Baby milk and food
Cow’s Milk and Milk Alternatives | Nutrition
alert icon
Information about finding infant formula can be found
here.external iconAdditional information to help families during the infant formula shortage can be found
here.
Your growing child needs vitamins and minerals like vitamin D and calcium to build strong bones. Pasteurized, whole cow’s milk and soy beverages that have been fortifiedalert icon with vitamin D are good sources of vitamin D and calcium. Most cow’s milk sold in the United States is fortified with vitamin D.
Choose milk or milk alternatives that are unflavored and unsweetened. Flavored cow’s milk and fortified soy beverages can have added sugars. Your child does not need added sugars.
When Should I Introduce My Child to Cow’s Milk?
At 12 months old (but not before), your child can be introduced to cow’s milk. Before your child is 12 months old, cow’s milk may put him or her at risk for intestinal bleeding. It also has too many proteins and minerals for your baby’s kidneys to handle and does not have the right amount of nutrients your baby needs.
How Much, and How Often?
Cow’s milk or fortified soy beverages can be a part of a child’s balanced and diverse diet but not the only thing. The Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommend children aged 12 through 23 months get 1⅔ to 2 cup equivalents of dairy a day, including cow’s milk, yogurt, cheese, fortified soy beverages, and soy-based yogurt. If your child drinks too much cow’s milk, he or she may not be hungry for other foods with important nutrients. Some experts say that consuming too much cow’s milk can make it harder for your child’s body to absorb the iron he or she needs from foods.
Continue to follow your child’s cues to decide when he or she is hungry or full. Talk with your child’s doctor or nurse for more questions about adding cow’s milk or fortified soy beverages in his or her diet.
Whole Cow’s Milk or Lower Fat Cow’s Milk?
Children can drink unflavored, unsweetened whole cow’s milk. Whole cow’s milk is the same as lower fat cow’s milk except that it is higher in fat. It is important for young children to get fat in their diet for healthy growth and development. If your child has excessive weight gain or a family history of obesity, high cholesterol or triglycerides, or cardiovascular disease, talk to your child’s doctor or nurse about the type of cow’s milk to give.
Raw Milk
Raw milk and raw milk products from cows, goats, and sheep can carry harmful bacteria and other germs that can make your child very sick and can be life-threatening. Raw milk can also be called unpasteurized milk. Do not give your child raw or unpasteurized milk.
Milk Alternatives
Milk alternatives can include beverages made from plants, such as soy, oat, rice, coconut, cashew, and almond.
If you choose a milk alternative, here are things to remember:
- Milk alternatives should not be given before 12 months.

- Fortified soy beverages are the only milk alternative that help meet a child’s recommended dairy needs.
- Choose one that is unflavored and unsweetened. Your child does not need added sugars.
- Choose one that is fortified with vitamin D and calcium. Check labels, since nutrient content can vary between brands.
- Talk with your child’s doctor or nurse about the milk alternative you are using, because the vitamins and minerals in these types of milks are different than in cow’s milk.
Visit Vitamins & Minerals to learn more about the vitamins and minerals your child needs.
Top of Page
When, What, and How to Introduce Solid Foods | Nutrition
For more information about how to know if your baby is ready to starting eating foods, what first foods to offer, and what to expect, watch these videos from 1,000 Days.
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend children be introduced to foods other than breast milk or infant formula when they are about 6 months old. Introducing foods before 4 months old is not recommended. Every child is different. How do you know if your child is ready for foods other than breast milk or infant formula? You can look for these signs that your child is developmentally ready.
Introducing foods before 4 months old is not recommended. Every child is different. How do you know if your child is ready for foods other than breast milk or infant formula? You can look for these signs that your child is developmentally ready.
Your child:
- Sits up alone or with support.
- Is able to control head and neck.
- Opens the mouth when food is offered.
- Swallows food rather than pushes it back out onto the chin.
- Brings objects to the mouth.
- Tries to grasp small objects, such as toys or food.
- Transfers food from the front to the back of the tongue to swallow.
What Foods Should I Introduce to My Child First?
The American Academy of Pediatrics says that for most children, you do not need to give foods in a certain order. Your child can begin eating solid foods at about 6 months old. By the time he or she is 7 or 8 months old, your child can eat a variety of foods from different food groups. These foods include infant cereals, meat or other proteins, fruits, vegetables, grains, yogurts and cheeses, and more.
If your child is eating infant cereals, it is important to offer a variety of fortifiedalert icon infant cereals such as oat, barley, and multi-grain instead of only rice cereal. Only providing infant rice cereal is not recommended by the Food and Drug Administration because there is a risk for children to be exposed to arsenic. Visit the U.S. Food & Drug Administrationexternal icon to learn more.
How Should I Introduce My Child to Foods?
Your child needs certain vitamins and minerals to grow healthy and strong.
Now that your child is starting to eat food, be sure to choose foods that give your child all the vitamins and minerals they need.
Click here to learn more about some of these vitamins & minerals.
Let your child try one single-ingredient food at a time at first. This helps you see if your child has any problems with that food, such as food allergies. Wait 3 to 5 days between each new food. Before you know it, your child will be on his or her way to eating and enjoying lots of new foods.
Introduce potentially allergenic foods when other foods are introduced.
Potentially allergenic foods include cow’s milk products, eggs, fish, shellfish, tree nuts, peanuts, wheat, soy, and sesame. Drinking cow’s milk or fortified soy beverages is not recommended until your child is older than 12 months, but other cow’s milk products, such as yogurt, can be introduced before 12 months. If your child has severe eczema and/or egg allergy, talk with your child’s doctor or nurse about when and how to safely introduce foods with peanuts.
How Should I Prepare Food for My Child to Eat?
At first, it’s easier for your child to eat foods that are mashed, pureed, or strained and very smooth in texture. It can take time for your child to adjust to new food textures. Your child might cough, gag, or spit up. As your baby’s oral skills develop, thicker and lumpier foods can be introduced.
Some foods are potential choking hazards, so it is important to feed your child foods that are the right texture for his or her development. To help prevent choking, prepare foods that can be easily dissolved with saliva and do not require chewing. Feed small portions and encourage your baby to eat slowly. Always watch your child while he or she is eating.
To help prevent choking, prepare foods that can be easily dissolved with saliva and do not require chewing. Feed small portions and encourage your baby to eat slowly. Always watch your child while he or she is eating.
Here are some tips for preparing foods:
- Mix cereals and mashed cooked grains with breast milk, formula, or water to make it smooth and easy for your baby to swallow.
- Mash or puree vegetables, fruits and other foods until they are smooth.
- Hard fruits and vegetables, like apples and carrots, usually need to be cooked so they can be easily mashed or pureed.
- Cook food until it is soft enough to easily mash with a fork.
- Remove all fat, skin, and bones from poultry, meat, and fish, before cooking.
- Remove seeds and hard pits from fruit, and then cut the fruit into small pieces.
- Cut soft food into small pieces or thin slices.
- Cut cylindrical foods like hot dogs, sausage and string cheese into short thin strips instead of round pieces that could get stuck in the airway.

- Cut small spherical foods like grapes, cherries, berries and tomatoes into small pieces.
- Cook and finely grind or mash whole-grain kernels of wheat, barley, rice, and other grains.
Learn more about potential choking hazards and how to prevent your child from choking.
Top of Page
Manufacturers have warned of a possible increase in prices for baby food - Agroinvestor
The baby food industry is not experiencing problems associated with a high level of counterfeiting A. Gordeev The business proposes to exclude products for children from the labeling experiment for canned meats, vegetables and fruits. This follows from a letter from the association of manufacturers "Rusbrand" (includes Nestle, Danone, etc.) to the Ministry of Economic Development, which Izvestia has read. The letter notes that for foreign products, the developer offered more expensive technical solutions, which threatens with a shortage of goods on the shelf and an increase in prices "by at least 10%". nine0003
nine0003
The level of imports in this segment is 25-30%, Rusbrand estimates. Also, the association does not understand what problem labeling will solve, because there are no known cases of counterfeiting in the industry recorded by regulators: the industry has established state control over the production, distribution and sale of baby food, increased requirements are imposed on raw materials and materials, and the finished product is packaged in sealed packaging, which undergoes sterilization.
The Ministry of Industry and Trade proposes to conduct an experiment on labeling canned food for children from vegetables and meat, as well as jams, jellies and nut butters from May 1, 2022 to February 28, 2023. The draft government decree on the experiment was prepared on behalf of the president. An objective assessment of the costs of introducing marking is possible only during the experiment; support measures have been developed for the companies participating in it, including soft loans for the purchase of marking equipment, says a representative of the department. nine0003
nine0003
Chairman of the Board of the Dairy Union of Russia Lyudmila Manitskaya told Agroinvestor that baby food is not getting more expensive because of labeling. “Prices in this segment will increase for the same reason as for other products: the cost of all components of production is growing. We are talking about fuel, electricity, imported components and so on. In addition, inflation is rising, and the ruble is weakening, ”commented Manitskaya. According to her, falsified products are periodically found in the baby food segment. “Full-fledged labeling for baby food has not yet been introduced, so we do not yet understand how it will work and how it will protect the buyer,” added Manitskaya. nine0003
Dmitry Leonov, Deputy Chairman of the Board of Rusprodsoyuz, is sure that labeling will invariably lead to an increase in prices on the shelf. According to the most modest forecasts, the growth per unit of goods will be from 10%, he believes. “In a situation of rising prices for all components of the cost of production - raw materials, logistics, packaging - and the ongoing trend of falling incomes of the population, the introduction of an additional financial burden on both business and consumers is unacceptable.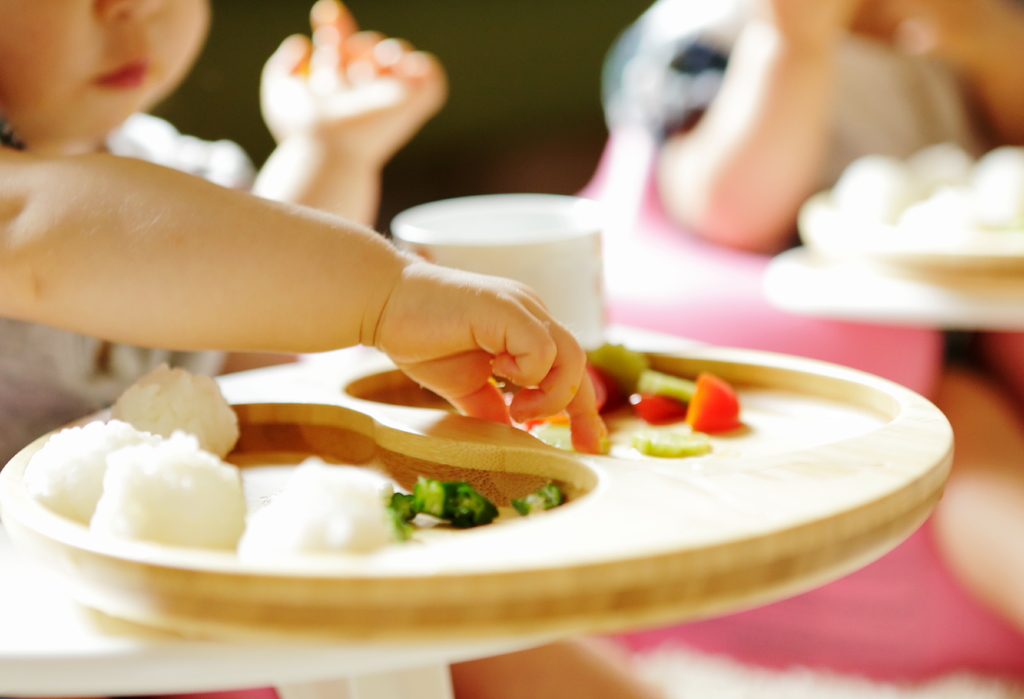 According to dairy producers, where labeling has already been introduced, it has become one of the most expensive regulatory measures in the history of the sector,” Leonov told Agroinvestor. nine0003
According to dairy producers, where labeling has already been introduced, it has become one of the most expensive regulatory measures in the history of the sector,” Leonov told Agroinvestor. nine0003
In his opinion, the introduction of mandatory labeling for certain categories must be approached "extremely balanced and cautious." It is worth starting with independent research of the counterfeit market in these categories and discussion with the business community of all the risks and expediency of labeling. The total introduction of labeling without objective indicators of a high level of counterfeiting in a category is fraught with a significant increase in prices for many groups of goods, Leonov warns.
The baby food industry is not experiencing problems with high levels of counterfeiting, he continues, adding that these may be isolated cases. This is due to rather strict state control over the production and sale of baby food at all levels "from the field / farm to the counter. " “Increased requirements are imposed on raw materials, equipment and materials that are used for the preparation of children's preservation. In addition, products for children do not go through a simplified procedure for declaring safety, but a strict certification system,” Leonov emphasizes. nine0003
" “Increased requirements are imposed on raw materials, equipment and materials that are used for the preparation of children's preservation. In addition, products for children do not go through a simplified procedure for declaring safety, but a strict certification system,” Leonov emphasizes. nine0003
CRPT specialists are confident that information about the impact of labeling on the cost of baby food "does not correspond to reality and is not supported by calculations." “Having looked at the price dynamics in those industries for which labeling has already become mandatory, we can make an unambiguous conclusion that in none of the industries, labeling has led to price increases that buyers could notice,” said Revaz Yusupov, Deputy General Director of the Advanced Technologies Development Center. (quote from the center). “We are convinced that in this industry, too, all these apocalyptic forecasts will remain nothing more than forecasts.” nine0003
Whole milk. Food for a child.

Milk is one of the important foods for babies. But in order for the child’s acquaintance with him to be successful and bring only benefits to the baby, you need to know how and when to introduce milk into the crumbs menu.
Almost all types of dairy products can be used in the nutrition of a child, but the timing of their introduction is different, and the products themselves are prepared according to a special, "children's" technology. The baby begins to get acquainted with this group of products quite late - at about 9For months, fermented milk products are introduced, and milk itself is used as the basis for cereals.
In the past, the timing of complementary milk feeding was different, and many "old school" pediatricians sometimes recommend regimens developed in the late 1980s. These outdated data are still found on the labels of many industrial dairy products, because no documents regulating them have yet been developed. However, they still should not be guided by, because the new terms of introduction are based on the latest studies of domestic and foreign pediatricians over the past 20–30 years and are scientifically substantiated. nine0004
nine0004
WHOLE MILK
Pediatricians do not get tired of repeating the indisputable truth that the best food for a baby is mother's milk. However, circumstances vary, and if your baby is unable to breastfeed for some reason, work with your doctor to find a good, highly adapted formula.
Now the choice of mixtures is quite extensive both in terms of the composition of its components and in terms of pricing policy. Feed the artificial baby until 8-9months of age with whole milk of animals (cow, goat, sheep and others) is in no case impossible. Unreasonably early introduction of whole milk is dangerous because it can cause a lot of health problems in a child. Not only is the milk itself low in iron, but it also provokes its increased loss from the body of the crumbs.
Long-term studies have been conducted, as a result of which it has been proved that unreasonably early complementary foods introduced into the child's menu - vegetable purees on whole milk from 3 months, cereals on whole cow's milk from 4 months of age - provoke an increased loss of hemoglobin. And this, in turn, a high risk of developing iron deficiency anemia in children. Babies 4-7 months of age are especially susceptible to this, when their iron stores are depleted, and the supply of new ones is difficult. nine0004
And this, in turn, a high risk of developing iron deficiency anemia in children. Babies 4-7 months of age are especially susceptible to this, when their iron stores are depleted, and the supply of new ones is difficult. nine0004
Early introduction of milk may cause the baby to refuse breastfeeding or formula feeding with a very different taste of cow's milk, which will cause additional feeding difficulties.
Animal milk is too high in protein compared to breast milk or formula, and too high in sodium salts. This leads to an excessive load on the baby's excretory system and its vessels. In terms of nutrients, whole cow's milk contains more other minerals (calcium, phosphorus, chlorine, magnesium and potassium), few healthy carbohydrates, essential fatty acids (linoleic, alpha-linolenic) and long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids, iron, zinc, vitamin C and niacin. nine0004
Not unimportant is lactose intolerance, which is quite abundant in cow's milk. In addition, the proteins in it are potentially allergenic for an infant. This, by the way, is fundamentally different from goat's milk, which we will talk about a little later.
This, by the way, is fundamentally different from goat's milk, which we will talk about a little later.
Therefore, we will postpone acquaintance with whole cow's milk for the second year of the baby's life and start it with 100 ml per day. However, it is worth noting that in the preparation of baby food, milk can be successfully used even earlier: in cereals and puddings from 8 months, in fermented milk products from 9 months.months.
The minerals that make up the milk are perfectly correlated with each other. For example, the ratio of calcium and phosphorus in milk is 2:1 - the ideal proportion for the absorption of calcium in the body.
WHAT ARE THE ADVANTAGES OF GOAT MILK FORMULA?
Aleksey Rykunov, family doctor (GMS clinic), expert on MD mil products:
Goat milk formulas can be an appropriate substitute or essential addition to breast milk. The mixture should be adapted (with the addition of whey proteins), with nucleotides and prebiotics. A worthy example is the MD Mil Goat mixture, which also includes docosahexaenoic acid, which contributes to the development of the child's intellect. nine0004
A worthy example is the MD Mil Goat mixture, which also includes docosahexaenoic acid, which contributes to the development of the child's intellect. nine0004
Key benefits:
1. Goat milk formulas are less allergenic, they do not contain α-1S-casein and γ-casein, the main allergens in cow's milk.
2. Cow's and goat's milk proteins are different in structure, so babies with intolerance to cow's milk proteins can easily digest goat's milk formulas.
ARGUMENTS FOR MILK
Another thing is the use of milk in children older than a year - here it will show all its beneficial properties. Milk contains all the necessary groups of nutrients at the same time: building proteins for muscles, calcium for the skeleton. Under the influence of digestive juice, milk proteins are easily broken down into amino acids, building blocks for building a child's body, among which there are irreplaceable ones, so they must be obtained from food. nine0004
nine0004
Enough content in milk of energy substances - fats and milk sugar. Dairy fats are in the composition of milk in the form of an emulsion, and therefore they are easy to break down and assimilate by the digestive enzymes of the crumbs that have matured by this time. Fat also contains a whole set of biologically active substances (unsaturated fatty acids, phosphatides, fat-soluble vitamins), which are essential for the growing body of a child. One of the important elements of milk is milk sugar - lactose. It is an excellent source of energy: it is easily digested and gives a feeling of satiety. In addition, it also contributes to the development of beneficial microflora in the intestines of children - bifidobacteria, which have protective properties against gastrointestinal disorders. nine0004
In addition, it contains substances that regulate metabolism: vitamins, minerals and enzymes. In addition to calcium, it also contains phosphorus, potassium, sodium, magnesium, iron and a number of others. All of them are found in milk in a form that is easily absorbed by the body. Milk contains many well-known vitamins, especially fat-soluble (A, E, D) and part of the B vitamins (B1, B2, B12, PP) and others. However, their number depends on the season of milk collection (summer or winter), the food base, the state of health and breed of the animal, the methods of obtaining milk, its storage and processing method. nine0004
All of them are found in milk in a form that is easily absorbed by the body. Milk contains many well-known vitamins, especially fat-soluble (A, E, D) and part of the B vitamins (B1, B2, B12, PP) and others. However, their number depends on the season of milk collection (summer or winter), the food base, the state of health and breed of the animal, the methods of obtaining milk, its storage and processing method. nine0004
Milk has a positive effect on the functioning of the digestive system as a whole, because the digestion and assimilation of milk protein requires 3-4 times less effort than other products. That is why milk and its derivatives are actively used in baby food and diets.
So the song “Drink, children, milk, you will be healthy”, familiar from childhood, is absolutely true for babies after a year.
Introduction to whole cow's milk should start when the baby is one year old nine0004
GOAT MILK
For infants with hypersensitivity or allergy to cow's milk protein, goat's milk or infant formula based on it becomes a nutritional alternative. The protein composition of this milk is different from cow's and rarely causes allergic reactions. So, according to scientists, nine out of ten people who are allergic to cow's milk perfectly tolerate goat's. This is because goat's milk protein is closer in structure to women's milk proteins. In the stomach of babies, the proteins of any milk coagulate and turn into clots. However, goat milk, like breast milk, curdles into softer and smaller flakes than cow milk. The result is a lump that is smaller in size and density. And that means it's easier to digest. In addition, goat's milk lacks the same protein that cow's milk often causes allergies in children. Eating goat milk can reduce not only the manifestations of allergies, but also its complications. nine0004
The protein composition of this milk is different from cow's and rarely causes allergic reactions. So, according to scientists, nine out of ten people who are allergic to cow's milk perfectly tolerate goat's. This is because goat's milk protein is closer in structure to women's milk proteins. In the stomach of babies, the proteins of any milk coagulate and turn into clots. However, goat milk, like breast milk, curdles into softer and smaller flakes than cow milk. The result is a lump that is smaller in size and density. And that means it's easier to digest. In addition, goat's milk lacks the same protein that cow's milk often causes allergies in children. Eating goat milk can reduce not only the manifestations of allergies, but also its complications. nine0004
Let's take a closer look at the advantages and disadvantages of goat's milk, and note that there are not so many of the latter.
Disadvantages. Goat milk is deficient in iron and vitamins A and D, and low in folate compared to breast milk. But given that it is introduced from 9 months, the missing need for the listed substances can be easily compensated for with other complementary foods. Many opponents of goat milk consider its taste unpleasant and specific, although the actual taste of goat milk depends on the conditions under which the animal was kept, as well as on the quality of the feed. nine0004
But given that it is introduced from 9 months, the missing need for the listed substances can be easily compensated for with other complementary foods. Many opponents of goat milk consider its taste unpleasant and specific, although the actual taste of goat milk depends on the conditions under which the animal was kept, as well as on the quality of the feed. nine0004
Dignity. Goat milk is a valuable product for the child, strengthening the immune system due to its composition, and regular consumption of goat milk can help in the mineralization of the bones of the skeleton. By itself, milk is more homogeneous, contains more free nitrogen, its protein composition is more diverse and better, it is increased in thiamine content, and it belongs to the most important B vitamins, without which a person is not able to do in any of the periods of life. It is also useful for diathesis, gastric and many other diseases. nine0004
For children from 9-12 months of age, the use of goat's milk does not pose any danger, since the lack of nutrients is compensated by a more varied menu than in infants. On the contrary, thanks to the inclusion of goat's milk in the child's diet, the treatment of diseases such as eczema or frequent colds and ear infections is much faster and more effective. Goat milk contains a sufficient amount of vitamin PP, which helps to improve oxidative processes in the body. Goats do not suffer from tuberculosis, brucellosis, and other diseases that cows suffer from, which means they cannot betray them to a child. nine0004
On the contrary, thanks to the inclusion of goat's milk in the child's diet, the treatment of diseases such as eczema or frequent colds and ear infections is much faster and more effective. Goat milk contains a sufficient amount of vitamin PP, which helps to improve oxidative processes in the body. Goats do not suffer from tuberculosis, brucellosis, and other diseases that cows suffer from, which means they cannot betray them to a child. nine0004
Fresh goat milk has bactericidal properties because it contains biologically active substances. Thanks to this, goat's milk stays fresh for a long time. It does not turn sour for three days at room temperature, and can be stored in the refrigerator for more than a week. For the same reason, fresh milk is most useful, and then every hour its valuable qualities are lost. Goat milk contains a lot of potassium, the role of which is especially great in the activity of the cardiovascular system. Goat milk contains a lot of cobalt, which is part of vitamin B12, which is responsible for hematopoiesis and controls metabolic processes. nine0004
nine0004
Goat's milk contains less lactose (milk sugar) than cow's milk, so it does not cause diarrhea and is suitable for those who are lactose intolerant. In addition, goat milk contains lysozyme, a substance that has wound healing properties. That is why it is used for diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, and is also actively added to children's cosmetics.
Adding goat's milk to cereals increases their nutritional value, improves the balance of amino acids and some mineral salts. At the same time, cereals enrich milk with an important amino acid, arginine, which promotes growth, which is especially important for young children. In milk, cereals such as rice, millet, pearl barley are poorly boiled soft. They are boiled first in water and then poured with boiling milk. nine0004
Globulins contained in milk are involved in the synthesis of immune bodies, thus forming immunity. Therefore, milk is especially useful during a cold.
CREAM AND SOUR CREAM
Cream is a derivative of milk that contains a lot of fat.