Feeding premature babies formula
Formula Feeding a Premature Infant
Parents choose to bottle-feed babies for many reasons. Here are some tips to help you be successful feeding your preemie with formula.
What kind of formula should I use?
Be sure to use the type of formula and the concentration that were prescribed when your baby was discharged. Preemie formulas and "follow-up" formulas are specially designed for premature babies. These may be better for your baby than regular formulas. With many formulas, the brand is not important but the content is. Most babies should be taking cow-milk-protein-based formula with iron. Ask your baby's healthcare provider if you have questions. Always wash your hands before preparing formula.
If using powder:
Follow package directions for mixing. Make sure you use the right amount of water and powder. Too much, or too little water can cause diarrhea, constipation, or other problems for your baby.
Try mixing with room temperature water in a blender to help dissolve the powder.
If you have any concerns about the safety of your water supply, use bottled water. You can check with your local health department to help determine whether your water supply is safe.
Use all of the powder within one month after opening the package.
Keep mixed formula in the refrigerator when not in use. Don’t keep mixed formula for longer than 24 hours.
Don't use the leftover formula from a partially finished bottle. Once a bottle of formula has been at room temperature for an hour, it needs to be discarded.
If using concentrate:
Follow package directions for mixing. Make sure you use the right amount of water. Too much, or too little water can cause diarrhea, constipation, or other problems for your baby.
Seal the package and keep it in the refrigerator after opening.
Use within 48 hours of opening the package.
Never heat a bottle of formula in the microwave. The liquid may heat unevenly and can burn your baby's mouth.
The liquid may heat unevenly and can burn your baby's mouth.
How do I know when my baby needs to be fed?
Preemies may not cry when they’re hungry. Instead, they may move around and become restless. Get to know your baby’s cues. If your baby is feeding less than the recommended amount, or not gaining weight on schedule, tell your baby’s healthcare provider.
Ask your healthcare provider:
How often should I feed my baby? ________________
How much should I feed my baby?
How much weight should my baby gain per week? _____________
Caring for bottles and other equipment
If your baby drinks from a bottle but does not finish all of the formula within 1 hour, discard the remaining liquid and give your baby a new bottle at the next feed.
Glass and metal items can be washed in a dishwasher. The following items should be hand washed in hot soapy water and rinsed in hot, clean water:
|
|
How to Feed Preemie Babies
Feeding Your Premature Baby
Whether you choose to breastfeed or formula feed, meal time is an important opportunity for bonding with your baby. Here are a few tips to help you both have a successful experience.
Here are a few tips to help you both have a successful experience.
If you choose to formula feed, ask your baby's doctor which formula is appropriate for your baby.
If you choose to breastfeed, ask your baby's doctor if supplements and vitamins are appropriate for your baby.
In This Article
About Formula | Preparing Bottles | Feeding Your Baby | How to Tell if Your Baby's Getting Enough to Eat | What You Can Learn From Her Diaper
About Formula
Ready-to-use and Concentrated Liquid infant formulas are commercially sterile in the sealed container.
Powdered infant formulas are not sterile and should not be fed to premature infants or infants who might have immune problems, unless directed and supervised by your baby's doctor.
Remember that improper hygiene, preparation, dilution, use or storage may result in severe harm.
Ask your baby's doctor which formula is appropriate for your baby.
» Return to top
Preparing Bottles
- Wash everything—bottles, nipples, and caps—in hot, soapy water before using.

- Check with your baby's doctor about the need to use cooled, boiled water for mixing and the need to boil clean utensils, bottles, and nipples in water before use.
- To prepare your baby's formula, make sure you follow the label directions.
- Once prepared, infant formula can spoil quickly.
- After opening, containers of liquid formula need to be fed immediately or covered and refrigerated and used within 48 hours.
- Formula prepared from powder needs to be fed immediately or covered and refrigerated and used within 24 hours (check product label for specific guidelines).
- Most babies don't seem to mind whether their bottle is warmed or straight out of the refrigerator. Some may prefer a consistent temperature from one feeding to the next.
- If you want to warm a bottle that has been in the refrigerator, run warm tap water over the bottle or place the bottle in a pan of hot (not boiling) water. Take care that the cap and nipple do not get wet.

- Shake the bottle occasionally while warming. The warming time should be less than 15 minutes.
- Test the formula temperature before feeding; it should not feel warm or cold when dropped on your hand—neutral is close to body temperature (about 100°F). Warmed formula should be discarded within one hour.
- Discard formula remaining in the bottle within one hour after feeding begins.
WARNING: Never warm formula in a microwave. Serious burns can result.
» Return to top
Feeding Your Baby
Whether you're breastfeeding or bottle-feeding your baby, use these guidelines as you learn more about your baby's feeding schedule:
- Support your baby's head during feedings, keeping it higher than her stomach. This aids in digestion and helps avoid ear infections.
- Your baby will eat at her own pace. You'll soon recognize her pattern of swallowing and breathing. Babies who eat slowly seem to take more milk at each feeding and may be satisfied and sleep longer between feedings.

- If your baby ever seems to have trouble catching her breath while eating, or is coughing, choking, or sputtering, sit her up until she seems ready to eat again.
- Keep feedings relaxed, with as few interruptions as possible.
- Keep your baby from swallowing air by keeping the bottle nipple full of formula. She shouldn't suck on an empty bottle or drain the bottle.
- When your baby is finished eating, the nipple will fall out of her mouth and her whole body will become relaxed. Your baby will probably need about 20 to 30 minutes to finish her bottle.
- If she seems finished after only 15 or 20 minutes, you may want to wake her and try to get her to eat for a little longer. If possible, you want her to feel full enough to be satisfied for another few hours.
Feeding Tips
- It's important to hold the bottle at a 45-degree angle so your baby can get the right suction.
- Your baby may need to eat on demand—or may feed well on a newborn schedule.
 A breastfed baby usually has 8 to 12 feedings in 24 hours, while a bottle-fed baby may have 8 to 10 feedings during that time. Whatever feeding method you choose, your baby will need small, frequent feedings around the clock.
A breastfed baby usually has 8 to 12 feedings in 24 hours, while a bottle-fed baby may have 8 to 10 feedings during that time. Whatever feeding method you choose, your baby will need small, frequent feedings around the clock. - You may need to wake your baby every three hours or so if she's sleeping through a feeding. Wake your baby gently by removing her blanket or stroking her arms and legs. Don't rush her or she may be too upset to eat.
- Once she's wide awake, hold her, and touch your nipple, or the bottle nipple, to her cheek or lip. She'll be encouraged to open her mouth and turn toward it to eat.
- If your baby takes less than 15 minutes to eat, you may want to use a nipple with a smaller hole. If she takes longer than normal and doesn't seem to be sucking actively, make sure the nipple hole isn't clogged.
» Return to top
How To Tell If Your Baby's Getting Enough To Eat
- The best way to tell if your baby's getting enough to eat is to check her growth.
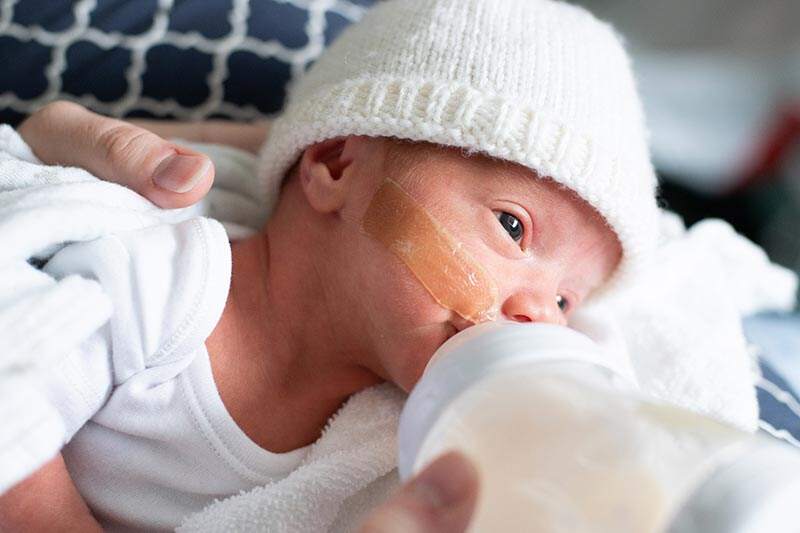 She should be gaining about an ounce a day during the first few weeks home from the hospital.
She should be gaining about an ounce a day during the first few weeks home from the hospital. - During the first few months, her doctor will carefully watch her weight gain to make sure it's increasing steadily. Also, if your baby has six or more wet diapers a day and seems happy between feedings, she's probably getting plenty to eat.
- Your baby may give you signs when she's had enough to eat. She may fall asleep or close her mouth and turn away from her bottle. She may also bite or play with the bottle nipple, or even fuss if you keep trying to feed her. Follow your baby's lead.
If you're worried that your baby isn't eating like she should, talk with the pediatrician. If you notice any of these signs, take your baby to the doctor:
- Constant or inconsolable crying
- You cannot wake your baby
- Consistent feeding refusals
- Persistent coughing, choking, or breathing problems
- Noticeably fewer wet or soiled diapers
» Return to top
What You Can Learn From Her Diaper
Breastfed babies usually have softer, yellow stools. Formula-fed babies usually have yellow, brown, or green stools. Occasional changes in the color and consistency of stools are normal.
Formula-fed babies usually have yellow, brown, or green stools. Occasional changes in the color and consistency of stools are normal.
» Return to top
You may also like
Premature and Small Birth Formulas: The Best Milk Formulas for Weight Gain
09/23/2019 Reading time: 3.5 min 57906 nine0010
Contents of the article
- Premature babies - who are they?
- What is the best formula for premature babies?
- What should be in the pre-blend?
- How long should the pre-mix be used?
Premature babies - who are they?
Premature is considered to be children who, for some reason, were born prematurely - before the 38th week of pregnancy (with a period of less than 37 full weeks). nine0010
nine0010
What is the best formula for premature babies?
For newborns born before the planned date of birth, breast milk is definitely the best food. The milk of a mother who gave birth to a baby earlier than expected is energetically more valuable and nutritious, it has a higher content of proteins, fats and protective immune substances. Unfortunately, a woman who has given birth to a child prematurely cannot always fully provide the baby with breast milk, and sometimes milk does not come at all. nine0010
To solve this problem, specialized milk formulas for premature babies have been developed. Such mixtures can be recognized by the presence of the word "PRE" in the title. All milk PRE-mixes are distinguished by a higher nutritional and energy value. Infant formula for premature babies contains more proteins, fats and other important nutritional nutrients that an immature baby needs. Also in these mixtures, the amount of lactose is reduced to avoid additional burden on the child's digestion. nine0010
nine0010
What should be in the pre-mix?
Infant formula for premature babies should contain an increased amount of the main food ingredients: proteins, fats, the energy value of the pre-mixture is higher. When choosing a mixture, pay attention to the presence of certain components in the composition:
- Omega-6 and omega-3 - essential fatty acids for the development of the child's intelligence and brain nine0023
- Nucleotides - are necessary for the proper formation of immunity and digestion
- Inositol - promotes lung development
- Choline - needed to improve the functioning of the cells of the brain and nervous system
- MCT (medium chain triglycerides) - fatty component in a special, easily digestible form
- L-carnitine- improves fat absorption
How long should I use the pre-mix?
Feeding with a special PRE-mixture should be continued until the baby reaches a weight of 3000 g, after which the child is gradually transferred to the usual adapted infant formula.
If necessary and according to the indications of a doctor, infant formula for premature babies can remain in the baby's diet for several months in the amount of 1-2 feedings. nine0010
Premature and LBW Formulas: Milk Formulas for Weight Gain - Baby Food for PrematurityWhat does Nutrilak offer?
Nutrilak Premium PRE - Premature Infant Formula is formulated to meet all the needs of preterm babies.
This is the only formula for premature babies that contains milk fat. The presence of this important component brings composition 9 as close as possible0039 Nutrilak Premium PRE for breast milk. Milk fat contains important nutrients necessary for the formation of the brain, and is also a source of energy for the speedy growth of premature babies. Nutrilak Premium PRE contains all the components necessary for a premature baby: MCT (medium chain triglycerides), high levels of inositol and choline, nucleotides, essential omega-3 and 6 fatty acids, prebiotics. nine0010
nine0010
Powdered milk formula Nutrilak Premium PRE was created jointly with the Scientific Center for Children's Health of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation.
(14 ratings; article rating 3.0)
Features of feeding premature babies
Successful nursing of premature newborns, in addition to therapeutic measures, largely depends on the creation of optimal external conditions and adequate nutrition. According to modern theory of nutrition programming the quantity and quality of nutrients supplied during the prenatal period and the first months of a child's life determines the nature of metabolism and, as a result, affects the state of human health throughout later life.
Proper and nutritious nutrition in the early stages of life affects the overall development of the child, and also contributes in direct proportion to reducing the development of chronic diseases in adulthood (such as diabetes and arterial hypertension). nine0010
nine0010
The purpose of enteral nutrition is to provide the body with the nutrients it needs to grow and develop.
Providing a premature newborn with an optimal amount of nutrients is quite difficult, given the morphofunctional immaturity of the digestive system and the lability of metabolic processes. The relatively high need of premature infants for nutrients is in conflict with the limited ability to assimilate them.
Feeding methods for premature babies are determined by the severity of their condition and depend on the body weight and gestational age of the baby at birth.
Successful feeding of a newborn is possible when sucking, swallowing and breathing become well coordinated.
The swallowing reflex is well developed by 28-30 weeks of gestational age, but it is very quickly depleted. Fully matures by 34 weeks of gestation. When does sucking and swallowing coordinate? Already at 28 weeks of gestational age, all the components of sucking and swallowing take place, but the child is not yet able to coordinate them. Partially, this occurs by 32-34 weeks of gestation. Coordination of sucking and swallowing fully matures around 36-38 weeks of gestational age. From 37 to 38 weeks of gestational age, newborns are able to coordinate sucking, swallowing, and breathing without difficulty. nine0010
Partially, this occurs by 32-34 weeks of gestation. Coordination of sucking and swallowing fully matures around 36-38 weeks of gestational age. From 37 to 38 weeks of gestational age, newborns are able to coordinate sucking, swallowing, and breathing without difficulty. nine0010
When feeding premature babies, you should pay attention to four points: when, what, how much, what method to feed .
It is advisable to start the first feeding as soon as it becomes clinically possible. Earlier introduction of breast milk helps to reduce the frequency of infections, maturation of the gastrointestinal tract, immune functions, and improved calcium metabolism.
Newborns weighing more than 2000 g and gestational age more than 33 weeks, who do not have other diseases, can be attached to the mother's breast as early as the first day of life. In this case, you should carefully monitor the appearance of signs of fatigue (cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle, shortness of breath, etc. ). Their appearance is an indication for the transition to feeding expressed breast milk from a bottle. Efforts should be aimed at preserving breast milk as much as possible, taking into account the special biological value of mother's native milk for an immature child and the important role of mother-child contact during feeding. For premature babies, free feeding is unacceptable due to their inability to regulate the amount of sucked milk and the high incidence of perinatal pathology. nine0010
). Their appearance is an indication for the transition to feeding expressed breast milk from a bottle. Efforts should be aimed at preserving breast milk as much as possible, taking into account the special biological value of mother's native milk for an immature child and the important role of mother-child contact during feeding. For premature babies, free feeding is unacceptable due to their inability to regulate the amount of sucked milk and the high incidence of perinatal pathology. nine0010
Babies born before 33 weeks' gestation are usually tube-fed to avoid the risk of aspiration resulting from a lack of coordination between sucking and swallowing. With a non-severe condition of the child and a body weight approaching 2000 g, a trial feeding from a bottle can be carried out, with unsatisfactory sucking activity, tube feeding is prescribed in full or in part. In order to maintain and maintain lactation in the mother, regular expression of breast milk is necessary. nine0010
Enteral feeding of very preterm infants (weighing less than 1500 g and less than 30 weeks' gestation) is carried out through a tube.
The caloric method is used to calculate the required amount of feeding for premature babies. The calorie content of the diet of a prematurely born child increases gradually and daily.
Caution and Graduality Feeding Guidelines for Premature Babies Less Than 33 Weeks Gestational Age Less Than 2000g
For a premature baby, the best bioavailability is the milk of a woman who has given birth prematurely, then formulas for premature babies, and then the milk of a woman who has given birth at term.
Women's milk after preterm birth has a special composition, it contains more protein, less lactose with the same total level of carbohydrates. In addition, it has a higher content of a number of protective factors, in particular lysozyme and secretory IgA. Despite the special composition, the milk of women who gave birth prematurely can satisfy the nutritional needs of only premature babies with a relatively large body weight - more than 1800-2000 g. Premature babies with a lower body weight are deficient in a number of nutrients. For them, breast milk must be further enriched with protein, calcium, phosphorus, iron, and vitamins. This can be achieved by replacing part of the required amount of breast milk with a specialized formula for premature babies or by adding breast milk enhancers. When enrichers (enhancers) are used, the main advantages of breastfeeding are preserved and at the same time the high nutritional requirements of the premature baby are ensured. With artificial feeding, specialized mixtures intended for feeding premature babies should be used. Cancellation of specialized mixtures for premature babies and their transfer to standard milk formulas is carried out gradually. The duration of use depends on the gestational age of the child. Premature babies with a gestational age of more than 31-33 weeks should receive specialized formulas until they reach a body weight of 2500-3000 g, after which they are completely transferred to standard adapted milk formulas.
Premature babies with a lower body weight are deficient in a number of nutrients. For them, breast milk must be further enriched with protein, calcium, phosphorus, iron, and vitamins. This can be achieved by replacing part of the required amount of breast milk with a specialized formula for premature babies or by adding breast milk enhancers. When enrichers (enhancers) are used, the main advantages of breastfeeding are preserved and at the same time the high nutritional requirements of the premature baby are ensured. With artificial feeding, specialized mixtures intended for feeding premature babies should be used. Cancellation of specialized mixtures for premature babies and their transfer to standard milk formulas is carried out gradually. The duration of use depends on the gestational age of the child. Premature babies with a gestational age of more than 31-33 weeks should receive specialized formulas until they reach a body weight of 2500-3000 g, after which they are completely transferred to standard adapted milk formulas.