Baby food test results
Homemade baby food contains as many toxic metals as store bought, report says
CNN —
Making baby food at home with store-bought produce isn’t going to reduce the amount of toxic heavy metals in the food your baby eats, according to a new report released exclusively to CNN.
“We found no evidence to suggest that homemade baby foods made from store-bought produce are better than store-bought baby foods when it comes to heavy metal contamination,” said the paper’s coauthor Jane Houlihan, research director for Healthy Babies, Bright Futures. An alliance of nonprofits, scientists and donors, HBBF, which produced the report, has a stated mission of reducing babies’ exposures to neurotoxic chemicals.
READ MORE: Manufacturers allowed baby food contaminated with heavy metals to remain on shelves, lawmakers say
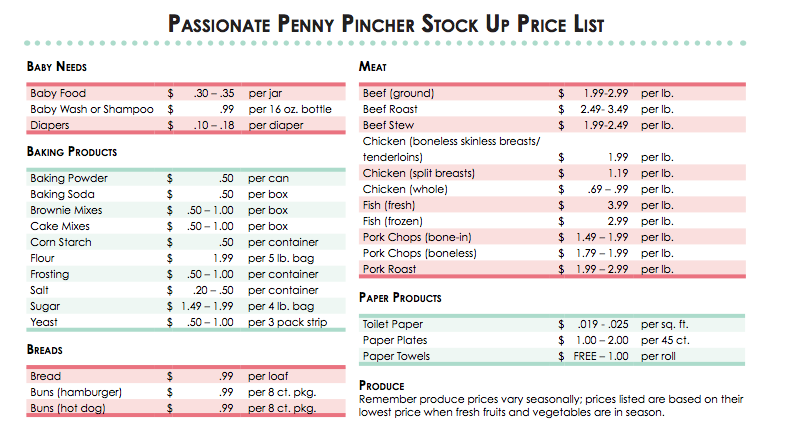
Researchers tested 288 foods bought at stores and farmers markets across the United States – including grains, fruits, vegetables, snacks, teething foods, and family items that babies eat, such as cereals and rice cakes – for lead, arsenic, mercury and cadmium. Those heavy metals are among the World Health Organization’s top 10 chemicals of concern for infants and children.
“Toxic metal exposure can be harmful to the developing brain. It’s been linked with problems with learning, cognition, and behavior,” according to the American Academy of Pediatrics.
It’s been linked with problems with learning, cognition, and behavior,” according to the American Academy of Pediatrics.
Researchers also pored over data from 7,000 additional food tests reported in published studies and by the US Food and Drug Administration.
Results showed 94% of manufactured baby foods, family foods and homemade purees made from purchased raw foods contained detectable amounts of one or more heavy metals.
Lead was found in 90% of manufactured baby food bought by shoppers for the report and 80% of store-bought family food and homemade purees. There is no safe level of lead, according to the AAP.
There is no safe level of lead, according to the AAP.
Arsenic was found in 68% store-bought baby food and 72% of family food either purchased or prepared at home. Cadmium was found in 65% of purchased baby food and 60% of family foods, and mercury was in 7% of store-bought baby food and 10% of family foods. (The highest levels of mercury are found in seafood, which was not tested in this analysis.)
READ MORE: 95% of tested baby foods in the US contain toxic metals, report says
The new report is a follow-up to a November 2019 report in which Healthy Babies, Bright Futures tested 168 foods purchased from major baby food manufacturers.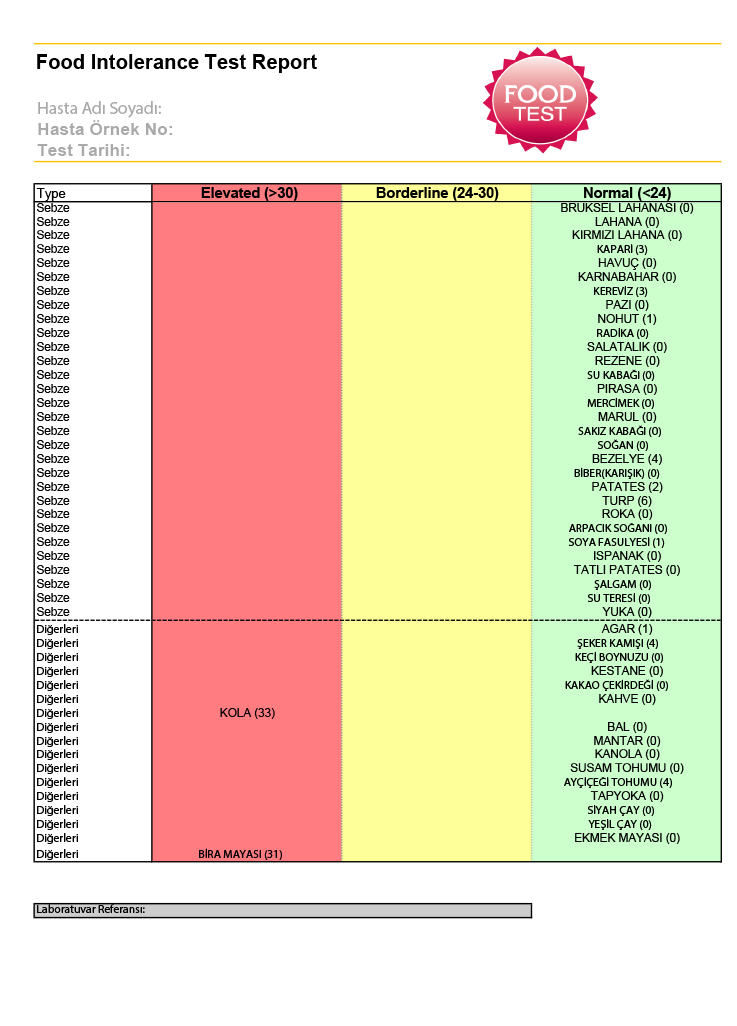 That analysis found 95% of store-bought baby food contained lead, 73% contained arsenic, 75% contained cadmium and 32% contained mercury. One-fourth of the foods tested that year contained all four heavy metals.
That analysis found 95% of store-bought baby food contained lead, 73% contained arsenic, 75% contained cadmium and 32% contained mercury. One-fourth of the foods tested that year contained all four heavy metals.
“After that report we saw so many people saying you can get around this problem by making your own baby food at home, so we decided to check,” Houlihan said. “We suspected we’d find heavy metals in all kinds of food because they’re ubiquitous contaminants in the environment.
“And that is exactly what we found – heavy metals were in foods from every section of the store,” Houlihan said. “What this says is that as the FDA is setting standards for heavy metals in baby food, they need to go beyond the baby food aisle. ”
”
What’s a parent or caregiver to do? Feed baby with as many different types of foods as possible, said pediatrician Dr. Mark Corkins, chair of the Committee on Nutrition of the American Academy of Pediatrics. He was not involved in the study.
“If you spread foods out, and offer a wide variety of options, you’ll have less toxicity,” Corkins said. “And nutritionally that’s always been the right thing to do to get the most micronutrients from the food you eat.”
The report found buying organic didn’t lower heavy metal levels either, which was “not shocking or surprising,” said Corkins, a professor of pediatrics at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center and Le Bonheur Children’s Hospital in Memphis, Tennessee.
“It’s the soil and water that’s contaminated with arsenic and other heavy metals, so it doesn’t matter if it’s organic or traditional farming methods,” Corkins said. That would apply to locally grown crops or even backyard gardens, if the soil had not been verified to be metal-free.
However, buying organic can help avoid other toxins the new report did not consider, such as herbicides and pesticides, said Dr. Leonardo Trasande, director of environmental pediatrics at NYU Langone Health. He was not involved in the study.
“There are other benefits to eating organic food, including a reduction in synthetic pesticides that are known to be as bad for babies, if not even more problematic,” Trasande said.
READ MORE: Doctors should test levels of PFAS in people at high risk, report says
“We’ve seen multiple studies show significant effects of synthetic pesticides on cognitive function in children as a result of prenatal exposure. We’ve seen images of the brain where certain parts are smaller that are crucial for higher order functioning after exposure,” he added. “A simple step would simply be to say eat organic because regardless of anything we’re talking about in this report, it’s good for you.”
Experts agree that battling toxins in baby foods is a job for government organizations who will need to work with growers, suppliers and manufacturers to institute regulations and safeguards. In the meantime, parents can make a difference.
In the meantime, parents can make a difference.
“Making even one simple choice every day to lower a child’s exposure will make a difference, whether that’s staying away from rice-based snacks and serving a diced apple instead or choosing not to serve carrots and sweet potatoes every day,” Houlihan said.
“With heavy metals and other toxins the risks add up over a lifetime,” she added. “So even if some of these foods had been served to a child up to their second birthday, starting from there to lower exposure to toxins is going to add up. Every choice matters.”
Tested foods with low metal content contain one-eighth as much heavy metal contamination as foods with the highest levels, Houlihan said. These are foods that can be “eaten freely,” the report suggested.
These are foods that can be “eaten freely,” the report suggested.
Fresh bananas, with heavy metal levels of 1.8 parts per billion, were the least contaminated of foods tested for the report. That’s an “82-fold difference in average level of total heavy metals” from the most contaminated food, rice cakes, which tested at 147 parts per billion, according to the investigation.
READ MORE: ‘Consider chemical hazards’ in the baby foods you sell, FDA warns manufacturers
After bananas, the least contaminated foods were grits, manufactured baby food meats, butternut squash, lamb, apples, pork, eggs, oranges and watermelon, in that order. Other foods with lower levels of contamination included green beans, peas, cucumbers, and soft or pureed home-cooked meats, the report found.
Other foods with lower levels of contamination included green beans, peas, cucumbers, and soft or pureed home-cooked meats, the report found.
Infant formula made with lead-free tap water was recommended. Tap water that has been tested and is free of lead is always a good choice. Milk is also a good choice, but only for babies 12 months and older.
Some healthy lower-metal foods, such as yogurt, unsweetened applesauce, beans, cheese, hard-boiled eggs and grapes that have been cut lengthwise, were good choices for snacks for babies, according to the report.
Fresh and frozen fruit – including those used in homemade purees – were options as well. But don’t use canned fruits if you can avoid it: “Tests find lead 30 times more often in canned fruit than in fresh and frozen fruit,” the report stated.
But don’t use canned fruits if you can avoid it: “Tests find lead 30 times more often in canned fruit than in fresh and frozen fruit,” the report stated.
Parents and caregivers can also lower their baby’s exposure to heavy metals by making some smart substitutions, the report said.
Using a frozen banana for a teething baby instead of a rice-based teething biscuit or rice rusk could lower total intake of heavy metals by 95%, according to the report. Another suggested teething aid: peeled and chilled cucumber spears.
The most heavily contaminated foods eaten by babies were all rice-based: “Rice cakes, rice puffs, crisped rice cereals and brown rice with no cooking water removed are heavily contaminated with inorganic arsenic, which is the more toxic form of arsenic,” Houlihan said.
Arsenic is a natural element found in soil, water and air, and because rice is grown in water, it is especially good at absorbing inorganic arsenic. (“Inorganic” is a chemical term and has nothing to do with the method of farming.) Brown and wild rice are the worst offenders, as the bran contains the highest arsenic concentrations.
READ MORE: New FDA limits on arsenic levels in infant rice cereals don’t adequately protect children, critics say
Prior research has shown that even low levels of inorganic arsenic exposure can impact a baby’s neurodevelopment. A meta-analysis of studies on the topic found a 50% increase in arsenic levels in urine would be associated with a 0.4-point decrease in the IQ of children between the ages of 5 and 15.
A meta-analysis of studies on the topic found a 50% increase in arsenic levels in urine would be associated with a 0.4-point decrease in the IQ of children between the ages of 5 and 15.
Testing by HBBF found rice cakes were the most contaminated with inorganic arsenic, followed by crisped rice cereal, rice-based puffs and brown rice. The report recommended those foods be avoided entirely, unless the brown rice is cooked with extra water that is poured off before consumption (much like pasta). It’s best to do that with all rice, including white and wild rice, the report said, as it can reduce arsenic levels by up to 60%.
Rice-based teething biscuits or rusks and white rice came next on the most contaminated list, the report said. White rice is milled to remove the outer layers, but experts say arsenic levels remain high enough to be concerning, especially if rice is a daily staple.
White rice is milled to remove the outer layers, but experts say arsenic levels remain high enough to be concerning, especially if rice is a daily staple.
“Inorganic arsenic averaged 100 parts per billion in brown rice infant cereal and 74 parts per billion in white rice infant cereal in our tests,” Houlihan said. “Baby food companies have taken brown rice cereal off the market because of its high arsenic levels.”
READ MORE: Water- and stain-resistant products contain toxic plastics, study says. Here’s what to do
Parents and caregivers can help by staying away from high-arsenic varieties of white rice grown in Arkansas, Louisiana, Texas, or simply “US” and instead choosing lower-arsenic basmati rice from California, India and Pakistan, as well as sushi rice from the US, the report said.
After rice-based foods, the analysis found the highest levels of heavy metals in raisins, non-rice teething crackers, granola bars with raisins and oat-ring cereals. But those were not the only foods of concern: Dried fruit, grape juice, arrowroot teething crackers and sunflower seed butter all contained high amounts of at least one toxic metal, according to the report.
“Many foods have a kind of unique, heavy metal profile,” Houlihan explained. “For example, we saw very high levels of cadmium in things like spinach, leaf lettuce and peanut butter.”
However, the human body doesn’t absorb cadmium as easily as other heavy metals, and for that reason “it doesn’t have as high a level of concern,” Houlihan added.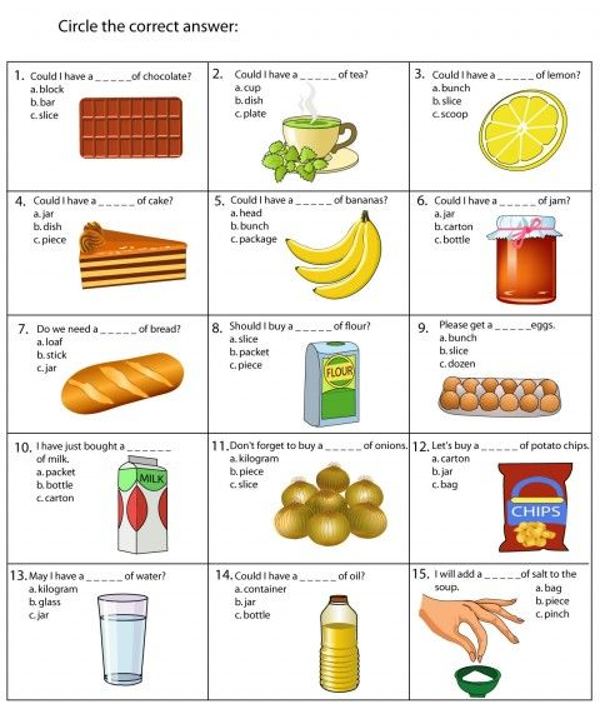
“There’s also not as much evidence that cadmium is neurotoxic to babies, or at least the body of evidence isn’t there at the same levels as lead and arsenic,” she said. “Lead and arsenic damage isn’t reversible – these are permanent impacts on IQ, learning ability and behavior, so it’s a big deal.”
Root and tuber vegetables may have higher levels of heavy metals like lead and arsenic because they grow underground. In fact, the investigation found that nutritious baby favorites like carrots, sweet potatoes, squash and many types of potatoes did have concerning levels of heavy metals.
READ MORE: Dangerous chemicals found in food wrappers at major fast-food restaurants and grocery chains, report says
Even the same food could have varying levels of toxic metals, according to the report. For example, a shopper in Raleigh, North Carolina, bought a sweet potato with 60.7 parts per billion of lead – 10 times more than the store-bought sweet potato puree she purchased. A Chicago shopper purchased a fresh carrot with eight times more arsenic than the premade carrot baby food she took home, the investigation found.
Yet shoppers in Tennessee and California found the opposite – their fresh produce had minimal levels of heavy metals compared with the manufactured baby food brands they bought.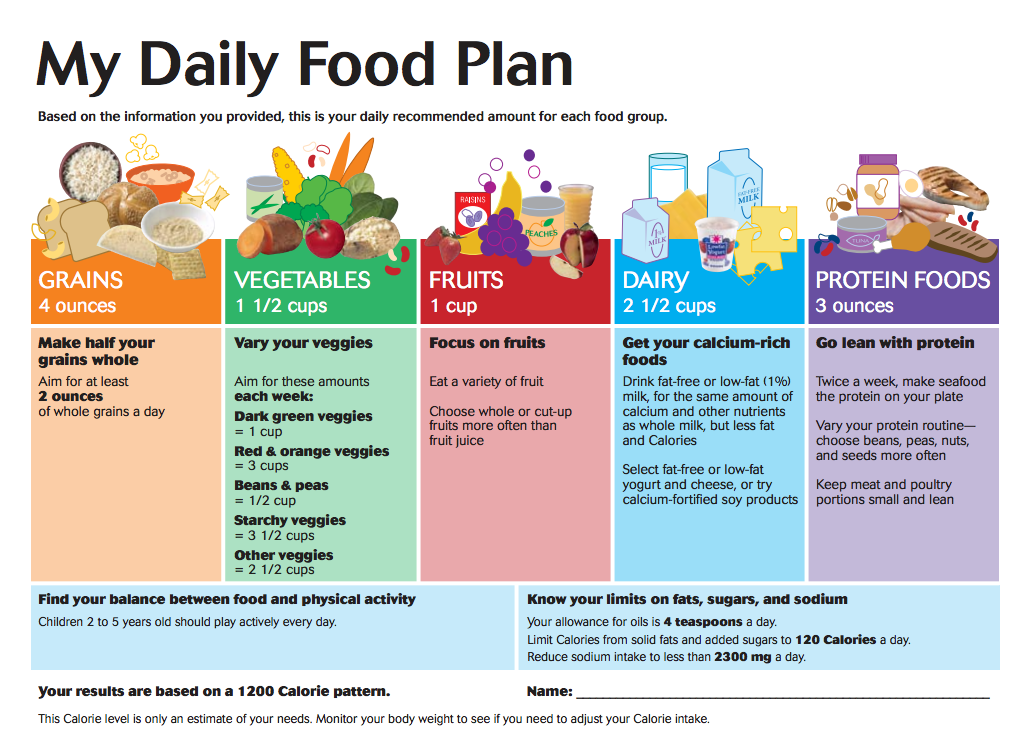
“As a parent, you don’t know what you’re picking up out of the produce bin,” Houlihan said. “Is it elevated because of the cultivar – the particular type of sweet potato or carrot? Or is it elevated because it’s grown in an area where the soil has naturally high levels of lead?
Answering these questions will be the responsibility of government regulators and industry, Houlihan said. The FDA has a Closer to Zero campaign, for example, which could take on the issue.
CNN has reached out to the FDA for comment but hasn’t yet received a response.
“And remember, if you’re protecting the basic ingredients that parents are using to make food at home, you’re not only protecting babies and toddlers, you’re protecting pregnant women as well. Babies in utero are particularly vulnerable to toxins while the brain is growing at such a rapid pace.”
With no way of knowing levels of toxic metals in the soil where produce is grown, parents and caregivers need to add one more step to their efforts to avoid these substances, Houlihan suggested. In addition to mixing up the variety of foods and not serving the same options each day, parents can “choose different brands or varieties of foods or shop in different stores from week to week to avoid choosing a high-metal source regularly. ”
”
Sign up for CNN’s Eat, But Better: Mediterranean Style. Our eight-part guide shows you a delicious expert-backed eating lifestyle that will boost your health for life.
New test results of heavy metals in baby food require immediate action by FDA, Congress
WASHINGTON – New Consumer Reports test results released today have found dangerous levels of inorganic arsenic in three popular brands of infant rice cereals, prompting the Environmental Working Group to again urge the Food and Drug Administration to follow through immediately on its plan to set mandatory limits on heavy metals in baby food.
“These new results further illustrate the need for immediate action to protect children’s health,” said Scott Faber, EWG’s senior vice president for government affairs. “Parents should not have to worry if the food they’re feeding their kids is full of toxic heavy metals, which we know even at low levels can cause serious and often irreversible damage to babies’ brains. ”
”
Last April, the FDA pledged to propose draft limits for some toxic metals but did not say when it would set final limits for some metals or when companies would have to meet these limits.
Under the proposal, draft levels for lead in baby food would be set sometime this year. Draft levels for arsenic would be set sometime before 2024, and draft levels for cadmium and mercury in 2024 or later.
Final levels for lead would be set sometime between now and 2024, and final action levels for arsenic wouldn’t be set until 2024 or later.
EWG also urges Congress to swiftly pass the Baby Food Safety Act of 2021, introduced last year by Sens. Amy Klobuchar (D-Minn.) and Tammy Duckworth (D-Ill.) and Reps. Raja Krishnamoorthi (D-Ill.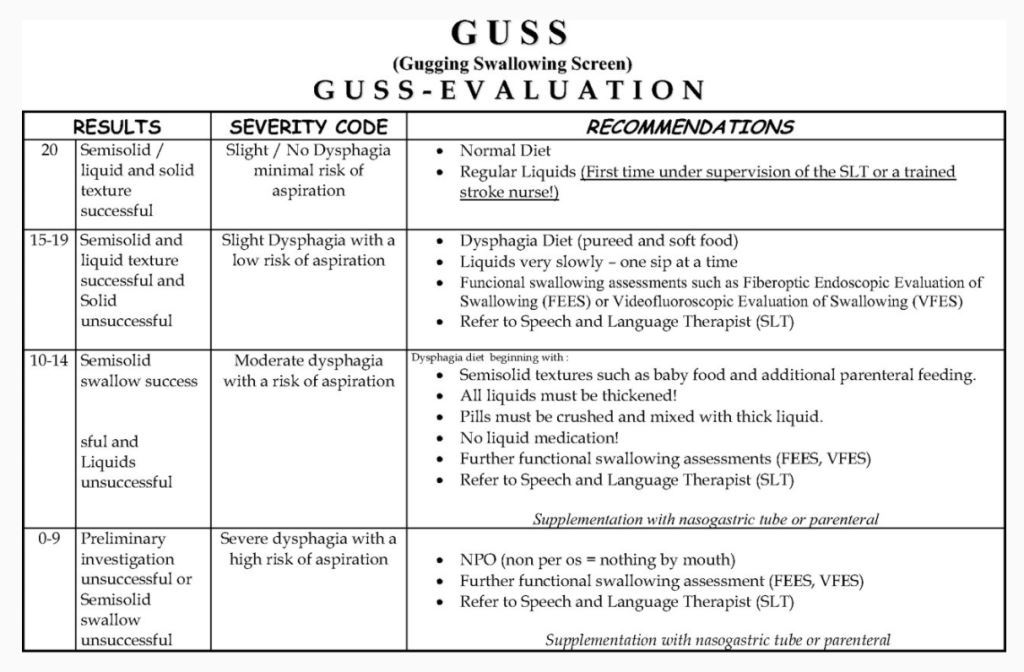 ) and Tony Cárdenas (D-Calif.). The bill would set tough interim limits for toxic metals in baby food that manufacturers would have to meet within a year.
) and Tony Cárdenas (D-Calif.). The bill would set tough interim limits for toxic metals in baby food that manufacturers would have to meet within a year.
“The longer Congress waits to take action, the more children are potentially put at risk,” said Melanie Benesh, EWG legislative attorney. “Congress should quickly require companies to meet interim limits on heavy metals in baby foods.”
EWG recommends for parents look for a variety of baby foods and cereals, including a variety of grains, to help decrease the exposure to potentially elevated levels of arsenic in rice-based products. EWG also urges baby food manufacturers to conduct continuous testing of heavy metals in all their products and make all testing results publicly available.
###
The Environmental Working Group is a nonprofit, non-partisan organization that empowers people to live healthier lives in a healthier environment. Through research, advocacy and unique education tools, EWG drives consumer choice and civic action.
Protect babies from toxic heavy metals in baby food
EWG is calling on Congress to take action NOW to protect kids from toxic heavy metals. Will you join us?
How to analyze the state of production of baby food
Goods for children always show increased attention. For the manufacture and sale of baby food, manufacturers must undergo a certification procedure. Analysis of the state of production is the most important component of such a procedure, which is necessary to confirm the compliance of manufactured products with the requirements of regulatory documents.
Children's food businesses are subject to the most stringent requirements to ensure product quality
Regulatory documents for baby food
Technical regulation of the Customs Union "On the requirements for the safety of baby food products, the processes of their production, storage, transportation and sale" is only being developed and has not yet entered into force. To date, manufacturers use other regulatory documents that must comply with baby food.
Three technical regulations of the Customs Union are considered to be the main ones: TR CU 021/2011 “On food safety”, TR CU 033/2013 “On safety of milk and dairy products” and TR CU 022/2011 “Food products in terms of their labeling ". To confirm the compliance of baby food with the requirements of these documents, it is necessary to carry out the procedure for declaring the conformity of products. The validity period of the document depends on the chosen declaration scheme, but cannot be more than 5 years.
In addition, there are standards for certain types of products:
- GOST R 54628-2011 “Products for baby food. Canned meat. Puree for feeding infants. Specifications";
- GOST 32218-2013 “Fruit-based canned food for feeding young children. General technical conditions”;
- GOST 30626-98 "Dry milk products for baby food";
- GOST 30545-2015 "Meat and meat-containing canned food for feeding young children";
- GOST R 57150-2016 "Canned poultry meat for feeding young children";
- GOST 34423-2018 "Chopped sterilized meat and vegetable canned food for children over three years old";
- GOST 33633 "Butter for baby food";
- GOST R 52474-2005 “Canned food.
 Juices, nectars and cocktails for the nutrition of young children”;
Juices, nectars and cocktails for the nutrition of young children”; - GOST 31801-2012 “Canned meat (class A). Meat puree for children” and many others.
In order to confirm the compliance of manufactured products with the requirements of these standards, it is necessary to undergo a voluntary certification procedure.
Regulatory documents for the analysis of the state of production of baby food
To analyze the state of production of baby food, the following regulatory documents are used:
- sanitary and epidemiological rules and regulations SanPiN 2.3.2.1940-05 "Organization of baby food";
- VNTP 12-92 KD "Temporary norms for technological design of enterprises for the production of canned food for baby food";
- GOST R 54293-2010 "Analysis of the state of production when confirming compliance";
- GOST R ISO 22000-2019 “Food safety management systems. Requirements for organizations involved in the food production chain.

Baby food production facility must comply with several regulations
What are the requirements for the production of baby food
The above regulations impose certain requirements on the production of baby food, which are checked during its analysis.
SanPiN 2.3.2.1940-05:
- A list of raw materials and components with certain parameters that cannot be used for the manufacture of baby food is specified.
- Provides a list of chemicals and ingredients that must not be contained in prepared baby foods.
- Mineral salts and vitamins are indicated, which are recommended for use in the production of baby food.
- Provides labeling and packaging requirements for baby foods.
- Lists the general requirements for the equipment and processes by which products are manufactured.
- The processes that are checked when organizing a system for monitoring the quality and safety of children's food are indicated.
- The requirements for industrial premises, water supply and sewerage are given.
- V VNTP 12-92 KD:
- The main principles of organizing the production of canned food for baby food are given, including requirements for containers for transportation, storage and packaging, production and storage facilities, used raw materials.
- Specifies the requirements for technological processes and equipment for the manufacture of food products.
- Provides requirements for safety and industrial sanitation, water supply, sewerage, heating, ventilation, electricity and air conditioning.
- Specifies the requirements that manufacturing laboratories must meet.
The main provisions of the program for the analysis of the state of the production of baby food
The program for the analysis of the state of the production of baby food includes the following steps:

According to the results of the analysis of the state of production, one of the decisions is made:
- production complies with the requirements of regulatory documents;
- establish deadlines for the development and implementation of corrective actions to eliminate identified nonconformities;
- suspend permits for the production of baby food products.
Conclusion
Analyzing the state of baby food production is an important and complex task. It allows you to confirm the safety of products and their compliance with the requirements of technical regulations. Specialists Certification Center "Garant" are ready to perform this task with high quality and in the shortest possible time.
It allows you to confirm the safety of products and their compliance with the requirements of technical regulations. Specialists Certification Center "Garant" are ready to perform this task with high quality and in the shortest possible time.
Infant Food Allergen IgE, mix fx5: Egg white, Milk, Fish, Wheat, Peanut, Soybean - f1, f2, f3, f4, f13, f14)
Description
Method of determination Immunofluorescence assay (ImmunoCAP).
Test material Serum
Home visit available
Online check-in
Detection of specific IgE to six food allergens that most often cause allergies in children. Used for laboratory confirmation of IgE sensitization in skin/food allergy symptoms. The answer is general for the mixture.
Food allergies and atopic dermatitis/eczema are most common among young children. Sometimes the causal dependence of allergic-like manifestations on certain food allergens can be established by excluding the suspected product and assessing the patient's condition after cessation of contact with him. For the same purposes, skin allergy tests and / or blood tests are used to detect specific IgE antibodies, confirming the presence of allergic sensitization to the corresponding allergens. This is important for making the right recommendations for monitoring the child's condition, determining (if necessary) appropriate treatment, and timely referral to an allergist for follow-up. Food allergies and atopic dermatitis in the first years of life and familial predisposition are considered risk factors for the subsequent development of allergy to inhalant allergens ("allergic march").
Sometimes the causal dependence of allergic-like manifestations on certain food allergens can be established by excluding the suspected product and assessing the patient's condition after cessation of contact with him. For the same purposes, skin allergy tests and / or blood tests are used to detect specific IgE antibodies, confirming the presence of allergic sensitization to the corresponding allergens. This is important for making the right recommendations for monitoring the child's condition, determining (if necessary) appropriate treatment, and timely referral to an allergist for follow-up. Food allergies and atopic dermatitis in the first years of life and familial predisposition are considered risk factors for the subsequent development of allergy to inhalant allergens ("allergic march").
A test that detects the presence of specific IgE to a mixture of six common food allergens can be used in addition to clinical assessment to screen for suspected food allergies in children. If the result of this study is positive, subsequent testing should be aimed at identifying specific causative allergens and based on the patient's history, taking into account the allergens with which he comes into contact.
If the result of this study is positive, subsequent testing should be aimed at identifying specific causative allergens and based on the patient's history, taking into account the allergens with which he comes into contact.
Preparation
Preferably 4 hours after the last meal, no requirement. Antihistamines do not affect the result. It is undesirable to conduct a study against the background of the use of glucocorticoid hormone preparations (you should consult with your allergist about the advisability of conducting a study or the conditions for canceling the corresponding drug).
Indications for use
in the presence of allergic-like symptoms (including skin, gastrointestinal) for the purpose of screening to confirm / exclude sensitization to common food allergens listed in the mixture, which most often cause food allergies in children.
Interpretation of results
Interpretation of test results contains information for the attending physician and is not a diagnosis. The information in this section should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. An accurate diagnosis is made by the doctor, using both the results of this examination and the necessary information from other sources: history, results of other examinations, etc.
The information in this section should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. An accurate diagnosis is made by the doctor, using both the results of this examination and the necessary information from other sources: history, results of other examinations, etc.
Units: kU/l.
Limits of detection: 0.1-100 kU/l.
Reference values:
Interpretation of results
Increasing levels
- A result above the specified threshold confirms the presence of sensitization to one or more food allergens in the mixture, higher values indicate the level of sensitization. The causative allergen should be clarified by further testing. The diagnosis of allergy is established on the basis of clinical symptoms, taking into account the patient's history and examination results.
- False positive due to very high levels of total IgE.
Reduced levels
No sensitization to food allergens in the mixture.