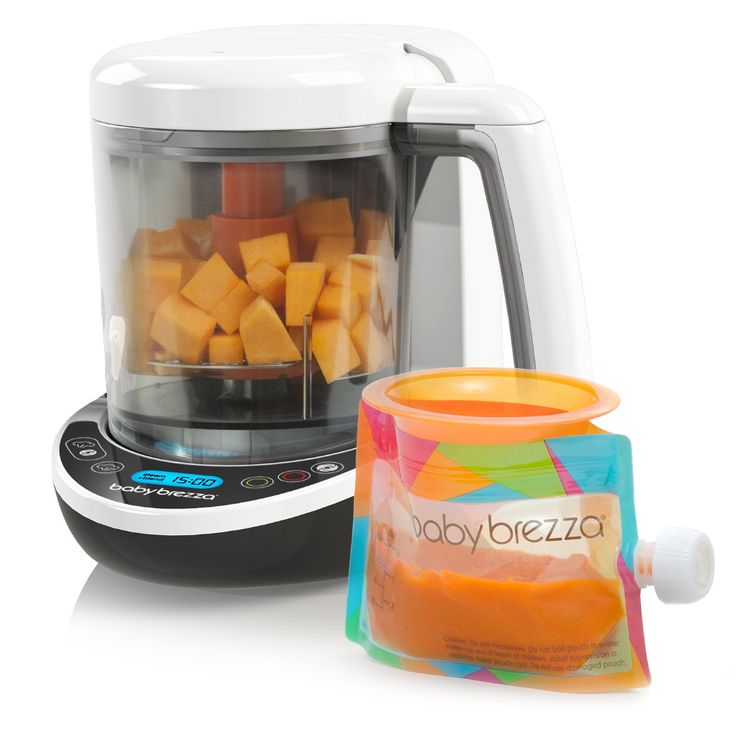
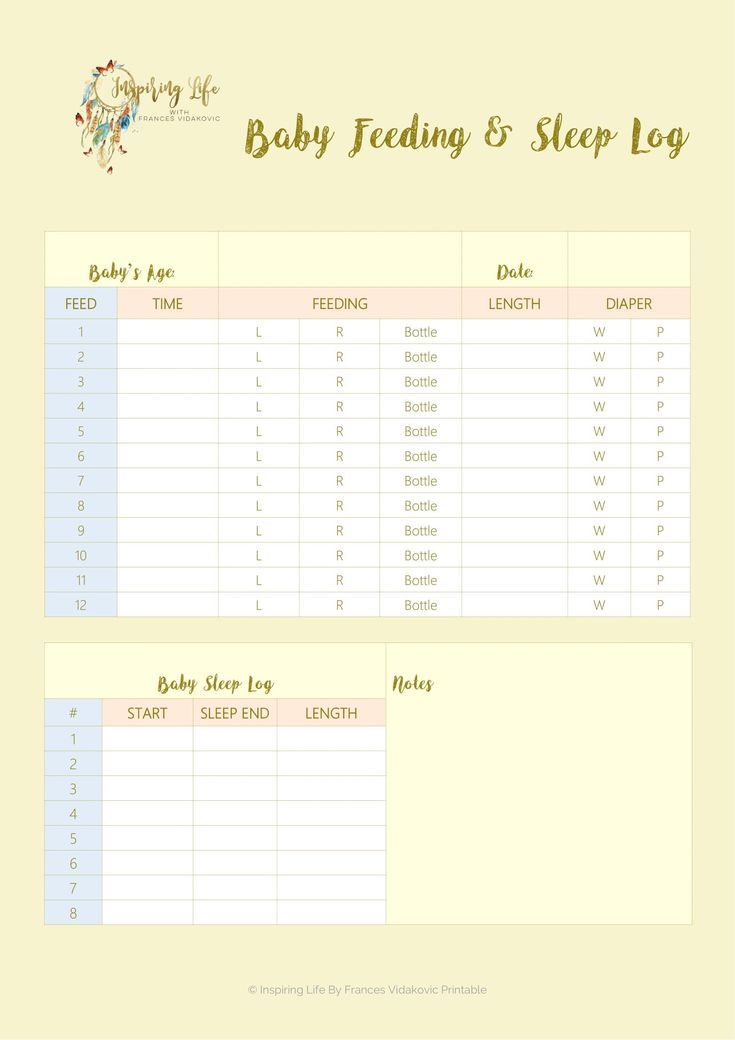
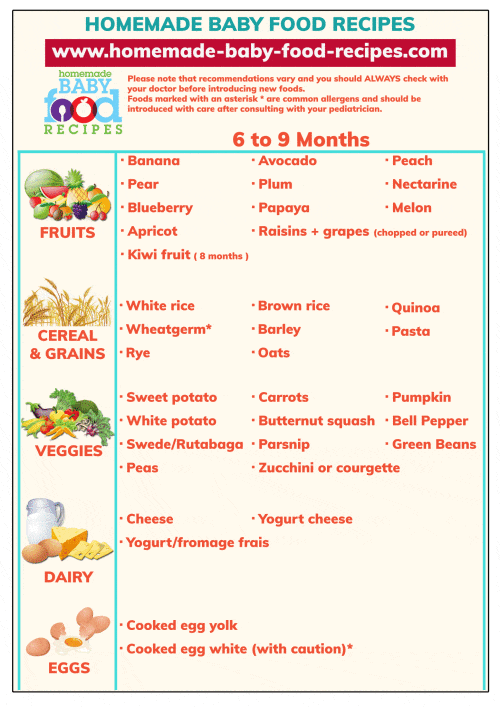
After 6 months baby food chart for indian
6 Months Baby Food Chart
Start your little one’s journey into solid foods the right way with our 6 months Baby Food Chart! Includes healthy and nutritious Indian recipes too!
Things to Remember before Weaning your Baby
Basic Tips for Feeding your 6 Month Old Baby:
6 Months Baby Food Chart with Indian Recipes
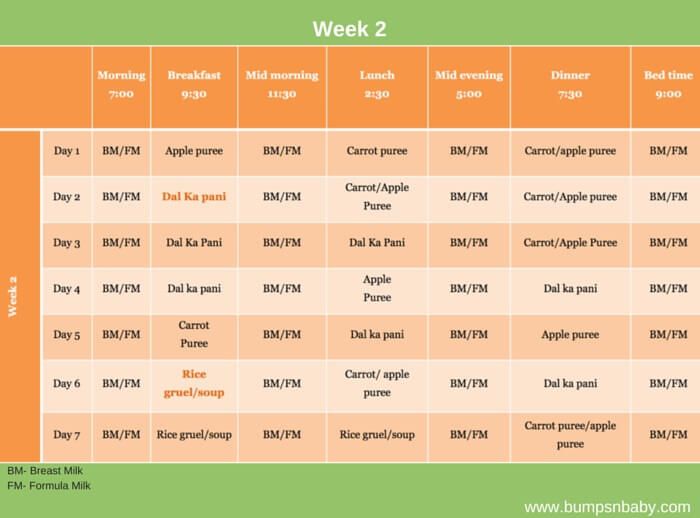
Week 1 – 6 Months Baby Food Chart
Week 2 -6 Months Baby Food Chart
Week 3- 6 Months Baby Food Chart
Week 4- 6 Months Baby Food Chart
How do you know that your baby has an allergy to a particular food?
What to do if your baby is allergic to a particular food?
Buy Healthy Nutritious Baby, Toddler food made by our own Doctor Mom !
So your baby is 6 months old – congratulations, she’s ready to start solid foods! Many Moms eagerly wait for that moment when their little ones start eating new foods. It’s so much fun to watch the expressions on those little faces change as they taste new flavors!
Things to Remember before Weaning your Baby
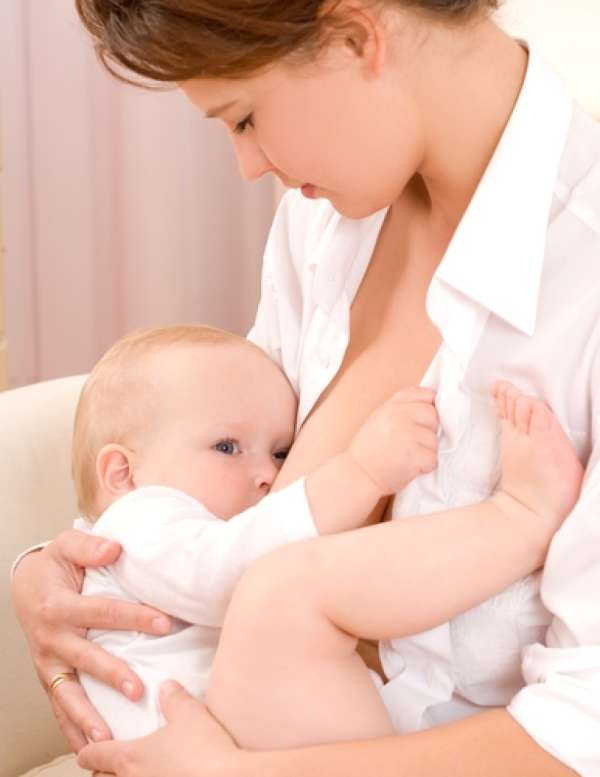
Be sure that your baby is ready for starting solids by checking her physical developmental milestones. Please remember that at this age, breast milk is still the major part of your baby’s diet. WHO recommends exclusive breastfeeding till 6 months of age, and breast milk to complement solids for the next year or more.
Make sure you are well prepared with all the essentials for weaning your baby.
Your baby’s immune system is still weak and she is vulnerable to all kinds of germ attacks. So, ensure that all your baby’s feeding utensils are absolutely clean and sterilized. If you’re confused about how to do it, then this video on how to sterilize the feeding utensils for babies should help.
Initially, it can be difficult to know exactly how much solid food for 6 month old . You don’t really need a lot of solid food for your baby at this age. About 90 ml per feed twice a day should be enough to begin with. Before starting out, you may want to check our post on how to introduce solids to Baby for some useful tips and tricks.
About 90 ml per feed twice a day should be enough to begin with. Before starting out, you may want to check our post on how to introduce solids to Baby for some useful tips and tricks.
Here is a look at the foods you can introduce this month:
Basic Tips for Feeding your 6 Month Old Baby:- You can make any of the purees or porridge runny by adding breast milk or formula milk
- Thicker purees will help add calories
- Follow a routine to feed baby, like tying on the bib, putting him in his chair, etc.
- Continue to breastfeed on demand
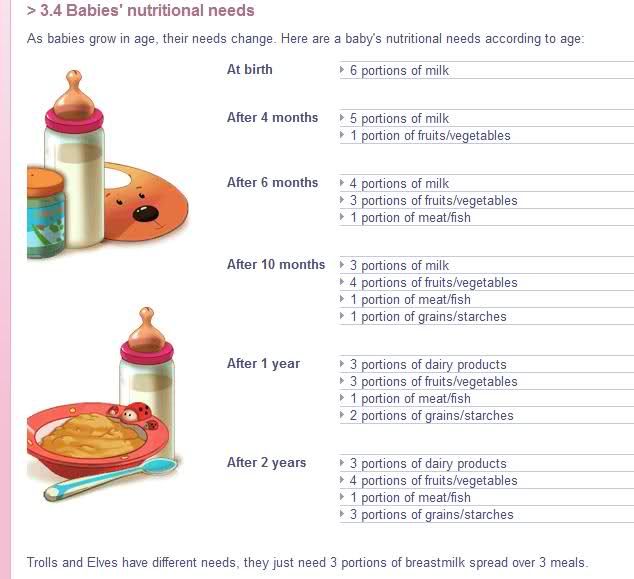
Here is the 6 months baby food chart for indian babies.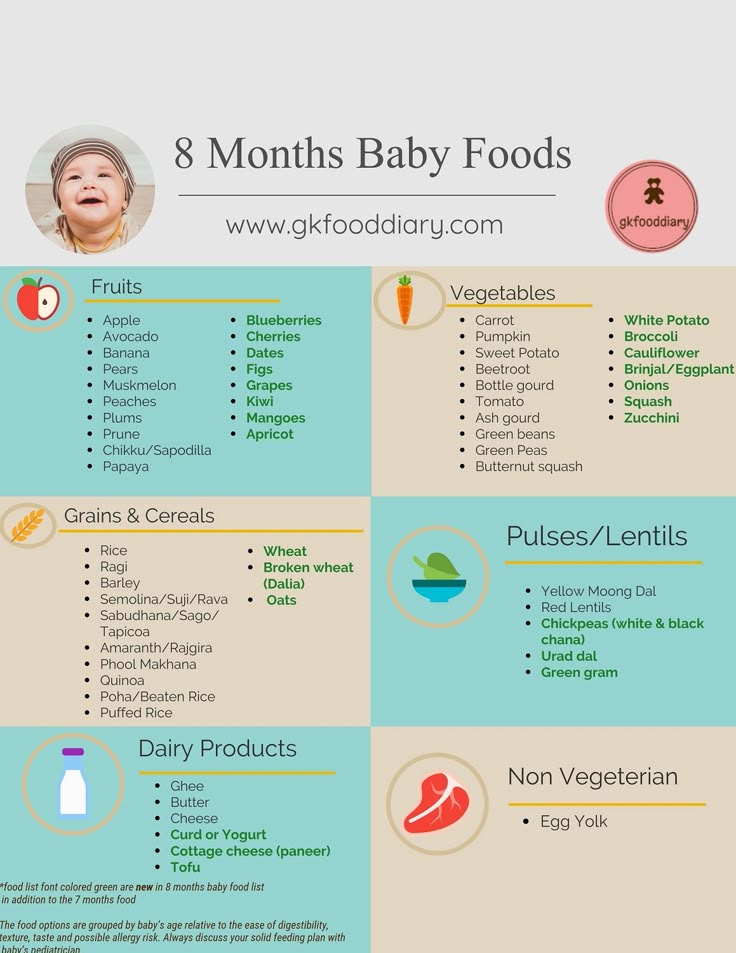
Week 1 – 6 Months Baby Food Chart
Day 1 – The best choice for a baby’s first food is fruit. Start with 1 tablespoon of Apple puree once a day.
Day 2 – Increase to 2 tablespoons of Apple Puree twice a day.
Day 3 – Increase to 3 tablespoons of Apple Puree twice a day.
Day 4 – You can now introduce a new solid, a vegetable. You can start with carrot, by giving 1 tablespoon Carrot Puree once a day.
Day 5 – Increase to 2 tablespoon of carrot puree twice a day.
Day 6 – Increase to 3 tablespoon of carrot puree twice a day.
Day 7 – Go with apple puree in the morning and carrot puree in the evening.
Week 2 -6 Months Baby Food Chart
Now that your baby has gotten used to a texture other than that of milk, you can continue with two solid meals a day. The recommended feeding schedule for 6 month old babies is somewhere during mid morning and early afternoon ,around 3:00 PM, but you can adjust it to your baby’s liking. You can find the recipes mentioned in the chart by clicking on the links below.
You can find the recipes mentioned in the chart by clicking on the links below.
Week 3- 6 Months Baby Food Chart
Continue with the same timings as earlier, with two solid meals per day. You can introduce some new grains, fruit and vegetables this week. Get the recipes of the dishes in the chart by clicking on the links below.
Week 4- 6 Months Baby Food Chart
This week, you can continue with baby’s familiar foods, and introduce some new ones. If anyone in the family has celiac disease, gluten intolerance or any kind of wheat allergy, talk to your doctor before introducing wheat. Get the recipes by clicking the links below.
Please note that these meal plans aren’t written in stone! This is just a guide that gives you an idea about what to feed your baby, when to feed and how much to feed. You can customize these meal plans to your baby’s convenience and routine. If she doesn’t like a food, wait a few weeks before introducing it again. Be patient, don’t expect your baby to polish off the plate at every meal! It’ll take another two months for her to completely finish the portions, so don’t try to force feed the remaining food on the plate.
However, do consider the risk of food allergies. You can’t be sure if your baby is allergic to any food, so always follow the 3 Day Rule before introducing any new food to your baby. This will also help you rule out any foods that are causing indigestion in your baby.
How do you know that your baby has an allergy to a particular food?
If a food doesn’t suit your baby, your baby may present with the following symptoms:
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Vomiting
- Rashes
- Incessant Crying (due to stomach pain)
What to do if your baby is allergic to a particular food?
If your baby is allergic to a particular food, stop it immediately and restart it after 2 months. At every point, be sure to follow the 3 day rule – whether introducing a new food or reintroducing an old one. You can start a “Baby Food Diary” to keep track of your little one’s favorite recipes and specific food allergies.
Please click this link for other 6 months Baby Food Recipes.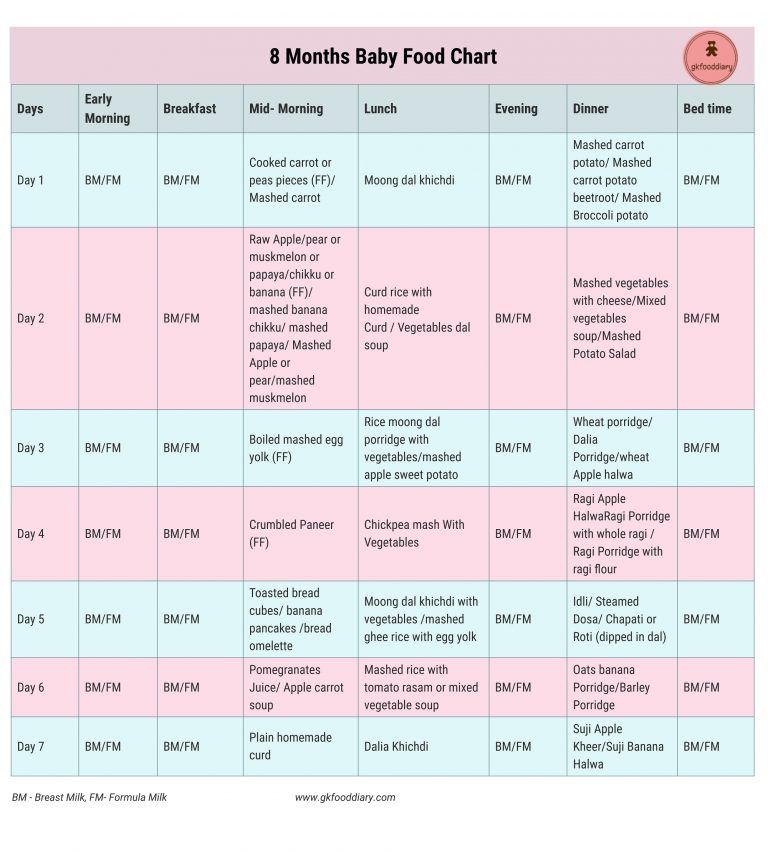
Looking for best first baby foods ? We have got you covered, I make baby food in my own kitchen and we sell through LittleMoppet Foods ! A brand of wholesome and pure homemade baby food products, made without preservatives, added flavors, added sugar or salt. 100% Organic & Natural.
No time to prepare baby food at home? Don’t worry, we prepare it hygienically and ship it to your doorstep. All food products are made FRESH only after the order is placed
Buy Now
Use these food charts and plan your baby’s meals using a Printable Meal Planner. You can also keep a “Baby Food Diary” to track your little one’s favorite recipes and food allergies if any.
If you wish to get a 6 months baby food chart pdf then you can sign up here
Check out 6 to 12 months baby food chart pdf here:
- 7 Months Baby Food Chart
- 8 Months Baby Food Chart
- 9 Months Baby Food Chart
- 10 Months Baby Food Chart
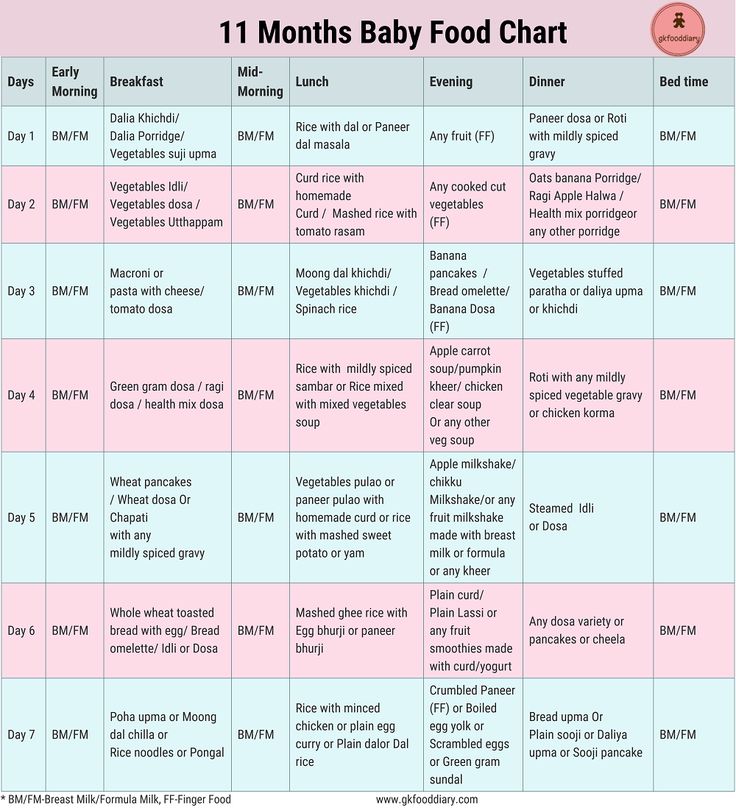
- 11 Months Baby Food Chart
- 1 Year Baby Food Chart
Many moms ask about food for 6 month baby to gain weight, we have covered that also in this article, let us know if you find it useful.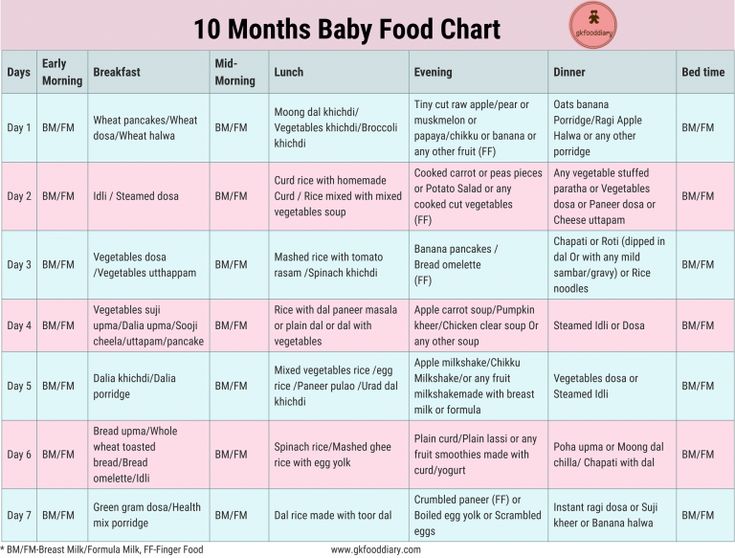
Post Updated on – 11 June 2019, 19 May 2021, 20 March 2022
Post first published on – 7
Make life easier with our eBook, ‘50 First Foods for Babies‘ that has recipes and meal suggestions for every stage of weaning. You can download it for free here.
The information presented here is meant to be a guide and does not replace professional medical advice. You should always discuss your baby’s dietary requirements with your doctor.
Buy Healthy Nutritious Baby, Toddler food made by our own Doctor Mom !
Shop now!6 months baby food chart with baby food recipes
By Swasthi on August 6, 2022, Comments,
6 months baby food chart with baby food recipes. The best time to start solids for babies is after 6 months. There are many sources suggesting introduction of solids from 3 to 4 months. But an early introduction of solids can lead to more colic, digestive troubles and allergies.
But an early introduction of solids can lead to more colic, digestive troubles and allergies.
A baby develops digestive enzymes in between 4 to 6 months which are crucial for digestion of foods. It is a good choice to wait until the baby develops these enzymes completely.
A baby typically begins to develop head control from 3 to 4 months and gains strong head to neck muscles by 6 months. A strong head to neck control helps the baby to accept solids well and can easily swallow.
So by 6 months a baby has a better digestive system and a good head control which are needed before the introduction of solids.
Breast milk is the best bet for the overall growth of a baby. It is recommended to exclusively breast feed a baby for the first 6 months.
As an exception, formula milk is an alternate for women who cannot breast feed baby due to professional, personal or medical reasons.
If you have a baby older than 7 months, you can follow this complete
baby food chart for 8 months old and above
How do you know your baby is ready for solids?
1. The baby’s head & neck are stable. This means baby can accept food and swallow.
The baby’s head & neck are stable. This means baby can accept food and swallow.
2. Baby must be able to sit stable with or without support.
3. Shows interest in food when others are eating.
4. Baby must be able to open the mouth when food is offered.
5. Baby is still hungry after breastfeeding or formula feed.
Tips on how to start solids for baby
First consult your pediatrician to confirm if your baby is ready for solids. It is very important to plan well before you introduce any other foods apart from breast milk.
Make your own feeding schedule along with the foods you intend you try and get an approval from your pediatrician. Most clinics and hospitals also provide a diet chart or at least a guide.
I have made this from the guidelines I got from the Clinics here in Singapore. I have followed the same for both my babies.
1. Always start with a single food. Either a fruit, vegetable or grain. Avoid a mixture of foods.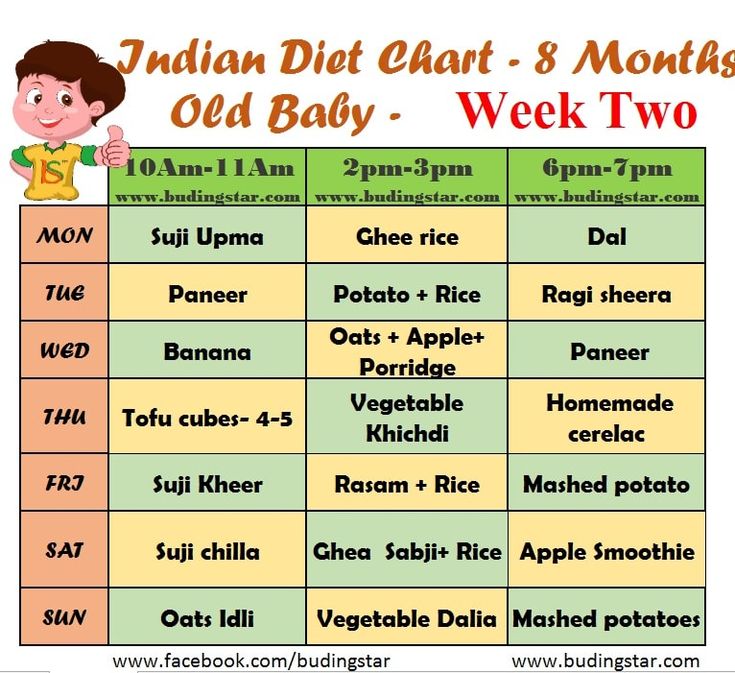 You can start with mashed fruit first. The presence of digestive enzymes in fruits helps the baby to digest them better.
You can start with mashed fruit first. The presence of digestive enzymes in fruits helps the baby to digest them better.
2. After a week, while you continue feeding fruit, you can start rice water (kanji), after a week clear dal soup or boiled vegetable broth / water.
3. Always follow the 3 day wait rule for every food you introduce. Wait for the results until the 4th day. Please see the doctor immediately if your baby develops rashes, runny nose, watery eyes, colic etc.
4. Introduce new foods to your baby during breakfast or lunch. Avoid trying new foods during the later time of the day as it is easy to get a control over the problems.
5. A 7 month old baby can eat only a tsp of mashed food initially. Slowly by 4 weeks increase the quantity to a tbsp and then more.
Helpful tips – introducing solids for baby
1. Use stainless steel or glass bowls and cups for preparation of baby foods. Avoid plastic ware even made of any superior material, including virgin plastic or graded as BPA free.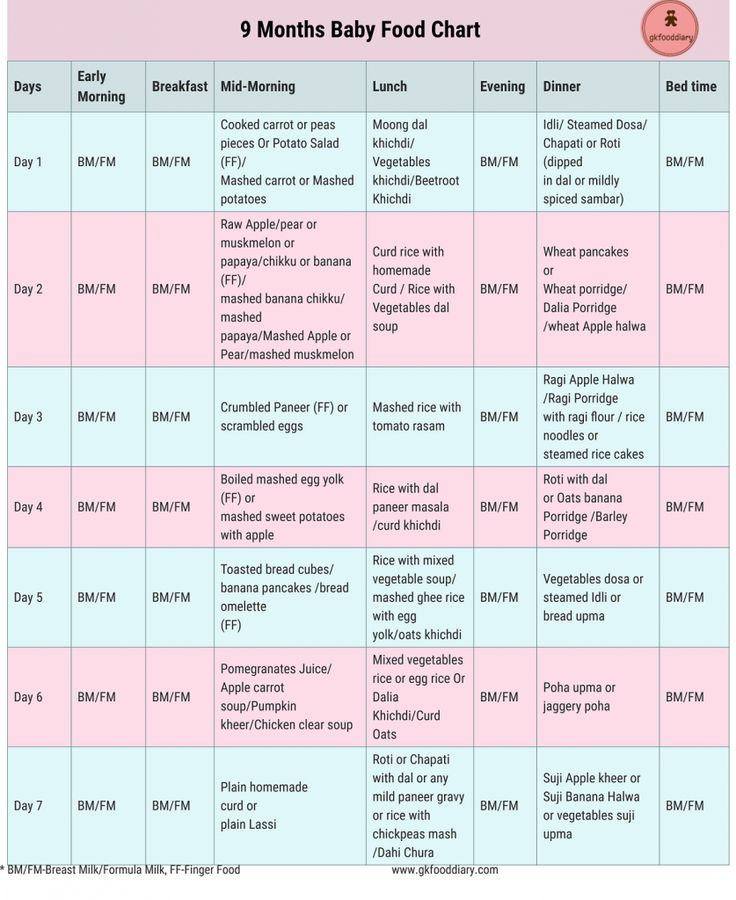 Any kind of plastic ware consists of plasticizers that are used to make the containers flexible.
Any kind of plastic ware consists of plasticizers that are used to make the containers flexible.
Plasticizers are similar to BPA and are an endocrine disruptor. Even BPA free plastic and virgin plastic ware have chemical plasticizers. Please use google search for more info.
2. Always feed the baby in a calm, quite environment and in a steady place like – on the lap, in a high chair or on the floor.
3. While feeding, refrain the baby from activities like watching a TV show, playing with a hand held gadget like mobile, and tablet or game devices. Some of these emit radiation that is not good for the baby.
4. Meal time has to be a learning for the baby, speaking to your baby about the food – its texture, taste and color helps the baby to develop a liking for the food. Or narrate a good story to the baby, do not encourage the baby to talk while eating. This may seem to be over disciplined but this is the only way i have found to grow fuss free kids. They will begin to love any food that is served.
5. Introduce water from a steel cup or a glass not from a feeding bottle or sipper. A 90 ml cup is best suited. This makes the transition from teat to cup easy when the baby grows up.
6 months baby food chart
To follow this baby chart please ensure your baby has completed 6 months and you have an approval from your pediatrician for the same.
A baby usually consumes milk every 2 to 3 hours. Solids should be served in between the feeds. Use plain boiled and cooled water to puree the fruits if needed. Avoid mixing milk or any other ingredient with fruit.
The combination of fruit and milk products results in indigestion, loss of appetite, no weight gain and accumulation of toxins.
Clear soups can be used to make pureed rice, oats or ragi cereal. Feeding only clear soups regularly is not a good idea as they lack the nutrition that is provided by a semi solid food or milk.
I have shared a sample baby food chart below which shows the quantities of fruits and vegetables.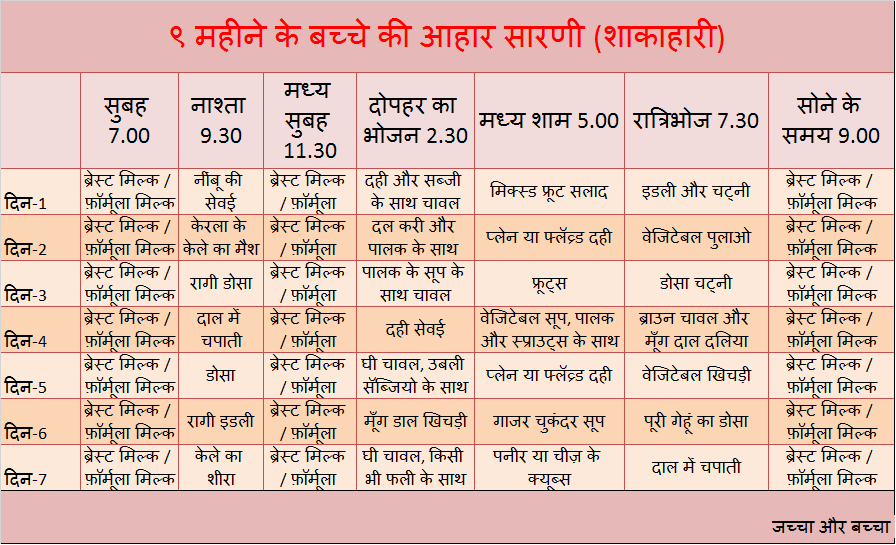 From the chart (day 13 to day 20), you can replace potato with rice porridge (kanji) or dal soup or ragi porridge.
From the chart (day 13 to day 20), you can replace potato with rice porridge (kanji) or dal soup or ragi porridge.
This is an alternate table which you can follow if your baby is in between 6 and 7 months.
| Breastfeed or formula milk. What ever time your baby wakes up. |
7.30 to 8 am fruit puree |
| One of the following: (only after 1½ to 2 hours of milk). You can use boiled cooled water to thin down the puree. 1. Banana- mash with a fork or run in a blender. 2. Apple- peel,core,steam for about 5 to 6 minutes. Puree in a blender 3. Chickoo (sapota)- mash with a fork and spoon 4. Pear- peel and core, steam for 5 to 6 minutes 5. Papaya – mash with a fork or blend 6. Ripe avocado – add it to a blender and puree |
11.30 to 12.30 pm |
After introducing fruits, you can try these. Continue to feed fruits for breakfast. Continue to feed fruits for breakfast.first 1 week – rice cereal 2nd week apple rice or rice cereal with boiled carrot 3rd week ragi porridge Or apple ragi or oats porridge Or apple oats Or clear moong dal soup 4th week – Repeat the foods mentioned above. You can also introduce soupy khichdi. You will have to make it following the same method I mentioned for rice cereal above. |
| Breast feed or formula (only after 1.5 to 2 hours of lunch) |
Baby food recipes for 6 months old along with ingredients and instructions to prepare
These are the quantities i followed for my kids i got from the Health Promotion Board,Singapore.Use any one
Quantity of fruits for 6 months to 9 months
½ small apple
½ small pear
½ cup sapota
½ cup papaya
½ medium banana
How many times can the same fruit be given in a week?
Including a variety of fruits will provide different kinds of nutrients to the baby.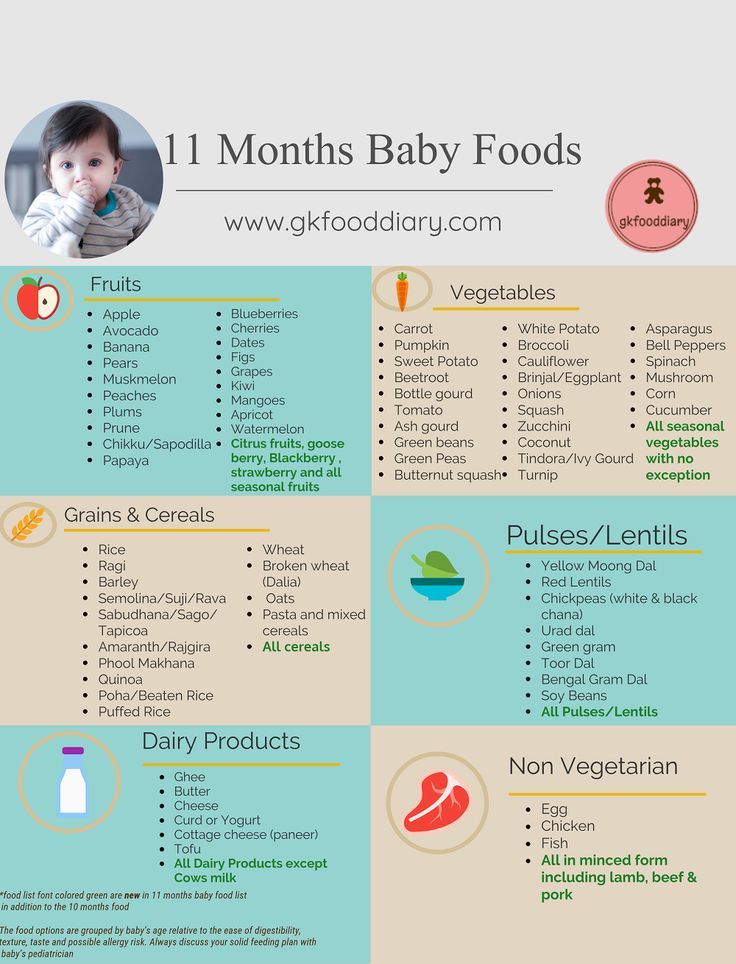
Banana – 3 to 4 times
Apple – daily
Chickoo- daily
Pear- 3 to 4 times
Papaya – 4 to 5 times
Avocado- 3 to 4 times or daily
Do read the complete post before you attempt any of these recipes
More tips on preparing Lunch
from 3 rd week – Rice, ragi or oats. Clear dal soup with veggie.
first 7 days (from 3rd week) -Single grain with milk (formula or breast milk). You can also use gluten free or baby oats or ragi to make porridge.
next 7 days – Rice with a single veggie or apple. You can use steamed or boiled carrots.
VEGETABLES to prefer
1. carrots
2. pumpkin
LENTIL/ DAL to prefer
1. moong dal
2. toor dal
About Swasthi
I’m Swasthi Shreekanth, the recipe developer, food photographer & food writer behind Swasthi’s Recipes. My aim is to help you cook great Indian food with my time-tested recipes. After 2 decades of experience in practical Indian cooking I started this blog to help people cook better & more often at home. Whether you are a novice or an experienced cook I am sure Swasthi’s Recipes will assist you to enhance your cooking skills.
Whether you are a novice or an experienced cook I am sure Swasthi’s Recipes will assist you to enhance your cooking skills.
Follow Swasthi’s Recipes
Sign up to receive awesome Swasthi’s Recipes in your inbox *
Popular Recipes
Featured Recipes
diet for a 6-month-old baby with breast and artificial feeding, an approximate menu for a week in the table, a diet for a day
Published: 02/10/2021
Reading time: 4 min.
Number of reads: 172490
Author of the article: Ponomareva Yuliya Vladimirovna
Pediatrician, candidate of medical sciences, allergist-immunologist
Changes in a child in the first year of life are very rapid, and each month is not like another. The 6-month milestone is very important, it is largely evaluative and transitional. By this age, most babies have doubled their birth weight, are about 15 cm tall, and some babies have already erupted their teeth. The age of 6 months is also transitional in terms of nutrition. Breast milk or an adapted formula is still the basis of the diet, but with the beginning of the second half of life, all children, without exception, should begin to receive complementary foods. Despite the general graph of growth and weight gain and indicators of psychomotor development, the status and diet of children at 6 months can be very different.
By this age, most babies have doubled their birth weight, are about 15 cm tall, and some babies have already erupted their teeth. The age of 6 months is also transitional in terms of nutrition. Breast milk or an adapted formula is still the basis of the diet, but with the beginning of the second half of life, all children, without exception, should begin to receive complementary foods. Despite the general graph of growth and weight gain and indicators of psychomotor development, the status and diet of children at 6 months can be very different.
Content: Hide
- The first feeding of 6 months
- The start of complementary foods at 4-5 months
- The second half of the life
- for a week for a child at 6 months
The first feeding of
If the baby is healthy and breastfed, and his mother eats a full and varied diet, exclusive breastfeeding is possible until this age. Cereal complementary foods in this case are preferable to start. This is due to the high energy and nutritional value of cereals, the ability to significantly enrich the baby's diet with a delayed start of the introduction of complementary foods.
This is due to the high energy and nutritional value of cereals, the ability to significantly enrich the baby's diet with a delayed start of the introduction of complementary foods.
However, the rate of expansion of the child's diet in this situation will be accelerated. Before the 8th month of life, it is necessary to introduce all basic food groups into the baby’s menu, since in the second half of the year the need for additional intake of nutrients and micronutrients is very high. Another reason explaining the importance of the rapid introduction of complementary foods is the formation of immunity of the immune cells of the intestine to ordinary food. If a child is introduced to these foods at the age of 4-8 months, the risk of developing food allergies has been proven to be reduced.
Complementary feeding starts at 4-5 months
In today's life, the nutrition of a nursing mother, unfortunately, is not always complete. Therefore, for most breastfed babies, complementary foods already need to be introduced from 5 months in order to prevent deficient conditions.
If a child is bottle-fed, then by the 4th month of life, the baby will not have enough adapted formula alone, and in this group of children, the timing of the introduction of complementary foods usually shifts a month earlier than in breast-fed babies. Accordingly, by 6 months, children will have vegetable puree and gluten-free porridge (buckwheat, corn and rice) in their diet. In the first half of life, monocomponent meals are used (that is, from one type of grain and vegetables), prepared on the basis of water, breast milk or an adapted mixture.
Fruit puree and juice can be another possible complementary food for children under 6 months of age without allergy symptoms. In a child with a risk of developing or manifesting allergies, the timing of the introduction of fruit complementary foods is shifted to the 8th month.
Second six months of life
Children over 6 months of age can supplement their diet with cereals containing gluten. First of all, these are oatmeal and wheat porridge, and then multi-cereal dishes with the addition of other cereals (millet, barley, rye). If the child does not have any manifestations of allergies, milk porridge can be included in the menu at this age. Bebi Premium industrial baby food products include specially prepared milk that is safe to use in healthy babies in the first year of life.
If the child does not have any manifestations of allergies, milk porridge can be included in the menu at this age. Bebi Premium industrial baby food products include specially prepared milk that is safe to use in healthy babies in the first year of life.
From the age of 6 months, the baby's diet is expanded with such important products as meat and cottage cheese. These products are a source of high-quality protein, fats, and are also rich in minerals such as iron, calcium, and phosphorus. Pediatricians and nutritionists recommend introducing meat and cottage cheese as part of combined dishes based on a fruit and vegetable and / or grain component in a ratio of 1 (cottage cheese / meat): 4–5 (fruits / vegetables / cereals).
To enrich the diet with polyunsaturated fatty acids in the second half of the year, the menu includes vegetable oil in the amount of 3–5 grams per day, which can be added to the complementary food dish. The volume of each feeding is approximately 150-170 ml, and the child can already stand up to 3.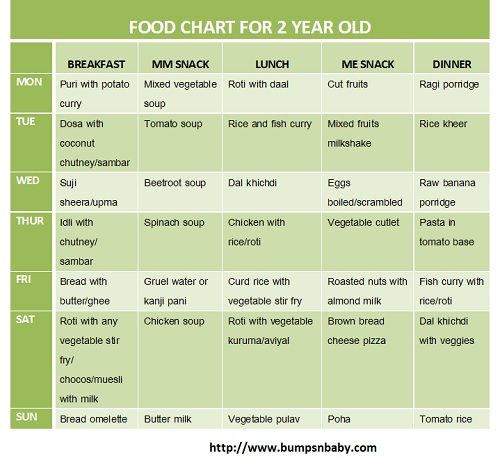 5 hours between meals.
5 hours between meals.
In the table below, we offer a menu of 6 months for a week for a child who started receiving complementary foods at the age of 4-5 months, and by the time the second half of life begins, dairy-free gluten-free cereals, vegetable and fruit purees have already been introduced into his diet.
1st day
| Seeing | 0065 50|||
| Lunch (12.30) | Vegetable soup with beef, olive oil | 100/30/3 | compot of drocked | 900 |
| Afternoon snack (16.00) | Plum puree with cottage cheese | 60/40 | |
| Breast milk/formula | 60 062 | ||
| food reception | menu | ml/g | |
| Early morning | breast milk/mixture | 150 | Milki | & Bashas Breakfast (09 cherry Bebi Premium» | 100 |
| 0065 Breast milk/mixture | 150 | ||
| children's soluble cookies "BEBIKI" Classic | |||
| GRUSHERS with rice and Claus | GRUSHIOUS WITH RISE and CRETURE 30 | ||
| Bebi Premium Kids Instant Herbal Tea | 50 | ||
| Bedtime 065 Breast milk/formula | 150 | ||
Rate the article
(Number of votes: 20, average 4. 8)
8)
Share with friends:
Education in India is third after China and the USA
Education in India, where such sharp contrasts between wealth and poverty, seems to lose all interest for an immigrant. However, the practice of studying in this exotic country shows very different results. A large enrollment flow rushes towards India every year. The goal of each potential student is a good education for little money, in the long term - life abroad.
The history of Indian education and basic principles
The history of the development of the education system in India is a long period of time, the beginning of which, according to various estimates, falls on the 5th century BC. Even then, educational institutions endowed with the properties of a higher school were created in Ancient Taxila.
The ancient city of Taxila was considered the center of higher education in India .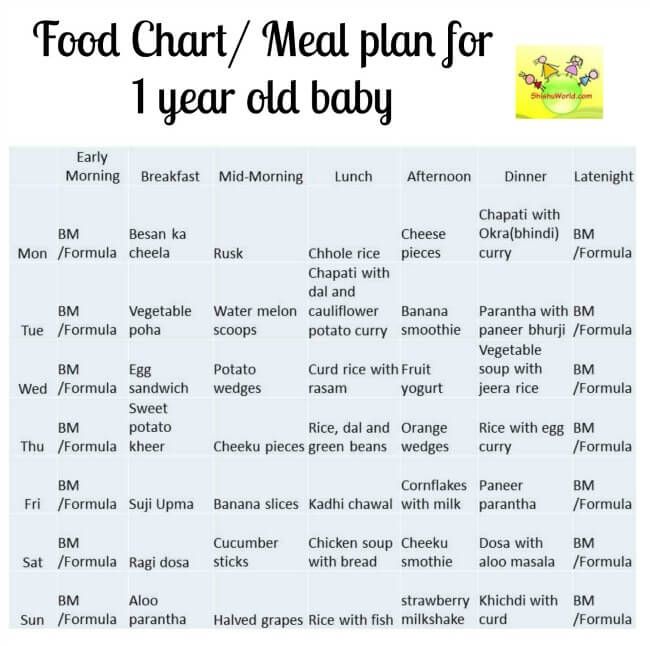 It was there, along with Hindu temples and Buddhist monasteries, that secular institutions first began to be created. These institutions attracted foreigners with training in Indian medicine. However, in addition to the study of living matter, Indian education opened the way to knowledge of logic, grammar, and Buddhist literature.
It was there, along with Hindu temples and Buddhist monasteries, that secular institutions first began to be created. These institutions attracted foreigners with training in Indian medicine. However, in addition to the study of living matter, Indian education opened the way to knowledge of logic, grammar, and Buddhist literature.
Education in India began to emerge in the 5th century BC
The ancient educational system of India supported the principle of dividing society into castes. Depending on belonging to a particular caste, she gave people the necessary knowledge. The modern world has changed somewhat. Indian education in its current form allows you to learn any skill, regardless of the caste of a person.
The country adheres to the main principle of educating its citizens - "10 + 2 + 3" . This model provides for 10 years of schooling, 2 years of college, plus 3 more years of study is allocated to the first stage of higher education.
Ten years of school includes 5 years of elementary education, 3 years of high school education and 2 years of vocational training.
Features of Indian education
Early childhood education
The upbringing of Indian children before entering school goes through a system of nurseries and kindergartens. The nursery accepts babies aged 6 months and older. At this stage, the educational process can continue until the age of three. From three to five (six) years old, kids are educated in kindergartens, which are usually the first element of primary school.
Indian educational system from beginning to end
There are public and private preschools in India . Moreover, there are almost 2 times more private kindergartens. The services of municipal children's institutions are usually free of charge, except for small fees for household needs from the administration and donations from parents. However, the quality of education here is lower than in private institutions where parents pay for the service.
…My son went to kindergarten in India, and now he goes to Moscow.
My personal opinion is that in an Indian kindergarten, a child is given almost free of charge something for which in Moscow you need to lay out a lot of money. For in the state kindergartens in Moscow, children are not taught, but supported. Moreover, constant fees from the parent committee is not clear for what. At the first opportunity, while in India, I will try to send my son to a local traditional kindergarten. The only problem was food, in Moscow they feed, in India they don’t ...
Nadezda Lisina
Private. But only children from the poorest families go to state kindergartens. Ours costs just over $10 a month. Many people can afford this…
ttshka
1040 School Education in India Compulsory schooling is required for children between the ages of 5 and 14. The school year in Indian schools begins in late March - early April. Studying in schools is divided into two semesters: April-September, October-March. School education is compulsory in India Compulsory education is a public policy priority in India . Approximately 80% of primary schools are state-owned or supported by the authorities. Education is free. Parents of students pay only small amounts for school needs. All tuition costs are covered by the state. Indian schools are divided into types: Public and non-government schools are operated and funded locally by state governments and local national governments. As a general rule, parents of public school students pay the tuition fee for their children once, at the time of admission. Most public schools in India are affiliated with the CBSE (Central Board of Secondary Education) and ICSE (International Center for Secondary Education) organizations. Public schools are funded and run exclusively by the national government. This type of institution is characterized by the lowest cost of education services. Maintenance funds are provided by the state and CBSE affiliates operating in the area where the school is located. In public schools, all teachers are male. Students are required to wear school uniform . Moreover, each school provides students with uniforms of an individual style. Many private schools in India require uniforms to be worn State-supported private schools are not owned by the government, but operate under rules set by the Indian authorities. Tuition here varies depending on the level of service and prestige of . Therefore, rates can range from $15 for a month of training to $15 for one day of lessons. Boarding schools are an educational structure that provides not only conditions for studying, but also for living. The services of boarding schools are paid - from $2,300 to $6,000 per year. Special schools in India are for children in need of special care with developmental disabilities. Children receive standard or vocational education in special schools, acquire the skills necessary for a fulfilling life. ... Every Indian school has its own school uniform, which includes not only shirts, skirts, jackets and trousers, but even socks, ties and boots. The smallest ones must wear badges with their name and address ... Anna Aleksandrova http://pedsovet.su/publ/172–1-0–5156  The longest school holidays are in May-June, when heat (45-55º C) covers many parts of India.
The longest school holidays are in May-June, when heat (45-55º C) covers many parts of India.
Video about the school from the lips of an Indian student senior high school course, Indians usually complete in 6 years (12–18). The last two years are considered high-level secondary education with a vocational focus.
Already from the age of 15, everyone is given the opportunity to take exams approved by the directives UGC, NCERT, CBSE .
UGC (University Grants Commission) is a university grants commission in Sri Lanka.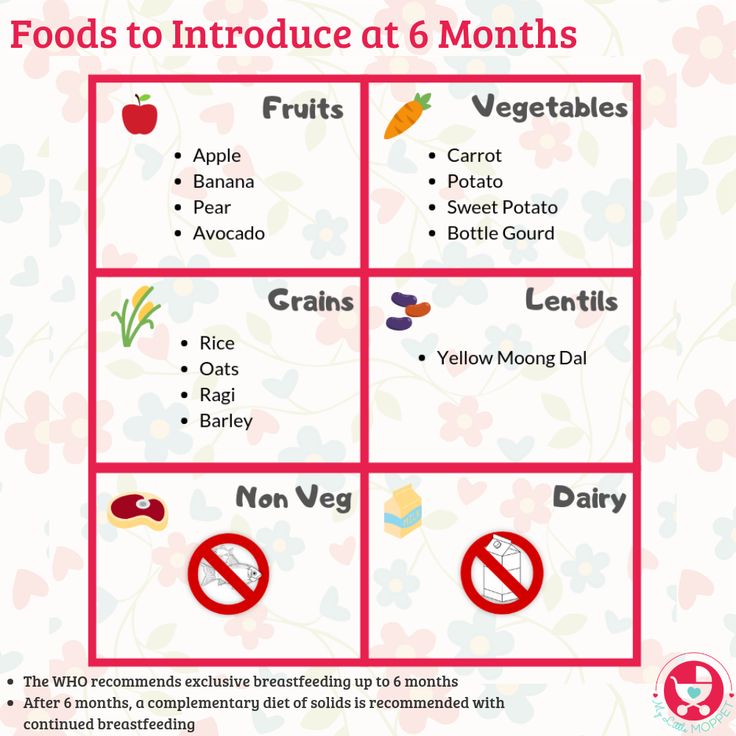 He is engaged, among other things, in regulating the admission of applicants to universities. NCERT (National Council Of Educational Research) is the national council of educational research. CBSE (Central Board of Secondary Education) is the central board of secondary education that approves examination processes in schools.
He is engaged, among other things, in regulating the admission of applicants to universities. NCERT (National Council Of Educational Research) is the national council of educational research. CBSE (Central Board of Secondary Education) is the central board of secondary education that approves examination processes in schools.
The standard examination process is for students aged 17-18 (completion of high school). Successful completion of the examination procedure is the receipt of a certificate of completed secondary education. The document is necessary for everyone who plans to improve knowledge through the higher school of India.
International Schools
In January 2015, there were over 400 International Schools (ISCs) in India. International schools provide complete secondary education, usually in English. In addition to school knowledge, ISC students acquire vocational skills.
Many of the international schools are positioned as public .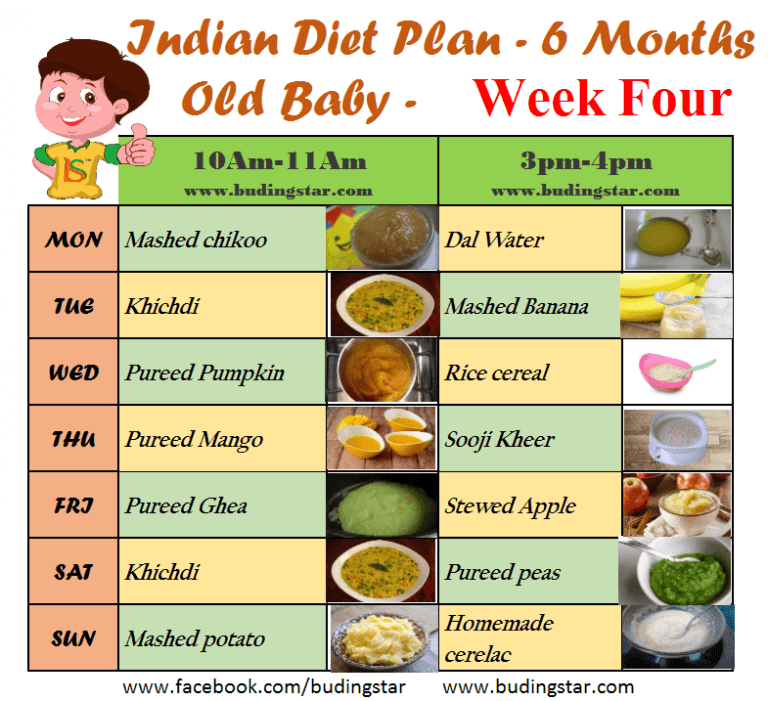 Teaching in such institutions is modeled on British public schools. These are expensive and prestigious educational institutions, among which are, for example, Delhi Public Schools or Frank Anthony Public Schools.
Teaching in such institutions is modeled on British public schools. These are expensive and prestigious educational institutions, among which are, for example, Delhi Public Schools or Frank Anthony Public Schools.
Indian college education
The number of Indian colleges in 2011 exceeded 33,000 institutions. Of this number, 1800 had the status of women's educational institutions. In fact, this type of educational sites belongs to the country's higher education system. On the basis of colleges, numerous courses are organized, covering the humanities and natural sciences, as well as courses in foreign languages, in particular English. Many colleges are owned by Indian universities. In fact, all of them are the initial stage of university education.
Colleges, as a rule, represent the initial stage of university education
The priority direction of study in colleges is technical and technological specialties. Medical education and business management are also popular. Technical colleges in India are often referred to as institutes. The list of the best institutes contains more than 500 positions. Here are just the first 5 of the list:
Technical colleges in India are often referred to as institutes. The list of the best institutes contains more than 500 positions. Here are just the first 5 of the list:
- Indian Institute of Technology in Bombay.
- Indian Institute of Technology at Madras.
- Kanpur Institute of Technology.
- Tiruchirappalli National Institute of Technology.
- Punjab Institute of Engineering and Technology.
India's university education system
India's higher education system is second only to China and the US in terms of scale . The peak of development of Indian higher education fell on the period 2000-2011. At the end of 2011, more than 40 international universities, about 300 state universities, 90 private. Another 130 educational institutions were at the stage of transition to the university rank. The following Indian institutions of higher education stand out as a high level of education recognized at the global world level:
- National Institute of Technology.
- Indian Institute of Information Technology.
- Indian Institute of Management.
- International Institute of Information Technology.
- University of Mumbai.
- Jawaharlal Nehru University.
- Indira Gandhi National Open University.
Students are usually admitted without exams . The academic year for universities in India starts in August and ends in April. Traditionally, Indian universities taught on the principle of a single semester, covering a period of 10 to 12 months. At the end of each year, students take exams.
Now there is a reform taking into account European principles. Many higher education institutions have already switched to a scheme of two semesters lasting 5-6 months each. Exams are taken at the end of each semester. English is the main language of instruction for the vast majority of universities. Students are offered a wide range of educational programs. For example, from the following set:
- India - The IT Superpower,
- Sample IT Curricula,
- English Training,
- Internship Programs.
…I was applying for a master's degree at Bangalore University. Requires a translation of a Russian diploma (degree certificate) into English (you can do it without a notary and an apostille. We did it in India). At the same time, they are interested in the final score as a percentage. We used to not put interest in diplomas. The result was not even indicated by numbers, but by the words: “good”, “excellent”, “satisfactory” ...
Rajkumar College is one of the oldest colleges in India providing students with K-12 (12-year vocational education) . Located in the center of Rajkot city. The institution was built back in 1868 by a certain Colonel Keating. However, today it has the most modern facilities and a comfortable student hostel.
Indira Gandhi National Open University is an institution of higher learning administered by the Government of India . One of the largest universities, where, in addition to standard types of education, distance learning is offered.
In total, the university provides higher education to more than 4 million students.
The Calcutta Institute of Engineering is actually the world's largest multidisciplinary engineering professional community . The institute was founded in 1920. And in 1935, the institution was registered by Royal Charter. Students from different countries receive here high-quality higher education in the field of mechanical engineering and other technical areas.
Indian Institute of Architects is another unique institution established in 1917 . The Institute provides professional education in four areas of architectural art. On the basis of the institute, there are numerous courses that teach the basics of urban planning, infrastructure development and other subtleties of the construction sector.
Photo Gallery of Popular Educational Institutions in India
- Calcutta Institute of Engineering is a full member of Royal Charter
- Administrative Corps of the National Open University of Indira Gandhi is always ready to accept students
- College Razhkumar for many years of their activities have prepared many specialists in the basis of the Suhydramic training - National Virgins
9ARS
- The Indian Institute of Architects prepares high-class specialists for a unique field of activity
Video: Indian education in Delhi
Tuition fees in India
Free education in India for Russians, Ukrainians, Kazakhs is possible, but only within the framework of the Indian economic program ITEC. Advanced training and internships are the main areas of short-term (2-3 months) education provided by the ITEC program. Everything else is paid at established international rates.
Since 2008, spending on educational services in India has multiplied . Secondary education and vocational education is costing the Indian government more and more each year. The Ministry of Statistics recently published information on this matter.
Spending on Indian education has increased by 175% in a few years
However, the cost of Indian higher education remains low for locals . Indians pay about $300–350 per semester to study at a university for a bachelor's degree. International students pay more, up to $6,000 per academic year.
…When a representative of the Indian consulate in St. Petersburg came to our faculty with a lecture, he strongly recommended the ITEC program. This, of course, cannot be called either a magistracy or a graduate school, but it is free, provided that you are selected ... =6673234#t6673234
…Studied for a year at Hyderabad Central University for an MA in Anthropology through ICCR. Education and accommodation are free, they pay a scholarship. Applications must be submitted in January. From good universities: IFLU in Haida, in Pune, Delhi University and J. Nehru University are also in Delhi. Looks good in Pondicherry, and the city is great…
zaryaa
http://ru-india.livejournal.com/824658.html?thread=6672978#t6672978
The step-by-step process is as follows:
- make a request to an educational institution through any modern means of communication,
- select the faculty of interest,
- apply for admission (by regular mail, online, in another way),
- if approved, fill in a temporary application, pay an entrance fee of €1000 + €100 for service,
- receive a certificate confirming the fact of admission,
- apply for a student visa at the Indian Embassy, presenting a certificate of admission,
- complete a permanent student questionnaire and send along with a package of documents.

A package of documents for the student's application (translated into English):
- certificate or diploma,
- list of qualification exam subjects certified by the administration of the former educational institution,
- certified copy of the passport,
- student visa (original),
- medical certificate, including HIV test results,
- certificate of English proficiency (if required by the university) ,
- medical insurance premium for the first year of study in the amount of €45.
Scholarships and grants for Russians and not only
Each new academic year, the Government of India approves a package of scholarships and grants for foreign students. Usually, all available scholarship offers are sent to different countries of the world through diplomatic missions. Therefore, all information on state Indian scholarships and grants can be obtained from the embassy or consulate of India.
Russian, Ukrainian, Kazakh students are interested in scholarships and grants, which are provided according to the following schemes:
- General Cultural Scholarship Scheme (GCSS) - General Cultural Scholarship Scheme.
- Indian Council for Cultural Relations (ICCR) is a scheme of the Indian Council for Cultural Relations.
- Commonwealth Fellowship Plan - Commonwealth Fellowship Plan (Postgraduate only).
Student Housing and Living Costs
The level of expenses for accommodation, meals, entertainment, etc. depends on the location of the student. If you study in cities such as Delhi or Mumbai, you should be prepared for the fact that the standard of living in these cities is comparable to major cities in Europe, Australia, and the USA. In general, the cost of living in India is significantly lower than in other countries of the world.
Common student housing options are campus or private housing .
The device on student campuses is free only for local citizens. Foreigners have the opportunity to live in dormitories for students, but for a fee - from $60 to $100 per month. Renting an apartment is about $150-200 (two-room apartment in Mumbai). On average, $100–150 is spent on food and other needs per month.
Visa Conditions
Immigrant student must have:
- original passport and photocopies of important pages,
- printout of the visa application form in duplicate, pre-filled online on the website of the Government of India (both copies of the document must be signed ),
- one photo 2x2 cm, color, on a white background (full face, without glasses),
- letter from the administration of the educational institution where the student entered (indicating the details of training),
- a photocopy of an identity card issued in the student's country of residence,
- a bank statement showing sufficient funds to study and live in India.

All student visa fees must also be paid. If accompanying persons are sent to the country with the applicant, they also need to issue an entry permit and a residence permit.
Work while studying, job prospects
There are practically no opportunities for foreign students in India to work while studying . The administration of universities treats work while studying, to put it mildly, unfriendly. But after graduation, graduates have good job prospects. High-tech graduates can always count on profitable contracts. Such specialists are in great demand by foreign companies. Engineers and architects, financiers and technologists are also valued.
… You can't work. The scholarship is tiny, I agree, therefore, the help of parents is needed in any way. You can live in a student hostel or rent an apartment, which is more expensive, but better. Learning is interesting, which covers all the disadvantages ...
The level of living comfort and the quality of food are not always satisfactory There are prospects for getting a good job after graduation Employment opportunities after graduation strongly depend on the specialty Climate conditions allow for a few expenses for clothing 6 6 the summer months are very hot, which is unusual for Europeans Studying in India, as shown by student examples, allows you to successfully achieve your goals.