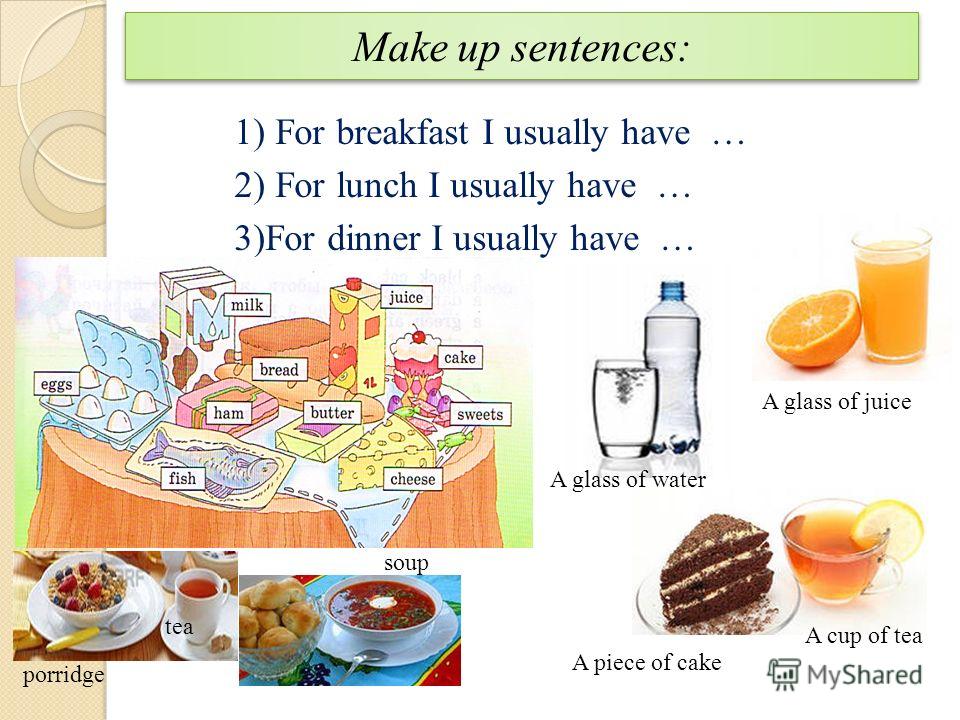
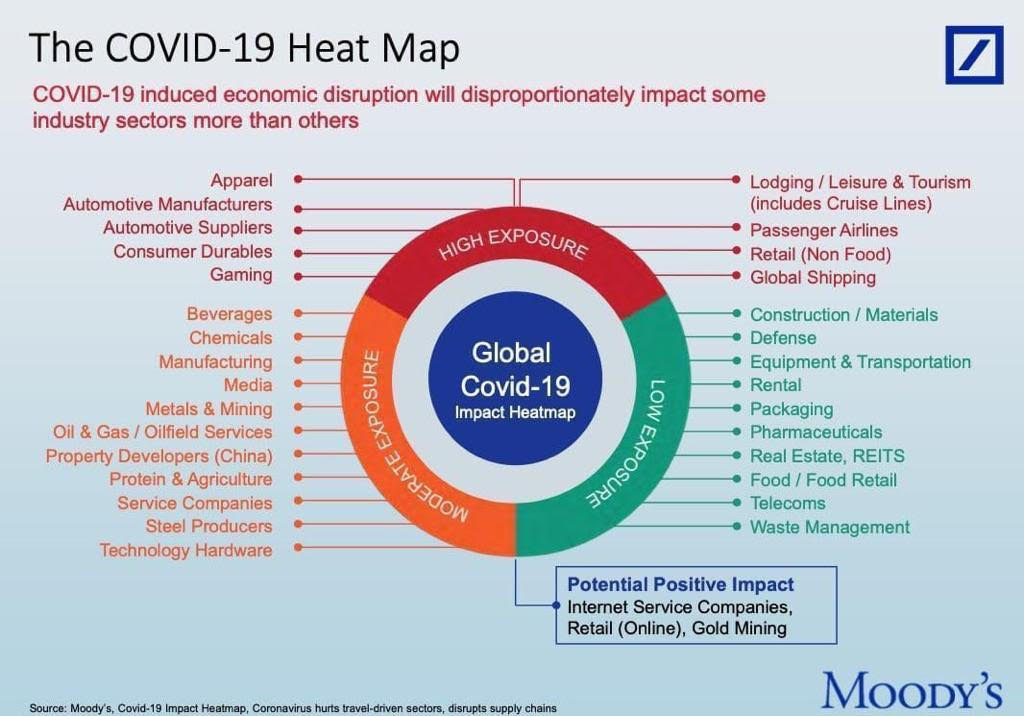
Baby food market in india ppt
PPT – Baby Food Market in India PowerPoint presentation | free to download
About This Presentation
Transcript and Presenter's Notes
Title: Baby Food Market in India
1
Baby Food Market in India
2
Summary
- India baby food products category is one of the
fastest growing markets in baby care and overall
FMCG industry of the country. Baby food market is
segmented mainly into infant milk formula, baby
cereals, follow-up formula and other products
(baby juice, baby soup, and prepared baby food
products). - The report covers the detailed insights of the
baby food products market in the Indian market.
The report covers the Indian baby food market in
a detailed segmental analysis with the value
analysis. The report also covers the leading
companies that are involved in the manufacturing
of the various baby food products. - The different brands and companies involved in
the organized baby food market in India are also
analyzed in this report. The report also gives an
idea on the product variant pricing analysis of
each of the product available in the baby food
market.
www. marketreportsonindia.com
3
(No Transcript)
4
- Baby food products have witnessed significant
growth in the past few years. Increasing
prosperity, steady urbanization, growing middle
class people, growing number of working women and
the increasing concerns regarding the fulfillment
of nutrition and vitamins at growing stage of
infants have been some of the major growth
drivers of baby food market in India. - India baby food market grew with a CAGR of about
14.37 in the period of five years from 2010 to
2015. In the current scenario, Infant milk
formula based products are generating the largest
revenue within baby food market.
- Baby cereals are the fastest growing segment as
mothers prefer to feed grain cereals to their
babies after 6 months. Follow-up formula based
products are desired for babies aged above 6
months which is expected to grow with the
forecasted CAGR of 16.86 during 2016-2021.
www. marketreportsonindia.com
5
- India Baby Food Market Outlook, 2021, the
Indian baby food market is anticipated to
represent the CAGR of 16.83 during forecast
period. Overall, baby food market is small as
compared to other developing countries across
Asia. - Baby food market is largely unorganized where
non-organic baby food is a large segment. The
market is dominated by Nestle India which is
operating with its 6 baby food brands in India.
There has been seen very low penetration in
organic baby food category due to less number of
players. - However, the category is expected to grow with a
fast phase owing to increasing concerns regarding
safety ingredients. In terms of geography, south
In terms of geography, south
and north India constituting for larger share in
baby food market across India, whereas
penetrations levels in East India is low.
www. marketreportsonindia.com
6
Table of Content
- Research Methodology
- Executive Summary
- India Infant/Child Demographics (Birth Rate,
Fertility Rate) - India Baby Food Market Outlook
- Product, Variant Pricing Analysis
- Channel Partner Analysis
- India Economic Profile - 2014
- Raw Material Analysis
- Policy Regulatory Landscape
- PEST Analysis
www. marketreportsonindia.com
7
Full Report
Baby Food Market in India
Contact Us Market Reports on India Phone
no912227810772 / 73 E-mail to
info_at_marketreportsonindia.com Website
https//www.marketreportsonindia.com Twitter
_at_ReportsonIndia Facebook India Market
Reports Linkedin Market Reports on India
About PowerShow. com
com
PPT – Baby Food Industry in India PowerPoint presentation | free to download
About This Presentation
Transcript and Presenter's Notes
Title: Baby Food Industry in India
1
Baby Food Industry in India
2
Summary
The BRIC Baby Food industry profile provides
top-line qualitative and quantitative Summary
information including market share, market size
(value and volume 2011-15, and forecast to
2020). The profile also contains descriptions of
the leading players including key financial
metrics and analysis of competitive pressures
within the market.
3
Key Findings
- Save time carrying out entry-level research by
- identifying the size, growth, major segments, and
- leading players in the BRIC baby food market
- Use the Five Forces analysis to determine the
competitive intensity and therefore
attractiveness of the BRIC baby food market - Leading company profiles reveal details of key
baby food market playersâ BRIC operations and
financial performance - Add weight to presentations and pitches by
understanding the future growth prospects of the
BRIC baby food market with five year forecasts by
both value and volume - Compares data from Brazil, Russia, India, and
China, alongside individual chapters on each
country
4
(No Transcript)
5
Synopsis
Essential resource for top-line data and analysis
covering the BRIC baby food market. Includes
Includes
market size and segmentation data, textual and
graphical analysis of market growth trends and
leading companies.
6
Reasons To Buy
- What was the size of the BRIC baby food
- market by value in 2015?
- What will be the size of the BRIC baby food
market - in 2020?
- What factors are affecting the strength of
competition in the BRIC baby food market? - How has the market performed over the last five
years? - Who are the top competitors in the BRIC baby food
market?
7
Key Highlights
- Brazil, Russian Federation, India and China
(BRIC) are the emerging and fast growing
countries within the baby food industry and had a
total market value of 18,259.1 million in 2015.
India was the fastest growing country with a CAGR
of 12.7 over the 2011-15 period. - Within the baby food industry, China is the
leading country among the BRIC nations with
market revenues of 13,741.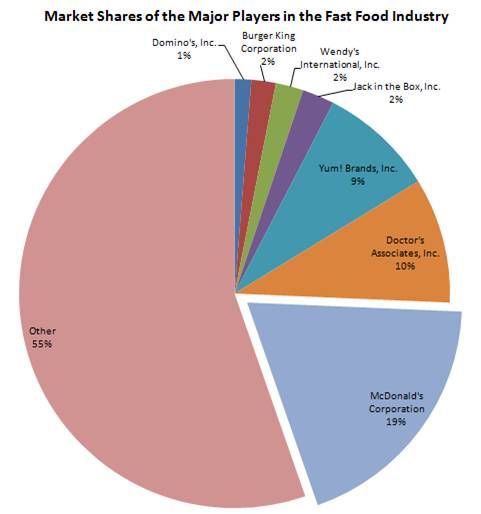 1 million in 2015.
1 million in 2015. - This was followed by India, Russia and Brazil
with a value of 2,103.0, 1,454.0, and 961.0
million, respectively. - China is expected to lead the baby food industry
in the BRIC nations with a value of 24,358.4
million in 2020, followed by India, Russia,
Brazil with expected values of 4,030.9, 2,165.6
and 1,404.0 million, respectively.
8
Table of Content
- Introduction
- What is this report about?
- Who is the target reader?
- How to use this report
- Definitions
- BRIC Baby food
- Industry Outlook
- Baby Food in Brazil
- Market Overview
- Market Data
- Market Segmentation
- Market outlook
9
Full Report
Baby Food Industry in India
Contact Us Market Reports on India Phone no
912227810772 / 73 E-mail to
info_at_marketreportsonindia. com Twitter
com Twitter
_at_ReportsonIndia Facebook India Market
Reports Linkedin Market Reports on India
About PowerShow.com
Business dialogue “An hour with the Trade Representative of Russian Children’s Products Industry: Russia – India” took place at the XII IDT Congress
Color scheme:
C C C C
Font
Arial Times New Roman
Font Size
A A A
Kerning
1 2 3
Images:
Regular version
Information
12/23/2021
Views: 315
Within the framework of the XII Congress of the Children's Goods Industry, an online business dialogue "An Hour with the Trade Representative of the Russian Children's Products Industry": Russia - Delhi" was held, organized by the Ministry of Industry and Trade of Russia and the Association of Children's Goods Industry Enterprises. The main speakers of this session were Evgeny Ostapkevich, Head of the Operations Department of the Trade Representation of the Russian Federation in the Republic of India, Anna Krotova, Head of the International Economic Center, and Nikita Semenov, member of the Board of Directors of the Topol Group of Companies. Anastasia Vasilkova, co-founder and head of the direction for the development of export of goods and services of Choupette, moderated the hour with the trade representative.
Anastasia Vasilkova, co-founder and head of the direction for the development of export of goods and services of Choupette, moderated the hour with the trade representative.
Yevgeny Ostapkevich, Head of the Operations Department of the Trade Mission of the Russian Federation in the Republic of India, spoke about the specifics of interaction with Indian partners and measures to support exporters provided by the Trade Mission of India. The speaker spoke about the general economic situation in India and the state of affairs in the Russian-Indian trade and economic cooperation, with a special emphasis on children's products that could be in demand in India.
The expert named two categories of goods: children's toys and baby food, and explained why, according to the trade mission, they will be in demand in the growing Indian market.
India's children's toy market reached US$1.2 billion in 2020. Of these, only 20% are produced in India, 80% are exported from other countries, primarily from China: the export of toys from China reached 600 million US dollars. According to analysts' forecasts, the children's toys market in India will grow by another 12% over the next 5 years.
According to analysts' forecasts, the children's toys market in India will grow by another 12% over the next 5 years.
The Indian government is trying to stimulate its own production of toys, in particular, protective import duties. For some goods, the duty rate reaches 60%.
Basically, toys in India are produced by small and medium-sized businesses. Clusters in which producers work on favorable terms are usually created by the states and they operate on the basis of a common message - "Make in India". Indian authorities give their producers significant preferences.
In this regard, the Trade Representation recommends that Russian companies enter the Indian toy market, taking into account local realities - the prospect of localizing production in India, which will help to avoid barriers in the form of high duties and expensive logistics.
The second interesting niche for export is baby food. The mentality needs to be taken into account here - Indians have a traditional way of thinking and don't really trust packaged baby food, especially for babies. But at the same time, the demand for baby food is growing along with an increase in the birth rate.
But at the same time, the demand for baby food is growing along with an increase in the birth rate.
In addition, in India, the number of working women who have to look for a replacement for traditional nutrition is constantly increasing. The main export segments, as seen by the Trade Delegation, are milk formulas, cereals for baby food and ready-made mixtures of vegetables and fruits. These prepared food segments are the fastest growing and are expected to grow by another 22% in the near future.
Baby food, like toys, is subject to high import duties. The import of food products in India is controlled by a special division, and a license will be required for a particular manufacturer or supplier.
In general, for all comers who would like to enter the Indian market with Russian goods, a "field" or "desk" study will be mandatory. If you come to the conclusion that your product will be in demand, study the sales channels - they often do not coincide with Russian ones. The third step is to bring products in line with international and Indian standards and identify partners correctly. The most reliable payment system when dealing with Indians is a letter of credit.
The third step is to bring products in line with international and Indian standards and identify partners correctly. The most reliable payment system when dealing with Indians is a letter of credit.
The Indians discuss each clause of the treaty for a very long time, they do not make hasty decisions. When entering the Indian market, one should not expect an instant result, one must be prepared for lengthy negotiations, including on opening part of the production in India and creating jobs there.
The Trade Delegation is ready to advise anyone who would like to enter the Indian market and can provide a partner search service with a preliminary check of interest. Together with the REC, the Trade Representation organized a special export support group.
The recording of the event is available at the link.
A conversation about how to properly enter and promote Russian manufacturers of children's goods in different countries, not only in India, will be one of the topics of discussion at the Secrets of Children's Marketing forum, which will be held on March 16-17, 2022.
Reference
The Children's Goods Industry Congress is the main industry event of the year, which is held to organize a dialogue between business and the state, popularize the best practices of industry leaders, and form new tools for international and scientific and industrial cooperation. The event is held with the assistance and support of the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation, the Ministry of Economic Development, the Ministry of Education, the Ministry of Education and Science, the Ministry of Finance, the Ministry of Labor, the Ministry of Culture, the Ministry of Natural Resources and other departments.
Representatives of the Russian and international children's goods market, industry experts and organizations were invited to participate in the XII IDT Congress in 2021. Participation in the event is free.
The main topic of the XII Congress of the children's goods industry was the concept of sustainable development in the interests of childhood, which is reflected in the Action Plan ("road map") for the development of the children's goods industry until 2024, approved by the order of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 1813-r dated 11.07.2020. and determining all the important and complex tasks of industry for a given period.
1813-r dated 11.07.2020. and determining all the important and complex tasks of industry for a given period.
Entering the Indian market: export documents
Recommendations for promotional events
India has about 300 television channels, 12 thousand newspapers, 60-65 thousand magazines, 12-13 thousand cinemas and 1 thousand radio stations. At the same time, almost 65% of the country's population lives in rural areas, and six out of 10 consumers still do not have access to the media. Such a large number of diverse media highlights the linguistic diversity of the Indian nation. There are 22 official languages in the country, but Hindi is the most widely spoken. From these facts, it follows that it is incredibly difficult to advertise something in India. You need to clearly understand the Indian mentality, understand the languages and the needs of the population of various states.
The best option for an advertising company in India is to cooperate with local marketing agencies. Indian employees who have a good understanding of the home market and consumer mentality will be able to use the advertising budget as efficiently as possible.
Indian employees who have a good understanding of the home market and consumer mentality will be able to use the advertising budget as efficiently as possible.
Settlement options
Exchange regulation in India is carried out in accordance with the Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 (Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999). The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is entrusted with the functions of state currency control and regulation by issuing relevant regulations and circulars. RBI issues permission to open accounts for foreign companies operating in India. In addition, the Department for Struggle Against Offences is vested with supervisory functions, which, although structurally related to the Ministry of Finance, is actually an independent organization. He can make claims and decide on the application of penalties to organizations that violate the currency laws of India. All foreign exchange transactions carried out in the country require the permission of the RBI. All authorized dealers and banks that have licenses for transactions with foreign currency (currency transactions) are required to strictly comply with the "Instructions on Currency Control" issued by the RBI. This also applies to various projects, the implementation of which requires foreign exchange transactions. The Law on Currency Regulation (clause 5) contains an indication that the Government has the right, if necessary, to impose restrictions on transactions on current accounts, based on public interests and in agreement with the RBI. For violation of the law on currency regulation, instructions or regulations adopted in accordance with it and on the basis of a court decision, an individual or legal entity may be fined an amount exceeding 3 times the amount received from an illegal transaction. Also, in cases of violation of the norms of currency legislation, for the period of the proceedings, the licenses of violators are revoked, and their accounts are frozen. In India since 19Since 1973, the Enforcement Directorate has been functioning, which is part of the Department of Taxes and Duties of the Ministry of Finance.
All authorized dealers and banks that have licenses for transactions with foreign currency (currency transactions) are required to strictly comply with the "Instructions on Currency Control" issued by the RBI. This also applies to various projects, the implementation of which requires foreign exchange transactions. The Law on Currency Regulation (clause 5) contains an indication that the Government has the right, if necessary, to impose restrictions on transactions on current accounts, based on public interests and in agreement with the RBI. For violation of the law on currency regulation, instructions or regulations adopted in accordance with it and on the basis of a court decision, an individual or legal entity may be fined an amount exceeding 3 times the amount received from an illegal transaction. Also, in cases of violation of the norms of currency legislation, for the period of the proceedings, the licenses of violators are revoked, and their accounts are frozen. In India since 19Since 1973, the Enforcement Directorate has been functioning, which is part of the Department of Taxes and Duties of the Ministry of Finance. This Directorate has the right to make claims, conduct investigations and make decisions on the application of sanctions against violators of the country's currency legislation. The Directorate, headquartered in New Delhi, has 7 zonal, 9 sub-zonal offices in cities throughout India.
This Directorate has the right to make claims, conduct investigations and make decisions on the application of sanctions against violators of the country's currency legislation. The Directorate, headquartered in New Delhi, has 7 zonal, 9 sub-zonal offices in cities throughout India.
The main statutory act governing the formation, reorganization and liquidation of legal entities in India is the Companies Act, 2013 (The Companies Act, 2013), which provides for the possibility of creating the following types of legal entities: 1. Private company (private company) ) - a company created by two or more persons with an authorized capital of at least 100,000 Indian rupees (1500 USD), without the right of participants to alienate their shares to third parties. 2. Public company (public company) - a company established by seven or more persons with an authorized capital of at least 500,000 Indian rupees (7600 USD), with the right of participants to freely sell their shares to third parties. These companies can be created as a company with liability up to the value of shares (company limited by shares), or as a company with liability of participants within a certain guaranteed amount (company limited by guarantee). In addition, there are companies that do not have limits on the amount of liability (unlimited company). All companies established on the territory of the Republic of India undergo state registration at the Registrars of Companies. Upon registration, a company is assigned a Corporate Identification Number (CIN) and all data about such a company is entered into the database of the Ministry of Corporate Affairs of the Government of India (Ministry of Corporate Affairs, www.mca.gov.in). The list of documents that must be submitted for registration of a company is specified in part 1 of article 7 of the Companies Act 2013. After a company with foreign capital has passed state registration, it has all the rights and obligations equal to Indian companies provided for by the legislation of the Republic of India, with the exception of specially established restrictions and prohibitions.
These companies can be created as a company with liability up to the value of shares (company limited by shares), or as a company with liability of participants within a certain guaranteed amount (company limited by guarantee). In addition, there are companies that do not have limits on the amount of liability (unlimited company). All companies established on the territory of the Republic of India undergo state registration at the Registrars of Companies. Upon registration, a company is assigned a Corporate Identification Number (CIN) and all data about such a company is entered into the database of the Ministry of Corporate Affairs of the Government of India (Ministry of Corporate Affairs, www.mca.gov.in). The list of documents that must be submitted for registration of a company is specified in part 1 of article 7 of the Companies Act 2013. After a company with foreign capital has passed state registration, it has all the rights and obligations equal to Indian companies provided for by the legislation of the Republic of India, with the exception of specially established restrictions and prohibitions.
Checking a trading partner
Due to the increase in the number of fraudulent schemes, obtaining reliable, objective and up-to-date information about a foreign partner in order to minimize commercial risks is a prerequisite for concluding contracts and conducting various negotiations.
The Ministry of Corporate Affairs of India has created an Internet site www.mca.gov.in, which has a large amount of useful information in the public domain regarding various legal entities - state enterprises, private companies and entrepreneurs officially registered in the territory of the Republic of India. The site database contains information about more than 150 thousand companies, as well as the texts of legal acts regulating entrepreneurial activity in India.
To search for company data, you must log in to www.mca.gov.in, then to the "MCA Services" section. On the expanded page, in the column in the "Master Data" section, enter the "View Company or LLP Master Data" subsection (or from the "Company Services" subsection - in the "Check Company Name" column).
www.watchoutinvestors.com also searches for Indian companies without additional user registration. Based on the search result, the screen displays information about whether the company is registered by the relevant government authority (usually the Registrar of Companies, http://dca.nic.in), as well as the date of the decision to register or liquidate, history registration decisions on changing the name or legal form of the company, mergers and acquisitions, the current status of the company as of the date of the request (active, liquidated, in bankruptcy or already liquidated). The site also provides information about companies seen in default and non-payment , non-compliance with legal requirements.
Separately, you can get information about companies and officials who did not submit financial documentation to the authorized bodies within the deadlines established by law, about persons guilty of violations of legal deadlines, indicating the dates of violations and references to violated legal acts.
Some customs information is also available on the website of the Ministry of Corporate Affairs of India (www.mca.gov.in), which is issued after the mandatory free user registration. In addition, there you can also get background information on the list of disqualified directors with the name of the companies where they worked at the time the penalties were applied.
For a more complete and comprehensive check of the business reputation of an Indian partner, you need to contact specialized law firms that provide paid services. In this case, either remote collection of multidisciplinary information about the company of interest is possible, or by direct agreement with the Indian partner company, a comprehensive check of the state of affairs and documentation can be carried out during the procedure (Due Diligence), which is widely used in international and Indian practice. The list of law firms is given below in the section "Law and Law Offices of India for the protection of the rights of exporters". The cost of legal services depends on the amount of information requested and the timing of its preparation, so this issue is the subject of a separate discussion during negotiations. If you need to obtain additional information about legal entities - state-owned enterprises and private companies officially registered in the country, as well as their commercial practices, you can contact the largest associations of Indian business circles: FICCI (www.ficci.in) and CII (www.cii .in).
The cost of legal services depends on the amount of information requested and the timing of its preparation, so this issue is the subject of a separate discussion during negotiations. If you need to obtain additional information about legal entities - state-owned enterprises and private companies officially registered in the country, as well as their commercial practices, you can contact the largest associations of Indian business circles: FICCI (www.ficci.in) and CII (www.cii .in).
Opportunities, risks and threats for product promotion in India
India is a country with one of the most significant development and growth potentials in the foreseeable future. This is facilitated by a combination of a number of factors, including the second largest population after China, a relatively large territory, the availability of skilled workers in certain sectors of the economy, and the still very low average income levels of the population.
Features:
1. Large area and large population.
Large area and large population.
2. Availability of qualified personnel in various sectors of the economy.
3. Great need for investment in many areas of the economy
4. Need for the transfer of experience and technology from the Russian agricultural industry.
5. The Russian Federation and India have long-standing and friendly relations.
Risks and Threats:
1. Significant influence of British law on the legislative framework of India.
2. The presence of various religious and local laws that may interfere with business.
3. Unstable political situation.
4. The deterioration of natural conditions will lead to a deterioration in financial performance and may provoke social conflicts.
5. A deterioration in India's external position could lead to a weakening of the rupee, making imported products unprofitable for consumers.
Conclusion
India has many of the problems of developing countries, including the presence of a double deficit: the state budget and the current account. In the past few years, the Indian authorities have made some progress in reducing both deficits, and this trend may continue in the coming years, although the speed and scale of reductions are likely to slow down. This is facilitated by a number of government steps, including the demonetization carried out at the end of 2016 (withdrawal of 86% of cash from circulation, with the simultaneous introduction of new banknotes and the conversion of part of the cash into bank deposits) and the planned tax reform. In addition to the improvement in the current account, in recent years there has also been an increase in the interest of foreign investors in the Indian economy, with an increasing number of companies seeking to enter the local market and occupy a certain niche in this market. In addition to these problems, India has a number of its own challenges, which are exacerbated by the size and density of the population, the territory of the country. Unlike China, India still has a significant shortage of adequate infrastructure, both from transport and telecommunications necessary for dynamic economic development, and to basic, including the provision of quality housing and communal services.
In the past few years, the Indian authorities have made some progress in reducing both deficits, and this trend may continue in the coming years, although the speed and scale of reductions are likely to slow down. This is facilitated by a number of government steps, including the demonetization carried out at the end of 2016 (withdrawal of 86% of cash from circulation, with the simultaneous introduction of new banknotes and the conversion of part of the cash into bank deposits) and the planned tax reform. In addition to the improvement in the current account, in recent years there has also been an increase in the interest of foreign investors in the Indian economy, with an increasing number of companies seeking to enter the local market and occupy a certain niche in this market. In addition to these problems, India has a number of its own challenges, which are exacerbated by the size and density of the population, the territory of the country. Unlike China, India still has a significant shortage of adequate infrastructure, both from transport and telecommunications necessary for dynamic economic development, and to basic, including the provision of quality housing and communal services.