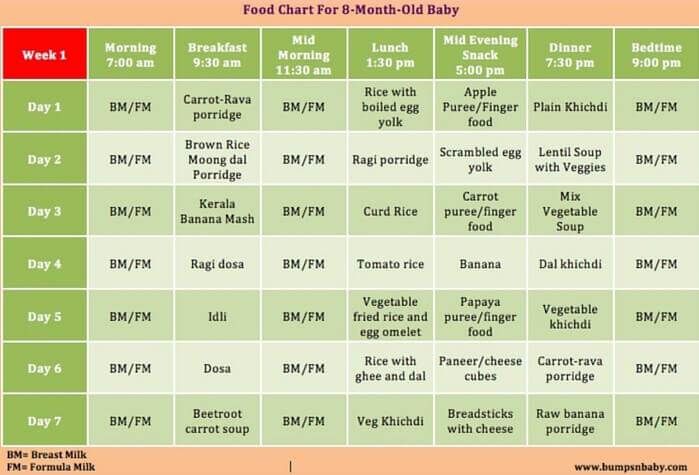
Baby make sound while feeding
My baby makes a clicking sound when nursing. Is this a problem? • KellyMom.com
By Kelly Bonyata, BS, IBCLC
A clicking (or clucking or chucking) sound during nursing indicates that baby is repeatedly breaking the seal or suction.
Try to notice when it occurs in the feeding. Is it more noticeable during let-down, or is it constant? Also try to notice if you have discomfort of any kind during the clicking.
.
If the clicking causes discomfort or pain, or if baby is not gaining weight as expected, it would be a good idea to get an evaluation by an experienced lactation consultant.
Sometimes the click is normal and not an indication of a problem. Whatever the cause of the clicking, as long as baby is growing well and mom is comfortable (no nipple soreness or pain), don’t worry about it.
Engorgement can make latch on difficult and baby may have a hard time maintaining suction.
Poor positioning and/or latch: for example, if baby is retracting the tongue or curling the tongue up when nursing, it can cause a clicking sound as the suction is broken. With poor positioning, baby may have a hard time maintaining a good seal at the breast.
Breastmilk oversupply and/or fast let-down. Baby will often break suction if the milk is coming too fast for him to handle.
Teething may be a cause of temporary clicking. If your baby has a sore mouth from the teething he may be trying to relieve it somewhat by not getting as tight of a seal around the breast or by repeatedly breaking the suction (thus the clicking). He could also be doing the same thing just because he’s not yet used to the feel of teeth in his mouth when he’s nursing.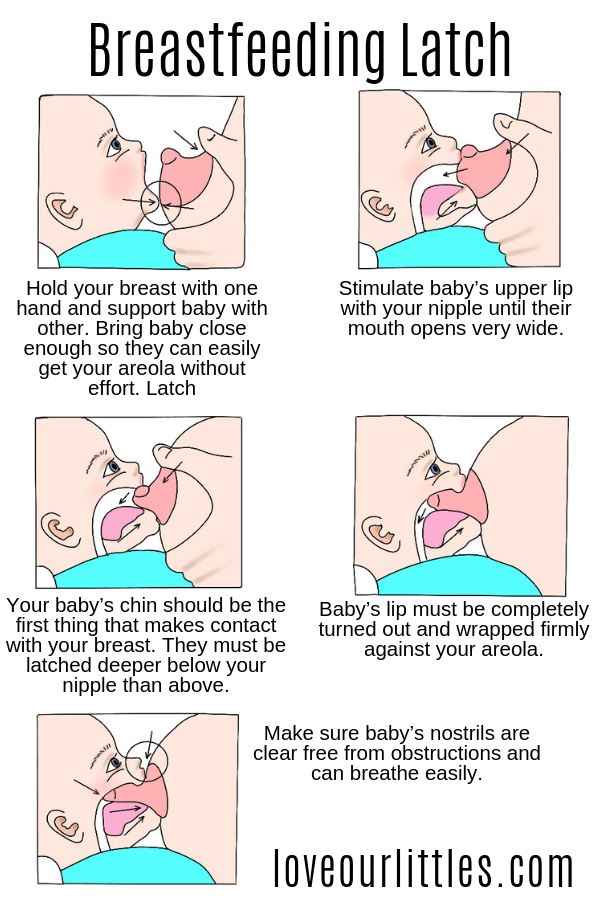
Ear infection could throw baby’s suck “off” temporarily. There is usually some pressure that builds in the ear when sucking and when there is ear pain, that pressure can be extremely uncomfortable. Baby may try to relieve it somewhat by not getting as tight of a seal around the breast or by repeatedly breaking the suction (thus the click).
Thrush can make baby’s mouth sore or itchy, causing him to break suction.
Babies who suck their tongues sometimes click. Such a baby is accustomed to the sensation of his own tongue up against the roof of his mouth and may latch too quickly with a shallow latch as soon as he senses something entering his mouth. You’ll often see cheek dimpling when this sort of clicking is going on.
Less commonly, anatomical variations in the infant’s oral cavity can cause clicking, if baby cannot get the nipple/breast fully into the mouth and compressed against the roof of the mouth.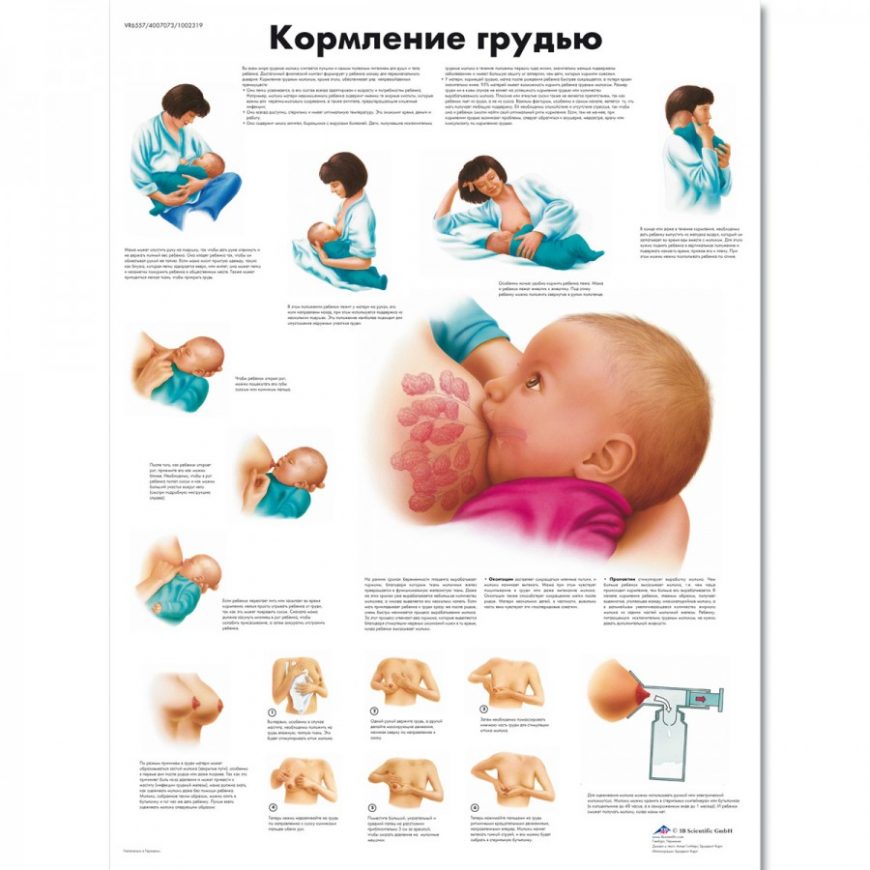 Examples include:
Examples include:
- Tongue tie/tight frenulum: A baby with tongue tie may be unable to keep the tongue extended for the relatively prolonged job of nursing, and thus the tongue will “snap back” when baby can no longer keep it in place. When he pulls the tongue back, suction is broken and you hear a click.
- Highly-arched palate or other palate variations;
- Cleft of the soft palate;
- Unusually small or large tongue, etc.
The Sounds of Breastfeeding | La Leche League Canada
First time parents are often surprised by the feeding noises that come with breastfeeding a baby. Breastfeeding and parenting books don’t usually mention these sounds. Photos are silent and many expectant parents have never spent time with a breastfeed baby. So, what are the sounds of breastfeeding and what do they tell us?
In the first three to five days your milk volume is small to match your baby’s small tummy size. Your baby may suck several times before you hear a swallowing sound. As the milk volume increases your baby will suck rapidly at the beginning of each feeding to trigger the letdown of your milk (milk ejection reflex). Once your milk starts flowing, your baby will usually suck once or twice for each swallow. A baby who is getting a good mouthful of milk with each suck makes a small gulping noise with each swallow. This is sometimes too quiet to hear. After swallowing, your baby will breathe out with a puff of air that sounds like a “k-ah” sound. After breathing out (exhaling) your baby will breathe in and swallow again, repeating the cycle. When your milk is letting down strongly, your baby will suck, swallow, breath, suck, swallow, breathe in a rhythmic gulp/”k-ah” pattern.
Your baby may suck several times before you hear a swallowing sound. As the milk volume increases your baby will suck rapidly at the beginning of each feeding to trigger the letdown of your milk (milk ejection reflex). Once your milk starts flowing, your baby will usually suck once or twice for each swallow. A baby who is getting a good mouthful of milk with each suck makes a small gulping noise with each swallow. This is sometimes too quiet to hear. After swallowing, your baby will breathe out with a puff of air that sounds like a “k-ah” sound. After breathing out (exhaling) your baby will breathe in and swallow again, repeating the cycle. When your milk is letting down strongly, your baby will suck, swallow, breath, suck, swallow, breathe in a rhythmic gulp/”k-ah” pattern.
Sometimes you may hear a “clicking” sound. Your baby may or may not also have noticeable dimples in the cheeks with each suck. And you may have sore nipples. These signs, together or individually, may suggest that your baby has not achieved a deep latch. A “click” indicates that your baby is breaking the seal on the breast. This causes your nipple to slip in your baby’s mouth and often creates a sore nipple. If you are hearing clicking, try improving the latch by bringing your baby’s chin deeply onto your breast. Your baby’s nose should tilt away from the breast as your baby’s head tips back. The nose often touches the breast but it shouldn’t be poking into it. You shouldn’t feel like you have to hold your breast back so your baby can breathe. Chin in, nose tilting away, head back is the same position you take when you drink something. (Try it now, pretend to take a drink of water. See how your chin goes forward and your head tips back?)
A “click” indicates that your baby is breaking the seal on the breast. This causes your nipple to slip in your baby’s mouth and often creates a sore nipple. If you are hearing clicking, try improving the latch by bringing your baby’s chin deeply onto your breast. Your baby’s nose should tilt away from the breast as your baby’s head tips back. The nose often touches the breast but it shouldn’t be poking into it. You shouldn’t feel like you have to hold your breast back so your baby can breathe. Chin in, nose tilting away, head back is the same position you take when you drink something. (Try it now, pretend to take a drink of water. See how your chin goes forward and your head tips back?)
When you feel that your baby is not latched well, it is important to deal with it right away. If it feels painful you may have to unlatch your baby from the breast by slipping a finger in the corner of her mouth to break the suction. Then you can try latching again. However, usually the latch can be adjusted while your baby is still latched. If your baby’s chin is tucked into her chest, she will not be able to hold onto the breast with her mouth. She will have difficulty swallowing. (Try it now. Tuck your chin into your chest and swallow. It is very hard.) You can try adjusting your baby so that her chin presses into your breast and her head tips back. In this position your baby can drink comfortably, just like you do.
If your baby’s chin is tucked into her chest, she will not be able to hold onto the breast with her mouth. She will have difficulty swallowing. (Try it now. Tuck your chin into your chest and swallow. It is very hard.) You can try adjusting your baby so that her chin presses into your breast and her head tips back. In this position your baby can drink comfortably, just like you do.
If the clicking, dimpling or sore nipples persist, contact a La Leche League Leader or an International Board Certified Lactation Consultant (IBCLC) to review your latch. In most cases, an adjustment to the positioning fit between you and your baby quickly resolves the problem. Persistent soreness or poor latch may need further investigation to ensure that your baby does not have a tongue or lip tie or some other issue.
You may hear something that sounds like your milk is hitting the back of your baby’s throat, or like your baby is drowning when your milk lets down. Some mothers have a strong milk ejection reflex.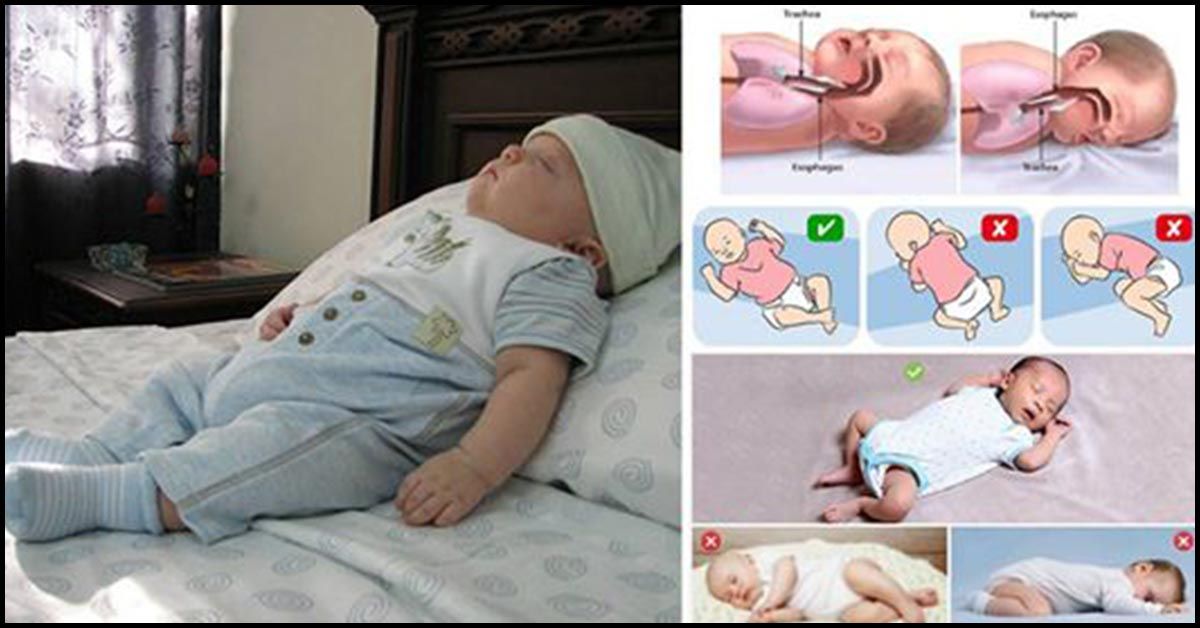 This means that your baby can get a lot of milk with each suck. Your newborn may find this amount of milk hard to handle. This may make your baby pull away from the breast when the flow is strongest. Adjusting your position so you are laying back with your baby on top of your breast can help manage the milk flow. This is another situation in which a La Leche League Leader can help you work out the best positioning for you and your baby.
This means that your baby can get a lot of milk with each suck. Your newborn may find this amount of milk hard to handle. This may make your baby pull away from the breast when the flow is strongest. Adjusting your position so you are laying back with your baby on top of your breast can help manage the milk flow. This is another situation in which a La Leche League Leader can help you work out the best positioning for you and your baby.
Sometimes babies make grunting noises or have raspy or squeaky breathing. These sounds may be fine but you should discuss with your healthcare provider or International Board Certified Lactation Consultant (IBCLC).
The most important thing to remember is that breastfeeding should not be painful. If you are experiencing nipple pain something is not right, no matter how good the latch looks from the outside. The next thing to consider is whether or not your baby is producing adequate wet and poopy diapers for his age and is gaining weight appropriately. See the LLLC article How to Know Your Baby is Getting Enough Milk for more information.
See the LLLC article How to Know Your Baby is Getting Enough Milk for more information.
If you are pain free and your baby is growing well then the noises of breastfeeding are just funny noises and you will probably learn to love them.
Please consider supporting LLLC.
Updated 2022
Sounds that a baby makes in a dream: how to distinguish normal from disturbing ones
Baby
The image of a baby sleeping like an angel is touching only when you have no children. Because every mom is faced with the fact that her baby spends half the night grunting, gurgling, sneezing, food and whimpering.
All these strange sounds often seem very disturbing to parents: what if something is wrong with their child? Let's try to figure out in which cases it is really worth worrying.
- Photo
- kieferpix / iStock / Getty Images
Babies naturally sleep restlessly.![]() Sounds and movements in sleep are the result of the immature nervous system and reflexes of the newborn. Circadian rhythms do not develop until about six weeks of age. This means that the sleep cycles of these young children are irregular, it is difficult for them to distinguish between night and day, and they often wake up.
Sounds and movements in sleep are the result of the immature nervous system and reflexes of the newborn. Circadian rhythms do not develop until about six weeks of age. This means that the sleep cycles of these young children are irregular, it is difficult for them to distinguish between night and day, and they often wake up.
Until about six months old, babies spend at least 50% of their time in REM sleep. This is the period when the brain is most active and often produces vivid dreams. During REM sleep, a child may move according to their dreams or simply because of the activity taking place in their brain. All this movement can be accompanied by sounds from gurgling to whimpering - and this is absolutely normal.
Infant sleep cycles are only about 50 minutes long, with many transitions between sleep states and phases. It is between the phases of sleep that babies move, make noise and wake up.
Since young children want to eat every few hours, including in the middle of the night, hunger can also be the cause of some of the sounds. While sleeping, they may smack their lips, suck their fists, and even begin to whimper.
While sleeping, they may smack their lips, suck their fists, and even begin to whimper.
- Photo
- Amax Photo / E+ / Getty Images
Sounds to worry about
Gurgling / guttural sounds : newborns do not develop the mechanism of swallowing at first, so they may "gurgle" regularly during sleep.
Nasal obstruction : newborns have noisy breathing due to the tiny nasal passages of the newborn and the protective role of mucus. In addition, their respiratory system is not yet fully developed.
Sneeze / snort / wheeze / whistle : again, this is because they "breathe through the nose" and not "breathe through the mouth" and because their nasal passages are very narrow. It stops after about six months.
Cough : newborns often cough during their sleep, and this is normal.![]() If the cough persists, you can hold the baby in your arms, hold him upright to help burp, or lightly pat him on the back to clear his lungs.
If the cough persists, you can hold the baby in your arms, hold him upright to help burp, or lightly pat him on the back to clear his lungs.
Tummy sounds : Babies tend to continue digesting food during the night. Therefore, perfectly healthy sounds can be belching, hiccups, growling in the stomach, gurgling or gassing.
- Photo
- Ridofranz / iStock / Getty Images
See your baby for these signs
Get help right away if you notice any of these breathing difficulties:
-
Baby's face turns blue.
-
Difficulty or restricted breathing.
-
Pauses of breathing lasting more than a few seconds.
-
Breast retraction.
-
Fever that accompanies any breathing or digestive problems.
-
Rapid breathing that lasts longer than usual or has 60 or more breaths per minute.

-
Repeated groaning at the end of each breath.
Lida Buslaeva
Today they are reading
“My mother-in-law scolded me: ‘I married a simple guy, not a prince – now don’t complain!’”
“We always celebrate the New Year with the mother-in-law, whom you cannot please. How can this tradition be changed?
A lot of tenderness and funny daughter outfits: 30 best photos of Irina Shayk and Bradley Cooper
Live stream and funeral at sunset: 8 features of the burial of Elizabeth II
In love and happy: Charles III and Camilla showed their first Christmas card
on breastfeeding
Mommy, your milk is always what I want: sometimes it is filled with the aroma of spring herbs, sometimes sweet like honey, sometimes light like dew, sometimes enveloping like white clouds. How many times it healed me and I became strong again, or wrapped me in a sweet slumber when I was very tired. At your chest, I heard the singing of a lark high in the sky, and the whisper of leaves in a birch grove, and autumn rain outside the window, and the chime of waxwings on a winter day.
Even after many years I will remember it, we will remember it...
E. Ibragimova
Published in the special issue of the magazine "Liza.My child" special issue 01/2016
Many mothers, expecting their first baby, seriously think about how childbirth will take place, and less often they think about how they will feed the baby. Meanwhile, childbirth is a very short period of time, and the rest of the time of life with the baby will be devoted to building relationships with him through breastfeeding.
Some mothers-to-be are hesitant to breastfeed at all.
Let's look at their assumptions first:
- Does breastfeeding ruin breast shape?
Breast shape changes during pregnancy. On the contrary, when feeding for more than a year and smooth weaning, the breast acquires an almost “pre-pregnant” shape. According to studies, smoking has a stronger effect on the shape of the breast than feeding.
- Will it be impossible to leave the child?
The first 3 months are possible short (1-1.5 hours) separation from the child, from 3 months absence can be longer, after 9months, the mother can go to work full-time, leaving the baby with expressed milk.
- If the mother is nervous or very tired, does the milk “burn out” or become bad for the baby?
There are no conditions in the mammary gland for "burning out" of milk. When breastfeeding, endorphins are released into the blood of a woman, and HB helps her to endure stress more easily and is the best prevention of depression. Yes, and the child himself calms down at the breast, even if before that he sees the unusual behavior of his mother.
- Is formula practically the same as breast milk?
In order for women to have such a doubt, manufacturers of infant formula have tried hard, investing millions of dollars in advertising and bribes.
Let's look at a few differences between breastfeeding and formula feeding:
|
| GV | Blend |
| Economy | free | about 100 tr. in the first year of a child's life. If hypoallergenic mixtures are required, then about 240 tr. |
| Number of substances | over 700! | 30- 50 |
| Stem cells | yes | no |
| Antibodies against diseases | yes | no |
| Growth factors for maturation of the intestines | enough | little |
| Effect of | normal maturation of the gastrointestinal tract, normal development of the immune system | constipation, diarrhea, increased risk of many diseases: allergies, gastrointestinal problems, various infections, diabetes, etc. |
| Proteins | easily absorbed whey
| hard to digest casein clots
|
| Change in composition | adapts to the needs of the baby (varies depending on the season, time of day, age of the baby, etc.) | composition is the same for all children |
| Vitamins and minerals | easily digestible | low absorption |
| Availability | no need to cook | it is necessary to go to shops, sterilize the bottle, dilute the formula with water, etc. |
| Excess substances | no | cases of salmonella infection, radioactive particles, etc. |
| Emotional connection between mother and child | strong | weak |
And the list of differences goes on.
Imagine, can a baby bottle with formula replace the happy moments at the mother's breast?
With information and help, almost any woman can successfully breastfeed for a long time. And you can!
What information can help you?
First , immediately after delivery (before measurements) skin-to-skin contact between the newborn and the mother (a method that involves placing the naked child on the mother’s abdomen or chest), the child must be dried, covered with a dry diaper, contact duration - at least 40 minutes, optimally 2 hours or more. (This right of mother and child is also enshrined in the Methodological Letter of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated July 13, 2011 N 15-4 / 10 / 2-6796 "On the organization of the work of the obstetric service in the context of the introduction of modern perinatal technologies").
Why is this important:
a) At the same time, the baby's body is colonized by the same bacteria that live on the body of his mother. This, in combination with HB, is considered an important prevention of allergic diseases.
b) If a newborn is separated from his mother immediately after birth, he becomes vulnerable to aggressive hospital flora, the risk of nosocomial infections increases dramatically.
c) This calms the baby and mother, because they both experience great stress in childbirth.
d) The baby is more likely to be able to latch on correctly (especially if the birth was completed without medication).
Second , breastfeed within the first hour after birth. Don't panic if the baby doesn't take the breast right away. Children should eat when they show they are ready, and if the child is in close contact with the mother, she will notice this readiness. The recommended duration of application is at least 20 minutes from each breast.
The baby's first food should be colostrum. Colostrum is the secret of the mammary glands, which is produced during pregnancy and the first 3-5 days after childbirth (before milk arrives). It is a saturated thick liquid from light yellow to orange color. Do not be afraid that there is not enough colostrum. Colostrum is very concentrated, so the baby needs just drops.
Why it's important:
A) Colostrum contains several times more protein than mature milk, especially immunoglobulin A. Immunoglobulins are responsible for protecting the baby from infections and allergens, thanks to special mechanisms they are quickly absorbed in the baby's stomach and intestines.
B) It has laxative properties to help the baby quickly get rid of the original stool - meconium, and also reduces the risk of physiological jaundice in the baby.
C) The mother triggers the oxytocin reflex, which contributes to uterine contraction and faster recovery after childbirth.
Thirdly, the correct position of the baby at the breast and the correct attachment of to the breast. Let's dwell on the key points.
For example, you feed sitting. How to hold a baby:
a) The child's body and head are on the same line.
b) The baby's belly should be turned towards the mother's belly and touch it.
c) The WHOLE body of the child must be supported.
The baby is brought to the breast with the NOSE to the nipple so that it is necessary to reach for the breast. When he opens his mouth wide, we press the baby to ourselves.
If it is not possible to attach the baby well, gently insert the little finger into the corner of the mouth and open the gums, remove the breast.
What does proper attachment look like? The baby's mouth is open wide; lips turned out; his chin touches his mother's breasts; areola capture radius is 2-3 cm from the base of the nipple; except for swallowing, sniffing and even breathing, no other sounds are heard (smacking, etc. ); mom is not in pain.
); mom is not in pain.
There are many positions for feeding - sitting, lying down, close at hand, relaxed feeding, etc.
Nuance: good breast sucking is affected by the frenum under the tongue of the baby, ask the pediatrician at the maternity hospital to check it. If it turns out to be short, it is better to cut it immediately.
Fourth, frequent breastfeeding . The term “on demand” is commonly used, which confuses many moms. Many people think that a baby "demands" when it cries. At the same time, crying is the last thing a hungry child decides to do.
Signs of readiness to suckle in a newborn :
Muscles tense in the child, for example, he clenched his fists and flexed his arms at the elbows.
The child rolls, twists and arches his back.
The child makes different sounds.
The child draws his hands to his mouth (even if his eyes are closed, he can suck his own hand).
If the child's hand is close to the face, he turns towards the hand, pokes, opens his mouth.
A newborn in the first 3 months of life may want to kiss 15-25 times a day. After all, his stomach is very small (on the 1st day after birth - 5-7 ml, on the 3rd day - 22-27 ml, on the 7th day - 45-60 ml) and breast milk is quickly absorbed. In addition to receiving nourishment, the child also finds comfort in his mother's breast. Therefore, it is not recommended to feed the baby "according to the regime" - for example, once every 3 hours or to limit his time at the breast - for example, to feed no more than 15 minutes. Night feedings are crucial for successful lactation - thanks to them, the level of prolactin is maintained at the required level.
Why frequent breastfeeding is important:
a) The number of prolactin receptors in the breast increases, which further contributes to sufficient milk production.
b) Promotes a more relaxed flow of milk, without pronounced symptoms of engorgement.
c) When feeding “according to the regimen”, there is a high risk that the child will be offended by the mother (after all, they do not immediately respond to his needs) and will behave restlessly at the breast.
Fifth, it is not recommended to give pacifiers to the child.
Why it's important:
a) Soothers artificially delay feeding time, resulting in poor weight gain and decreased milk production.
b) The child finds solace not at the mother's breast, but in a silicone object and may refuse the breast.
c) It spoils the grip of the breast, which leads to cracks, lactostasis.
Sixth, if it is necessary to supplement with expressed milk and/or formula, then avoid the use of bottles.
Why is this important:
A) The baby gets used to a strong and constant flow of milk from the bottle and begins to behave restlessly at the breast, “lazy” to suck.
B) When sucking a bottle and a breast, different muscle groups are used, so the grip on the breast often deteriorates, the child sucks milk poorly, gains weight worse.
Seventh, the joint sleep of mother and child.
It is perfectly normal to sleep with your baby. A child should not be spoiled with attention or held too much in his arms. The more children are held in their arms, the more attention is paid to them, the better they grow. The presence of the mother, her smell, constantly encourages him to suckle the breast more often, which means sucking out more milk.
Western parents are advised to leave their child to “shout out” before going to bed in order to raise an independent child who is used to loneliness and is able to calm himself. However, modern research shows that in this case, the child's brain is irreparably damaged.
Safe sleep:
- The child should sleep on a clean and hard surface.
- Avoid sleeping with your baby if you are overly tired.
- Do not leave your baby unattended in an adult bed.
- In cold weather, cover yourself with several layers of thin bed linen instead of one thick layer.
- Pets must not be in bed
- No one should smoke in the room where the baby sleeps.

Now consider some common cases:
- Mother's Rh negative or blood type incompatibility is not a contraindication to breastfeeding. Rh-conflict, blood type conflict or hemolytic disease of the newborn is not a contraindication. Rh antibodies are destroyed in the gastric juice of the newborn. Studies also show that in children with hemolytic disease, HB does not increase the breakdown of erythrocytes, red blood cells.
- The administration of anti-Rh immunoglobulin to prevent Rh conflicts in subsequent pregnancies in an Rh-negative mother is not a contraindication to breastfeeding. Anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin almost does not penetrate into breast milk. Most immunoglobulins are destroyed in the gastric juice of the newborn.
- Is it possible to breastfeed with jaundice?
Even with severe physiological jaundice in children in the first days of life, it is impossible to refuse breastfeeding. Early attachment of the baby to the breast and frequent feedings are an important factor in the prevention of jaundice, since colostrum, having a laxative effect, leads to a faster discharge of meconium (original feces). With insufficient nutrition of a newborn baby, jaundice may be more intense and prolonged due to the thickening of bile. (source - NATIONAL PROGRAM OF OPTIMIZATION OF FEEDING OF CHILDREN OF THE FIRST YEAR OF LIFE IN THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION, p.17).
With insufficient nutrition of a newborn baby, jaundice may be more intense and prolonged due to the thickening of bile. (source - NATIONAL PROGRAM OF OPTIMIZATION OF FEEDING OF CHILDREN OF THE FIRST YEAR OF LIFE IN THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION, p.17).
It is absolutely pointless to give the child water, glucose, activated charcoal, smectite, etc. in such a situation. - from this, the activity of liver enzymes, the function of which is reduced, will not increase. In some cases, it may be necessary to carry out phototherapy with special lamps, which can usually be rented from the hospital home.
- What to do if you are separated from your child?
It is recommended to express at least eight times a day. Whether you can pump something or not, breast stimulation is important to maintain and increase your milk supply.
If there is no joint stay in the maternity hospital, or if the baby was taken to the children's department for some medical reasons - do not hesitate to visit him and feed him there! If your and his condition allows, try to feed the baby only colostrum and then breast milk.
Try not to give supplements from a bottle, but from a spoon, pipette or syringe without a needle.
"Arrival" of milk.
Milk comes on 3-4 days after birth, less often - on 5-7. Your chest becomes hot, heavy, tight. If the mother rarely put the baby to the breast before, then engorgement may occur. At the same time, remember that you can do without pain and rough straining. Act according to the scheme: heat - light massage - removal of swelling from the areola - decant a little - attach the child - cold compress.
"Hard" straining, which is often used in the hospital, leads to severe swelling and worsening of the situation. Alcohol compresses, Vishnevsky ointment, etc. are not recommended.
How to remove swelling from the areola? Use the Pressure Softening technique introduced by international consultant Jean Kotterman.
It is necessary to evenly and gently press on the areola towards the chest and hold the pressure for at least a full minute (up to 2-3 minutes).
How to express properly? Fingers are placed on the border of the areola and white skin. First, the fingers are pressed in the direction of the chest: you seem to grab the milk-filled ducts that lie under the areola, and only then roll over them with your fingers. Important: the fingers do not fidget over the skin, they stand in one place on it.
How do you know if your baby is getting enough milk?
Newborns lose up to 6-10% of their birth weight in the first two days of their lives. This is a physiological norm. Most children regain their weight or begin to put on weight by 5-7 days of life.
- Wet diaper test .
Urination rate (per day) for a child under 10 days old = number of days + 1.
That is, for example, a 2-day-old baby who has enough milk pees 3 times a day.
Babies over 10 days of age should write 12 or more times a day.
These calculations are correct if there is no water addition and no drips.
- Weight set . The rate of weight gain for babies in the first 6 months of life is from 500 to 2000 g per month.
The set is not calculated from birth weight, but from the minimum (usually this is discharge weight). If the weight gain is less than 150g per week, we advise you to contact the AKEV specialists and the pediatrician.
- An infant should have at least 3-4 bowel movements per day (up to about 3-6 weeks). Then the chair is reduced - up to 1 time per day or less.
All other signs - baby crying, little pumping from the breast, no milk leakage, etc. - are not reliable signs of milk sufficiency / lack of milk .
Breastfeeding lifestyle:
- Care: it is recommended to wash the breasts 1-2 times a day while taking a shared shower (just water, no soap).
- Diet: you should not sit on a "dry ration", the menu should be varied and healthy (without the use of chemical additives), eat according to your appetite.