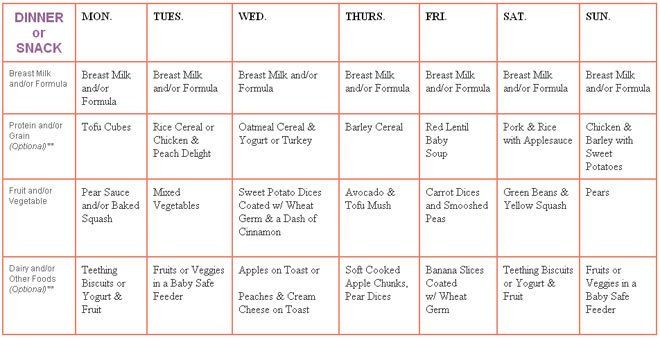
Feeding a baby too much
How To Tell If You're Overfeeding Baby
We spend so much time fussing over whether baby is getting enough formula or breast milk—and for new parents it can be hard to tell what’s actually enough. Many parents may try to coax baby to finish their bottle or worry that baby isn’t eating enough, when really, baby has just had their fill. So can that well-intentioned fussing possibly lead to overfeeding baby?
Keep in mind that signs of a healthy baby may differ across cultures. “Different cultures have different feelings about how much a baby should eat, how often they should eat and what they should look like,” says Alanna Levine, MD, a pediatrician at Orangetown Pediatric Associates in Orangeburg, New York. Some parents consider a roly-poly baby a sign of a job well done, while other parents see a round baby and visualize an obese teen.
While cultural perceptions of a healthy baby may vary, when it comes to feeding, there are few things to keep in mind. Read on to learn how overfeeding baby can happen, signs to look for and what to do going forward.
In this article:
Can you overfeed a baby?
What leads to overfeeding?
Signs of overfeeding baby
How to avoid overfeeding baby
Can You Overfeed a Baby?
You can probably breathe a sigh of relief: Overfeeding baby is almost impossible, and most of the anxiety over babies’ food intake and appearance is pointless. “If baby is gaining weight and growing and your pediatrician isn’t concerned, you don’t need to worry,” Levine says. Different babies grow at different rates and eat different amounts at different times.
Babies come with an incredibly sophisticated self-regulation system: When they’re hungry, they eat, and when they’re full, they stop. (Sadly, we’ve lost this mechanism by the time we become parents.) So when babies turn away from the bottle or breast and refuse to even consider another nip, they’re telling you they’re full. When baby keeps coming back for more, that’s a sign they’re truly hungry (even if they just finished a full six ounces!).
Overfeeding breastfed babies vs. formula-fed babies
Pediatricians Dina DiMaggio, MD, and Anthony F. Porto, MD, MPH, authors of The Pediatrician’s Guide to Feeding Babies and Toddlers, echo the importance of listening to your child’s cue, regardless of whether they’re breastfed or formula-fed. “We are often asked, ‘how come my child didn’t finish their bottle of formula?’ but are rarely asked that when children are breastfed.” (Probably because it’s a lot easier to see—and worry about—how much milk went into a bottle.)
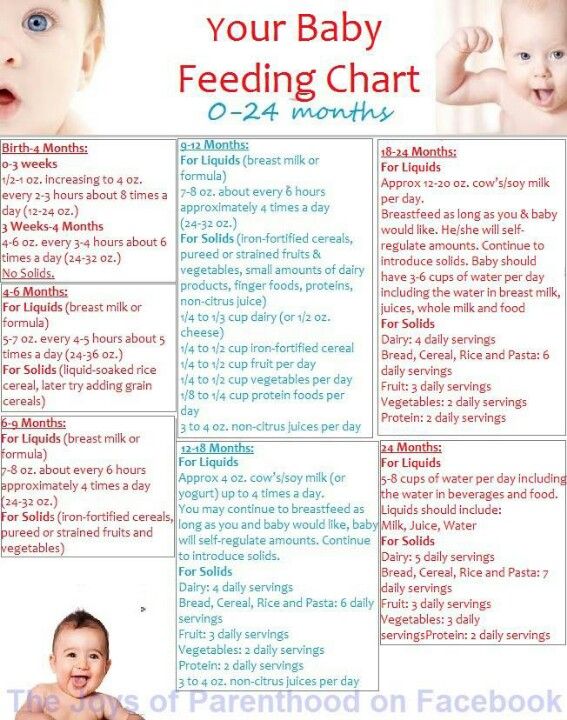
On average, a full-term newborn drinks 2 ounces of formula per bottle every three to four hours, or breastfeeds on demand (about eight to 12 times a day), according to DiMaggio and Porto. At one month old, baby will likely drink 3 to 4 ounces of formula per bottle every three to four hours, while a breastfeeding baby may feed approximately seven or eight times a day. This pattern of baby drinking more ounces of formula or breastfeeding fewer times a day lasts until they are eight to 12 months old, at which point baby may drink seven to eight ounces of formula per bottle or breastfeed three to four times a day.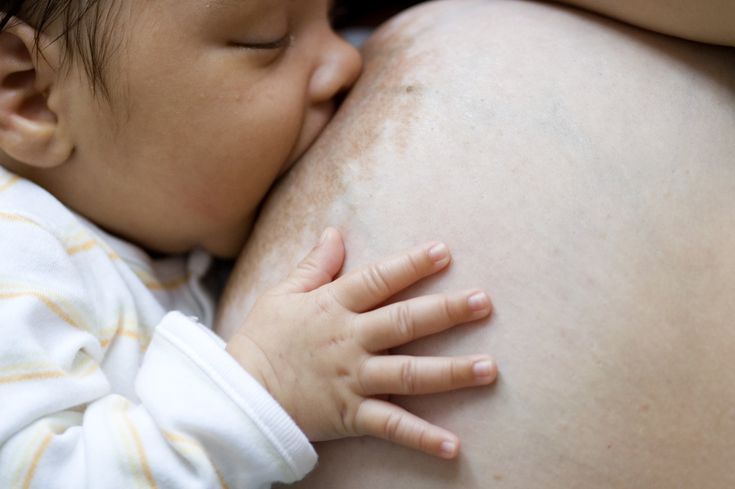
While these figures will vary with each child, it’s important to remember it’s perfectly normal for baby not to finish their bottle, as long as they’re hydrated and eating enough throughout the day. “Infants have a better understanding of when they’re full and, unlike most adults, don’t just eat whatever serving size is put in front of them,” DiMaggio and Porto say.
What Leads to Overfeeding?
Overfeeding baby is very rare, but it can happen. It’s more common in bottle-fed babies, simply because it’s easier for parents to see how much food their child is consuming. It also takes less effort to drink from a bottle, so babies (who love to suck) may inadvertently get too much milk while feeding.
If you’re concerned about possibly overfeeding baby, talk to your pediatrician. The doctor will look at baby’s length, weight and development, but as long as baby is thriving, they’re probably eating just fine.
Signs of Overfeeding Baby
The good news is, since you’ll likely be visiting a pediatrician often in first few months, you can track baby’s weight gain and feeding patterns. But don’t rely on weight as an indicator of whether you’re overfeeding baby. Instead, spitting up could be a sign you’ve pushed baby to take in extra food—for example, if baby spits up after draining a bottle you kept offering after they turned away. But more often than not, spitting up is a typical infant reaction or reflux.
But don’t rely on weight as an indicator of whether you’re overfeeding baby. Instead, spitting up could be a sign you’ve pushed baby to take in extra food—for example, if baby spits up after draining a bottle you kept offering after they turned away. But more often than not, spitting up is a typical infant reaction or reflux.
If you’re worried baby is eating too much for their age or has symptoms of vomiting, your pediatrician might recommend limiting how many ounces baby is drinking or how many times they feed, DiMaggio and Porto say. In most cases, however, as long as baby is healthy and doing well, feeding changes aren’t necessary.
How to Avoid Overfeeding Baby
If you learn you’ve been overfeeding baby, make a point of respecting your child’s feeding cues going forward. “If baby turns away before the bottle is finished or before your usual nursing time is up, accept the fact that they may not be hungry now,” Levine says. Don’t focus on the numbers: It doesn’t matter how many ounces baby finishes at each feeding. What matters is that baby is healthy and happy overall.
What matters is that baby is healthy and happy overall.
Updated February 2020
Expert bios:
Alanna Levine, MD, is a pediatrician at Orangetown Pediatric Associates in Orangeburg, New York, and works on staff at Englewood Hospital and Medical Center in New Jersey. In addition, she serves as a spokesperson for the American Academy of Pediatrics.
Dina DiMaggio, MD, and Anthony F. Porto, MD, MPH, are co-authors of The Pediatrician’s Guide to Feeding Babies and Toddlers: Practical Answers to Your Questions on Nutrition, Starting Solids, Allergies, Picky Eating and More, as well as spokespeople for the American Academy of Pediatrics. DiMaggio is a clinical assistant professor in the department of pediatrics at NYU Langone in New York City, and Porto is a pediatric gastroenterologist at Yale New Haven Health and medical director of the Yale Pediatric Celiac Program in New Haven, Connecticut.
Please note: The Bump and the materials and information it contains are not intended to, and do not constitute, medical or other health advice or diagnosis and should not be used as such. You should always consult with a qualified physician or health professional about your specific circumstances. Plus, more from The Bump:
Your Ultimate Guide to How to Bottle-Feed a Baby
Breastfeeding 101: How to Breastfeed Baby
What You Need to Know About Baby Growth Spurts
Can a Newborn Eat Too Much? How to Not Overfeed Your Baby
Signs of newborn overeating and ways to give the proper nutrition
By NewFolks
Can you overfeed a newborn? In short, yes, you can, but it doesn’t happen often. Every newborn has differences in appetite where one might drink a bottle or breastfeed longer than the other. Regardless, you can recognize the signs when your child has overeaten. Overfeeding a newborn often causes discomfort to the child because they can’t properly digest all breast milk or formula.
Regardless, you can recognize the signs when your child has overeaten. Overfeeding a newborn often causes discomfort to the child because they can’t properly digest all breast milk or formula.
Contents
- Signs of overfeeding baby on a regular basis
- What causes a newborn to eat too much?
- How to deal with overeating in a newborn
When overeating, the child can also ingest air, which may produce gas, increase abdominal discomfort, or cause crying. A child can even spit more than usual and have a soft stool. Although the discomfort of crying is not colic, they can cry more frequently than a child who already has colic. Therefore, you’ll need to watch for the signs of overfeeding your baby.
These are the signals that will clue you into how hungry (or not) your baby is.
- Holding the breast or bottle and continuously sucking (which indicates hunger)
- Taking longer breaks between sucking (meaning that he or she is full)
- Moving away from the breast or bottle (signaling fullness)
The amount of food each newborn needs will vary, but there are signs that generally show that a baby is gaining enough nutrition, such as a happy demeanor and good muscle tone.
Overeating, however, means that the baby consumes more milk (breast milk or formula) than they need for growth. Getting too much milk can overload a child’s small stomach and consequently get in the way of proper digestion.
Signs of overfeeding baby on a regular basis
Likewise, here are the signs of overfeeding a newborn that you’ll need to be aware of.
- Above-average weight gain
- Frequent, nauseating bowel movements
- Large burping
- Milk regurgitation
- Irritability
- Sleep disturbance
Symptoms associated with overeating are usually mistaken for colic, reflux, allergies, or intolerances to milk protein, or lactose intolerances. What separates the overeating from these conditions is that your child shows healthy growth, which does not happen when he or she has a digestive issue or a food allergy.
What causes a newborn to eat too much?
There are plenty of reasons a newborn overeats which include:
- Sleep deprivation: Lack of sleep disrupts the hormonal balance, which regulates appetite, resulting in increased appetite.

- Development: Babies are at the stage of oral development. In addition to wanting to suck when they are hungry, they also like to suck when they are tired, bored, uncomfortable, frustrated, or simply because they want to.
- Active sucking reflex: Babies have a limited ability to stop when they’ve had enough milk due to the sucking reflex, especially when feeding quickly.
- Fast feeding: This increases the likelihood that a child will ingest more milk than the stomach can contain or more than their tiny digestive system can adequately digest.
- Association of feeding and sleep: A child who falls asleep regularly by sucking a bottle can learn that the way they fall asleep is with a bottle in their mouth. This means that a child may want a bottle not only when they are hungry, but also when they are tired.
- Ignoring the signs of satiety: Satiety means that the child is full. The caregiver may try to force the child to consume the amount in the bottle after the child has shown signs of being full.
 Forced feeding of the baby is easy to implement while the baby’s sucking reflex is active (from birth to 3-4 months), and therefore it is easy to force the baby to take more than necessary.
Forced feeding of the baby is easy to implement while the baby’s sucking reflex is active (from birth to 3-4 months), and therefore it is easy to force the baby to take more than necessary.
How to deal with overeating in a newborn
For starters, it is important not to limit the baby’s milk intake, but to help them to self-regulate. If you happen to overload the baby, don’t stress too much. In the future, you would need to watch for signs of being full. If he or she moves away before the end of the bottle or before the usual time of breastfeeding ends, then your baby is saying that the feeding was enough. If you are concerned about your child overeating, talk to your pediatrician. The doctor will examine the length, weight, and development of the baby and make some recommendations.
Overfeeding a newborn is very rare, but it can happen. It is more common in children who breastfeed, simply because parents can’t exactly determine the quantity that the baby has taken in. However, don’t focus on the amount because the quantity varies with each feeding. After all, you’ll be able to tell if your child is healthy and happy.
However, don’t focus on the amount because the quantity varies with each feeding. After all, you’ll be able to tell if your child is healthy and happy.
Editors' Recommendations
- Typical toddler behavior or autism? Key differences
- 5 vegetarian baby food recipes that are easy to make
- Some babies want to be held while sleeping: Here’s why
- 6 of the best toddler cereals to offer your child that aren’t packed with sugar
- How to stop food obsession in children
Too much milk? Reduced lactation
Sometimes you may feel like you are producing too much milk, especially in the first weeks of breastfeeding. After reading our article, you will find out if you really have too much milk, and what can be done to reduce it.
Share this information
Breast milk is very healthy, so it's good to have a lot of it, right? However, this is not always the case. Babies can sometimes have a hard time coping with the rapid rush of milk that usually accompanies excess lactation. And mothers who have too much milk often experience discomfort due to the constant leakage of milk and often suffer from mastitis. nine0003
Babies can sometimes have a hard time coping with the rapid rush of milk that usually accompanies excess lactation. And mothers who have too much milk often experience discomfort due to the constant leakage of milk and often suffer from mastitis. nine0003
Fortunately, there are a number of ways to help in this situation. But before you use them, answer two important questions:
Do I really have too much milk?
Some of the symptoms of over-lactation (listed below) may occur for very different reasons. You should not try to reduce the production of breast milk, if you are not sure that it is the overabundance of it that is the main problem. Otherwise, this can lead to the fact that your baby will produce less milk than your baby needs, especially in the critical first month when production is just being established. nine0003
Is being overweight a problem for me or my baby?
If you are sure that you have an excess of milk, but this does not cause problems for you and your baby, you do not need to do anything. In most cases, everything returns to normal within the first few months. As the baby grows, he will learn to better cope with the rapid flow of milk and will feed with pleasure.
In most cases, everything returns to normal within the first few months. As the baby grows, he will learn to better cope with the rapid flow of milk and will feed with pleasure.
Leakage is not always a sign of too much milk
During the first four to six weeks of your baby's birth, the level of prolactin, the hormone responsible for milk production, will rise each time the breast is emptied. In these first weeks, the breast learns to produce milk in the amount that the baby needs, depending on the time of day. Therefore, excessive leakage, rapid filling of the breast, and even splashing of milk during a rush are the norm. 1
At the same time, your baby is learning to suck and swallow milk, so you shouldn't be surprised if he suddenly coughs or chokes when he suckles. nine0003
After about four to six weeks, the spikes in prolactin levels will begin to fade and milk production will become more balanced, adjusting to your baby's needs on a supply and demand basis. 2 However, given the many hormonal changes that occur in the body of a young mother, such a restructuring may take some time. In some mothers, milk production is established quickly, in others a little longer.
2 However, given the many hormonal changes that occur in the body of a young mother, such a restructuring may take some time. In some mothers, milk production is established quickly, in others a little longer.
Behavior of the child, which may indicate an excess of milk
When overproduced, milk is usually released very quickly, especially during the first flush. As a result, the baby may cough or choke at the beginning of a feed, push back, or hold the breast loose in the mouth. The baby may pull away from the chest, frightened by a quick rush, and then cry because he hasn’t eaten. He can swallow milk in large volumes and with a lot of air, and after that he will spit up a lot. Try to be as careful as possible when you help him burp - sudden movements combined with a full tummy can cause the baby to vomit and scare him even more. nine0003
At the start of a feed, milk is relatively low in fat and consists mainly of lactose (sugar) and proteins. As the breast is fed and emptied, the fat content constantly increases. In the case of excess milk production, your baby may feel full before he completely empties his breast. This means that he will get a lot of lactose-rich milk, but not enough fat-rich milk that comes towards the end of a feed. Excess lactose instead of a balanced diet can make digestion difficult and cause hard, frothy, and greenish stools. nine0003
In the case of excess milk production, your baby may feel full before he completely empties his breast. This means that he will get a lot of lactose-rich milk, but not enough fat-rich milk that comes towards the end of a feed. Excess lactose instead of a balanced diet can make digestion difficult and cause hard, frothy, and greenish stools. nine0003
Oddly enough, in such a situation, the baby may constantly want to eat and behave restlessly between feedings. Despite the high calorie content, the low fat content of milk prevents it from being fully satiated. It is the fat contained in food that gives us a feeling of satiety. What happens if you eat a few dozen rice crackers or a slice of cheese with a cookie instead? You will fill up on cheese faster, as it is more saturated with fats.
However, all these symptoms can be caused by completely different problems, such as reflux, allergies, or even vice versa, insufficient milk production. An excess of breast milk can indeed cause these symptoms, but only if they are accompanied by excessive weight gain. Children usually dial around 900 g per month, but in the case of an excess of milk, they can gain much more, often almost twice as much. 1 If you feel like you are having too much milk but your baby is gaining weight normally, contact your lactation consultant or your healthcare provider.
Children usually dial around 900 g per month, but in the case of an excess of milk, they can gain much more, often almost twice as much. 1 If you feel like you are having too much milk but your baby is gaining weight normally, contact your lactation consultant or your healthcare provider.
Symptoms that may indicate an excess of milk in mothers
Mothers with an excess of breast milk often experience swelling and tightness in the breast, which constantly seems full. nine0029 3 As already noted, the leakage of breast milk in the first six weeks does not indicate its excess. However, if this continues at every feeding and after this period, it may be that the problem is in the overabundance.
A baby cannot always empty a full breast, so when there is an excess of breast milk, blockage of the milk ducts or periodic bouts of mastitis often occur. However, these problems can also be caused by other reasons.
How to reduce milk production
If you have found that you have too much breastmilk and this is causing you concern, here are a few simple things that can help. For some mothers, they are enough.
- Try feeding in a relaxed position. Reclining or lying down feeding will allow the baby to better control the process. In this position, the baby sets the rhythm of feeding himself and can always raise his head to take a break if the milk is released too quickly. Don't forget to put a towel over to soak up spilled milk. nine0066
- Release pressure. If full breasts make you uncomfortable, try expressing some milk by hand or with a breast pump, but try to express as little milk as possible. Every time you empty your breast, you send a signal to her to produce even more milk. Therefore, pumping provides short-term relief, but with prolonged use, it can only aggravate the situation. If you need to express and store milk to feed your baby when you are not around, it is best to address the problem of excess production first. nine0066
- Try bra pads. If you have milk leaks, put special pads or pads in your bra to collect milk* to keep your underwear dry.
 If your milk leakage is moderate and already decreasing, or your breasts leak slightly during pregnancy, ultra-thin disposable pads will help you feel confident in any life situation.
If your milk leakage is moderate and already decreasing, or your breasts leak slightly during pregnancy, ultra-thin disposable pads will help you feel confident in any life situation. - Avoid teas and lactation supplements. nine0014 If you have been drinking teas, eating special biscuits, or taking supplements to improve breast milk production, this should be stopped now to resolve the problem.
"Breast Watch" to reduce milk production
If all the above methods fail, you can try a technique called "Breast Watch", which allows you to better control milk production. However, before trying this method, check with a lactation consultant or healthcare provider. nine0003
On breastfeeding, you feed your baby on demand, but only on one breast for four hours. The second breast during this time is strongly filled. Since breast milk contains what is known as a "feedback lactation inhibitor", due to overfullness, the body sends a signal to that breast to slow down milk production. This is a natural way to protect the breast from endless filling.
This is a natural way to protect the breast from endless filling.
This technique must be applied for 24 hours, changing breasts every four hours. If the milk does not become less, try increasing the duration of the "watch" to six hours. nine0003
Complete emptying and “breast duty” technique
If after another day there is still a lot of milk produced,
you can try another version of this technique, which is recommended in cases of extreme overabundance. It is called "complete emptying and duty of the breast." 3
In this method, both breasts must be completely emptied in the morning with an electric breast pump and breastfeeding should be started immediately. The flow of milk will be weaker and allow the baby to eat calmly. In addition, he will get more fat-rich milk, which comes at the end of feeding, which means he will feel more full. nine0003
After that, you can continue the "breast watch" for four hours, as described above. If that doesn't help, try increasing the interval to six, eight, or twelve hours the next day, depending on the extent of the problem. Before using this technique, be sure to consult with your doctor.
Before using this technique, be sure to consult with your doctor.
You may not need to completely empty your breasts after the first use of this technique, but some mothers have to do this once or twice. Improvement usually occurs within the first two days or a little later, but in no case should "breast watch" be used for more than five days. nine0003
Literature
1 Morbacher N. Breastfeeding answers made simple. Amarillo TX , USA : Hale Publishing ; 2010. - Morbacher N., "Simple answers to questions about breastfeeding." Amarillo, Texas, USA: Publishing Hale 0106 et al . Blood and milk prolactin and the rate of milk synthesis in women. Exp Physiol. 1996;81(6):1007-1020. - Cox D.B. et al., Effects of blood and milk prolactin on milk production in women. Exp Physiol. 1996;81(6):1007-1020.
1996;81(6):1007-1020.
3 van Veldhuizen-Staas CG. Overabundant milk supply: an alternative way to intervene by full drainage and block feeding. Int Breastfeed J . 2007;2(1):11. - van Velhusen-Staas SJ, "Milk Overabundance: An Alternative Countermeasure by Total Drying and Blocking of Feeds." Int Brestfeed J (International Journal of Breastfeeding). 2007;2(1):11.
Read instructions before use. Consult a specialist about possible contraindications.
* RC № FZZ 2010/07352 dated 19.07.2010
Six first week breastfeeding solutions
Are you having difficulty breastfeeding your newborn baby? Read on for expert advice on tackling the main challenges of the first week of breastfeeding.
Share this information
Cathy Garbin, child health nurse, midwife and lactation consultant:
Cathy, a mother of two, was a research fellow at the renowned Human Lactation Research Institute, founded by Peter Hartmann, for seven years, providing support to breastfeeding mothers in clinics and at home. Today, she still works as a family counselor, and also conducts seminars for attending physicians and speaks at international conferences. nine0003
Today, she still works as a family counselor, and also conducts seminars for attending physicians and speaks at international conferences. nine0003
Breastfeeding is not always easy, so if
you are having difficulty, know that you are not alone. A US study found that out of 500 new mothers surveyed, 92% experienced breastfeeding problems by the third day. 1 Fortunately, most early breastfeeding problems are easy to resolve. Below you can read recommendations for solving the main problems that mothers often face in the first week of feeding. nine0003
Problem #1. Breastfeeding hurts!
Pain during feeding is usually associated with tenderness or inflammation of the nipples, especially when milk "comes" on the second to fourth day after birth. 2 The baby will beg for a breast every couple of hours, and this can quickly aggravate the problem: for some mothers, the nipples crack, bleed or blister. This is, of course, very annoying.
Solutions 3
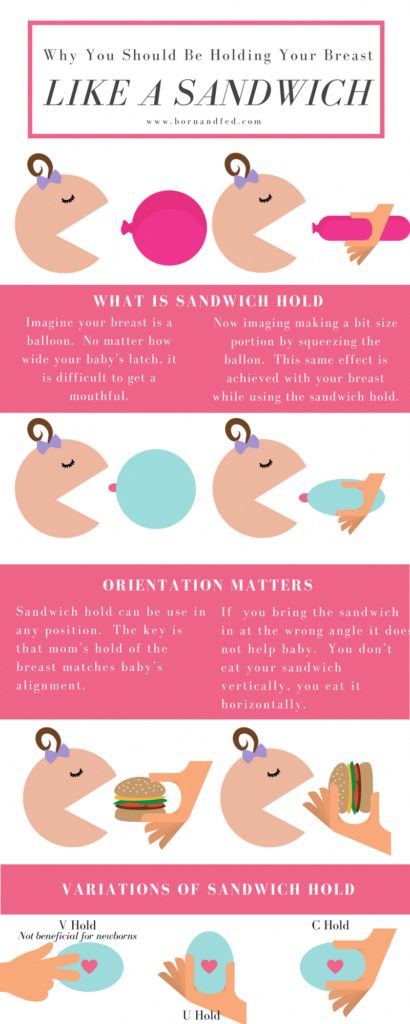
- Check how the baby latch on.
 An incorrect latch is one of the most common causes of pain during breastfeeding. A newborn baby should take most of the lower half of the areola (dark skin around the nipple) into his mouth, and your nipple should rest against his palate, supported from below by the tongue.
An incorrect latch is one of the most common causes of pain during breastfeeding. A newborn baby should take most of the lower half of the areola (dark skin around the nipple) into his mouth, and your nipple should rest against his palate, supported from below by the tongue. - Contact a lactation consultant or healthcare professional to make sure your baby's mouth and torso are properly positioned during feeding and there are no other latch-on problems. The doctor may also examine the baby's mouth for physical abnormalities. nine0066
- Try other feeding positions. Reclining, cross cradle, underarm, or lying positions can relieve pressure on the most painful areas of your breasts.
- Gently wipe soaked nipples with water-dampened cotton swabs after each feed to remove milk residues that can cause infection.
- Air dry nipples or pat dry with a clean, soft muslin or flannel cloth to prevent bacterial growth in humid environments.
 Use disposable or reusable bra pads to absorb leaking milk and remember to change them regularly. nine0066
Use disposable or reusable bra pads to absorb leaking milk and remember to change them regularly. nine0066 - Soften your nipples. An ultra-pure lanolin treatment will help relieve inflammation and dry skin. You can also apply a few drops of your own breast milk to your nipples. In both cases, you do not have to wash your breasts before the next feeding. You can also apply refrigerated hydrogel pads* to your nipples. They soothe the nipples and help relieve pain during feeding, as well as speed up healing.
- Protect your nipples. nine0014 Nipple shields* protect the sore area from rubbing against clothing.
- Be patient. Inflammation usually resolves after a few days as your body adjusts to breastfeeding and your baby learns to suckle.
- Seek medical attention, if pain during feeding does not improve after a few days. Constant inflammation of the nipples may indicate an infection that requires prompt treatment.
Problem #2. Baby doesn't latch on properly
Some newborns do not immediately latch on properly. Maybe both of you just need more time to learn how to breastfeed, or maybe the baby was born prematurely, feels unwell after a difficult birth, or mom has flat or inverted nipples.
Solutions
- Contact a lactation consultant or healthcare professional who can help identify the cause of the problem and suggest solutions. nine0066
- Flat or inverted nipples must be pulled out. Nipple formers* fit comfortably in the bra and apply gentle pressure to the nipples to help them come out for easier feeding.
- Try different positions and ways to support your newborn. The baby needs to feel supported. He must be comfortable and breathe freely in order to suckle properly. Do not hold the child by the head and do not put pressure on it. Lean back and let your child take the lead.
 This stimulates his natural reflexes and helps him find and latch on to his breasts. nine0029 4
This stimulates his natural reflexes and helps him find and latch on to his breasts. nine0029 4 - When feeding, try to find the optimal position. Instead of putting your baby on and off, stressing both of you, try to position him in a way that is easy and comfortable for him. Hold the torso and legs of the baby close to you, support him by the shoulders and hold him firmly so that he feels safe. Let the baby's head rest freely on your arm so that he can tilt it back slightly and breathe freely. The chin should be pressed against your chest. If these small adjustments don't make feeding more comfortable for your baby, seek help from a lactation consultant or healthcare professional. nine0066
- Use nursing pads. If your baby is having trouble latching on, a lactation consultant or healthcare professional may suggest trying nursing pads*. A nipple with an overlay is more convenient to take in the mouth, so it is larger and more rigid.
 Do not use nursing pads for a long time.
Do not use nursing pads for a long time.
Problem #3. Not enough breast milk
You will produce little breast milk at the very beginning, as the hormonal changes that trigger milk production occur slowly and do not end until the second or fourth day after birth. nine0029 2 You may be worried that your baby is not getting enough milk, but in the early days his stomach is still too small and feedings are frequent, so don't worry. The only things to worry about these days are excessive weight loss, too few wet and soiled diapers, or signs of dehydration in the baby. For more information on how often a newborn should urinate and void, see Breastfeeding Newborns: What to Expect in the First Week. nine0003
Solutions
- Contact a Lactation Consultant or your healthcare provider who can determine if you are having problems with milk production. The sooner you do this, the better.
- Feed your baby on demand, not on a schedule.
 In the first week after birth, your baby will ask to breastfeed every two to three hours (or more often!), both day and night. Such frequent feeding helps to establish the production of breast milk. nine0066
In the first week after birth, your baby will ask to breastfeed every two to three hours (or more often!), both day and night. Such frequent feeding helps to establish the production of breast milk. nine0066 - Take care of yourself. It's not always easy with a newborn, but try to rest whenever you can, eat right, and accept any help around the house or with older children that your loved ones can give you to fully focus on breastfeeding.
- Try expressing milk. If a baby is feeding frequently but not gaining any weight, a lactation consultant or doctor may recommend pumping to increase breast milk production. If milk is not coming out at all, you can try the Medela Symphony Dual Electric Clinical Breast Pump**. It features an Initiate program that mimics a baby's natural sucking rhythm for the first few days. nine0066
Problem #4. Breast full and heavy
Your breasts will become fuller and heavier as milk comes in.
If the baby suckles well and often, this should not cause any problems. However, in some women, the breasts become so full that they become hard and painful. This condition, called breast swelling, can cause discomfort. The swollen chest seems to be “burning”, now all the activity of your body is concentrated in it, resembling a busy traffic at rush hour. Fortunately, this condition usually resolves within 24 to 48 hours. However, due to the swelling of the mammary glands, the nipples can become flat and the baby may have difficulty latch-on. nine0029 5
Solutions
- Feed your baby often. Try to breastfeed at least 8-12 times a day. This is the main way to alleviate this condition. For more tips and tricks, see the article on Breast Swelling. 6.7
- Call your healthcare provider, if symptoms persist for more than 48 hours, you have a fever, or your baby is unable to breastfeed due to swelling.

Problem #5. Milk is leaking
Breast leakage is very common in the early days of breastfeeding when milk production begins. Milk may leak from one breast while you are feeding the other, when you sleep on your stomach, or when something accidentally triggers the milk flow reflex, such as when you hear a baby crying in a store. The leakage usually stops after about six weeks.
Solutions
- Protect clothes from stains will help disposable or reusable bra pads to be used day and night. nine0066
- Don't waste precious drops! Breast milk collection pads* fit inside the bra and collect any leaking milk. This is a very useful thing when there is too much milk and the pads are not absorbing well, or when one breast is leaking while you are feeding the other. If you want to save the collected milk, use only the milk collected at the feeding. Place it in a sterile container and refrigerate immediately if you are not supplementing with it right away.
 Collected milk must be used within 24 hours. The breast milk collection sleeves should not be worn for more than two to three hours at a time. nine0066
Collected milk must be used within 24 hours. The breast milk collection sleeves should not be worn for more than two to three hours at a time. nine0066
Problem #6. There seems to be too much milk
Sometimes when milk comes in, too much is produced! In the first few weeks there may be an overabundance of milk, but usually everything returns to normal soon. 7 Up to this point, the breasts may be heavy and sore almost all the time, even immediately after a feed, and a lot of milk may leak. A strong flush can cause a baby to cough or choke, vomit immediately after a feed, have tummy discomfort, or have hard, frothy, greenish stools. These are all signs that you are having too much milk, but the problem may resolve itself as your breasts get used to the new function. nine0003
Solutions
- Express some milk by hand at the start of each feed to ease the force of the flush.
- Try to feed while leaning back: this will help your baby control the flow of milk.
 The "cradle" position is also good: hold the baby obliquely by the shoulders so that the head can lean back slightly while on your arm. The torso of the baby will be located diagonally on you.
The "cradle" position is also good: hold the baby obliquely by the shoulders so that the head can lean back slightly while on your arm. The torso of the baby will be located diagonally on you. - Be gentle and patient. Let your baby rest and digest milk both during and after feeding. Don't move your baby too much or too fast, as this can make him nauseous. As the baby grows, he will learn to better cope with the rush of milk, which is likely to weaken anyway.
- Use the towel or swaddle to soak up spilled milk if the baby can't handle the flush, and place the breast milk collection pad on the other breast to catch any spilled milk. nine0066
- Contact a lactation consultant or doctor if problems persist after a few weeks . He will examine you and may suggest one-sided feedings or hourly breast changes (“breast duty”) to reduce your milk supply.
Related materials: Difficulties in breastfeeding in the next few weeks and problems with breastfeeding after the first month
Literature
1 Wagner EA et al. Breastfeeding concerns at 3 and 7 days postpartum and feeding status at 2 months. Pediatrics . 2013: peds -2013. - Wagner I.A. et al., "Breastfeeding Problems at Days 3 and 7 of a Child's Life and Type of Feeding at 2 Months". Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 2013:e865–e875.
Breastfeeding concerns at 3 and 7 days postpartum and feeding status at 2 months. Pediatrics . 2013: peds -2013. - Wagner I.A. et al., "Breastfeeding Problems at Days 3 and 7 of a Child's Life and Type of Feeding at 2 Months". Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 2013:e865–e875.
2 Pang WW, Hartmann PE. Initiation of human lactation: secretory differentiation and secretory activation. J9 Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia . 2007;12(4):211-221. - Pang, W.W., Hartmann, P.I., "Lactation initiation in the lactating mother: secretory differentiation and secretory activation." G Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2007;12(4):211-221.
3 Cadwell K. Latching - On and Suckling of the Healthy Term Neonate: Breastfeeding Assessment. J Midwifery & Women ’ s Health 2007;52(6):638-642. — Cadwell, K., "Latching and sucking in healthy newborns: evaluation of breastfeeding." F Midwifery Women Health. 2007;52(6):638-642.
— Cadwell, K., "Latching and sucking in healthy newborns: evaluation of breastfeeding." F Midwifery Women Health. 2007;52(6):638-642.
4 Colson SD et al. Optimal positions for the release of primitive neonatal reflexes stimulating breastfeeding. Early Hum Dev . 2008;84(7):441-449. - Colson S.D. et al., "Optimal Positions for Provoking Primitive Innate Reflexes to Induce Breastfeeding." Airlie Hume Dev. 2008;84(7):441-449.
5 Jacobs A et al. S3-guidelines for the treatment of inflammatory breast disease during the lactation period. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 2013;73(12):1202-1208. - Jacobs A. et al., "Recommendations 2014;9(5):239-243.
7 Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine Protocol Committee. ABM clinical protocol # 20: Engorgement. Breastfeed Med . 2009;4(2):111-113. - Protocol Committee of the Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine, "AVM Clinical Protocol No.