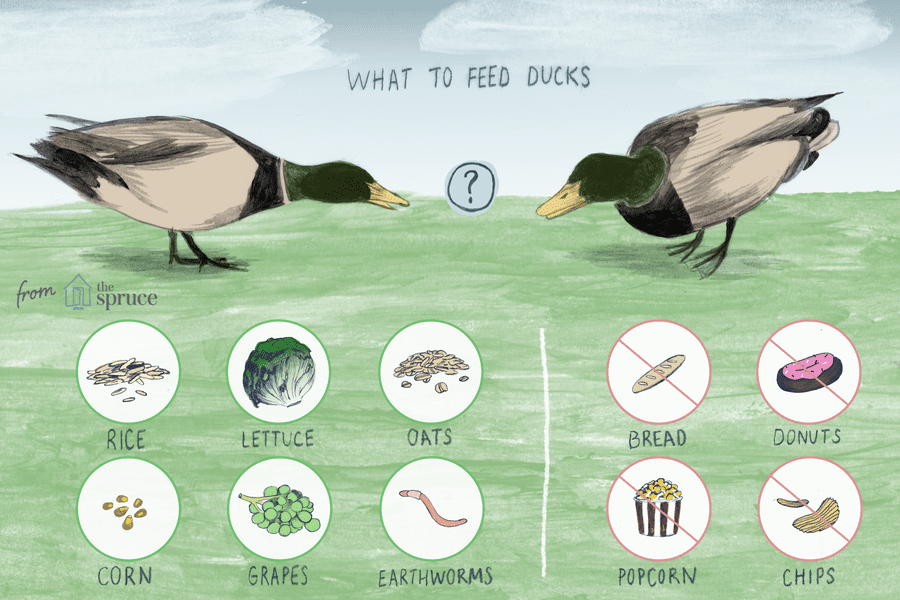
Baby fussy when feeding
My baby fusses or cries when breastfeeding
By Kelly Bonyata, BS, IBCLC
© Lsantilli - Fotolia.com
Some babies will fuss, cry or pull off the breast during breastfeeding. There are a number of reasons why this might be happening. It’s pretty common to see this type of behavior at around 6-8 weeks, though it can occur at any time. If your baby is generally fussy (not just when nursing) see My baby is fussy! Is something wrong?
Determining the problem
Here are some of the problem-solving steps I go through when my baby is fussy at the breast or a mother asks me why her baby is fussing while breastfeeding:
.
How old is baby? Most babies go through growth spurts during the first few days at home and around 7-10 days, 2-3 weeks, 4-6 weeks, 3 months, 4 months, 6 months, 9 months, etc. Many babies are fussy during growth spurts.
Is baby working on anything new developmentally? Babies who are starting to notice the world around them can be notoriously distractible. Any kind of new developmental step that baby is working on can affect nursing temporarily, whether it be fussy nursing behavior or simply more frequent nursing.
When is baby fussing? To figure out the cause it’s helpful to pay attention to when the fussy behavior happens, both during the nursing session and during the day.
If baby is fussy right when your milk is letting down (or immediately after), there’s a good chance that the fussy nursing is related to a fast let-down. If baby is fussy before let-down, or a few minutes into nursing (and a while after let-down), then baby may be impatient for the fast flow of milk that comes with let-down. Fussing at the end of a nursing session (or what seems to be the end) may mean that baby needs to burp, or is ready to finish nursing, or just wants to suck (and doesn’t want to deal with a new let-down at this point), or wants to continue nursing on the other side or with a faster flow of milk.
If the fussy behavior is mainly in the mornings, it might be due to a faster than usual let-down if baby has just had a longer sleep period and mom’s breasts are fuller than usual. If baby is fussier during evening nursings, it may be due to the normal fussy time that most babies have during the evening. Although most babies don’t react to foods that mom eats, some do. If you eat a particular food at about the same time each day (or most days) and baby has a regular time where she fusses during nursing, try not eating that food for a week or two to see if things improve.
If baby is fussier during evening nursings, it may be due to the normal fussy time that most babies have during the evening. Although most babies don’t react to foods that mom eats, some do. If you eat a particular food at about the same time each day (or most days) and baby has a regular time where she fusses during nursing, try not eating that food for a week or two to see if things improve.
Does fussing occur on both sides equally or only on one side? Most moms have a faster let-down and/or a more abundant milk supply on one side than the other, so if your baby fusses more on one side, it may be due to these differences.
What else is going on with baby? Is she sick or teething? Is something new or different going on in her environment? Has she started solids or is she trying a new food? Is she exhibiting other symptoms besides the fussy nursing?
Below are discussions of some of the different things that can lead to fussy nursing behavior. Keep in mind that the problem may also be a combination of several things.
Keep in mind that the problem may also be a combination of several things.
Does baby need to burp?
Many babies will cry, fuss, pull off the breast, etc. if they need to burp. Try to burp between breasts and after a feeding, but don’t worry if baby does not burp and is content. Breastfed babies overall don’t take in as much air during a feeding as bottle-fed babies do, so usually don’t need to burp as often. If baby has been crying before she nurses, or is so hungry that she nurses “frantically” or if mom has a fast let-down, baby could be taking in more air and may need to be burped more often.
Burping is usually only necessary during the first few months, though it may extend longer. Once your baby is moving more freely, she will be able to relieve the gastric gas herself. This usually will occur between the 4th and 6th month, but may be shorter in some children and longer in others.
If baby has a hard time burping, try burping more often during a feeding. The best burping position is one that applies firm pressure to the baby’s tummy. Placing baby over the shoulder way up so that there is pressure on baby’s abdomen often works well. Walking around while doing this might distract her long enough to get a good burp. You may even want to lie baby down on her stomach and burp her that way.
The best burping position is one that applies firm pressure to the baby’s tummy. Placing baby over the shoulder way up so that there is pressure on baby’s abdomen often works well. Walking around while doing this might distract her long enough to get a good burp. You may even want to lie baby down on her stomach and burp her that way.
Growth spurt
Babies often pull off and fuss during growth spurts. Most babies go through growth spurts, sometimes called frequency days, during the first few days at home and around 7-10 days, 2-3 weeks, 4-6 weeks, 3 months, 4 months, 6 months and 9 months (more or less). More growth spurt information in this link.
Distractible baby
If baby seems to be pulling off the breast at any distraction (real or imaginary), then see The Distractible Baby.
Forceful let-down
Some babies will pull off the breast soon after let-down if mom has a forceful let-down. Baby may be frustrated by the too-fast flow of milk with let-down. A too-forceful let-down can also cause excessive gas or spitting up/vomiting. There is more information here on symptoms of and how to deal with a fast let-down reflex.
A too-forceful let-down can also cause excessive gas or spitting up/vomiting. There is more information here on symptoms of and how to deal with a fast let-down reflex.
Slow let-down
Some babies get very impatient if mom has a slow let-down. There is more information here on speeding up a slow let-down reflex.
Baby wants a faster milk flow
Even very young babies can be quick to notice that pulling off, kneading the breast, etc. can cause an additional let-down, and can facilitate a faster, easier milk flow. Some babies become impatient with the slower milk flow following the initial fast flow at let-down. This may or may not be related to a slow let-down.
When a feeding begins at the breast there are drops of milk. Then when the initial let-down occurs (several seconds to a minute into the feeding), the milk flow speeds up quite a bit. At that time it may drip very quickly, squirt, or even spray. Some minutes later it slows again and the baby must continue to suck vigorously in order to elicit further let-downs. This pattern can continue through successive, multiple let-downs as long as the baby is continuing to nurse vigorously. Eventually, baby will learn that the flow will pick back up again if she’ll only continue to vigorously suck/swallow.
This pattern can continue through successive, multiple let-downs as long as the baby is continuing to nurse vigorously. Eventually, baby will learn that the flow will pick back up again if she’ll only continue to vigorously suck/swallow.
With bottle feeding, the flow is instant and continuous. The baby is required to work very little. Once a baby has had a bottle, especially a lot of bottles, she may begin to prefer the ease of bottle-feeding over the work of breastfeeding. She may become frustrated at the breast after the first let-down occurs and the flow of milk begins to slow.
If baby is getting bottles you might consider putting them away, at least for a while. When you must use a bottle, only use a newborn nipple for as long as baby will tolerate it so that she never gets a really fast flow of milk from the bottle, but has to work a little more to get the milk.
Sometimes babies of moms with oversupply or fast let-down will also get very used to the fast flow and object when it normally slows somewhere between 3 weeks to 3 months.
It can be helpful to do some breast compression when this fussiness starts or right before you expect it to. This will help speed up the milk flow again. Once compression stops helping, try switching baby to the other side when she begins to fuss and back and forth again (after using compression) as you need to.
Baby is done nursing for the moment
If baby is fussing after she’s been nursing for a while, and you’ve ruled out other causes, she may be in the process of changing her nursing pattern. Babies become very efficient at the breast with growth and maturity. They can milk the breast in a lot less time per feeding session than they required before. Baby’s frustration may just be a sign that she’s finished and wants to move on.
On a similar note, an occasional baby will just want to suck at the end of a nursing session and the flow of milk with let-down frustrates her. You might see if offering her a finger or pacifier (if baby is older than 4-6 weeks) to suck on during these times seems to help.
Baby prefers one side
Sometimes babies will refuse or fuss at a breast when the let-down is slower or too forceful, or the supply a bit lower. They in turn will prefer the side which lets down more/less quickly and in which the supply is more bountiful. See also: Lopsided! What can I do?
Fussy in the evening
Many young babies tend to pull off and fuss at the breast in the evening. See the article Cluster Feeding and Fussy Evenings.
Teething
Teething can cause fussy nursing behavior, as some babies experience gum discomfort with sucking. Baby might start to nurse, but then pull off and cry or fuss and not want to nurse anymore. See Teething for more information and tips.
Thrush
Frequent pulling off the breast can be a symptom of thrush.
Stuffy nose
A stuffy nose can cause fussy nursing behavior. If your baby has a stuffy nose and is having a hard time breathing and nursing at the same time, see colds & congestion.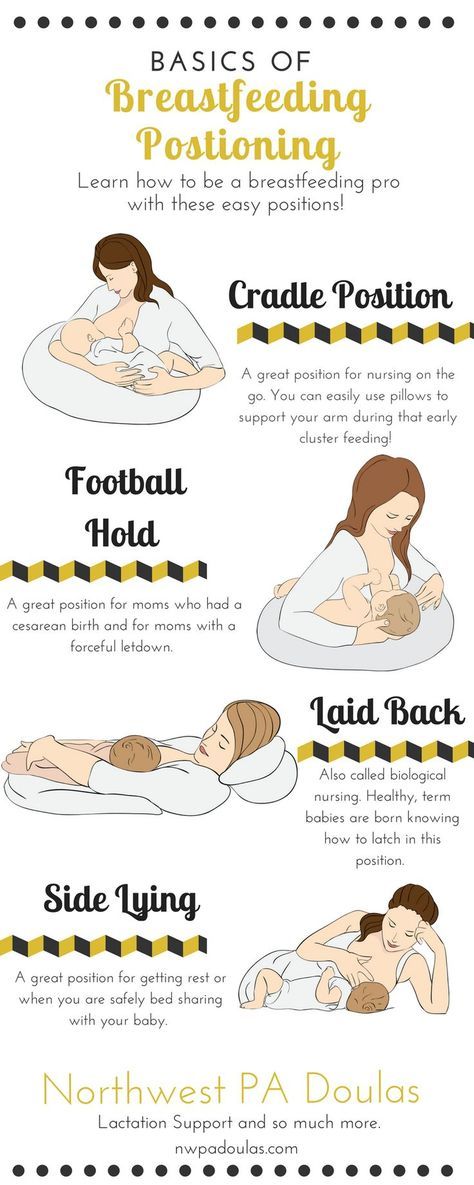
Allergy or food sensitivity
Some babies with allergies or food sensitivities exhibit fussy nursing behavior. Often when there is a sensitivity to something in mom’s diet, baby will come to the breast hungry but when she tastes/smells something in the milk that will cause her GI distress, she pulls off, bats her head back and forth, etc. Sensitivities to foods in mom’s diet are rare. If this is the problem, you will most likely notice other symptoms, such as excessive spitting up or vomiting, colic, diarrhea, rash, persistent congestion or runny nose, or excessive gas. More information on food sensitivities in babies and links to more allergy information can be found in my article Dairy and other Food Sensitivities in Breastfed Babies.
Low milk supply
Low milk supply can cause baby to be fussy at the breast. If you feel that your milk supply may be low, see this page for more info: Increasing low milk supply.
Reflux
Reflux can result in baby being fussy at the breast. See Reflux and Breastfeeding for more information.
See Reflux and Breastfeeding for more information.
Tongue-Tie
Tongue-Tie can result in baby being fussy at the breast. See Breastfeeding a Baby with Tongue-Tie (Resources) for more information.
The Distractible Baby • KellyMom.com
By Kelly Bonyata, BS, IBCLC
- Is my baby distractible?
- What can I do about it?
- Additional Information
Is my baby distractible?
Latch on, suck a moment, pull off… latch on, suck a moment, pull off. Nurse a minute, pull away to smile at mom. Nurse a minute, pull away to see who just walked in the room. Nurse a minute, pull away to listen to the TV. Nurse a moment, pull away because the dog wagged his tail.
Sound familiar?? Baby starts to nurse and just as soon as your milk starts to let-down, baby pulls off and wiggles around in your lap. Babies aged two to six months are notorious for pulling off the breast at any distraction (real or imaginary) and tend to forget to let go before they turn around (ouch!).
.
This is a passing developmental stage that can be quite a nuisance – it’s usually at it’s worst between four and five months. At around 2 months, your baby will become able to see things clearly across the room. At around 3 months, he’ll start to stay awake longer and take a greater interest in the world around him. Your baby is also beginning to recognize that he is separate from mom. All of these things can result in a distractible baby. When baby first becomes aware of the rest of the world, he will have a hard time concentrating on nursing. In effect, he will be unable to “walk and chew gum at the same time.” Once he gets a little older, he’ll find it easier to both nurse and take in the world around him at the same time.
Distractibility is also common around 8-10 months, and can lead mom to think that her baby is trying to wean. If your baby is younger than a year, it’s highly unlikely that this temporary disinterest is self-weaning. It’s very rare for a baby younger than 12 months to self-wean.
What can I do about it?
Many moms find it more and more difficult to nurse a distractible baby, and sometimes even interpret it personally (“I don’t want mom any more” or “I don’t want to nurse any more”). At the very least, it’s frustrating to deal with a distractible baby. Less frequent/shorter nursing during this distractible stage can lead to a low milk supply, so do your best to get in a few decent feedings during the day.
Until this stage has passed, baby may need a quiet place to nurse and/or more night nursing until he’s figured out how to deal with distraction. Do take advantage of night nursing during this time – it doesn’t matter when baby takes in his calories during a 24-hour period. One study showed that older babies can consume as much as 25% of their total daily intake of mother’s milk during the night, probably partly because of daytime distractibility.
Nursing in a quiet, darkened, boring room often helps. Talk in quiet, soothing tones (if you talk at all). Nurse while lying down; nap nurse. Cover baby with a shawl or put him in a sling to nurse. Nursing while in motion (walking, rocking) can also help baby to focus better on nursing. Try to catch your baby when he’s more willing, such as when he’s just waking up, already a little sleepy, or actually asleep. Baby’s initial pulling off is probably not an indication that he is finished – just an indication that he saw/heard something interesting across the room. When he pulls off, try to coax him back to the breast a few more times before giving up.
Nurse while lying down; nap nurse. Cover baby with a shawl or put him in a sling to nurse. Nursing while in motion (walking, rocking) can also help baby to focus better on nursing. Try to catch your baby when he’s more willing, such as when he’s just waking up, already a little sleepy, or actually asleep. Baby’s initial pulling off is probably not an indication that he is finished – just an indication that he saw/heard something interesting across the room. When he pulls off, try to coax him back to the breast a few more times before giving up.
If baby pulls away without letting go, keep a finger ready to break the suction as soon as he starts to pull away. You can also nurse baby in the football (clutch) hold so you have better control of his head, or nurse him in the cradle hold in a sling. This type of behavior sometimes leads to biting; if your baby bites, see When Baby Bites.
If baby is not nursing as much because of distractibility, offer the breast often (even when he doesn’t “ask” to nurse). Make up for lost time by nursing more often during the night. Older babies may nurse better if you try different and novel nursing positions in which they have more control – baby standing up, sitting on your lap facing you, etc.
Make up for lost time by nursing more often during the night. Older babies may nurse better if you try different and novel nursing positions in which they have more control – baby standing up, sitting on your lap facing you, etc.
Additional information
Wakeful 4 Month Olds by Jan Barger, RN, MA, IBCLC @
Breastfeeding as Baby Grows. This article, by Becky Flora, IBCLC, talks about baby’s different developmental stages during the first year and how they affect breastfeeding.
What is Normal? by Paula Yount discusses the variations of normal that you can expect throughout your breastfeeding experience.
My baby fusses or cries during nursing – what’s the problem? This article discusses some possible reasons for fussy nursing behavior. If you’re looking for the rest of the info that used to be on this page, it’s in this article (with more added).
Is my older baby getting enough milk? If you feel that your baby is not nursing enough, this page may be helpful.
why the baby cries while feeding
While the baby is quite a baby, crying is the only way of his communication with his mother and the outside world. If the baby is restless during feeding, he will let you know that he is uncomfortable. We will analyze what can cause baby crying in such a situation.
Dry milk drink "Baby milk" Valio Baby 3 NutriValio for feeding children over 12 months Read more
As a rule, the causes of a baby’s tears at the breast or bottle with a mixture are physiological, and there may be several of them.
Abdominal pain
Most likely, the child is worried about colic (they can start from 2-4 weeks of age and usually end by 3 months). Unpleasant sensations are associated with the fact that the infant has an insufficiently developed intestinal microflora and it is difficult for the digestive system to cope with the task assigned to it. Children's crying during colic is accompanied by arching the back and pulling the legs to the stomach - the pain from the formation of gases in the intestines is always acute. To alleviate the condition of the crumbs, it is useful for a nursing mother to drink teas with fennel, cumin or anise. If your baby is formula-fed, choose formula carefully. Valio Baby baby food is as close as possible to the composition of breast milk and contains the GOS prebiotic, which is necessary for the health of the child's digestive system. The cause of colic is also the wrong feeding technique and, as a result, the capture of excess air by the baby. nine0003
Children's crying during colic is accompanied by arching the back and pulling the legs to the stomach - the pain from the formation of gases in the intestines is always acute. To alleviate the condition of the crumbs, it is useful for a nursing mother to drink teas with fennel, cumin or anise. If your baby is formula-fed, choose formula carefully. Valio Baby baby food is as close as possible to the composition of breast milk and contains the GOS prebiotic, which is necessary for the health of the child's digestive system. The cause of colic is also the wrong feeding technique and, as a result, the capture of excess air by the baby. nine0003
#PROMO_BLOCK#
Earache
Children under one year old often suffer from otitis media, this is due to the anatomical features of the structure of the nasopharynx in babies in the first months of life. A baby may cry during feeding because swallowing causes a sharp pain in his ears. Very carefully touch the tragus of the baby's auricles - if he cries, then you need to see a doctor.
It is no secret that many neurological disorders are accompanied by headaches. It becomes especially strong when swallowing. If the baby is constantly crying during feeding, be sure to make an appointment with a pediatric neurologist.
Inflammation of the oral mucosa
Crying during feeding may signal that the baby is experiencing discomfort in the mouth or throat. Its cause is most often thrush or pharyngitis. These diseases require treatment under the supervision of a pediatrician. nine0003
Lack or excess of breast milk
The lactation of a nursing woman is affected by a considerable number of factors - the psychological state, fatigue, stress, malnutrition and its lack, improper organization of breastfeeding. The baby may cry because he does not have enough milk. Whether the food shortage is really critical is easy to check using the wet diaper method. By the way, the crying of a baby may also indicate that there is too much milk - the stream is too strong and the baby simply chokes. nine0003
nine0003
Unusual taste of breast milk
If a mother ate, for example, something spicy on the eve of feeding, this will certainly affect the taste of milk. The baby, of course, will cry. This cause of children's "grief" is the most easily eliminated - be attentive to your menu and do not upset your beloved baby.
In addition to the reasons described, the reason for children's tears during feeding can be erupting teeth and inflammation of the gums, as well as nasal congestion with allergies and SARS. Be attentive to your baby. If all is well, the baby should not cry while feeding. nine0003
3.46 37
Power supplyShare:
Author: Reetta Tikanmäki
Palm oil in baby food
Infant milk formulas are made from cow's milk. However, in terms of fat composition, it differs significantly from that of the mother.
However, in terms of fat composition, it differs significantly from that of the mother.
Read
Author: Ivargizova Oksana
How to choose milk formula for a baby
Breast milk is the best food for a newborn baby. It contains all the necessary nutritional components that fully meet the needs of the child and are necessary for his healthy and harmonious development. nine0003
Read
Show all
Why does the baby cry during breastfeeding
Ekaterina Andreevna Yakovleva
pediatrician, consultant on breastfeeding
Why does baby cry while breastfeeding? The answer may lie on the surface and depend on the situation. Some mothers themselves begin to put forward theories that are often incorrect - “I don’t have milk”, “I ate something wrong”, “The milk became tasteless and bitter”, “I shouldn’t have bought silicone pads” . .. Consider the most frequent causes of crying at the breast and options for helping the baby together with Ekaterina Andreevna Yakovleva, pediatrician, breastfeeding consultant and mother of two babies. She knows about the tears of babies not only from professional, but also from maternal experience. nine0003
.. Consider the most frequent causes of crying at the breast and options for helping the baby together with Ekaterina Andreevna Yakovleva, pediatrician, breastfeeding consultant and mother of two babies. She knows about the tears of babies not only from professional, but also from maternal experience. nine0003
WHY A CHILD CRYS DURING FOOD
— Ekaterina Andreevna, is crying during feeding dangerous?
— Crying during feeding is a normal way for a baby to communicate with the outside world. So he calls his mother, shows that he wants to eat or something bothers him. The only thing that crying can affect is that the baby will come off the chest and take in air. This will lead to more abundant regurgitation, increased pain in the tummy.
Table. Newborn cries during feeding - 9 reasons0091
— Can a change in priorities of a child affect his behavior at the breast?
- Up to three months, babies have one priority - they need to either eat and sleep or change a wet diaper.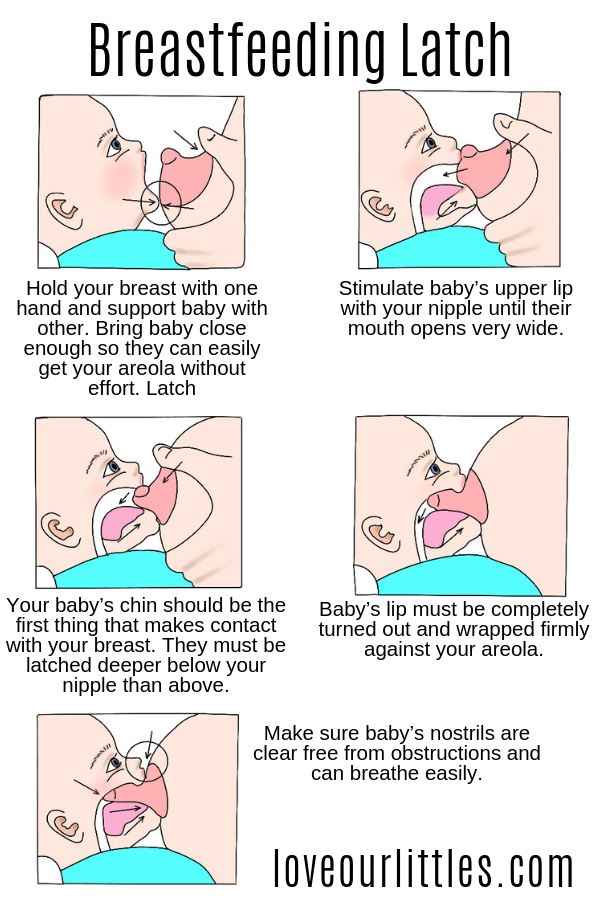 After the children become more active, they are already interested in the world around them. Therefore, when feeding in public places, and also when the mother combines the process with talking on the phone or watching TV, the child can be distracted: suck - turn away - suck, ask for different breasts in turn, indulge. nine0003
After the children become more active, they are already interested in the world around them. Therefore, when feeding in public places, and also when the mother combines the process with talking on the phone or watching TV, the child can be distracted: suck - turn away - suck, ask for different breasts in turn, indulge. nine0003
After three or four months, the baby should not be on the breast very often, but mothers find it difficult to readjust and continue to breastfeed constantly to soothe him. But in fact, the child’s needs are already different - he wants to be vilified on the handles, paid attention to him, played with him, showed him toys.
- Let's discuss misattachment in more detail. What can a mother do wrong if the child does not eat well and cries?
- A very common symptom of improper attachment or refusal of the breast is trouble-free feeding only in sleep. When the child sleeps, he eats calmly, and when he is awake, he begins to twist at the chest, cry. Mom can get tired of this, and in order to calm and feed the baby, during the day she gives him a bottle. In such a situation, it makes sense to talk about breastfeeding and work to restore normal feeding. nine0003
Mom can get tired of this, and in order to calm and feed the baby, during the day she gives him a bottle. In such a situation, it makes sense to talk about breastfeeding and work to restore normal feeding. nine0003
Problems may arise from awkward or repetitive posture during feeding. By trial and error, the mother should choose the position that will be most convenient for her and the child. However, if a baby is fed only lying down from birth, at an older age he may refuse to eat in his arms, break out and cry.
A CHILD CRYING WHEN FEEDING - HOW TO HELP
- Ekaterina Andreevna, everything is very individual for small children. How to understand why a child eats and cries? nine0010
— If the baby is crying during feeding, the mother should gradually study the possible reasons for such behavior and:
- Eliminate the reasons related to the child's well-being, which she can deal with herself.
- Practice breastfeeding techniques.

- Seek medical attention if all else fails - child continues to cry and has additional questionable symptoms.
Triad of symptoms that are always alarming
You should also consult a doctor if, during feeding, the child wriggles and cries from constant acute pain, cannot calm down, vomiting, blood and mucus in the stool, rashes in the mouth, stuffy nose are observed. Fever is an acute condition that is not associated with constant (for example, for a month) baby crying during feeding.
— What should I do if my baby refuses to breastfeed?
— The main thing for a mother is to remain calm and adequate. For a breastfed baby, one break can last an hour, and another five to six hours if the baby has slept long and well. Taking long breaks during the day, the child will still finish his daily allowance in order to develop normally. For example, if he has not eaten for six hours during the daytime, he will breastfeed more often at night. Therefore, in feeding children in the first half of life during the day, it is better not to take breaks for more than 3-3.5 hours. With the introduction of complementary foods, the intervals may be slightly longer. nine0003
Therefore, in feeding children in the first half of life during the day, it is better not to take breaks for more than 3-3.5 hours. With the introduction of complementary foods, the intervals may be slightly longer. nine0003
Night breaks are individual and depend only on the child - some children are born with a 6-8 hour interval, and some sleep at night for eight to twelve hours or eat every hour.
Read also
- About the reasons why a child refuses breast milk and whether it is necessary to switch to mixed or artificial feeding in such cases.
— Should I stop feeding if the baby is naughty?
- Depends on age. Mom should feel what exactly the child needs at this moment. If a newborn cries and refuses to breastfeed, you can calm him down, vilify him with a column, shake him, and then attach him to the breast again. If, having calmed down, the child turns away from the chest, then he has eaten.
An older child is distracted from the breast, becoming interested in something else. Do not force feed him. We must try to remove all irritants - feed in isolation in a separate room, not be distracted by gadgets, sounds, or give the child the opportunity to satisfy his interests, and then offer the breast again. nine0003
Do not force feed him. We must try to remove all irritants - feed in isolation in a separate room, not be distracted by gadgets, sounds, or give the child the opportunity to satisfy his interests, and then offer the breast again. nine0003
— What else can help calm the baby?
- Since most causes of crying are not related to medical problems, medication is not needed. It is necessary to relax, set up the baby, pump him, try to competently organize breastfeeding - apply correctly, do not give a dummy, nipple, supplement from a cup or syringe without a needle. As a rule, this is how most feeding problems go away.
— In what situations can a breast be replaced with a bottle? nine0010
— It is not worth replacing breastfeeding with formula feeding without acute vital signs. When a baby is not accepting the breast well, it is worth removing all bottles, continuing to supplement with “non-sucking” items, and contacting a breastfeeding specialist to try to establish attachment and breastfeeding. This is done by a lot of people.
This is done by a lot of people.
- Does changing the feeding regimen help to get rid of crying?
- Rather, these are unrelated things. It is not worth forcibly adjusting the feeding regimen, you need to listen to the child - in the first three months, the children constantly hang on their chest, after they begin to form a regimen and the intervals between meals increase. It is important to feel the needs of the child, because not only hunger, but also other things can disturb him, and if he constantly poke his chest, he will not be very pleased. nine0003
Table. Errors during breastfeeding
The baby cries during breastfeeding for many reasons. It can be improper attachment to the breast, "tangled nipples", inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity, runny nose, colic, teething, lactase deficiency, or a very nervous state of the mother. It is possible to understand what the problem is only by eliminating the organic and psychological causes of crying.