Babies foods to avoid
Foods to avoid giving babies and young children
Salt
Babies should not eat much salt, as it's not good for their kidneys.
Do not add salt to your baby's food or cooking water, and do not use stock cubes or gravy, as they're often high in salt.
Remember this when you're cooking for the family if you plan to give the same food to your baby.
Avoid salty foods like:
- bacon
- sausages
- chips with added salt
- crackers
- crisps
- ready meals
- takeaways
Sugar
Your baby does not need sugar.
By avoiding sugary snacks and drinks (including fruit juice and other fruit drinks), you'll help prevent tooth decay.
Saturated fat
Do not give your child too many foods that are high in saturated fat, such as crisps, biscuits and cakes.
Checking the nutrition labels can help you choose foods that are lower in saturated fat.
See more on food labels.
Honey
Occasionally, honey contains bacteria that can produce toxins in a baby's intestines, leading to infant botulism, which is a very serious illness.
Do not give your child honey until they're over 1 year old. Honey is a sugar, so avoiding it will also help prevent tooth decay.
Whole nuts and peanuts
Whole nuts and peanuts should not be given to children under 5 years old, as they can choke on them.
You can give your baby nuts and peanuts from around 6 months old, as long as they're crushed, ground or a smooth nut or peanut butter.
If there's a history of food allergies or other allergies in your family, talk to your GP or health visitor before introducing nuts and peanuts.
See more on food allergies in babies and young children.
Some cheeses
Cheese can form part of a healthy, balanced diet for babies and young children, and provides calcium, protein and vitamins.
Babies can eat pasteurised full-fat cheese from 6 months old. This includes hard cheeses, such as mild cheddar cheese, cottage cheese and cream cheese.
Babies and young children should not eat mould-ripened soft cheeses, such as brie or camembert, or ripened goats' milk cheese and soft blue-veined cheese, such as roquefort.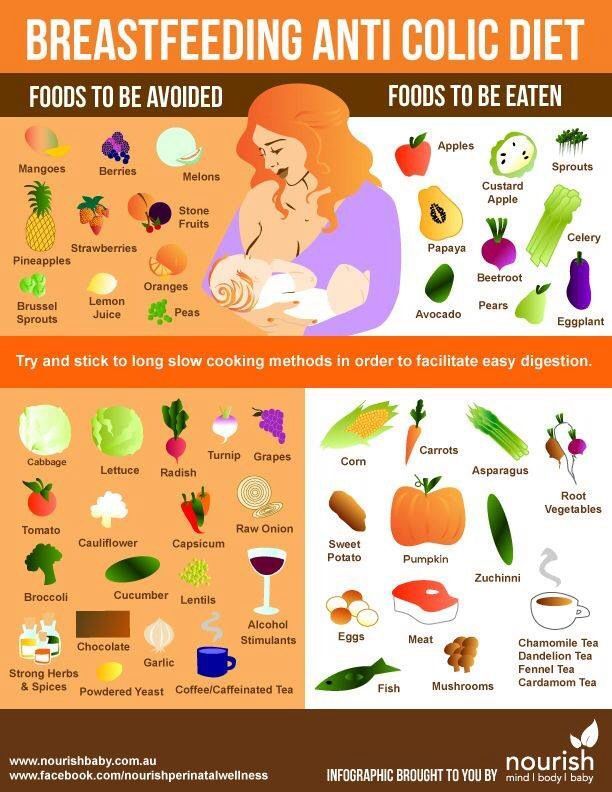 There's a higher risk that these cheeses might carry a bacteria called listeria.
There's a higher risk that these cheeses might carry a bacteria called listeria.
Many cheeses are made from unpasteurised milk. It's better to avoid these because of the risk of listeria.
You can check labels on cheeses to make sure they're made from pasteurised milk.
But these cheeses can be used as part of a cooked recipe as listeria is killed by cooking. Baked brie, for example, is a safer option.
Raw and lightly cooked eggs
Babies can have eggs from around 6 months.
If the eggs are hens' eggs and they have a red lion stamped on them, or you see a red lion with the words "British Lion Quality" on the box, it's fine for your baby to have them raw (for example, in homemade mayonnaise) or lightly cooked.
Hens' eggs that do not have the red lion mark should be cooked until both the white and yolk are solid. So should duck, goose or quail eggs.
So should duck, goose or quail eggs.
Avoid raw eggs, including uncooked cake mixture, homemade ice creams, homemade mayonnaise, or desserts that contain uncooked egg that you cannot confirm are red lion stamped.
Rice drinks
Children under 5 years old should not have rice drinks as a substitute for breast milk or infant formula (or cows' milk after 1 year old) as they may contain too much arsenic.
Arsenic is found naturally in the environment and can find its way into our food and water.
Rice tends to take up more arsenic than other grains, but this does not mean that you or your baby cannot eat rice.
In the UK, there are maximum levels of inorganic arsenic allowed in rice and rice products, and even stricter levels are set for foods intended for young children.
Do not worry if your child has already had rice drinks. There's no immediate risk to them, but it's best to switch to a different kind of milk.
There's no immediate risk to them, but it's best to switch to a different kind of milk.
Raw jelly cubes
Raw jelly cubes can be a choking hazard for babies and young children.
If you're making jelly from raw jelly cubes, make sure you always follow the manufacturers' instructions.
Raw shellfish
Raw or lightly cooked shellfish, such as mussels, clams and oysters, can increase the risk of food poisoning, so it's best not to give it to babies.
Shark, swordfish and marlin
Do not give your baby shark, swordfish or marlin. The amount of mercury in these fish can affect the development of a baby's nervous system.
Further information
For more information and advice about babies and food, see:
- food allergies in babies and young children
- your baby's first solid foods
- baby and toddler meal ideas
Foods to avoid feeding your baby
Foods to avoid giving your baby include honey, cow's milk, soy milk, fruit juice, sugar-sweetened beverages, unpasteurized foods, and foods with added sugars or too much sodium. Choking hazards are a serious concern, so don't offer large chunks, raw vegetables, nuts and seeds, hard or crunchy foods, sticky foods, or dollops of nut butters. If allergies run in your family or your baby has eczema, check with the doctor about introducing allergenic foods such as egfgs, peanuts, tree nuts, wheat, soy, fish, and shellfish.
Choking hazards are a serious concern, so don't offer large chunks, raw vegetables, nuts and seeds, hard or crunchy foods, sticky foods, or dollops of nut butters. If allergies run in your family or your baby has eczema, check with the doctor about introducing allergenic foods such as egfgs, peanuts, tree nuts, wheat, soy, fish, and shellfish.
As your baby grows, they'll be eager to sample food from your plate – and you'll be eager to introduce some variety. But not all foods are safe for your child.
Foods to avoid: Birth to 6 months
All food and beverages except breast milk or formula: The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommends feeding your baby only breast milk or formula for about the first 6 months.
Foods to avoid: 6 to 12 months
Honey: Honey can harbor spores of Clostridium botulinum, which causes botulism. An adult's intestinal tract can prevent the growth of these spores, but in a baby the spores can grow and produce life-threatening toxins.
Cow's milk and soy milk: Stick with breast milk or formula until your child's first birthday. Why? Your baby can't digest the proteins in cow's milk and soy milk during the first year, and these beverages contain minerals in amounts that can damage your baby's kidneys.
Fruit juice and sugar-sweetened beverages: Juice (even 100 percent fruit juice) and sugar-sweetened beverages such as soda and sports drinks aren't recommended for children under 12 months. When babies fill up on these drinks, they miss out on getting the nutrients they need. And though fruit juice seems healthy, it has far more calories and sugar than fresh fruit and can contribute to weight gain and tooth decay. The AAP recommends no fruit juice for babies, and just 4 ounces per day maximum for toddlers ages 1 to 3.
Unpasteurized foods: Don't give babies and children unpasteurized juice or cider or unpasteurized (raw) dairy products. These may contain harmful bacteria and parasites that can lead to serious illness or death.
Added sugars: Avoid added sugar in the diets of children under age 2, the U.S. Department of Agriculture and U.S. Department of Health and Human Services advise. These are sugars and syrups that are added to foods or beverages when they are processed or prepared. This doesn't include sugars found in milk and fruits. Too much added sugar in children's diets has been linked to obesity and increased risk for future health problems such as diabetes and heart disease. Check the Nutrition Facts label on packaged foods, and avoid those that list 1 g or more of "Added Sugars."
Too much sodium: Sodium is an essential nutrient primarily consumed as salt. However, too much can be harmful. Children this age don't need more than 1,200 mg of sodium per day, according to the USDA and DHHS. Check the Nutrition Facts label when buying canned, frozen, and packaged foods.
Large chunks: A chunk of food can get stuck in your baby's throat. The AAP recommends that you cut food into pieces no larger than 1/2 inch. For example, cut up fruits such as grapes, cherry tomatoes, and strawberries, and shred or finely chop meats, vegetables, and cheeses.
The AAP recommends that you cut food into pieces no larger than 1/2 inch. For example, cut up fruits such as grapes, cherry tomatoes, and strawberries, and shred or finely chop meats, vegetables, and cheeses.
Raw vegetables: Soft-cook vegetables such as carrots, celery, and broccoli, and dice, shred, or cut them into pieces no larger than 1/2 inch before serving.
Nuts and seeds: Remove seeds and pits from fresh fruit such as watermelon, peaches, plums, and cherries before serving. And don't feed your baby nuts or seeds, such as sunflower or pumpkin seeds. Seeds may be too small to choke on but can get stuck in a child's airway and cause an infection.
Hard or crunchy foods: Nuts, popcorn, and pretzels are all choking hazards, as are all hard candies and cough drops.
Sticky foods: Chewing gum and sticky foods – such as jelly or gummy candies, dried fruit, and marshmallows – can get lodged in your baby's throat. Stringy, melted cheese can also be a choking hazard.
Stringy, melted cheese can also be a choking hazard.
Nut butter: The sticky consistency of peanut butter and other nut butters can make it hard for your baby to swallow it. Spread nut butter thinly on bread or crackers. Or thin it with water or applesauce.
Learn more about preventing choking in young children.
Find out about choosing safe finger foods and which foods can be unsafe for toddlers and children up to age 5.
The latest on children and food allergies
Doctors used to recommend waiting until age 1 or even later to introduce solid foods that are common allergens, especially with children at risk for allergies. But the AAP has changed its tune, because studies show that these delays don't help prevent allergies and may even increase the risk of them.
You may be told to introduce foods one at a time, waiting three to five days after each new food to watch for any allergic reaction. Or your doctor may say it's fine to start multiple new foods at once. If you believe your baby is likely to have food allergies – for example, if allergies run in your family or your baby has eczema – check with their doctor to determine the best strategy for introducing allergenic foods, which include eggs, milk, peanuts, wheat, soy, tree nuts, fish, and shellfish.
If you believe your baby is likely to have food allergies – for example, if allergies run in your family or your baby has eczema – check with their doctor to determine the best strategy for introducing allergenic foods, which include eggs, milk, peanuts, wheat, soy, tree nuts, fish, and shellfish.
Read more about food allergies in children.
7 foods that are undesirable to give to children under one year old
Of course, modern mothers know that sausages should not be given to babies, soda and cream cakes. What else can not eat children under one year old? We made a list of 7 less obvious foods.
1. Salt
Excess salt in the diet is harmful to the baby's kidneys and can lead to swelling and dehydration. Of course, a lack of salt is also not useful, but in real life, with a normal diet, it practically does not occur: salt is contained in sufficient quantities in most foods, and there is no need to add salt on purpose. And if for us, adults, baby purees and cereals without salt and sugar seem tasteless and disgusting, don’t worry, for a baby, the situation is completely different.
The taste perception of young children is not yet spoiled by excessively sweet and salty foods, flavors and flavor enhancers. If your child refuses mashed broccoli, then most likely he just does not like the taste and texture of broccoli, and not at all the lack of salt.
2. Sugar
Everyone knows the dangers of excess sugar - dental problems, obesity, associated cardiovascular diseases and the risk of developing diabetes. However, it can be very difficult to refuse a cookie or candy to a child familiar with the sweet taste, and tears are usually inevitable. What to do?
The secret is simple - introduce foods with added sugar into your baby's diet as late as possible, at the earliest in the year, although it is better to wait until two years. The National Nutrition Optimization Program for Children aged 1 to 3 years recommends limiting sugar in the diet of toddlers 1 to 3 years of age to 25-30 grams per day, taking into account the sugar found in special baby foods, juices, yogurts, etc.
3. Honey
It would seem that honey is a wonderful and healthy alternative to sugar, so why is it not recommended for babies under one year old? In fact, the reasons several. First, honey can contain spores bacteria Clostridium botulinum. The immune system of adults and children older people can easily cope with them, but in babies they can cause a deadly disease called infantile botulism.
Secondly, honey is the strongest allergen, so it is better to postpone acquaintance with it until a later age.
4. Fruit juices and drinks
American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) released in 2017 New recommendations for adequate intake of fruit juices in infants, young children and adolescents who begin with advice to completely avoid fruit juice for feeding infants life. According to AAP, excessive juice consumption can lead to diarrhea, overeating or, conversely, malnutrition, as well as to occurrence of dental caries*. At the same time, babies can and should be offered Whole fruit, mashed or pureed.
A various fruit drinks and nectars in addition to natural sugar from fruits often contain added sugar, which makes them perfectly unsuitable for feeding babies up to a year.
Breeding of juices and nectars with water does not completely solve the problem, since it does not reduce dental risks. If your child refuses to drink water, try compotes and fruit or herbal teas.
5. Foods that are easy to choke on
The danger of a product to children is determined by several characteristics: consistency, shape, and size. Most often babies gagging slippery, round, sticky, fibrous and hard products.
The most dangerous are all round and large enough to block the airways: lozenges, grapes, cherry tomatoes, nuts**. Not far behind in sad dangerous food rating other candies (especially sticky ones), fish bones and meat and, in fact, the meat itself ***.
Remember that theoretically a child can choke on any food, so never leave your baby unsupervised eating.
6. Egg white
Have you ever wondered why in all complementary feeding schemes is it the yolk, not the whole egg? Nothing surprising: egg protein is one of the strongest allergens. Up to a year is better limit the baby to only the yolk, and introduce the protein a little later.
Only make sure the eggs are thoroughly cooked. Raw and half-raw eggs may contain a bacterium that causes salmonellosis, a disease deadly for young children.
7. Cow and goat milk
Surprised? Whole cow's milk is the main cause of allergies in children under one year old. In addition, it contains a large amount of lactose, milk sugar, which some babies have difficulty digesting due to the fact that their gastrointestinal tract is not yet sufficiently developed. There are studies linking the early introduction of animal milk into the diet as a substitute for mother's milk or infant formula with an increased risk of iron deficiency anemia and type 1 diabetes. ****
****
Goat milk is actually not much different from cow milk, goat and cow are evolutionarily close, goat milk proteins are very similar in structure to cow proteins, and almost as often cause allergies.
It is advisable to introduce cow's milk into the diet of a child not earlier than 1 year. Interestingly, this rule does not apply to special children's fermented milk products, they are easier to digest and useful for babies.
When using any materials from the site nutriclub.ru, a link to the site is required.
© Nutriclub, 2020
You will also be interested
- Nutriclub - healthy nutrition and child development
- 0-12 months
- Lure
- unwanted foods for children
Prohibited foods for children
List of prohibited foods for children.
Feeding a child with illness
What foods should not be eaten by children with various illnesses?
Anxious mood of parents is often associated with the problem of poor appetite of their own child. Moms and dads are worried about what to feed the child so that he eats with appetite and, God forbid, does not lose weight. But most of the problems arise with feeding the baby, when he has health problems and there are severe dietary restrictions. What kind of food should not be eaten by children with this or that disease?
Moms and dads are worried about what to feed the child so that he eats with appetite and, God forbid, does not lose weight. But most of the problems arise with feeding the baby, when he has health problems and there are severe dietary restrictions. What kind of food should not be eaten by children with this or that disease?
Prohibited Foods for Children
The small organism grows rapidly and requires proper and balanced nutrition for its development. Carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, macro- and microelements are necessary substances for the normal physiological development of muscle and bone tissue, the brain, the proper formation of internal organs: the heart, kidneys, lungs, spleen, liver.
Proper nutrition of a child in the first years of life determines his subsequent health and the possibility of fulfilling himself in adulthood. Therefore, it is important to lay the foundation for proper nutrition from an early age in order to avoid health problems in the future.
What should not be eaten by children under one year old?
Most pediatricians have come to the conclusion that breastfed babies should not receive whole cow's and goat's milk in any form. If a child is deprived of the opportunity to receive mother's milk, then such children are recommended adapted milk formulas for breast milk.
Cow's and goat's milk
Cow's milk is considered heavy food for the baby. It contains a large amount of proteins, fats, mineral salts. The kidneys of the child begin to work with great effort, which leads to their overload. The liquid is excreted in a larger amount than necessary according to the physiological norm, which leads to the thirst of the baby. He receives a new portion of milk, so a "closed ring" is created.
Cow's milk does not contain enough iron for a growing baby. Goat's milk contains less vitamin A than cow's milk, although in other respects it is closest to mother's milk.
The use of cow's milk in early life can lead to the development of diabetes mellitus, iron deficiency anemia, and allergic diseases.
In addition, babies under two years of age have not yet formed enzymes that can break down the nutritional components of cow's milk. As a rule, cow's milk is not completely absorbed by the child's body.
IMPORTANT: It is not recommended to give yogurt to children under one year old, as it has a high acidity and contains alcohol.
What should children under 3 not eat?
Sugar and salt
Salt and sugar should not be given to children, at least as long as they can be dispensed with. And it is best not to give these products until the age of three. Since the addition of salt and sugar is considered traditional in cooking, the baby will sooner or later get acquainted with the taste of salted and sweet food in kindergarten or school.
IMPORTANT: As shown by Roskontrol: many children's fermented milk products contain a high percentage of sugar. Therefore, babies should be given unsweetened and not very acidic natural fermented milk products with a short shelf life.
Semolina
Gone are the days when semolina was considered an indispensable product for baby food. It turns out that semolina contains gliadin, one of the components of gluten that makes it difficult for children's intestines to work. Fitin - another ingredient in semolina, inhibits the absorption of vitamin D and calcium.
Semolina gluten can cause allergic manifestations in the child in the form of red itchy spots. Excessive feeding of semolina often leads to overweight children, which is difficult to get rid of later.
Juice or puree?
Many pediatricians disagree: is it possible to give children juices of industrial production and their own preparation? Some allow giving juice to babies, other doctors do not recommend drinking juice for babies up to a year and a half, but insist on the use of fruit and vegetable purees. Their motivation is based on the fact that such food is rich in plant fiber and has a beneficial effect on the baby's intestines.
What should children 4-5 years old not eat?
Babies at the age of 4-5 years old parents often transfer to adult food.
IMPORTANT: Dairy and sour-milk products made according to general production standards, and not according to special baby food technology, are of particular danger to children.
Honey
Honey is a useful natural product containing many biologically active components, macro- and microelements, and vitamins. But this bee product can cause allergic manifestations. In early childhood, it is better to give up honey and carefully introduce it into baby food later.
Sausages and sausages
Sausages and frankfurters are allowed to be given to children after the age of three, prepared according to a special technology for baby food. Labels on such products are usually provided with inscriptions from what age this product can be consumed. There will be no great harm to the health of the child if he eats baby sausages no more than once every two weeks.
IMPORTANT: Roskontrol does not recommend giving young children sausage products intended for adult nutrition. These products contain many ingredients that are harmful to the child's body: preservatives, flavor enhancers, phosphates, nitrites and other harmful substances.
Chocolate
Sweet treats should not be given to babies for a number of reasons:
chocolate contains sugar
cocoa powder can provoke allergies
cocoa butter is difficult to digest in the gastrointestinal tract9 of a child
6 seafood and caviar red caviar is a healthy food product containing a lot of complete protein and other useful components. But this is not food for younger children. Sea food ingredients are very allergenic, besides, seafood products and red caviar are processed with many preservatives and have a strong salty taste, which is unacceptable in baby food.Strawberries, citrus fruits and other exotic fruits
Beautiful and tasty exotic fruits and fruits: kiwi, avocado, citrus fruits, pineapple, can cause severe allergic skin manifestations not only in babies, but also in older children. Strawberries, wild strawberries, raspberries also contain allergens, it is better not to give them to children, especially those who are prone to allergic reactions.
Strawberries, wild strawberries, raspberries also contain allergens, it is better not to give them to children, especially those who are prone to allergic reactions.
What is strictly prohibited for children to eat?
There are prohibited foods for babies in their first years of life:
whole milk
honey
Mushrooms
Nuts
Black and green tea
Coffee
Chocolate
Fastfood
In industrial production of children's food, there is a list of products unacceptable for children:
Vinegar
Ethyl alcohol with a concentration of more than 0.2%
apricot kernels
sweeteners (except those special for dietary and baby food)
artificial flavors
benzoic and sorbic acids (they are used as preservatives)
hot and hot spices: pepper, mustard, horseradish
red meat, fish and poultry after refreezing
trans fats and hydrogenated oils
juice concentrates
food additives (various E additives not allowed in Russia for the production of baby food)
Prohibited products for children with various diseases
Childhood illnesses are a test not only for the child's body, but also for parents. Only by the joint efforts of a doctor and loving moms and dads can the child’s recovery be accelerated, and these are: drug treatment, proper regimen and hygiene, good nutrition, excluding certain foods from the diet for various diseases.
Only by the joint efforts of a doctor and loving moms and dads can the child’s recovery be accelerated, and these are: drug treatment, proper regimen and hygiene, good nutrition, excluding certain foods from the diet for various diseases.
What should not be eaten in children with lactose?
Lactase deficiency is associated with the absence or insufficient amount of an enzyme that can break down milk sugar - lactose, which enters the body with dairy products.
In this disease, children experience disorders of the gastrointestinal tract: diarrhea or constipation, weight loss, fetid frothy stools, regurgitation, vomiting, colic, bloating.
If lactose intolerance is suspected, babies are placed on a lactose-free or low-lactose diet. After the diagnosis and treatment of the disease that caused lactase deficiency, the child undergoes control tests. With positive dynamics, the doctor may give permission for the gradual introduction of fermented milk products into the diet.
IMPORTANT: Lactose is not only found in milk and dairy products, it is used in the manufacture of medicines, margarine, candy, bread, ham and sausages. Before buying certain products, you should carefully read their composition on the label.
What should not be eaten by children with angina?
Angina is a disease caused by viruses and bacteria. It is characterized by severe sore throat and high fever. During illness, the child's appetite is usually absent and this worries parents very much.
During an acute illness, do not force-feed your baby. Lack of appetite is a protective reaction of the body to the disease. After a few days, the child will begin to recover and the desire to eat will appear again.
Children with angina should not be given solid food. Food should be well ground, preferably to a puree state. Sour drinks, hot and cold dishes are contraindicated for an inflamed throat. Food should be warm and good tasting.
What should children not eat if they have allergies?
Allergic manifestations in children are caused by many reasons: food intolerance, drug intolerance, allergy to dust, animal dander, plant pollen, etc. During allergic manifestations, it is very important to adhere to the right diet and completely eliminate the products that provoke the appearance of allergies.
Allergic products
cow's milk
chicken eggs
bakery and pasta products containing gluten
honey
chocolate
citrus fruits
red berries: strawberries, wild strawberries, raspberries
chicken meat
seafood and some types of fish
Chickenpox is an infectious viral disease that affects almost all children attending preschool or school institutions. The acute period of the disease is associated with a rise in temperature, headache, itchy skin rashes in the form of fluid-filled vesicles.
To help your child cope with the disease and move to the recovery stage faster, you need to follow the right diet, consisting of healthy and complete foods. During illness, food should be excluded, which is difficult for the child's body to digest and can cause a number of complications from the gastrointestinal tract.
During illness, food should be excluded, which is difficult for the child's body to digest and can cause a number of complications from the gastrointestinal tract.
It is not recommended to feed a sick child with fatty, spicy, salty, sour and fried foods. Food should be balanced, light, soft, warm. Too hot and cold food is contraindicated for the child.
Foods to avoid during chickenpox:
milk
garlic
ginger
citrus fruits
red meat
What should children not eat with dysbacteriosis?
Dysbacteriosis is a disease associated with disturbances in the normal intestinal microflora of the body. An imbalance between “beneficial bacteria” and pathogenic bacteria causes improper bowel function.
The child is concerned about:
intestinal motility disorder (constipation or diarrhea)
abdominal pain
vomiting
Bloating of abdomen
Apathy and lethargy
Lack of appetite
causes of dysbiosis in children are different:
consequences of antibiotic therapy
Militable power
Vitamin deficiency 9000 9000
with dysbacteriosis and the exclusion of unacceptable products contribute to the rapid recovery of the baby.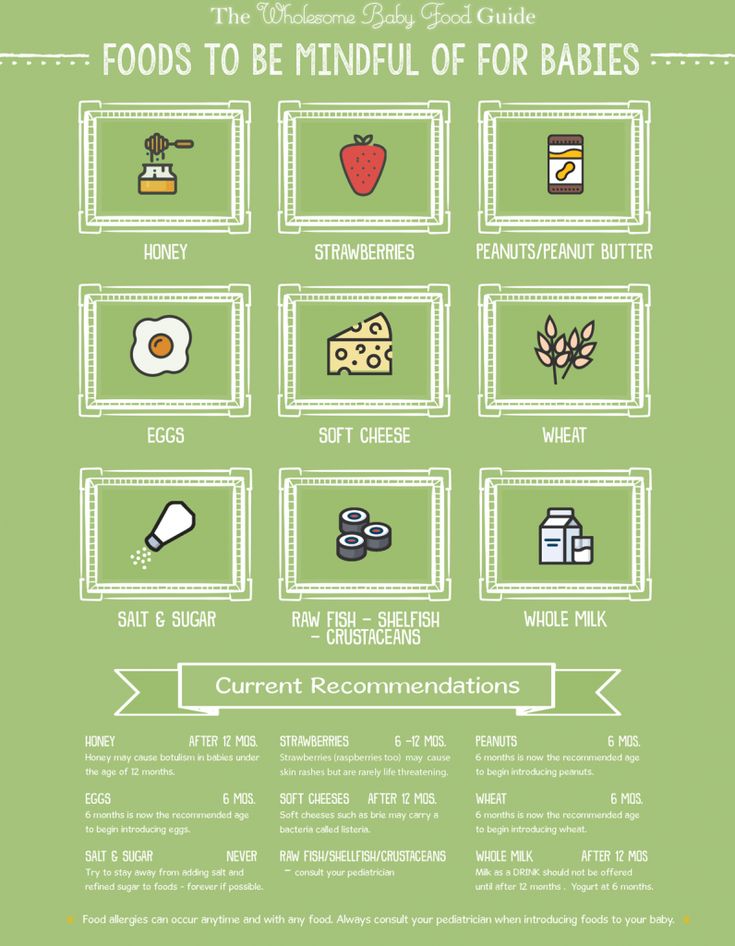
Foods to avoid in dysbacteriosis:
sour berries and fruits (cherries, sour apples, cranberries, pomegranates, tangerines)
raw vegetables and fruits
products that cause fermentation in the intestines (grapes, cabbage, legumes, carbonated drinks)
sweets
canned food
smoked meats
fast food dishes
What should not be eaten when a child has colic?
Colic often accompanies the little man in the first months of life. The baby is born with a sterile intestine and an immature gastrointestinal tract. In the body of a child, there are still not enough enzymes that can fully break down food. That is why a nursing mother should pay great attention to her nutrition.
Products that should not be included in the diet of a nursing mother
whole milk
cabbage
Shipped water
store vegetables and fruit juices
Sweets and SDOBA
Chocolate
Bob
To prevent colic baby, the diet of a nursing mother should consist of steamed, boiled or baked foods. Preference should be given to vegetables and fruits with a green color. With further maturation of the child and the disappearance of colic, the choice of food products can be expanded, based on the recommendations of the doctor.
Preference should be given to vegetables and fruits with a green color. With further maturation of the child and the disappearance of colic, the choice of food products can be expanded, based on the recommendations of the doctor.
What should not be eaten if a child has diarrhea?
Diarrhea in a child can be caused by various reasons. These include poisoning, viral and infectious diseases, teething, gastrointestinal diseases, etc. But whatever the appearance of a digestive tract disorder is associated with, the key to a successful recovery of the body is properly prescribed nutrition in case of illness
breastfeeding should not stop breastfeeding. Pediatricians recommend increasing the number of feedings, but reducing the dose of milk to avoid overfeeding and reduce the load on the baby's gastrointestinal tract
Formula-fed babies should be fed in the same way. That is, reduce the dose of formula for one feeding, but increase the frequency of feedings. In this case, it is recommended to use adapted fermented milk and low-lactate mixtures
In this case, it is recommended to use adapted fermented milk and low-lactate mixtures
For older children who have switched to "adult food", a special diet should also be developed by a doctor. At the same time, food must be prepared according to certain rules.
Food products that are difficult to digest and cause fermentation processes in the intestines should be discarded. Food is recommended to boil, bake, steam. Food products should be crushed with a blender or rubbed through a sieve. You can not eat fatty foods. Kashi (rice, oatmeal, buckwheat) should be boiled in water without adding milk.
Products prohibited during diarrhea in children
Fresh vegetables, fruits and berries
Fatty meat
Fresh bread
Assed drinks
concentrated meat broth
What can not be eaten under the rotary unit for children?
Rotavirus infection is called "intestinal flu". The disease is transmitted by viruses through food, especially dairy products. Babies from 6 months to 2 years of age are most often infected with a viral infection.
Babies from 6 months to 2 years of age are most often infected with a viral infection.
Intoxication of the child's body leads to fever, intestinal colic, liquid diarrhea, dehydration.
IMPORTANT: Young children become dehydrated very quickly. With intestinal flu, a loss of 10% of fluid can seriously affect the health of the baby, and in some cases even lead to death.
If the child is sick with rotavirus infection and refuses to eat, do not insist and force-feed the baby. But you need to drink the child often in small portions of water every half hour. This is an important and strict requirement that must be met in order to avoid fluid loss.
For intestinal flu in children, follow the recommendations:
In the acute period of infection, accompanied by high fever and vomiting, it is better not to feed the child, but to give him saline rehydration solutions and drinking water
Infants should be given breast milk little by little, and in between between feedings - water
Infants who are bottle-fed should switch to lactose-free formulas during the period of illness, in consultation with a pediatrician.
Eliminate from the diet foods that irritate the intestines: fried, salty, canned foods, foods containing coarse fiber
Feed the child often in small portions cook boiled dairy-free cereals, weak meat and vegetable broths, give mashed fruits and vegetables, fermented milk products
IMPORTANT: Until the stool normalizes, the following should be excluded from the child's diet: whole milk, juices, fresh fruits and vegetables
What can not be eaten with stomatitis in children?
Stomatitis is a disease associated with inflammation of the oral mucosa. The disease causes the child suffering in the form of pain, high fever, inability to eat due to sores in the oral cavity. It is extremely difficult to feed a child with such a disease. This circumstance worries parents a lot.
Nutrition recommendations for a child with stomatitis
Do not feed your child with spicy, sour and salty foods that can irritate the oral mucosa
The temperature of food should be warm, comfortable for consumption. Hot and cold foods are not suitable for feeding a child
Hot and cold foods are not suitable for feeding a child
Cocoa, chocolate are excluded from the menu, sweet foods are limited as much as possible
Solid texture of food is not suitable for eating. Food should be in the form of purees, soups, liquid cereals
It is not recommended to eat dry bread and coarse-ground bakery products
Tomatoes, sour berries and fruits, citrus fruits are excluded from the diet.
Garlic, onion, radish, spices that irritate the oral mucosa are not allowed in the diet. Lack of appetite and unwillingness to eat in the early days of illness is normal. You can not force the child to eat at this time.
At high temperatures, it is preferable for children to drink plenty of water in the form of sweetened teas, fruit drinks, compotes with dried fruits, jelly. Such drinks are rich in vitamins, which a sick child really needs.
IMPORTANT: At a high temperature, all dairy products should be excluded from the child's diet: whole milk, cottage cheese, kefir, yogurt, cheese. It is not recommended to use cereals cooked in milk.
It is not recommended to use cereals cooked in milk.
Milk protein (casein) is practically indigestible at high temperatures. Products containing milk in the baby's stomach churn into a rubbery mass. When the temperature drops, there is a high risk of acetonemic syndrome, which manifests itself in the form of vomiting.
What not to eat after mantoux for a child
The Mantoux test is performed to diagnose tuberculosis in children. The examination is carried out by intradermal injection of tuberculin, which is a collection of filtrates of mycobacteria that died during heating.
Tuberculin is a strong allergen that can cause an allergic reaction in allergic children.
IMPORTANT: In order not to distort the true reaction of the child to the Mantoux test, foods that can cause an allergic reaction should be excluded from his diet.
Allergen products that are not allowed before and after the Mantoux test:
cow's milk
fish
seafood (shrimps, lobsters, crayfish, oysters)
red caviar
chicken meat and broth
chocolate
nuts
citrus and exotic fruits (pineapple, persimmon, mango)
fruits and berries with a predominance of red and bright orange pigment (strawberries, raspberries, red apples, apricots)
canned food
sweets
industrial food products with food additives (chips, crackers)
fast food
What should not be eaten by a child with constipation?
Due to the imperfection of the child's gastrointestinal tract, malnutrition, insufficient water intake and many other factors, children may develop constipation from time to time.











