4 day old baby feeding how much
How Often and How Much Should Your Baby Eat?
By: Sanjeev Jain, MD, FAAP
One of the most common questions new parents have is how often their baby should eat. The best answer is surprisingly simple: in general, babies should be fed whenever they seem hungry.
How do I know when my baby is hungry?
For babies born
prematurely or with certain medical conditions, scheduled feedings advised by your pediatrician are best. But for most healthy, full-term infants, parents can look to their baby rather than the clock for hunger cues. This is called feeding on demand, or
responsive feeding.
Hunger cues
A hungry baby often will cry. But it's best to watch for hunger cues before the baby starts crying, which is a late sign of hunger and can make it hard for them to settle down and eat.
Some other typical hunger cues in babies:
Licking lips
Sticking tongue out
Rooting (moving jaw and mouth or head in search of breast)
Putting his/her hand to mouth repeatedly
Opening her mouth
Fussiness
Sucking on everything around
It is important to realize, however, that every time your baby cries or sucks it is not necessarily because he or she is hungry. Babies suck not only for hunger, but also for comfort; it can be hard at first for parents to tell the difference. Sometimes, your baby just needs to be cuddled or changed.
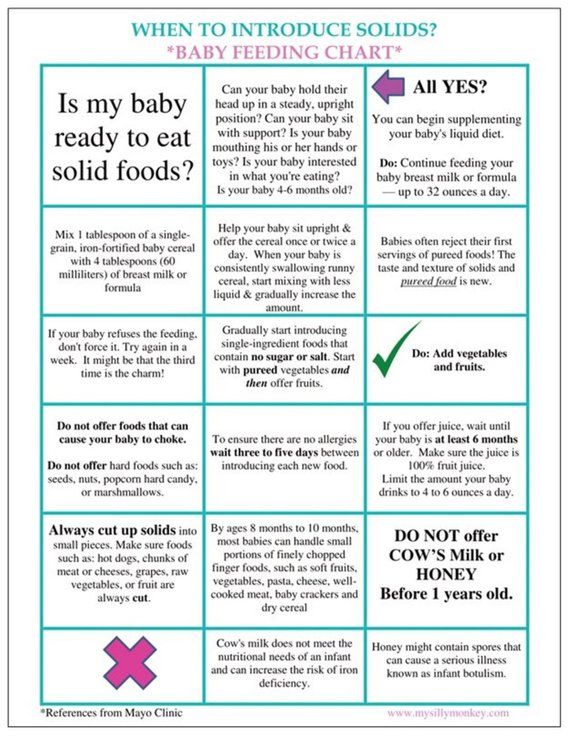
General guidelines for baby feeding
It is important to remember all babies are different―some like to snack more often, and others drink more at one time and go longer between feedings. However, most babies will drink more and go longer between feedings as they get bigger and their tummies can hold more milk:
Most newborns eat every 2 to 3 hours, or 8 to 12 times every 24 hours. Babies might only take in half ounce per feeding for the first day or two of life, but after that will usually drink 1 to 2 ounces at each feeding. This amount increases to 2 to 3 ounces by 2 weeks of age.
At about 2 months of age, babies usually take 4 to 5 ounces per feeding every 3 to 4 hours.
At 4 months, babies usually take 4 to 6 ounces per feeding.

At 6 months, babies may be taking up to 8 ounces every 4 to 5 hours.
Most babies will increase the amount of formula they drink by an average of 1 ounce each month before leveling off at about 7 to 8 ounces per feeding. Solid foods should be started at about 6 months old.
Concerns about overfeeding or underfeeding your baby
Too full?
Babies are usually pretty good at eating the right amount, but they can sometimes take in more than they need. Infants who are bottle feeding may be more likely to overfeed, because drinking from a bottle may take less effort than breastfeeding.
Overfed babies can have stomach pains, gas, spit up or vomit and be at higher risk for obesity later in life. It's better to offer less, since you can always give more if your baby wants it. This also gives babies time to realize when they're full.
If you are concerned your baby wants to eat
all the time―even when he or she is full―talk with your pediatrician. Pacifiers may be used after feeding to help sooth healthy-weight babies who like to suck for comfort, rather than nutrition. For babies who are breastfed, it's best to wait to offer pacifiers until around 3 to 4 weeks of age, when breastfeeding is well-established.
Pacifiers may be used after feeding to help sooth healthy-weight babies who like to suck for comfort, rather than nutrition. For babies who are breastfed, it's best to wait to offer pacifiers until around 3 to 4 weeks of age, when breastfeeding is well-established.
Trouble gaining weight?
Most babies will double their birth weight by 5 months of age and triple their birth weight by their first birthday. If your baby is having trouble gaining weight, don't wait too long between feeding―even if it means waking your baby. Be sure to talk with your pediatrician about how often and how much to feed your baby.
How do I know if my baby is getting enough to eat?
Daily diapers
A newborn's
diaper is a good indicator of whether he or she is getting enough to eat. In the first few days after birth, a baby should have 2 to 3 wet diapers each day. After the first 4 to 5 days, a baby should have at least 5 to 6 wet diapers a day. Stool frequency is more variable and depends whether your baby is
breastfed or formula fed.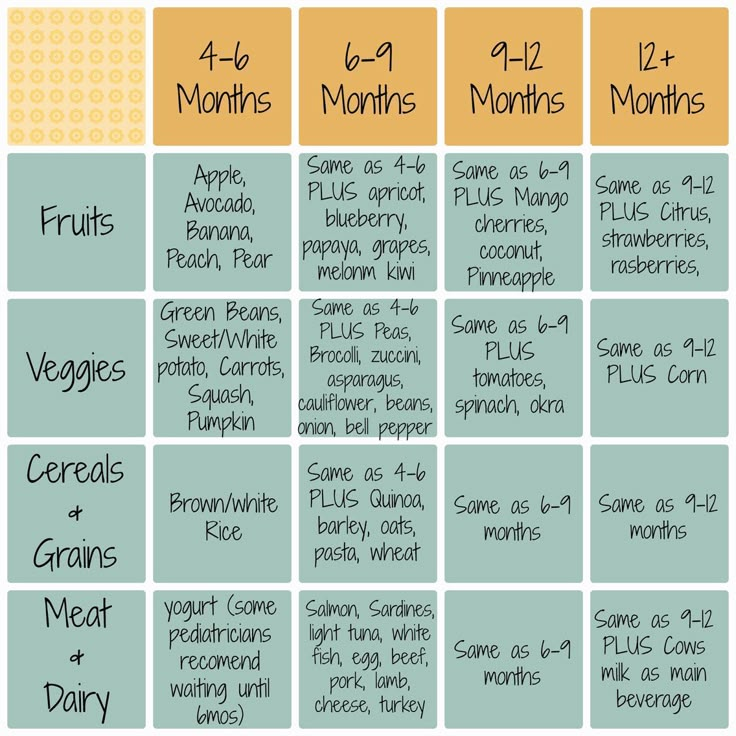
Growth charts
During regular health check-ups, your pediatrician will check your baby's weight and plot it on a growth chart. Your baby's progress on the growth chart is one way to tell whether or not they are getting enough food. Babies who stay in healthy growth percentile ranges are probably getting a healthy amount of food during feedings.
Remember
Talk with your pediatrician if you have any questions or concerns about your baby getting the right amount to eat.
More information:
- Making Sure Your Baby is Getting Enough Milk
- Amount and Schedule of Formula Feedings
- Is Your Baby Hungry or Full? Responsive Feeding Explained (Video)
- Remedies for Spitty Babies
- Ask the Pediatrician: With the baby formula shortage, what should I do if I can't find any?
- Ask the Pediatrician: How should we feed our baby if we're running low on money?
-
Airplane Choo Choo: A Feeding Guide for Children (National Dairy Council)
About Dr.
 Jain:
Jain:
Sanjeev Jain, MD, FAAP, is a Clinical Associate Professor of General Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine at the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health. Within the American Academy of Pediatrics, he is a member of the Section on International Child Health and the Wisconsin State Chapter.
The information contained on this Web site should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician. There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
Amount and Schedule of Baby Formula Feedings
- In the first week after birth, babies should be eating no more than about 1 to 2 ounces (30 to 60 ml) per feed.
- During the first month, babies gradually eat more until they take 3 to 4 ounces (90 to 120 ml) per feed, amounting to 32 ounces per day.
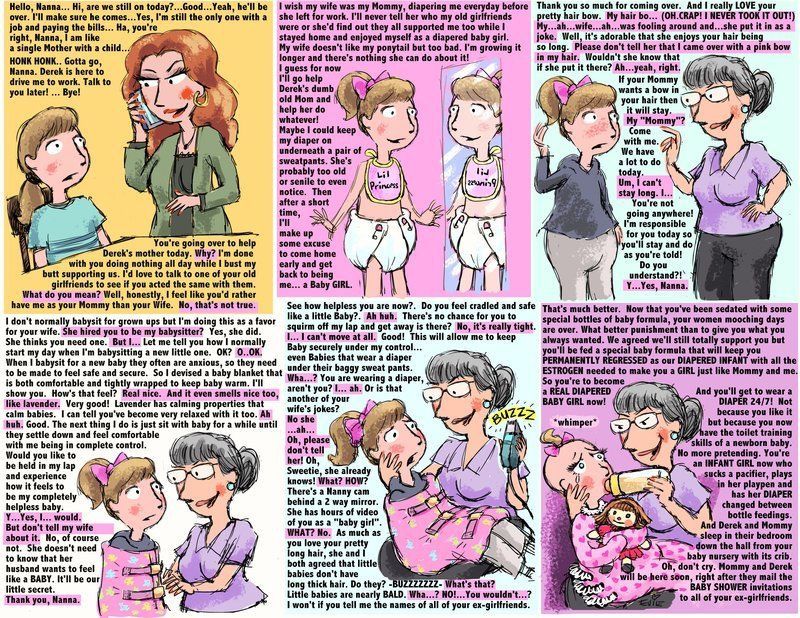 Formula-fed babies typically feed on a more regular schedule, such as every 3 or 4 hours. Breastfed babies usually take smaller, more frequent feedings than formula-fed infants.
Formula-fed babies typically feed on a more regular schedule, such as every 3 or 4 hours. Breastfed babies usually take smaller, more frequent feedings than formula-fed infants.
If your baby sleeps longer than 4 to 5 hours during the first few weeks after birth and starts missing feedings, wake them up and offer a bottle.
By the end of the first month: Your baby will be up to at least 3 to 4 ounces (120 mL) per feeding, with a fairly predictable schedule of feedings about every 3 to 4 hours.
By 6 months: Your baby will consume 6 to 8 ounces (180–240 mL) at each of 4 or 5 feedings in 24 hours.
Formula feeding based on body weight
On average, your baby should take in about 2½ ounces (75 mL) of infant formula a day for every pound (453 g) of body weight. But they probably will regulate their intake from day to day to meet their own specific needs, so let them tell you when they've had enough. If they become fidgety or easily distracted during a feeding, they're probably finished. If they drain the bottle and continues smacking their lips, they might still be hungry.
If they become fidgety or easily distracted during a feeding, they're probably finished. If they drain the bottle and continues smacking their lips, they might still be hungry.
There are high and low limits, however. If your baby consistently seems to want more or less than this, discuss it with your pediatrician. Your baby should usually drink no more than an average of about 32 ounces (960 mL) of formula in 24 hours. Some babies have higher needs for sucking and may just want to suck on a pacifier after feeding.
On-demand feeding
Initially it is best to feed your formula-fed newborn a bottle on demand, or whenever they cry with hunger. As time passes, your baby will begin to develop a fairly regular timetable of their own. As you become familiar with their signals and needs, you'll be able to schedule their feedings around their routine.
Eating & sleeping patterns
Between 2 and 4 months of age (or when the baby weighs more than 12 lb. [5.4 kg]), most formula-fed babies no longer need a middle-of-the-night feedings. They're consuming more during the day, and their sleeping patterns have become more regular (although this varies considerably from baby to baby). Their stomach capacity has increased, too, which means they may go longer between daytime feedings—occasionally up to 4 or 5 hours at a time.
They're consuming more during the day, and their sleeping patterns have become more regular (although this varies considerably from baby to baby). Their stomach capacity has increased, too, which means they may go longer between daytime feedings—occasionally up to 4 or 5 hours at a time.
If your baby still seems to feed very frequently or consume larger amounts, try distracting them with play or with a pacifier. Sometimes patterns of obesity begin during infancy, so it is important not to overfeed your baby.
Getting to know your baby's feeding needs
The most important thing to remember, whether you breastfeed or bottlefeed, is that your baby's feeding needs are unique. No book―or website―can tell you precisely how much or how often they need to be fed or exactly how you should handle them during feedings. You will discover these things for yourself as you and your baby get to know each other.
More information
- How Often and How Much Should Your Baby Eat?
- Making Sure Your Baby is Getting Enough Milk
- Is Your Baby Hungry or Full? Responsive Feeding Explained (Video)
- Remedies for Spitty Babies
- Last Updated
- 5/16/2022
- Source
- Adapted from Caring for Your Baby and Young Child: Birth to Age 5 7th Edition (Copyright © 2019 American Academy of Pediatrics)
The information contained on this Web site should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician. There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
sleep, feeding and development of the baby
04/11/2019
109
By 4 months, the biological rhythms of the child are finally formed, and the structure of his sleep becomes the same as in adults. Therefore, the old ways of laying often stop working, the baby may fall asleep longer, wake up more often at night and constantly breastfeed, and the existing daily routine may no longer work. What to do in this case?
Use our tips to improve your child's routine!
4 months
At this age, children still cannot live according to a clear daily schedule, as they still sleep short dreams during the day and are not able to stay awake for a long time. Therefore, the daily routine of four months. is built based on the time of wakefulness, which is no more than 1.5-2 hours between sleeps. At the same time, an infant needs 9-10 hours of sleep per night with awakenings for feeding and 3-4 daytime sleeps with a total duration of about 4-5 hours. That is, the baby will sleep with this schedule 3-4 times a day. The time of evening bedtime will vary and depend on the end of the last day's sleep. To get your baby to bed on time, be alert for signs of fatigue and stay awake for more than 2 hours. So you will prevent overworking the baby, which will improve the quality of his nightly sleep and reduce the number of night awakenings. Morning should start no later than 07:00-07:30 to form the physiological regime of the day.
That is, the baby will sleep with this schedule 3-4 times a day. The time of evening bedtime will vary and depend on the end of the last day's sleep. To get your baby to bed on time, be alert for signs of fatigue and stay awake for more than 2 hours. So you will prevent overworking the baby, which will improve the quality of his nightly sleep and reduce the number of night awakenings. Morning should start no later than 07:00-07:30 to form the physiological regime of the day.
What to do if a 4-month-old baby slept well but now has trouble getting to bed:
-
Enter a bedtime ritual if you haven't already done so. In the evening, this can be bathing, light massage, putting on a diaper and clothes for sleep, lullaby and feeding. During the day, the ritual can be left the same, only without hygiene procedures. The ritual should be repeated daily and consist of the same actions. It is carried out by one person - either mom or dad.
-
Check that the room has suitable sleeping conditions for a baby: the temperature is no more than 21-23 degrees in winter and no more than 25 degrees in summer, and the air humidity is approximately 40-60%.
 It is also important to darken the room for all dreams, including daytime, and use white noise.
It is also important to darken the room for all dreams, including daytime, and use white noise. -
Organize your baby's rest in the crib. The last daytime nap can be done outside in a stroller.
-
Prolong the child's sleep by any means, if the morning and afternoon sleep lasts no more than 30-40 minutes.
-
If nothing helps and the baby still constantly wakes up at night, neither motion sickness, nor the breast, nor the nipple work to prolong sleep, then it is worth teaching the child to fall asleep on his own.
-
Make sure your baby gets enough sleep. Otherwise, overwork will accumulate, which will manifest itself in frequent nocturnal awakenings. This is where following a routine can help.
Check our chart to see if your baby is getting enough sleep
How many feeds does a baby need at night?
At four months old, breast milk or formula is still the main food in his diet.
The diet of the breastfed baby this month will consist of feedings every 3-4 hours. The volume of breast milk drunk at a time will be about 118-210 ml. The duration of feeding may vary.
When formula-fed, the volume of the mixture should be calculated from the recommendations of the pediatrician. This is usually 1/6 of the child's actual body weight. At four months, the baby will eat 800-1000 ml. mixture per day every 3-4 hours during the day.
The baby is becoming more and more interested in the world around him and during feeding he can start to be distracted, not eat enough and make up for hunger at night. Therefore, it is better to feed the baby in a calm environment.
2-3 feedings are enough at night for a four-month-old baby.
Does the baby wake up at night shortly after feeding and start crying? Instead of refeeding him, try other ways to calm him down, such as petting his tummy and peeing. So the child will not form the habit of falling asleep only with the help of feeding.
So the child will not form the habit of falling asleep only with the help of feeding.
Should we start complementary foods at 4 months? WHO (World Health Organization) recommends introducing complementary foods from 6 months. Therefore, before introducing adult food, it is worth consulting with a pediatrician.
Physical development of a 4-month-old baby
The fourth month is the age when a child already knows a lot and masters new skills.
He is already confidently using both hands at the same time and grasping toys, colorful and shiny objects near him. Soft books, teething rings are a good choice for this age.
For reading, choose large books with different textures inside to develop tactile sensations. Read and sing to your baby every day for a few minutes. This develops the attention and speech of the child. Take a closer look at children's bathing books - their puffy pages are easy to flip through. In addition, they still often squeak, and the pictures in them are bright.⠀
In addition, they still often squeak, and the pictures in them are bright.⠀
The baby is already holding his head and chest well, being on his stomach and pushing off the surface with his hands. Also, the child can already begin to roll over from his stomach to his back and push with his legs.
The baby sees better, begins to distinguish colors and notice objects in the distance, although he still prefers to look at faces and things near him. During walks in the fresh air, tell the baby about the surrounding objects, point to them and describe them.
From the age of 4 months, the first teeth erupt. If the baby's salivation increased, redness appeared around the mouth, he began to bite, refuse to eat, became moody, his night's sleep worsened, then most likely the child has a new tooth. In the acute period, teething rings, anesthetic gel recommended by the pediatrician, more attention and warmth from the mother's side will help.
Important changes occur in communication with the baby at 4 months. He realizes that his mother is coming to his crying, and begins to use different sounds when communicating with others: oooh .., aah .., aha ... Catch the moment when the child “talks” more than usual and play “echo” with him. He says - you repeat.
Such a game gives the child confidence that his mother listens to him and is happy to talk to him. And, of course, develops the speech of the child. Try it - you'll like it.
Also at this age, finger games will already be useful, for example, "Ladushki", "A horned goat is coming", "Magpie-crow" - they are aimed at developing the child's fine motor skills, which in turn is important for the formation of speech.
If your 4-month-old baby does not sleep well at night, we recommend that you watch the free master class "MY BABY SLEEPS BADLY at NIGHT: 3 SOLUTIONS"
What is the daily routine of your baby at 4 months old?
Like this article? Rate:
Votes: 805
how much milk a baby needs for 1 feeding, the rate of formula and breast milk
The birth of a baby is a very joyful event. However, along with the joy of parents, many more questions arise. After all, it is so important that the baby grows up healthy and actively develops. One of the first such questions is usually: "How much does a newborn eat per feeding?" It would seem that feeding is such a natural process that it should not cause difficulties. However, most mothers are concerned that the baby does not have enough milk or, on the contrary, he overeats. How to strike a balance? Let's talk about it in this article.
However, along with the joy of parents, many more questions arise. After all, it is so important that the baby grows up healthy and actively develops. One of the first such questions is usually: "How much does a newborn eat per feeding?" It would seem that feeding is such a natural process that it should not cause difficulties. However, most mothers are concerned that the baby does not have enough milk or, on the contrary, he overeats. How to strike a balance? Let's talk about it in this article.
Breastfeeding is good for both the baby and the mother:
- it helps the baby to get the substances necessary for growth, development and immunity and simply satisfy hunger;
- promotes active contraction of the woman's uterus (under the influence of sucking movements) and a faster recovery process after childbirth.
About colostrum
Newborns eat little, their sucking reflex is just developing and is beginning to be put into practice. In addition, a woman's milk is not produced immediately.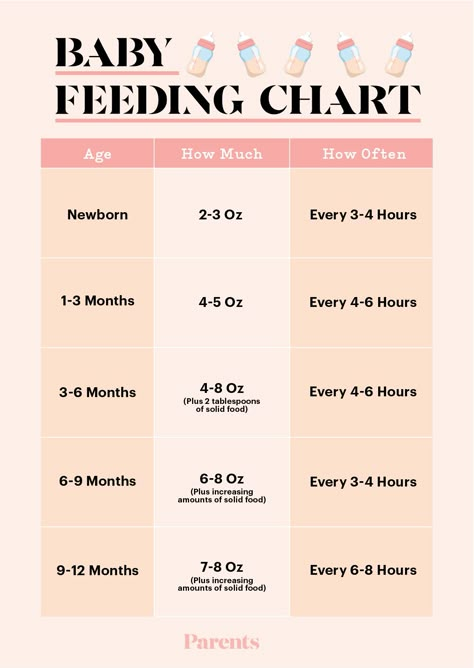 In the mammary glands at the end of pregnancy and in the first hours after childbirth, colostrum is formed. This is not exactly milk, it even outwardly differs from mature milk, and in its chemical composition it is similar to blood. This is a very valuable product. It is high in fat and contains immunoglobulins and antitoxins, which strengthen the immune system and protect the baby's body from infections. After a few days, colostrum is replaced by transitional milk. It is lighter, but also quite oily.
In the mammary glands at the end of pregnancy and in the first hours after childbirth, colostrum is formed. This is not exactly milk, it even outwardly differs from mature milk, and in its chemical composition it is similar to blood. This is a very valuable product. It is high in fat and contains immunoglobulins and antitoxins, which strengthen the immune system and protect the baby's body from infections. After a few days, colostrum is replaced by transitional milk. It is lighter, but also quite oily.
Read also: Complementary foods for artificial feeding
Consumption rates
This is important!
A mother should not worry that her baby was hungry, even if she breastfed him 10 times, but it seems that he has not eaten almost a drop. The size of the stomach of a newborn is very small, so only about 10 ml is eaten per feeding. Thus, for the whole day the baby can drink up to 100 ml.
On average, milk arrives 3-4 days after birth and its quantity gradually increases.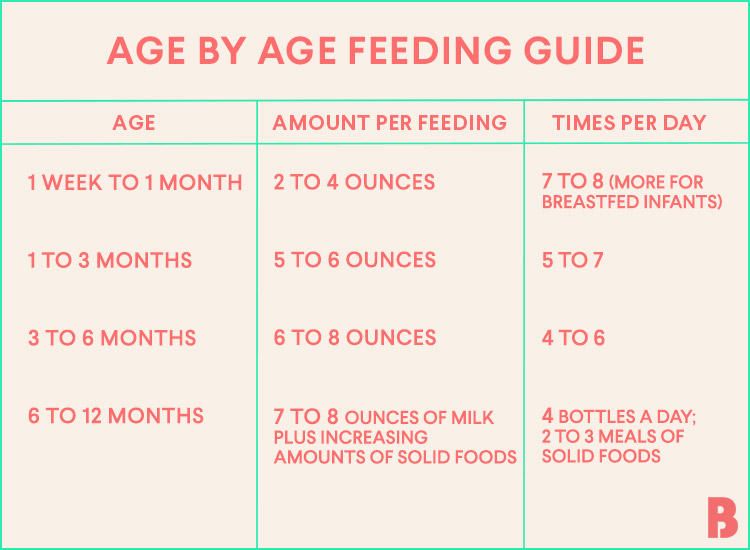 The stomach of the baby also grows. This means that the amount of milk consumed also increases. So, for the first day, a newborn can drink 10 ml per feeding, for the second day - 20 ml, and for the third - 30 ml. But remember that each organism is individual and there are no strict limits here. However, if by the 4-5th day of life the child's body weight does not increase, but only decreases (by more than 8%), then this requires the attention of a specialist.
The stomach of the baby also grows. This means that the amount of milk consumed also increases. So, for the first day, a newborn can drink 10 ml per feeding, for the second day - 20 ml, and for the third - 30 ml. But remember that each organism is individual and there are no strict limits here. However, if by the 4-5th day of life the child's body weight does not increase, but only decreases (by more than 8%), then this requires the attention of a specialist.
There is a folk way to determine the rate of consumption of breast milk. You need to multiply the number of days that have passed since the day of birth by 10. But this method is inaccurate and has no scientific confirmation.
So how much should a newborn eat per feeding? The table shows the daily and one-time volume of milk by months for children under 1 year old.
| Child's age | Milk volume for one feeding (ml) | Milk rate per day (ml) |
| 3-4 days | 9000-60 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 | |
| 1 week | 50–80 | 400 |
| 2 weeks | 9000-61/6 body weight | |
| 4 months | 180–210 9000 | 1/7 body weight |
| 7–12 months | 210–240 | 1/8–1/9 of body weight |
breastfeeding, complementary foods are introduced at about 6 months.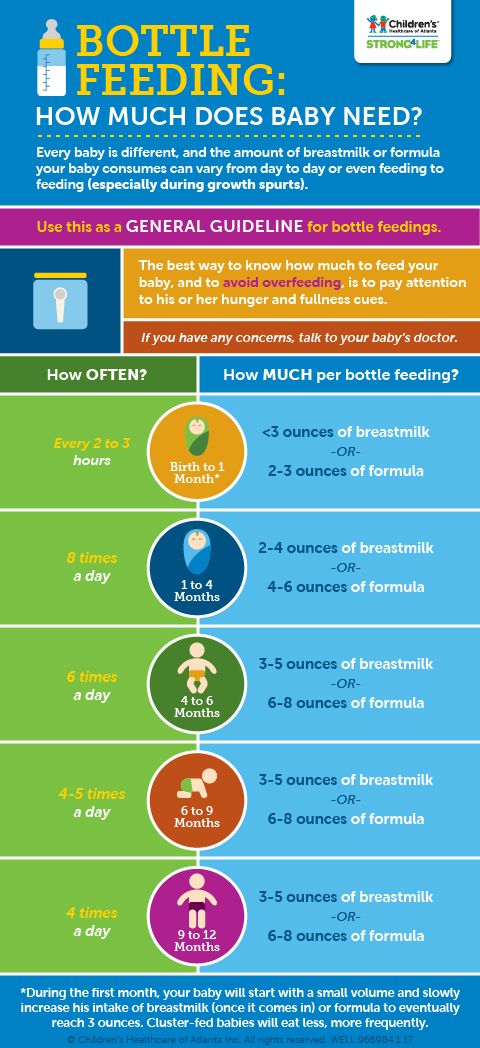 This means that the amount of milk consumed is reduced, giving way to more adult foods.
This means that the amount of milk consumed is reduced, giving way to more adult foods.
How to calculate the amount eaten
In terms of measuring the amount eaten, formula feeding seems to be just perfect. Here is a bottle with a scale, here is water, here is a measuring spoon. However, in terms of its benefits, formula milk will never be compared with breast milk. And besides, making measurements is not as difficult as it seems at first glance. Babies just need to be weighed before and after feeding on a baby scale. To ensure the accuracy of the result, you need to weigh several times a day. If nothing threatens the health of the baby, he does not look thin and pale, develops according to age, and the mother has enough milk, then monthly weighing in the clinic is usually enough.
Feeding schedule
For breastfed babies, there is a rule - to put the baby to the breast on demand. Previously, it was believed that it was necessary to maintain an interval of 3 hours, but now pediatricians agree that the breaks between feedings can be 1. 5–2 hours. This does not mean at all that the baby will overeat.
5–2 hours. This does not mean at all that the baby will overeat.
Video: Does a child get enough food in the first months of life?
Author: pediatrician, Ph.D. Komarovsky E.O.
The duration of one feeding is usually 15-30 minutes. Although there are deviations from the norm. For example, a woman has a lot of milk, and the child is full in 5-10 minutes. Or, on the contrary, there is not enough milk, and the baby can suck out the remains for a long time. Some babies just enjoy suckling and use their mother's breast as a pacifier.
What is important to consider
At first, mother and baby are just getting used to the ongoing changes, so the feeding regimen may not be ideal. However, you should adhere to the following rules.
- In the first couple of weeks, a woman needs a lot of dedication, because the interests of the child in the matter of satisfying hunger come to the fore.
 You can’t refuse food to a baby, even if it costs a sleepless night.
You can’t refuse food to a baby, even if it costs a sleepless night. - If there is any doubt that the baby is undernourished or overeating, it is best to start monitoring the frequency of feedings. So, you need to mark the time at which the baby was really hungry, mark the intervals between feedings. This information may also be useful at the appointment with the pediatrician.
- It is impossible to establish a clear feeding regime, as with artificial feeding, especially in the first weeks after birth. Maintaining intervals of more than 2–3 hours during the day and 3–4 hours at night is highly discouraged.
- Do not try to force feed your baby. He is still too young to realize the need for food, and is guided solely by his feeling of hunger. If the baby persistently refuses the breast, you need to try to offer him to eat a little later. If the interval is too large, it is better to contact a specialist for advice.
- It is important that your baby latch on correctly.
 His mouth should capture not only the nipple, but also the areola. Thus, the milk will properly enter the mouth, and the woman will reduce the risk of cracked nipples.
His mouth should capture not only the nipple, but also the areola. Thus, the milk will properly enter the mouth, and the woman will reduce the risk of cracked nipples. - Soothers and bottles are not recommended for breastfed babies. Such products can reduce the intensity of sucking movements.
- It is best to give your baby only one breast at a time. In the mammary gland, fore milk is formed, with which the baby quenches his thirst, and hind milk, with which he "eats up", since it is more nutritious in composition.
- Hold the baby upright for about 10 minutes after each feeding. This helps to free the tummy from air and excess milk.
As a rule, with a normal feeding regimen and a sufficient amount of milk from the mother, by the month the weight of the child increases by 500–600 g.
Features of artificial feeding Now consider the situation when the mother does not have the opportunity to breastfeed the baby. In this case, it is necessary to choose a quality milk formula that will cover the nutritional needs.
 The pediatrician should help in this matter. The doctor will always take into account the peculiarities of the child's health and will be able to advise a regular or medicinal product. Do not forget that when breastfeeding, the baby makes more effort. He drinks milk gradually and feels full. When feeding with a formula, a strict dosage is needed, since usually saturation does not come immediately, and the baby may require a supplement that he does not really need (the feeling of hunger should disappear after a few minutes).
The pediatrician should help in this matter. The doctor will always take into account the peculiarities of the child's health and will be able to advise a regular or medicinal product. Do not forget that when breastfeeding, the baby makes more effort. He drinks milk gradually and feels full. When feeding with a formula, a strict dosage is needed, since usually saturation does not come immediately, and the baby may require a supplement that he does not really need (the feeling of hunger should disappear after a few minutes). Consumption rates
Almost all known mixtures require 8 or 7 meals a day with an interval of 3 hours. Night feedings are also included. When the baby grows up a little, it will be possible to skip them and sleep 5-6 hours until morning. With regard to formula milk, the principle of feeding on demand is not suitable. Therefore, it is necessary to observe both the dosage indicated by the manufacturer and the regimen.
It will not be difficult to calculate how much the baby eats for feeding.
| Age | Daily milk rate from body weight | |
| 10 days - 1.5 months | 1/5 9000 months | 1/6 |
| 4–6 months | 1/7 | |
| 6–8 months | 9000 | 1/9 |
For example, a baby is 2 months old and weighs 4800 grams. According to the table, we divide 4800 by 6 and get the daily rate - 800 ml of milk formula per day. To calculate the volume of one feeding, divide 800 by 6 (number of feedings per day). Thus, the child eats about 130 ml of formula at a time.
Not everyone can find the right mixture right away, but do not despair. Even with allergies, digestive problems, cow's milk protein intolerance, you can find a suitable product, but only under the strict supervision of a doctor.