around dreams and night sucking persist. Therefore, if a mother says that a child suckles once or twice a day, this means that there is no feeding at the request of the child. There are restrictions imposed by the mother, with which the baby has come to terms. He treats breast sucking like food, sucks on a pacifier or a finger to fall asleep or soothe, or falls asleep just like that, without calming down. - At twelve months, the baby is applied in about the same way.
- At the age of one and a half years, there may already be one daytime nap, so there are fewer attachments associated with sleep. Preserved for morning sucking. The baby is very free with his mother's breasts. Sometimes it happens that he comes up to suck just for fun. For example, like this: he comes up, climbs on his knees, looks into his mother’s face, smiles, starts to swarm in his shirt, gets breasts, smiles at his breasts, sucks for 30 seconds and leaves.
As for the number of feedings per day when feeding a child on demand, their number is almost never less than 12. A newborn has 12 or more attachments, mostly they are all associated with dreams. And a child, say 1.5-2 years old, can also have about 12 attachments, only 3-4 are associated with sleep, and the rest are short-term attachments for various reasons. I suggest to all mothers reading this text - do not count the application, do not notice their duration. Breastfeed your baby as often as he asks, when you feel the need to.
A newborn has 12 or more attachments, mostly they are all associated with dreams. And a child, say 1.5-2 years old, can also have about 12 attachments, only 3-4 are associated with sleep, and the rest are short-term attachments for various reasons. I suggest to all mothers reading this text - do not count the application, do not notice their duration. Breastfeed your baby as often as he asks, when you feel the need to.
Moms who don't think about breastfeeding without looking at the clock may get the impression that when breastfeeding on demand, the mother can do nothing but feed the baby. This is wrong. After the birth of a baby, a mother begins another life, she is called life with a baby. That's all. The child is with the mother, not the mother with the child! Feel the difference! You need to be able to organize your life in a different way, in the first months, of course, the help of loved ones is very necessary. In the tradition of many peoples, it was customary for the first 40 days after childbirth to remove a woman from any housework and household chores, she was engaged only in a child. In some nations, objects that the mother of a newborn touched were considered “unclean”, therefore, they preferred to protect the mother from the rest of the household, allocating her a separate “corner” of the house, where no one bothered her and she did not interfere with anyone. Among the Slavs, such a restrictive custom was called a six-week. By 1.5-2 months, the rhythm of daytime dreams begins to form, and the baby has a kind of “regime”, the mother becomes more free.
In some nations, objects that the mother of a newborn touched were considered “unclean”, therefore, they preferred to protect the mother from the rest of the household, allocating her a separate “corner” of the house, where no one bothered her and she did not interfere with anyone. Among the Slavs, such a restrictive custom was called a six-week. By 1.5-2 months, the rhythm of daytime dreams begins to form, and the baby has a kind of “regime”, the mother becomes more free.
For a mother who can't imagine breastfeeding without looking back at the clock, and who is sure that the “right” baby is the baby lying quietly in her crib all the time, feeding on demand will be a complete hassle. It will be much easier for such a mother if she stops looking at the clock and ties the baby to herself with a large scarf or uses a patchwork holder (sling). It will become easier for her if she stops running between the nursery and the kitchen, but takes the baby with her to the kitchen and carries him around the house with her, doing housework, in a box, a cradle, a special chair, if she tries not to put him off often, and pick up as soon as possible, postponing the baby only in case of emergency and not for long.
Breastfeeding is not the same as house arrest. In the conditions of modern society, it is possible to organize the exit of a nursing mother to work from about 6 months of age of the baby. If necessary, you can start working from the age of 4 months, but, of course, it is better not every day of the week and not full time. It is the responsibility of a breastfeeding consultant to help a mother organize her return to work.
Sometimes, when I advise mothers on breastfeeding, I suggest that they forget for a second that they are already living in the 21st century. I propose to return, for example, to the cave and ask what they will do if the child woke up at night, how to calm him down? If you are walking through the forest and trying not to attract the attention of predators, how to make the baby silent? If the child is thirsty, what will you give him? What is the baby used to, for thousands of years of its existence? To the fact that he sleeps on his mother while she wanders through the forest with a digging stick in search of roots, and wakes up when mother stops. Since mom stopped, then there is time to wake up and suck. Therefore, even now the child sleeps well, tied to the mother with a patchwork holder, wakes up when the mother, having done a few household chores, sits in a chair to take care of the baby.
Since mom stopped, then there is time to wake up and suck. Therefore, even now the child sleeps well, tied to the mother with a patchwork holder, wakes up when the mother, having done a few household chores, sits in a chair to take care of the baby.
Some mother, reading about the cave, will be offended, saying that she is a civilized creature. But please think. Man, mother's breast and mother's milk have been created by evolution over millions of years. They are made for each other. Baby food has created progress and more recently. The skills of motherhood and breastfeeding have also been lost by our society quite recently. A person is not physiologically adapted to artificial feeding and a pacifier. The mother's breast will not produce enough milk at 6-7 feedings per day. Nature did not know, when creating man as a mammal, that the time would come when the need for breastfeeding would be satisfied by some kind of pacifiers and nipples.
Changes that occur during the formation of the personality of a child who did not have full contact with the mother during prolonged breastfeeding are noted by modern research by psychologists and sociologists. These are changes with a minus sign. It would be better if they were not, these changes.
These are changes with a minus sign. It would be better if they were not, these changes.
Breastfeeding is not only important for the baby, it is also important for the mother. During on-demand feeding, the woman's feelings change, a stronger attachment to the baby is formed, the woman becomes more sensitive to the needs of the baby. Deeper affection and understanding are not only preserved in infancy. They persist for life. For clarity, imagine what happens to a woman’s feelings if she tries to “withstand” a child, endures his crying, anxiety. What happens to a woman if she uses the recommendation from one very popular parenting book: "Go to the child if he cries for more than 15 minutes"? Speaking in abstract terms, humanity is interested in reviving the practice of breastfeeding. The revival of this practice is impossible without mothers realizing the true reasons for the child's need for attachment to the breast.
Lilia Kazakova, pediatrician,
leader of lactation and childcare counselors
Should the baby be woken up to feed
Some mothers worry that their baby does not ask for food at night. We figure out whether it is necessary to wake the baby for feeding at night or for his growth and development, daytime nutrition is enough, as well as how to properly disturb sleep and feed the baby, if necessary. What to give the child, how often and up to what age and how to solve the problem of night awakenings? We will talk about all this with our permanent expert - pediatrician, consultant of the SMART MAMA project Polina Aleksandrovna Kizino.
We figure out whether it is necessary to wake the baby for feeding at night or for his growth and development, daytime nutrition is enough, as well as how to properly disturb sleep and feed the baby, if necessary. What to give the child, how often and up to what age and how to solve the problem of night awakenings? We will talk about all this with our permanent expert - pediatrician, consultant of the SMART MAMA project Polina Aleksandrovna Kizino.
— Polina Aleksandrovna, why do babies eat at night?
- Active growth and weight gain in the first months of life, the growing needs of the body for building material and energy costs require a large amount of nutrients. But the baby cannot eat a lot of food at once in order to accumulate it and use the reserves all night. Therefore, the younger the child, the more often he will eat at night. A newborn baby suckles a breast or a bottle day and night at almost the same intervals, but the older he gets, the less often he feeds at night.
— How to organize the nutrition of a breastfed and formula-fed baby?
— In this matter, it is extremely important for parents to separate the concepts of food and sleep. A small child does not need to eat during the falling asleep period, he is able to eat between feedings during wakefulness and at night during sleep. These two processes go hand in hand, but they should not be strictly tied to each other. Therefore, it is important to understand how much the baby needs to sleep and what should be the intervals between feedings.
Norms of sleep and feeding a child up to a year
| Feed the child at the request or under the regime | Wake up the baby for feeding at night 9010 |
breast
Milk formula | Night feedings during the newborn period and up to three months
Night feedings for older children
|
How much sleep should a child sleep at night? Age norms change every month, but sleep and nutrition are extremely important. For example, a three-month-old baby sleeps normally 10-12 hours a night. But this does not mean that during this time he does not need to eat. As soon as a hungry baby begins to fiddle and worry, mom should offer him breasts or formula. The child eats and continues to sleep, and the sleep process is not interrupted.
As soon as a hungry baby begins to fiddle and worry, mom should offer him breasts or formula. The child eats and continues to sleep, and the sleep process is not interrupted.
— How many months should I feed my baby at night and how often?
— There are different situations. From birth, the intervals between feedings at night are the same as during the day, then the child gradually begins to skip night feedings, the intervals increase, and on average, by the age of one, the baby stops eating at night.
It is necessary to wake the baby for feedings in the first month, but initially it is worth looking at how long the baby will wake up on its own. For example, if the interval is 2.5-3 hours, and the child wakes up on his own after 3.5 hours, this is acceptable. But the situation when the newborn is sleeping is completely incorrect 9-10 hours and does not receive food all this time.
- Advise parents who want to adjust their feeding schedule.
- You can increase the intervals between feedings over time and gradually, and in the first months you need to see how much the baby is gaining weight. If the increase is adequate, then the child needs so much food, perhaps an indulgence. If the increase does not correspond to the desired, then, on the contrary, it will be necessary to supplement the baby more actively. With older children, they are guided by the behavior of the child during the day, his weight and height gains.
If the increase is adequate, then the child needs so much food, perhaps an indulgence. If the increase does not correspond to the desired, then, on the contrary, it will be necessary to supplement the baby more actively. With older children, they are guided by the behavior of the child during the day, his weight and height gains.
Read also: how to create a feeding schedule and daily ration for a newborn who is breastfed, formula-fed or formula-fed
— When can a child sleep through the night without feeding?
— Children are all different. Rare babies begin to sleep at night from the third month. If a child eats his daily allowance during the day and at the same time gains weight normally, there is no need to force-feed him. But there are children who wake up for feeding and a year. The norm at this age is one nightly feeding. By about fourteen or fifteen months, babies stop eating at night, in terms of nutritional needs. After pediatricians do not recommend feeding at night.
It's not just that you need to refuse a child food at night - you should pay attention to his food during the day and assess its sufficiency. At the same time, it is recommended to deal with the sleep regime: when the regime is violated, overwork occurs. Perhaps the child does not know how to prolong sleep on his own, and he needs a breast or a bottle to fall asleep. Then night feedings appear, without which he cannot sleep.
— Is it better to feed at night: breast milk, infant formula or complementary foods?
| Breastfeeding: give breast or bottle expressed breast milk. | Mixed feeding: breast milk if the mother is trying to keep lactating, or bottle formula if the mother is weaning. | Formula Feeding: dilute a portion of formula according to age and doctor's recommendations. |
Complementary foods are not suitable for night feeding, because they require spoon feeding. Do not bottle feed your baby anything other than breast milk, adapted formula, or water.
Do not bottle feed your baby anything other than breast milk, adapted formula, or water.
— How many times should a baby be fed at night?
— When the child wakes up and asks for food, then they feed him, or on the recommendation of a doctor. If the child needs additional food, but he does not ask, the mother should still feed him in the amount in which the doctor prescribed it.
Night feeding rules
- Night feedings usually accompany sleep and do not require waking up.
- The more calm conditions (dimmed light, silence) created during feeding, the better.
- Frequent awakenings at intervals of 40-60 minutes or 1 hour 30 minutes, especially in a child older than four months, usually do not indicate hunger, but an association with falling asleep or prolonging sleep only with breast / bottle sucking.
- With the exception of periods of lactation crisis, when the baby often asks for a breast, nightly intervals between feedings should be the same as during the day, or more.
 Gradually, the intervals between feedings should be increased.
Gradually, the intervals between feedings should be increased.
— Does the quality of food at dinner affect your night's sleep?
— Nocturnal awakenings are influenced not so much by the last feeding as by the food of the day as a whole. It is a mistake to believe that if you give your child a huge portion at night, he will sleep better. On the contrary, it is more difficult to fall asleep on a full stomach. And, with the exception of very young children, it would be rational, as the child grows, to increase the interval between the last feeding and going to sleep.
- A 1-month-old baby will fall asleep on the breast or at the bottle: at this age, the wake time is short and feeding usually causes the baby to fall asleep. The process of eating for him is a big burden, but at the same time, sucking relaxes and calms.
- After three to four months, you can gradually separate feeding from falling asleep and make longer intervals - starting from 10 minutes, reaching 1.
 5-2 hours by the year.
5-2 hours by the year.
Being full before bed does not reduce awakenings, so the baby should be fed as usual. At an older age, one of the complementary foods can be given at night: porridge with milk or meat puree with vegetables, but one should not think that they will somehow affect nighttime awakenings if the child ate little during the day.
— How to wake up a newborn to feed at night?
- To feed a baby, it is enough to offer a breast or a bottle and not wake him up - with a maximum probability he will start sucking. There are situations when the child is very lethargic and you need to fill his nutritional needs. In this case, you can “wake up” and use tactile or sound stimuli - take the baby in your arms and change the position of his body, undress him, stroke him, start talking to him quietly so as not to injure or scare him. Any impact should be smooth and progressive until the baby wakes up. But he can suck in a dream.
If the child gains weight adequately, eats enough during the day, feels well, then the absence of awakenings should not be frightening.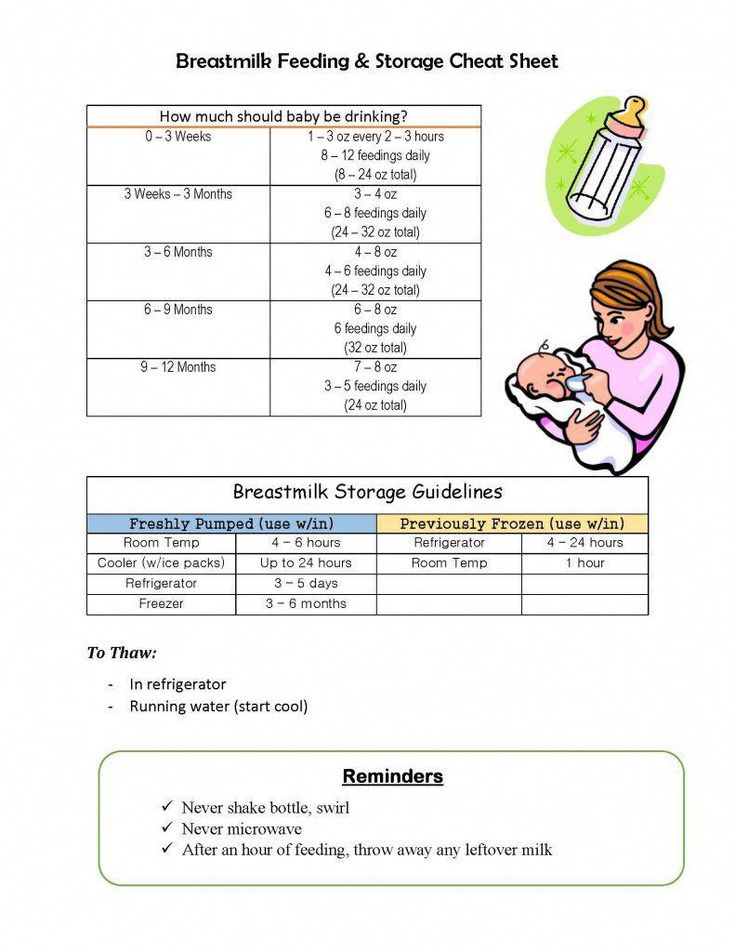 The priority is how the child develops: with adequate development, night feedings are not insisted.
The priority is how the child develops: with adequate development, night feedings are not insisted.
— Let's discuss the problems that parents face during night feedings.
- The child often wakes up at night and cries
- Often the child wakes up at night not from hunger, but to calm himself and prolong his sleep, but he does not know how to do this except with a breast or a bottle.
Parents often underestimate the regime, but it is extremely important, because the violation of the regime significantly affects the functioning of the nervous system. If sleep is not organized, then any irritants are quickly unsettled, the baby can react violently to everything. It is worth paying attention to the rituals that precede going to sleep, associations that accompany falling asleep, living conditions - separate and / or joint sleep. Some babies sleep very restlessly after feeding. There may also be reasons for sleep disturbances.
- Refusal of night feedings
— Parents face a problem when they decide to stop night feedings prematurely. Within reason, you need to follow the child, give him the opportunity to regulate his desires. Ideally, you do not need to feed specially or, on the contrary, stop force-feeding the baby, although there are exceptions in case of violations of his health.
Within reason, you need to follow the child, give him the opportunity to regulate his desires. Ideally, you do not need to feed specially or, on the contrary, stop force-feeding the baby, although there are exceptions in case of violations of his health.
- The baby does not want to eat or eats little and falls asleep
- The baby suckles sluggishly if he does not like the shape of the nipple, bottle or if it is uncomfortable at the breast and it is difficult to get milk. If the baby falls asleep after a short suck, but he needs to be given a certain portion of milk or formula, then he needs to be woken up and fed. During sleep, it is sometimes easier to feed than during the day.
If the child wakes up and does not want to eat, but at the same time he adds normally, then you need to deal with other reasons for awakening. In a healthy child, they look at the organization of sleep, wakefulness and nutrition during the day. Neurological symptoms against the background of sleep disturbance require examination of the baby by a doctor.
Neurological symptoms against the background of sleep disturbance require examination of the baby by a doctor.
— How to normalize sleep and nutrition in infants?
— The norms of sleep and feeding are conditional, therefore, first of all, it is necessary to observe the behavior and physiological needs of the child. If he gains weight well, develops adequately without striking deviations from the norm and negative conditions, then there is no point in adhering to strict rules.
Norms are a guide that allows you to quickly react in a situation where something is wrong with your child. If the baby is very worried, often wakes up at night, gains weight poorly, is naughty during the day, then the norms will help correct his condition. If the child develops well, he is active, stable, there is no reason to adapt to the pattern.
Each age has its own dietary and sleep norms. A child under one year old quite justifiably asks for food at night, and it makes no sense for him to refuse it.