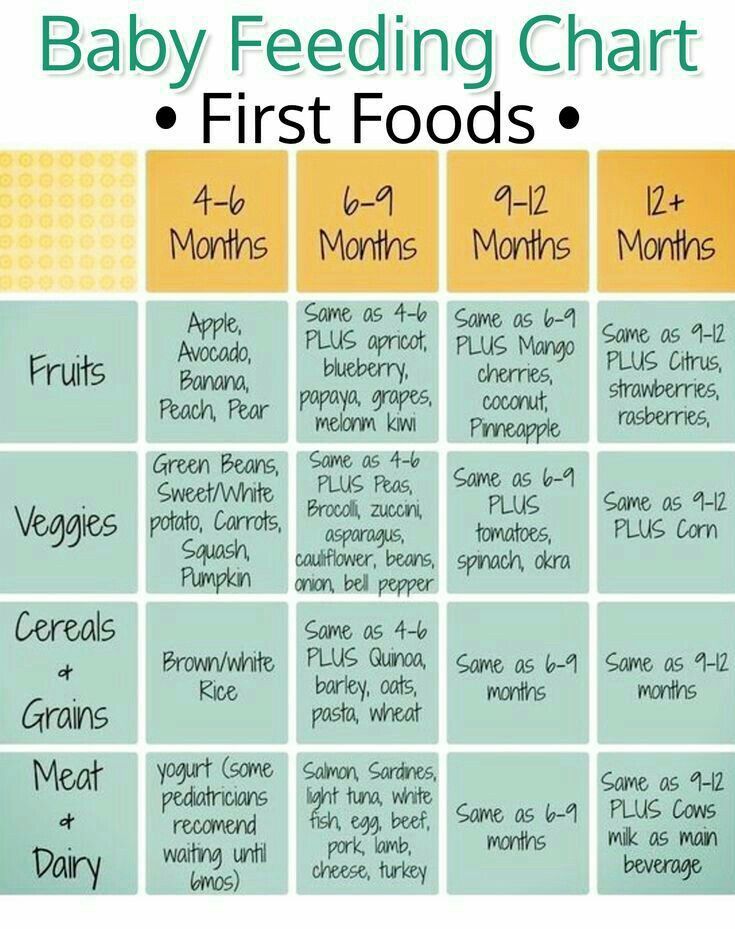
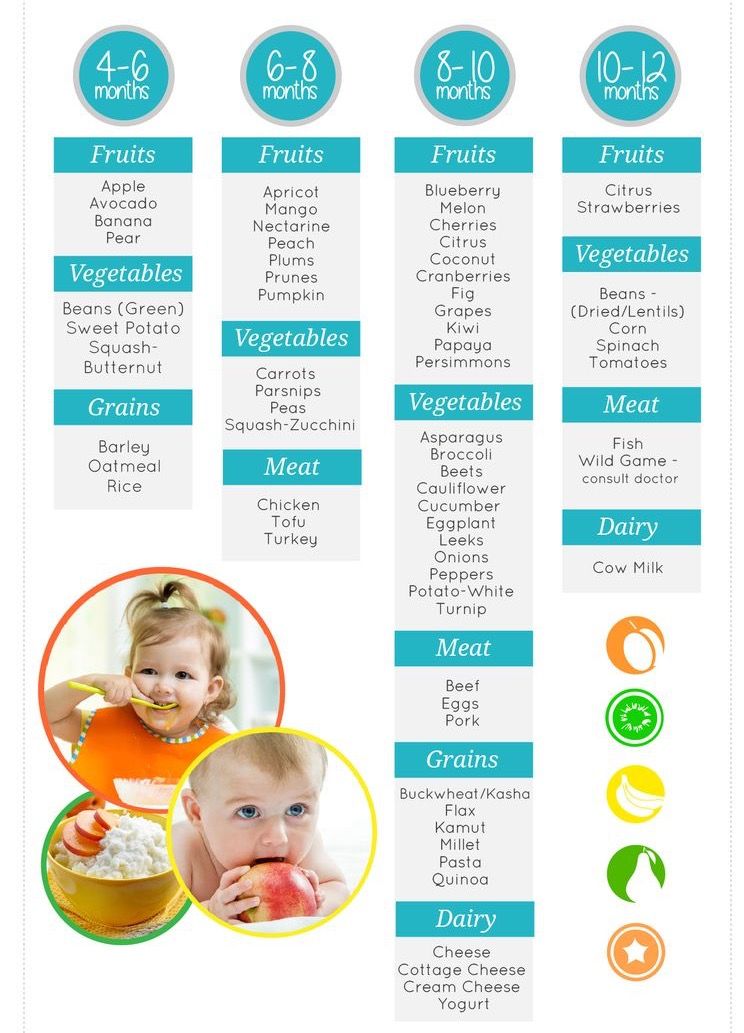
Baby discomfort when feeding
Baby Cries After Feeding: What Should I Do?
Medically reviewed by Karen Gill, M.D. — By Chaunie Brusie on October 3, 2018
My daughter, the “crier”
My second daughter was what my oldest fondly referred to as a “crier.” Or, in other words, she cried. A lot. The crying with my baby girl seemed to intensify after every single feeding and particularly at night.
It was those hellish hours between darkness and dawn when my husband and I would take turns walking around the house with her in our arms, praying and, mostly in my case, sobbing because we couldn’t console our baby.
I didn’t know it then in my sleep-deprived state, but my daughter’s crying after feedings wasn’t that uncommon. In combination with her frequent spitting up, it was pretty much a classic textbook case of colic.
Colic
Colic, in technical terms, simply means a “crying, fussy baby that doctors can’t figure out.”
OK, so that’s not really the definition, but in essence, that’s what it boils down to. The British Medical Journal (BMJ) lists one criterion for colic: A baby that cries for at least three hours a day, three or more days a week, and is under 3 months old. Check, check, and check.
There isn’t one single known cause of colic. Even the actual clinical incidence of colic, estimated by BMJ to be around 20 percent of all babies, can be tricky.
Acid reflux
One of those causes of crying after feeding and spitting up in babies is actually acid reflux. This condition is known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) if it also causes significant symptoms such as poor weight gain.
When my “crier” daughter was 5, she frequently complained of her stomach hurting and as a result, had to undergo a series of testing with a gastroenterologist, a doctor that specializes in the GI system.
At our first appointment, the very first question he asked me was if she had colic as a baby and if she spit up a lot, to both of which I practically shouted, “Yes! How did you know?!”
He explained that acid reflux or GERD can manifest as symptoms similar to colic in babies, stomach pain in school-aged children, and later as actual heartburn pain in adolescents.
While many infants spit up, fewer have actual GERD, which can be caused by an underdeveloped flap between the esophagus and stomach or a higher-than-normal production of stomach acid.
In most cases, a diagnosis of infant reflux is simply based on your baby’s symptoms. If your doctor suspects a severe case however, there are several different tests that actually diagnose infant reflux.
Testing can involve taking a biopsy of your baby’s intestine or using a special type of X-ray to visualize any affected areas of obstruction.
Food sensitivities and allergies
Some babies, especially breastfed babies, may be allergic to certain food particles that their mothers are eating.
The Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine notes that the most common offender is cow’s milk protein in the mother’s milk, but even a true allergy is very rare. Only about 0.5 to 1 percent of exclusively breastfed babies are thought to be allergic to cow’s milk protein.
The other most common culprits, according to the ABM, are egg, corn, and soy, in that order.
If your baby is displaying symptoms of extreme irritability after feedings and has other symptoms, such as bloody stools (poop), you should speak with your healthcare provider about getting them tested for allergies.
Aside from a true allergy, there’s also been some evidence that following a low allergen diet while breastfeeding (essentially avoiding those top allergy foods, such as dairy, eggs, and corn) may be beneficial for infants with colic.
Strict elimination diets can have their own risks, so speak with your doctor before significantly changing your diet.
In our situation, I found that dairy, caffeine, and certain seeded fruit exacerbated my daughter’s crying and spitting up. By eliminating those foods and substances from my diet, I was able to help lessen her discomfort.
If you have a baby with colic, you might want to try anything at all to help ease your baby’s crying. If you’re curious to see if your diet has any effect, you can start by logging your food in a food journal and writing down your baby’s reactions after each meal.
Next, you can eliminate one food at a time and see if reducing your intake of certain foods seems to make a difference in your baby’s behavior. If you hit on one you feel helps your baby to cry less, this does not mean they will not be able to eat that food in the future.
Just be sure to keep in mind that a true allergy is rare. Also, be sure to monitor for any additional symptoms, such as blood in your baby’s poop.
Gas
If your baby is crying a lot after every feeding, it may simply be a buildup of air swallowed while eating. It’s thought that bottle-fed babes in particular may be more prone to swallowing a lot of air during a feeding. This can trap gas in their stomachs and be uncomfortable.
In general, breastfed babies swallow less air while eating simply due to the way they eat. But every baby is different and even breastfed babies may need to be burped after a feeding.
Trying keeping your baby upright after a feeding and burping gently from the bottom of their back and up through the shoulders to work the gas bubbles up and out. Also check out this illustrated guide to burping a sleeping baby.
Also check out this illustrated guide to burping a sleeping baby.
Formula
If your baby is formula-fed, swapping out the formula you use may be a simple solution to a crying baby after feedings. Every formula is a little bit different and certain brands make formulas for more sensitive baby tummies.
If you decide to try this, talk to your baby’s pediatrician about whether an elemental formula would be a good choice to try for a week. If you try one different brand and you see no change in your baby’s fussiness, continuing to try different brands is unlikely to help.
Takeaway
Colic, along with a few other common conditions, might be the culprit if you too have a “crier” on your hands.
If your baby doesn’t find relief after dietary changes or additional burping, then make an appointment to see their doctor.
Share on Pinterest
Chaunie Brusie, BSN, is a registered nurse with experience in labor and delivery, critical care, and long-term care nursing. She lives in Michigan with her husband and four young children, and is the author of the book “Tiny Blue Lines.”
She lives in Michigan with her husband and four young children, and is the author of the book “Tiny Blue Lines.”
Last medically reviewed on October 3, 2018
- Parenthood
- Baby
- 06 Months
How we reviewed this article:
Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
- ABM clinical protocol #24: Allergic proctocolitis in the exclusively breastfed infant. (2011). DOI:
10.1089/bfm.2011.9977 - Harrel MC, et al. (2015). Is there a correlation between maternal diet in breastfeeding mothers and infantile colic? DOI:
10.1097/01.EBP.0000541032.94135.ca - Mayo Clinic Staff. (2018). Infant reflux.
mayoclinic. org/diseases-conditions/infant-acid-reflux/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20351412
org/diseases-conditions/infant-acid-reflux/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20351412 - Rosen LD, et al. (2007). Complementary, holistic, and integrative medicine.
pedsinreview.aappublications.org/content/28/10/381 - Saavedra MA, et al. (2003). Infantile colic incidence and associated risk factors: A cohort study. .
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14502331 - Sung V, et al. (2014). Treating infant colic with the probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri: Double blind, placebo controlled randomised trial. DOI:
10.1136/bmj.g2107 - Symptoms & causes of GER and GERD in infants. (2015).
niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/acid-reflux-ger-gerd-infants/symptoms-causes
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Current Version
Oct 3, 2018
Written By
Chaunie Brusie
Edited By
Nizam Khan (TechSpace)
Medically Reviewed By
Karen Richardson Gill, MD
Share this article
My baby fusses or cries when breastfeeding
By Kelly Bonyata, BS, IBCLC
© Lsantilli - Fotolia. com
com
Some babies will fuss, cry or pull off the breast during breastfeeding. There are a number of reasons why this might be happening. It’s pretty common to see this type of behavior at around 6-8 weeks, though it can occur at any time. If your baby is generally fussy (not just when nursing) see My baby is fussy! Is something wrong?
Determining the problem
Here are some of the problem-solving steps I go through when my baby is fussy at the breast or a mother asks me why her baby is fussing while breastfeeding:
.
How old is baby? Most babies go through growth spurts during the first few days at home and around 7-10 days, 2-3 weeks, 4-6 weeks, 3 months, 4 months, 6 months, 9 months, etc. Many babies are fussy during growth spurts.
Is baby working on anything new developmentally? Babies who are starting to notice the world around them can be notoriously distractible. Any kind of new developmental step that baby is working on can affect nursing temporarily, whether it be fussy nursing behavior or simply more frequent nursing.
When is baby fussing? To figure out the cause it’s helpful to pay attention to when the fussy behavior happens, both during the nursing session and during the day.
If baby is fussy right when your milk is letting down (or immediately after), there’s a good chance that the fussy nursing is related to a fast let-down. If baby is fussy before let-down, or a few minutes into nursing (and a while after let-down), then baby may be impatient for the fast flow of milk that comes with let-down. Fussing at the end of a nursing session (or what seems to be the end) may mean that baby needs to burp, or is ready to finish nursing, or just wants to suck (and doesn’t want to deal with a new let-down at this point), or wants to continue nursing on the other side or with a faster flow of milk.
If the fussy behavior is mainly in the mornings, it might be due to a faster than usual let-down if baby has just had a longer sleep period and mom’s breasts are fuller than usual. If baby is fussier during evening nursings, it may be due to the normal fussy time that most babies have during the evening. Although most babies don’t react to foods that mom eats, some do. If you eat a particular food at about the same time each day (or most days) and baby has a regular time where she fusses during nursing, try not eating that food for a week or two to see if things improve.
If baby is fussier during evening nursings, it may be due to the normal fussy time that most babies have during the evening. Although most babies don’t react to foods that mom eats, some do. If you eat a particular food at about the same time each day (or most days) and baby has a regular time where she fusses during nursing, try not eating that food for a week or two to see if things improve.
Does fussing occur on both sides equally or only on one side? Most moms have a faster let-down and/or a more abundant milk supply on one side than the other, so if your baby fusses more on one side, it may be due to these differences.
What else is going on with baby? Is she sick or teething? Is something new or different going on in her environment? Has she started solids or is she trying a new food? Is she exhibiting other symptoms besides the fussy nursing?
Below are discussions of some of the different things that can lead to fussy nursing behavior. Keep in mind that the problem may also be a combination of several things.
Keep in mind that the problem may also be a combination of several things.
Does baby need to burp?
Many babies will cry, fuss, pull off the breast, etc. if they need to burp. Try to burp between breasts and after a feeding, but don’t worry if baby does not burp and is content. Breastfed babies overall don’t take in as much air during a feeding as bottle-fed babies do, so usually don’t need to burp as often. If baby has been crying before she nurses, or is so hungry that she nurses “frantically” or if mom has a fast let-down, baby could be taking in more air and may need to be burped more often.
Burping is usually only necessary during the first few months, though it may extend longer. Once your baby is moving more freely, she will be able to relieve the gastric gas herself. This usually will occur between the 4th and 6th month, but may be shorter in some children and longer in others.
If baby has a hard time burping, try burping more often during a feeding. The best burping position is one that applies firm pressure to the baby’s tummy. Placing baby over the shoulder way up so that there is pressure on baby’s abdomen often works well. Walking around while doing this might distract her long enough to get a good burp. You may even want to lie baby down on her stomach and burp her that way.
The best burping position is one that applies firm pressure to the baby’s tummy. Placing baby over the shoulder way up so that there is pressure on baby’s abdomen often works well. Walking around while doing this might distract her long enough to get a good burp. You may even want to lie baby down on her stomach and burp her that way.
Growth spurt
Babies often pull off and fuss during growth spurts. Most babies go through growth spurts, sometimes called frequency days, during the first few days at home and around 7-10 days, 2-3 weeks, 4-6 weeks, 3 months, 4 months, 6 months and 9 months (more or less). More growth spurt information in this link.
Distractible baby
If baby seems to be pulling off the breast at any distraction (real or imaginary), then see The Distractible Baby.
Forceful let-down
Some babies will pull off the breast soon after let-down if mom has a forceful let-down. Baby may be frustrated by the too-fast flow of milk with let-down. A too-forceful let-down can also cause excessive gas or spitting up/vomiting. There is more information here on symptoms of and how to deal with a fast let-down reflex.
A too-forceful let-down can also cause excessive gas or spitting up/vomiting. There is more information here on symptoms of and how to deal with a fast let-down reflex.
Slow let-down
Some babies get very impatient if mom has a slow let-down. There is more information here on speeding up a slow let-down reflex.
Baby wants a faster milk flow
Even very young babies can be quick to notice that pulling off, kneading the breast, etc. can cause an additional let-down, and can facilitate a faster, easier milk flow. Some babies become impatient with the slower milk flow following the initial fast flow at let-down. This may or may not be related to a slow let-down.
When a feeding begins at the breast there are drops of milk. Then when the initial let-down occurs (several seconds to a minute into the feeding), the milk flow speeds up quite a bit. At that time it may drip very quickly, squirt, or even spray. Some minutes later it slows again and the baby must continue to suck vigorously in order to elicit further let-downs. This pattern can continue through successive, multiple let-downs as long as the baby is continuing to nurse vigorously. Eventually, baby will learn that the flow will pick back up again if she’ll only continue to vigorously suck/swallow.
This pattern can continue through successive, multiple let-downs as long as the baby is continuing to nurse vigorously. Eventually, baby will learn that the flow will pick back up again if she’ll only continue to vigorously suck/swallow.
With bottle feeding, the flow is instant and continuous. The baby is required to work very little. Once a baby has had a bottle, especially a lot of bottles, she may begin to prefer the ease of bottle-feeding over the work of breastfeeding. She may become frustrated at the breast after the first let-down occurs and the flow of milk begins to slow.
If baby is getting bottles you might consider putting them away, at least for a while. When you must use a bottle, only use a newborn nipple for as long as baby will tolerate it so that she never gets a really fast flow of milk from the bottle, but has to work a little more to get the milk.
Sometimes babies of moms with oversupply or fast let-down will also get very used to the fast flow and object when it normally slows somewhere between 3 weeks to 3 months.
It can be helpful to do some breast compression when this fussiness starts or right before you expect it to. This will help speed up the milk flow again. Once compression stops helping, try switching baby to the other side when she begins to fuss and back and forth again (after using compression) as you need to.
Baby is done nursing for the moment
If baby is fussing after she’s been nursing for a while, and you’ve ruled out other causes, she may be in the process of changing her nursing pattern. Babies become very efficient at the breast with growth and maturity. They can milk the breast in a lot less time per feeding session than they required before. Baby’s frustration may just be a sign that she’s finished and wants to move on.
On a similar note, an occasional baby will just want to suck at the end of a nursing session and the flow of milk with let-down frustrates her. You might see if offering her a finger or pacifier (if baby is older than 4-6 weeks) to suck on during these times seems to help.
Baby prefers one side
Sometimes babies will refuse or fuss at a breast when the let-down is slower or too forceful, or the supply a bit lower. They in turn will prefer the side which lets down more/less quickly and in which the supply is more bountiful. See also: Lopsided! What can I do?
Fussy in the evening
Many young babies tend to pull off and fuss at the breast in the evening. See the article Cluster Feeding and Fussy Evenings.
Teething
Teething can cause fussy nursing behavior, as some babies experience gum discomfort with sucking. Baby might start to nurse, but then pull off and cry or fuss and not want to nurse anymore. See Teething for more information and tips.
Thrush
Frequent pulling off the breast can be a symptom of thrush.
Stuffy nose
A stuffy nose can cause fussy nursing behavior. If your baby has a stuffy nose and is having a hard time breathing and nursing at the same time, see colds & congestion.
Allergy or food sensitivity
Some babies with allergies or food sensitivities exhibit fussy nursing behavior. Often when there is a sensitivity to something in mom’s diet, baby will come to the breast hungry but when she tastes/smells something in the milk that will cause her GI distress, she pulls off, bats her head back and forth, etc. Sensitivities to foods in mom’s diet are rare. If this is the problem, you will most likely notice other symptoms, such as excessive spitting up or vomiting, colic, diarrhea, rash, persistent congestion or runny nose, or excessive gas. More information on food sensitivities in babies and links to more allergy information can be found in my article Dairy and other Food Sensitivities in Breastfed Babies.
Low milk supply
Low milk supply can cause baby to be fussy at the breast. If you feel that your milk supply may be low, see this page for more info: Increasing low milk supply.
Reflux
Reflux can result in baby being fussy at the breast. See Reflux and Breastfeeding for more information.
See Reflux and Breastfeeding for more information.
Tongue-Tie
Tongue-Tie can result in baby being fussy at the breast. See Breastfeeding a Baby with Tongue-Tie (Resources) for more information.
Solutions to six breastfeeding problems in the first week
Are you having difficulty breastfeeding your newborn baby? Read on for expert advice on tackling the main challenges of the first week of breastfeeding.
Share this information
Cathy Garbin, child health nurse, midwife and lactation consultant:
Cathy, a mother of two, was a research fellow at the renowned Human Lactation Research Institute, founded by Peter Hartmann, for seven years, providing support to breastfeeding mothers in clinics and at home. Today, she still works as a family counselor, and also conducts seminars for attending physicians and speaks at international conferences. nine0003
Breastfeeding is not always easy, so if
you are having difficulty, know that you are not alone. A US study found that out of 500 new mothers surveyed, 92% experienced breastfeeding problems by the third day. 1 Fortunately, most early breastfeeding problems are easy to resolve. Below you can read recommendations for solving the main problems that mothers often face in the first week of feeding. nine0003
A US study found that out of 500 new mothers surveyed, 92% experienced breastfeeding problems by the third day. 1 Fortunately, most early breastfeeding problems are easy to resolve. Below you can read recommendations for solving the main problems that mothers often face in the first week of feeding. nine0003
Problem #1. Breastfeeding hurts!
Pain during feeding is usually associated with tenderness or inflammation of the nipples, especially when milk "comes" on the second to fourth day after birth. 2 The baby will beg for a breast every couple of hours, and this can quickly aggravate the problem: some mothers' nipples crack, bleed, or blister. This is, of course, very annoying.
Solutions 3
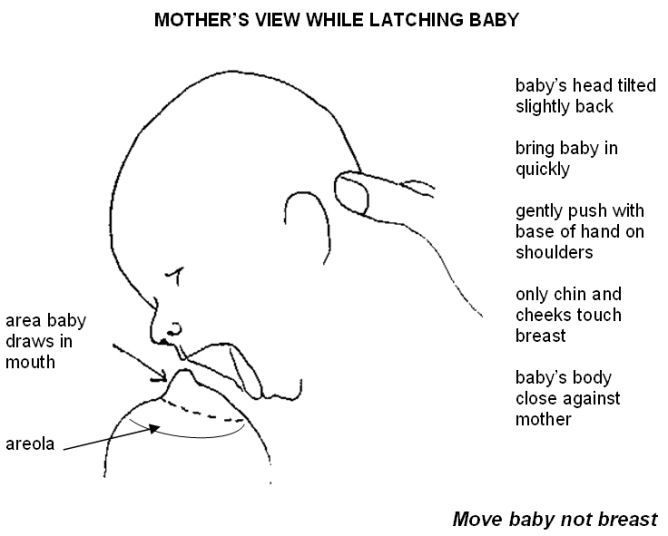
- Check how the baby latch on. An incorrect latch is one of the most common causes of pain during breastfeeding. A newborn baby should take most of the lower half of the areola (dark skin around the nipple) into his mouth, and your nipple should rest against his palate, supported from below by the tongue.
- Contact a lactation consultant or healthcare professional to make sure your baby's mouth and torso are properly positioned during feeding and there are no other latch-on problems. The doctor may also examine the baby's mouth for physical abnormalities. nine0032
- Try other feeding positions. Reclining, cross cradle, underarm, or lying positions can relieve pressure on the most painful areas of your breasts.
- Gently wipe soaked nipples with water-soaked cotton swabs after each feed to remove milk residues that can cause infection.
- Air dry nipples or blot with a clean, soft muslin or flannel cloth to prevent bacterial growth in a humid environment. Use disposable or reusable bra pads to absorb leaking milk and remember to change them regularly. nine0032
- Soften your nipples. An ultra-pure lanolin treatment will help relieve inflammation and dry skin. You can also apply a few drops of your own breast milk to your nipples.
 In both cases, you do not have to wash your breasts before the next feeding. You can also apply refrigerated hydrogel pads* to your nipples. They soothe the nipples and help relieve pain during feeding, as well as speed up healing.
In both cases, you do not have to wash your breasts before the next feeding. You can also apply refrigerated hydrogel pads* to your nipples. They soothe the nipples and help relieve pain during feeding, as well as speed up healing. - Protect your nipples. nine0008 Nipple shields* protect the sore area from rubbing against clothing.
- Be patient. The inflammation usually resolves after a few days as your body adjusts to breastfeeding and your baby learns to suckle.
- Seek medical attention, if pain during feeding does not go away after a few days. Constant inflammation of the nipples may indicate an infection that requires prompt treatment.
Problem #2. Baby doesn't latch on properly
Some newborns do not latch on properly right away. Maybe both of you just need more time to learn how to breastfeed, or maybe the baby was born prematurely, feels unwell after a difficult birth, or mom has flat or inverted nipples.
Solutions
- Contact a lactation consultant or healthcare professional who can help identify the cause of the problem and suggest solutions. nine0032
- Flat or inverted nipples must be pulled out. Nipple formers* fit comfortably in the bra and apply gentle pressure to the nipples to help them come out for easier feeding.
- Try different positions and ways to support your newborn. The baby needs to feel supported. He must be comfortable and breathe freely in order to suckle properly. Do not hold the child by the head and do not put pressure on it. Lean back and let your child take the lead. This stimulates his natural reflexes and helps him find and latch on to his breasts. nine0013 4
- When feeding, try to find the optimal position. Instead of putting your baby on and off, stressing both of you, try to position him in a way that is easy and comfortable for him.
 Hold the torso and legs of the baby close to you, support him by the shoulders and hold him firmly so that he feels safe. Let the baby's head rest freely on your arm so that he can tilt it back slightly and breathe freely. The chin should be pressed against your chest. If these small adjustments don't make feeding more comfortable for your baby, seek help from a lactation consultant or healthcare professional. nine0032
Hold the torso and legs of the baby close to you, support him by the shoulders and hold him firmly so that he feels safe. Let the baby's head rest freely on your arm so that he can tilt it back slightly and breathe freely. The chin should be pressed against your chest. If these small adjustments don't make feeding more comfortable for your baby, seek help from a lactation consultant or healthcare professional. nine0032 - Use nursing pads. If your baby is having difficulty latch-on, a lactation consultant or healthcare professional may suggest trying nursing pads*. A nipple with an overlay is more convenient to take in the mouth, so it is larger and more rigid. Do not use nursing pads for a long time.
Problem #3. Not enough breast milk
You will produce little breast milk at the very beginning, as the hormonal changes that trigger milk production occur slowly and do not end until the second or fourth day after birth. nine0013 2 You may be worried that your baby is not getting enough milk, but in the early days his stomach is still too small and feedings are frequent, so don't worry.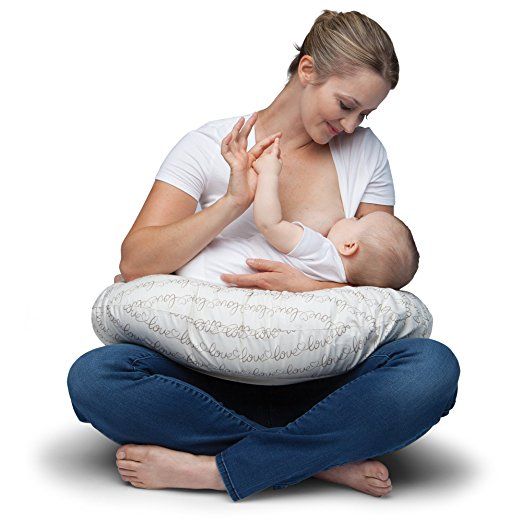 The only things to worry about these days are excessive weight loss, too few wet and soiled diapers, or signs of dehydration in the baby. For more information on how often a newborn should urinate and void, see Breastfeeding Newborns: What to Expect in the First Week. nine0003
The only things to worry about these days are excessive weight loss, too few wet and soiled diapers, or signs of dehydration in the baby. For more information on how often a newborn should urinate and void, see Breastfeeding Newborns: What to Expect in the First Week. nine0003
Solutions
- Contact a Lactation Consultant or your healthcare provider who can determine if you have problems with milk production. The sooner you do this, the better.
- Feed your baby on demand, not on a schedule. In the first week after birth, your baby will ask to breastfeed every two to three hours (or more often!), both day and night. Such frequent feeding helps to establish the production of breast milk. nine0032
- Take care of yourself. It's not always easy with a newborn, but try to rest whenever you can, eat right, and accept any help around the house or with older children that your loved ones can give you to fully focus on breastfeeding.

- Try expressing milk. If a baby is feeding frequently but not gaining any weight, a lactation consultant or doctor may recommend pumping to increase breast milk production. If milk is not coming out at all, you can try the Medela Symphony Dual Electric Clinical Breast Pump**. It features an Initiate program that mimics a baby's natural sucking rhythm for the first few days. nine0032
Problem #4. Breast full and heavy
Your breasts will become fuller and heavier as milk comes in.
If the baby suckles well and often, this should not cause any problems. However, in some women, the breasts become so full that they become hard and painful. This condition, called breast swelling, can cause discomfort. The swollen chest seems to be “burning”, now all the activity of your body is concentrated in it, resembling a busy traffic at rush hour. Fortunately, this condition usually resolves within 24 to 48 hours. However, due to the swelling of the mammary glands, the nipples can become flat and the baby may have difficulty latch-on. nine0013 5
nine0013 5
Solutions
- Feed your baby often. Try to breastfeed at least 8-12 times a day. This is the main way to alleviate this condition. For more tips and tricks, see the article on Breast Swelling. 6.7
- Call your healthcare provider, if symptoms persist for more than 48 hours, you have a fever, or your baby is unable to breastfeed due to swelling.
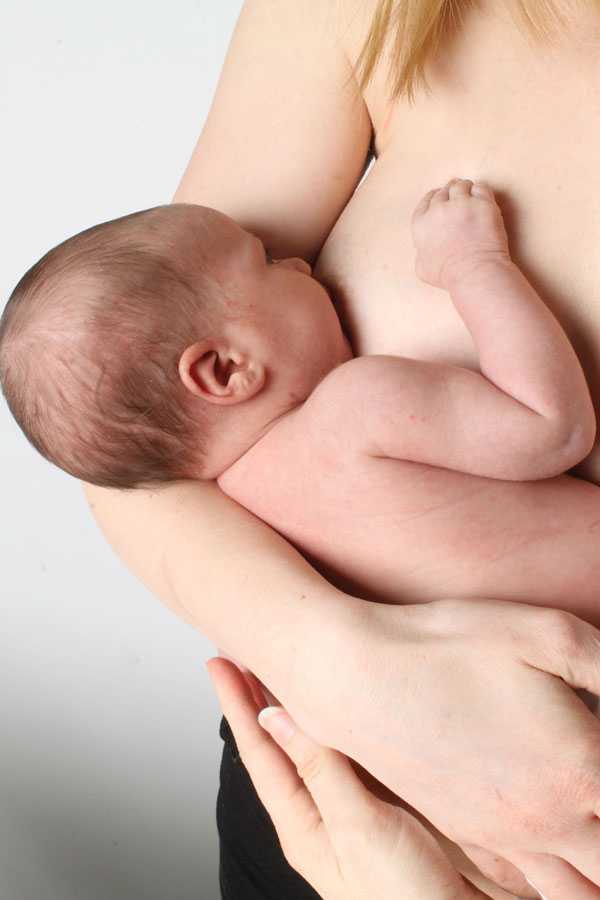
Problem #5. Milk is leaking
Breast leakage is very common in the early days of breastfeeding when milk production begins. Milk may leak from one breast while you are feeding the other, when you sleep on your stomach, or when something accidentally triggers the milk flow reflex, such as when you hear a baby crying in a store. The leakage usually stops after about six weeks.
Solutions
- Protect clothes from stains will help disposable or reusable bra pads to be used day and night.
 nine0032
nine0032 - Don't waste precious drops! Breast milk collection pads* fit inside the bra and allow you to collect any leaking milk. This is a very useful thing when there is too much milk and the pads are not absorbing well, or when one breast is leaking while you are feeding the other. If you want to save the collected milk, use only the milk collected at the feeding. Place it in a sterile container and refrigerate immediately if you are not supplementing with it right away. Collected milk must be used within 24 hours. The breast milk collection sleeves should not be worn for more than two to three hours at a time. nine0032
Problem #6. There seems to be too much milk
Sometimes when milk comes in, too much is produced! In the first few weeks there may be an overabundance of milk, but usually everything returns to normal soon. 7 Up to this point, the breasts may be heavy and sore almost all the time, even immediately after a feed, and a lot of milk may leak.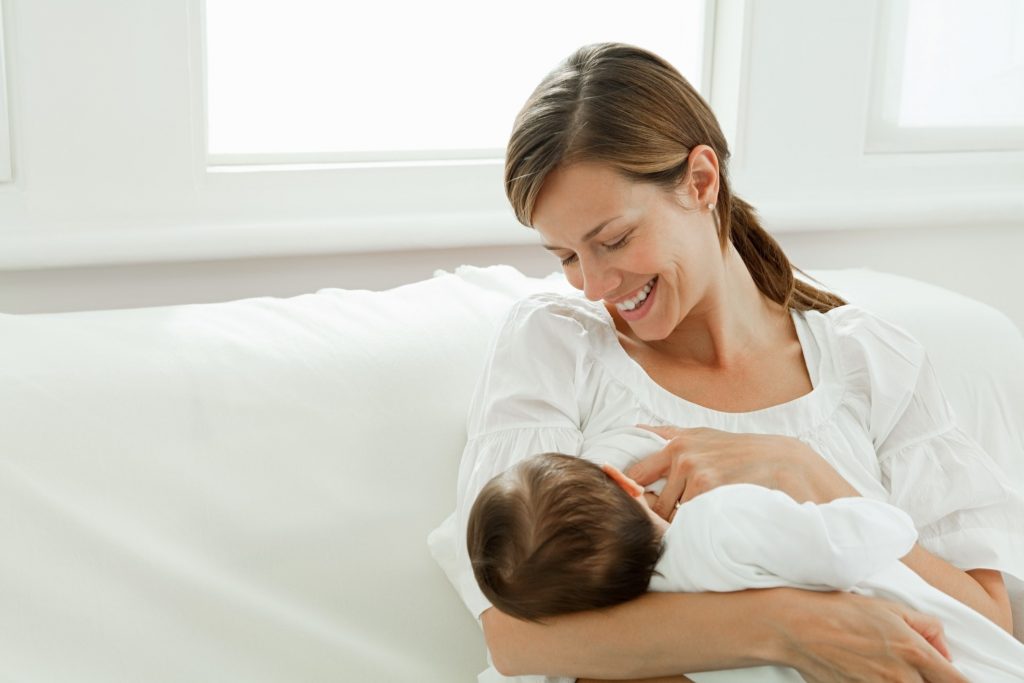 A strong flush can cause a baby to cough or choke, vomit immediately after a feed, have tummy discomfort, or have hard, frothy, greenish stools. These are all signs that you are having too much milk, but the problem may resolve itself as your breasts get used to the new function. nine0003
A strong flush can cause a baby to cough or choke, vomit immediately after a feed, have tummy discomfort, or have hard, frothy, greenish stools. These are all signs that you are having too much milk, but the problem may resolve itself as your breasts get used to the new function. nine0003
Solutions
- Express some milk by hand at the beginning of each feed to ease the force of the flush.
- Try to feed while leaning back: this will help your baby control the flow of milk. The "cradle" position is also good: hold the baby obliquely by the shoulders so that the head can lean back slightly while on your arm. The torso of the baby will be located diagonally on you.
- Be kind and patient. Let your baby rest and absorb milk both during and after feeding. Don't move your baby too much or too fast, as this can make him nauseous. As the baby grows, he will learn to better cope with the rush of milk, which is likely to weaken anyway.

- Use the towel or swaddle to soak up spilled milk if the baby can't handle the flush, and place the breast milk collection pad on the other breast to catch any spilled milk. nine0032
- Contact a lactation consultant or doctor if problems persist after a few weeks . He will examine you and may suggest one-sided feedings or hourly breast changes (“breast duty”) to reduce your milk supply.
Related materials: Difficulties in breastfeeding in the next few weeks and problems with breastfeeding after the first month
Literature
1 Wagner EA et al. Breastfeeding concerns at 3 and 7 days postpartum and feeding status at 2 months. Pediatrics . 2013: peds -2013. - Wagner I.A. et al., "Breastfeeding Problems at Days 3 and 7 of a Child's Life and Type of Feeding at 2 Months". Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 2013:e865–e875.
2 Pang WW, Hartmann PE. Initiation of human lactation: secretory differentiation and secretory activation. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 2007;12(4):211-221. - Pang, W.W., Hartmann, P.I., "Lactation initiation in the lactating mother: secretory differentiation and secretory activation." G Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2007;12(4):211-221.
Initiation of human lactation: secretory differentiation and secretory activation. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 2007;12(4):211-221. - Pang, W.W., Hartmann, P.I., "Lactation initiation in the lactating mother: secretory differentiation and secretory activation." G Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2007;12(4):211-221.
3 Cadwell K. Latching - On and Suckling of the Healthy Term Neonate: Breastfeeding Assessment. J Midwifery & Women ’ s 2007;52(6):638-642. — Cadwell, K., "Latching and sucking in healthy newborns: evaluation of breastfeeding." F Midwifery Women Health. 2007;52(6):638-642.
4 Colson SD et al. Optimal positions for the release of primitive neonatal reflexes stimulating breastfeeding. Early Hum Dev . 2008;84(7):441-449. - Colson S.D. et al., "Optimal Positions for Provoking Primitive Innate Reflexes to Induce Breastfeeding." Airlie Hume Dev. 2008;84(7):441-449.
2008;84(7):441-449. - Colson S.D. et al., "Optimal Positions for Provoking Primitive Innate Reflexes to Induce Breastfeeding." Airlie Hume Dev. 2008;84(7):441-449.
5 Jacobs A et al. S3-guidelines for the treatment of inflammatory breast disease during the lactation period. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 2013;73(12):1202-1208. - Jacobs A. et al., "Recommendations S -3 for the treatment of inflammatory diseases of the breast during breastfeeding. Geburtskhilfe und Frauenheilkünde. . ABM Clinical Protocol# 4: Mastitis , Revised MARCH 2014. Breastfeed - 9020: 5): 5) H., Academy of Breastfeeding Protocol Committee, AVM Clinical Protocol #4: Mastitis, March 2014 edition of Brestfeed Med (Breastfeeding Medicine). 2014;9(5):239-243.
7 Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine Protocol Committee. ABM clinical protocol # 20: Engorgement. Breastfeed Med . 2009;4(2):111-113. - Protocol Committee of the Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine, "AVM Clinical Protocol No. 20: Engorgement, Revision 2016". Brestfeed Med (Breastfeeding Medicine). 2009;4(2):111-113.
Breastfeed Med . 2009;4(2):111-113. - Protocol Committee of the Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine, "AVM Clinical Protocol No. 20: Engorgement, Revision 2016". Brestfeed Med (Breastfeeding Medicine). 2009;4(2):111-113.
Read instructions before use. Consult a specialist about possible contraindications. nine0017
* RU No. ФСЗ 2010/07352 of 07/19/10
** RU No. ФСЗ 2010/06525 of 03/17/2021
Home ›› Laktostasis: symptoms and treatment
Home ›› Laktostasis: symptoms and treatment known as milk stasis, or lactostasis. What sensations arise with a clogged milk duct? A sensitive seal appears in the chest, and slight pain and discomfort may occur. nine0009
We'll cover the most common questions about this problem and provide you with all the important information about blocked ducts, from symptoms of blocked ducts in the breast to treatments and tips to prevent the condition.
If you need more information, get another opinion.
Signs of blocked milk duct
What is blocked milk duct and how is it different from other breast conditions like mastitis? Blockage of the milk duct, also known as milk stasis or lactostasis, is a condition in which a milk clot forms in the breast, preventing milk from flowing out of the duct. A painful lump forms in the chest, and there may be a feeling of discomfort around it. nine0009
Common symptoms of blockage of the breast duct are:
- pain in a certain area of the breast;
- painful lump in the mammary gland the size of a pea or more;
- slight increase in temperature in the area of blockage;
- sometimes a small white bubble forms on the nipple.
In a nutshell, duct blockage is the formation of a localized lump in the chest that causes discomfort in the absence of any other signs of illness or fever. If there is a fever or flu-like symptoms and if the chest feels hot to the touch, it may be mastitis.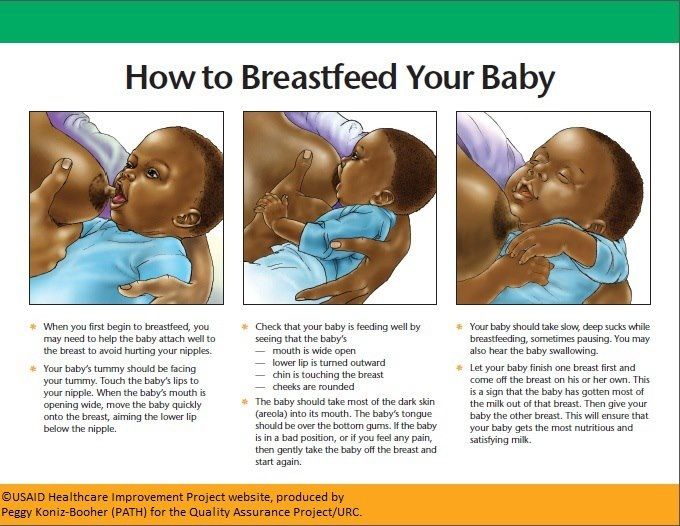 nine0009
nine0009
More information on symptoms and treatment for mastitis can be found here.
Causes of blockage of the breast duct
Blockage of the milk duct can occur for several reasons:
- incomplete flow of milk from the breast during feeding;
- incorrect attachment of the child, because of which he cannot fully suckle the breast;
- engorgement;
- excess milk production; nine0032
- abrupt cessation of breastfeeding;
- putting pressure on the mammary gland: for example, wearing tight clothing that squeezes the chest.
Blockage of the milk duct usually occurs as a result of incomplete emptying of the breast or excessive pressure on the breast for a long period of time.
How to remove blockage of the milk duct?
To prevent a breast infection, it is important to find a way to clear the blocked duct as soon as possible. nine0003
Here's what to do if your milk duct is blocked:
- Continue to breastfeed your baby.
 If the milk duct is blocked, you should continue to feed the baby and try to do it so that the baby sucks out all the milk. You can also try breastfeeding a baby with a blocked duct every two hours. This will help keep the milk flowing and possibly clear blockages. Continuous stimulation of the flow of milk is the key to eliminating blockage of the duct.
If the milk duct is blocked, you should continue to feed the baby and try to do it so that the baby sucks out all the milk. You can also try breastfeeding a baby with a blocked duct every two hours. This will help keep the milk flowing and possibly clear blockages. Continuous stimulation of the flow of milk is the key to eliminating blockage of the duct.
These bra pads help prevent milk stains on clothing while breastfeeding. Their porous top layer and excellent absorbency will help keep clothes dry and comfortable.
- Massage and express between feeds. Before each feeding, it is recommended that the mother massage the breast with stroking movements from the periphery of the breast to the nipple. This stimulates the flow of milk even before the start of feeding. After breastfeeding, a mother can express any milk left in a breast with a blocked duct to ensure that the ducts are completely emptied. Stimulating the flow of milk can help prevent blockages in the milk ducts, but there are times when a mother cannot be with her baby during breastfeeding.
 To stimulate the flow of milk in such situations, it is very important to express milk manually. nine0009
To stimulate the flow of milk in such situations, it is very important to express milk manually. nine0009
Check out these manual breast pumps for expressing milk anywhere, anytime.
- Latch the baby correctly to the breast. Attaching the baby to the breast in such a way that his chin is directed towards the blocked duct can help solve the problem. Such attachment to the breast will help the baby, when sucking, empty exactly the area of \u200b\u200bthe mammary gland where there is a blockage. You can try to apply the baby in different ways, so that it is more convenient for him to extract all the milk from different parts of the breast. nine0032
- Apply warm and cold compresses. As compresses, you can use a towel, as well as thermal pads 2 in 1. It is recommended to apply a warm thermal pad to the area of the clogged duct several times a day, while doing a light massage. Breast discomfort after feedings can be alleviated somewhat by using cooled thermal pads.

- Wear comfortable loose-fitting clothing. One of the causes of blockage of the milk ducts is excessive pressure on the mammary glands for an extended period of time. This pressure can be exerted by tight clothing or bras, so it is important to wear loose clothing to clear a blocked duct. Sometimes mothers also notice clogged pores on their breasts - loose clothing and a bra will also help to cope with this problem.
 nine0032
nine0032 - Tight clothing encourages more sweating and prevents sweat from evaporating, resulting in clogged pores. Moms should wear loose-fitting clothing to clear clogged pores and clear blocked milk ducts.
If following these tips fails to open the milk duct, it is recommended that you contact your doctor or lactation consultant to prevent infection.
How to prevent clogged milk ducts? nine0203
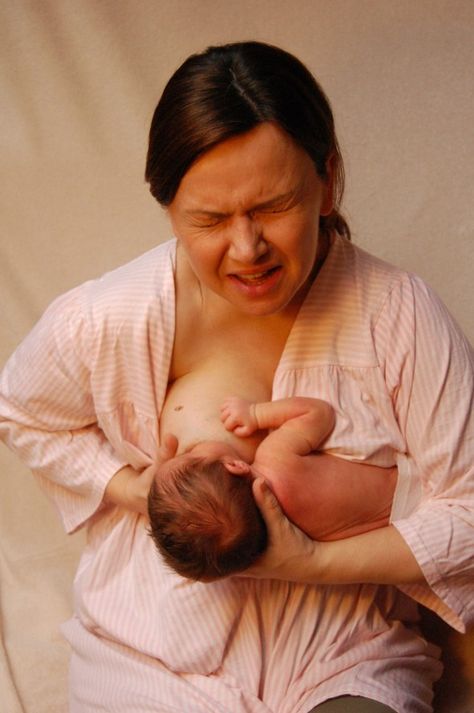
Every mother would like to avoid the problem of blocked milk ducts altogether. No one will give a 100% guarantee against blockage of the milk ducts, but you can try to prevent it by using a few useful tips.
- After each feeding, check that there is no feeling of fullness and discomfort in the chest. If it is, then it is necessary to additionally express milk, until a feeling of comfort.
- Feed your baby regularly for as long and as often as he wants
- Express milk between feedings if you experience discomfort and fullness in your breasts.

- Place the baby on the breast so that there is no undue pressure on the breast.
- Wear loose, comfortable clothing and bralettes.
When should I seek professional help?
When a blockage of the milk duct occurs, the mother should not panic. Despite the discomfort and pain, this condition is quite normal and usually goes away if treated immediately. nine0009
If you want to know how to clear a blocked milk duct, or if you are feeling a blocked milk duct, you should seek help from your doctor.
Find out more about other common breastfeeding problems and how to deal with them.
Articles & tips from Philips Avent
Links
The New Breastfeeding Guide for Mothers 3rd Edition (2017)
Baby+ app
Download the app and track your child's development and growth with trackers and keep those special moments forever.
Download app:
Pregnancy+ app
Download one of the world's best pregnancy tracking apps for weekly helpful information, articles and tips about pregnancy and baby development.