Baby feeding progression
Tips for the First Year
Eat, sleep, pee, poop, repeat. Those are the highlights in a day of the life of a brand new baby.
And if you’re a new parent, it’s the eating part that may be the source of many of your questions and worries. How many ounces should your baby take? Do you wake a sleeping baby to eat? Why do they seem hungry all the time? When can your child start solids?
Questions abound — and, despite Grandma’s insistence, the answers have changed since you were a tot. It’s now recommended that newborns, even formula-fed ones, eat on demand (consider it good preparation for the teenage years) and that babies wait to start solid foods until they’re 4 to 6 months old.
On day one of life, your baby’s stomach is the size of a marble and can only hold 1 to 1.4 teaspoons of liquid at a time. As your baby gets older, their stomach stretches and grows.
It’s hard (or impossible, really) to know how much milk your baby is taking in while breastfeeding. But if you’re bottle feeding due to any number of valid reasons, it’s a bit easier to measure.
Here, from the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), a typical feeding schedule for bottle-fed babies.
| Age | Ounces per feeding | Solid foods |
|---|---|---|
| Up to 2 weeks of life | .5 oz. in the first days, then 1–3 oz. | No |
| 2 weeks to 2 months | 2–4 oz. | No |
| 2–4 months | 4-6 oz. | No |
| 4–6 months | 4–8 oz. | Possibly, if your baby can hold their head up and is at least 13 pounds. But you don’t need to introduce solid foods yet. |
| 6–12 months | 8 oz. | Yes. Start with soft foods, like one-grain cereals and pureed vegetables, meats, and fruits, progressing to mashed and well-chopped finger foods. Give your baby one new food at a time. Continue supplementing with breast or formula feedings.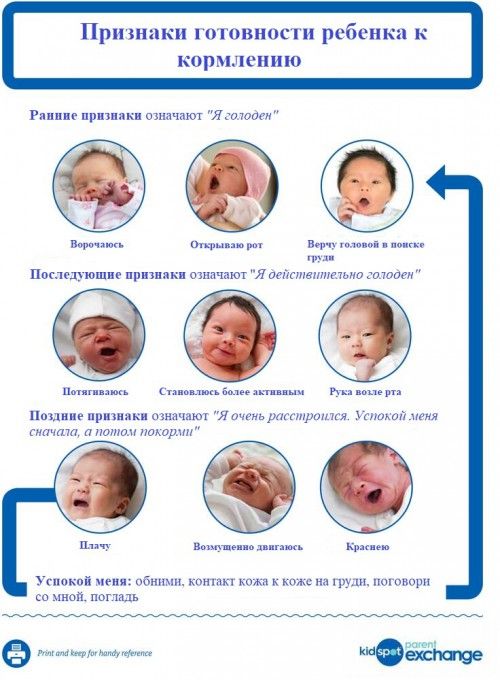 |
Every baby is unique — but one thing that’s pretty consistent is that breastfed babies eat more frequently than bottle-fed ones. That’s because breast milk is easily digested and empties from the stomach a lot quicker than formula.
Breastfed babies
There’s no rest for the weary. According to La Leche League International, you should begin nursing your baby within 1 hour of birth and provide about 8 to 12 feedings daily in the first few weeks of life (yeah, we’re exhausted for you).
At first, it’s important not to let your baby go more than 4 hours without feeding. You’ll likely need to wake them up if necessary, at least until breastfeeding is well established and they’re gaining weight appropriately.
As your baby grows and your milk supply amps up, your baby will be able to take in more milk in less time at one feeding. That’s when you might start to notice a more predictable pattern.
- 1 to 3 months: Your baby will feed 7 to 9 times per 24 hours.

- 3 months: Feedings take place 6 to 8 times in 24 hours.
- 6 months: Your baby will feed around 6 times a day.
- 12 months: Nursing may drop to about 4 times a day. The introduction of solids at about 6 months helps to fuel your baby’s additional nutritional needs.
Keep in mind that this pattern is just one example. Different babies have different paces and preferences, along with other factors that influence the frequency of feedings.
Bottle-fed babies
Like breastfed babies, bottle-fed newborns should eat on demand. On average, that’s about every 2 to 3 hours. A typical feeding schedule may look like this:
- Newborn: every 2 to 3 hours
- At 2 months: every 3 to 4 hours
- At 4 to 6 months: every 4 to 5 hours
- At 6+ months: every 4 to 5 hours
For both breastfed and bottle-fed babies
- Don’t give liquids other than formula or breast milk to babies under a year old. That includes juices and cow’s milk.
 They don’t provide the right (if any) nutrients and can be upsetting to your baby’s tummy. Water can be introduced around 6 months when you start offering a cup.
They don’t provide the right (if any) nutrients and can be upsetting to your baby’s tummy. Water can be introduced around 6 months when you start offering a cup. - Don’t add baby cereal to a bottle.
- It can create a choking hazard.
- A baby’s digestive system isn’t mature enough to handle cereal until about 4 to 6 months of age.
- You could overfeed your baby.
- Don’t give your baby any form of honey until after their first birthday. Honey can be dangerous for a baby, occasionally causing what’s called infant botulism.
- Do adjust your expectations based on your baby and their unique needs. Premature babies are likely to follow feeding patterns according to their adjusted age. If your baby has challenges like reflux or failure to thrive, you may need to work with your doctor on the appropriate feeding schedule and amount they should be eating.
Schedules are the holy grail of every parent. Your child will naturally start to fall into a feeding pattern as their tummy grows and they can take in more breast milk or formula at one sitting. This may begin to happen between 2 and 4 months of age.
This may begin to happen between 2 and 4 months of age.
For now, though, focus on learning your baby’s hunger cues, such as:
- rooting around your chest, looking for a nipple.
- putting their fist in their mouth
- smacking or licking their lips
- fussing that can escalate quickly (don’t wait until your baby’s hangry to feed them)
Once your baby is a few months old, you may be able to introduce a sleep/feed schedule that works for you.
Let’s say, for example, your 4-month-old wakes every 5 hours for a feeding. That means if you feed at 9 p.m., your baby wakes around 2 a.m. But if you wake and feed the baby at 11 p.m., just before you go to bed, they may not rouse until 4 a.m., giving you a decent chunk of nighttime winks.
In general, if your baby seems hungry, feed them. Your baby will naturally eat more frequently during growth spurts, which typically occur around 3 weeks, 3 months, and 6 months of age.
Some babies will also “cluster feed,” meaning they’ll feed more frequently during certain periods and less at others. For example, your baby may cluster feed during the late afternoon and evening and then sleep longer at night (yay!). This is more common in breastfed babies than bottle fed babies.
For example, your baby may cluster feed during the late afternoon and evening and then sleep longer at night (yay!). This is more common in breastfed babies than bottle fed babies.
Worried about overfeeding? While this isn’t really possible to do with an exclusively breastfed baby, you can overfeed a baby who’s taking a bottle — especially if they’re sucking on the bottle for comfort. Follow their hunger cues, but talk to your pediatrician if you’re worried your little one may be overeating.
Your baby is probably ready for solids if they’re 4 to 6 months old and:
- have good head control
- seem interested in what you’re eating
- reach for food
- weigh 13 or more pounds
Which food to start with? The AAP now says it doesn’t really matter much in what order you introduce foods. The only real rule: Stick with one food for 3 to 5 days before offering another. If there’s an allergic reaction (rash, diarrhea, vomiting are common first signs), you’ll know which food is causing it.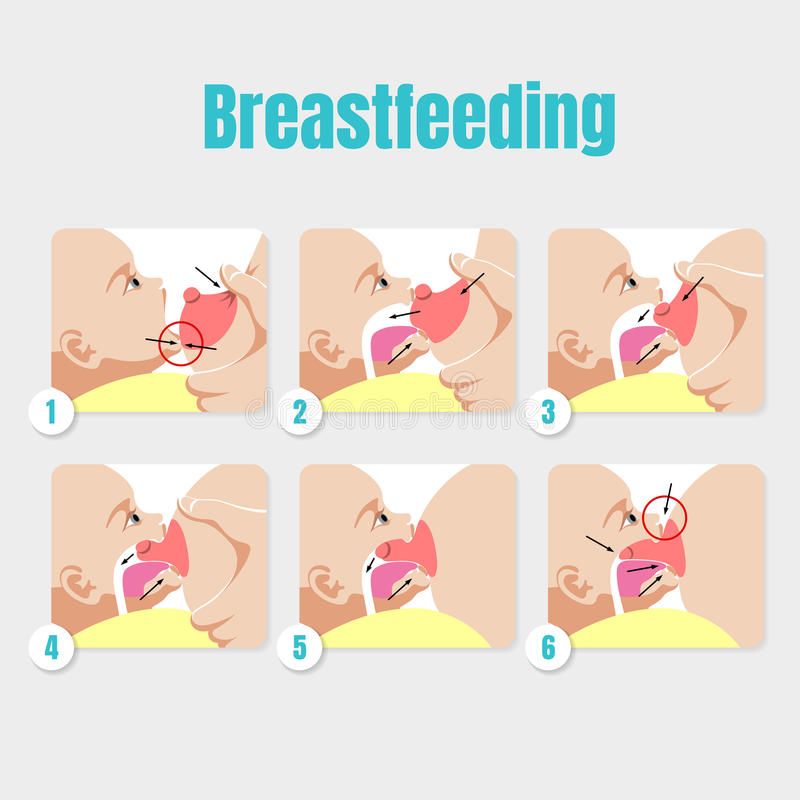
As your baby grows, move from pureed baby food to ones that have more texture (for example, mashed banana, scrambled egg, or well-cooked, chopped pasta). This generally happens around 8 to 10 months of age.
Your supermarket offers a variety of baby food products, but if you want to make your own, keep it sugar and salt free. Additionally, at this stage, don’t feed your baby anything that could be a choking hazard, including:
- hard foods, such as popcorn or nuts
- hard, fresh fruits, like apples; cook to soften or chop into very small pieces
- any meat that isn’t well cooked and very well chopped (this includes hot dogs)
- cheese cubes
- peanut butter (though talk to your pediatrician about this one — and the benefits of introducing diluted peanut butter before the age of 1)
As your baby nears their first birthday, they should be eating a variety of foods and taking in about 4 ounces of solids at each meal. Continue to offer breast milk or formula. By 8 months, babies are drinking about 30 ounces a day.
By 8 months, babies are drinking about 30 ounces a day.
Oh yeah, and buy some stock in a company that makes stain-fighting laundry detergent. It’ll pay for college.
Babies aren’t cookie cutter. Some will gain weight easily, while others will have problems. Things that can affect a baby’s weight gain include:
- having a birth defect like a cleft lip or palate, which creates problems feeding
- having a milk protein intolerance
- being premature
- being fed with a bottle versus the breast
A 2012 study of more than 1,800 babies found that the infants who were fed with a bottle — regardless of whether the bottle contained breast milk or formula — gained more weight in the first year than babies who nursed exclusively.
Your baby’s doctor is the best one to advise you on a healthy weight range for your baby.
How, when, and what to feed a baby are top worries of every parent — but there’s good news: Most babies are pretty good judges of when they’re hungry and when they’re full — and they’ll let you know it.
You just need to present them with the right choices at the right time and pay attention to their cues. If you have any questions or concerns, your pediatrician is there to help you along the way.
Baby formula feeding chart: How much formula by weight and age
Is your baby getting too much or too little formula? It's an important question that worries many new parents, especially those with newborns. When deciding how much formula to give your baby, it's important to watch their hunger cues as well as looking at guidelines based on age and weight. In general, before they're eating solids, babies need 2.5 ounces of formula per pound of body weight each day.
These guidelines are for babies who are exclusively formula-fed for the first 4 to 6 months, and then fed a combination of formula and solids up to age 1. If your baby is getting a combination of breast milk and formula, talk to their doctor for separate advice.
Your pediatrician can tell you where your baby falls on the growth charts, make sure they're growing steadily on their own growth curve, and help you ensure that they're getting a healthy amount of formula.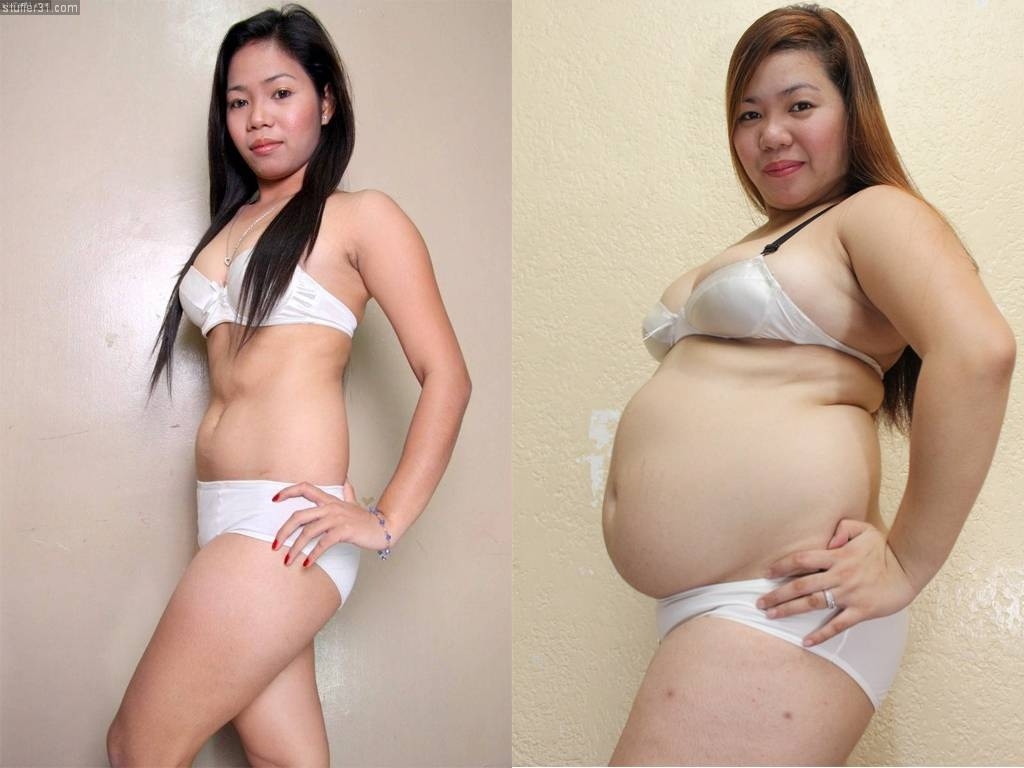 If you're ever worried about your baby's growth, behavior, or development, talk with their doctor.
If you're ever worried about your baby's growth, behavior, or development, talk with their doctor.
How much formula for a newborn
For the first few days, offer your newborn 1 to 2 ounces of formula every 2 or 3 hours. (At first, newborns may only take a half ounce of formula at a time.)
After the first few days, give your newborn 2 to 3 ounces of formula every 3 to 4 hours.
Initially it's best to feed your formula-fed newborn on demand, whenever they show signs that they're hungry. Because your little one can't tell you when they want a bottle, you'll need to learn to read their hunger cues. Crying is often a late sign of hunger, so if you can, try to catch the earlier signs that it's time for a feeding.
Here are some hunger cues to watch for:
- Smacking or licking their lips
- Rooting (moving their jaw, mouth, or head in search of food)
- Putting their hands to their mouth
- Opening their mouth
- Fussiness
- Sucking on things
- Becoming more alert
- Crying
As time passes, your newborn will begin to develop a fairly regular feeding schedule. You'll become familiar with their cues and needs, and knowing when and how much to feed them will be much easier.
You'll become familiar with their cues and needs, and knowing when and how much to feed them will be much easier.
Formula feeding chart by weight
During the first 4 to 6 months, when your baby isn't eating solid foods, here's a simple rule of thumb: Offer 2.5 ounces of formula per pound of body weight every 24 hours, with a maximum of about 32 ounces.
Advertisement | page continues below
| Weight | Ounces of formula |
|---|---|
| 6 pounds | 15 fl oz every 24 hours |
| 7 pounds | 17.5 fl oz every 24 hours |
| 8 pounds | 20 fl oz every 24 hours |
| 9 pounds | 22.5 fl oz every 24 hours |
| 10 pounds | 25 fl oz every 24 hours |
| 11 pounds | 27.5 fl oz every 24 hours |
| 12 pounds | 30 fl oz every 24 hours |
These numbers aren't rigid rules. They offer a rough estimate for what your baby may need. Some babies will grow well while taking less than the recommended amount, while others consistently need more. Your baby's daily feedings will also vary according to their individual needs – in other words, they may want a bit more on some days and a bit less on others.
Some babies will grow well while taking less than the recommended amount, while others consistently need more. Your baby's daily feedings will also vary according to their individual needs – in other words, they may want a bit more on some days and a bit less on others.
Formula feeding chart by age
Here are typical amounts per day based on age:
| Age | Ounces of formula |
|---|---|
| Full-term newborn | 2 ounces per bottle every 3 to 4 hours |
| 1 month old | 3 to 4 ounces per bottle every 3 to 4 hours |
| 2 month old | 4 to 5 ounces per bottle every 3 to 4 hours |
| 3 month old | 4 to 6 ounces per bottle every 3 to 4 hours |
| 4 month old | 4 to 6 ounces per bottle, 4 to 6 times a day |
| 5 month old | 4 to 6 ounces per bottle, 4 to 6 times a day |
| 6 month old | 6 to 8 ounces per bottle, 4 to 5 times a day |
| 7 month old | 6 to 8 ounces per bottle, 3 to 5 times a day |
From 8 months old until their first birthday, you can expect your baby to have 7 to 8 ounces per bottle, 3 to 4 times a day.
As your baby gets older – and their tummy gets bigger – they'll drink fewer bottles a day with more formula in each. It's important not to overfeed your baby so they'll stay at a healthy weight. Your baby shouldn't have more than 32 ounces of formula in 24 hours.
When they reach their first birthday, they can stop drinking formula and transition to cow's milk in a bottle, sippy cup, straw cup, or open cup. Limit your toddler to 16 to 24 ounces (2 to 2.5 cups) a day of whole milk, so they have room for other healthy foods.
Here are signs that your baby's getting all the formula they need:
- Steady weight gain. They continue to gain weight after their first 10 days and follow a healthy growth curve during their first year. (Most babies lose up to 7 to 10 percent of their birth weight in the first few days and then regain it by the time they're about 2 weeks old.)
- Happy baby. They seem relaxed and satisfied after a feeding.

- Wet diapers. They wet two to three diapers a day in the first few days after birth. Over the next few days, the amount should increase to at least five to six wet diapers a day.
Babies are usually good at eating the amount they need, but bottle-fed babies can drink too much at times. Here are the signs that they're getting too much formula:
- Vomiting after a feeding may be a sign that your baby had too much. (Spitting up is normal, vomiting isn't.)
- Tummy pain after a feeding can also be a sign of overfeeding. If your baby draws up their legs or their tummy seems tense, they may be in pain. (See other possible reasons for stomach pain in babies.)
If your baby seems to want to eat all the time, even after finishing a bottle, talk to your pediatrician. Using a pacifier may help soothe their need to suck.
Formula-feeding tips
- In general, babies eat when they're hungry and stop when they're full, so resist the temptation to encourage your baby to finish each bottle.
 Overfeeding during infancy can contribute to obesity later in life.
Overfeeding during infancy can contribute to obesity later in life. - Don't respond to your baby's every cry with a bottle. They may be crying because their diaper is wet, they're cold or hot, they need to be burped, or they want to be close to you. (Learn more about why babies cry, and how to soothe them.)
- Your baby may be hungrier than usual during growth spurts. These typically occur 10 to 14 days after birth and around 3 weeks, 6 weeks, 3 months, and 6 months of age.
Read more:
- Formula Feeding Problem Solver
- How to safely store and use formula
Positions for breastfeeding | Philips
Search Support IconSearch Keywords
Home ›› Newborn Feeding Positions and Good Latching
↑ Top
Although breastfeeding can be a natural element of motherhood practice, patience and a little advance preparation. So, if you decide to breastfeed your baby, be prepared for the fact that you may encounter the often encountered problem of proper breastfeeding. However, do not be upset.
However, do not be upset.
Breast latch is one of the most important things about breastfeeding and can be difficult for new moms, and understandably so; It is essential that the baby properly latch on to the nipple during breastfeeding so that he can get enough breast milk. Proper breast latch is also important because it allows the mother to avoid problems such as blockage of the milk ducts and sore nipples.
Learn more about how to properly care for your breasts in the Quick Guide to Breast Care.
One of the best ways to teach your baby to latch on properly is to find a breastfeeding position that is comfortable for both you and your baby. Here we will discuss different breastfeeding positions as well as other useful tips to help you achieve a proper breastfeeding. If you have any questions or concerns, please contact your doctor or lactation specialist for further support.
Helping your baby latch on properly
Before looking at the different positions for breastfeeding, there are a few things you can do to help your baby: [1]
- Create a calm and relaxing environment.
 Your comfort is key when breastfeeding, so find a position that is comfortable for you to breastfeed. In a chair, or on a bed, or listening to relaxing music, make sure you are calm and relaxed before feeding.
Your comfort is key when breastfeeding, so find a position that is comfortable for you to breastfeed. In a chair, or on a bed, or listening to relaxing music, make sure you are calm and relaxed before feeding. - Skin to skin contact. Breastfeeding is a great opportunity to bond with your baby. Awaken your newborn's natural instincts by holding him, dressed only in a diaper, against your bare chest.
- Let your child take the lead. Gradually you will learn to understand the individual signs of hunger in your child. Usually, children begin to shake and nod their heads in the direction of the mother, toss and turn, lick their lips, stick out their tongue, showing that they are hungry.
- Try not to force things. Help the baby find the breast, but try not to push the nipple into the baby's mouth.
Sensitive nipple protection. If your nipples are sore or cracked, try using soft, ultra-thin nipple guards to relieve sore nipples during feeding and prevent further nipple trauma.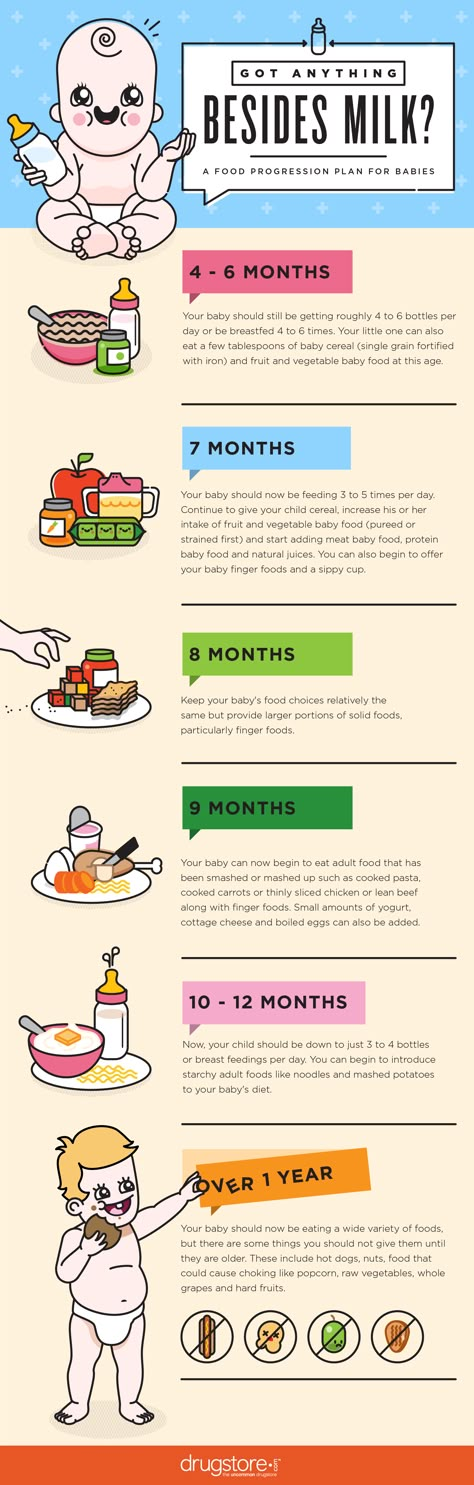 Due to the fact that the pads are made of thin silicone, the baby will still feel the warmth and smell of the mother's breast.
Due to the fact that the pads are made of thin silicone, the baby will still feel the warmth and smell of the mother's breast.
Popular breastfeeding positions to help ensure proper breastfeeding
In addition to these beneficial nursing steps, it is important to adopt a position that is comfortable for both you and your baby. Experiment with different positions until you find the one that makes you feel comfortable and helps your baby latch on properly.
Here are some of the most common positions that will help you and your baby get a good latch on during feeding: [1]
breastfeeding positions
1. Feeding in a reclining position.
The reclining or leaning back position is ideal for mothers who are breastfeeding for the first time. To try it, simply lean back into a reclining position with pillows under your neck, shoulders, and arms. Once you have established belly-to-belly contact with your baby, let him find the breast while supporting him as much as possible.
2. Feeding in the side lying position.
If you are looking for a feeding position that allows you to feed your baby and rest at the same time, the side lying position may be perfect for you. Lie on your side, leaning on a special roller or pillow. Facing you, the baby will be able to take the breast, which lies on the pillow. You can put a towel or blanket behind your baby to keep him in place while you feed. Also, this position is well suited for mothers who cannot sit after a caesarean section.
3. Feeding in the cross cradle position.
Another great position for getting your baby to latch on properly while breastfeeding is the “cross cradle,” which involves placing a pillow on your lap and placing your baby on the side facing you. During feeding, support the baby's back and head with the arm opposite the breast you are feeding.
4. Feeding in the "soccer ball" or "under the arm" position.
To assume this pose, you need to sit comfortably on a chair (in an armchair), leaning on pillows. Place the child on a pillow on the back so that his legs are under your arm and pointing towards the back of the chair. Supporting the back and shoulders of the baby, hold his head with the same hand, and with the other hand you can support the breast that you feed.
As you experiment with feeding positions, you may notice that your baby may like certain positions more. Once you have found the right position for feeding, look out for the following signs that your baby is latching on well: [2] [3]
- You do not feel acute pain.
- The baby's mouth is wide open, the baby's lower lip is turned out and the upper lip is in the normal position.
- The lower part of the areola (the areola) is in the baby's mouth.
- Baby's chin touches your breast.
Useful tip if you have flat or inverted nipples
If you have inverted or flat nipples, you need to help your baby achieve a good latch - grab the nipple along with most of the areola. Here are some helpful tips for breastfeeding mothers with flat or inverted nipples:
Here are some helpful tips for breastfeeding mothers with flat or inverted nipples:
- Help yourself with your fingers: you can try to stretch the nipples by rolling them between your fingers in the center where the hole is located, so they create a slight pressure, and the nipple is pushed out.
- If these suggestions do not help, then use a nipple shield when breastfeeding for the first time so that the baby can latch onto the nipple and pull it out over time.
It's the journey that counts, not the destination
You are now armed with the knowledge you need to know about the basic nursing positions, as well as tips to help you get a good latch on while breastfeeding.
Remember that breastfeeding gets better with time and practice, so don't be discouraged if you run into obstacles or difficulties along the way, such as a bad latch.
Enjoy this special time with your baby and don't forget to consult your doctor or lactation specialist with any questions or concerns you may have.
Baby+ app
Download the app and track your child's development and growth with trackers, and keep those special moments forever.
Download app:
Pregnancy+ 9 App0003
You are leaving the Philips Healthcare (“Philips”) official website. Any links to third party websites that may be included on this site are provided solely as a convenience to you. Philips makes no warranties regarding any third party websites or the information they contain.
I understand
You are about to visit a Philips global content page
Continue
You are about to visit the Philips USA website.
I understand
Breathe to eat?!
08/15/2016
The topic of breastfeeding is very relevant both for those who are just preparing to become a mother, and for those who are already clutching their first child to their breasts.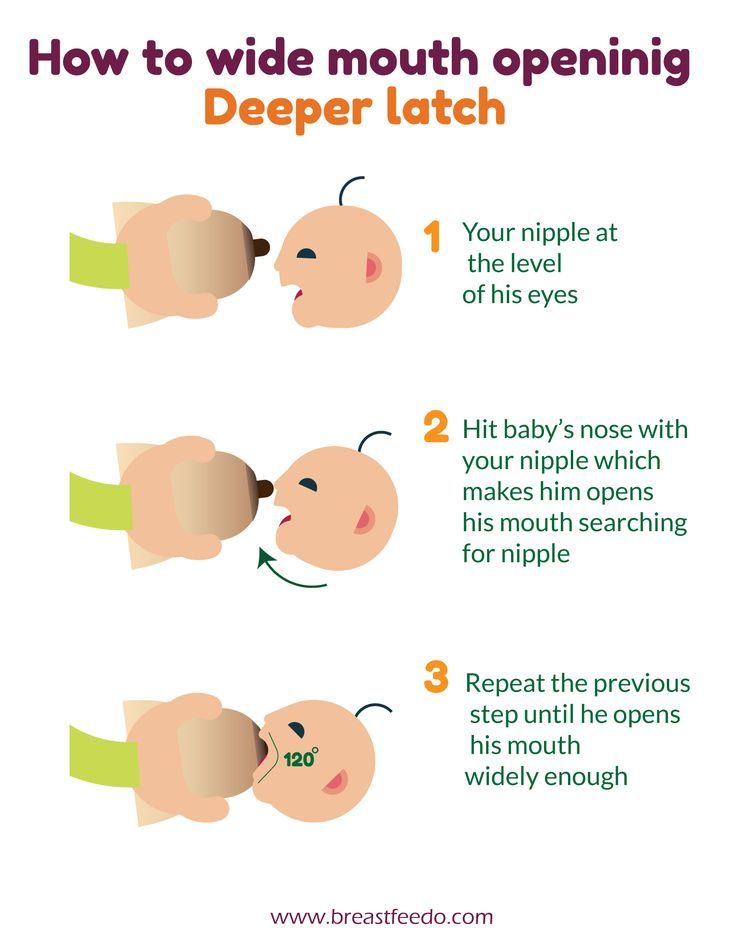 Mother's milk is truly the best food that can only be offered to a child up to a year old. It helps the baby grow healthy and strengthens his immunity. That is why it is especially necessary for a child in the first six months of life. Breast milk contains all the necessary nutrients for the baby, and in the optimal ratio and form, adapted to the characteristics of the digestive system of the newborn. In addition, it is rich in vitamins, enzymes, minerals and contributes to the creation of the necessary conditions for the formation of the "correct" intestinal microbial biocenosis.
Mother's milk is truly the best food that can only be offered to a child up to a year old. It helps the baby grow healthy and strengthens his immunity. That is why it is especially necessary for a child in the first six months of life. Breast milk contains all the necessary nutrients for the baby, and in the optimal ratio and form, adapted to the characteristics of the digestive system of the newborn. In addition, it is rich in vitamins, enzymes, minerals and contributes to the creation of the necessary conditions for the formation of the "correct" intestinal microbial biocenosis.
In addition, during breastfeeding there is direct communication between mother and child, which contributes to the formation of a positive emotional bond between them. The very act of sucking is extremely important for the baby. Sucking for an infant is a need and a pleasure that is not directly related to the feeling of hunger. Thanks to sucking, the baby develops the jaw apparatus, muscles of the mouth and tongue, which is especially important in the future, for example, in the development of speech.
But sometimes the process of feeding may not go as smoothly as a mother would like. One of the most common reasons a baby refuses to breastfeed is difficulty in breathing through the nose. A significant role in the development of this condition is given to the physiological characteristics of the nasal mucosa of the newborn, as well as the anatomical features of the child's nose. In an infant, the nasal passages are much wider and shorter, the mucous lining the nasal cavity is thickened and rich in a dense network of blood vessels, while the number of glands that produce mucus is not yet large. Even a small swelling of the mucosa can block nasal breathing. During breastfeeding, the baby has to suck and breathe at the same time, and if the nose is clogged, it is simply impossible to combine these processes. If the baby does not breathe through the nose, feeding turns into torment - the baby cannot suckle without interruption, because he is suffocating.
The child constantly has to let go of the chest in order to breathe in air through the mouth.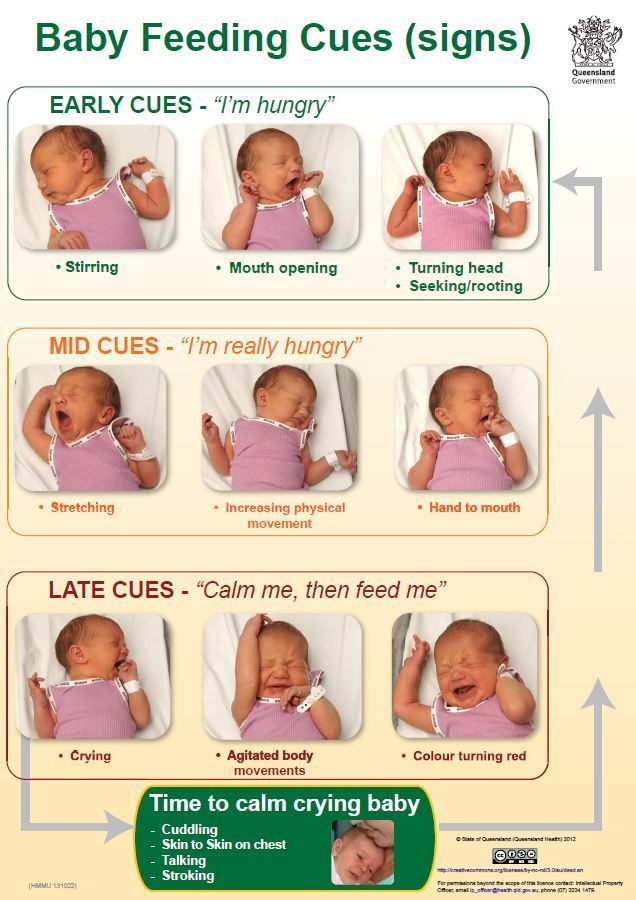 This is repeated several times, and as a result, the baby drops the breast. In addition, swallowing air through the mouth contributes to its entry into the stomach, followed by regurgitation of its contents. Frequent regurgitation, in turn, contributes to irritation of the nasal mucosa and nasopharynx with gastric contents and the development of inflammation - rhinitis, which is manifested by prolonged difficulty in nasal breathing.
This is repeated several times, and as a result, the baby drops the breast. In addition, swallowing air through the mouth contributes to its entry into the stomach, followed by regurgitation of its contents. Frequent regurgitation, in turn, contributes to irritation of the nasal mucosa and nasopharynx with gastric contents and the development of inflammation - rhinitis, which is manifested by prolonged difficulty in nasal breathing.
That is why it is so important for newborns to pay close attention to nasal hygiene to ensure and maintain free nasal breathing. On the Internet, you can find recommendations advising mothers to instill vasoconstrictors for babies in the nose of babies before feeding. Such advice can be useful only if the child has a runny nose, in all other cases, one should be aware of side effects and the inadmissibility of long-term use of such drugs, as well as the need to consult a doctor.
For daily care and cleansing of the nasal mucosa, special products based on natural sea water have been developed. One of these products is the RINOSTOP® AQUA product line.
One of these products is the RINOSTOP® AQUA product line.
RINOSTOP® AQUA contains 100% natural sea water, widely known for its beneficial properties. No preservatives, stabilizers or other chemicals that can cause irritation of the nasal mucosa are used in the process of production and purification of water; preserved macro- and microelements of natural sea water (K, Mg, Na, Ca, Cl).
The products of the line are available in bottles of different sizes; equipped with nozzles that take into account the anatomical structure of the nose and provide a continuous spray of water of different intensity - in the form of a jet, shower or soft shower.
The special design of the "BAG-ON-VALVE" bottles makes it possible to use products in any position of the bottles with a full consumption of the contents without residue.
RINOSTOP® AQUA BABY is perfect for daily hygiene and moisturizing of little noses from birth. It contains sea water in an isotonic concentration close in its physiological characteristics to human plasma.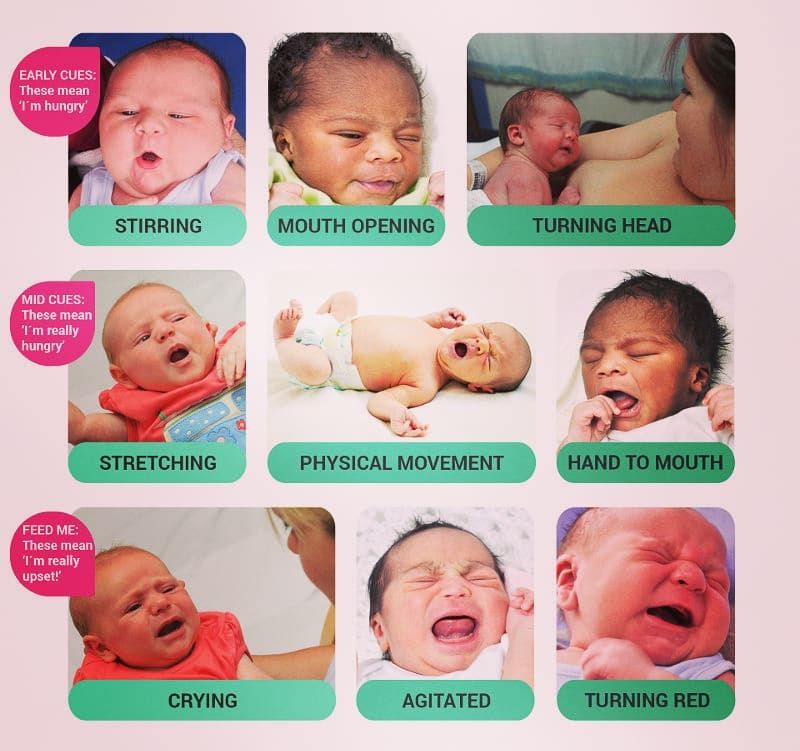 Micro-diffusion water supply in the form of a soft shower provides:
Micro-diffusion water supply in the form of a soft shower provides:
- gentle care for the delicate nasal mucosa of babies;
- uniform irrigation of the entire surface of the mucosa by spraying sea water in the form of tiny particles mixed with air - "water vapor"; it is this spray that minimizes the risk of getting into the middle ear cavity;
- cleansing of mucus, crusts, dust and small foreign particles;
- maintaining the normal physiological state of the nasal mucosa and facilitating nasal breathing in babies, contributing to the normalization of good sleep and optimizing the process of breastfeeding;
- moisturizing the nasal mucosa of infants, incl. with excessive dryness of the air;
- increased local immunity, stimulation of the protective function of the ciliated epithelium of the nasal mucosa of infants.
Comfortable, taking into account the anatomy of a child's nose, the spray nozzle RINOSTOP® AQUA BABY has a special restrictive ring that determines the depth of its introduction in order to avoid injury to the sensitive nasal mucosa of the crumbs.